YAP1 Expression in HR+HER2− Breast Cancer: 21-Gene Recurrence Score Analysis and Public Dataset Validation
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
- Inclusion criteria:
- patients aged ≥20 years;
- invasive breast cancer confirmed by pathological diagnosis;
- available ODX RS;
- ER- and/or PR-positive and HER2-negative cancer.
- Exclusion criteria:
- any other carcinoma in situ;
- other cancer histories (except for thyroid cancer);
- inaccessible electronic medical records;
- received neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC).
2.2. Oncotype Dx® Assays
2.3. Pathologic Review of Breast Cancer Slides
2.3.1. Histologic Evaluation of the Tumor–Stroma Ratio (TSR) and Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs)
2.3.2. IHC for Clinical Subtype
2.4. Tissue Microarray (TMA) Construction
2.5. YAP1 IHC and Interpretation
2.6. Public Dataset Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basal Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Comparison of Clinicopathologic Factors Based on YAP1 Expression and ODX RS
3.3. Correlation of YAP1 Expression and ODX RS Using Regression Analysis
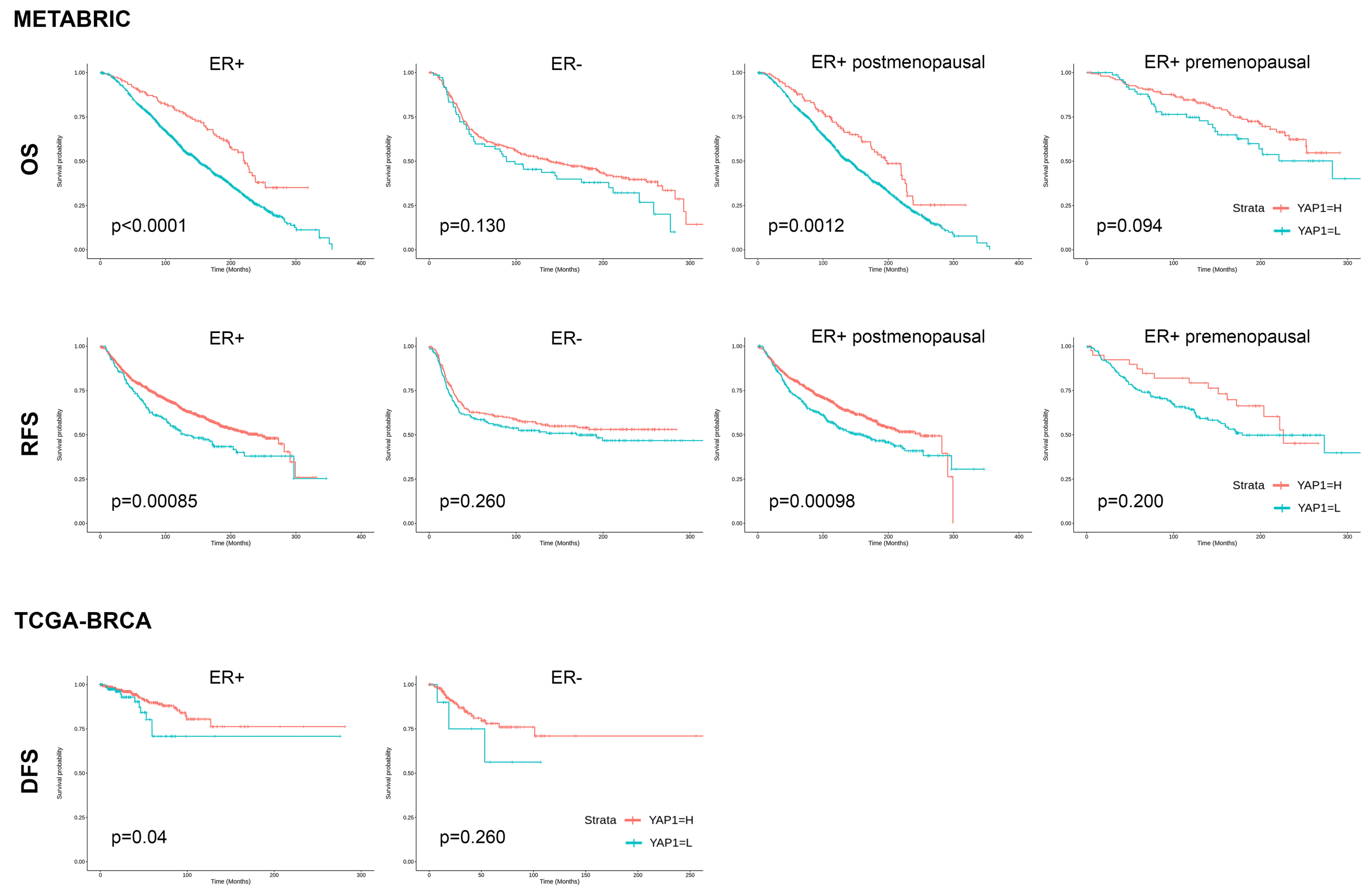
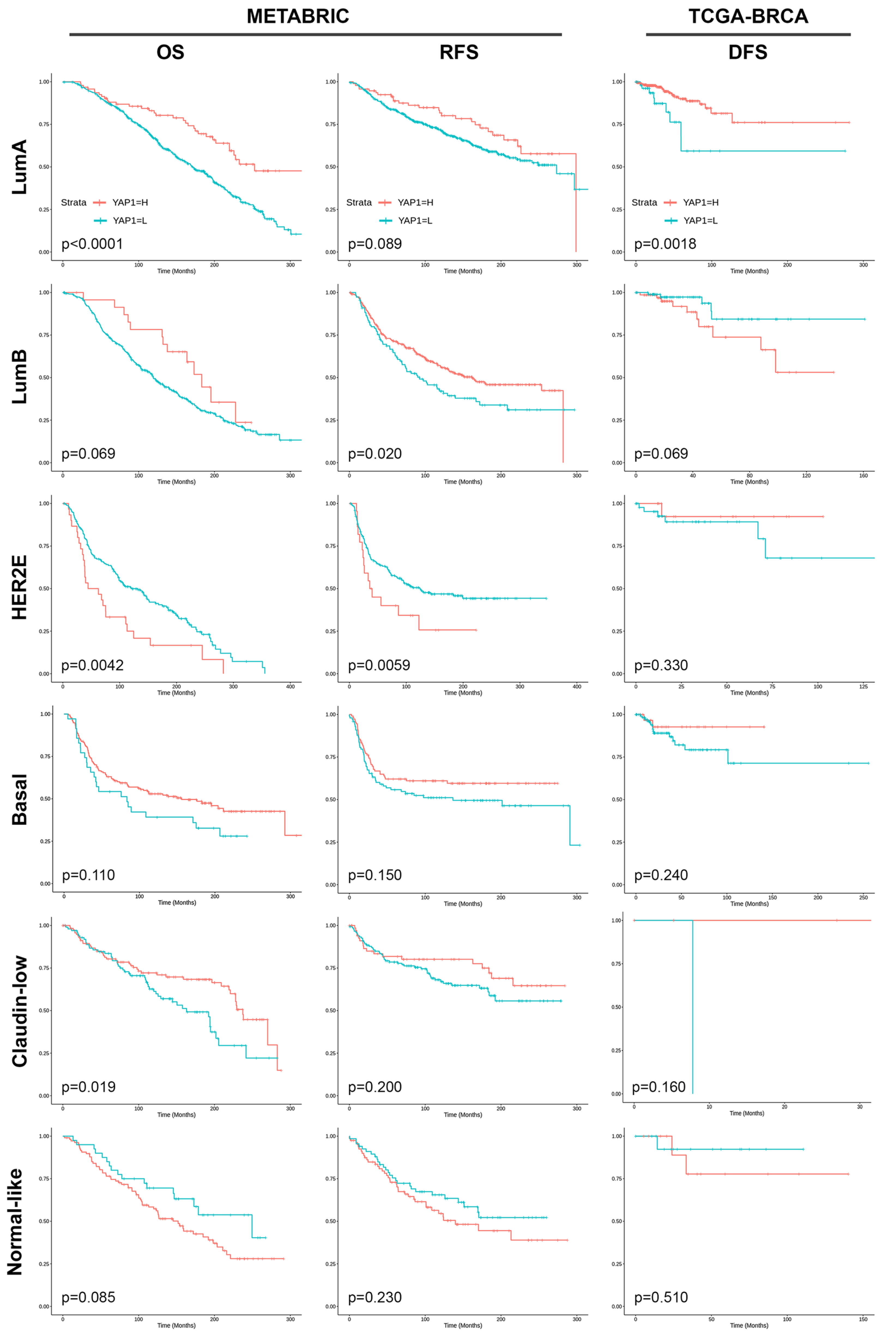
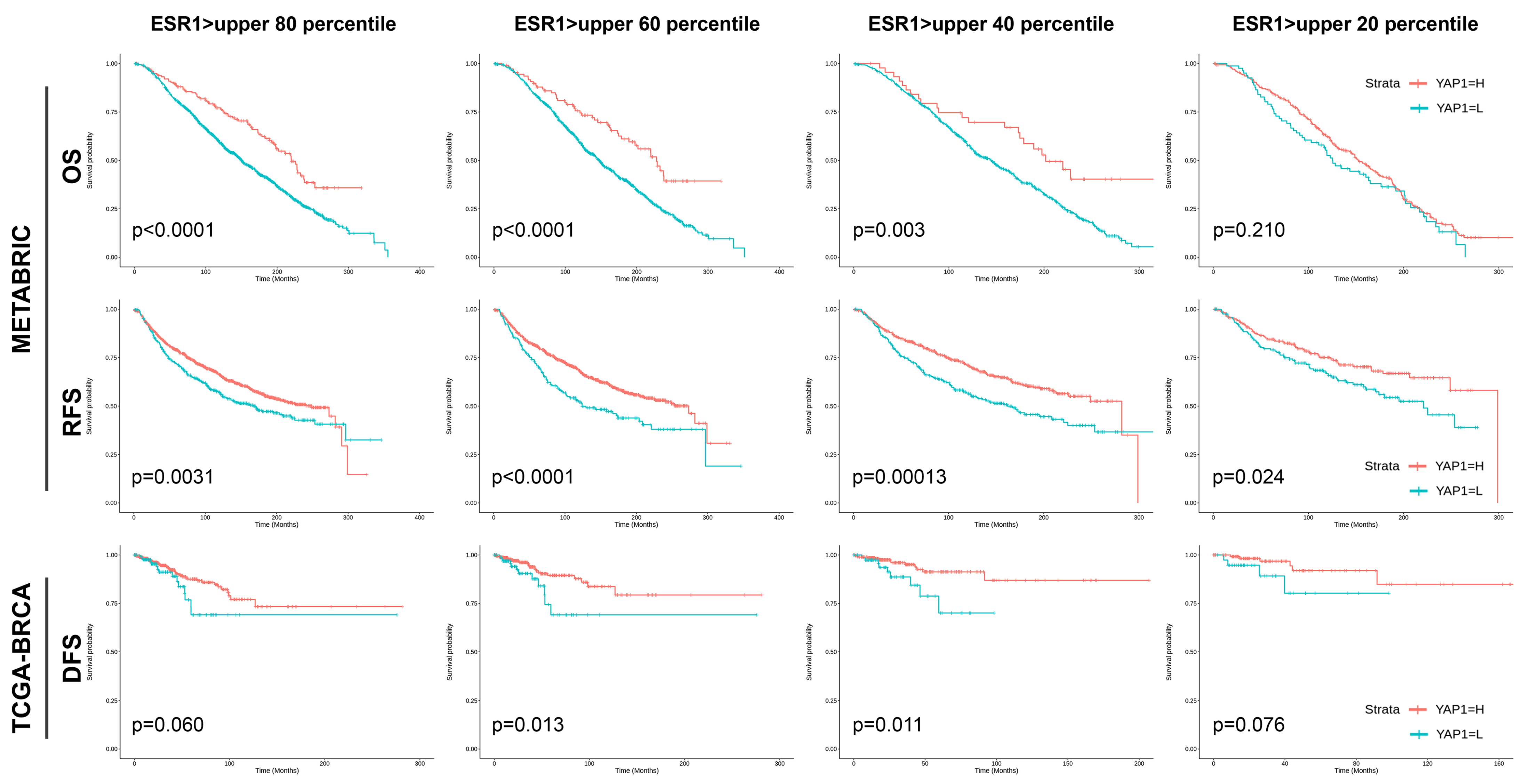
3.4. Validation of the Prognostic Effect of YAP1 Expression in Public Datasets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surveillance Research Program, N.C.I. Seer*explorer: An Interactive Website for Seer Cancer Statistics. Data Source(s): Seer Incidence Data, November 2022 Submission (1975–2020). Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statistics-network/explorer/ (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Paik, S.; Shak, S.; Tang, G.; Kim, C.; Baker, J.; Cronin, M.; Baehner, F.L.; Walker, M.G.; Watson, D.; Park, T.; et al. A multigene assay to predict recurrence of tamoxifen-treated, node-negative breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2817–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wu, S.; Barrera, J.; Matthews, K.; Pan, D. The hippo signaling pathway coordinately regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by inactivating yorkie, the drosophila homolog of yap. Cell 2005, 122, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.A.; Wang, R.; Miao, J.; Oliva, E.; Shen, X.; Wheeler, T.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Orsulic, S.; Goode, S. Hippo pathway effector yap is an ovarian cancer oncogeneyap is an ovarian cancer oncogene. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8517–8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; George, J.; Deb, S.; Degoutin, J.L.; Takano, E.A.; Fox, S.B.; Bowtell, D.D.; Harvey, K.F. The hippo pathway transcriptional co-activator, yap, is an ovarian cancer oncogene. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2810–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, E.; Qiu, X. Overexpression of yes-associated protein contributes to progression and poor prognosis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, T.; Imoto, I.; Matsui, T.; Kozaki, K.-I.; Haruki, S.; Sudol, M.; Shimada, Y.; Tsuda, H.; Kawano, T.; Inazawa, J. Yap is a candidate oncogene for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Gwak, J.W.; Shin, Y.C.; Moon, D.; Ahn, J.; Sol, H.W.; Kim, S.; Kim, G.; Shin, H.M.; Lee, K.H.; et al. Expression of hippo pathway genes and their clinical significance in colon adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 4926–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Bauden, M.; Andersson, R.; Hu, D.; Marko-Varga, G.; Xu, J.; Sasor, A.; Dai, H.; Pawłowski, K.; Said Hilmersson, K.; et al. Yap1 is an independent prognostic marker in pancreatic cancer and associated with extracellular matrix remodeling. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Tomlinson, V.; Lara, R.; Holliday, D.; Chelala, C.; Harada, T.; Gangeswaran, R.; Manson-Bishop, C.; Smith, P.; Danovi, S.A.; et al. Yes-associated protein (yap) functions as a tumor suppressor in breast. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 1752–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo-Rodríguez, Y.; Cerda-Flores, R.M.; Ruiz-Ramos, R.; López-Márquez, F.C.; Calderón-Garcidueñas, A.L. Yap expression in normal and neoplastic breast tissue: An immunohistochemical study. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhou, J.; Chang, C.; Zhi, W. Feasibility of shear wave elastography imaging for evaluating the biological behavior of breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 820102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Jung, W.H.; Koo, J.S. Yes-associated protein (yap) is differentially expressed in tumor and stroma according to the molecular subtype of breast cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 3224–3234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Chen, Y.; Luo, J.; Zheng, J.; Shao, G. Yap1 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis of breast cancer patients and induces breast cancer cell growth by inhibiting pten. FEBS Open Bio 2019, 9, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Bae, S.J.; Eun, N.L.; Ahn, S.G.; Jeong, J.; Cha, Y.J. Correlation of yes-associated protein 1 with stroma type and tumor stiffness in hormone-receptor positive breast cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkenburg, K.C.; de Groot, A.E.; Pienta, K.J. Targeting the tumour stroma to improve cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.J.; Kim, H.H.; Cha, J.H.; Shin, H.J.; Kim, H.; Chae, E.Y.; Hong, M.J. Predicting prognostic factors of breast cancer using shear wave elastography. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2014, 40, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.K.; Pepin, K.; Brandt, K.R.; Mazza, G.L.; Pockaj, B.A.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Northfelt, D.W.; Anderson, K.; Kling, J.M.; et al. Association of breast cancer risk, density, and stiffness: Global tissue stiffness on breast mr elastography (mre). Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 194, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemici, A.A.; Ozal, S.T.; Hocaoglu, E.; Inci, E. Relationship between shear wave elastography findings and histologic prognostic factors of invasive breast cancer. Ultrasound Q. 2020, 36, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youk, J.H.; Son, E.J.; Jeong, J.; Gweon, H.M.; Eun, N.L.; Kim, J.A. Shear-wave elastography-based nomograms predicting 21-gene recurrence score for adjuvant chemotherapy decisions in patients with breast cancer. Eur. J. Radiol. 2023, 158, 110638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elston, C.W.; Ellis, I.O. Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: Experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 1991, 19, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparano, J.A.; Gray, R.J.; Makower, D.F.; Pritchard, K.I.; Albain, K.S.; Hayes, D.F.; Geyer, C.E., Jr.; Dees, E.C.; Goetz, M.P.; Olson, J.A., Jr.; et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy guided by a 21-gene expression assay in breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemi, N.; Eskuri, M.; Herva, A.; Leppänen, J.; Huhta, H.; Helminen, O.; Saarnio, J.; Karttunen, T.J.; Kauppila, J.H. Tumour-stroma ratio and prognosis in gastric adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, R.; Denkert, C.; Demaria, S.; Sirtaine, N.; Klauschen, F.; Pruneri, G.; Wienert, S.; Van den Eynden, G.; Baehner, F.L.; Pénault-Llorca, F. The evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (tils) in breast cancer: Recommendations by an international tils working group 2014. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, M.; Hayes, D.F.; Dowsett, M.; Allred, D.C.; Hagerty, K.L.; Badve, S.; Fitzgibbons, P.L.; Francis, G.; Goldstein, N.S.; Hayes, M. College of american pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2784–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, A.C.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Allison, K.H.; Harvey, B.E.; Mangu, P.B.; Bartlett, J.M.S.; Bilous, M.; Ellis, I.O.; Fitzgibbons, P.; Hanna, W.; et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American society of clinical oncology/college of american pathologists clinical practice guideline focused update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2105–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surveillance Research Program, N.C.I. Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer Subtypes. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast-subtypes.html (accessed on 21 May 2023).
- Sheen-Chen, S.M.; Huang, C.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Liu, Y.W.; Wu, S.C.; Huang, C.C.; Eng, H.L.; Chan, Y.C.; Ko, S.F.; Tang, R.P. Yes-associated protein is not an independent prognostic marker in breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 3321–3325. [Google Scholar]
- Lehn, S.; Tobin, N.P.; Sims, A.H.; Stål, O.; Jirström, K.; Axelson, H.; Landberg, G. Decreased expression of yes-associated protein is associated with outcome in the luminal a breast cancer subgroup and with an impaired tamoxifen response. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlug, E.J.; van de Ven, R.A.; Vermeulen, J.F.; Bult, P.; van Diest, P.J.; Derksen, P.W. Nuclear localization of the transcriptional coactivator yap is associated with invasive lobular breast cancer. Cell. Oncol. 2013, 36, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Sun, P.L.; Yao, M.; Jia, M.; Gao, H. Expression of yes-associated protein (yap) and its clinical significance in breast cancer tissues. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 68, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, D.M.; Russell, C.; McCullough, D.; Tierno, M.; Morrow, M. Lymph node status in breast cancer does not predict tumor biology. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 2884–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tevis, S.E.; Bassett, R.; Bedrosian, I.; Barcenas, C.H.; Black, D.M.; Caudle, A.S.; DeSnyder, S.M.; Fitzsullivan, E.; Hunt, K.K.; Kuerer, H.M.; et al. Oncotypedx recurrence score does not predict nodal burden in clinically node negative breast cancer patients. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, S.; Al-Mushawa, F.; Heena, H.; Wani, T.; Al-Qahtani, A. Relationship of oncotype dx score with tumor grade, size, nodal status, proliferative marker ki67 and nottingham prognostic index in early breast cancer tumors in saudi population. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2021, 51, 151674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Lu, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, P.; Ran, Z. The value of shear wave elastography in the diagnosis of breast cancer axillary lymph node metastasis and its correlation with molecular classification of breast masses. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 846568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Tang, T.; Probst, G.; Konradi, A.; Jin, C.; Li, F.; Gutkind, J.S.; Fu, X.D.; Guan, K.L. Transcriptional repression of estrogen receptor alpha by yap reveals the hippo pathway as therapeutic target for er(+) breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wu, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhang, J.; Johnson, R.L.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Guan, K.L. Hippo signalling maintains er expression and ER+ breast cancer growth. Nature 2021, 591, E1–E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Son, S.; Ko, Y.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, S.; Shin, I. Yap, ctgf and cyr61 are overexpressed in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer and induce transcriptional repression of erα. J. Cell Sci. 2021, 134, jcs256503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Jang, S.K.; Hong, S.E.; Park, C.S.; Seong, M.K.; Kim, H.A.; Park, K.S.; Kim, C.H.; Park, I.C.; Jin, H.O. Knockdown of yap/taz sensitizes tamoxifen-resistant mcf7 breast cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 601, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musgrove, E.A.; Sutherland, R.L. Biological determinants of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrida, I.; Mulita, F. The clinical significance of her2 expression in dcis. Med. Oncol. 2022, 40, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
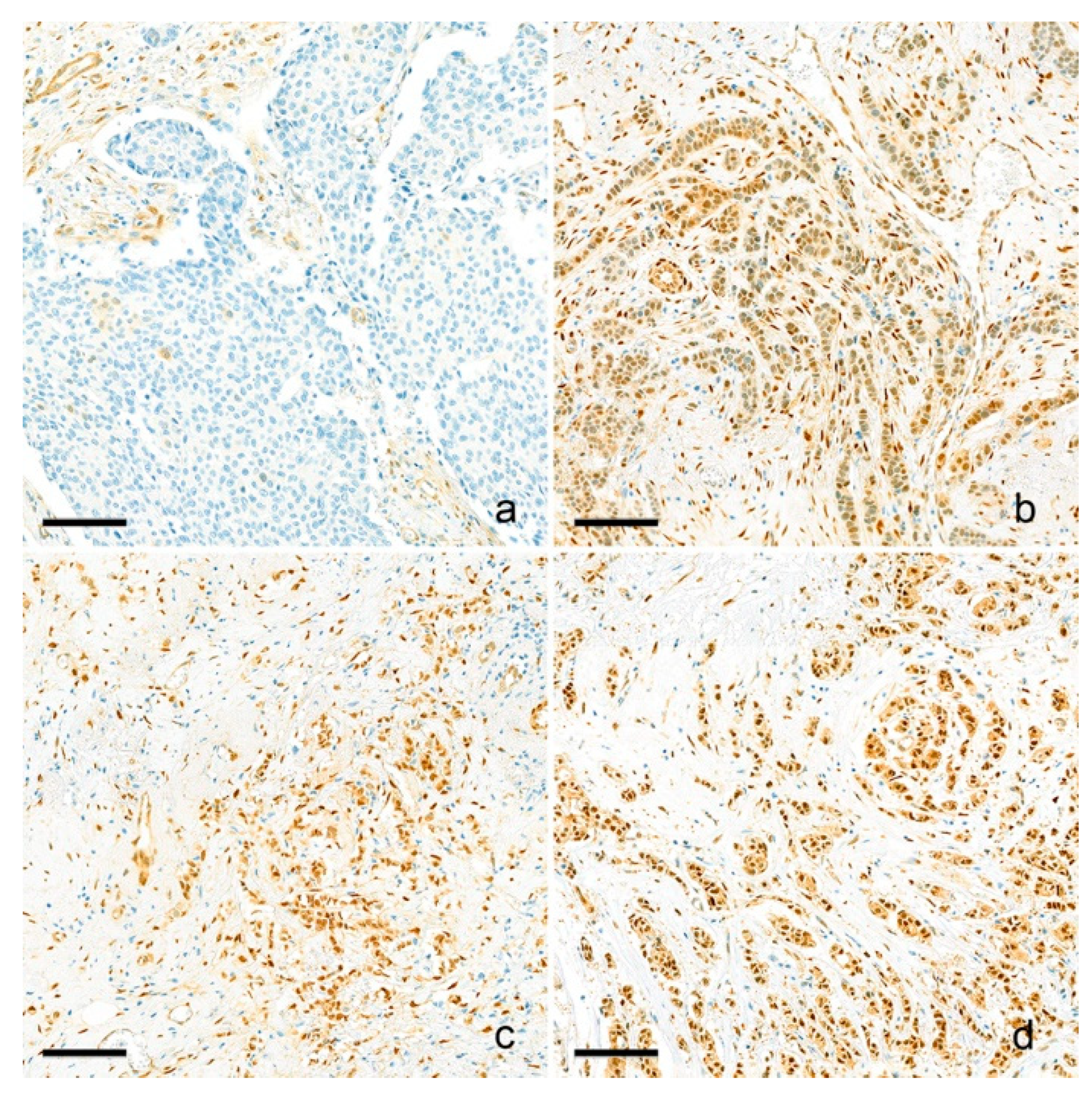
| Parameters | YAP1-Low (n = 139) | YAP1-High (n = 262) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Menopausal Status, n (%) | 0.343 | ||
| Premenopausal | 75 (54.0) | 160 (61.1) | |
| Menopause | 59 (42.4) | 96 (36.6) | |
| Not assessable | 5 (3.6) | 6 (2.3) | |
| Oncotype Dx RS (mean ± SD) | 20.4 ± 11.6 | 16.8 ± 7.2 | 0.001 |
| ODX risk group, n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Low-risk (<26) | 103 (74.1) | 237 (90.5) | |
| High-risk (≥26) | 36 (25.9) | 25 (9.5) | |
| Histologic grade, n (%) | 0.001 | ||
| I | 17 (12.2) | 46 (17.6) | |
| II | 104 (74.8) | 207 (79.0) | |
| III | 18 (12.9) | 9 (3.4) | |
| Tumor size, cm (mean ± SD) | 2.0 ± 0.8 | 2.0 ± 0.8 | 0.405 |
| Lymph node metastasis, n (%) | 0.624 | ||
| Absent | 108 (77.7) | 197 (75.2) | |
| Present | 31 (22.3) | 65 (24.8) | |
| Lympovascular invasion, n (%) | 1.000 | ||
| Absent | 97 (69.8) | 182 (69.5) | |
| Present | 42 (30.2) | 80 (30.5) | |
| TIL level, % (mean ± SD) | 11.6 ± 17.3 | 11.0 ± 11.4 | 0.693 |
| TIL group, n (%) | 0.903 | ||
| Low-TIL (≤10%) | 104 (74.8) | 198 (75.6) | |
| High-TIL (>10%) | 35 (25.2) | 64 (24.4) | |
| TSR, % (mean ± SD) | 71.9 ± 15.7 | 70.5 ± 1.2 | 0.454 |
| TSR group, n (%) | 0.226 | ||
| Stroma-low (TSR >50%) | 124 (89.2) | 221 (84.4) | |
| Stroma-high (TSR ≤50%) | 15 (10.8) | 41 (15.6) | |
| Ki67 LI, % (mean ± SD) | 13.8 ± 9.5 | 10.9 ± 10.9 | 0.007 |
| Parameters | High-Risk (RS ≥ 26) (n = 61) | Low-Risk (RS < 26) (n = 340) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Menopausal Status, n (%) | 0.001 | ||
| Premenopausal | 23 (37.7) | 212 (62.4) | |
| Menopause | 37 (60.7) | 118 (34.7) | |
| Not assessable | 1 (1.6) | 10 (2.9) | |
| YAP1 expression, n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Low-YAP1 | 36 (59.0) | 103 (30.3) | |
| High-YAP1 | 25 (41.0) | 237 (69.7) | |
| Histologic grade, n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| I | 4 (6.6) | 59 (17.4) | |
| II | 46 (75.4) | 265 (77.9) | |
| III | 11 (18.0) | 16 (4.7) | |
| Tumor size, cm (mean ± SD) | 2.0 ± 0.7 | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 0.919 |
| Lymph node metastasis, n (%) | 0.001 | ||
| Absent | 57 (93.4) | 248 (72.9) | |
| Present | 4 (6.6) | 92 (27.1) | |
| Lymphovascular invasion, n (%) | 0.047 | ||
| Absent | 49 (80.3) | 230 (67.6) | |
| Present | 12 (19.7) | 110 (32.4) | |
| TIL, % (mean ± SD) | 14.5 ± 20.7 | 10.6 ± 12.0 | 0.157 |
| TIL group, n (%) | 0.762 | ||
| Low-TIL (≤10%) | 45 (73.8) | 257 (75.6) | |
| High-TIL (>10%) | 16 (26.2) | 83 (24.4) | |
| TSR, % (mean ± SD) | 70.2 ± 18.1 | 71.2 ± 18.2 | 0.695 |
| TSR group, n (%) | 0.847 | ||
| Stroma-low (TSR >50%) | 52 (85.2) | 293 (86.2) | |
| Stroma-high (TSR ≤50%) | 9 (14.8) | 47 (13.8) | |
| Ki67 LI, % (mean ± SD) | 20.3 ± 12.2 | 10.4 ± 9.4 | <0.001 |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | ||
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | |||||
| Menopausal status | <0.001 | |||||||
| Premenopausal | Ref | Ref | ||||||
| Menopause | 2.890 | 1.639 | 5.095 | 2.897 | 1.538 | 5.454 | 0.001 | |
| YAP1 expression | <0.001 | |||||||
| Low | Ref | Ref | ||||||
| High | 0.302 | 0.172 | 0.528 | 0.373 | 0.198 | 0.703 | 0.002 | |
| Tumor size | 1.018 | 0.720 | 1.441 | 0.918 | ||||
| Histologic grade | ||||||||
| I | Ref | |||||||
| II | 2.560 | 0.887 | 7.390 | 0.082 | ||||
| III | 10.140 | 2.846 | 36.136 | <0.001 | 4.625 | 1.070 | 19.99 | 0.040 |
| Lymph node metastasis | 0.002 | |||||||
| Absent | Ref | Ref | ||||||
| Present | 0.189 | 0.067 | 0.536 | 0.270 | 0.091 | 0.801 | 0.018 | |
| Lymphovascular invasion | 0.051 | |||||||
| Absent | Ref | |||||||
| Present | 0.512 | 0.262 | 1.002 | |||||
| TIL | ||||||||
| Low-TIL | Ref | |||||||
| High-TIL | 1.017 | 1.000 | 1.035 | 0.045 | ||||
| TSR | ||||||||
| Stroma-low | Ref | |||||||
| Stroma-high | 0.997 | 0.982 | 1.012 | 0.695 | ||||
| Ki67 LI | 1.078 | 1.05 | 1.107 | <0.001 | 1.062 | 1.035 | 1.09 | <0.001 |
| Univariate Analysis | Beta | SE | 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||
| Menopausal Status | 2.167 | 0.938 | 0.324 | 4.011 | 0.021 |
| Histologic grade | 4.128 | 0.954 | 2.251 | 6.004 | <0.001 |
| Tumor size | 0.592 | 0.581 | −0.551 | 1.734 | 0.309 |
| Lymph node metastasis | −4.064 | 1.045 | −6.118 | −2.010 | <0.001 |
| Lymphovascular invasion | −0.852 | 0.986 | −2.791 | 1.087 | 0.388 |
| TIL | 0.091 | 0.033 | 0.027 | 0.156 | 0.006 |
| TSR | −0.009 | 0.025 | −0.058 | 0.040 | 0.718 |
| Ki67 LI | 0.299 | 0.041 | 0.219 | 0.379 | <0.001 |
| YAP1 | −3.619 | 0.970 | −5.461 | −1.777 | <0.001 |
| Multivariate Analysis | Beta | SE | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Lower | Upper | ||||
| Menopausal Status | 1.713 | 0.862 | 0.019 | 3.407 | 0.047 |
| Histologic grade | |||||
| Tumor size | |||||
| Lymph node metastasis | −2.973 | 0.997 | −4.933 | −1.014 | 0.003 |
| Lymphovascular invasion | |||||
| TIL | |||||
| TSR | |||||
| Ki67 LI | 0.270 | 0.041 | 0.189 | 0.350 | <0.001 |
| YAP1 | −2.816 | 0.894 | −4.575 | −1.014 | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, I.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Bae, S.J.; Ahn, S.G.; Jeong, J.; Cha, Y.J. YAP1 Expression in HR+HER2− Breast Cancer: 21-Gene Recurrence Score Analysis and Public Dataset Validation. Cancers 2023, 15, 5034. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15205034
Park I, Lee Y, Kim JH, Bae SJ, Ahn SG, Jeong J, Cha YJ. YAP1 Expression in HR+HER2− Breast Cancer: 21-Gene Recurrence Score Analysis and Public Dataset Validation. Cancers. 2023; 15(20):5034. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15205034
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Inho, Yangkyu Lee, Jee Hung Kim, Soong June Bae, Sung Gwe Ahn, Joon Jeong, and Yoon Jin Cha. 2023. "YAP1 Expression in HR+HER2− Breast Cancer: 21-Gene Recurrence Score Analysis and Public Dataset Validation" Cancers 15, no. 20: 5034. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15205034
APA StylePark, I., Lee, Y., Kim, J. H., Bae, S. J., Ahn, S. G., Jeong, J., & Cha, Y. J. (2023). YAP1 Expression in HR+HER2− Breast Cancer: 21-Gene Recurrence Score Analysis and Public Dataset Validation. Cancers, 15(20), 5034. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15205034







