Genetic Alterations and Risk Factors for Recurrence in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Who Underwent Complete Surgical Resection
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Detection of EGFR Mutations
2.3. Detection of ALK Rearrangements
2.4. Detection of ROS1 Fusion
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Overall Patients
3.2. Prevalence of Genetic Alterations
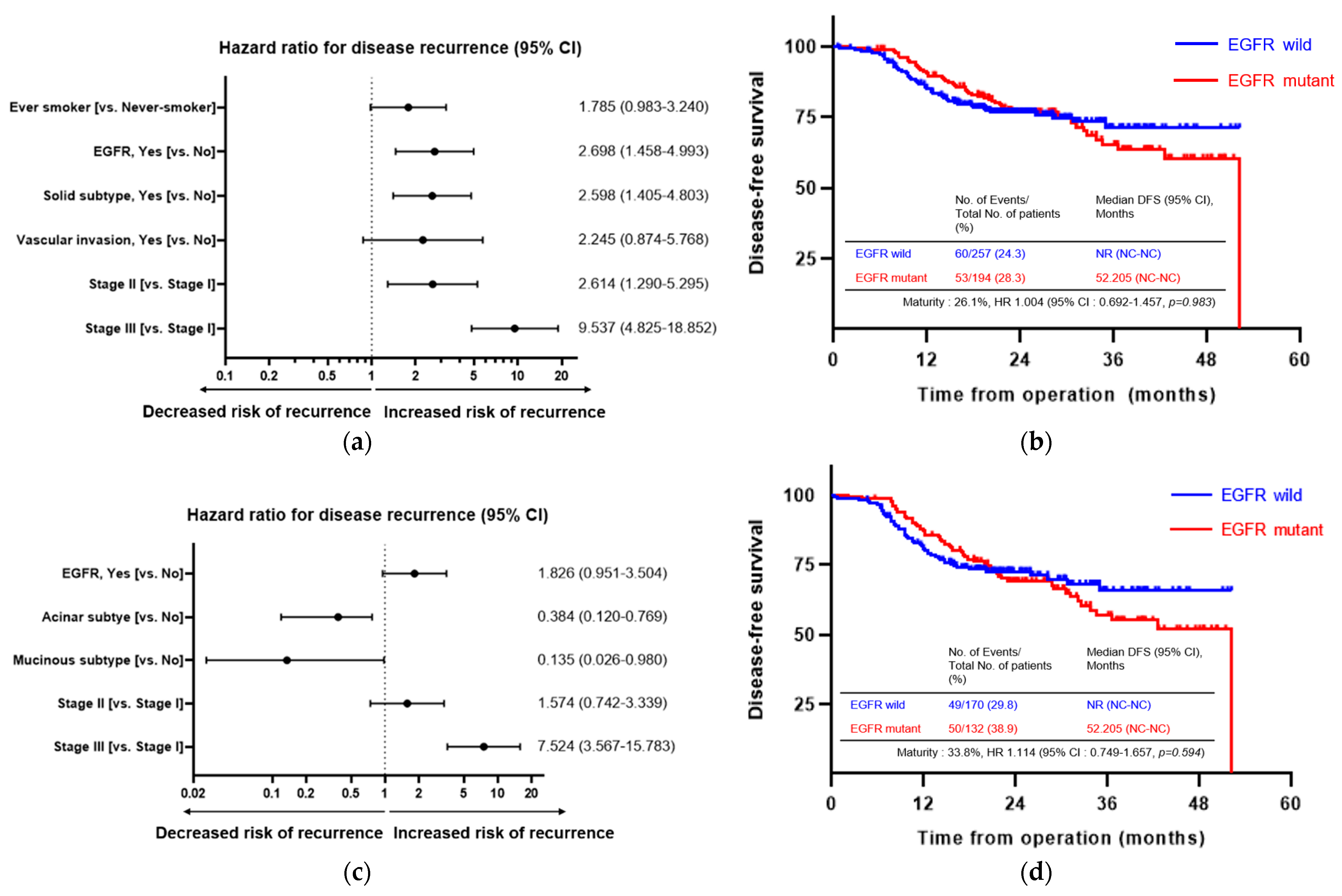
3.3. Prognostic Factors Associated with Disease Recurrence
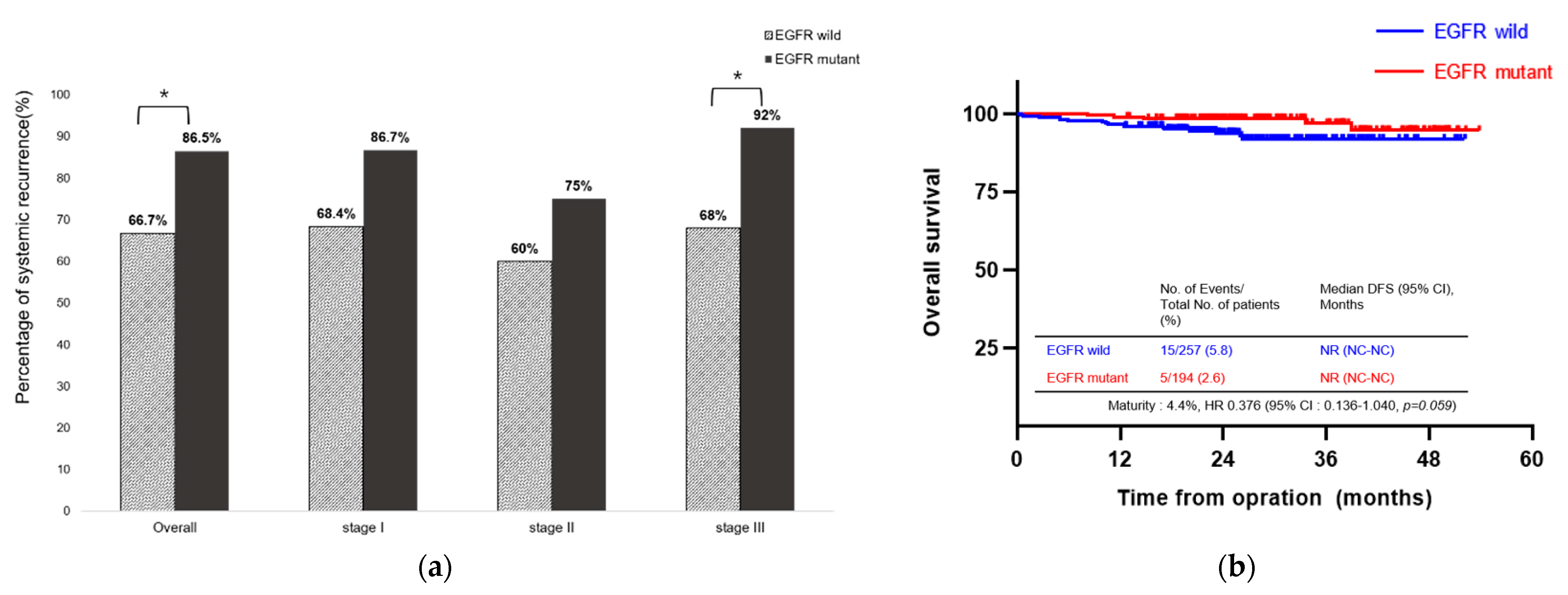
3.4. Association between EGFR Mutations and Type of Recurrence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blandin Knight, S.; Crosbie, P.A.; Balata, H.; Chudziak, J.; Hussell, T.; Dive, C. Progress and prospects of early detection in lung cancer. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 170070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SEER*Explorer: An Interactive Website for SEER Cancer Statistics. Surveillance Research Program, National Cancer Institute; 19 April 2023. Updated 8 June 2023. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statistics-network/explorer/ (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Lim, J.U. Update on Adjuvant Treatment in Resectable Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Potential Biomarkers Predicting Postoperative Relapse. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2023, 86, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasberg, J.D.; Pass, H.I.; Donington, J.S. Sublobar resection: A movement from the Lung Cancer Study Group. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1583–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, H.; Hu, X.; Zhang, S.; Song, Y.; Chirovsky, D.; Gao, C.; Lerner, A.; Jiang, A.; Signorovitch, J.; Samkari, A. Treatment Patterns and Outcomes in Resected Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: An Analysis of the SEER-Medicare Data. Clin. Lung Cancer 2023, 24, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Wood, D.E.; Aisner, D.L.; Akerley, W.; Bauman, J.R.; Bharat, A.; Bruno, D.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Chirieac, L.R.; DeCamp, M.; et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 2.2023. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2023, 21, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Au, J.S.; Thongprasert, S.; Srinivasan, S.; Tsai, C.M.; Khoa, M.T.; Heeroma, K.; Itoh, Y.; Cornelio, G.; Yang, P.C. A prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Miyata, Y.; Tsutani, Y.; Ito, H.; Nakayama, H.; Imai, K.; Ikeda, N.; Okada, M. Positive EGFR mutation status is a risk of recurrence in pN0-1 lung adenocarcinoma when combined with pathological stage and histological subtype: A retrospective multi-center analysis. Lung Cancer 2020, 141, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvez, C.; Jacob, S.; Finkelman, B.S.; Zhao, J.; Tegtmeyer, K.; Chae, Y.K.; Mohindra, N.; Salgia, R.; Jovanovic, B.; Behdad, A.; et al. The role of EGFR mutations in predicting recurrence in early and locally advanced lung adenocarcinoma following definitive therapy. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 1953–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.Z.; Wang, Q.; Mao, W.M.; Xu, S.T.; Wu, L.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Chen, C.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, L.; et al. Gefitinib versus vinorelbine plus cisplatin as adjuvant treatment for stage II-IIIA (N1-N2) EGFR-mutant NSCLC (ADJUVANT/CTONG1104): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Su, C.; Liang, W.; Xu, S.; Wu, L.; Fu, X.; Zhang, X.; Ge, D.; Chen, Q.; Mao, W.; et al. Icotinib versus chemotherapy as adjuvant treatment for stage II-IIIA EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer (EVIDENCE): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.L.; Tsuboi, M.; He, J.; John, T.; Grohe, C.; Majem, M.; Goldman, J.W.; Laktionov, K.; Kim, S.W.; Kato, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Resected EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboi, M.; Herbst, R.S.; John, T.; Kato, T.; Majem, M.; Grohé, C.; Wang, J.; Goldman, J.W.; Lu, S.; Su, W.-C.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Resected EGFR-Mutated NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisters, K.; Kris, M.G.; Gaspar, L.E.; Ismaila, N. Adjuvant Systemic Therapy and Adjuvant Radiation Therapy for Stage I-IIIA Completely Resected Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: ASCO Guideline Rapid Recommendation Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remon, J.; Soria, J.C.; Peters, S. Early and locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: An update of the ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines focusing on diagnosis, staging, systemic and local therapy. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhen, H.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, L.; Cao, B. Efficacy and safety of adjuvant EGFR-TKIs for resected non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis based on randomized control trials. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Pan, H.; Li, J. Molecular Insights into Potential Contributions of Natural Polyphenols to Lung Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2019, 11, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.Y.; Oh, H.J.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, T.O.; Park, C.K.; Shin, H.J.; Lim, J.H.; Kwon, Y.S.; Oh, I.J.; Kim, Y.I.; et al. Quantification of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation may be a predictor of EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment response. Thorac. Cancer 2016, 7, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Choi, Y.D.; Oh, I.J.; Kim, K.S.; Choi, H.; Chang, J.; Shin, H.J.; Park, C.K.; Kim, Y.C. Peptide Nucleic Acid Clamping Versus Direct Sequencing for the Detection of EGFR Gene Mutation in Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 47, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.U.; Lee, J. Peptide Nucleic Acid Clamping and Direct Sequencing in the Detection of Oncogenic Alterations in Lung Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Yonsei Med. J. 2018, 59, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, V.; Bernasconi, B.; Merlo, E.; Balzarini, P.; Vermi, W.; Riva, A.; Chiaravalli, A.M.; Frattini, M.; Sahnane, N.; Facchetti, F.; et al. ALK testing in lung adenocarcinoma: Technical aspects to improve FISH evaluation in daily practice. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; Lian, F.; Guo, L.; Qiu, T.; Ling, Y.; Ying, J.; Lin, D. Detection of ROS1 gene rearrangement in lung adenocarcinoma: Comparison of IHC, FISH and real-time RT-PCR. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skov, B.G.; Høgdall, E.; Clementsen, P.; Krasnik, M.; Larsen, K.R.; Sørensen, J.B.; Skov, T.; Mellemgaard, A. The prevalence of EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung cancer in an unselected Caucasian population. Apmis 2015, 123, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, C.; Xu, C.R.; Zhang, M.F.; Peng, X.X.; Wei, X.W.; Gao, X.; Yan, H.H.; Zhou, Q. EGFR mutations in early-stage and advanced-stage lung adenocarcinoma: Analysis based on large-scale data from China. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearden, S.; Stevens, J.; Wu, Y.L.; Blowers, D. Mutation incidence and coincidence in non small-cell lung cancer: Meta-analyses by ethnicity and histology (mutMap). Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2371–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midha, A.; Dearden, S.; McCormack, R. EGFR mutation incidence in non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology: A systematic review and global map by ethnicity (mutMapII). Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 2892–2911. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, R.; Kinoshita, T.; Sasaki, N.; Uematsu, M.; Sugita, Y.; Shima, T.; Harada, M.; Hishima, T.; Horio, H. Clinicopathological Factors Related to Recurrence Patterns of Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujiie, H.; Kadota, K.; Chaft, J.E.; Buitrago, D.; Sima, C.S.; Lee, M.-C.; Huang, J.; Travis, W.D.; Rizk, N.P.; Rudin, C.M.; et al. Solid Predominant Histologic Subtype in Resected Stage I Lung Adenocarcinoma Is an Independent Predictor of Early, Extrathoracic, Multisite Recurrence and of Poor Postrecurrence Survival. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2877–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Apple, J.; Belli, A.J.; Barcellos, A.; Hansen, E.; Fernandes, L.L.; Zettler, C.M.; Wang, C.K. Real-world study of disease-free survival & patient characteristics associated with disease-free survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective observational study. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2023, 36, 100742. [Google Scholar]
- Saw, S.P.L.; Zhou, S.; Chen, J.; Lai, G.; Ang, M.K.; Chua, K.; Kanesvaran, R.; Ng, Q.S.; Jain, A.; Tan, W.L.; et al. Association of Clinicopathologic and Molecular Tumor Features with Recurrence in Resected Early-Stage Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2131892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishii, T.; Yokose, T.; Miyagi, Y.; Daigo, Y.; Ito, H.; Isaka, T.; Imai, K.; Murakami, S.; Kondo, T.; Saito, H.; et al. Clinicopathological features and EGFR gene mutation status in elderly patients with resected non-small-cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonobe, M.; Manabe, T.; Wada, H.; Tanaka, F. Mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor gene are linked to smoking-independent, lung adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 93, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.L.; Seol, H.; Lee, H.J.; Yoo, S.B.; Kim, H.; Xu, X.; Jheon, S.; Lee, C.T.; Lee, J.S.; Chung, J.H. High incidence of EGFR mutations in Korean men smokers with no intratumoral heterogeneity of lung adenocarcinomas: Correlation with histologic subtypes, EGFR/TTF-1 expressions, and clinical features. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasada, S.; Miyata, Y.; Mimae, T.; Mimura, T.; Okada, M. Impact of Lepidic Component Occupancy on Effects of Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Lung Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 100, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, J.H.; Garg, K.; Aberle, D.; Yankelevitz, D.; Kuriyama, K.; Lee, H.J.; Brambilla, E.; Travis, W.D. Radiologic implications of the 2011 classification of adenocarcinoma of the lung. Radiology 2013, 266, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Song, X.; Liu, M.; He, W.; Wang, H.; Wu, C.; Fei, K.; Jiang, G. EGFR L858R mutation is associated with lung adenocarcinoma patients with dominant ground-glass opacity. Lung Cancer 2015, 87, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Mitsudomi, T.; Sakao, Y.; Yatabe, Y. Genetic features of pulmonary adenocarcinoma presenting with ground-glass nodules: The differences between nodules with and without growth. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.F.; Chang, T.H.; Wu, S.G.; Yang, H.Y.; Hsu, Y.C.; Yang, P.C.; Shih, J.Y. EGFR-L858R mutant enhances lung adenocarcinoma cell invasive ability and promotes malignant pleural effusion formation through activation of the CXCL12-CXCR4 pathway. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Tanaka, F.; Yoneda, K.; Takuwa, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Okumura, Y.; Kondo, N.; Tsubota, N.; Tsujimura, T.; Tabata, C.; et al. Significant increase in circulating tumour cells in pulmonary venous blood during surgical manipulation in patients with primary lung cancer. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 18, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.Y.; Na, I.I.; Kim, C.H.; Park, S.; Baek, H.; Yang, S.H. EGFR mutation and brain metastasis in pulmonary adenocarcinomas. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Luo, S.; Lin, H.; Yang, H.; Chen, H.; Liao, Z.; Lin, W.; Zheng, W.; Xie, X. Correlation between EGFR mutation status and the incidence of brain metastases in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 2510–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Goffin, J.R.; Arnold, A.; Ellis, P.M. Survival of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer after a diagnosis of brain metastases. Curr. Oncol. 2013, 20, e300–e306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouaid, C.; Danson, S.; Andreas, S.; Siakpere, O.; Benjamin, L.; Ehness, R.; Dramard-Goasdoue, M.H.; Barth, J.; Hoffmann, H.; Potter, V.; et al. Adjuvant treatment patterns and outcomes in patients with stage IB-IIIA non-small cell lung cancer in France, Germany, and the United Kingdom based on the LuCaBIS burden of illness study. Lung Cancer 2018, 124, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sara Kuruvilla, M.; Liu, G.; Syed, I.; Gwadry-Sridhar, F.; Sheffield, B.S.; Sachdeva, R.; Pencz, A.; Zhan, L.; Hueniken, K.; Patel, D.; et al. EGFR mutation prevalence, real-world treatment patterns, and outcomes among patients with resected, early-stage, non-small cell lung cancer in Canada. Lung Cancer 2022, 173, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.N.; Yan, H.H.; Wang, J.; Chu, X.Y.; Liu, Z.D.; Shen, Y.; Ma, H.T.; Fu, X.N.; Hu, J.; Zhou, N.K.; et al. Real-World Survival Outcomes Based on EGFR Mutation Status in Chinese Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma After Complete Resection: Results from the ICAN Study. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2022, 3, 100257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotolo, F.; Dunant, A.; Le Chevalier, T.; Pignon, J.P.; Arriagada, R. Adjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy in nonsmall-cell lung cancer: New insights into the effect on failure type via a multistate approach. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 2162–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; McNamee, C.J.; Toloza, E.; Negrao, M.V.; Lin, J.; Shum, E.; Cummings, A.L.; Kris, M.G.; Sepesi, B.; Bara, I.; et al. Neoadjuvant Targeted Therapy in Resectable NSCLC: Current and Future Perspectives. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 1458–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratella, E.; Cernic, S.; Minelli, P.; Furlan, G.; Crimì, F.; Rocco, S.; Ruaro, B.; Cova, M.A. Accuracy of CT-Guided Core-Needle Biopsy in Diagnosis of Thoracic Lesions Suspicious for Primitive Malignancy of the Lung: A Five-Year Retrospective Analysis. Tomography 2022, 8, 2828–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | Total (n = 659) | Non-Recurrence (n = 529) | Recurrence (n = 130) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 65.86 [65.14–66.57] | 65.61 [64.82–66.41] | 66.86 [65.22–68.50] | 0.126 |
| Sex | 0.039 | |||
| Female | 260 (39.5) | 219 (41.4) | 41 (31.5) | |
| Male | 399 (60.5) | 310 (58.6) | 89 (68.5) | |
| Smoking status | 0.054 | |||
| Never smoked | 327 (49.6) | 272 (51.4) | 55 (42.3) | |
| Current smoker | 153 (23.2) | 124 (23.4) | 29 (22.3) | |
| Ex-smoker | 179 (27.2) | 133 (25.2) | 46 (35.4) | |
| Second-hand smoking | 21 (3.2) | 17 (3.2) | 4 (3.1) | >0.999 |
| Comorbidity | ||||
| HTN | 264 (40.1) | 209 (39.5) | 55 (42.3) | 0.560 |
| DM | 147 (22.3) | 112 (21.2) | 35 (26.9) | 0.158 |
| Coronary disease | 51 (7.7) | 37 (7.0) | 14 (10.8) | 0.149 |
| Vascular disease | 2 (0.3) | 1 (0.2) | 1 (0.8) | 0.353 |
| Liver disease | ||||
| History of pulmonary tuberculosis | 33 (5.0) | 26 (4.9) | 7 (5.4) | 0.826 |
| ILD | 14 (2.1) | 8 (1.5) | 6 (4.6) | 0.040 |
| COPD | 78 (11) | 60 (11.3) | 18 (13.8) | 0.428 |
| Other malignancy | 103 (15.6) | 80 (15.1) | 23 (17.7) | 0.470 |
| Family history | 8 (1.2) | 8 (1.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0.223 |
| ECOG PS score | 0.007 | |||
| 0 | 500 (75.9) | 414 (78.3) | 86 (66.2) | |
| 1 | 155 (23.5) | 113 (21.4) | 42 (32.3) | |
| 2 | 4 (0.6) | 2 (0.3) | 2 (1.5) | |
| Pulmonary function (n = 650) | ||||
| FEV1, L | 2.41 [2.37–2.45] | 2.42 [2.36–2.47] | 2.39 [2.30–2.47] | 0.825 |
| FVC, L | 3.25 [3.14–3.36] | 3.26 [3.12–3.39] | 3.23 [3.11–3.36] | 0.611 |
| DLCO, mL/mmHg/min | 17.97 [17.29–18.66] | 17.65 [17.27–18.03] | 19.29 [16.20–22.37] | 0.779 |
| DLCO, % | 94.16 [90.54–97.78] | 93.18 [89.57–96.78] | 98.13 [86.99–109.26] | 0.608 |
| Serum CEA (n = 229) | 5.87 [4.39–7.35] | 5.59 [4.08–7.10] | 6.69 [2.79–10.58] | 0.001 |
| Serum proGRP (n = 229) | 49.79 [45.15–54.42] | 50.19 [44.11–56.27] | 48.58 [44.60–52.57] | 0.137 |
| Serum Cyfra21-1 (n = 229) | 3.50 [2.66–4.34] | 3.45 [2.43–4.47] | 3.63 [2.16–5.11] | 0.009 |
| Histology | 0.243 | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 491 (74.5) | 394 (74.5) | 97 (74.6) | |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 143 (21.7) | 118 (22.3) | 25 (19.2) | |
| Other non-small cell carcinoma | 25 (3.8) | 17 (3.2) | 8 (6.2) | |
| Histologic subtype (n = 477) | ||||
| Acinar | 335 (70.2) | 275 (71.8) | 60 (63.8) | 0.084 |
| Papillary | 310 (65.0) | 242 (63.2) | 68 (72.3) | 0.060 |
| Micropapillary | 92 (19.3) | 59 (15.4) | 33 (35.1) | <0.001 |
| Lepidic | 136 (28.5) | 126 (32.9) | 10 (10.6) | <0.001 |
| Solid | 112 (23.5) | 68 (17.8) | 44 (46.8) | <0.001 |
| Cribriform | 5 (1.0) | 4 (1.0) | 1 (1.1) | 0.668 |
| Mucinous | 36 (7.5) | 33 (8.6) | 3 (3.2) | 0.050 |
| Others | 10 (2.1) | 9 (2.3) | 1 (1.1) | 0.695 |
| Pathologic stage (TNM) | <0.001 | |||
| Stage I | 421 (63.9) | 377 (71.3) | 44 (33.8) | |
| Stage II | 127 (19.3) | 100 (18.9) | 27 (20.8) | |
| Stage III | 111 (16.8) | 52 (9.8) | 59 (45.4) | |
| Driver mutation | ||||
| EGFR (n = 451) | 194 (43.0) | 142 (41.2) | 52 (49.1) | 0.151 |
| ALK (n = 453) | 26 (5.7) | 15 (4.3) | 11 (10.6) | 0.016 |
| ROS1 (n = 441) | 7 (1.6) | 4 (1.2) | 3 (2.9) | 0.204 |
| PD-L1 (SP263) (n = 479) | 0.734 | |||
| TPS < 1% | 295 (61.6) | 221 (61.6) | 74 (61.6) | |
| TPS ≥ 1%–< 50% | 113 (23.6) | 87 (21.2) | 26 (21.7) | |
| TPS ≥ 50% | 71 (14.8) | 51 (14.2) | 20 (16.7) | |
| Initial therapy | 0.121 | |||
| Operation | 645 (97.8) | 520 (98.3) | 125 (96.1) | |
| Chemotherapy | 5 (0.8) | 4 (0.8) | 1 (0.8) | |
| Radiotherapy | 1 (0.2) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.8) | |
| Concurrent chemoradiotherapy | 8 (1.2) | 5 (0.9) | 3 (2.3) | |
| Operation type | 0.954 | |||
| Wedge resection | 13 (2.0) | 10 (1.9) | 3 (2.3) | |
| Segmentectomy | 37 (5.6) | 31 (5.9) | 6 (4.6) | |
| Lobectomy | 577 (87.6) | 461 (87.1) | 116 (89.2) | |
| Bilobectomy | 26 (3.9) | 22 (4.2) | 4 (3.1) | |
| Pneumonectomy | 6 (0.9) | 5 (0.9) | 1 (0.8) | |
| Approach | <0.001 | |||
| VATS | 502 (76.2) | 423 (80.0) | 79 (60.8) | |
| Non-VATS | 157 (23.8) | 106 (20.0) | 51 (39.2) | |
| Tumor location | 0.879 | |||
| Right upper lobe | 160 (24.3) | 129 (24.4) | 31 (23.8) | |
| Right middle lobe | 48 (7.3) | 37 (7.0) | 11 (8.5) | |
| Right lower lobe | 152 (23.0) | 123 (23.3) | 29 (22.3) | |
| Left upper lobe | 164 (24.9) | 129 (24.4) | 35 (26.9) | |
| Left lower lobe | 131 (19.9) | 107 (20.2) | 24 (18.5) | |
| Other | 4 (0.6) | 4 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Visceral pleural invasion (n = 658) | 0.013 | |||
| Yes | 140 (21.3) | 102 (19.3) | 38 (29.2) | |
| No | 518 (78.7) | 426 (80.7) | 92 (70.8) | |
| Lymphatic invasion (n = 658) | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 91 (13.8) | 49 (9.3) | 42 (32.3) | |
| No | 567 (86.2) | 479 (90.7) | 88 (67.7) | |
| Vascular invasion (n = 658) | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 46 (7.0) | 24 (4.5) | 22 (7.7) | |
| No | 612 (93.0) | 504 (95.5) | 108 (92.3) | |
| Neural invasion (n = 658) | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 16 (2.4) | 6 (1.1) | 10 (7.7) | |
| No | 642 (97.6) | 522 (98.9) | 120 (92.3) | |
| Adjuvant therapy (n = 243) | 0.117 | |||
| Platinum-based chemotherapy | 236 (97.1) | 162 (98.2) | 74 (94.9) | |
| Target therapy | 1 (0.4) | 1 (0.6) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Concurrent chemoradiotherapy | 6 (2.5) | 2 (1.2) | 4 (5.1) | |
| Survival | <0.001 | |||
| Alive | 572 (86.8) | 479 (90.5) | 93 (71.5) | |
| Death | 27 (4.1) | 10 (1.9) | 17 (13.1) | |
| Censored | 60 (9.1) | 40 (7.6) | 20 (15.4) |
| EGFR Mutation | Total (n = 193) | Non-Recurrence (n = 142) | Recurrence (n = 51) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L858R | 101 (52.4) | 75 (52.8) | 26 (50.9) | 0.896 |
| L858R only | 97 (50.3) | 72 (50.7) | 25 (49.0) | |
| L858R + T790M | 4 (2.1) | 3 (2.1) | 1 (1.9) | |
| Ex19del | 79 (40.9) | 58 (40.8) | 21 (41.2) | |
| Ex19del only | 76 (39.4) | 56 (39.4) | 20 (39.2) | |
| Ex19del + T790M | 2 (1.0) | 1 (0.7) | 1 (2.0) | |
| Ex19del + G719C | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.7) | 0 | |
| L858R + Ex19del | 2 (1.0) | 1 (0.7) | 1 (2.0) | |
| Others * | 11 (5.7) | 8 (5.6) | 3 (5.9) |
| EGFR Status | Wild-Type (n = 54) | Mutant (n = 52) | Unknown (n = 24) | HR [95% CI] | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lung or regional lymph node | 34 (63.0) | 26 (50.0) | 17 (70.8) | 0.588 [0.271–1.277] | 0.180 |
| Central nervous system | 5 (9.3) | 14 (26.9) | 4 (16.7) | 3.611 [1.195–10.907] | 0.023 |
| Bone | 17 (31.5) | 12 (23.1) | 1 (4.2) | 0.653 [0.275–1.549] | 0.333 |
| Extrathoracic visceral pleura | 4 (7.4) | 2 (3.8) | 1 (4.2) | 0.500 [0.088–2.855] | 0.435 |
| Pleura | 8 (14.8) | 14 (26.9) | 1 (4.2) | 2.118 [0.804–5.583] | 0.129 |
| Peritoneum | 1 (1.9) | 2 (3.8) | 0 (0.0) | 2.121 [0.186–24.114] | 0.545 |
| Head and neck | 1 (1.9) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Others | 5 (9.3) | 3 (5.8) | 3 (12.5) | 0.600 [0.136–2.649] | 0.500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.K.; Choi, Y.D.; Yun, J.-S.; Song, S.-Y.; Na, K.-J.; Yoon, J.Y.; Yoon, C.-S.; Oh, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-C.; Oh, I.-J. Genetic Alterations and Risk Factors for Recurrence in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Who Underwent Complete Surgical Resection. Cancers 2023, 15, 5679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235679
Park HK, Choi YD, Yun J-S, Song S-Y, Na K-J, Yoon JY, Yoon C-S, Oh H-J, Kim Y-C, Oh I-J. Genetic Alterations and Risk Factors for Recurrence in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Who Underwent Complete Surgical Resection. Cancers. 2023; 15(23):5679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235679
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Hwa Kyung, Yoo Duk Choi, Ju-Sik Yun, Sang-Yun Song, Kook-Joo Na, Joon Young Yoon, Chang-Seok Yoon, Hyung-Joo Oh, Young-Chul Kim, and In-Jae Oh. 2023. "Genetic Alterations and Risk Factors for Recurrence in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Who Underwent Complete Surgical Resection" Cancers 15, no. 23: 5679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235679
APA StylePark, H. K., Choi, Y. D., Yun, J.-S., Song, S.-Y., Na, K.-J., Yoon, J. Y., Yoon, C.-S., Oh, H.-J., Kim, Y.-C., & Oh, I.-J. (2023). Genetic Alterations and Risk Factors for Recurrence in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Who Underwent Complete Surgical Resection. Cancers, 15(23), 5679. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235679







