CAR-NK Cells Targeting HER1 (EGFR) Show Efficient Anti-Tumor Activity against Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Cell Lines
2.2. Isolation and MACS-Sorting of Primary HNSCC Cells
2.3. Generation of Retroviral Vectors and Viral Supernatant Production
2.4. Transduction of Cell Lines with Retroviral Vectors
2.5. Bradford Assay and Western Blotting
2.6. gDNA Isolation and Vector Copy Number Determination
2.7. Optical Genome Mapping
2.8. Flow Cytometry: Cytotoxicity Assay
2.9. Automated Live-Cell Imaging: Cytotoxicity Assay and 3D Spheroid Assay
2.10. CD107a Degranulation Assay
2.11. IFNγ Secretion
2.12. Immunohistochemistry Staining and Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
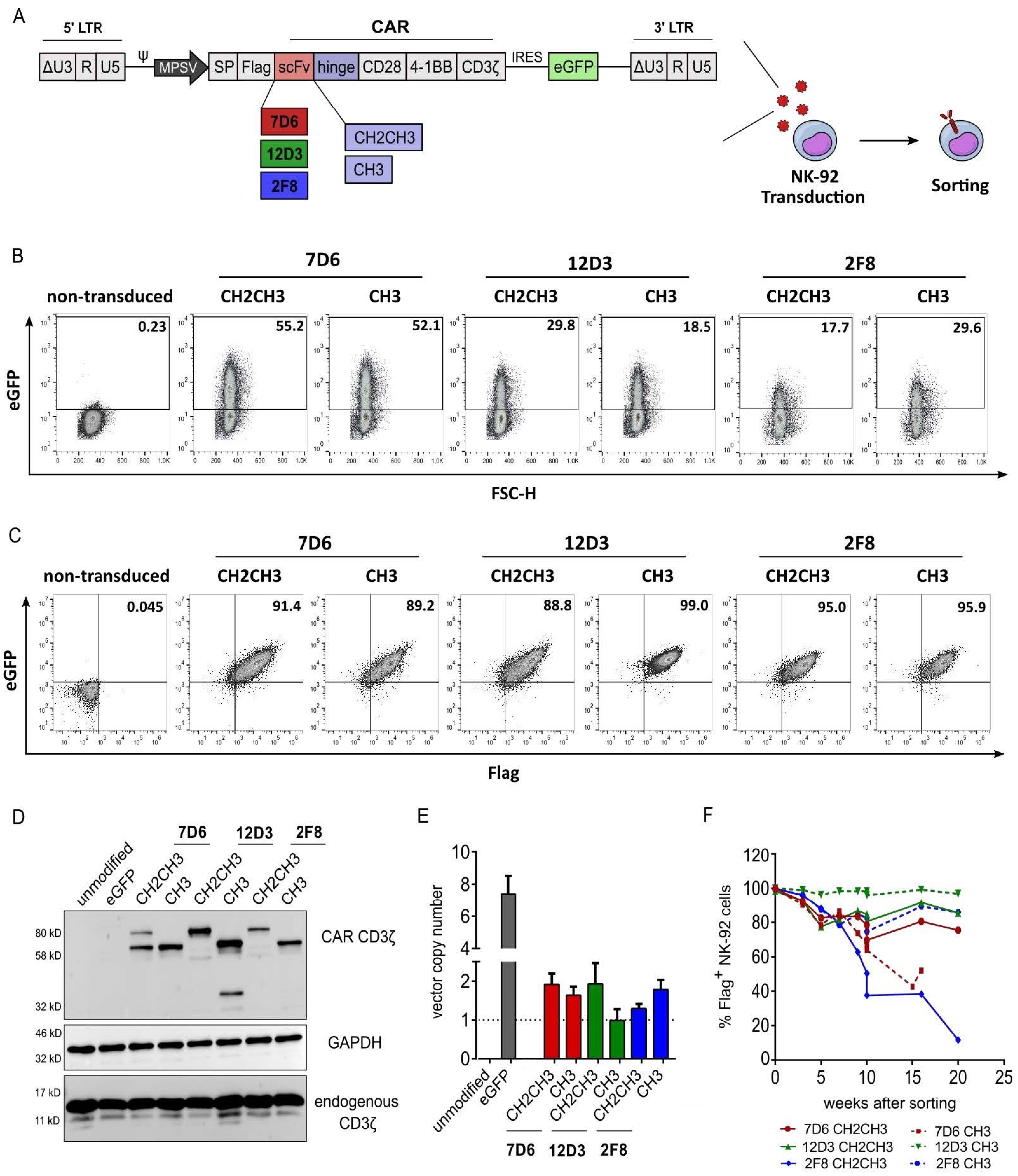
3.1. Validation of Anti-HER1 CAR Expression in NK-92 Cells
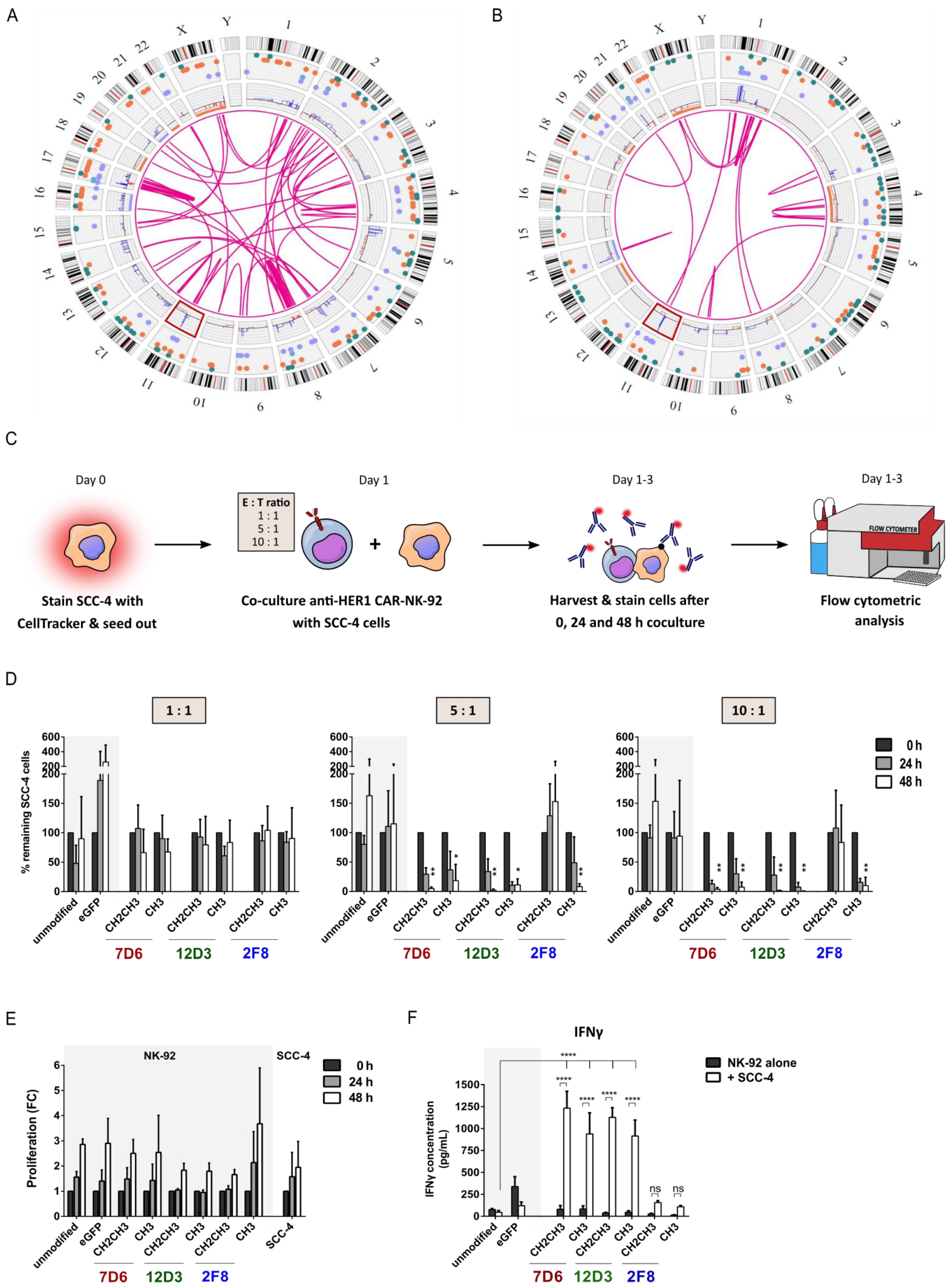
3.2. Functional Screening of Six Anti-HER1 CAR-NK-92 Cell Variants
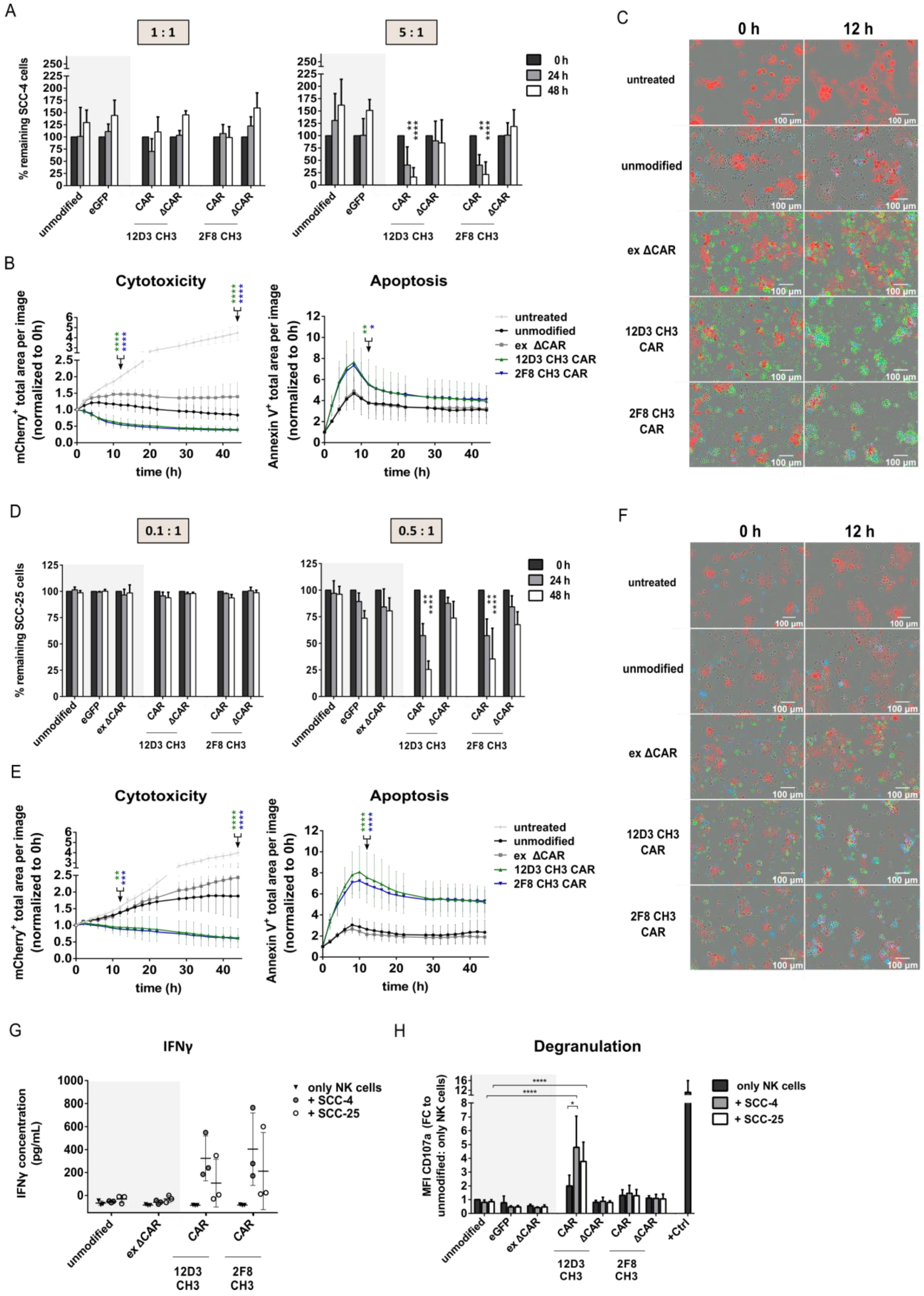
3.3. Anti-HER1 CAR-NK-92 Variants Showed Enhanced Killing, Apoptosis Induction and Degranulation against SCC-4 and SCC-25 Cell Lines
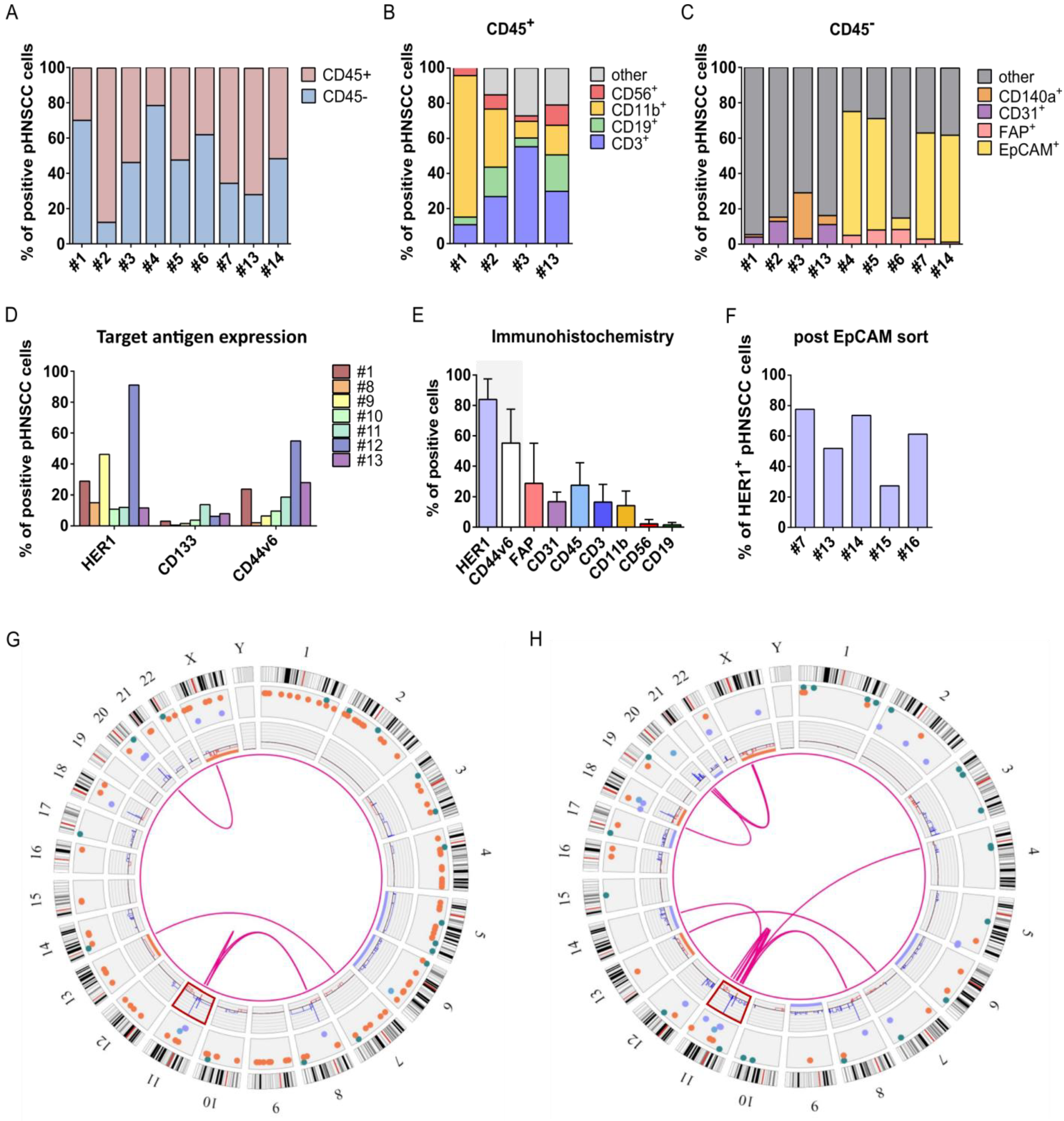
3.4. Isolation and Characterization of Primary HNSCC Tumor-Derived Cells
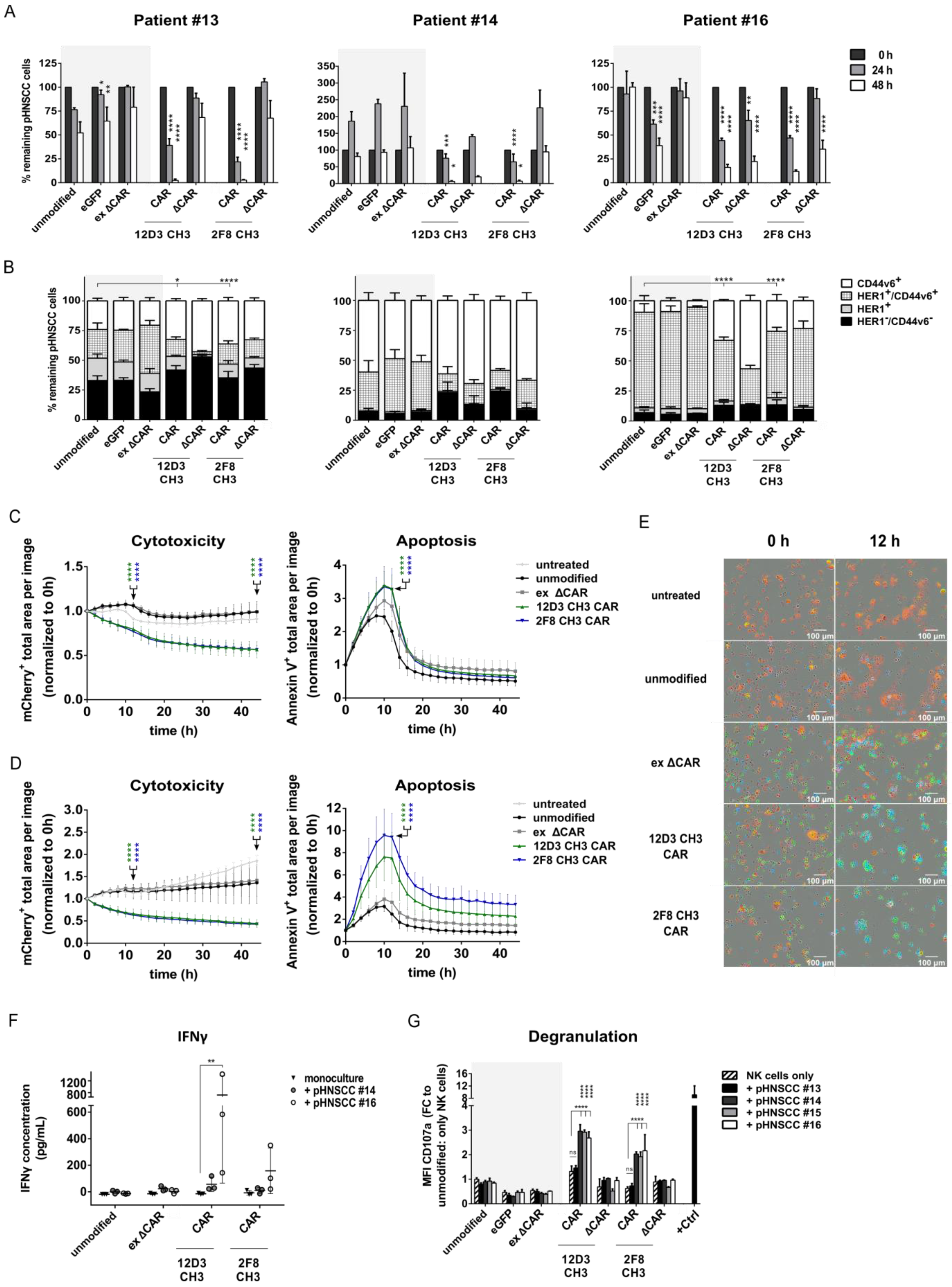
3.5. Anti-HER1 CAR-NK-92 Cells Show Enhanced Killing, Apoptosis and Degranulation against pHNSCC Cells
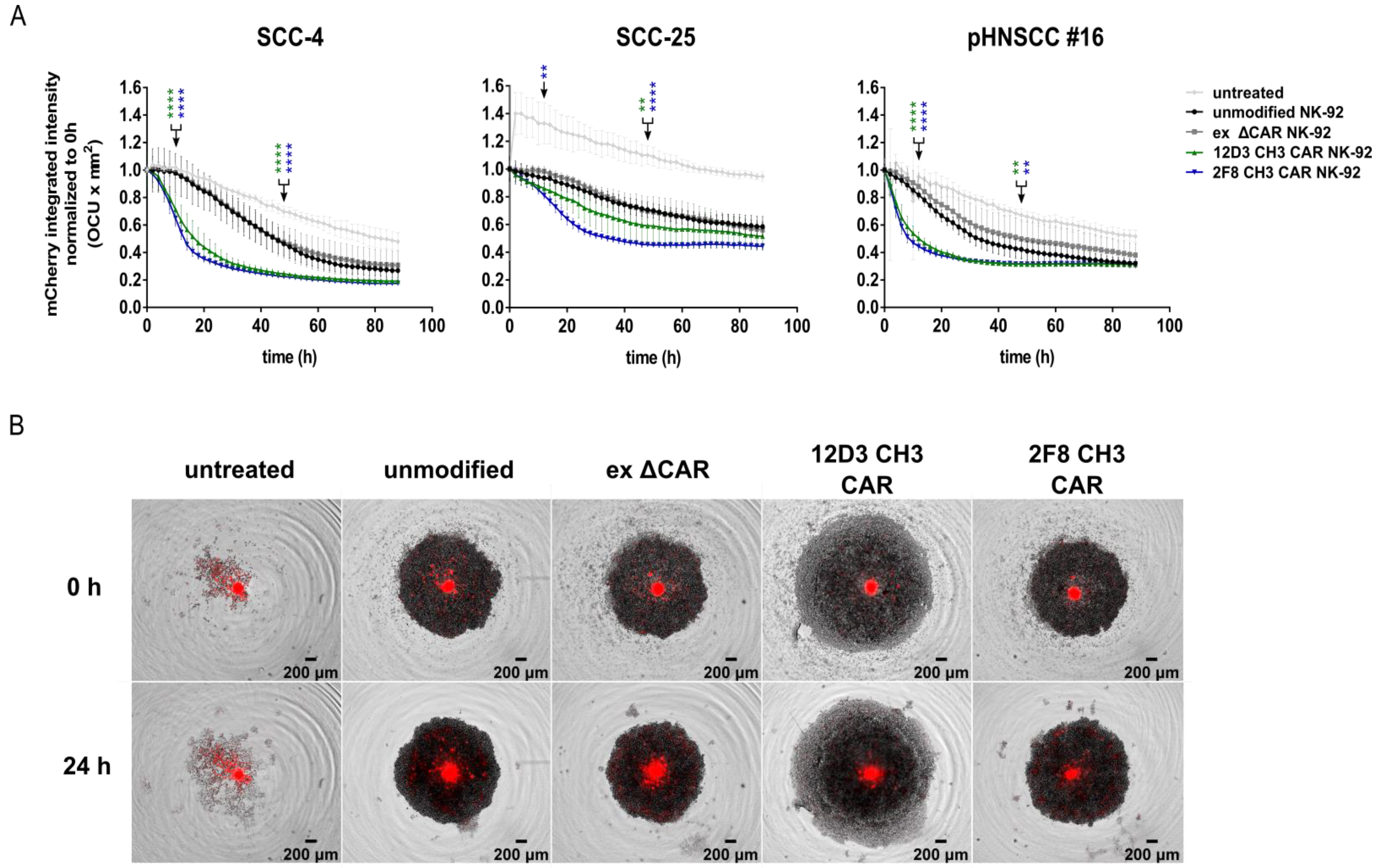
3.6. Anti-HER1 CAR-NK-92 Treatment Resulted in Faster Spheroid Disruption
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, K.K.; Harris, J.; Wheeler, R.; Weber, R.; Weber, R.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Nguyen-Tân, P.F.; Westra, W.H.; Chung, C.H.; Jordan, R.C.; et al. Human Papillomavirus and Survival of Patients with Oropharyngeal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 363, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermorken, J.B.; Mesia, R.; Rivera, F.; Remenar, E.; Kawecki, A.; Rottey, S.; Erfan, J.; Zabolotnyy, D.; Kienzer, H.-R.; Cupissol, D.; et al. Platinum-Based Chemotherapy plus Cetuximab in Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, H.-F.; Lou, P.-J. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Current landscape and future directions. Head Neck 2019, 41, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Z.; Zhang, K.; Lam, A.K.; Huang, J.; Qiu, F.; Qiao, B.; Zhang, Y. MUC1 as a target for CAR-T therapy in head and neck squamous cell carinoma. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geldres, C.; Savoldo, B.; Hoyos, V.; Caruana, I.; Zhang, M.; Yvon, E.; Del Vecchio, M.; Creighton, C.J.; Ittmann, M.; Ferrone, S.; et al. T lymphocytes redirected against the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan-4 control the growth of multiple solid tumors both in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yan, Z.; Wenjie, L.; Qi, T.; Renjie, C.; Jin, Z.; Zhenqing, F. T cells expressing a LMP1-specific chimeric antigen receptor mediate antitumor effects against LMP1-positive nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Biomed. Res. 2014, 28, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, Y.; Greene, S.; Friedman, J.; E Clavijo, P.; Van Waes, C.; Fabian, K.P.; Padget, M.R.; Sater, H.A.; Lee, J.H.; Soon-Shiong, P.; et al. Tumor control via targeting pd-l1 with chimeric antigen receptor modified nk cells. eLife 2020, 9, e54854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, S.; Adami, A.; Metoudi, M.; Achkova, D.; van Schalkwyk, M.; Pereira, A.P.; Bosshard-Carter, L.; Whilding, L.; van der Stegen, S.; Davies, D.; et al. A phase I trial of T4 CAR T-cell immunotherapy in head and neck squamous cancer (HNSCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, S.; van Schalkwyk, M.; Maher, J. Clinical Evaluation of ErbB-Targeted CAR T-Cells, Following Intracavity Delivery in Patients with ErbB-Expressing Solid Tumors. In Gene Therapy of Solid Cancers—Methods and Protocols; Walther, W., Stein, U., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2015; Volume 1317, 387p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Santomasso, B.D.; Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Turtle, C.J.; Brudno, J.N.; Maus, M.V.; Park, J.H.; Mead, E.; Pavletic, S.; et al. ASTCT Consensus Grading for Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurologic Toxicity Associated with Immune Effector Cells. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Tong, Y.; Dotti, G.; Shaim, H.; Savoldo, B.; Mukherjee, M.; Orange, J.; Wan, X.; Lu, X.; Reynolds, A.; et al. Cord blood NK cells engineered to express IL-15 and a CD19-targeted CAR show long-term persistence and potent antitumor activity. Leukemia 2018, 32, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.; Marin, D.; Banerjee, P.; Macapinlac, H.A.; Thompson, P.; Basar, R.; Kerbauy, L.N.; Overman, B.; Thall, P.; Kaplan, M.; et al. Use of CAR-transduced natural killer cells in CD19-positive lymphoid tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.A.; Law, A.D.; Routy, B.; Denhollander, N.; Gupta, V.; Wang, X.-H.; Chaboureau, A.; Viswanathan, S.; Keating, A. A phase I trial of NK-92 cells for refractory hematological malignancies relapsing after autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation shows safety and evidence of efficacy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 89256–89268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Sheng, L.; Shui, Y.; Hu, Q.; Nordgren, H.; Carlsson, J. EGFR, HER2, and HER3 expression in laryngeal primary tumors and corresponding metastases. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Saba, N.F.; Chen, G.; Shin, D.M. Targeting HER (ERBB) signaling in head and neck cancer: An essential update. Mol. Asp. Med. 2015, 45, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suerth, J.D.; Labenski, V.; Schambach, A. Alpharetroviral vectors: From a cancer-causing agent to a useful tool for human gene therapy. Viruses 2014, 6, 4811–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, D.; Millon, R.; Velten, M.; Bronner, G.; Jung, G.; Engelmann, A.; Flesch, H.; Eber, M.; Methlin, G.; Abecassis, J. Amplification of 11q13 DNA markers in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: Correlation with clinical outcome. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 2203–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schartinger, V.H.; Schmutzhard, J.; Wurm, M.; Schwentner, I.M.; Obrist, P.; Oberaigner, W.; Sprinzl, G.M. The expression of EGFR, HER2 and EpCam in Head and Neck squamous cell carcinomas. memo Mag. Eur. Med. Oncol. 2009, 2, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, J.H.; Graham, M.P.; Chinn, S.B.; Darr, O.F.; Chepeha, D.B.; Wolf, G.T.; Bradford, C.R.; Carey, T.E.; Prince, M.E. Novel method of cell line establishment utilizing fluorescence-activated cell sorting resulting in 6 new head and neck squamous cell carcinoma lines. Head Neck 2016, 38, E459–E467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, R.; Şenbabaoğlu, Y.; Desrichard, A.; Havel, J.J.; Dalin, M.G.; Riaz, N.; Lee, K.-W.; Ganly, I.; Hakimi, A.A.; Chan, T.A.; et al. The head and neck cancer immune landscape and its immunotherapeutic implications. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e89829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puram, S.V.; Tirosh, I.; Parikh, A.S.; Patel, A.P.; Yizhak, K.; Gillespie, S.; Rodman, C.; Luo, C.L.; Mroz, E.A.; Emerick, K.S.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Primary and Metastatic Tumor Ecosystems in Head and Neck Cancer. Cell 2017, 171, 1611–1624.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S. The Immune Infiltration in HNSCC and Its Clinical Value: A Comprehensive Study Based on the TCGA and GEO Databases. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 1163250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Shi, S.; Yen, Y.; Brown, J.; Ta, J.Q.; Le, A.D. A subpopulation of CD133+ cancer stem-like cells characterized in human oral squamous cell carcinoma confer resistance to chemotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2010, 289, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, D.S.; Snyderman, C.; Gollin, S.M.; Pan, S.; Walker, E.; Deka, R.; Barnes, E.L.; Johnson, J.T.; Herberman, R.B.; Whiteside, T.L. Biology, cytogenetics, and sensitivity to immunological effector cells of new head and neck squamous cell carcinoma lines. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 5167–5175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- White, J.S.; Weissfeld, J.L.; Ragin, C.C.; Rossie, K.M.; Martin, C.L.; Shuster, M.; Ishwad, C.S.; Law, J.C.; Myers, E.N.; Johnson, J.T.; et al. The Influence of Clinical and Demographic Risk Factors on the Establishment of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines. Oral Oncol. 2007, 43, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jutz, S.; Leitner, J.; Schmetterer, K.; Doel-Perez, I.; Majdic, O.; Grabmeier-Pfistershammer, K.; Paster, W.; Huppa, J.B.; Steinberger, P. Assessment of costimulation and coinhibition in a triple parameter T cell reporter line: Simultaneous measurement of NF-κB, NFAT and AP-1. J. Immunol. Methods 2016, 430, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, A.H.; Haso, W.H.; Shern, J.F.; Wanhainen, K.M.; Murgai, M.; Ingaramo, M.; Smith, J.P.; Walker, A.J.; Kohler, M.E.; Venkateshwara, W.R.; et al. 4-1BB Costimulation Ameliorates T Cell Exhaustion Induced by Tonic Signaling of Chimeric Antigen Receptors. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alter, G.; Malenfant, J.M.; Altfeld, M. CD107a as a functional marker for the identification of natural killer cell activity. J. Immunol. Methods 2004, 294, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzewski, K.; Gil-Krzewska, A.; Nguyen, V.; Peruzzi, G.; Coligan, J.E. LAMP1/CD107a is required for efficient perforin delivery to lytic granules and NK-cell cytotoxicity. Blood 2013, 121, 4672–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Qu, D.; Sun, R.; Zhang, M.; Nan, K. NK cell-produced IFN-γ regulates cell growth and apoptosis of colorectal cancer by regulating IL-15. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 19, 1400–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Jaw, J.J.; Stutzman, N.C.; Zou, Z.; Sun, P.D. Natural killer cell-produced IFN-γ and TNF-α induce target cell cytolysis through up-regulation of ICAM-1. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopal, S.; Kwon, S.J.; Ku, B.; Lee, D.W.; Kim, J.; Dordick, J.S. 3D tumor spheroid microarray for high-throughput, high-content natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’rourke, D.M.; Nasrallah, M.P.; Desai, A.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Mansfield, K.; Morrissette, J.J.D.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Brem, S.; Maloney, E.; Shen, A.; et al. A single dose of peripherally infused EGFRvIII-directed CAR T cells mediates antigen loss and induces adaptive resistance in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaaa0984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Rivière, I.; Gonen, M.; Wang, X.; Sénéchal, B.; Curran, K.J.; Sauter, C.; Wang, Y.; Santomasso, B.; Mead, E.; et al. Long-Term Follow-up of CD19 CAR Therapy in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günthert, U.; Hofmann, M.; Rudy, W.; Reber, S.; Zöller, M.; Haußmann, I.; Matzku, S.; Wenzel, A.; Ponta, H.; Herrlich, P. A New Variant of Glycoprotein CD44 Confers Metastatic Potential to Rat Carcinoma Cells. Cell 1991, 55, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, R.L.; Blumenschein, G.; Fayette, J.; Guigay, J.; Colevas, A.D.; Licitra, L.; Harrington, K.; Kasper, S.; Vokes, E.E.; Even, C.; et al. Nivolumab in Patients with Recurrent or Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: Efficacy and Safety in CheckMate 141 by Prior Cetuximab Use. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5221–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pauw, I.; Lardon, F.; Van den Bossche, J.; Baysal, H.; Fransen, E.; Deschoolmeester, V.; Pauwels, P.; Peeters, M.; Vermorken, J.B.; Wouters, A. Simultaneous targeting of EGFR, HER2, and HER4 by afatinib overcomes intrinsic and acquired cetuximab resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 830–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haist, C.; Schulte, E.; Bartels, N.; Bister, A.; Poschinski, Z.; Ibach, T.C.; Geipel, K.; Wiek, C.; Wagenmann, M.; Monzel, C.; et al. CD44v6-targeted CAR T-cells specifically eliminate CD44 isoform 6 expressing head/neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Oral Oncol. 2021, 116, 105259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spranger, S.; Spaapen, R.M.; Zha, Y.; Williams, J.; Meng, Y.; Ha, T.T.; Gajewski, T.F. Up-regulation of PD-L1, IDO, and Tregs in the melanoma tumor microenvironment is driven by CD8+ T cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 200ra116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Kim, S.-E.; Keam, B.; Park, H.-R.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.; Kim, T.M.; Doh, J.; Kim, D.-W.; Heo, D.S. Anti-tumor effects of NK cells and anti-PD-L1 antibody with antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in PD-L1-positive cancer cell lines. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, K.; Paterson, S.; Mulholland, T.; Coffelt, S.B.; Zagnoni, M. Assessment of CAR-T Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity in 3D Microfluidic Cancer Co-Culture Models for Combination Therapy. J. Eng. Med. Biol. 2022, 3, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.N.; Fong, S.Y.; Tan, W.W.S.; Tan, S.Y.; Liu, M.; Cheng, J.Y.; Lim, S.; Suteja, L.; Huang, E.K.; Chan, J.K.Y.; et al. “stablishment and characterization of humanized mouse NPC-PDX model for testing immunotherapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.N.; So, W.Y.; Harden, S.L.; Fong, S.Y.; Wong, M.X.Y.; Tan, W.W.S.; Tan, S.Y.; Ong, J.K.L.; Rajarethinam, R.; Liu, M.; et al. Successful targeting of PD-1/PD-L1 with chimeric antigen receptor-natural killer cells and nivolumab in a humanized mouse cancer model. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eadd1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.W.; Jeong, J.-U.; Lee, K.-H.; Uong, T.N.T.; Rhee, J.H.; Ahn, S.-J.; Kim, S.-K.; Cho, D.; Nguyen, H.P.Q.; Pham, C.T.; et al. Combined NK cell therapy and radiotherapy exhibit long-term therapeutic and anti-metastatic effects in a human triple negative breast cancer model. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 108, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walle, T.; Kraske, J.A.; Liao, B.; Lenoir, B.; Timke, C.; Halbach, E.v.B.U.; Tran, F.; Griebel, P.; Albrecht, D.; Ahmed, A.; et al. Radiotherapy orchestrates natural killer cell dependent antitumor immune responses through CXCL8. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabh4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canter, R.J.; Grossenbacher, S.K.; Foltz, J.A.; Sturgill, I.R.; Park, J.S.; Luna, J.I.; Kent, M.S.; Culp, W.T.N.; Chen, M.; Modiano, J.F.; et al. Radiotherapy enhances natural killer cell cytotoxicity and localization in pre-clinical canine sarcomas and first-in-dog clinical trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2017, 5, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapdor, R.; Wang, S.; Hacker, U.; Büning, H.; Morgan, M.; Dörk, T.; Hillemanns, P.; Schambach, A. Improved Killing of Ovarian Cancer Stem Cells by Combining a Novel Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Based Immunotherapy and Chemotherapy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2017, 28, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Region | HPV Status | Tumor Occurrence | Treatment Post Biopsy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | Tongue | negative | primary | primary RCTx |
| #2 | Tonsil right | negative | primary | primary RCTx |
| #3 | Parapharyngeal | / | primary | primary RCTx |
| #4 | Nose skin | negative | primary | surgery, no RCTx |
| #5 | Tonsil left | positive | primary | surgery, no RCTx |
| #6 | Soft palate | negative | primary | primary RCTx |
| #7 | Oropharynx right | negative | primary | primary RCTx |
| #8 | Larynx | / | primary | / |
| #9 | Tongue basis | positive | primary | primary RCTx |
| #10 | Hypolarynx | negative | primary | primary RCTx |
| #11 | Larynx | negative | secondary | surgery, no RCTx |
| #12 | Uvula | positive | primary | none |
| #13 | Uvula | negative | primary | primary RCTx |
| #14 | Tonsils | negative | primary | primary RCTx |
| #15 | Tonsil | negative | primary | primary RCTx |
| #16 | Tongue | negative | secondary | Surgery, no RCTx |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nowak, J.; Bentele, M.; Kutle, I.; Zimmermann, K.; Lühmann, J.L.; Steinemann, D.; Kloess, S.; Koehl, U.; Roßberg, W.; Ahmed, A.; et al. CAR-NK Cells Targeting HER1 (EGFR) Show Efficient Anti-Tumor Activity against Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). Cancers 2023, 15, 3169. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123169
Nowak J, Bentele M, Kutle I, Zimmermann K, Lühmann JL, Steinemann D, Kloess S, Koehl U, Roßberg W, Ahmed A, et al. CAR-NK Cells Targeting HER1 (EGFR) Show Efficient Anti-Tumor Activity against Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). Cancers. 2023; 15(12):3169. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123169
Chicago/Turabian StyleNowak, Juliette, Marco Bentele, Ivana Kutle, Katharina Zimmermann, Jonathan Lukas Lühmann, Doris Steinemann, Stephan Kloess, Ulrike Koehl, Willi Roßberg, Amed Ahmed, and et al. 2023. "CAR-NK Cells Targeting HER1 (EGFR) Show Efficient Anti-Tumor Activity against Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC)" Cancers 15, no. 12: 3169. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123169
APA StyleNowak, J., Bentele, M., Kutle, I., Zimmermann, K., Lühmann, J. L., Steinemann, D., Kloess, S., Koehl, U., Roßberg, W., Ahmed, A., Schaudien, D., Neubert, L., Kamp, J.-C., Kuehnel, M. P., Warnecke, A., Schambach, A., & Morgan, M. (2023). CAR-NK Cells Targeting HER1 (EGFR) Show Efficient Anti-Tumor Activity against Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). Cancers, 15(12), 3169. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123169








