Integrated Neurosurgical Management of Retroperitoneal Benign Nerve Sheath Tumors
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
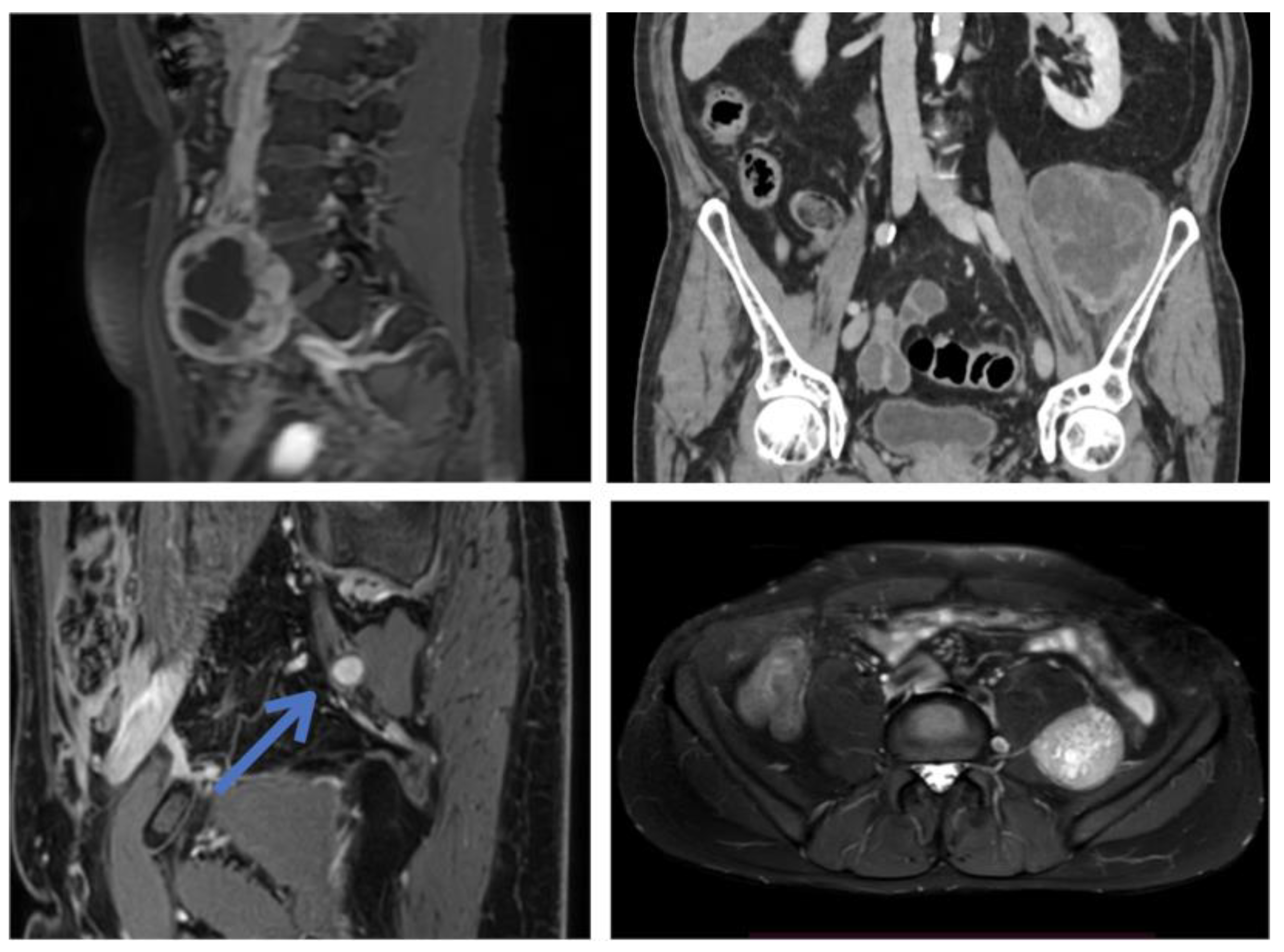
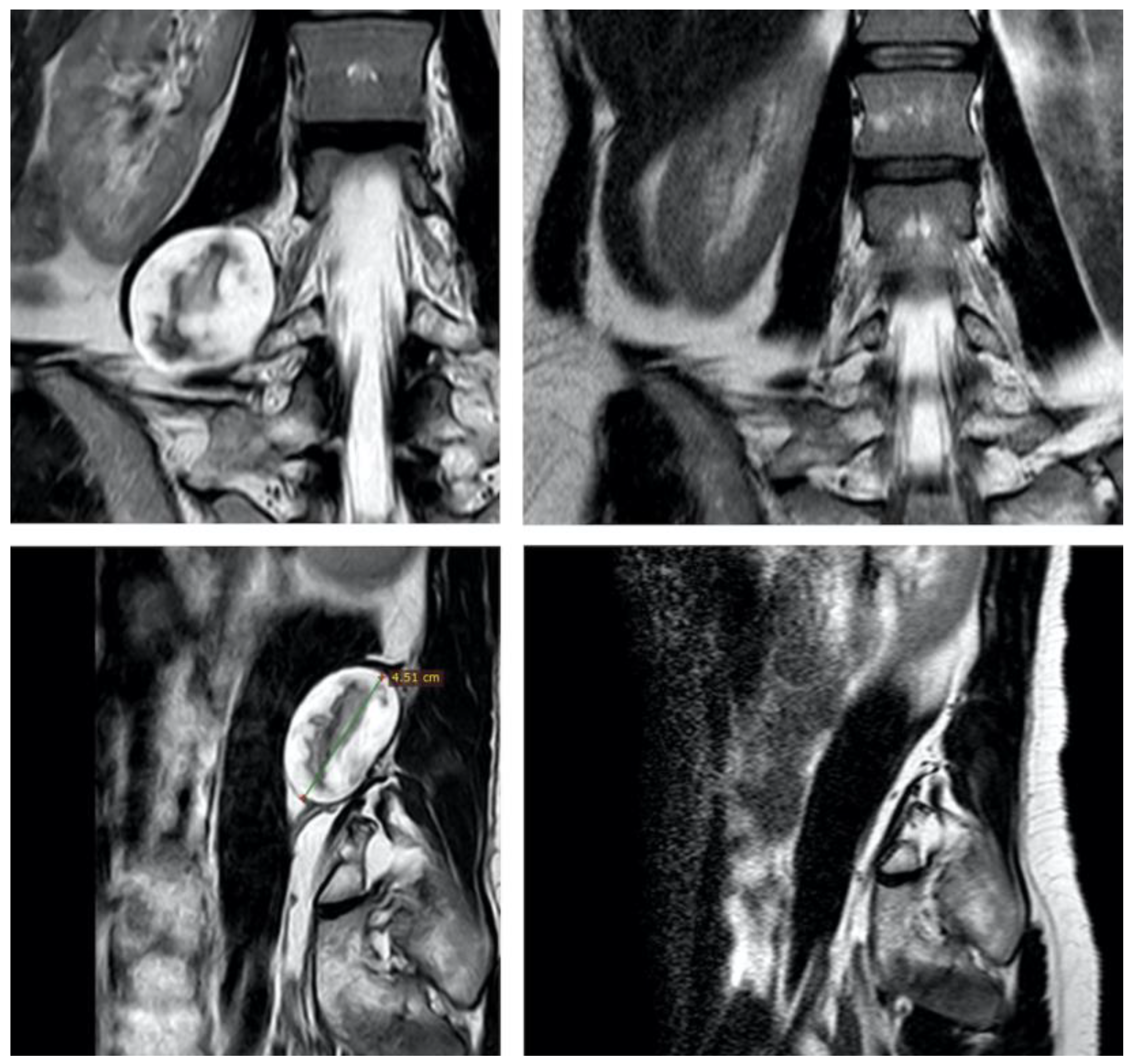
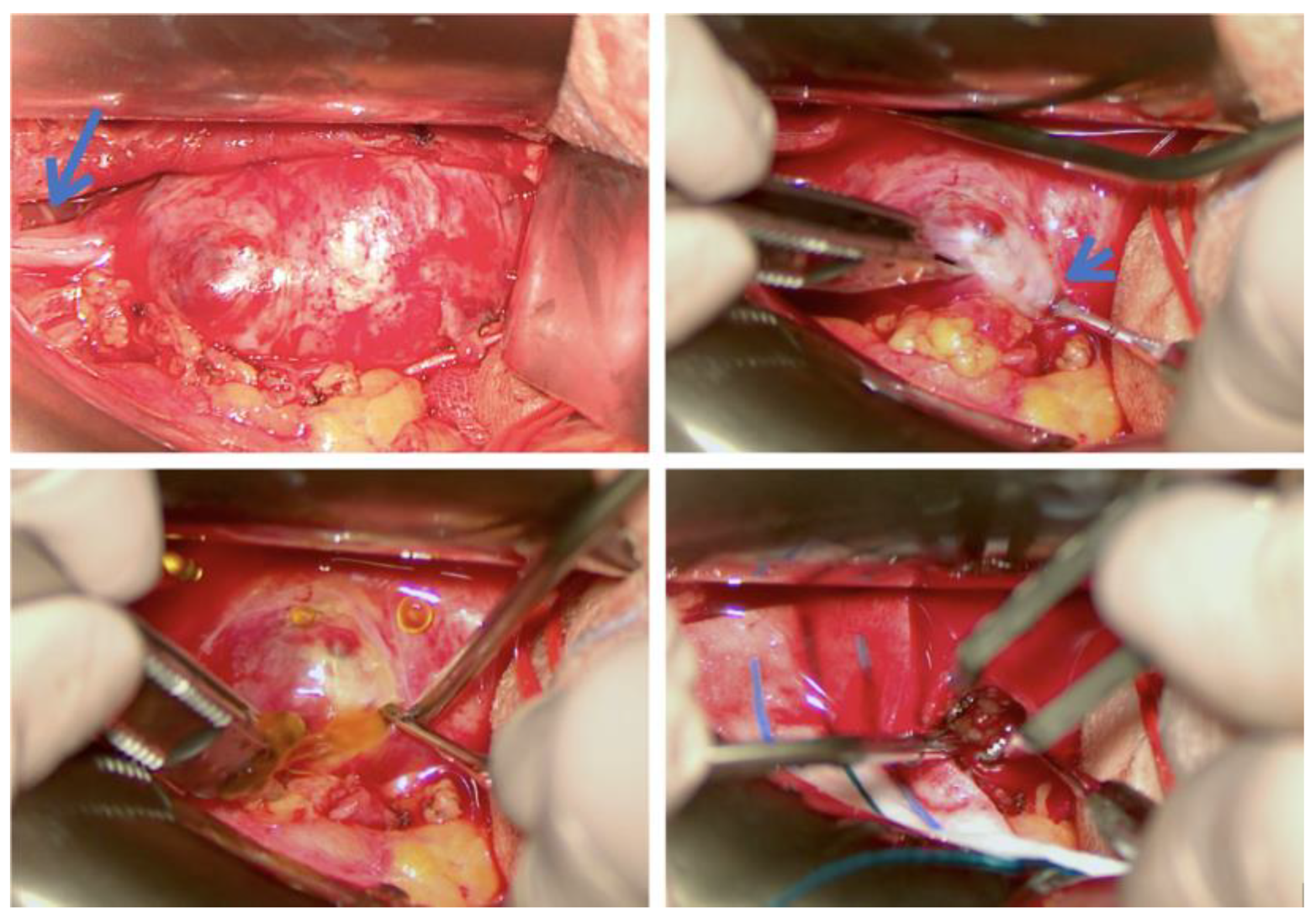
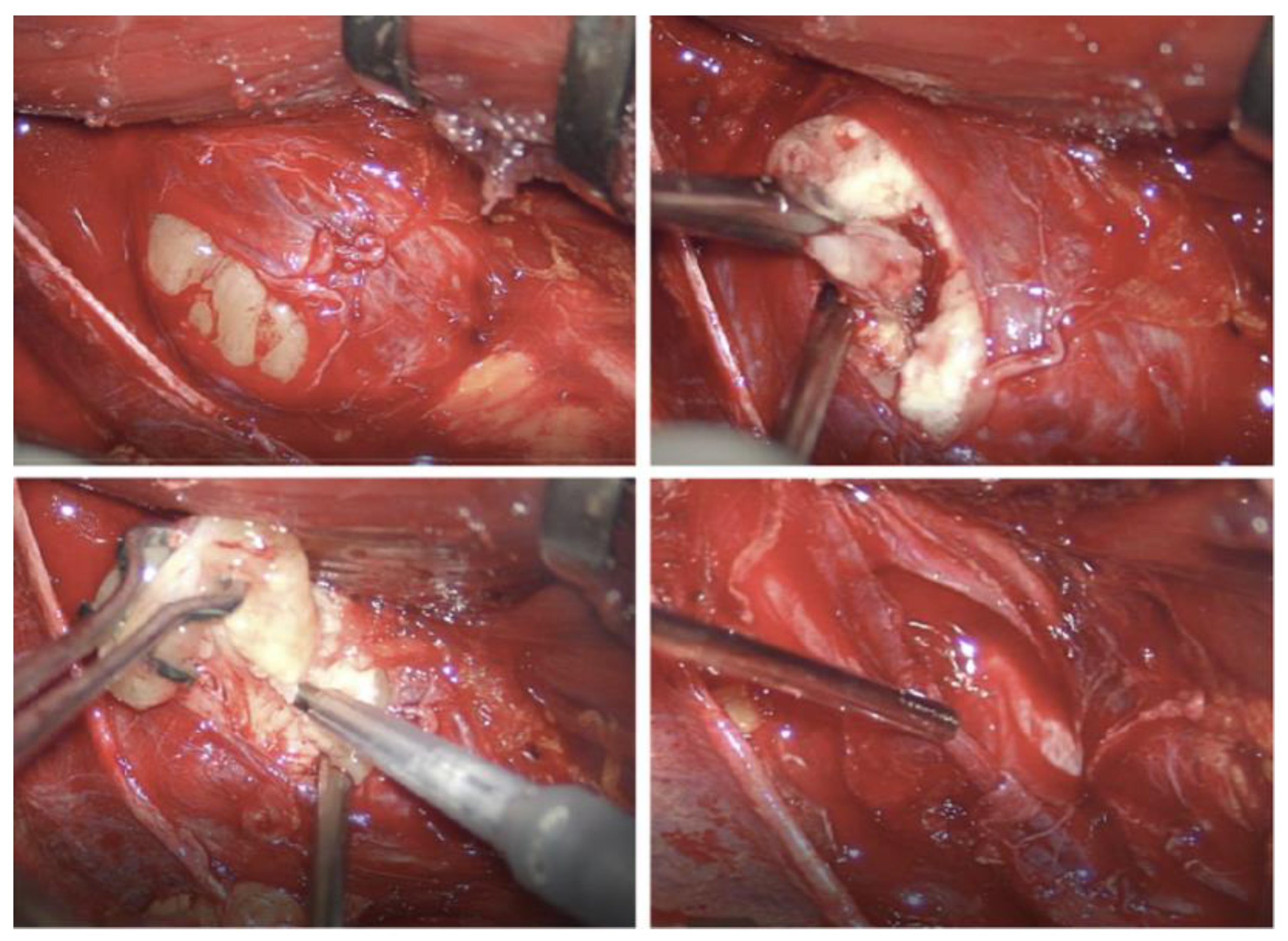
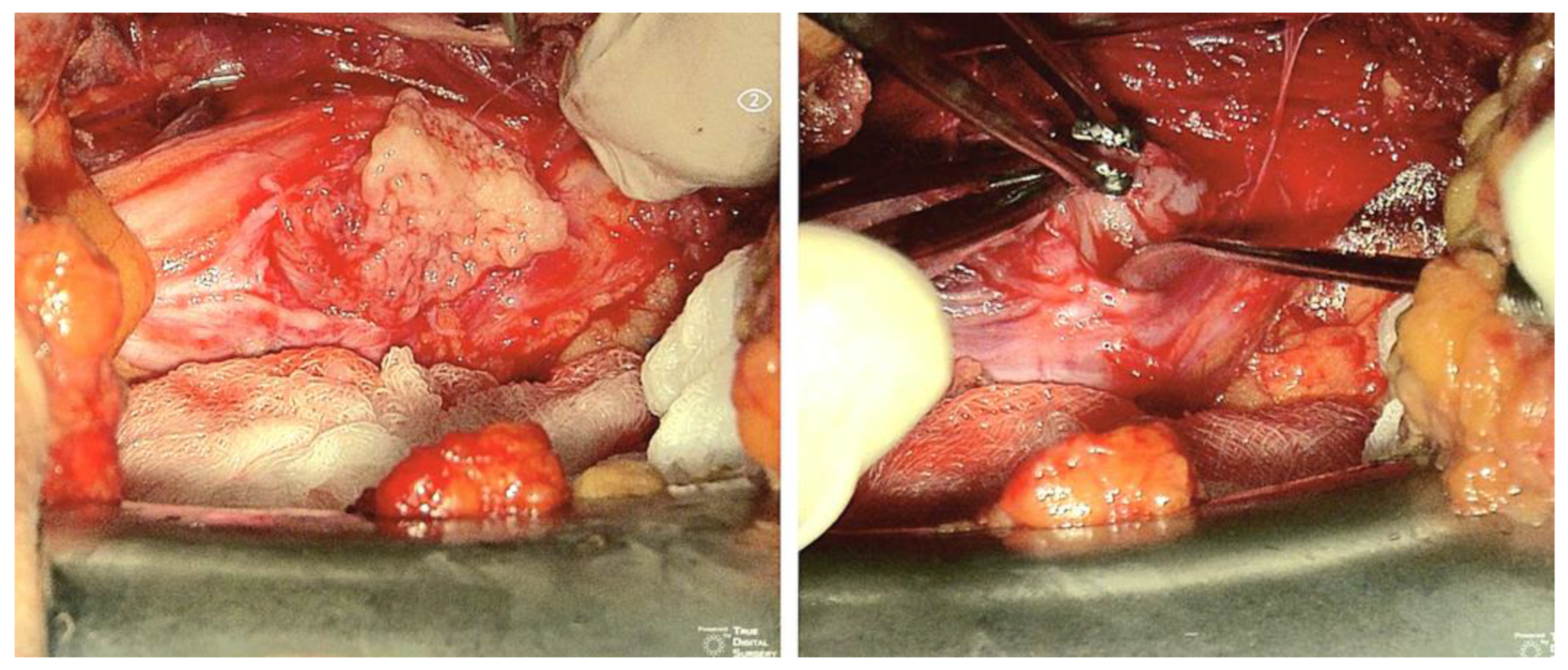
3.1. Original Surgical Series
3.2. Review of the Literature
| Age, Sex | Origin, Location | Histology | Size (mm) | Symptoms | Surgical Approach | Surgical Time (min) | Blood Loss; Transfusion | Follow-Up (mos) | Clinical Outcome | Residue; Recurrence | Preop Biopsy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient 1 | 55, M | Right obturator nerve, postero-lateral to psoas | S | 40 | None | Lateral retroperitoneal | 300 | 850 mL, no | 108 | Right medial thigh hypoesthesia | No, no | No |
| Patient 2 | 27, F | Right femoral nerve, pelvis lateral to psoas | S | 60 | None | Lateral retroperitoneal | 240 | 400 mL, no | 108 | Ambulating on P.O. day 1; no new deficits | No; no | No |
| Patient 3 | 60, F | Left femoral nerve, pelvis anterior to psoas | S | 60 | Left groin and thigh pain | Lower midline laparotomy; transperitoneal | 180 | 450 mL, no | 36 | Ambulating on P.O. day 1; no new deficits | No; no | No |
| Patient 4 | 40, F | Right obturator nerve, postero-medial to psoas | N | 45 | Abdominal and groin pain | Midline laparotomy; transperitoneal | 120 | 200 mL; no | 30 | Ambulating on P.O. day 1; no new deficits; transient paresthesias on left obturator territory | No; no | No |
| Patient 5 | 36, F | Sacral plexus (S1-S2), pelvic presacral | S | 130 | Left sciatic hypoestesia | Lower midline laparotomy; retroperitoneal | 480 | 3000 mL; yes | 30 | Ambulating on P.O. day 1; no new deficits; paresthesias on sciatic territory (improving) | Yes; no | Yes (open) |
| Patient 6 | 56, F | Left sciatic nerve, pelvis lateral to sacrum | S | 50 | Left sciatic pain | Pfannestiel incision; transperitoneal | 420 | 500 mL; no | 24 | Ambulating on P.O. day 1; no new deficits; pain remission; paresthesias on sciatic territory (improving) | Yes; no | Yes (open) |
| Patient 7 | 60, F | Left genitofemoral nerve, pelvis medial to psoas | S | 20 | None | Lower midline laparotomy | NA | NA | 24 | Ambulating on P.O. day 1; no new deficits | No, no | No |
| Patient 8 | 46, F | Right sciatic nerve; pelvis lateral to sacrum | S | 20 | Severe sciatic pain | Laparoscopic converted to lower midline laparotomy; transperitoneal | NA | 150 mL; no | 20 | Ambulating on P.O. day 1; pain remission; no new deficits | No, no | No |
| Patient 9 | 45, M | Sacral plexus; midline sacral promontory | S | 75 | Lower abdominal pain; abdominal mass | Lower midline laparotomy; transperitoneal | 150 | 200 mL; no | 18 | Ambulating on P.O. day 1; no new deficits | No; no | Yes (percutaneous) |
| Patient 10 | 17, F | Right lumbosacral trunk; lateral to sacrum | S | 40 | Abdominal pain | Lower midline laparotomy; transperitoneal | 360 | 100 mL; no | 18 | Ambulating on P.O. day 1; no new deficits | No; no | No |
| Patient 11 | 42, F | Left femoral nerve, upper pelvis anterior to psoas | S | 35 | Left thigh pain | Lower midline laparotomy; transperitoneal | 150 | 400 mL, no | 16 | Ambulating on P.O. day 1; no new deficits | No; no | No |
| Patient 12 | 67, M | Left lumbosacral plexus, medial to psoas | S | 60 | None | Lower midline laparotomy; transperitoneal | 360 | 100 mL; no | 12 | Transient ileus, managed non-operatively; no new deficits | No; no | No |
| Patient 13 | 28, M | Left femoral nerve, lateral to psoas | S | 75 | Left tight numbness | Lateral retroperitoneal | 360 | 500 mL; no | 12 | Ambulating on P.O. day 1; unchanged left tight numbness | No; no | Yes (percutaneous) |
| Patient 14 | 72, F | Left femoral plexus branch, medial to psoas | S | 60 | Left inguinal and thigh pain | Midline laparotomy; transperitoneal | 540 | 300 mL; no | 3 | Ambulating on P.O. day 1; no new deficits; pain remission | No; no | No |
| Patient 15 | 75, M | Left femoral nerve, lateral to psoas | S | 100 | Left sciatic pain (compression) | Lateral retroperitoneal | 220 | 400 mL; no | 1 | Ambulating on P.O. day 1; no new deficits; pain remission | No, no | Yes (percutaneous) |
| Source, Expertise | No. of Patients (% Male) | Age | Follow-Up (mos) | Histology | Size | Pre-Operative Biopsy | Surgical Approach | Resection (% of Cases) | Blood Loss | Preoperative Symptoms | Neurological Outcomes | Recurrence/Regrowth% (Time) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regan 1977, abdominal surgery [9] | 5 (80%) | 55 | 48 | “Neurilemmoma” (100%) | 13 cm | 20%, misleading | Laparotomy | Macroscopic en bloc (40%), partial (40%) | >3000 mL in 40% of cases | Abdominal pain (60%), abdominal mass (40%) | Severe leg pain (20%) | 0% | The authors recommend preoperative arteriography to estimate tumor vascularity. Two cases of infection following percutaneous or transrectal puncture of the tumor. |
| Guz 1989, abdominal surgery [7] | 6 (33%) | 45 | 16 | S (50%), N (50%) | NR | 50%, misleading | Laparotomy | Macroscopic en bloc (100%) | NR | Radiculopathy (33%), Abdominal pain (33%), abdominal mass (17%), urinary symptoms (17%) | NR | 0% | The authors recommend complete surgical excision vs. “enucleation” due to the risk of missing malignant cases |
| Gubbay 1995, abdominal surgery [10] | 5 (40%) | 38 | 73 | S (100%) | 8 cm | 60%, 2/3 non diagnostic | Laparotomy | Macroscopic en bloc (100%) | NR | Abdominal discomfort (60%), abdominal mass (20%), obstructed labor (20%) | Transient motor deficit (20%) | 0% | In two cases (40%), resection hindered by significant bleeding |
| Goh 2005, abdominal surgery [5] | 7 (86%) | 43 | 17 | S (100%) | 7 cm | 14%, misleading | Laparotomy | Macroscopic en bloc (100%) | NR | Abdominal discomfort (28%) | NR | 0% | No tumor was associated with significant nerve trunks |
| Li 2007, abdominal surgery [11] | 38 (46%) | 44 | 63 (6–404) | S (98%), MPNST (2%) | 15 cm | 2%, correct | Laparotomy | Macroscopic en bloc (73%), Subtotal (13%), limited (11%) | NR | Abdominal discomfort (50%), back pain (6%) | 1% quadriceps paralysis | 1% recurrence (3 years) | Large series with long follow-up; important data on disease recurrence |
| Theodosopoulos 2008, abdominal surgery [12] | 5 (40%) | 56 | 35 (6–75) | S (100%) | 13 cm | None | Laparotomy | Macroscopic en bloc (80%), subtotal (20%) | NR | Abdominal discomfort (60%), abdominal mass (20%), DVT (20%) | Sensory and motor deficit (20%) | 0% | Embolization facilitated resection/dissection in one case. In two cases tumor resected from major nerve root with deficit in one case |
| Dozois 2009, abdominal surgery, neurosurgery, etc. [13] | 46 (50%) | 44 | - | S (61%), N (37%), ganglioneuroma 2%) | NR | Most patients (% NR) | Laparotomy | Macroscopic intralesional or en bloc | NR | Low back or pelvic pain (50%) | NR | NR | Neurosurgeons/microsurgeons involved in some cases but no separate data for benign and malignant tumors |
| Strauss 2011, abdominal surgery [14] | 28 (25%) | 47 | 39 | S (100%) | 9 cm | 68% (correct) | Laparotomy | Macroscopic en bloc (85%), subtotal (15%) | NR | Abdominal discomfort (29%), abdominal mass (25%) | NR | 0%, one malignant transformation (3%) | Neurological outcomes not reported. one case of malignant transformation during FU (patient’s features not specified). |
| Ningshu 2012, urology [15] | 6 (50%) | 49 | 26 (12–48) | S (100%) | 6 cm | None | Laparoscopic | Macroscopic resection from nerve trunk (66%), enucleation (33%) | 100 mL | Abdominal discomfort | Permanent deficit (33%), transient deficit (33%) | 0% | Six cases of obturator nerve schwannoma. In two cases, nerve was sacrified. In four cases, tumor was resected from nerve (with transient deficit in two cases) |
| Arrabal-Polo 2013, urology [16] | 5 (0%) | 38 | 70 (36–120) | S (80%), melanocytic schwannoma (20%) | 129 cc | None | Lumbotomy (80%), laparoscopic (20%) | Macroscopic en bloc (100%) | NR | Abdominal discomfort (100%) | NR | 0% | One case of melanocytic histology |
| Zhang 2016, urology [17] | 10 (NR) | NR | NR | S (100%) | NR | NR | Retroperitoneoscopic | Macroscopic en bloc (100%) | - | NR | NR | NR | Retroperitoneoscopic technique |
| Ji 2017, abdominal surgery [18] | 26 (23%) | 48 | 15 | “Neurilemmoma” (100%) | 5 cm | NR | Laparoscopic (60%), laparotomy (40%) | Macroscopic en bloc (100%) | 500 mL (laparotomy), 100 mL (laparoscopic) | NR | NR | 0% | Comparative series of laparoscopic vs. laparotomic cases |
| Hajiabadi 2020, neurosurgery and abdominal surgery [19] | 16 (50%) | 46 | 26 (3–117) | S (75%), N (19%), Ganglioneuroma (6%) | 66 cc | 25%, correct | Laparotomy | Microsurgical intracapsular complete (88%), partial (12%) | 680 | Radiculopathy (44%), back pain (12%) | Pain relief (78%), no improvement (11%); transient leg numbness (6%) | 0% (12% stable residue) | First interdisciplinary series with consistent neurosurgical expertise. Most patients with involvement of lumbosacral nerve trunks |
4. Discussion
4.1. General Issues
4.2. Surgical Issues
4.2.1. Type of Resection and Complications
4.2.2. Vascular Features
4.3. Surgical Advances
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stone, J.J.; Spinner, R.J. Go for the Gold: A “Plane” and Simple Technique for Resecting Benign Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors. Oper. Neurosurg. 2020, 18, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, H.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Sun, Z.; Ye, H. MR imaging features of benign retroperitoneal paragangliomas and schwannomas. BMC Neurol. 2018, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastoraki, A.; Toska, F.; Tsiverdis, I.; Kyriazi, M.; Tsagkas, A.; Danias, N.; Smyrniotis, V.; Arkadopoulos, N. Retroperitoneal Schwannomas: Dilemmas in Diagnostic Approach and Therapeutic Management. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2013, 44, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Murovic, J.A.; Tiel, R.L.; Moes, G.; Kline, D.G. A series of 397 peripheral neural sheath tumors: 30-year experience at Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 102, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, B.K.; Tan, Y.-M.; Chung, Y.-F.A.; Chow, P.; Ooi, L.L.; Wong, W.-K. Retroperitoneal schwannoma. Am. J. Surg. 2006, 192, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshmand, S.; Youssefzadeh, D.; Chamie, K.; Boswell, W.; Wu, N.; Stein, J.P.; Boyd, S.; Skinner, D.G. Benign retroperitoneal schwannoma: A case series and review of the literature. Urology 2003, 62, 993–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guz, B.V.; Wood, D.P.; Montie, J.E.; Pontes, J.E. Retroperitoneal Neural Sheath Tumors: Cleveland Clinic Experience. J. Urol. 1989, 142, 1434–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Transatlantic Australasian Retroperitoneal Sarcoma Working Group; De Barros, J.M.; Hodson, J.; Glasbey, J.; Massey, R.; Rintoul-Hoad, O.; Chetan, M.; Desai, A.; Almond, L.M.; Gourevitch, D.; et al. Intercontinental collaborative experience with abdominal, retroperitoneal and pelvic schwannomas. Br. J. Surg. 2020, 107, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, J.F.; Juler, G.L.; Schmutzer, K.J. Retroperitoneal neurilemoma. Am. J. Surg. 1977, 134, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbay, A.D.; Moschilla, G.; Gray, B.N.; Thompson, I. Retroperitoneal schwannoma: A case series and review. Aust. N. Z. J. Surg. 1995, 65, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Gao, C.; Juzi, J.T.; Hao, X. Analysis of 82 cases of retroperitoneal schwannoma. Aust. N. Z. J. Surg. 2007, 77, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodosopoulos, T.; Stafyla, V.K.; Tsiantoula, P.; Yiallourou, A.; Marinis, A.; Kondi-Pafitis, A.; Chatziioannou, A.; Boviatsis, E.; Voros, D. Special problems encountering surgical management of large retroperitoneal schwannomas. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dozois, E.J.; Wall, J.C.H.; Spinner, R.J.; Jacofsky, D.J.; Yaszemski, M.J.; Sim, F.H.; Moran, S.L.; Cima, R.R.; Larson, D.R.; Haddock, M.G.; et al. Neurogenic Tumors of the Pelvis: Clinicopathologic Features and Surgical Outcomes Using a Multidisciplinary Team. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 16, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, D.C.; Qureshi, Y.A.; Hayes, A.J.; Thomas, J.M. Management of benign retroperitoneal schwannomas: A single-center experience. Am. J. Surg. 2011, 202, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ningshu, L.; Min, Y.; Xieqiao, Y.; Yuanqing, Y.; Xiaoqiang, M.; Rubing, L. Laparoscopic Management of Obturator Nerve Schwan-nomas: Experiences With 6 Cases and Review of the Literature. Surg. Laparosc. Endosc. Percutaneous Tech. 2012, 22, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Arrabal-Polo, M.; Merino-Salas’, S.; Arrabal-Martín, M.; Nogales, F.; Alaminos, M.; Campos, A.; Zuluaga-Gómez, A. Retroperitoneal Schwannoma. A Complex Surgical Treatment of a Tumor with Uncertain Behavior. Acta Chir. Belg. 2013, 113, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Cao, Q.; Li, P.; Qian, J.; Qin, C.; Li, J.; Shao, P.; Lv, Q.; Wang, Z. A Modified Retroperitoneoscopic Technique in Supine Position for Primary Retroperitoneal Tumors: Technique and Clinical Outcomes. J. Endourol. 2016, 30, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Kang, C.M.; Yoon, D.S.; Lee, W.J. Laparoscopic resection of retroperitoneal benign neurilemmoma. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2017, 92, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiabadi, M.M.; Campos, B.; Sedlaczek, O.; Khajeh, E.; Nikdad, M.; von Deimling, A.; Mehrabi, A.; Unterberg, A.; Ahmadi, R. Interdisciplinary approach allows minimally invasive, nerve-sparing removal of retroperitoneal peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2020, 405, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinen, C.; Schmidt, T.; Kretschmer, T. Decision Making in Retroperitoneal Nerve Sheath and Nerve-Associated Tumors: A Modular Approach. Neurosurgery 2020, 87, E359–E369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, N.; Kubo, T.; Hisaoka, M.; Udo, K.; Yokomizo, A.; Shibuya, T.; Wakeda, H.; Nishihara, K.; Moriya, R.; Iwakuma, K.; et al. Demographics, management and treatment outcomes of benign and malignant retroperitoneal tumors in Japan. Int. J. Urol. 2018, 25, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatera, H.; Takiuchi, H.; Namiki, M.; Takaha, M.; Ohnishi, S.; Sonoda, T. Retroperitoneal schwannoma. Urology 1986, 28, 529–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlawat, S.; Blakeley, J.O.; Langmead, S.; Belzberg, A.J.; Fayad, L.M. Current status and recommendations for imaging in neurofibromatosis type 1, neurofibromatosis type 2, and schwannomatosis. Skelet. Radiol. 2020, 49, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.J.; Hruban, R.H.; Fishman, E.K. Abdominal schwannomas: Review of imaging findings and pathology. Abdom. Imaging 2017, 42, 1864–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkowski, P.L.; Mullen, J.T. Management of the “Other” retroperitoneal sarcomas. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 117, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, A.W.; Shurell, E.; Singh, A.; Dry, S.M.; Eilber, F.C. Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 25, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimo, P.; Rao, G.; Schmidt, R.H.; Schmidt, M.H. Nerve sheath tumors involving the sacrum: Case report and classification scheme. Neurosurg. Focus 2003, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastounis, E.; Asimacopoulos, P.J.; Pikoulis, E.; Leppaniemi, A.K.; Aggouras, D.; Papakonstadinou, K.; Papalambros, E. Benign Retroperitoneal Neural Sheath Tumors in Patients Without von Recklinghausen’s Disease. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 1997, 31, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, K.; Ozawa, H.; Aizawa, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Kanno, H.; Tateda, S.; Itoi, E. Surgical Management of Giant Sacral Schwannoma: A Case Series and Literature Review. World Neurosurg. 2019, 129, e216–e223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongsthorn, C.; Ozawa, H.; Aizawa, T.; Kusakabe, T.; Nakamura, T.; Itoi, E. Giant sacral schwannoma: A report of six cases. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2010, 115, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, M.; Yang, H.; Qian, Z.; Wang, G.; Wu, G.; Zhu, X.; Sun, Z. Pre-operative embolization facilitating a posterior approach for the surgical resection of giant sacral neurogenic tumors. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 6, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coldwell, D.M. Embolization of paraspinal masses. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 1989, 12, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa, M.; Miguchi, M.; Yoshimitsu, M.; Oishi, K.; Kohashi, T.; Hihara, J.; Mukaida, H.; Kaneko, M.; Egi, H.; Ohdan, H.; et al. Laparoscopic excision of a retroperitoneal schwannoma: A case report. Asian J. Endosc. Surg. 2018, 12, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Su, X.; Li, W.-G.; Xu, X.-D.; Huang, J.-F.; Chen, J. Laparoscopic-Assisted Resection for Retroperitoneal Dumbbell-Shaped Lumbar Spinal Schwannomas: Operative Technique and Surgical Results. World Neurosurg. 2016, 91, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, N.; Scerrati, A.; Ricciardi, L.; Trevisi, G. The Exoscope in Neurosurgery: An Overview of the Current Literature of Intraoperative Use in Brain and Spine Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 11, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benato, A.; D’Alessandris, Q.G.; Murazio, M.; Pacelli, F.; Mattogno, P.P.; Fernández, E.; Lauretti, L. Integrated Neurosurgical Management of Retroperitoneal Benign Nerve Sheath Tumors. Cancers 2023, 15, 3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123138
Benato A, D’Alessandris QG, Murazio M, Pacelli F, Mattogno PP, Fernández E, Lauretti L. Integrated Neurosurgical Management of Retroperitoneal Benign Nerve Sheath Tumors. Cancers. 2023; 15(12):3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123138
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenato, Alberto, Quintino Giorgio D’Alessandris, Marino Murazio, Fabio Pacelli, Pier Paolo Mattogno, Eduardo Fernández, and Liverana Lauretti. 2023. "Integrated Neurosurgical Management of Retroperitoneal Benign Nerve Sheath Tumors" Cancers 15, no. 12: 3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123138
APA StyleBenato, A., D’Alessandris, Q. G., Murazio, M., Pacelli, F., Mattogno, P. P., Fernández, E., & Lauretti, L. (2023). Integrated Neurosurgical Management of Retroperitoneal Benign Nerve Sheath Tumors. Cancers, 15(12), 3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123138







