Diagnostic and Therapeutic Algorithm for Appendiceal Tumors and Pseudomyxoma Peritonei: A Consensus of the Peritoneal Malignancies Oncoteam of the Italian Society of Surgical Oncology (SICO)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rizvi, S.A.; Syed, W.; Shergill, R. Approach to pseudomyxoma peritonei. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2018, 10, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugarbaker, P.H.; Ronnett, B.M.; Archer, A.; Averbach, A.M.; Bland, R.; Chang, D.; Dalton, R.R.; Ettinghausen, S.E.; Jacquet, P.; Jelinek, J.; et al. Pseudomyxoma peritonei syndrome. Adv. Surg. 1996, 30, 233–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Järvinen, P.; Ristimäki, A.; Kantonen, J.; Aronen, M.; Huuhtanen, R.; Järvinen, H.; Lepistö, A. Comparison of serial debulking and cytoreductive surgery with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in pseudomyxoma peritonei of appendiceal origin. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2014, 29, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glehen, O.; Mohamed, F.; Sugarbaker, P.H. Incomplete Cytoreduction in 174 Patients with Peritoneal Carcinomatosis from Appendiceal Malignancy. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitch, K.; Bernstein, S.J.; Aguilar, M.D.; Burnand, B.; LaCalle, J.R. The Rand/UCLA Appropriateness Method User’s Manual; RAND Corporation: Santa Monica, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sugarbaker, P.H.; Chang, D. Results of Treatment of 385 Patients With Peritoneal Surface Spread of Appendiceal Malignancy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 1999, 6, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, N.J.; Sobin, L.H. Epithelial noncarcinoid tumors and tumor-like lesions of the appendix. Cancer 1995, 76, 2383–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronnett, B.M.; Zahn, C.M.; Kurman, R.J.; Kass, M.E.; Sugarbaker, P.H.; Shmookler, B.M. Disseminated peritoneal adenomucinosis and peritoneal mucinous carcinomatosis: A clinicopathologic analysis of 109 cases with emphasis on distinguishing pathologic features, site of origin, prognosis and relationship to “pseudomyxoma peritonei”. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1995, 19, 1390–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misdraji, J.; Yantiss, R.K.; Graeme-Cook, F.M.; Balis, U.J.; Young, R.H. Appendiceal mucinous neoplasms: A clinicopathologic analysis of 107 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2003, 27, 1089–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, R.K.; Longacre, T.A. Pseudomyxoma peritonei syndrome: Classification of appendiceal mucinous tumours. In Peritoneal Carcinomatosis: A Multidisciplinary Approach; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 134, pp. 71–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, R.F.; Stewart, J.H.; Russell, G.B.; Levine, E.A.; Geisinger, K.R. Pseudomyxoma Peritonei of Appendiceal Origin: A Clinicopathologic Analysis of 101 Patients Uniformly Treated at a Single Institution, with Literature Review. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2006, 30, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, N.J.; Cecil, T.D.; Mohamed, F.; Sobin, L.H.; Sugarbaker, P.H.; Gonzalez-Moreno, S.; Taflampas, P.; Chapman, S.; Moran, B.J.; Peritoneal Surface Oncology Group International. A consensus for classification and pathologic reporting of pseudomyxoma peritonei and associated appendiceal neoplasia. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taflampas, P.; Dayal, S.; Chandrakumaran, K.; Mohamed, F.; Cecil, T.; Moran, B. Pre-operative tumour marker status predicts recurrence and survival after complete cytoreduction and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy for appendiceal Pseudomyxoma Peritonei: Analysis of 519 patients. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 40, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, T.C.; Chong, C.H.; Liauw, W.; Zhao, J.; Morris, D.L. Inflammatory Markers in Blood and Serum Tumor Markers Predict Survival in Patients with Epithelial Appendiceal Neoplasms Undergoing Surgical Cytoreduction and Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy. Ann. Surg. 2012, 256, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, T.C.; Liauw, W.; Morris, D.L. Early recurrence of pseudomyxoma peritonei following treatment failure of cytoreductive surgery and perioperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy is indicative of a poor survival outcome. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2012, 27, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, T.C.; Yan, T.; Smigielski, M.; Zhu, K.J.; Ng, K.M.; Zhao, J.; Morris, D.L. Long-Term Survival in Patients with Pseudomyxoma Peritonei Treated with Cytoreductive Surgery and Perioperative Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy: 10 Years of Experience from a Single Institution. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 16, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Alzahrani, N.A.; Chua, T.C.; Morris, D.L. Histological Subtype Remains a Significant Prognostic Factor for Survival Outcomes in Patients with Appendiceal Mucinous Neoplasm with Peritoneal Dissemination. Dis. Colon Rectum 2017, 60, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.-L.; Liauw, W.; Chua, T.; Morris, D.L. Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA 19-9) is an independent prognostic indicator in pseudomyxoma peritonei post cytoreductive surgery and perioperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2013, 4, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozman, M.A.; Fisher, O.M.; Rebolledo, B.-A.J.; Valle, S.J.; Alzahrani, N.; Liauw, W.; Morris, D.L. CA 19-9 to peritoneal carcinomatosis index (PCI) ratio is prognostic in patients with epithelial appendiceal mucinous neoplasms and peritoneal dissemination undergoing cytoreduction surgery and intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 43, 2299–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusamura, S.; Hutanu, I.; Baratti, D.; Deraco, M. Circulating tumor markers: Predictors of incomplete cytoreduction and powerful determinants of outcome in pseudomyxoma peritonei. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 108, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bree, E.; Koops, W.; Kröger, R.; van Ruth, S.; Verwaal, V.; Zoetmulder, F. Preoperative computed tomography and selection of patients with colorectal peritoneal carcinomatosis for cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2006, 32, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, J.-L.; Yan, T.; Glenn, D.; Morris, D.L. Evaluation of Preoperative Computed Tomography in Estimating Peritoneal Cancer Index in Colorectal Peritoneal Carcinomatosis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 16, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menassel, B.; Duclos, A.; Passot, G.; Dohan, A.; Payet, C.; Isaac, S.; Valette, P.; Glehen, O.; Rousset, P. Preoperative CT and MRI prediction of non-resectability in patients treated for pseudomyxoma peritonei from mucinous appendiceal neoplasms. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 42, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, R.N.; Barone, R.M.; Lucero, J. Comparison of MRI and CT for Predicting the Peritoneal Cancer Index (PCI) Preoperatively in Patients Being Considered for Cytoreductive Surgical Procedures. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 1708–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, R.N.; Barone, R.M.; Lee, M.J. Surveillance MR Imaging is Superior to Serum Tumor Markers for Detecting Early Tumor Recurrence in Patients with Appendiceal Cancer Treated with Surgical Cytoreduction and HIPEC. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel, J.; Sugarbaker, P. Pseudomyxoma peritonei in a hernia sac: Analysis of 20 patients in whom mucoid fluid was found during a hernia repair. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2001, 27, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, G.H.C.; Shamji, T.; Mehta, A.; Chandrakumaran, K.; Dayal, S.; Mohamed, F.; Carr, N.J.; Rowaiye, B.; Cecil, T.; Moran, B.J. Diagnostic and therapeutic laparoscopy in assessment and management of patients with appendiceal neoplasms. Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 34, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, R.A.; Hemanth Raj, E. Diagnostic Laparoscopy in the Pre-operative Assessment of Patients Undergoing Cytoreductive Surgery and HIPEC for Peritoneal Surface Malignancies. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 7, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, E.M.A.; Farquharson, S.M.; Moran, B.J. Management of an unexpected appendiceal neoplasm. Br. J. Surg. 2006, 93, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.-S.; Choi, S.T.; Lee, J.N.; Kim, K.K.; Park, Y.H.; Baek, J.H. A retrospective clinicopathological analysis of appendiceal tumors from 3,744 appendectomies: A single-institution study. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2011, 26, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaglio, M.; Sinukumar, S.; Kusamura, S.; Milione, M.; Pietrantonio, F.; Battaglia, L.; Guadagni, S.; Baratti, D.; Deraco, M. Correction to: Clinical Surveillance After Macroscopically Complete Surgery for Low-Grade Appendiceal Mucinous Neoplasms (LAMN) with or Without Limited Peritoneal Spread: Long-Term Results in a Prospective Series. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pape, U.-F.; Niederle, B.; Costa, F.; Gross, D.; Kelestimur, F.; Kianmanesh, R.; Knigge, U.; Öberg, K.; Pavel, M.; Perren, A.; et al. ENETS Consensus Guidelines for Neuroendocrine Neoplasms of the Appendix (Excluding Goblet Cell Carcinomas). Neuroendocrinology 2016, 103, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, Y.J.; Mack, L.A.; Gui, X.; Carr, N.; Sideris, L.; Temple, W.J.; Dubé, P.; Chandrakumaran, K.; Moran, B.J.; Cecil, T.D. Cytoreductive Surgery with Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy: An Emerging Treatment Option for Advanced Goblet Cell Tumors of the Appendix. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clift, A.K.; Kornasiewicz, O.; Drymousis, P.; Faiz, O.; Wasan, H.S.; Kinross, J.M.; Cecil, T.; Frilling, A. Goblet cell carcinomas of the appendix: Rare but aggressive neoplasms with challenging management. Endocr. Connect. 2018, 7, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Meyerson, C.; Kassardjian, A.; Westbrook, L.; Zheng, W.; Wang, H.L. Goblet Cell Carcinoid/Carcinoma: An Update. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2019, 26, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yozu, M.; Johncilla, M.E.; Srivastava, A.; Ryan, D.P.; Cusack, J.C.; Doyle, L.; Setia, N.; Yang, M.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Odze, R.D.; et al. Histologic and Outcome Study Supports Reclassifying Appendiceal Goblet Cell Carcinoids as Goblet Cell Adenocarcinomas, and Grading and Staging Similarly to Colonic Adenocarcinomas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andréasson, H.; Graf, W.; Nygren, P.; Glimelius, B.; Mahteme, H. Outcome differences between debulking surgery and cytoreductive surgery in patients with pseudomyxoma peritonei. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 38, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, N.; Chandrakumaran, K.; Dayal, S.; Mohamed, F.; Cecil, T.D.; Moran, B.J. Cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in 1000 patients with perforated appendiceal epithelial tumours. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 42, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govaerts, K.; Lurvink, R.; De Hingh, I.; Van der Speeten, K.; Villeneuve, L.; Kusamura, S.; Kepenekian, V.; Deraco, M.; Glehen, O.; Moran, B.; et al. Appendiceal tumours and pseudomyxoma peritonei: Literature review with PSOGI/EURACAN clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis and treatment. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 11–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, R.N.; Barone, R.M.; Gurney, J.M.; Muller, W.D. Mucinous Appendiceal Neoplasms: Preoperative MR Staging and Classification Compared with Surgical and Histopathologic Findings. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 190, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, D.; Benizri, E.; Vernerey, D.; Eldweny, H.; Dipietrantonio, D.; Pocard, M. Preoperative criteria of incomplete resectability of peritoneal carcinomatosis from non-appendiceal colorectal carcinoma. Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 2005, 29, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benizri, E.I.; Bernard, J.-L.; Rahili, A.; Benchimol, D.; Bereder, J.-M. Small bowel involvement is a prognostic factor in colorectal carcinomatosis treated with complete cytoreductive surgery plus hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, B.; Baratti, D.; Yan, T.D.; Kusamura, S.; Deraco, M. Consensus statement on the loco-regional treatment of appendiceal mucinous neoplasms with peritoneal dissemination (pseudomyxoma peritonei). J. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 98, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayal, S.; Taflampas, P.; Riss, S.; Chandrakumaran, K.; Cecil, T.D.; Mohamed, F.; Moran, B.J. Complete Cytoreduction for Pseudomyxoma Peritonei Is Optimal but Maximal Tumor Debulking May Be Beneficial in Patients in Whom Complete Tumor Removal Cannot Be Achieved. Dis. Colon Rectum 2013, 56, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, S.; Mohamed, F.; Yadegarfar, G.; Youssef, H.; Moran, B. Prospective longitudinal study of quality of life following cytoreductive surgery and intraperitoneal chemotherapy for pseudomyxoma peritonei. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 36, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, T.C.; Moran, B.J.; Sugarbaker, P.H.; Levine, E.A.; Glehen, O.; Gilly, F.N.; Baratti, D.; Deraco, M.; Elias, D.; Sardi, A.; et al. Early- and Long-Term Outcome Data of Patients with Pseudomyxoma Peritonei from Appendiceal Origin Treated by a Strategy of Cytoreductive Surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2449–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Sweringen, H.L.; Hanseman, D.J.; Ahmad, S.A.; Edwards, M.J.; Sussman, J.J. Predictors of survival in patients with high-grade peritoneal metastases undergoing cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Surgery 2012, 152, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghav, K.P.; Shetty, A.V.; Kazmi, S.M.; Zhang, N.; Morris, J.; Taggart, M.; Fournier, K.; Royal, R.; Mansfield, P.; Eng, C.; et al. Impact of Molecular Alterations and Targeted Therapy in Appendiceal Adenocarcinomas. Oncologist 2013, 18, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, K.M.; Hanna, N.N.; Zhu, Y.; Jain, A.; Kesmodel, S.B.; Switzer, R.A.; Taylor, L.M.; Alexander, H.R. Assessment of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Operative Parameters and Outcome in Patients with Peritoneal Dissemination from High-Grade Appendiceal Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieu, C.; Lambert, L.; Wolff, R.; Eng, C.; Zhang, N.; Wen, S.; Rafeeq, S.; Taggart, M.; Fournier, K.; Royal, R.; et al. Systemic chemotherapy and surgical cytoreduction for poorly differentiated and signet ring cell adenocarcinomas of the appendix. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanov, V.; Sardi, A.; Ledakis, P.; Aydin, N.; Nieroda, C.; Sittig, M.; Nunez, M.; Gushchin, V. Systemic chemotherapy (SC) before cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (CRS/HIPEC) in patients with peritoneal mucinous carcinomatosis of appendiceal origin (PMCA). Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 41, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijelic, L.; Kumar, A.S.; Stuart, O.A.; Sugarbaker, P.H. Systemic chemotherapy prior to cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC for carcinomatosis from appendix cancer: Impact on perioperative outcomes and short-term survival. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 163284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratti, D.; Kusamura, S.; Nonaka, D.; Cabras, A.D.; Laterza, B.; Deraco, M. Pseudomyxoma peritonei: Biological features are the dominant prognostic determinants after complete cytoreduction and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Ann. Surg. 2009, 249, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackham, A.U.; Swett, K.; Eng, C.; Sirintrapun, J.; Bergman, S.; Geisinger, K.R.; Votanopoulos, K.; Stewart, J.H.; Shen, P.; Levine, E.A. Perioperative systemic chemotherapy for appendiceal mucinous carcinoma peritonei treated with cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 109, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Zuluaga, C.A.; King, M.C.; Ledakis, P.; Gushchin, V.; Sittig, M.; Nieroda, C.; Zambrano-Vera, K.; Sardi, A. Systemic chemotherapy before cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (CRS/HIPEC) in patients with high-grade mucinous carcinoma peritonei of appendiceal origin. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 45, 1598–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomas, D.A.; Miller, R.C.; Donohue, J.H.; Gill, S.; Thurmes, P.J.; Haddock, M.G.; Quevedo, J.F.; Gunderson, L.L. Intraperitoneal Treatment for Peritoneal Mucinous Carcinomatosis of Appendiceal Origin After Operative Management. Ann. Surg. 2009, 249, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asare, E.A.; Compton, C.C.; Hanna, N.N.; Kosinski, L.A.; Washington, M.K.; Kakar, S.; Weiser, M.R.; Overman, M.J. The impact of stage, grade, and mucinous histology on the efficacy of systemic chemotherapy in adenocarcinomas of the appendix: Analysis of the National Cancer Data Base. Cancer 2015, 122, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, K.A.; Russell, G.B.; Votanopoulos, K.I.; Shen, P.; Stewart, J.H.; Levine, E.A. Peritoneal dissemination from high-grade appendiceal cancer treated with cytoreductive surgery (CRS) and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC). J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2016, 7, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J.F.; Chase, J.L.; Wolff, R.A.; Lambert, L.A.; Mansfield, P.F.; Overman, M.J.; Ohinata, A.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Eng, C. Modern systemic chemotherapy in surgically unresectable neoplasms of appendiceal origin. Cancer 2010, 116, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farquharson, A.L.; Pranesh, N.; Witham, G.; Swindell, R.; Taylor, M.B.; Renehan, A.; Rout, S.; Wilson, M.S.; O’Dwyer, S.T.; Saunders, M.P. A phase II study evaluating the use of concurrent mitomycin C and capecitabine in patients with advanced unresectable pseudomyxoma peritonei. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 99, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrantonio, F.; Maggi, C.; Fanetti, G.; Iacovelli, R.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Ricchini, F.; Deraco, M.; Perrone, F.; Baratti, D.; Kusamura, S.; et al. FOLFOX-4 Chemotherapy for Patients with Unresectable or Relapsed Peritoneal Pseudomyxoma. Oncologist 2014, 19, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrantonio, F.; Berenato, R.; Maggi, C.; Caporale, M.; Milione, M.; Perrone, F.; Tamborini, E.; Baratti, D.; Kusamura, S.; Mariani, L.; et al. GNAS mutations as prognostic biomarker in patients with relapsed peritoneal pseudomyxoma receiving metronomic capecitabine and bevacizumab: A clinical and translational study. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraide, S.; Komine, K.; Sato, Y.; Ouchi, K.; Imai, H.; Saijo, K.; Takahashi, M.; Takahashi, S.; Shirota, H.; Takahashi, M.; et al. Efficacy of modified FOLFOX6 chemotherapy for patients with unresectable pseudomyxoma peritonei. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, A.; Corallo, S.; Niger, M.; Antista, M.; Randon, G.; Morano, F.; Milione, M.; Kusamura, S.; Baratti, D.; Guaglio, M.; et al. Metronomic Capecitabine with Cyclophosphamide Regimen in Unresectable or Relapsed Pseudomyxoma Peritonei. Clin. Color. Cancer 2019, 18, e179–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrantonio, F.; Perrone, F.; Mennitto, A.; Gleeson, E.M.; Milione, M.; Tamborini, E.; Busico, A.; Settanni, G.; Berenato, R.; Caporale, M.; et al. Toward the molecular dissection of peritoneal pseudomyxoma. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 2097–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, J.H.; Overman, M.J.; Fournier, K.F.; Royal, R.E.; Ohinata, A.; Rafeeq, S.; Beaty, K.; Phillips, J.K.; Wolff, R.A.; Mansfield, P.F.; et al. Improved Survival with Anti-VEGF Therapy in the Treatment of Unresectable Appendiceal Epithelial Neoplasms. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 2578–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, Y.; Fleten, K.G.; Abrahamsen, T.W.; Reed, W.; Davidson, B. Anti-Angiogenic Treatment in Pseudomyxoma Peritonei-Still a Strong Preclinical Rationale. Cancers 2021, 13, 2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Tamura, T.; Yamada, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Muranishi, S. Pharmacokinetics of Mitomycin C (MMC) after Intraperitoneal Administration of MMC-Gelatin Gel and Its Anti-tumor Effects against Sarcoma-180 Bearing Mice. J. Drug Target. 1997, 4, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Speeten, K.; Stuart, O.A.; Chang, D.; Mahteme, H.; Sugarbaker, P.H. Changes induced by surgical and clinical factors in the pharmacology of intraperitoneal mitomycin C in 145 patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 68, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.; Cecil, T.; Moran, B.; Sugarbaker, P.H. A New Standard of Care for the Management of Peritoneal Surface Malignancy. Curr. Oncol. 2011, 18, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, E.A.; Stewart, J.H.; Shen, P.; Russell, G.B.; Loggie, B.L.; Votanopoulos, K.I. Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy for Peritoneal Surface Malignancy: Experience with 1,000 Patients. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2014, 218, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, D.; Bonnay, M.; Puizillou, J.M.; Antoun, S.; Demirdjian, S.; El Otmany, A.; Pignon, J.P.; Drouard-Troalen, L.; Ouellet, J.F.; Ducreux, M. Heated intra-operative intraperitoneal oxaliplatin after complete resection of peritoneal carcinomatosis: Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution. Ann. Oncol. 2002, 13, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iv, J.H.S.; Shen, P.; Russell, G.; Rn, J.F.; Bs, L.M.; Ms, F.M.C.; Levine, K.; Jones, B.T.; Levine, E.A. A Phase I Trial of Oxaliplatin for Intraperitoneal Hyperthermic Chemoperfusion for the Treatment of Peritoneal Surface Dissemination from Colorectal and Appendiceal Cancers. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 2137–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Rieu, Q.C.; White-Koning, M.; Picaud, L.; Lochon, I.; Marsili, S.; Gladieff, L.; Chatelut, E.; Ferron, G. Population pharmacokinetics of peritoneal, plasma ultrafiltrated and protein-bound oxaliplatin concentrations in patients with disseminated peritoneal cancer after intraperitoneal hyperthermic chemoperfusion of oxaliplatin following cytoreductive surgery: Correlation between oxaliplatin exposure and thrombocytopenia. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 74, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomel, C.; Ferron, G.; Lorimier, G.; Rey, A.; Lhomme, C.; Classe, J.; Bereder, J.; Quenet, F.; Meeus, P.; Marchal, F.; et al. Hyperthermic intra-peritoneal chemotherapy using Oxaliplatin as consolidation therapy for advanced epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Results of a phase II prospective multicentre trial. CHIPOVAC study. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 36, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, E.A.; Votanopoulos, K.I.; Shen, P.; Russell, G.; Fenstermaker, J.; Mansfield, P.; Bartlett, D.; Stewart, J.H. A Multicenter Randomized Trial to Evaluate Hematologic Toxicities after Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy with Oxaliplatin or Mitomycin in Patients with Appendiceal Tumors. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2018, 226, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Statement | AMS | Appropriate | IPR | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 2 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 3 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 4 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 5 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 6 | 9 | Yes | 8–9 | valid |
| 7 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 8 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 9 | 9 | Yes | 8.7–9 | valid |
| 10 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 11 | 9 | Yes | 8.7–9 | valid |
| 12 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 13 | 9 | Yes | 8.7–9 | valid |
| 14 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 15 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 16 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 17 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 18 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 19 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 20 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 21 | 9 | Yes | 8.7–9 | valid |
| 22 | 9 | Yes | 8.7–9 | valid |
| 23 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 24 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 25 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 26 | 8 | Yes | 6.7–8 | not valid |
| 27 | 9 | Yes | 8.7–9 | valid |
| 28 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 29 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
| 30 | 9 | Yes | 8.7–9 | valid |
| 31 | 8 | Yes | 8–9 | valid |
| 33 | 9 | Yes | 8–9 | valid |
| 33 | 9 | Yes | 8.7–9 | valid |
| 34 | 9 | Yes | 9–9 | valid |
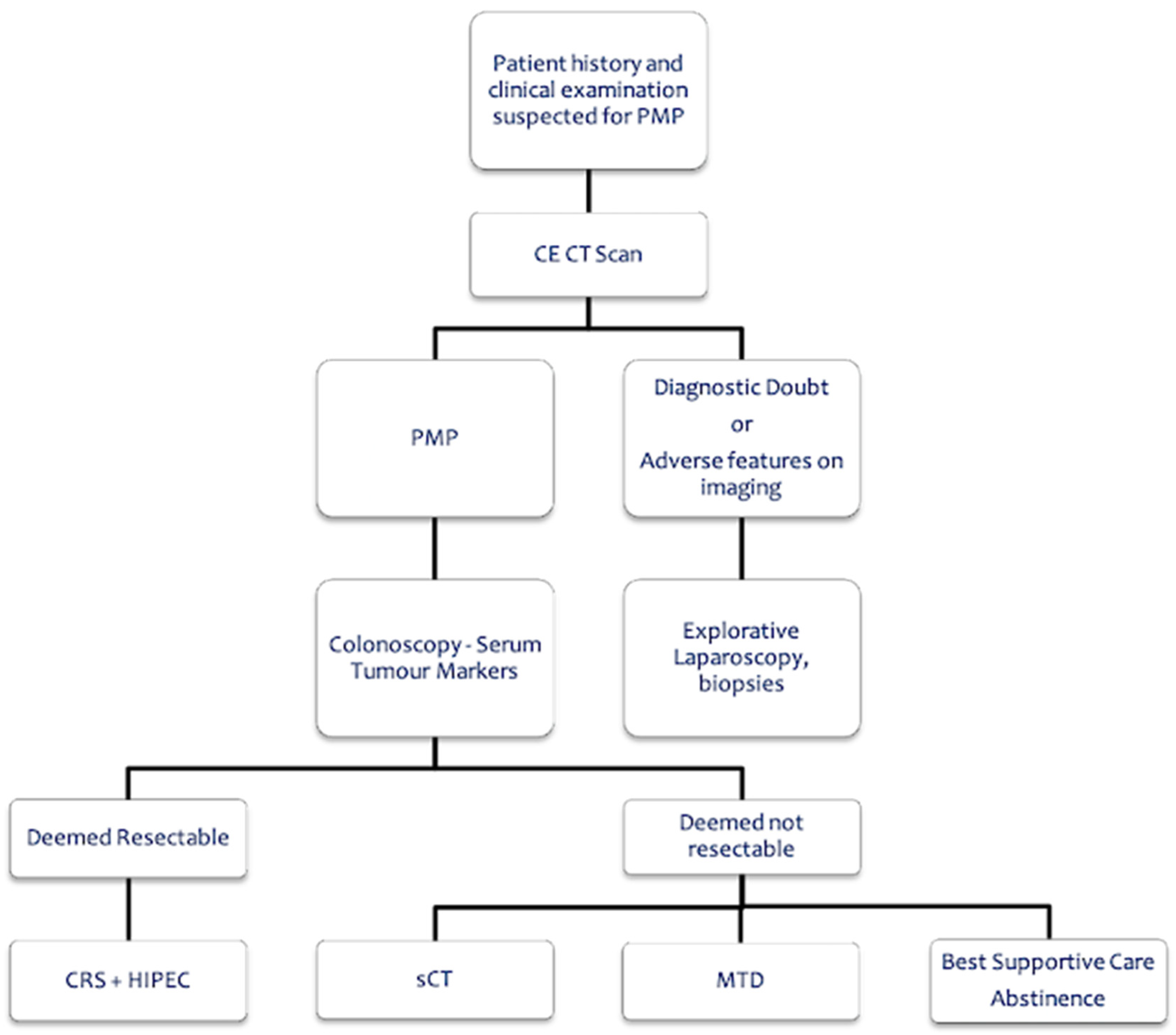
| Flowchart 1 | 8 | Yes | 8–9 | valid |
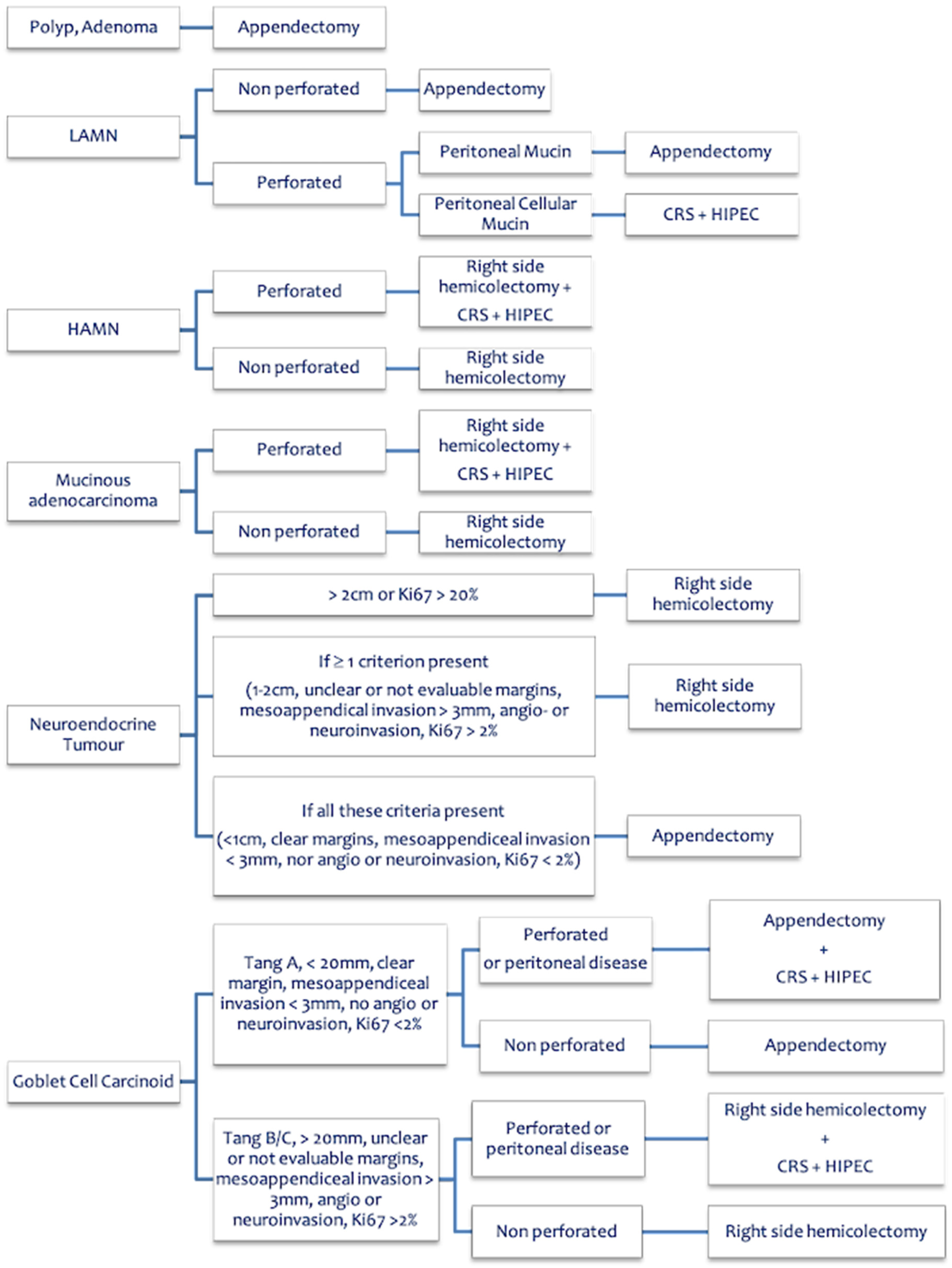
| Flowchart 2 | 9 | Yes | 8–9 | valid |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaira, M.; Robella, M.; Guaglio, M.; Berchialla, P.; Sommariva, A.; Valle, M.; Pasqual, E.M.; Roviello, F.; Framarini, M.; Fiorentini, G.; et al. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Algorithm for Appendiceal Tumors and Pseudomyxoma Peritonei: A Consensus of the Peritoneal Malignancies Oncoteam of the Italian Society of Surgical Oncology (SICO). Cancers 2023, 15, 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030728
Vaira M, Robella M, Guaglio M, Berchialla P, Sommariva A, Valle M, Pasqual EM, Roviello F, Framarini M, Fiorentini G, et al. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Algorithm for Appendiceal Tumors and Pseudomyxoma Peritonei: A Consensus of the Peritoneal Malignancies Oncoteam of the Italian Society of Surgical Oncology (SICO). Cancers. 2023; 15(3):728. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030728
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaira, Marco, Manuela Robella, Marcello Guaglio, Paola Berchialla, Antonio Sommariva, Mario Valle, Enrico Maria Pasqual, Franco Roviello, Massimo Framarini, Giammaria Fiorentini, and et al. 2023. "Diagnostic and Therapeutic Algorithm for Appendiceal Tumors and Pseudomyxoma Peritonei: A Consensus of the Peritoneal Malignancies Oncoteam of the Italian Society of Surgical Oncology (SICO)" Cancers 15, no. 3: 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030728
APA StyleVaira, M., Robella, M., Guaglio, M., Berchialla, P., Sommariva, A., Valle, M., Pasqual, E. M., Roviello, F., Framarini, M., Fiorentini, G., Sammartino, P., Ilari Civit, A., Di Giorgio, A., Ansaloni, L., & Deraco, M. (2023). Diagnostic and Therapeutic Algorithm for Appendiceal Tumors and Pseudomyxoma Peritonei: A Consensus of the Peritoneal Malignancies Oncoteam of the Italian Society of Surgical Oncology (SICO). Cancers, 15(3), 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030728







