Comparison of Two 2.45 GHz Microwave Ablation Devices with Respect to Ablation Zone Volume in Relation to Applied Energy in Patients with Malignant Liver Tumours
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
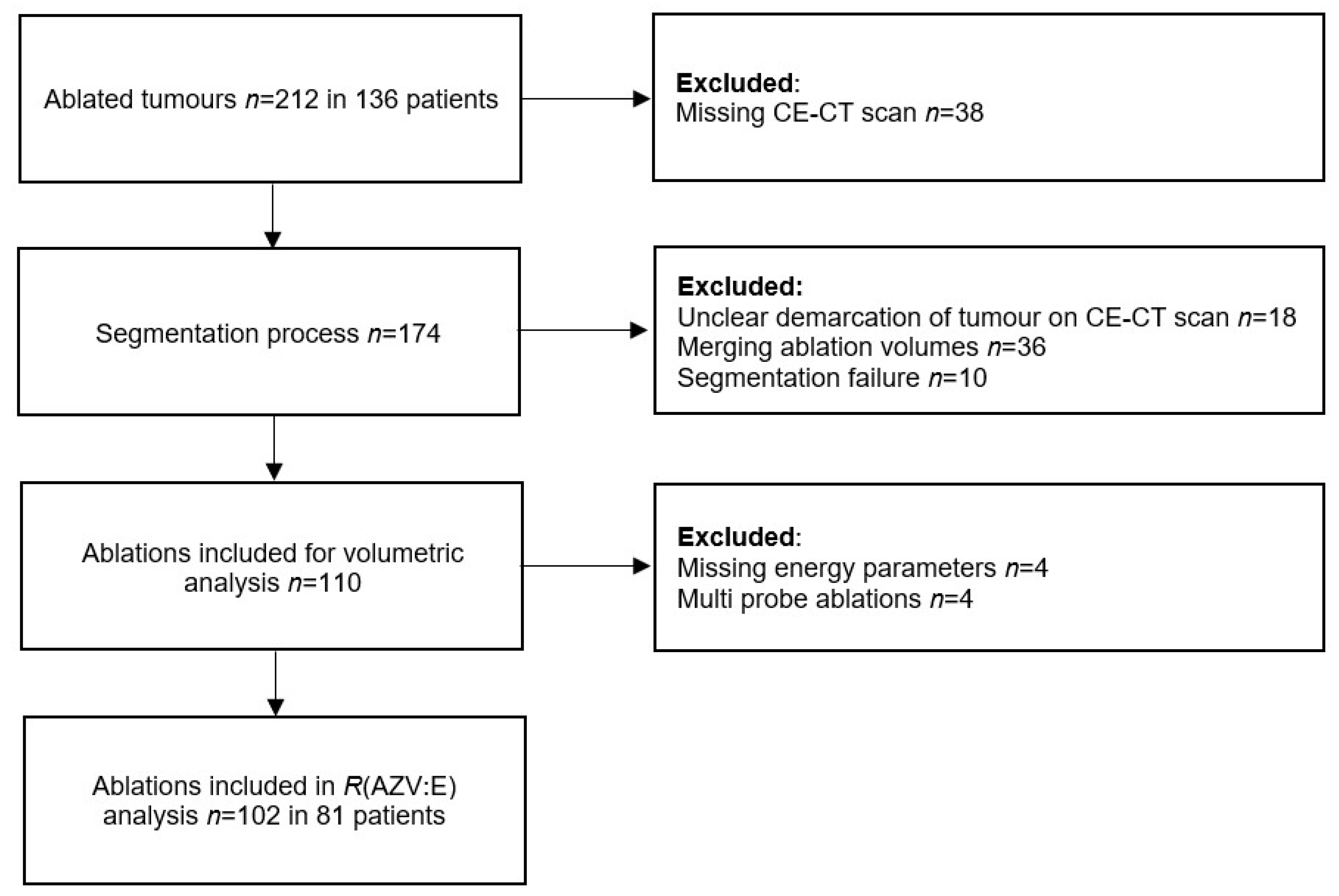
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Data Extraction and Analysis
2.4. Liver Steatosis
2.5. Statistic
3. Results
3.1. Patient and Tumour Characteristics
3.2. Comparison of Devices
3.3. Comparison of Tumour Types
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cervantes, A.; Adam, R.; Roselló, S.; Arnold, D.; Normanno, N.; Taïeb, J.; Seligmann, J.; De Baere, T.; Osterlund, P.; Yoshino, T.; et al. Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 25, 141604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, A.; Cervantes, A.; Chau, I.; Daniele, B.; Llovet, J.; Meyer, T.; Nault, J.C.; Neumann, U.; Ricke, J.; Sangro, B.; et al. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, iv238–iv255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hof, J.; Wertenbroek, M.W.J.L.A.E.; Peeters, P.M.J.G.; Widder, J.; Sieders, E.; de Jong, K.P. Outcomes after Resection and/or Radiofrequency Ablation for Recurrence after Treatment of Colorectal Liver Metastases. Br. J. Surg. 2016, 103, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanis, E.; Nordlinger, B.; Mauer, M.; Sorbye, H.; van Coevorden, F.; Gruenberger, T.; Schlag, P.M.; Punt, C.J.A.; Ledermann, J.; Ruers, T.J.M. Local Recurrence Rates after Radiofrequency Ablation or Resection of Colorectal Liver Metastases. Analysis of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer #40004 and #40983. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijerink, M.R.; Puijk, R.S.; van Tilborg, A.A.J.M.; Henningsen, K.H.; Fernandez, L.G.; Neyt, M.; Heymans, J.; Frankema, J.S.; de Jong, K.P.; Richel, D.J.; et al. Radiofrequency and Microwave Ablation Compared to Systemic Chemotherapy and to Partial Hepatectomy in the Treatment of Colorectal Liver Metastases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2018, 41, 1189–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinguely, P.; Dal, G.; Bottai, M.; Nilsson, H.; Freedman, J.; Engstrand, J. Microwave Ablation versus Resection for Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases—A Propensity Score Analysis from a Population-Based Nationwide Registry. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 46, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Pan, Y.L.; Zhou, P.P.; Li, S.S.; Li, K. Long-Term Outcomes of Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Microwave Ablation versus Resection for Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases: A Propensity-Score Matched Study. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Geest, T.W.; van Amerongen, M.J.; Nierop, P.M.H.; Höppener, D.J.; Grünhagen, D.J.; Moelker, A.; Fütterer, J.J.; Verhoef, C.; de Wilt, J.H.W. Propensity Score Matching Demonstrates Similar Results for Radiofrequency Ablation Compared to Surgical Resection in Colorectal Liver Metastases. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 48, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbanescu-Kele Apor de Zalán, C.M.C.; Ruiter, S.J.S.; van den Berg, A.P.; Pennings, J.P.; de Jong, K.P. Outcomes after Primary and Repeat Thermal Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with or without Liver Transplantation. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 4168–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, K.P.; Ruiter, S.J.S.; Pennings, J.P. Stereotactic Image Guided Microwave Ablation of HCC: A Step Forward and Still a Long Way to Go. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 1798–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kele, P.G.; Van der Jagt, E.J.; Krabbe, P.F.M.; de Jong, K.P. Lack of Anatomical Concordance between Preablation and Postablation CT Images: A Risk Factor Related to Ablation Site Recurrence. Int. J. Hepatol. 2012, 2012, 870306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriks, P.; Noortman, W.A.; Baetens, T.R.; van Erkel, A.R.; van Rijswijk, C.S.P.; van der Meer, R.W.; Coenraad, M.J.; de Geus-Oei, L.F.; Slump, C.H.; Burgmans, M.C. Quantitative Volumetric Assessment of Ablative Margins in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Predicting Local Tumor Progression Using Nonrigid Registration Software. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 4049287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiter, S.J.S.; Tinguely, P.; Paolucci, I.; Engstrand, J.; Candinas, D.; Weber, S.; de Haas, R.J.; de Jong, K.P.; Freedman, J. 3D Quantitative Ablation Margins for Prediction of Ablation Site Recurrence After Stereotactic Image-Guided Microwave Ablation of Colorectal Liver Metastases: A Multicenter Study. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 757167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laimer, G.; Jaschke, N.; Schullian, P.; Putzer, D.; Eberle, G.; Solbiati, M.; Solbiati, L.; Goldberg, S.N.; Bale, R. Volumetric Assessment of the Periablational Safety Margin after Thermal Ablation of Colorectal Liver Metastases. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 6489–6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, E.A.; Cornelis, F.H.; Petre, E.N.; Tyagi, N.; Shady, W.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Solomon, S.B.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Durack, J.C. Volumetric 3D Assessment of Ablation Zones after Thermal Ablation of Colorectal Liver Metastases to Improve Prediction of Local Tumor Progression. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 2698–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiter, S.J.S.; Heerink, W.J.; de Jong, K.P. Liver Microwave Ablation: A Systematic Review of Various FDA-Approved Systems. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 29, 4026–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amabile, C.; Ahmed, M.; Solbiati, L.; Meloni, M.F.; Solbiati, M.; Cassarino, S.; Tosoratti, N.; Nissenbaum, Y.; Ierace, T.; Goldberg, S.N. Microwave Ablation of Primary and Secondary Liver Tumours: Ex Vivo, in Vivo, and Clinical Characterisation. Int. J. Hyperth. 2017, 33, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyn, P.B.; Bird, J.R.; Koch, R.M.; Tatli, S.; Levesque, V.M.; Catalano, P.J.; Silverman, S.G. Hepatic Microwave Ablation Zone Size: Correlation with Total Energy, Net Energy, and Manufacturer-Provided Chart Predictions. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerink, W.J.; Solouki, A.M.; Vliegenthart, R.; Ruiter, S.J.S.; Sieders, E.; Oudkerk, M.; de Jong, K.P. The Relationship between Applied Energy and Ablation Zone Volume in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Colorectal Liver Metastasis. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3228–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolucci, I.; Ruiter, S.J.S.; Freedman, J.; Candinas, D.; de Jong, K.P.; Weber, S.; Tinguely, P. Volumetric Analyses of Ablation Dimensions in Microwave Ablation for Colorectal Liver Metastases. Int. J. Hyperth. 2022, 39, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Solbiati, L.; Brace, C.L.; Breen, D.J.; Callstrom, M.R.; Charboneau, J.W.; Chen, M.-H.; Choi, B.I.; de Baère, T.; Dodd, G.D.; et al. Image-Guided Tumor Ablation: Standardization of Terminology and Reporting Criteria—A 10-Year Update. Radiology 2014, 273, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshazer, G.; Merck, D.; Hagmann, M.; Dupuy, D.E.; Prakash, P. Physical Modeling of Microwave Ablation Zone Clinical Margin Variance. Med. Phys. 2016, 43, 1764–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Park, S.H.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, M.-Y.; Lee, Y.; Kim, T.K.; Khalili, K.; Bae, M.H.; et al. Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography for the Diagnosis of Fatty Liver: Prospective Study with Same-Day Biopsy Used as the Reference Standard. Eur. Radiol. 2010, 20, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schober, P.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, T.C.; Miller, G.; Patrie, J.; Angle, J.F. Relationship of Antenna Work and Ablation Cavity Volume Following Percutaneous Microwave Ablation of Hepatic Tumors. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 32, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winokur, R.S.; Du, J.Y.; Pua, B.B.; Talenfeld, A.D.; Sista, A.K.; Schiffman, M.A.; Trost, D.W.; Madoff, D.C. Characterization of In Vivo Ablation Zones Following Percutaneous Microwave Ablation of the Liver with Two Commercially Available Devices: Are Manufacturer Published Reference Values Useful? J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 1939–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Rhim, H.; Lee, M.W.; Kang, T.W.; Song, K.D.; Lee, J.K. Direction of Tissue Contraction after Microwave Ablation: A Comparative Experimental Study in Ex Vivo Bovine Liver. Korean J. Radiol. 2022, 23, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tilborg, A.A.J.M.; Scheffer, H.J.; Nielsen, K.; van Waesberghe, J.H.T.M.; Comans, E.F.; van Kuijk, C.; van den Tol, P.M.; Meijerink, M.R. Transcatheter CT Arterial Portography and CT Hepatic Arteriography for Liver Tumor Visualization during Percutaneous Ablation. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, L.; Nissenbaum, Y.; Cavagnaro, M.; Goldberg, S.N. Tissue Shrinkage in Microwave Thermal Ablation: Comparison of Three Commercial Devices. Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 34, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patient Characteristics | Total (n = 81) | Emprint (n = 55) | Neuwave (n = 26) | p-Value # |
| Sex (male:female) | 45:36 | 26:29 | 19:7 | 0.029 |
| Age in years at intervention * | 66.0 (1.0) | 64.3 (9.2) | 69.3 (7.4) | 0.012 |
| BMI * | 29.0 (0.7) | 28.8 (6.6) | 29.3 (4.0) | 0.627 |
| Liver parenchyma | ||||
| Normal Steatosis Cirrhosis | 31 (38.3) 24 (29.6) 26 (32.1) | 25 (45.5) 19 (34.5) 11 (20.0) | 6 (23.1) 5 (19.2) 15 (57.7) | 0.003 |
| Prior systemic chemotherapy | ||||
| No Neo-adjuvant for this ablation >6 months before | 57 (70.4) 16 (19.8) 8 (9.8) | 36 (65.5) 13 (23.6) 6 (10.9) | 21 (80.8) 3 (11.5) 2 (7.7) | 0.353 |
| Tumour Characteristics | Total (n = 102) | Emprint (n = 71) | Neuwave (n = 31) | p-Value # |
| Type of tumour | ||||
| CRLM HCC | 65 (63.7) 37 (36.3) | 56 (78.9) 15 (21.1) | 9 (29.0) 22 (71.0) | 0.001 |
| Location | ||||
| Left-sided liver | 37 (36.3)) | 24 (33.8) | 13 (41.9) | 0.504 |
| Right-sided liver | 65 (63.7) | 47 (66.2) | 18 (58.1) | |
| Subcapsular (<5 mm) | 66 (64.7) | 44 | 22 | 0.382 |
| Perivascular (<5 mm of >3 mm-sized vessel) | 30 (29.4) | 24 | 6 | 0.141 |
| Diameter (mm) at intervention † | 19 (14–27) | 19 (13–25) | 19 (10–28) | 0.743 |
| Volume (ml) at intervention † | 2.92 (1.07–7.95) | 2.7 (1.0–7.8) | 3.9 (1.1–9.4) | 0.385 |
| Emprint (n = 71) | Neuwave (n = 31) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| R(AZV:E) (ml/kJ) | 0.41 (0.33–0.56) | 0.81 (0.47–0.89) | <0.001 |
| Tumour diameter (mm) | 19 (13–25) | 19 (10–28) | 0.743 |
| Tumour volume (ml) | 2.7 (1.0–7.8) | 3.9 (1.1–9.4) | 0.385 |
| Ablation zone volume (ml) | 41.9 (24.1–58.7) | 41.1 (23.9–91.2) | 0.342 |
| Applied energy (kJ) | 85.5 (60.0–156.0) | 67.2 (24.0–126.0) | 0.062 |
| Needle positions (n) | 3 (1–4) | 3 (2–3) | 0.108 |
| R(T:AZV) | 0.06 (0.04–0.15) | 0.07 (0.04–0.15) | 0.513 |
| Emprint (n = 71) | Neuwave (n = 31) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCC (n = 15) | CRLM (n = 56) | p-Value | HCC (n = 22) | CRLM (n = 9) | p-Value | |
| R(AZV:E) (ml/kJ) | 0.38 (0.27–0.54) | 0.43 (0.34–0.57) | 0.398 | 0.79 (0.41–0.90) | 0.85 (0.66–0.90) | 0.384 |
| Tumour diameter (mm) | 23 (16–32) | 18 (13–26) | 0.073 | 18 (13–29) | 26 (14–34) | 0.337 |
| Tumour volume (ml) | 5.0 (2.2–13.0) | 2.3 (0.8–7.4) | 0.052 | 3.3 (1.1–8.3) | 4.6 (1.1–9.9) | 0.663 |
| Ablation zone volume (ml) | 36.1 (19.6–60.0) | 42.9 (24.5–55.6) | 0.866 | 32.2 (18.6–77.1) | 96.6 (48.3–109.3) | 0.005 |
| Applied energy (kJ) | 108.0 (57.6–162.0) | 85.1 (60.8–133.7) | 0.678 | 59.3 (23.0–109.2) | 126.0 (49.8–140.1) | 0.029 |
| Needle positions (n) | 3 (2–4) | 3 (2–4) | 0.609 | 3 (2–3) | 2 (2–3) | 0.752 |
| R(T:AZV) | 0.22 (0.05–0.38) | 0.06 (0.03–0.13) | 0.010 | 0.08 (0.05–0.21) | 0.04 (0.03–0.11) | 0.067 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiter, S.J.S.; de Jong, J.E.; Pennings, J.P.; de Haas, R.J.; de Jong, K.P. Comparison of Two 2.45 GHz Microwave Ablation Devices with Respect to Ablation Zone Volume in Relation to Applied Energy in Patients with Malignant Liver Tumours. Cancers 2022, 14, 5570. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225570
Ruiter SJS, de Jong JE, Pennings JP, de Haas RJ, de Jong KP. Comparison of Two 2.45 GHz Microwave Ablation Devices with Respect to Ablation Zone Volume in Relation to Applied Energy in Patients with Malignant Liver Tumours. Cancers. 2022; 14(22):5570. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225570
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiter, Simeon J. S., Jamila E. de Jong, Jan Pieter Pennings, Robbert J. de Haas, and Koert P. de Jong. 2022. "Comparison of Two 2.45 GHz Microwave Ablation Devices with Respect to Ablation Zone Volume in Relation to Applied Energy in Patients with Malignant Liver Tumours" Cancers 14, no. 22: 5570. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225570
APA StyleRuiter, S. J. S., de Jong, J. E., Pennings, J. P., de Haas, R. J., & de Jong, K. P. (2022). Comparison of Two 2.45 GHz Microwave Ablation Devices with Respect to Ablation Zone Volume in Relation to Applied Energy in Patients with Malignant Liver Tumours. Cancers, 14(22), 5570. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225570







