TRPV6 Channel Is Involved in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Aggressiveness and Resistance to Chemotherapeutics
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Tissue Data
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Transfection
2.4. RNA Sequencing
2.5. RT-PCR
2.6. Western Blot
2.7. Mn2+ Quench Experiments
2.8. Cell Count
2.9. Cell Cycle Assay
2.10. Cell Viability Analysis
2.11. MTS Assay
2.12. Annexin V Staining
2.13. Wound-Healing Assay
2.14. In Vivo Experiments
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. TRPV6 Expression in PDAC Tumor Tissues Correlates with Tumor Stage, Differentiation and Proliferation
3.2. Characterization of Panc-1 Cells with Altered TRPV6 Expression
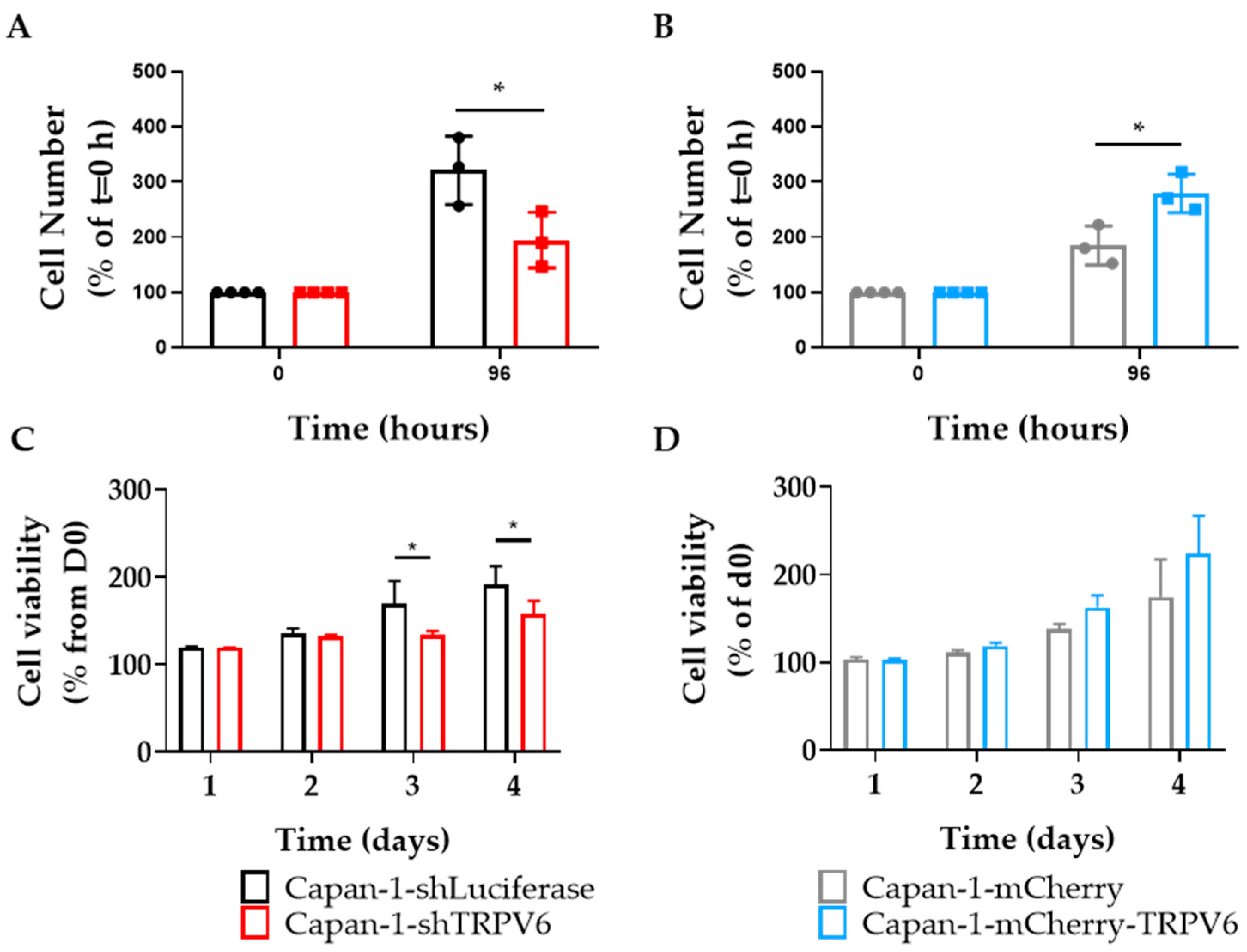
3.3. TRPV6 Knockdown Impairs Proliferation, Cell Survival and Cell Cycle Progression of Panc-1 Cells
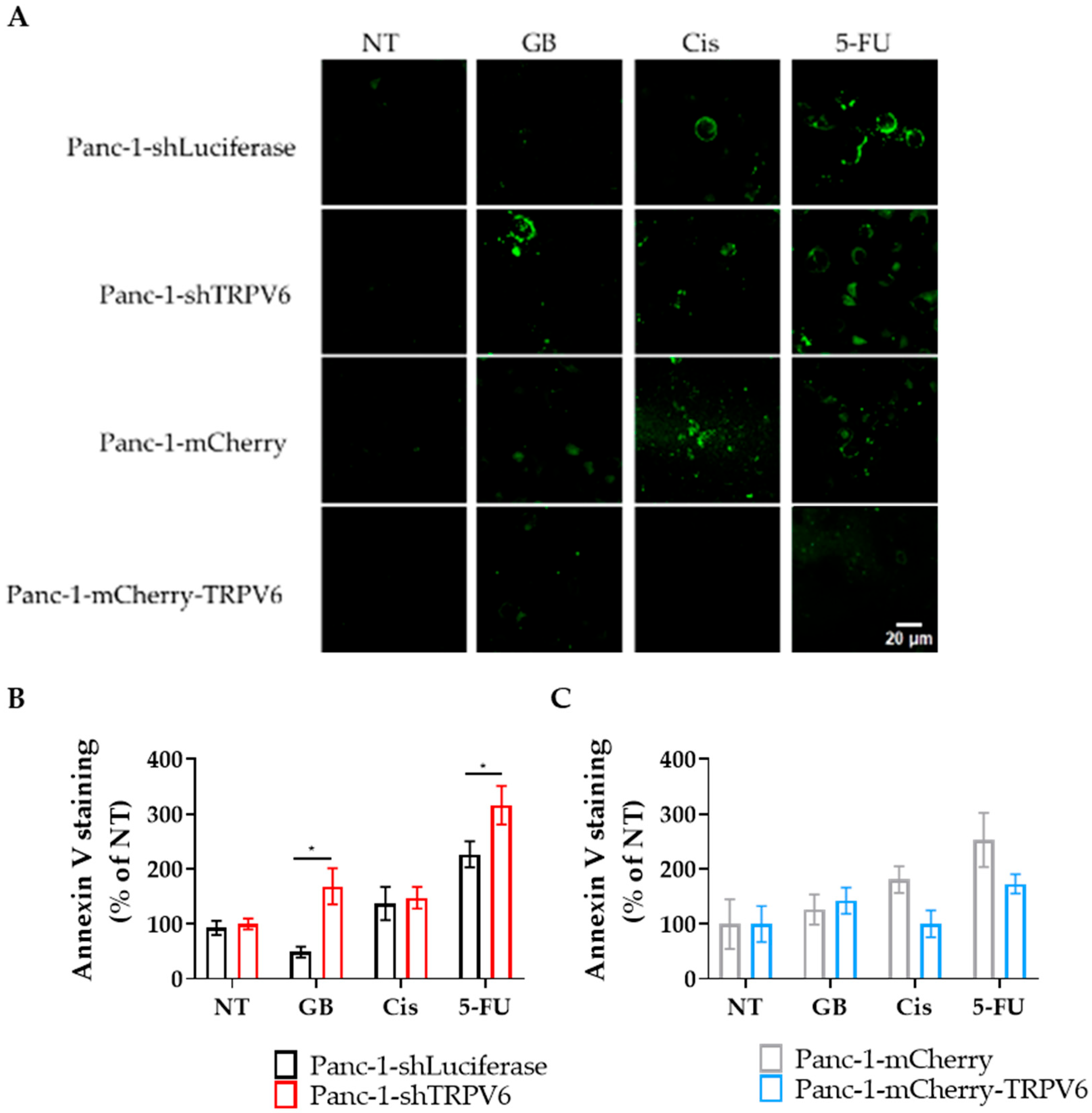
3.4. TRPV6 Increases Panc-1 Resistance to Chemotherapeutics
3.5. (Collective) Migration of Panc-1 Cells Depends on TRPV6 Channel Expression
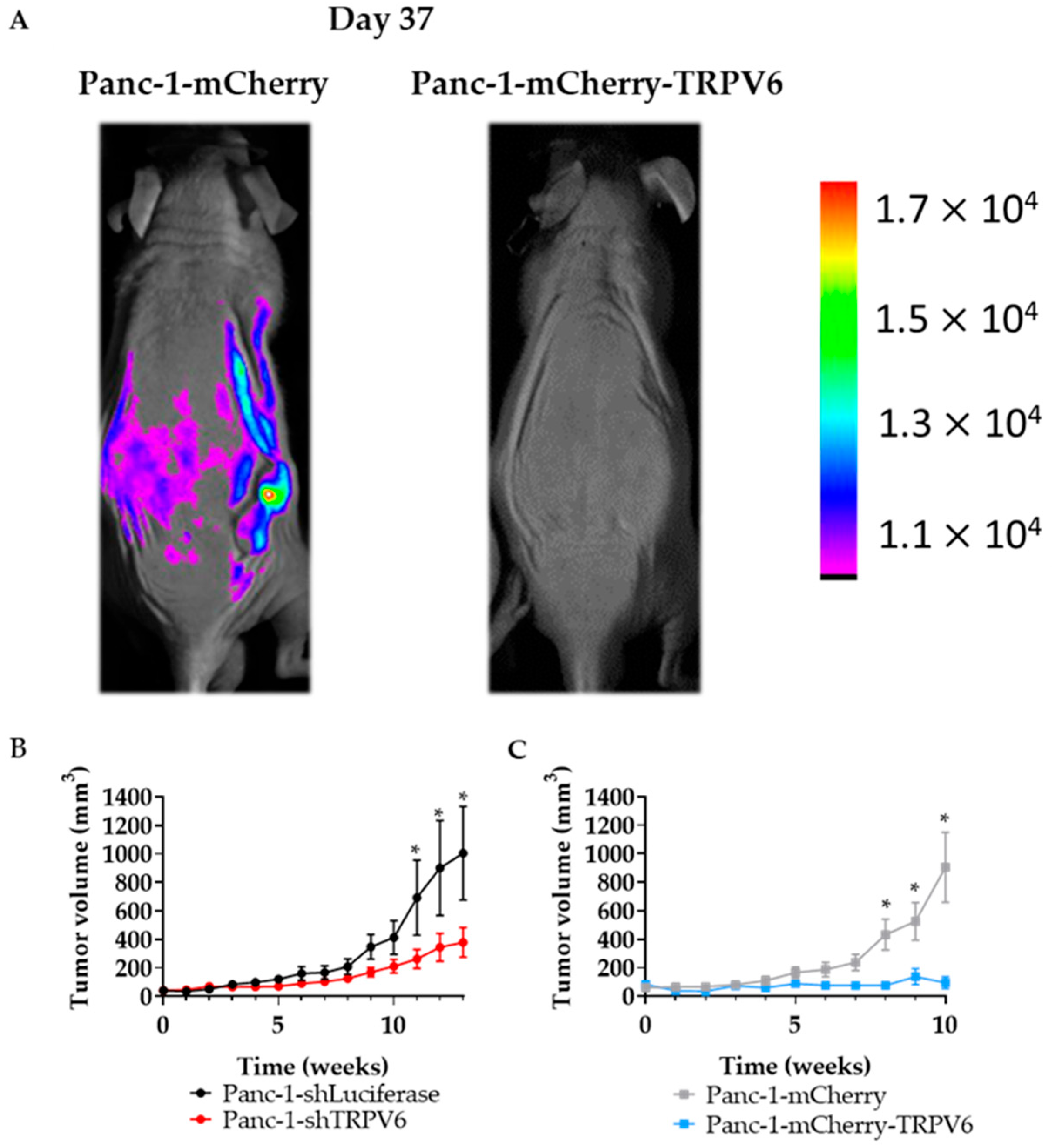
3.6. TRPV6 Dysregulation Inhibits Tumor Formation In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, J.; Chen, H.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, B.; You, L.; Zhang, T.; Dai, M.; Zhao, Y. Advances in the epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: Trends, risk factors, screening, and prognosis. Cancer Lett. 2021, 520, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarantis, P.; Koustas, E.; Papadimitropoulou, A.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Karamouzis, M.V. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Treatment hurdles, tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 12, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, L.; Peng, J.B.; Tou, L.; Takanaga, H.; Adam, R.M.; Hediger, M.A.; Freeman, M.R. Calcium-selective ion channel, CaT1, is apically localized in gastrointestinal tract epithelia and is aberrantly expressed in human malignancies. Lab. Investig. 2002, 82, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilius, B.; Szallasi, A. Transient receptor potential channels as drug targets: From the science of basic research to the art of medicine. Pharmacol. Rev. 2014, 66, 676–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevarskaya, N.; Skryma, R.; Shuba, Y. Ion Channels in Cancer: Are Cancer Hallmarks Oncochannelopathies? Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 559–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Wang, Y.; MacCormack, T.J.; Lutes, T.; Rice, C.; Davey, M.; Dugourd, D.; Ilenchuk, T.T.; Stewart, J.M. Inhibition of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 6 channel, elevated in human ovarian cancers, reduces tumour growth in a xenograft model. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3196–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhennin-Duthille, I.; Gautier, M.; Faouzi, M.; Guilbert, A.; Brevet, M.; Vaudry, D.; Ahidouch, A.; Sevestre, H.; Ouadid-Ahidouch, H. High expression of transient receptor potential channels in human breast cancer epithelial cells and tissues: Correlation with pathological parameters. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 28, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehen’kyi, V.; Flourakis, M.; Skryma, R.; Prevarskaya, N. TRPV6 channel controls prostate cancer cell proliferation via Ca(2+)/NFAT-dependent pathways. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7380–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, M.; Lehen’kyi, V.; Vandenberghe, M.; Beck, B.; Khalimonchyk, S.; Vanden Abeele, F.; Farsetti, L.; Germain, E.; Bokhobza, A.; Mihalache, A.; et al. TRPV6 calcium channel translocates to the plasma membrane via Orai1-mediated mechanism and controls cancer cell survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E3870–E3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landowski, C.P.; Bolanz, K.A.; Suzuki, Y.; Hediger, M.A. Chemical inhibitors of the calcium entry channel TRPV6. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, T.; Rajakyla, E.K.; Acheva, A.; Tojkander, S. TRPV6 calcium channel directs homeostasis of the mammary epithelial sheets and controls epithelial mesenchymal transition. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, J.K.; Brown, K.C.; Dom, A.M.; Witte, T.R.; Thornhill, B.A.; Crabtree, C.M.; Perry, H.E.; Brown, J.M.; Ball, J.G.; Creel, R.G.; et al. Capsaicin induces apoptosis in human small cell lung cancer via the TRPV6 receptor and the calpain pathway. Apoptosis 2014, 19, 1190–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Gou, H.; Zhu, J.; Tian, S.; Yu, L. Lidocaine inhibits the invasion and migration of TRPV6-expressing cancer cells by TRPV6 downregulation. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Dong, M.; Zhou, J.; Sheng, W.; Li, X.; Gao, W. Expression and prognostic significance of TRPV6 in the development and progression of pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccagnino, A.; Pilarsky, C.; Tawfik, D.; Sebens, S.; Trauzold, A.; Novak, I.; Schwab, A.; Kalthoff, H. In silico analysis of the transportome in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Eur. Biophys. J. 2016, 45, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oracz, G.; Zarod, M.; Ewers, M.; Laumen, H.; Gambin, T.; Kaminski, P.; Grabowska, I.; Drozak, A.; Kwiatkowski, S.; Wertheim-Tysarowska, K.; et al. Loss of function TRPV6 variants are associated with chronic pancreatitis in nonalcoholic early-onset Polish and German patients. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, I.A.; Prasad, H.; Banerjee, S.; Kurien, R.T.; Chowdhury, S.D.; Visweswariah, S.S. A novel frameshift mutation in TRPV6 is associated with hereditary pancreatitis. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1058057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masamune, A.; Kotani, H.; Sorgel, F.L.; Chen, J.M.; Hamada, S.; Sakaguchi, R.; Masson, E.; Nakano, E.; Kakuta, Y.; Niihori, T.; et al. Variants That Affect Function of Calcium Channel TRPV6 Are Associated With Early-Onset Chronic Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1626–1641.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haustrate, A.; Mihalache, A.; Cordier, C.; Gosset, P.; Prevarskaya, N.; Lehen’kyi, V. A Novel Anti-TRPV6 Antibody and Its Application in Cancer Diagnosis In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedchenko, N.; Reifenrath, J. Different approaches for interpretation and reporting of immunohistochemistry analysis results in the bone tissue—A review. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuntze, A.; Goetsch, O.; Fels, B.; Najder, K.; Unger, A.; Wilhelmi, M.; Sargin, S.; Schimmelpfennig, S.; Neumann, I.; Schwab, A.; et al. Protonation of Piezo1 Impairs Cell-Matrix Interactions of Pancreatic Stellate Cells. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehen’kyi, V.; Raphael, M.; Oulidi, A.; Flourakis, M.; Khalimonchyk, S.; Kondratskyi, A.; Gordienko, D.V.; Mauroy, B.; Bonnal, J.L.; Skryma, R.; et al. TRPV6 determines the effect of vitamin D3 on prostate cancer cell growth. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rhim, A.D.; Oberstein, P.E.; Thomas, D.H.; Mirek, E.T.; Palermo, C.F.; Sastra, S.A.; Dekleva, E.N.; Saunders, T.; Becerra, C.P.; Tattersall, I.W.; et al. Stromal elements act to restrain, rather than support, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinkawa, T.; Ohuchida, K.; Mochida, Y.; Sakihama, K.; Iwamoto, C.; Abe, T.; Ideno, N.; Mizuuchi, Y.; Shindo, K.; Ikenaga, N.; et al. Subtypes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on niche factor dependency show distinct drug treatment responses. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, I.A.; Lewis, P.D.; Mattos, C. A comprehensive survey of Ras mutations in cancer. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2457–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; McGoldrick, L.L.; Twomey, E.C.; Sobolevsky, A.I. Mechanism of calmodulin inactivation of the calcium-selective TRP channel TRPV6. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaau6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchtold, M.W.; Villalobo, A. The many faces of calmodulin in cell proliferation, programmed cell death, autophagy, and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 398–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Day, D.H.; Mathavarajah, S.; Myre, M.A.; Huber, R.J. Calmodulin-mediated events during the life cycle of the amoebozoan Dictyostelium discoideum. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2020, 95, 472–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettaieb, L.; Brule, M.; Chomy, A.; Diedro, M.; Fruit, M.; Happernegg, E.; Heni, L.; Horochowska, A.; Housseini, M.; Klouyovo, K.; et al. Ca2+ Signaling and Its Potential Targeting in Pancreatic Ductal Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, B.S.; Yuh, Y.J.; Song, H.S.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, K.H.; Jang, J.S.; Kim, S.R. Triplet cytotoxic chemotherapy with gemcitabine, 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin for advanced pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltai, T.; Reshkin, S.J.; Carvalho, T.M.A.; Di Molfetta, D.; Greco, M.R.; Alfarouk, K.O.; Cardone, R.A. Resistance to Gemcitabine in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Physiopathologic and Pharmacologic Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezencev, R.; Matyunina, L.V.; Wagner, G.T.; McDonald, J.F. Acquired resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to cisplatin is multifactorial with cell context-dependent involvement of resistance genes. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.B.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.P.; Zhang, T.P.; Liao, Q.; Shu, H. Recent studies of 5-fluorouracil resistance in pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 15682–15690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, G.; Akpinar, B.; Baran, Y.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Olsson, M. 5-Fluorouracil signaling through a calcium-calmodulin-dependent pathway is required for p53 activation and apoptosis in colon carcinoma cells. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4529–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principe, D.R.; Aissa, A.F.; Kumar, S.; Pham, T.N.D.; Underwood, P.W.; Nair, R.; Ke, R.; Rana, B.; Trevino, J.G.; Munshi, H.G.; et al. Calcium channel blockers potentiate gemcitabine chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2200143119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogel, A.; Fecher-Trost, C.; Wissenbach, U.; Flockerzi, V.; Schaefer, M. Ca2+ transport via TRPV6 is regulated by rapid internalization of the channel. Cell Calcium 2022, 106, 102634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallaher, J.A.; Brown, J.S.; Anderson, A.R.A. The impact of proliferation-migration tradeoffs on phenotypic evolution in cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Donatis, A.; Ranaldi, F.; Cirri, P. Reciprocal control of cell proliferation and migration. Cell Commun. Signal. 2010, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, A.S.; Shukla, P.K.; Bell, B.; Giorgianni, F.; Caires, R.; Fernandez-Pena, C.; Beranova, S.; Aihara, E.; Montrose, M.H.; Chaib, M.; et al. TRPV6 channel mediates alcohol-induced gut barrier dysfunction and systemic response. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilieva, I.O.; Tomilin, V.N.; Marakhova, I.I.; Shatrova, A.N.; Negulyaev, Y.A.; Semenova, S.B. Expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid channels TRPV5 and TRPV6 in human blood lymphocytes and Jurkat leukemia T cells. J. Membr. Biol. 2013, 246, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mesquita, G.; Haustrate, A.; Mihalache, A.; Soret, B.; Cordier, C.; Desruelles, E.; Duval, E.; Pethö, Z.; Prevarskaya, N.; Schwab, A.; et al. TRPV6 Channel Is Involved in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Aggressiveness and Resistance to Chemotherapeutics. Cancers 2023, 15, 5769. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245769
Mesquita G, Haustrate A, Mihalache A, Soret B, Cordier C, Desruelles E, Duval E, Pethö Z, Prevarskaya N, Schwab A, et al. TRPV6 Channel Is Involved in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Aggressiveness and Resistance to Chemotherapeutics. Cancers. 2023; 15(24):5769. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245769
Chicago/Turabian StyleMesquita, Gonçalo, Aurélien Haustrate, Adriana Mihalache, Benjamin Soret, Clément Cordier, Emilie Desruelles, Erika Duval, Zoltan Pethö, Natalia Prevarskaya, Albrecht Schwab, and et al. 2023. "TRPV6 Channel Is Involved in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Aggressiveness and Resistance to Chemotherapeutics" Cancers 15, no. 24: 5769. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245769
APA StyleMesquita, G., Haustrate, A., Mihalache, A., Soret, B., Cordier, C., Desruelles, E., Duval, E., Pethö, Z., Prevarskaya, N., Schwab, A., & Lehen’kyi, V. (2023). TRPV6 Channel Is Involved in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Aggressiveness and Resistance to Chemotherapeutics. Cancers, 15(24), 5769. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245769







