NRK-ABMIL: Subtle Metastatic Deposits Detection for Predicting Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer Whole-Slide Images
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset
3.2. MIL Method for WSI Classification
3.3. Attention-Based MIL (ABMIL) Method for WSI Classification
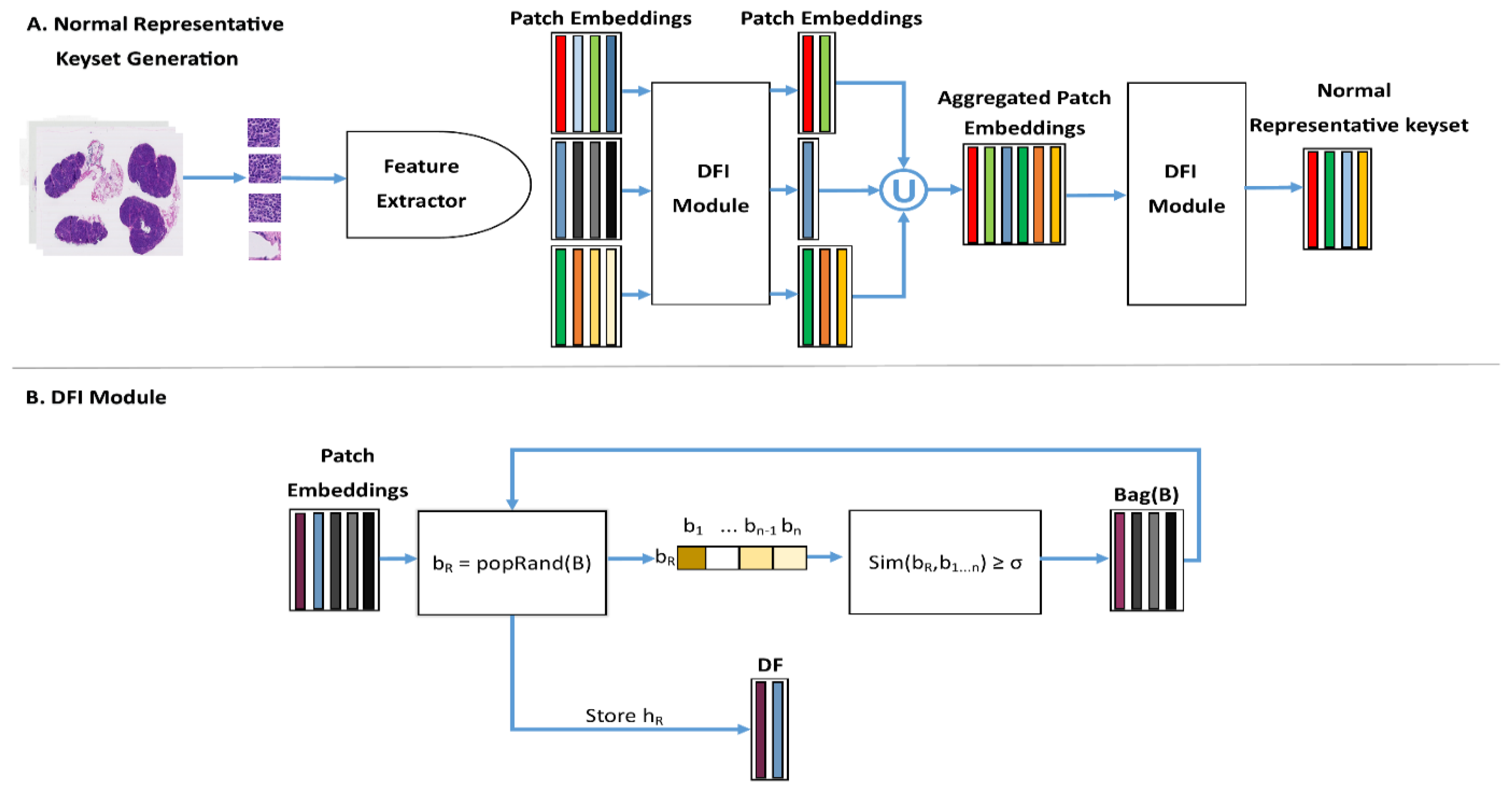
3.4. Normal Representative Keyset (NRK)
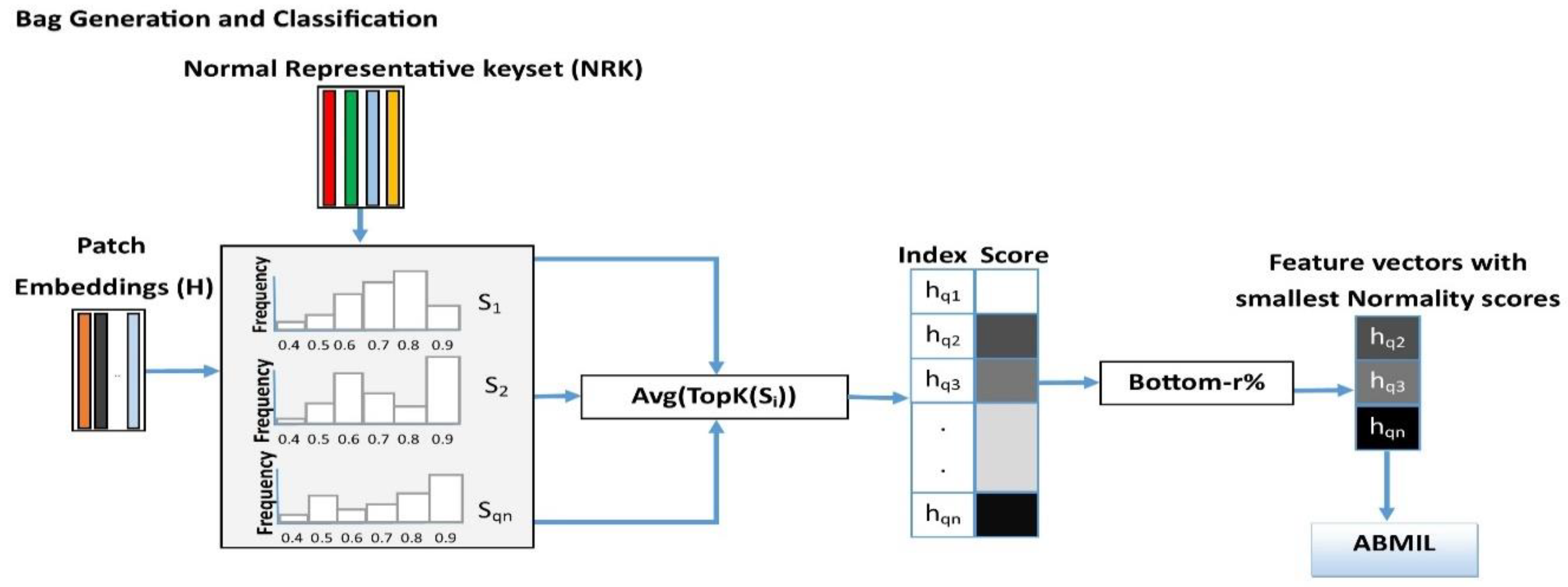
3.5. Instance Retrieval for WSIs Using Normal Representative Bag
3.6. Implementation Details
4. Results
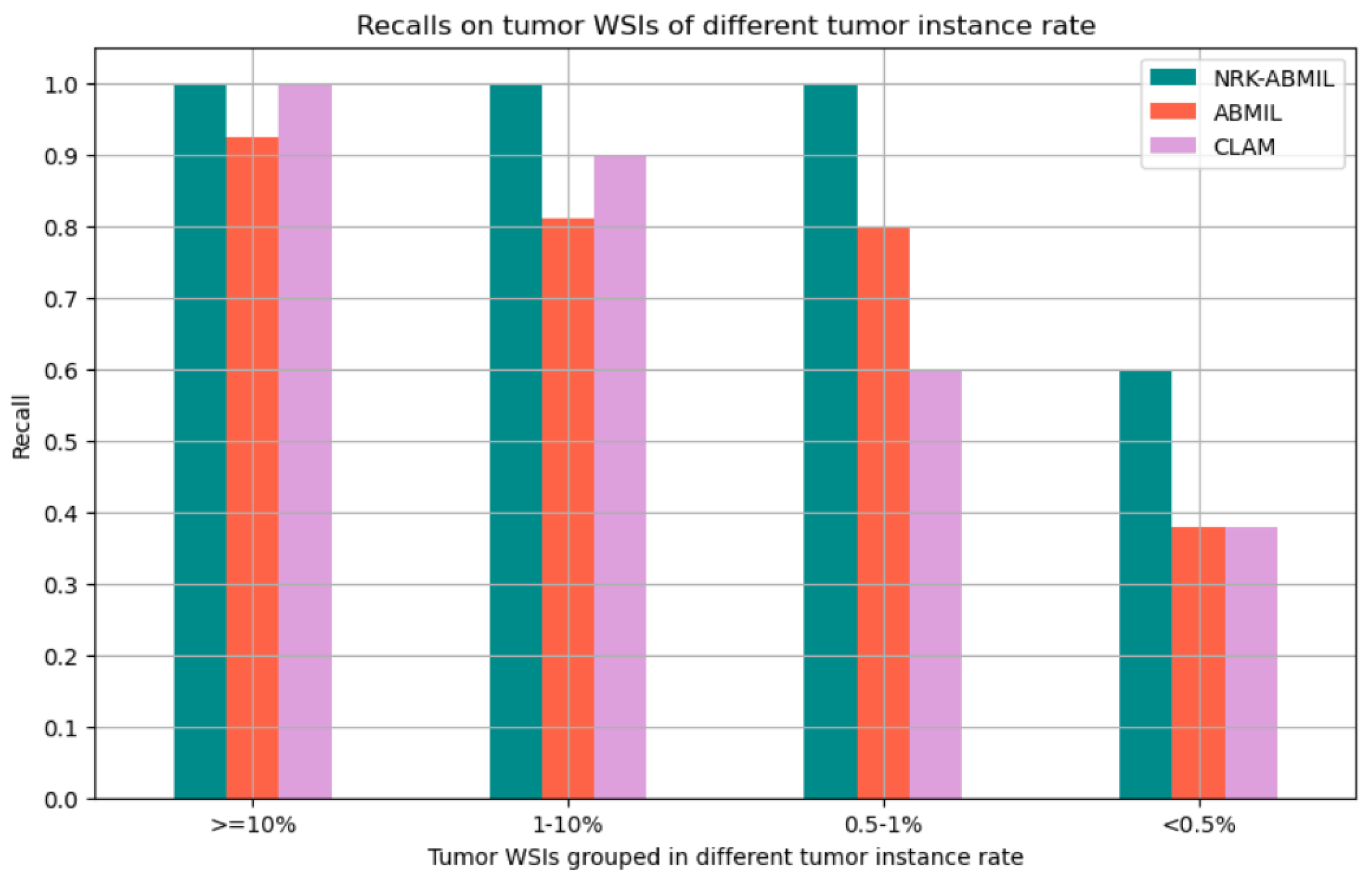
4.1. Results on WSI Classification
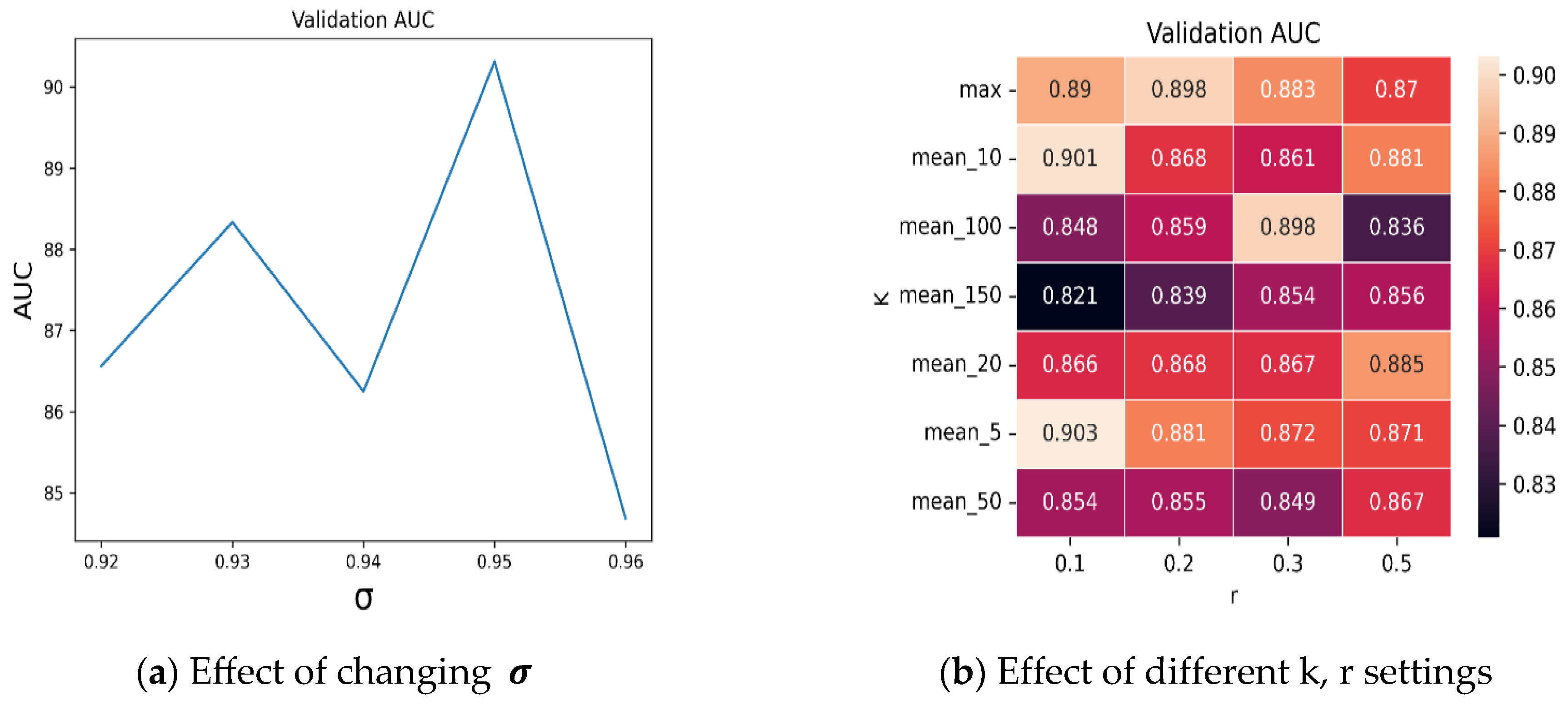
4.2. Ablation Studies
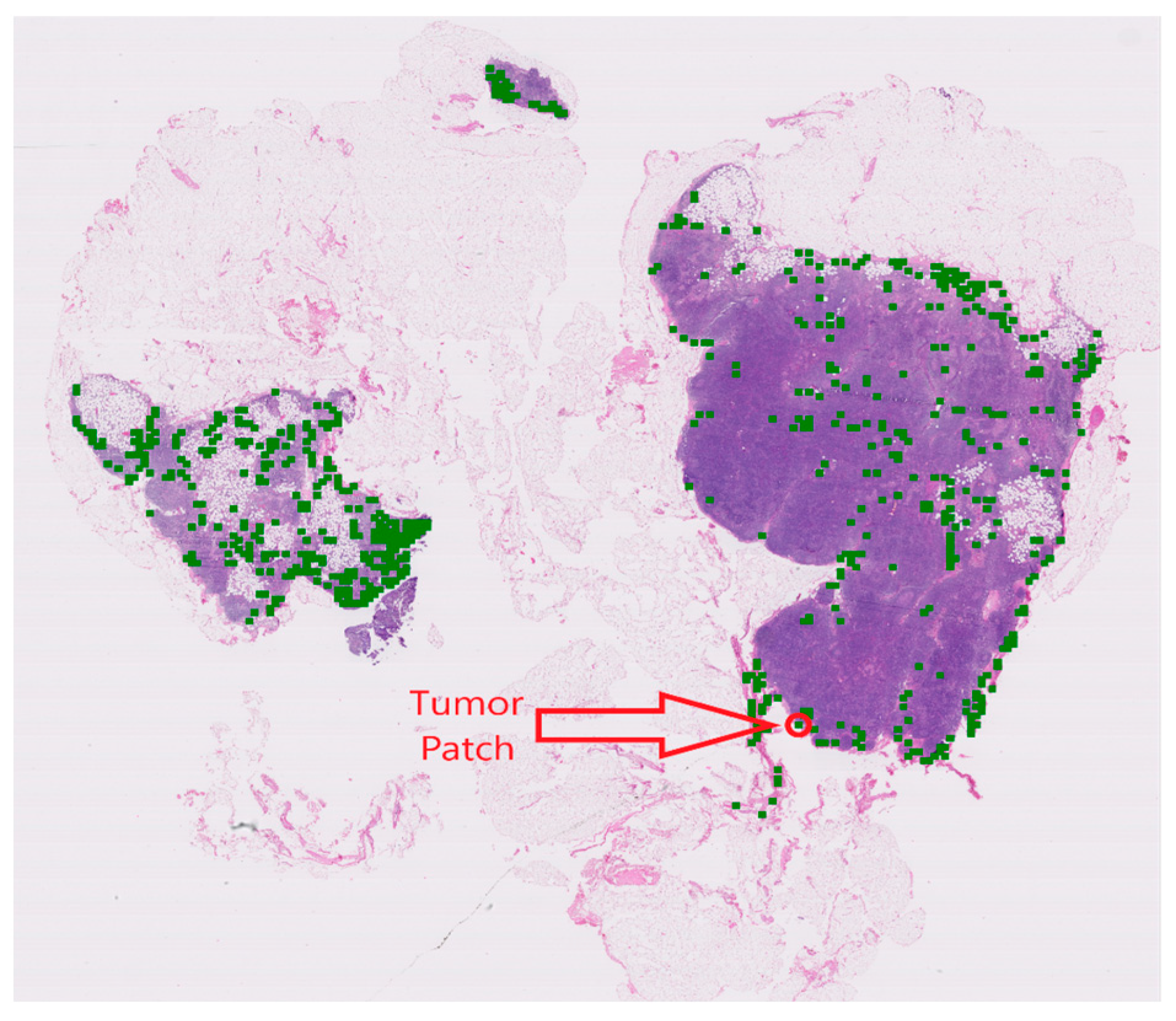
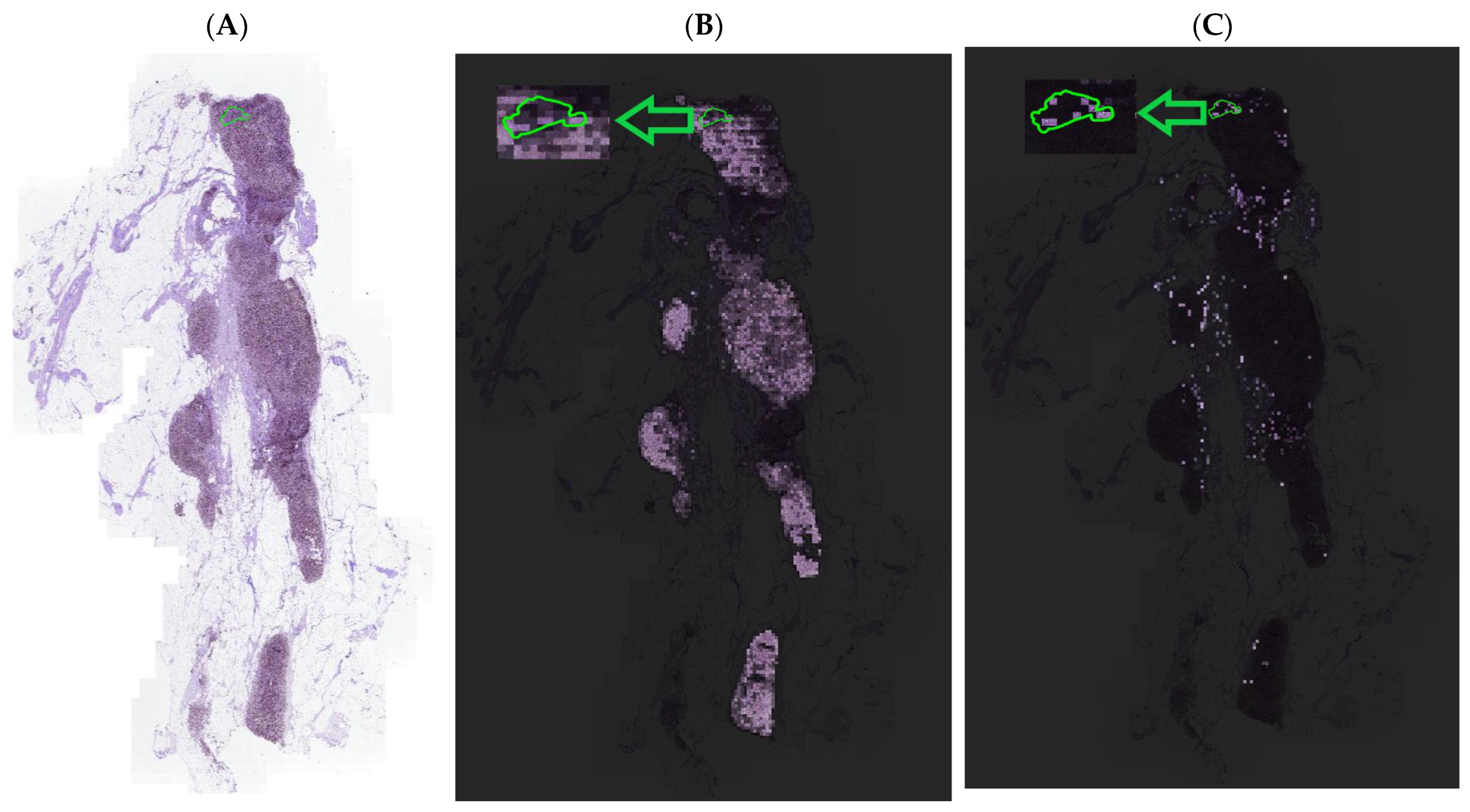
4.3. Visualization and Interpretability of NRK-ABMIL
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Algorithm A1 Normal representative keyset (NRK) |
| Input: The set of normal WSIs, , and a similarity threshold . |
| Step 1: for do |
|
| End (for) |
| Step 2: Set = {}. |
| Output: {}. |
| Algorithm A2 Distinct feature vector identifier (DFI) |
| Input: A set of feature vectors and a similarity threshold , where for . Moreover, set (empty set). |
| Step 1: Compute , where , for . |
| Step 2: While (empty set) do |
|
|
| where for |
|
| If ( ), then |
| , |
| where is a function that removes element from set . |
| End (for). |
|
| And |
| End (While) |
| Output: |
References
- Gurcan, M.N.; Boucheron, L.E.; Can, A.; Madabhushi, A.; Rajpoot, N.M.; Yener, B. Histopathological Image Analysis: A Review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 2, 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazi, M.K.K.; Parwani, A.V.; Gurcan, M.N. Digital pathology and artificial intelligence. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e253–e261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madabhushi, A. Digital pathology image analysis: Opportunities and challenges. Imaging Med. 2009, 1, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; Van Der Laak, J.A.; Van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteva, A.; Chou, K.; Yeung, S.; Naik, N.; Madani, A.; Mottaghi, A.; Liu, Y.; Topol, E.; Dean, J.; Socher, R. Deep learning-enabled medical computer vision. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.; Vu, Q.D.; Raza, S.E.A.; Azam, A.; Tsang, Y.W.; Kwak, J.T.; Rajpoot, N. Hover-Net: Simultaneous segmentation and classification of nuclei in multi-tissue histology images. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 58, 101563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinidhi, C.L.; Ciga, O.; Martel, A.L. Deep neural network models for computational histopathology: A survey. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 67, 101813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.Y.; Williamson, D.F.K.; Chen, T.Y.; Chen, R.J.; Barbieri, M.; Mahmood, F. Data-efficient and weakly supervised computational pathology on whole-slide images. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Bian, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Y. TransMIL: Transformer based Correlated Multiple Instance Learning for Whole Slide Image Classication. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.00908. [Google Scholar]
- Ilse, M.; Tomczak, J.; Welling, M. Attention-based Deep Multiple Instance Learning. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 2127–2136. [Google Scholar]
- Carbonneau, M.-A.; Cheplygina, V.; Granger, E.; Gagnon, G. Multiple instance learning: A survey of problem characteristics and applications. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 77, 329–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waks, A.G.; Winer, E.P. Breast cancer treatment: A review. JAMA 2019, 321, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van la Parra, R.; Peer, P.; Ernst, M.; Bosscha, K. Meta-analysis of predictive factors for non-sentinel lymph node metastases in breast cancer patients with a positive SLN. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 37, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, Y.; Eliceiri, K. Dual-stream Multiple Instance Learning Network for Whole Slide Image Classification with Self-supervised Contrastive Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.08939. [Google Scholar]
- Coudray, N.; Ocampo, P.S.; Sakellaropoulos, T.; Narula, N.; Snuderl, M.; Fenyö, D.; Moreira, A.L.; Razavian, N.; Tsirigos, A. Classification and mutation prediction from non–small cell lung cancer histopathology images using deep learning. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtiol, P.; Tramel, E.; Sanselme, M.; Wainrib, G. Classification and Disease Localization in Histopathology Using Only Global Labels: A Weakly-Supervised Approach. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.02212. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.; Tavolara, T.E.; Carreno-Galeano, G.; Lee, S.J.; Gurcan, M.N.; Niazi, M.K.K. Attention2majority: Weak multiple instance learning for regenerative kidney grading on whole slide images. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 79, 102462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, G.; Hanna, M.G.; Geneslaw, L.; Miraflor, A.; Werneck Krauss Silva, V.; Busam, K.J.; Brogi, E.; Reuter, V.E.; Klimstra, D.S.; Fuchs, T.J. Clinical-grade computational pathology using weakly supervised deep learning on whole slide images. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehteshami Bejnordi, B.; Veta, M.; Johannes van Diest, P.; van Ginneken, B.; Karssemeijer, N.; Litjens, G.; van der Laak, J.; Hermsen, M.; Manson, Q.F.; Balkenhol, M.; et al. Diagnostic Assessment of Deep Learning Algorithms for Detection of Lymph Node Metastases in Women With Breast Cancer. JAMA 2017, 318, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandi, P.; Geessink, O.; Manson, Q.; Van Dijk, M.; Balkenhol, M.; Hermsen, M.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Lee, B.; Paeng, K.; Zhong, A. From detection of individual metastases to classification of lymph node status at the patient level: The camelyon17 challenge. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 38, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The eighth edition AJCC cancer staging manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavolara, T.E.; Niazi, M.K.K.; Gurcan, M. Background detection affects downstream classification of Camelyon16 whole slide images. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2022: Digital and Computational Pathology, SPIE 2023, San Diego, CA, USA, 19–23 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Tang, P.; Bai, X.; Liu, W. Revisiting multiple instance neural networks. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 74, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Kai, L.; Li, F.-F. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Huang, J.; Han, X. Transformer-based unsupervised contrastive learning for histopathological image classification. Med. Image Anal 2022, 81, 102559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Kornblith, S.; Norouzi, M.; Hinton, G. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual Event, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 1597–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Huang, J.; Han, X. RetCCL: Clustering-guided contrastive learning for whole-slide image retrieval. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 83, 102645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuong, T.T.L.; Vu, Q.D.; Jahanifar, M.; Graham, S.; Kwak, J.T.; Rajpoot, N. IMPaSh: A Novel Domain-Shift Resistant Representation for Colorectal Cancer Tissue Classification. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2022 Workshops, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 543–555. [Google Scholar]
| Method | AUC | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABMIL [10] | 0.8127 0.034 0.8375 | 0.9108 0.0759 0.8684 | 0.6327 0.0827 0.6734 | 0.7392 0.040 0.7586 |
| CLAM [8] | 0.8580 0.027 0.8319 | 0.9120 0.009 0.8462 | 0.6780 0.024 0.6735 | 0.7770 0.016 0.7500 |
| TransMIL [9] | 0.8500 0.028 0.8403 | 0.8312 0.030 0.8471 | 0.7898 0.041 0.7913 | 0.7990 0.040 0.8182 |
| DSMIL [14] | 0.8294 0.8277 | 0.9077 0.9285 | 0.6485 0.6533 | 0.7590 0.7669 |
| Ours | 0.8967 0.016 0.9007 | 0.8589 0.044 0.8837 | 0.8000 0.041 0.7755 | 0.8269 0.0265 0.8239 |
| Method | AUC | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLAM [8] | 0.9339 0.015 0.9533 | 0.8913 0.062 0.9756 | 0.8489 0.033 0.8163 | 0.8673 0.019 0.8888 |
| TransMIL [9] | 0.9394 0.009 0.9313 | 0.9054 0.062 0.8723 | 0.8286 0.042 0.8367 | 0.8623 0.013 0.8541 |
| Ours | 0.9540 0.015 0.9701 | 0.8997 0.047 0.9750 | 0.8489 0.030 0.7959 | 0.8723 0.019 0.8764 |
| Method | AUC | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLAM [8] | 0.9305 0.015 0.9208 | 0.8404 0.066 0.8996 | 0.8101 0.042 0.8290 | 0.8219 0.022 0.8628 |
| TransMIL [9] | 0.9221 0.012 0.9180 | 0.8544 0.028 0.8752 | 0.82500.035 0.8146 | 0.8389 0.025 0.8438 |
| Ours | 0.9334 0.008 0.9254 | 0.9083 0.053 0.9772 | 0.8372 0.031 0.8333 | 0.8694 0.012 0.8995 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sajjad, U.; Rezapour, M.; Su, Z.; Tozbikian, G.H.; Gurcan, M.N.; Niazi, M.K.K. NRK-ABMIL: Subtle Metastatic Deposits Detection for Predicting Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer Whole-Slide Images. Cancers 2023, 15, 3428. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133428
Sajjad U, Rezapour M, Su Z, Tozbikian GH, Gurcan MN, Niazi MKK. NRK-ABMIL: Subtle Metastatic Deposits Detection for Predicting Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer Whole-Slide Images. Cancers. 2023; 15(13):3428. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133428
Chicago/Turabian StyleSajjad, Usama, Mostafa Rezapour, Ziyu Su, Gary H. Tozbikian, Metin N. Gurcan, and M. Khalid Khan Niazi. 2023. "NRK-ABMIL: Subtle Metastatic Deposits Detection for Predicting Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer Whole-Slide Images" Cancers 15, no. 13: 3428. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133428
APA StyleSajjad, U., Rezapour, M., Su, Z., Tozbikian, G. H., Gurcan, M. N., & Niazi, M. K. K. (2023). NRK-ABMIL: Subtle Metastatic Deposits Detection for Predicting Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer Whole-Slide Images. Cancers, 15(13), 3428. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133428






