Interleukin 24: Signal Transduction Pathways
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
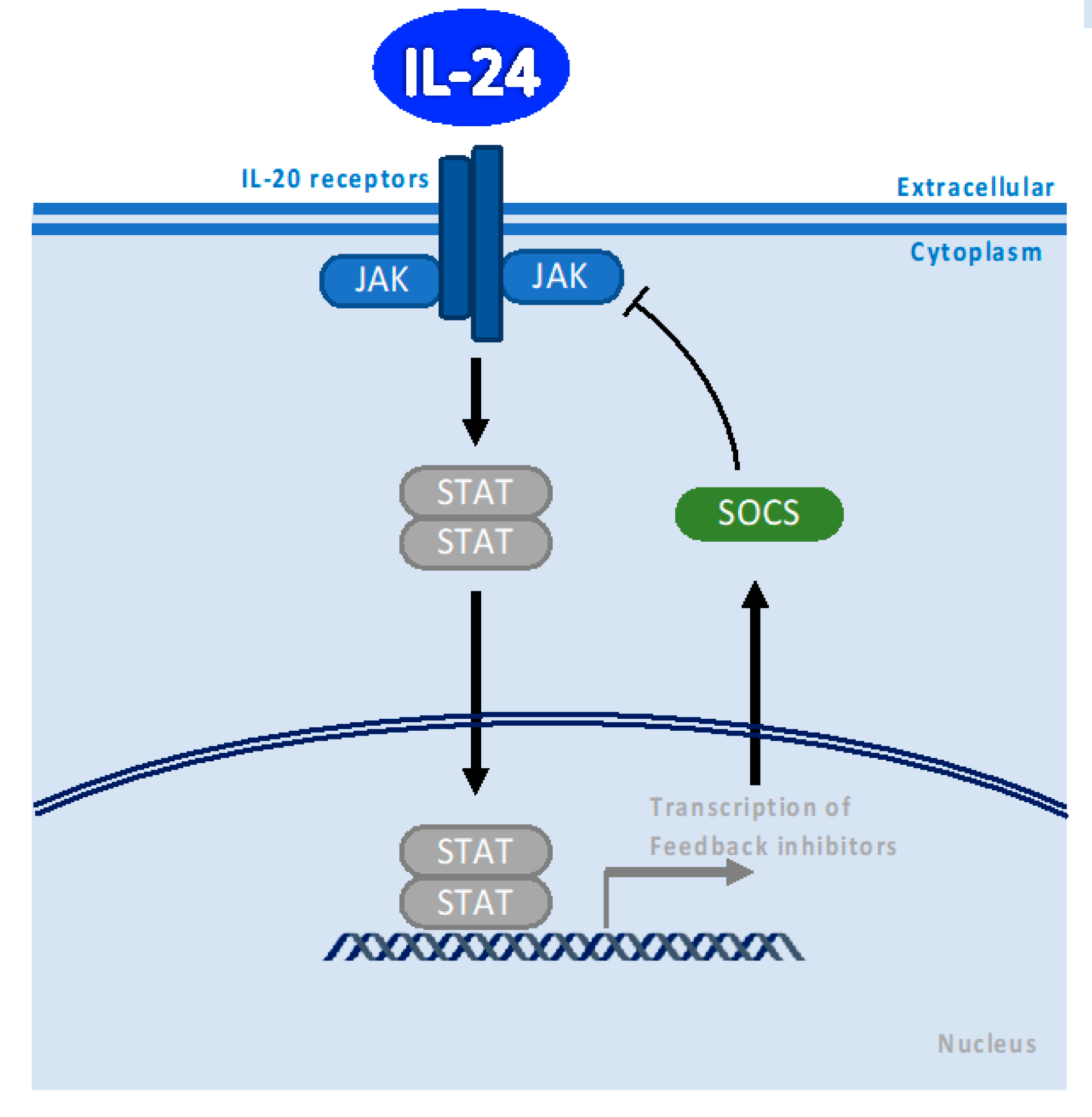
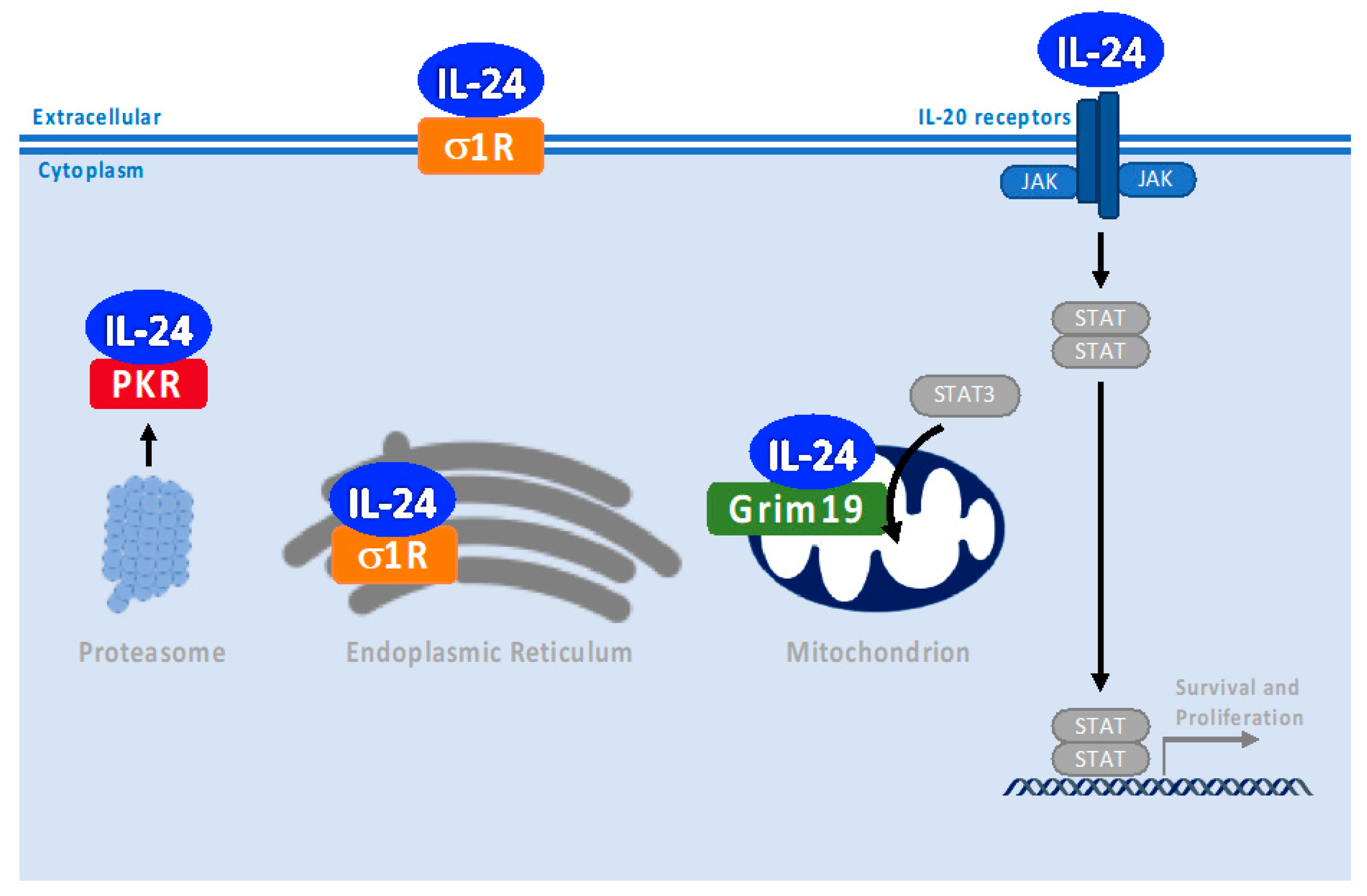
2. Canonical IL-24 Signaling through Binding to IL-20 Receptor and JAK/STAT Pathway Activation Depends on Concentration
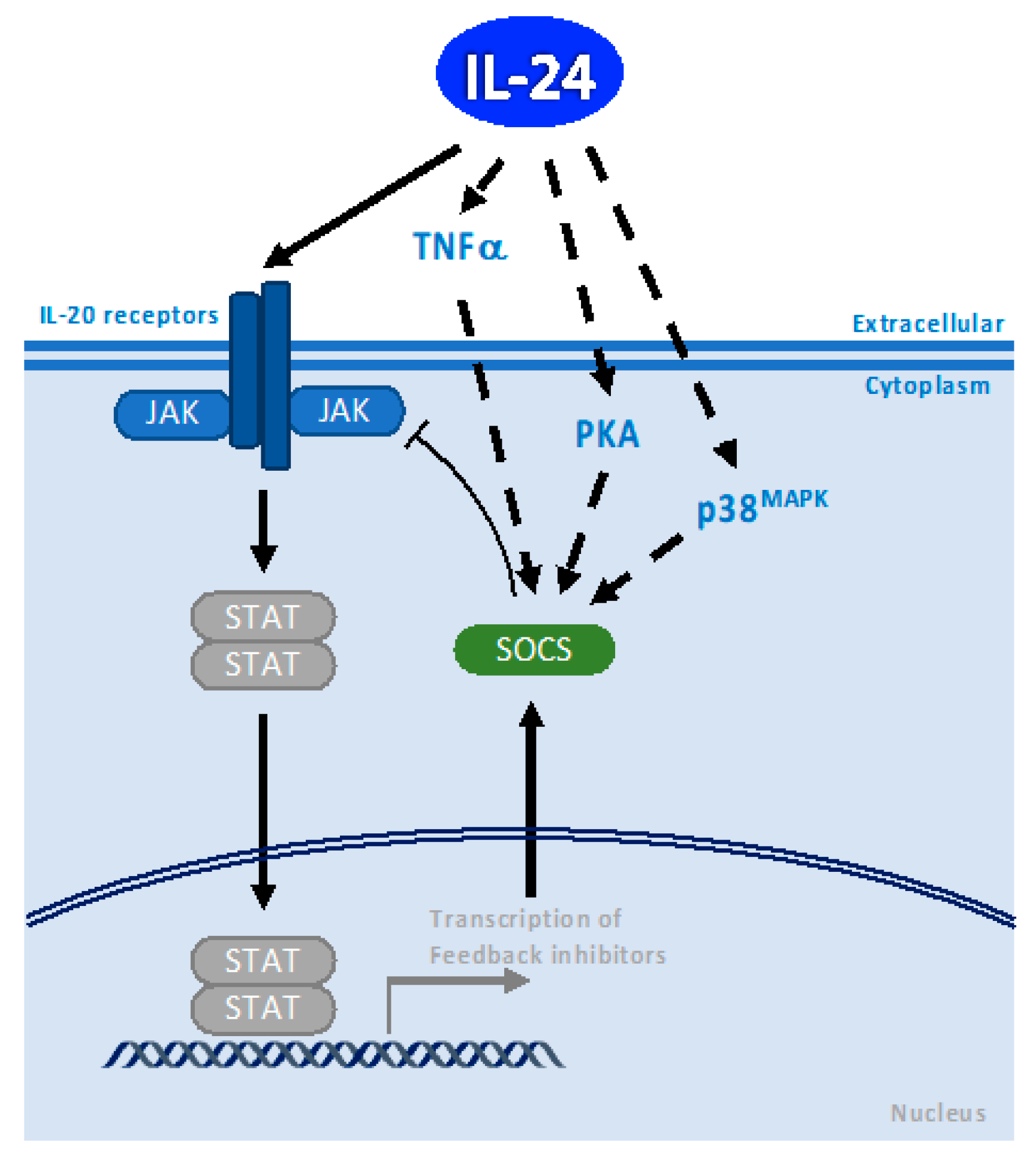
3. SOCS1/3 Pathway
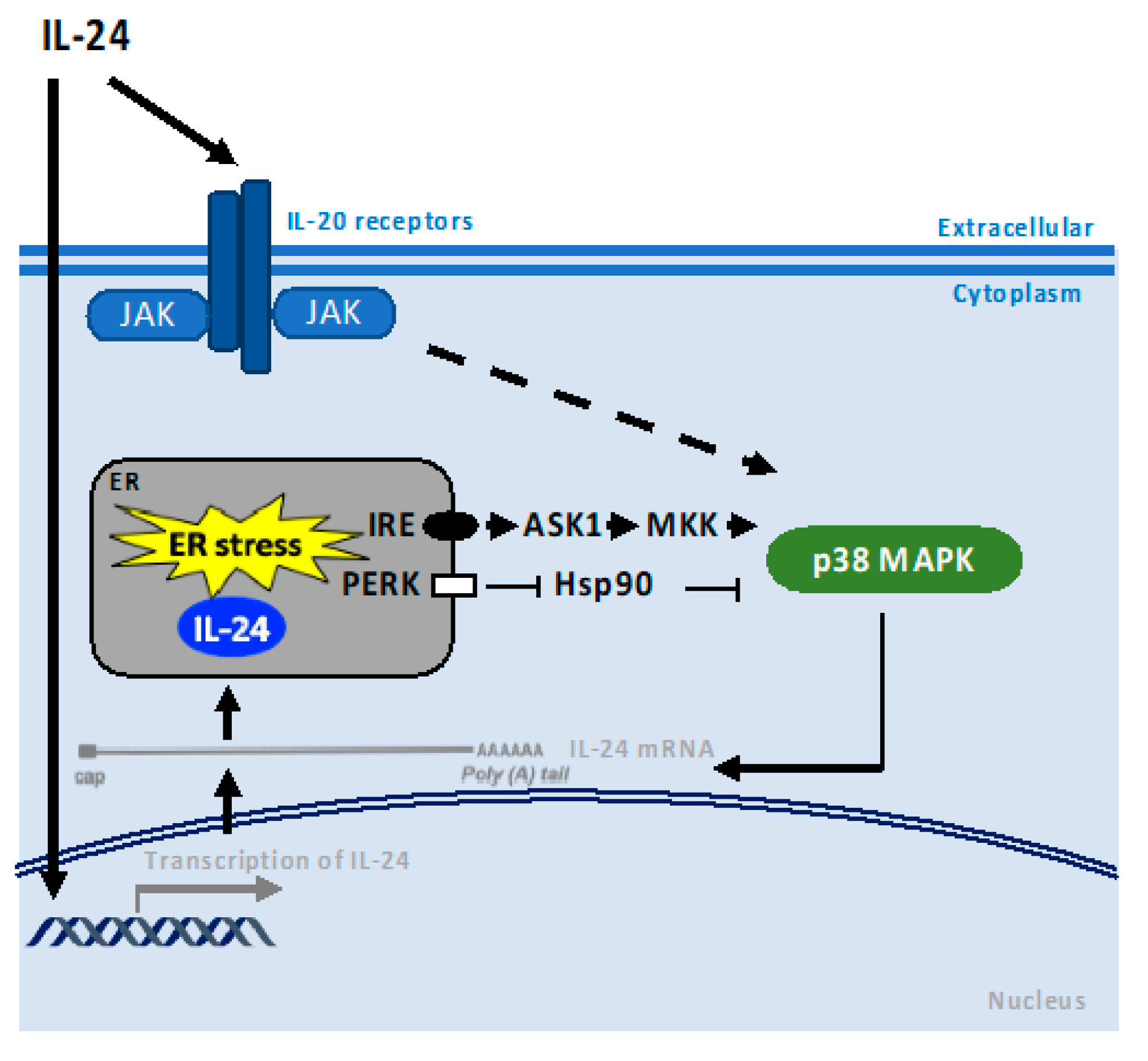
4. p38 MAPK Pathway
5. ROS Production
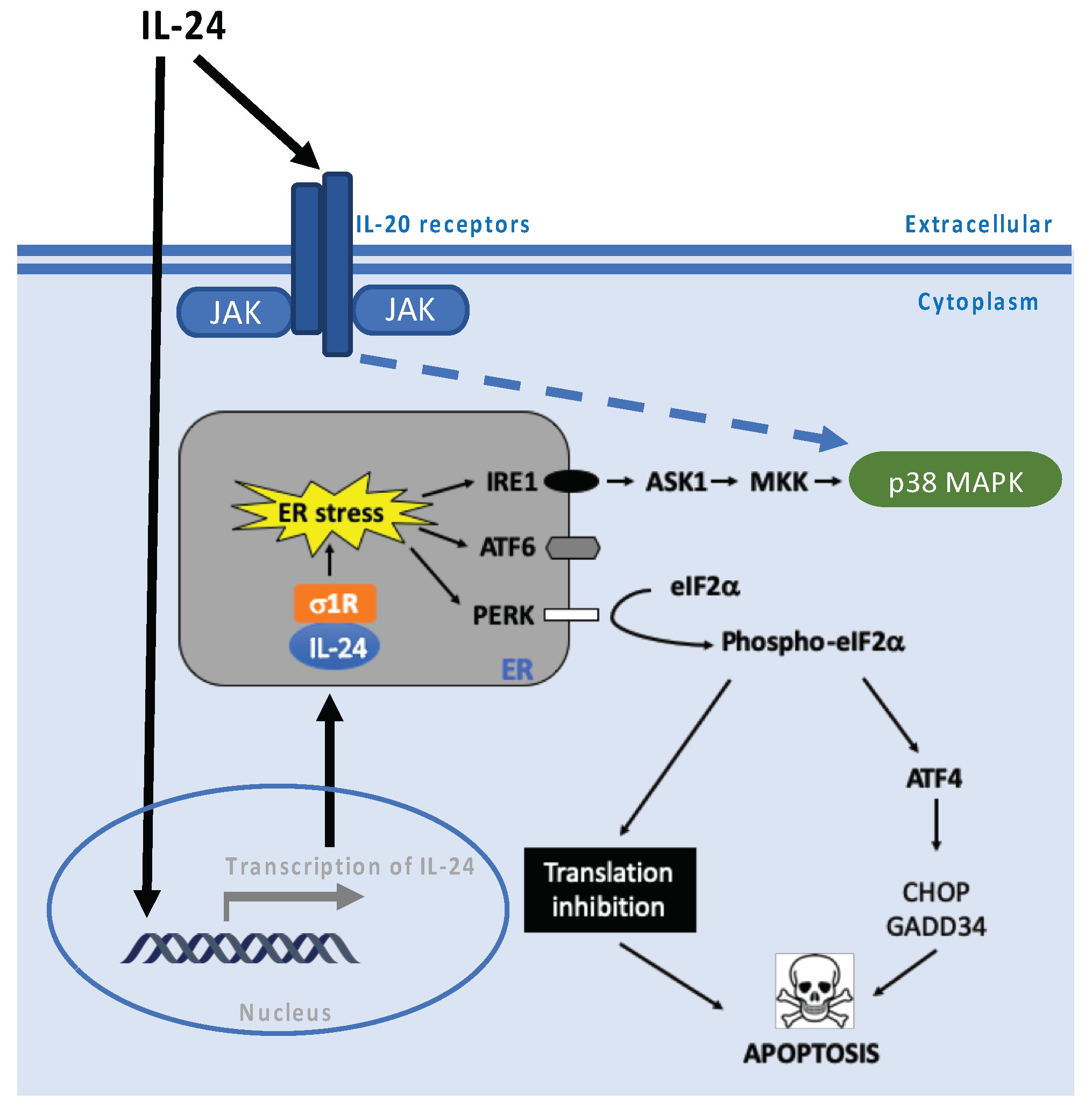
6. PKR and PERK Pathways
7. Chaperones—Role in Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Associated Pathways
8. Grim 19—Role in Mitochondria Autoimmune-Associated Pathways
9. Role in Lipid Homeostasis
10. PKA Pathway
11. Role in Translation Regulation
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moore, K.W.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; Coffman, R.L.; O’Garra, A. Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 683–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, W.; Rutz, S.; Crellin, N.K.; Valdez, P.A.; Hymowitz, S.G. Regulation and functions of the IL-10 family of cytokines in inflammation and disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 71–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabat, R. IL-10 family of cytokines. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010, 21, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garn, H.; Schmidt, A.; Grau, V.; Stumpf, S.; Kaufmann, A.; Becker, M.; Gemsa, D.; Siese, A. IL-24 is expressed by rat and human macrophages. Immunobiology 2002, 205, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hur, Y.H.; Cai, X.; Cong, Q.; Yang, Y.; Xu, C.; Bilate, A.M.; Gonzales, K.A.U.; Parigi, S.M.; Cowley, C.J.; et al. A tissue injury sensing and repair pathway distinct from host pathogen defense. Cell 2023, 186, 2127–2143.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauane, M.; Gopalkrishnan, R.V.; Sarkar, D.; Su, Z.Z.; Lebedeva, I.V.; Dent, P.; Pestka, S.; Fisher, P.B. MDA-7/IL-24: Novel cancer growth suppressing and apoptosis inducing cytokine. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003, 14, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sie, C.; Kant, R.; Peter, C.; Muschaweckh, A.; Pfaller, M.; Nirschl, L.; Moreno, H.D.; Chadimová, T.; Lepennetier, G.; Kuhlmann, T.; et al. IL-24 intrinsically regulates Th17 cell pathogenicity in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20212443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pataer, A.; Vorburger, S.A.; Chada, S.; Balachandran, S.; Barber, G.N.; Roth, J.A.; Hunt, K.K.; Swisher, S.G. Melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7 protein physically associates with the double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase PKR. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2005, 11, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, S.; Yu, C.-H.; Steiner, A.; Ebstein, F.; Baker, P.J.; Jarur-Chamy, V.; Hrovat Schaale, K.; Laohamonthonkul, P.; Kong, K.; Calleja, D.J.; et al. Protein kinase R is an innate immune sensor of proteotoxic stress via accumulation of cytoplasmic IL-24. Sci. Immunol. 2022, 7, eabi6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, R.; Kotenko, S.V.; Liang, P. Interleukin 24 (MDA-7/MOB-5) signals through two heterodimeric receptors, IL-22R1/IL-20R2 and IL-20R1/IL-20R2. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 7341–7347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Walter, M.R.; Su, Z.; Lebedeva, I.V.; Emdad, L.; Randolph, A.; Valerie, K.; Sarkar, D.; Fisher, P.B. BiP/GRP78 is an intracellular target for MDA-7/IL-24 induction of cancer-specific apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8182–8191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, W.; Herrera, C.; Mighty, J.; Shumskaya, M.; Redenti, S.M.; Sauane, M. Sigma 1 Receptor plays a prominent role in IL-24-induced cancer-specific apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 439, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrish-Novak, J.; Xu, W.; Brender, T.; Yao, L.; Jones, C.; West, J.; Brandt, C.; Jelinek, L.; Madden, K.; McKernan, P.A.; et al. Interleukins 19, 20, and 24 signal through two distinct receptor complexes. Differences in receptor-ligand interactions mediate unique biological functions. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 47517–47523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumoutier, L.; Leemans, C.; Lejeune, D.; Kotenko, S.V.; Renauld, J.C. Cutting edge: STAT activation by IL-19, IL-20 and mda-7 through IL-20 receptor complexes of two types. J. Immunol. Baltim. 2001, 167, 3545–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauane, M.; Gopalkrishnan, R.V.; Lebedeva, I.; Mei, M.X.; Sarkar, D.; Su, Z.-Z.; Kang, D.-C.; Dent, P.; Pestka, S.; Fisher, P.B. Mda-7/IL-24 induces apoptosis of diverse cancer cell lines through JAK/STAT-independent pathways. J. Cell. Physiol. 2003, 196, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chada, S.; Mhashilkar, A.M.; Ramesh, R.; Mumm, J.B.; Sutton, R.B.; Bocangel, D.; Zheng, M.; Grimm, E.A.; Ekmekcioglu, S. Bystander activity of Ad-mda7: Human MDA-7 protein kills melanoma cells via an IL-20 receptor-dependent but STAT3-independent mechanism. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2004, 10, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauane, M.; Lebedeva, I.V.; Su, Z.; Choo, H.; Randolph, A.; Valerie, K.; Dent, P.; Gopalkrishnan, R.V.; Fisher, P.B. Melanoma differentiation associated gene-7/interleukin-24 promotes tumor cell-specific apoptosis through both secretory and nonsecretory pathways. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2988–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, W.S.; Hilton, D.J. The role of suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins in regulation of the immune response. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 22, 503–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croker, B.A.; Kiu, H.; Nicholson, S.E. SOCS regulation of the JAK/STAT signalling pathway. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2008, 19, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, A.; Naka, T.; Kubo, M. SOCS proteins, cytokine signalling and immune regulation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trengove, M.C.; Ward, A.C. SOCS proteins in development and disease. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 2, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister, A.R.; Johnson, M.B.; Yaemmongkol, J.J.; Marriott, I. Murine astrocytes produce IL-24 and are susceptible to the immunosuppressive effects of this cytokine. J. Neuroinflam. 2019, 16, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, W.P.; Mattapallil, M.J.; Raychaudhuri, K.; Bing, S.J.; Wu, S.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, Z.; Silver, P.B.; Jittayasothorn, Y.; et al. The Cytokine IL-17A Limits Th17 Pathogenicity via a Negative Feedback Loop Driven by Autocrine Induction of IL-24. Immunity 2020, 53, 384–397.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andoh, A.; Shioya, M.; Nishida, A.; Bamba, S.; Tsujikawa, T.; Kim-Mitsuyama, S.; Fujiyama, Y. Expression of IL-24, an activator of the JAK1/STAT3/SOCS3 cascade, is enhanced in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Immunol. Baltim. 2009, 183, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, Y.; Naka, T.; Kawazoe, Y.; Fujimoto, M.; Narazaki, M.; Nakagawa, R.; Fukuyama, H.; Nagata, S.; Kishimoto, T. Signals transducers and activators of transcription (STAT)-induced STAT inhibitor-1 (SSI-1)/suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 (SOCS-1) suppresses tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced cell death in fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5405–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baetz, A.; Frey, M.; Heeg, K.; Dalpke, A.H. Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins indirectly regulate toll-like receptor signaling in innate immune cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 54708–54715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, A.; Ohishi, H.M.M.; Aki, D.; Hanada, T. Regulation of TLR signaling and inflammation by SOCS family proteins. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 75, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Su, Z.-Z.; Lebedeva, I.V.; Sauane, M.; Gopalkrishnan, R.V.; Valerie, K.; Dent, P.; Fisher, P.B. mda-7 (IL-24) Mediates selective apoptosis in human melanoma cells by inducing the coordinated overexpression of the GADD family of genes by means of p38 MAPK. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10054–10059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauane, M.; Su, Z.-Z.; Gupta, P.; Lebedeva, I.V.; Dent, P.; Sarkar, D.; Fisher, P.B. Autocrine regulation of mda-7/IL-24 mediates cancer-specific apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9763–9768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otkjaer, K.; Holtmann, H.; Kragstrup, T.W.; Paludan, S.R.; Johansen, C.; Gaestel, M.; Kragballe, K.; Iversen, L. The p38 MAPK regulates IL-24 expression by stabilization of the 3’ UTR of IL-24 mRNA. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Zhang, D.; Gao, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Cheng, Q.; Pei, D.; Zheng, J. MDA-7/IL-24 inhibits Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response through activation of p38 pathway and inhibition of ERK pathway involved in cancer cell apoptosis. Cancer Gene Ther. 2014, 21, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bech, R.; Jalilian, B.; Agger, R.; Iversen, L.; Erlandsen, M.; Otkjaer, K.; Johansen, C.; Paludan, S.R.; Rosenberg, C.A.; Kragballe, K.; et al. Interleukin 20 regulates dendritic cell migration and expression of co-stimulatory molecules. Mol. Cell. Ther. 2016, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubaki, M.; Takeda, T.; Matsuda, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Higashinaka, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Tsurushima, K.; Ishizaka, T.; Nishida, S. Interleukin 19 suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via the inhibition of NF-κB and p38MAPK activation and c-Fos expression in RAW264.7 cells. Cytokine 2021, 144, 155591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, S.; Beigel, F.; Olszak, T.; Zitzmann, K.; Eichhorst, S.T.; Otte, J.-M.; Diepolder, H.; Marquardt, A.; Jagla, W.; Popp, A.; et al. IL-22 is increased in active Crohn’s disease and promotes proinflammatory gene expression and intestinal epithelial cell migration. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 290, G827–G838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejeune, D.; Dumoutier, L.; Constantinescu, S.; Kruijer, W.; Schuringa, J.J.; Renauld, J.-C. Interleukin-22 (IL-22) activates the JAK/STAT, ERK, JNK, and p38 MAP kinase pathways in a rat hepatoma cell line. Pathways that are shared with and distinct from IL-10. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 33676–33682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolk, K.; Witte, E.; Wallace, E.; Döcke, W.-D.; Kunz, S.; Asadullah, K.; Volk, H.-D.; Sterry, W.; Sabat, R. IL-22 regulates the expression of genes responsible for antimicrobial defense, cellular differentiation, and mobility in keratinocytes: A potential role in psoriasis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 1309–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedeva, I.V.; Su, Z.-Z.; Sarkar, D.; Kitada, S.; Dent, P.; Waxman, S.; Reed, J.C.; Fisher, P.B. Melanoma differentiation associated gene-7, mda-7/interleukin-24, induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells by promoting mitochondrial dysfunction and inducing reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8138–8144. [Google Scholar]
- Sieger, K.A.; Mhashilkar, A.M.; Stewart, A.; Sutton, R.B.; Strube, R.W.; Chen, S.Y.; Pataer, A.; Swisher, S.G.; Grimm, E.A.; Ramesh, R.; et al. The tumor suppressor activity of MDA-7/IL-24 is mediated by intracellular protein expression in NSCLC cells. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2004, 9, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauane, M.; Gupta, P.; Lebedeva, I.V.; Su, Z.-Z.; Sarkar, D.; Randolph, A.; Valerie, K.; Gopalkrishnan, R.V.; Fisher, P.B. N-glycosylation of MDA-7/IL-24 is dispensable for tumor cell-specific apoptosis and “bystander” antitumor activity. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11869–11877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacoub, A.; Park, M.A.; Gupta, P.; Rahmani, M.; Zhang, G.; Hamed, H.; Hanna, D.; Sarkar, D.; Lebedeva, I.V.; Emdad, L.; et al. Caspase-, cathepsin-, and PERK-dependent regulation of MDA-7/IL-24-induced cell killing in primary human glioma cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-M.; Kang, H.-A.; Park, M.; Lee, H.-Y.; Song, M.-J.; Ko, K.; Oh, J.-W.; Kang, H.-S. Interleukin-24 suppresses the growth of vascular smooth muscle cells by inhibiting H2O2-induced reactive oxygen species production. Pharmacology 2012, 90, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedeva, I.V.; Su, Z.-Z.; Sarkar, D.; Gopalkrishnan, R.V.; Waxman, S.; Yacoub, A.; Dent, P.; Fisher, P.B. Induction of reactive oxygen species renders mutant and wild-type K-ras pancreatic carcinoma cells susceptible to Ad.mda-7-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 2005, 24, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.-K.; An, S.-J.; Han, N.-Y.; Lee, H.; Choi, B.-K. Regulation of IL-24 in human oral keratinocytes stimulated with Tannerella forsythia. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2019, 34, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.A.; Yacoub, A.; Sarkar, D.; Emdad, L.; Rahmani, M.; Spiegel, S.; Koumenis, C.; Graf, M.; Curiel, D.T.; Grant, S.; et al. PERK-dependent regulation of MDA-7/IL-24-induced autophagy in primary human glioma cells. Autophagy 2008, 4, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.A.; Walker, T.; Martin, A.P.; Allegood, J.; Vozhilla, N.; Emdad, L.; Sarkar, D.; Rahmani, M.; Graf, M.; Yacoub, A.; et al. MDA-7/IL-24-induced cell killing in malignant renal carcinoma cells occurs by a ceramide/CD95/PERK-dependent mechanism. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1280–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, L.; Mighty, J.; Zhong, X.; Francis, A.; Mendez, M.; Muharam, H.; Redenti, S.M.; Das, D.; Aktas, B.H.; Sauane, M. IL-24 Promotes Apoptosis through cAMP-Dependent PKA Pathways in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, L.; Zhong, X.; Alvarado, G.; Do, W.; Dejoie, J.; Zybtseva, A.; Aktas, B.H.; Sauane, M. eIF2α Phosphorylation Mediates IL24-Induced Apoptosis through Inhibition of Translation. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2017, 15, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pataer, A.; Vorburger, S.A.; Barber, G.N.; Chada, S.; Mhashilkar, A.M.; Zou-Yang, H.; Stewart, A.L.; Balachandran, S.; Roth, J.A.; Hunt, K.K.; et al. Adenoviral transfer of the melanoma differentiation-associated gene 7 (mda7) induces apoptosis of lung cancer cells via up-regulation of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR). Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 2239–2243. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, B.S.; Rautela, J.; Hertzog, P.J. Antitumour actions of interferons: Implications for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bina, S.; Hosseini, S.Y.; Shenavar, F.; Hosseini, E.; Mortazavi, M. The Effect of RGD/NGR Peptide Modification of Melanoma Differentiation-Associated Gene-7/Interleukin-24 on Its Receptor Attachment, an In Silico Analysis. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2017, 32, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, N.; Pantazi, E.; Pavlidis, P.; Tsakmaki, A.; Li, K.; Yang, F.; Parker, A.; Pin, C.; Cozzetto, D.; Minns, D.; et al. Interleukin-22 orchestrates a pathological endoplasmic reticulum stress response transcriptional programme in colonic epithelial cells. Gut 2020, 69, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallar, S.C.; Kalvakolanu, D.V. GRIM-19: A master regulator of cytokine induced tumor suppression, metastasis and energy metabolism. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017, 33, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, S.; Correia, M.; Soares, P.; Máximo, V. GRIM-19 function in cancer development. Mitochondrion 2011, 11, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammineni, P.; Anugula, C.; Mohammed, F.; Anjaneyulu, M.; Larner, A.C.; Sepuri, N.B.V. The import of the transcription factor STAT3 into mitochondria depends on GRIM-19, a component of the electron transport chain. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 4723–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauane, M.; Su, Z.-Z.; Dash, R.; Liu, X.; Norris, J.S.; Sarkar, D.; Lee, S.-G.; Allegood, J.C.; Dent, P.; Spiegel, S.; et al. Ceramide plays a prominent role in MDA-7/IL-24-induced cancer-specific apoptosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 222, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacoub, A.; Hamed, H.A.; Allegood, J.; Mitchell, C.; Spiegel, S.; Lesniak, M.S.; Ogretmen, B.; Dash, R.; Sarkar, D.; Broaddus, W.C.; et al. PERK-dependent regulation of ceramide synthase 6 and thioredoxin play a key role in mda-7/IL-24-induced killing of primary human glioblastoma multiforme cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huet, O.; Laemmel, E.; Fu, Y.; Dupic, L.; Aprico, A.; Andrews, K.L.; Moore, S.L.; Harrois, A.; Meikle, P.L.; Vicaut, E.; et al. Interleukin 10 antioxidant effect decreases leukocytes/endothelial interaction induced by tumor necrosis factor α. Shock 2013, 39, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, B.D.; Ashley, D.F.; Hänschke, L.; Daou, H.N.; Watt, N.T.; Murfitt, S.A.; MacCannell, A.D.V.; Whitehead, A.; Bowen, T.S.; Sanders, F.W.B.; et al. Long-chain ceramides are cell non-autonomous signals linking lipotoxicity to endoplasmic reticulum stress in skeletal muscle. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avni, D.; Philosoph, A.; Meijler, M.M.; Zor, T. The ceramide-1-phosphate analogue PCERA-1 modulates tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-10 production in macrophages via the cAMP-PKA-CREB pathway in a GTP-dependent manner. Immunology 2010, 129, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahan, K.; Khan, M.; Singh, I. Interleukin-10 and interleukin-13 inhibit proinflammatory cytokine-induced ceramide production through the activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J. Neurochem. 2000, 75, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapio, L.; Di Maiolo, F.; Illiano, M.; Esposito, A.; Chiosi, E.; Spina, A.; Naviglio, S. Targeting protein kinase A in cancer therapy: An update. EXCLI J. 2014, 13, 843–855. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, E.-A.; Kim, E.-J.; Kwak, S.-J.; Juhnn, Y.-S. cAMP signaling inhibits radiation-induced ATM phosphorylation leading to the augmentation of apoptosis in human lung cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneerselvam, J.; Srivastava, A.; Mehta, M.; Chen, A.; Zhao, Y.D.; Munshi, A.; Ramesh, R. IL-24 Inhibits Lung Cancer Growth by Suppressing GLI1 and Inducing DNA Damage. Cancers 2019, 11, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, S.; Ranjan, N. Translation Phases in Eukaryotes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2533, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.J.; Hellen, C.U.T.; Pestova, T.V. The mechanism of eukaryotic translation initiation and principles of its regulation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrick, W.C.; Pavitt, G.D. Protein Synthesis Initiation in Eukaryotic Cells. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a033092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Persaud, L.; Muharam, H.; Francis, A.; Das, D.; Aktas, B.H.; Sauane, M. Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 4A Down-Regulation Mediates Interleukin-24-Induced Apoptosis through Inhibition of Translation. Cancers 2018, 10, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Lin, J.J.; Su, Z.Z.; Goldstein, N.I.; Fisher, P.B. Subtraction hybridization identifies a novel melanoma differentiation associated gene, mda-7, modulated during human melanoma differentiation, growth and progression. Oncogene 1995, 11, 2477–2486. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, M.; Pratscher, B.; Roka, F.; Krepler, C.; Wacheck, V.; Schöfer, C.; Pehamberger, H.; Müller, M.; Lucas, T. Loss of novel mda-7 splice variant (mda-7s) expression is associated with metastatic melanoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 123, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiyari, S.; Salami, M.; Mahdian, R.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Oloomi, M.; Mohammadi Farsani, A.; Bouzari, S. sIL-24 peptide, a human interleukin-24 isoform, induces mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in human cancer cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.; Jung, Y.M.; Kwon, H.-K.; Yi, H.-J.; Lee, S.; Chang, S.; Park, Z.-Y.; Hwang, K.-C.; Im, S.-H. A novel splicing variant of mouse interleukin (IL)-24 antagonizes IL-24-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 28860–28872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarof, G.; Bouchet-Delbos, L.; Gary-Gouy, H.; Durand-Gasselin, I.; Krzysiek, R.; Dalloul, A. Interleukin-24 inhibits the plasma cell differentiation program in human germinal center B cells. Blood 2010, 115, 1718–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz-Perez, A.; Gary-Gouy, H.; Gaudin, F.; Maarof, G.; Marfaing-Koka, A.; de Revel, T.; Dalloul, A. IL-24 induces apoptosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells engaged into the cell cycle through dephosphorylation of STAT3 and stabilization of p53 expression. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 6051–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smith, S.; Lopez, S.; Kim, A.; Kasteri, J.; Olumuyide, E.; Punu, K.; de la Parra, C.; Sauane, M. Interleukin 24: Signal Transduction Pathways. Cancers 2023, 15, 3365. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133365
Smith S, Lopez S, Kim A, Kasteri J, Olumuyide E, Punu K, de la Parra C, Sauane M. Interleukin 24: Signal Transduction Pathways. Cancers. 2023; 15(13):3365. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133365
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmith, Simira, Sual Lopez, Anastassiya Kim, Justina Kasteri, Ezekiel Olumuyide, Kristian Punu, Columba de la Parra, and Moira Sauane. 2023. "Interleukin 24: Signal Transduction Pathways" Cancers 15, no. 13: 3365. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133365
APA StyleSmith, S., Lopez, S., Kim, A., Kasteri, J., Olumuyide, E., Punu, K., de la Parra, C., & Sauane, M. (2023). Interleukin 24: Signal Transduction Pathways. Cancers, 15(13), 3365. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133365





