GNL3 and PA2G4 as Prognostic Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
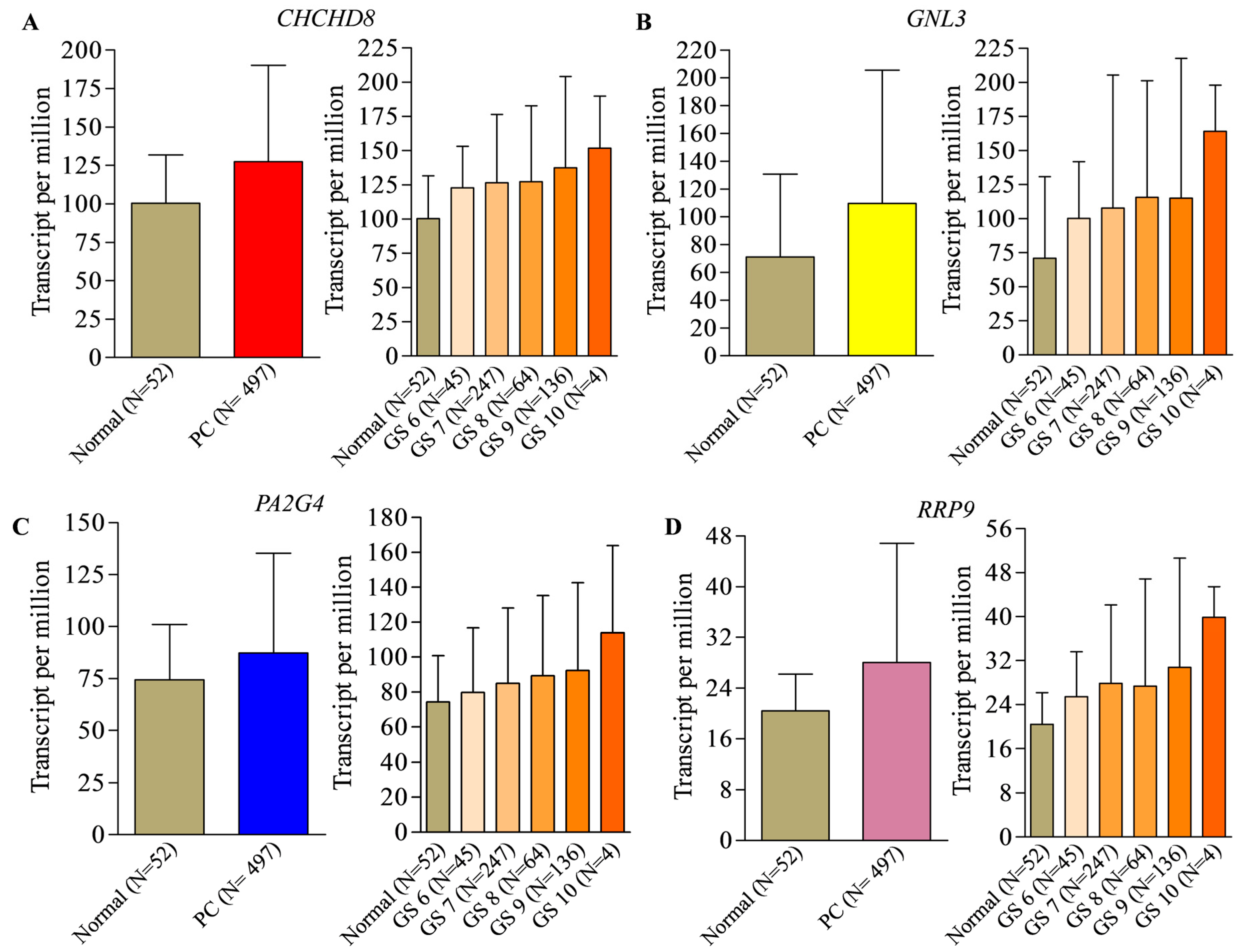
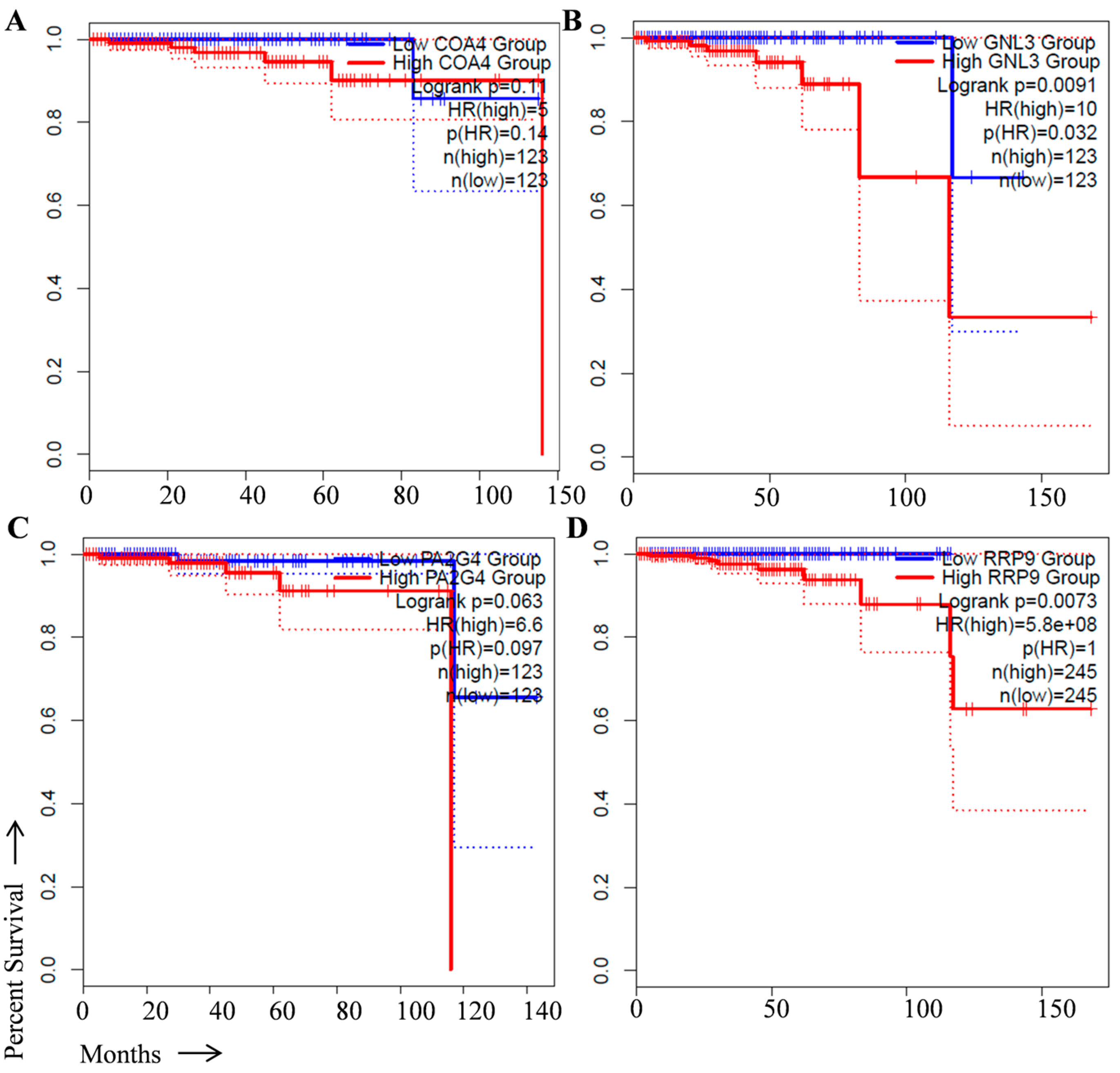
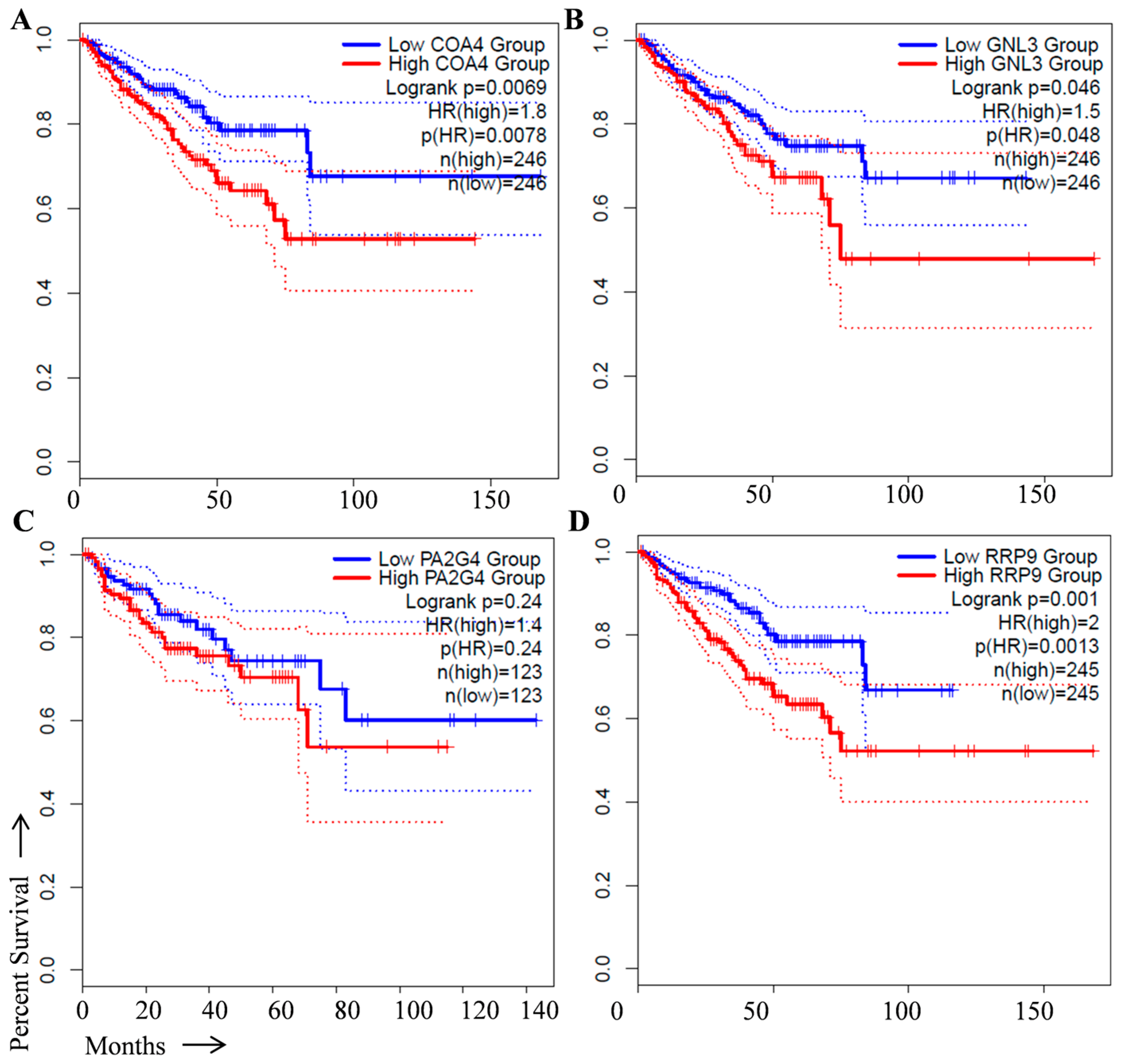
2. Identification of Prognostic Biomarker(s) in Prostate Cancer
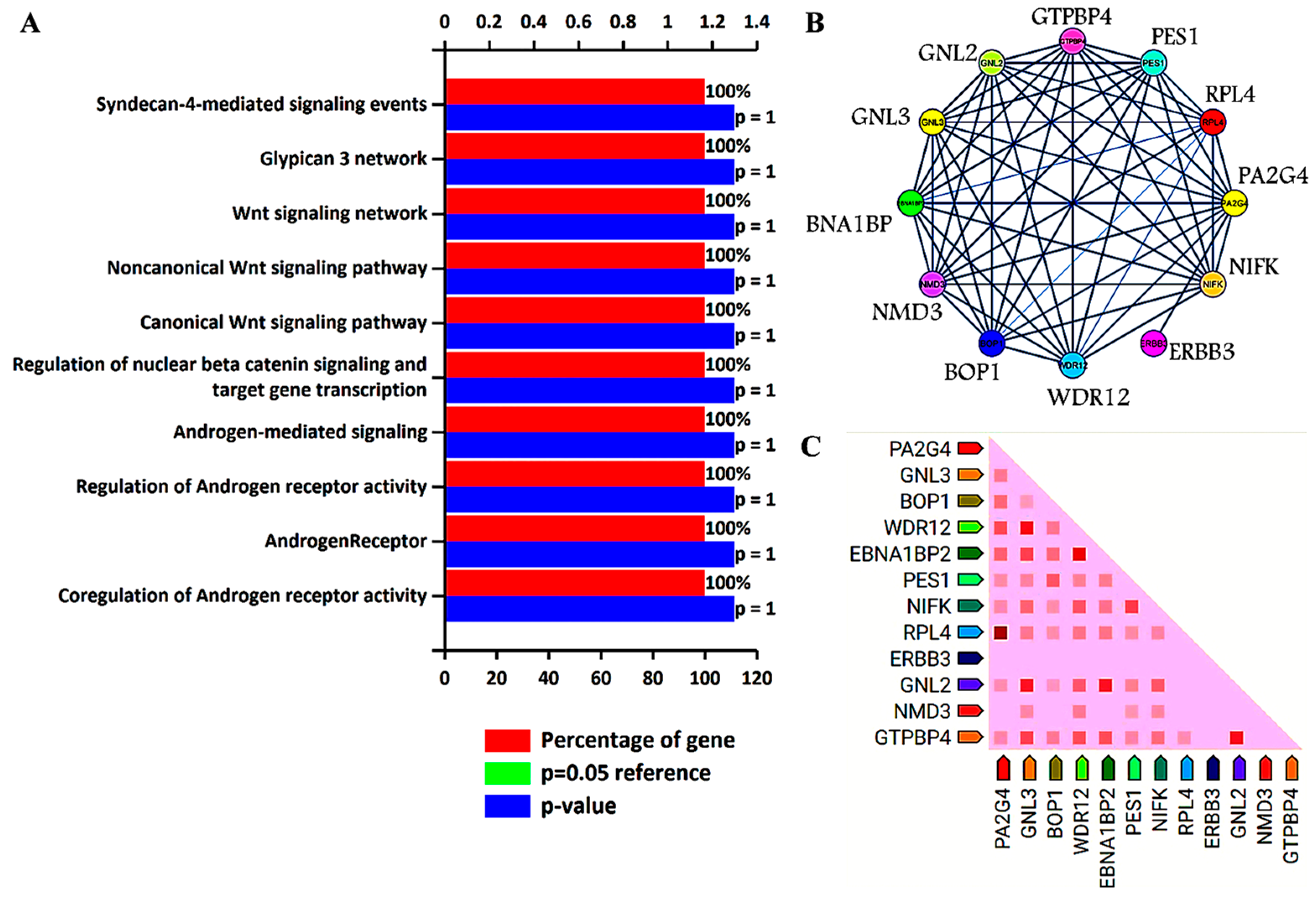
3. Biological Pathways and Protein–Protein Interaction Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalona, W.J. Prostate Cancer Screening. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 102, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, A.R.; Schoots, I.G.; Roobol, M.J. Prostate-Specific Antigen-Based Prostate Cancer Screening: Past and Future: Past and Future. Int. J. Urol. 2015, 22, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.; Castro, E.; Fizazi, K.; Heidenreich, A.; Ost, P.; Procopio, G.; Tombal, B.; Gillessen, S. Prostate Cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, M.G.; Cowling, T.E.; Sujenthiran, A.; Nossiter, J.; Berry, B.; Cathcart, P.; Aggarwal, A.; Payne, H.; van der Meulen, J.; Clarke, N.W.; et al. Risk stratification for prostate cancer management: Value of the Cambridge Prognostic Group classification for assessing treatment allocation. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troyer, D.A.; Mubiru, J.; Leach, R.J.; Naylor, S.L. Promise and Challenge: Markers of Prostate Cancer Detection, Diagnosis and Prognosis. Dis. Markers 2004, 20, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocetto, F.; Russo, G.; Di Zazzo, E.; Pisapia, P.; Mirto, B.F.; Palmieri, A.; Pepe, F.; Bellevicine, C.; Russo, A.; La Civita, E.; et al. Liquid biopsy in prostate cancer management—Current challenges and future perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14, 3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, X.; Moutereau, S.; Xylinas, E.; De La Taille, A. ProgensaTM PCA3 Test for Prostate Cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2011, 11, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatami, F.; Aghamir, S.M.K.; Salmaninejad, A.; Shivarani, S.; Khorrami, M.H. Biomarkers for prostate cancer diagnosis from genetic perspectives. Transl. Res. Urol. 2020, 2, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strimbu, K.; Tavel, J.A. What are biomarkers? Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2010, 5, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Karsh, L.I.; Nissenblatt, M.J.; Canfield, S.E. Androgen Receptor Splice Variant, AR-V7, as a Biomarker of Resistance to Androgen Axis-Targeted Therapies in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2020, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, N.; Kennedy, R.D.; Prise, K.M. The role of PTEN as a cancer biomarker. Oncoscience 2016, 3, 54–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Dean, D.C.; Hornicek, F.J.; Spentzos, D.; Hoffman, R.M.; Shi, H.; Duan, Z. Myc is a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target in osteosarcoma. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920922055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, P.P.; Verma, S.; Gupta, S. Aquaporins as Prognostic Biomarker in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanguedolce, F.; Cormio, A.; Brunelli, M.; D’Amuri, A.; Carrieri, G.; Bufo, P.; Cormio, L. Urine TMPRSS2: ERG Fusion Transcript as a Biomarker for Prostate Cancer: Literature Review. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2016, 14, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggener, S.E.; Badani, K.; Barocas, D.A.; Barrisford, G.W.; Cheng, J.S.; Chin, A.I.; Corcoran, A.; Epstein, J.I.; George, A.K.; Gupta, G.N.; et al. Gleason 6 prostate cancer: Translating biology into population health. J. Urol. 2015, 194, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klatte, T.; Waldert, M.; De Martino, M.; Schatzl, G.; Mannhalter, C.; Remzi, M. Age-Specific PCA3 Score Reference Values for Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. World J. Urol. 2012, 30, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocetto, F.; Barone, B.; Caputo, V.F.; Fontana, M.; de Cobelli, O.; Ferro, M. BRCA Germline Mutations in Prostate Cancer: The Future Is Tailored. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, C.M.; Ray, A.M.; Lange, E.M.; Zuhlke, K.A.; Robbins, C.M.; Tembe, W.D.; Wiley, K.E.; Isaacs, S.D.; Johng, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Germline mutations in HOXB13 and prostate-cancer risk. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allemailem, K.S.; Almatroudi, A.; Alrumaihi, F.; Makki Almansour, N.; Aldakheel, F.M.; Rather, R.A.; Afroze, D.; Rah, B. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in prostate cancer: Its implications in diagnostics and therapeutics. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 3868–3889. [Google Scholar]
- Ferro, M.; De Cobelli, O.; Lucarelli, G.; Porreca, A.; Busetto, G.M.; Cantiello, F.; Damiano, R.; Autorino, R.; Musi, G.; Vartolomei, M.D.; et al. Beyond PSA: The Role of Prostate Health Index (Phi). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, V.M.; Konety, B.R.; Warlick, C. Novel Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer: An Evidence-Based Review for Use in Clinical Practice. Int. J. Urol. 2017, 24, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccini, M.A.; Westfall, N.J.; Van Bokhoven, A.; Lucia, M.S.; Poage, W.; Maroni, P.D.; Wilson, S.S.; Glodé, L.M.; Arangua, P.; Newmark, J.; et al. The Effect of Digital Rectal Exam on the 4Kscore for Aggressive Prostate Cancer. Prostate 2018, 78, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, S.V.; Roobol, M.J. Improving the Evaluation and Diagnosis of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer in 2017. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2017, 27, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olleik, G.; Kassouf, W.; Aprikian, A.; Hu, J.; Vanhuyse, M.; Cury, F.; Peacock, S.; Bonnevier, E.; Palenius, E.; Dragomir, A. Evaluation of New Tests and Interventions for Prostate Cancer Management: A Systematic Review. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2018, 16, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kish, E.K.; Choudhry, M.; Gamallat, Y.; Buharideen, S.M.; Bismar, T.A. The expression of proto-oncogene ETS-related gene (ERG) plays a central role in the oncogenic mechanism involved in the development and progression of prostate cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, L.; Johnson, M.T. How precisely can prostate cancer be managed? Int. Neurourol. J. 2016, 20 (Suppl. S2), S120–S130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, K.M.; Wee, E.J.H.; Mainwaring, P.N.; Trau, M. A Simple, Rapid, Low-Cost Technique for Naked-Eye Detection of Urine-Isolated TMPRSS2:ERG Gene Fusion RNA. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haese, A.; Trooskens, G.; Steyaert, S.; Hessels, D.; Brawer, M.; Vlaeminck-Guillem, V.; Ruffion, A.; Tilki, D.; Schalken, J.; Groskopf, J.; et al. Multicenter Optimization and Validation of a 2-Gene MRNA Urine Test for Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer before Initial Prostate Biopsy. J. Urol. 2019, 202, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legisi, L.; DeSa, E.; Qureshi, M.N. Use of the prostate core mitomic test in repeated biopsy decision-making: Real-world assessment of clinical utility in a multicenter patient population. Am. Health Drug Benefits 2016, 9, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.E.; D’Amico, A.V.; Freedland, S.J. Which, when and why? Rational use of tissue-based molecular testing in localized prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2016, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toribio-Vázquez, C.; Rivas, J.G.; Yebes, Á.; Carrión, D.M.; Barrado, M.Y.; Álvarez-Maestro, M.; Martinez-Piñeiro, L. New strategies for decision making in prostate cancer. The role of oncotypedx. Actas Urol. Esp. 2022, 46, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falzarano, S.M.; Ferro, M.; Bollito, E.; Klein, E.A.; Carrieri, G.; Magi-Galluzzi, C. Novel biomarkers and genomic tests in prostate cancer: A critical analysis. Ital. J. Urol. Nephrol. 2015, 67, 211–231. [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava, H.K.; Leo, P.; Elliott, R.; Janowczyk, A.; Whitney, J.; Gupta, S.; Fu, P.; Yamoah, K.; Khani, F.; Robinson, B.D.; et al. Computationally Derived Image Signature of Stromal Morphology Is Prognostic of Prostate Cancer Recurrence Following Prostatectomy in African American Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Prajapati, K.S.; Kushwaha, P.P.; Shuaib, M.; Kumar Singh, A.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, S. Resistance to second generation antiandrogens in prostate cancer: Pathways and mechanisms. Cancer Drug Resist. 2020, 3, 742–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culig, Z.; Santer, F.R. Androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014, 33, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cheng, L.; Li, J.; Farah, E.; Atallah, N.M.; Pascuzzi, P.E.; Gupta, S.; Liu, X. Inhibition of the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Overcomes Resistance to Enzalutamide in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3147–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, E.; Franco, D.; Iqbal, O.; El-Hayek, V.; Gupta, S. Novel approach to therapeutic targeting of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 140, 109639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Xing, Q.S. Roles of Wnt Signaling Pathway and ROR2 Receptor in Embryonic Development: An Update Review Article. Epigenetics Insights 2022, 15, 25168657211064232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, T.; Wang, J.; Yin, L.; Pu, T.; Li, J.; Gao, J.; Lin, T.P.; Gao, A.C.; Wu, B.J. WLS-Wnt signaling promotes neuroendocrine prostate cancer. iScience 2021, 24, 101970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Q.; Xu, H. Wnt/β-catenin signal transduction pathway in prostate cancer and associated drug resistance. Discover. Oncology 2021, 12, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Wang, D.; Wan, X.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Kong, Z.; Li, D.; Gu, W.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Crosstalk Between AR and Wnt Signaling Promotes Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Growth. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 9257–9267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bestwick, M.; Jeong, M.Y.; Khalimonchuk, O.; Kim, H.; Winge, D.R. Analysis of Leigh Syndrome Mutations in the Yeast Surf1 Homolog Reveals a New Member of the Cytochrome Oxidase Assembly Factor Family. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 4480–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longen, S.; Bien, M.; Bihlmaier, K.; Kloeppel, C.; Kauff, F.; Hammermeister, M.; Westermann, B.; Herrmann, J.M.; Riemer, J. Systematic Analysis of the Twin Cx9C Protein Family. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 393, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, M.; Longen, S.; Morgan, B.; Peleh, V.; Dick, T.P.; Bihlmaier, K.; Herrmann, J.M. Inaccurately Assembled Cytochrome c Oxidase Can Lead to Oxidative Stress-Induced Growth Arrest. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 1597–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Guha, M.; Dong, D.W.; Whelan, K.A.; Ruthel, G.; Uchikado, Y.; Natsugoe, S.; Nakagawa, H.; Avadhani, N.G. Disruption of Cytochrome c Oxidase Function Induces the Warburg Effect and Metabolic Reprogramming. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1585–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krobthong, S.; Yingchutrakul, Y.; Sittisaree, W.; Tulyananda, T.; Samutrtai, P.; Choowongkomon, K.; Lao-On, U. Evaluation of Potential Anti-Metastatic and Antioxidative Abilities of Natural Peptides Derived from Tecoma stans (L.) Juss. Ex Kunth in A549 Cells. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Meng, L.; Hsu, J.K.; Lin, T.; Teishima, J.; Tsai, R.Y. GNL3L stabilizes the TRF1 complex and promotes mitotic transition. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 185, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, R.Y.L.; McKay, R.D.G. A Nucleolar Mechanism Controlling Cell Proliferation in Stem Cells and Cancer Cells. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2991–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Zha, L.; Li, H.; Liao, G.; Huang, Z.; Peng, X.; Wang, Z. Upregulation of GNL3 Expression Promotes Colon Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2023–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.L.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhao, W.M.; Wang, M.; Qi, S.Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.Z.; Xu, Y. Expression of nucleostemin in prostate cancer and its effect on the proliferation of PC-3 cells. Chin. Med. J. 2008, 121, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. GNL3 Regulates SIRT1 Transcription and Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Stem Cell-Like Features and Metastasis. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 1555670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Li, L.; Wu, X.; Tian, K.; Wang, Y. The oncogenic role of GNL3 in the progression and metastasis of osteosarcoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 2179–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Shi, J. G protein nucleolar 3 promotes non-Hodgkin lymphoma progression by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 409, 112911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, M.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.L.; Tsai, R.Y. Nucleostemin upregulation and STAT3 activation as early events in oral epithelial dysplasia progression to squamous cell carcinoma. Neoplasia 2021, 23, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, M.M.; Hachim, M.Y.; Hachim, I.Y.; Elbarkouky, A.H.; López-Ozuna, V.M. Nucleostemin expression in breast cancer is a marker of more aggressive phenotype and unfavorable patients’ outcome: A STROBE-compliant article. Medicine 2019, 98, e14744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Lin, T.C.; McGrail, D.J.; Bhupal, P.K.; Ku, Y.H.; Zhang, W.; Meng, L. Nucleostemin reveals a dichotomous nature of genome maintenance in mammary tumor progression. Oncogene 2019, 38, 3919–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, M.; Sun, J.T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.Z. Gene profiling after knocking-down the expression of NS gene in prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Chin. J. Oncol. 2009, 31, 561–565. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, M.; Sun, J.T.; Qi, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.Z. Expression of nucleostemin in prostate cancer tissues and its clinical significance. Natl. J. Androl. 2008, 14, 418–422. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, M.; Sun, J.T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.Z. Silencing nucleostemin expression reduces the proliferation of PC-3 cells. Natl. J. Androl. 2009, 15, 593–598. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.L.; Wang, W.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Xu, Y. Silencing effect of cell-specific RNA interference plasmid pPSMAe/p-shNS-ploy(A) loaded by transgenic vector Tf-PEG-PEI targeting nucleostemin on prostate cancer cells in vitro. Chin. J. Oncol. 2012, 34, 725–729. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.-Y.; Wang, X.W.; Rishi, A.K.; Lessor, T.; Xia, X.-M.; Gustafson, T.A.; Hamburger, A.W. Interaction of the PA2G4 (EBP1) Protein with ErbB-3 and Regulation of This Binding by Heregulin. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Lessor, T.J.; Zhang, Y.; Woodford, N.; Hamburger, A.W. Analysis of the expression pattern of Ebp1, an ErbB-3-binding protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 289, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gannon, P.O.; Koumakpayi, I.H.; Le Page, C.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Mes-Masson, A.-M.; Saad, F. Ebp1 Expression in Benign and Malignant Prostate. Cancer Cell Int. 2008, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, B.W.; Gorman, M.A.; Koach, J.; Cheung, B.B.; Marshall, G.M.; Parker, M.W.; Holien, J.K. A Structural View of PA2G4 Isoforms with Opposing Functions in Cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 16100–16112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wen, J.; Xue, L.; Han, S.; Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Yu, J.; et al. PA2G4 Promotes the Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Stabilizing FYN MRNA in a YTHDF2-Dependent Manner. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cai, H.; Tu, W.; Ding, L.; Luo, R. Increased PA2G4 Expression Is an Unfavorable Factor in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2021, 29, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, X.D.; Chen, H.Y.; Cui, J.S.; Xu, D.Y. Significance of Ebp1 and P53 Protein Expression in Cervical Cancer. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 11860–11866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Tang, W. Pseudogene PA2G4P4 Promotes Oncogene PA2G4 Expression and Nuclear Translocation to Affect Glioblastoma Cell Viability and Apoptosis. Life Sci. 2021, 265, 118793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellinghoff, I.K.; Tran, C.; Sawyers, C.L. Growth inhibitory effects of the dual ErbB1/ErbB2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor PKI-166 on human prostate cancer xenografts. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 5254–5259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agus, D.B.; Akita, R.W.; Fox, W.D.; Lewis, G.D.; Higgins, B.; Pisacane, P.I.; Lofgren, J.A.; Tindell, C.; Evans, D.P.; Maiese, K.; et al. Targeting Ligand-Activated ErbB2 Signaling Inhibits Breast and Prostate Tumor Growth. Cancer Cell 2002, 2, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, N.; Phillips, G.L.; Silva, J.; Schwall, R.; Wickramasinghe, D. Inhibition of ligand-mediated HER2 activation in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 5485–5488. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Fondell, J.D.; Wang, Q.; Xia, X.; Cheng, A.; Lu, M.L.; Hamburger, A.W. Repression of Androgen Receptor Mediated Transcription by the ErbB-3 Binding Protein, Ebp1. Oncogene 2002, 21, 5609–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.; Ezelle, H.; Hassel, B.A.; Hamburger, A.W. The ErbB3-Binding Protein EBP1 Modulates Lapatinib Sensitivity in Prostate Cancer Cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 405, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, J.; Ye, K. Structural and Functional Analysis of the U3 SnoRNA Binding Protein Rrp9. RNA 2013, 19, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerget, G.; Bourguignon-Igel, V.; Marmier-Gourrier, N.; Rolland, N.; Wacheul, L.; Manival, X.; Charron, C.; Kufel, J.; Méreau, A.; Senty-Ségault, V.; et al. Synergistic Defects in Pre-RRNA Processing from Mutations in the U3-Specific Protein Rrp9 and U3 SnoRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 3848–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Liu, F.; Chang, Y.; Tong, S.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Xie, P. Correction: Neddylation Modification of the U3 SnoRNA-Binding Protein RRP9 by Smurf1 Promotes Tumorigenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Yao, W.; Zhu, N.; Miao, R.; Liu, Z.; Song, X.; Xue, C.; Cai, C.; Cheng, M.; et al. RRP9 Promotes Gemcitabine Resistance in Pancreatic Cancer via Activating AKT Signaling Pathway. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
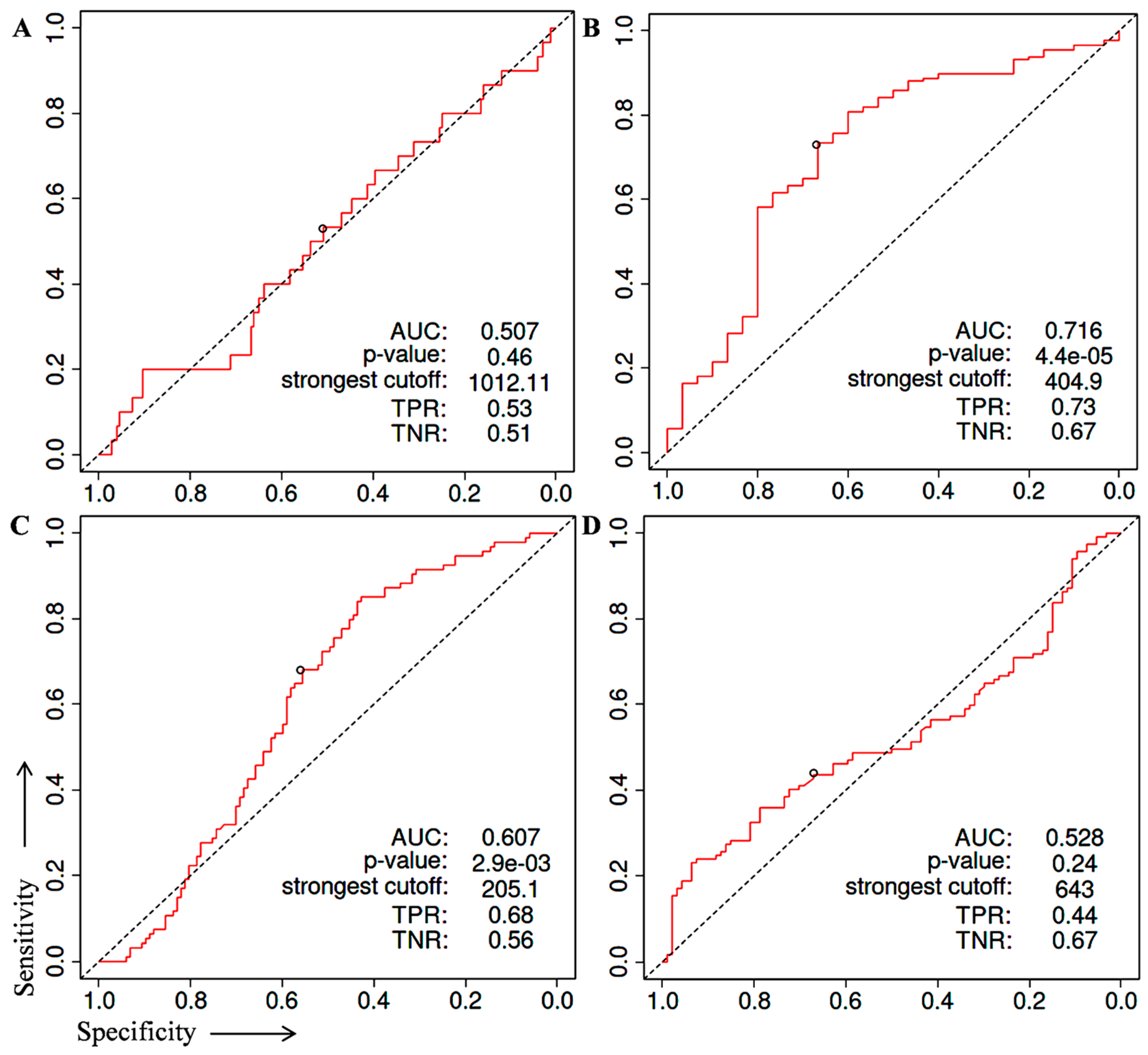
| Panel | Specimen | AUC for Prostate Cancer Detection | Limitations | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCA3 | Urine | 0.65 | Recommended only for the precise population of prostate cancer patients who have a first negative biopsy report. PCA3 score rises with age, independent of PC occurrence. | [17,18] |
| PHI | Serum | 0.70 | Used to detect the probability of finding any prostate cancer on repeat biopsy, irrespective of the GS. It does not have de facto common use because of pre-analytical stability of [2] proPSA and high cost. | [22,23] |
| 4Kscore® | Serum | 0.71 | 4Kscore® test has been restricted to those prostate cancer patients who have not had DRE in the previous 96 h. | [24] |
| ConfirmMDx® | Prostate biopsy tissues | 0.74 | Recommended for those prostate cancer patients who had negative prostate biopsy. There is no recommendation for the routine clinical application. | [25] |
| ExoDX Prostate IntelliScore | Urine | 0.70 | Lack of evidence in respect of clinical utility | [26] |
| Prostate Core Mitomic Test | Serum | - | False negative results in malice of high sensitivity. | [27,28] |
| MiPS Mi(chigan) Prostate Scor | Urine | 0.69 | Lack of evidence in respect of clinical utility | [26] |
| TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion | Urine | - | Not widely used due to long processing time, very high cost, and the necessity of dedicated equipment. | [28] |
| SelectMDX | Urine | 0.71–0.81 | Diagnostic as well as prognostic correctness in ethnically diverse study population is unidentified till date. SelectMDx shows declined sensitivity, specificity, and NPV. | [29,30] |
| Prolaris | Tissue | 0.78 | There is no evidence to describe the effect of the prolaris cell cycle progression test on patient-important clinical outcome results. | [30,31] |
| OncotypeDx | Tissue | 0.73 | This test is not intended to take ethnic discrimination into account. | [32,33] |
| ProMark | Tissue | 0.72 | Test is imperfect and skips the high-risk nearby zone of prostate tumor. | [26,33] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, S.; Shuaib, M.; AlAsmari, A.F.; Alqahtani, F.; Gupta, S. GNL3 and PA2G4 as Prognostic Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102723
Kumar S, Shuaib M, AlAsmari AF, Alqahtani F, Gupta S. GNL3 and PA2G4 as Prognostic Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(10):2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102723
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Shashank, Mohd Shuaib, Abdullah F. AlAsmari, Faleh Alqahtani, and Sanjay Gupta. 2023. "GNL3 and PA2G4 as Prognostic Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 10: 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102723
APA StyleKumar, S., Shuaib, M., AlAsmari, A. F., Alqahtani, F., & Gupta, S. (2023). GNL3 and PA2G4 as Prognostic Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer. Cancers, 15(10), 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15102723









