Therapeutic Potential of Deflamin against Colorectal Cancer Development and Progression
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Lentiviral Infection
2.3. Deflamin Purification
2.4. Cellular Viability Assay
2.5. Cellular Apoptosis Assay
2.6. Zymography
2.7. Wound Healing Migration Assay
2.8. 3D Cell Invasion Assay
2.9. Cell Labeling
2.10. In Vivo Zebrafish Xenograft Model
2.11. Immunofluorescence
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
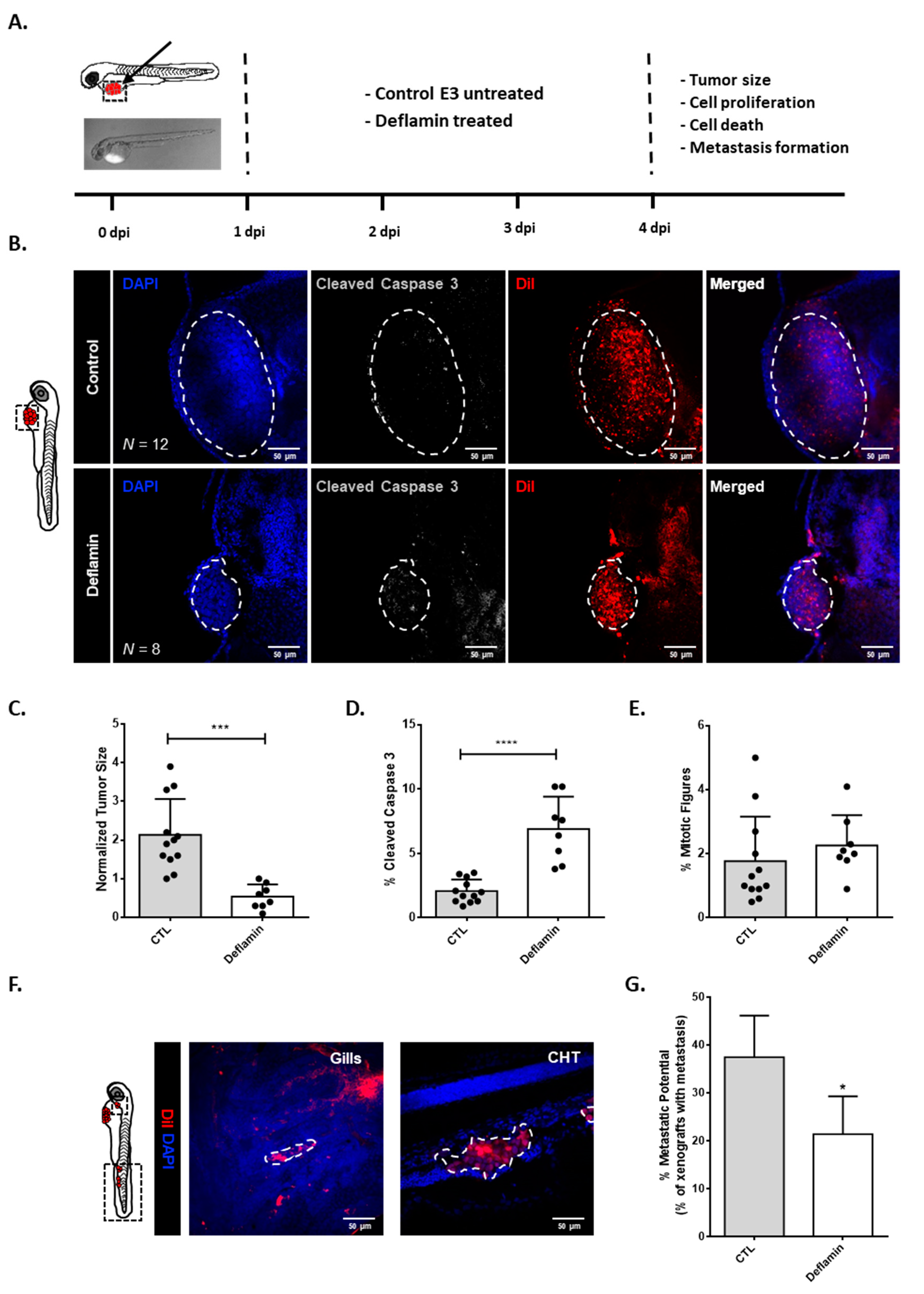
3.1. Deflamin Exhibits Anti-Tumor Activity in Zebrafish CRC Xenotransplanted Tumors
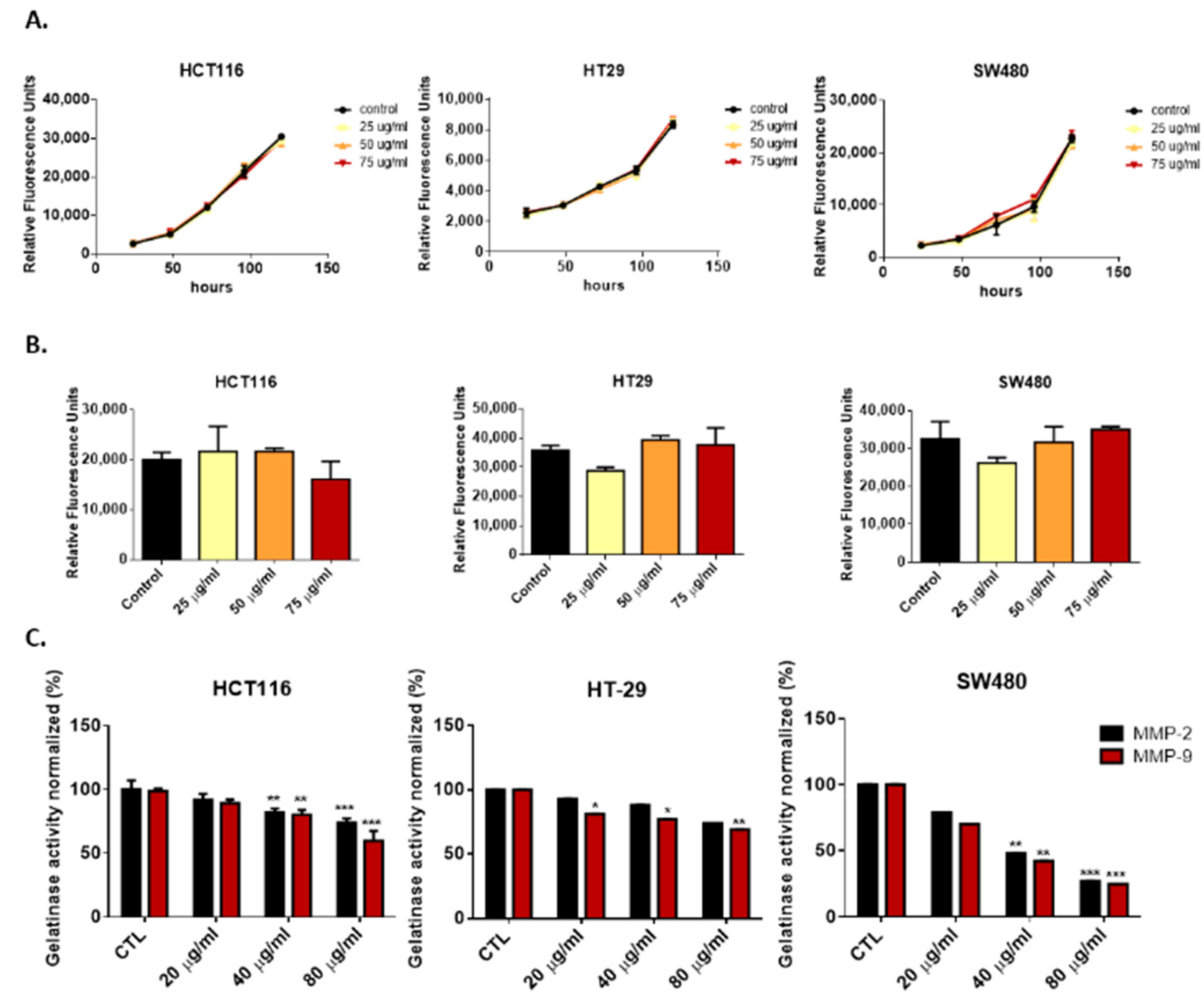
3.2. Deflamin Does Not Play a Direct Role in Cancer Cell Proliferation or Apoptosis
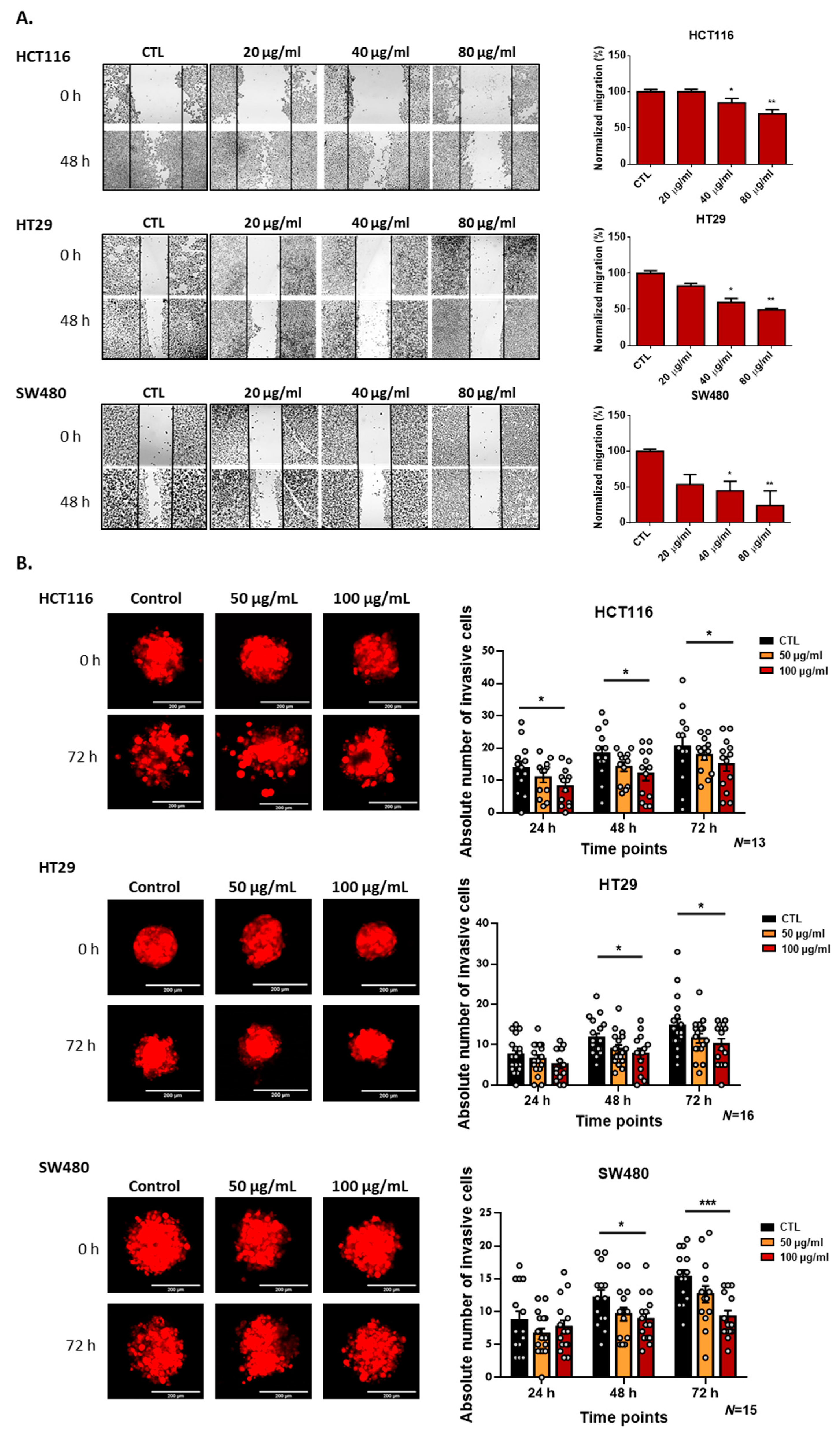
3.3. Deflamin Inhibits MMP-2 and MMP-9, Contributing to Impaired Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion
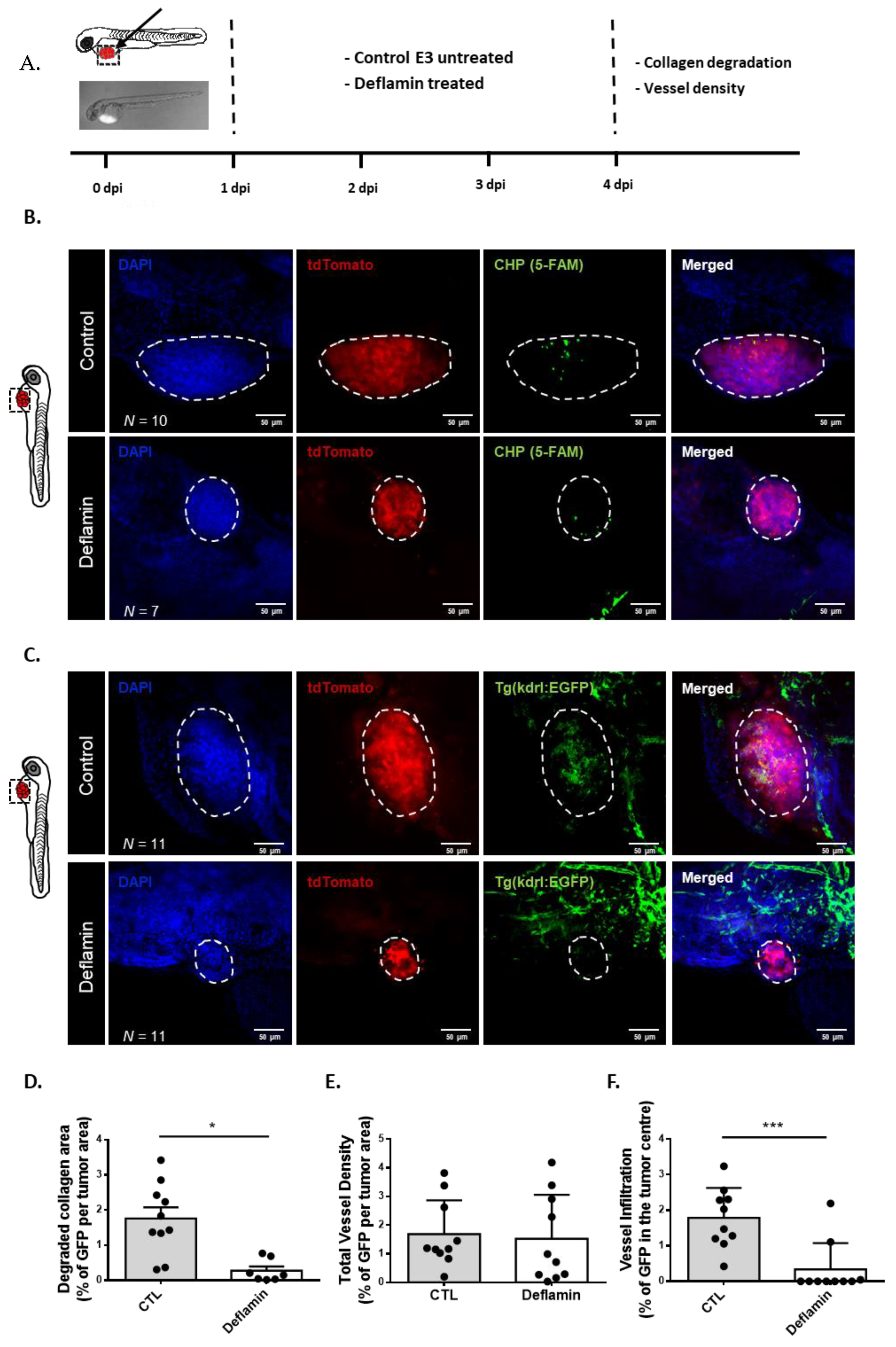
3.4. Deflamin Inhibits Collagen Degradation and Angiogenesis In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fares, J.; Fares, M.Y.; Khachfe, H.H.; Salhab, H.A.; Fares, Y. Molecular Principles of Metastasis: A Hallmark of Cancer Revisited. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gialeli, C.; Theocharis, A.D.; Karamanos, N.K. Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Cancer Progression and Their Pharmacological Targeting. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coussens, L.M.; Fingleton, B.; Matrisian, L.M. Matrisian Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors and Cancer—Trials and Tribulations. Science 2002, 295, 2387–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Tang, F.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, J.; Rao, Z. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Overexpression Is Closely Related to Poor Prognosis in Patients with Colon Cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, S.; MacDonald, I.C.; Varghese, H.J.; Schmidt, E.E.; Morris, V.L.; Groom, A.C.; Chambers, A.F. The Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitor Batimastat Inhibits Angiogenesis in Liver Metastases of B16F1 Melanoma Cells. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 1999, 17, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giavazzi, R.; Garofalo, A.; Ferri, C.; Lucchini, V.; Bone, E.A.; Chiari, S.; Brown, P.D.; Nicoletti, M.I.; Taraboletti, G. Batimastat, a Synthetic Inhibitor of Matrix Metalloproteinases, Potentiates the Antitumor Activity of Cisplatin in Ovarian Carcinoma Xenografts. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 985–992. [Google Scholar]
- Bramhall, S.R.; Schulz, J.; Nemunaitis, J.; Brown, P.D.; Baillet, M.; Buckels, J.A.C. A Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled, Randomised Study Comparing Gemcitabine and Marimastat with Gemcitabine and Placebo as First Line Therapy in Patients with Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 87, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirte, H.; Vergote, I.B.; Jeffrey, J.R.; Grimshaw, R.N.; Coppieters, S.; Schwartz, B.; Tu, D.; Sadura, A.; Brundage, M.; Seymour, L. A Phase III Randomized Trial of BAY 12-9566 (Tanomastat) as Maintenance Therapy in Patients with Advanced Ovarian Cancer Responsive to Primary Surgery and Paclitaxel/Platinum Containing Chemotherapy: A National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2006, 102, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparano, J.A.; Bernardo, P.; Stephenson, P.; Gradishar, W.J.; Ingle, J.N.; Zucker, S.; Davidson, N.E. Randomized Phase III Trial of Marimastat versus Placebo in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer Who Have Responding or Stable Disease after First-Line Chemotherapy: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Trial E2196. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 4631–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Otín, C.; Palavalli, L.H.; Samuels, Y. Protective Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases: From Mouse Models to Human Cancer. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 3657–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.S.; Lai, K.C.; Hsu, S.C.; Yang, J.S.; Kuo, C.L.; Lin, J.P.; Ma, Y.S.; Wu, C.C.; Chung, J.G. Curcumin Inhibits the Migration and Invasion of Human A549 Lung Cancer Cells through the Inhibition of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 and -9 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF). Cancer Lett. 2009, 285, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.H.; Ahn, K.S.; Bae, E.; Jeon, S.S.; Choi, H.Y. The Effects of Curcumin on the Invasiveness of Prostate Cancer in vitro and in vivo. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2006, 9, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yodkeeree, S.; Chaiwangyen, W.; Garbisa, S.; Limtrakul, P. Curcumin, Demethoxycurcumin and Bisdemethoxycurcumin Differentially Inhibit Cancer Cell Invasion through the down-Regulation of MMPs and UPA. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2009, 20, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.Y.; Chiang, E.P.I.; Sun, Y.C. Resveratrol Inhibits Heregulin-Β1-Mediated Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Expression and Cell Invasion in Human Breast Cancer Cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2008, 19, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoditti, E.; Calabriso, N.; Massaro, M.; Pellegrino, M.; Storelli, C.; Martines, G.; De Caterina, R.; Carluccio, M.A. Mediterranean Diet Polyphenols Reduce Inflammatory Angiogenesis through MMP-9 and COX-2 Inhibition in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells: A Potentially Protective Mechanism in Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease and Cancer. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 527, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Aggarwal, B.B. Suppression of 7,12-Dimethylbenz(a)Anthracene-Induced Mammary Carcinogenesis in Rats by Resveratrol: Role of Nuclear Factor-ΚB, Cyclooxygenase 2, and Matrix Metalloprotease 9. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4945–4954. [Google Scholar]
- Bennink, M.R. Consumption of Black Beans and Navy Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) Reduced Azoxymethane-Induced Colon Cancer in Rats. Nutr. Cancer 2002, 44, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; De Stefani, E.; Ronco, A.; Boffetta, P.; Deneo-Pellegrini, H.; Acosta, G.; Mendilaharsu, M. Legume Intake and the Risk of Cancer: A Multisite Case-Control Study in Uruguay. Cancer Causes Control 2009, 20, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, J.; Figueira, M.E.; Ferreira, R.B.; Lima, A. An Up-Scalable and Cost-Effective Methodology for Isolating a Polypeptide Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Inhibitor from Lupinus albus Seeds. Foods 2021, 10, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, J.; Direito, R.; Rocha, J.; Fernandes, J.; Sepodes, B.; Figueira, M.E.; Raymundo, A.; Lima, A.; Ferreira, R.B. Lupinus albus Protein Components Inhibit MMP-2 and MMP-9 Gelatinolytic Activity in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota, J.; Lima, A.; Ferreira, R.B.; Raymundo, A. Technological Potential of a Lupin Protein Concentrate as a Nutraceutical Delivery System in Baked Cookies. Foods 2021, 10, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.I.G.; Mota, J.; Monteiro, S.A.V.S.; Ferreira, R.M.S.B. Legume Seeds and Colorectal Cancer Revisited: Protease Inhibitors Reduce MMP-9 Activity and Colon Cancer Cell Migration. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, J.; Casimiro, S.; Fernandes, J.; Hartmann, R.M.; Schemitt, E.; Picada, J.; Costa, L.; Marroni, N.; Raymundo, A.; Lima, A.; et al. Lupin Protein Concentrate as a Novel Functional Food Additive That Can Reduce Colitis-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaco, A.C.M.; Rezaei, M.; Caliandro, M.F.; Lima, A.M.; Stehling, M.; Dhayat, S.A.; Haier, J.; Brakebusch, C.; Eble, J.A. The Interaction between Laminin-332 and A3β1 Integrin Determines Differentiation and Maintenance of Cafs, and Supports Invasion of Pancreatic Duct Adenocarcinoma Cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, R.L.; Marass, M.; Avdesh, A.; Helker, C.S.M.; Maischein, H.M.; Grosse, A.S.; Kaur, H.; Lawson, N.D.; Herzog, W.; Stainier, D.Y.R. Radial Glia Regulate Vascular Patterning around the Developing Spinal Cord. Elife 2016, 5, e20253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fior, R.; Póvoa, V.; Mendes, R.V.; Carvalho, T.; Gomes, A.; Figueiredo, N.; Ferreira, M.G. Single-Cell Functional and Chemosensitive Profiling of Combinatorial Colorectal Therapy in Zebrafish Xenografts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8234–E8243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y. Proteinases and Matrix Degradation, 10th ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Quintero-Fabián, S.; Arreola, R.; Becerril-Villanueva, E.; Torres-Romero, J.C.; Arana-Argáez, V.; Lara-Riegos, J.; Ramírez-Camacho, M.A.; Alvarez-Sánchez, M.E. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Angiogenesis and Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Foss, C.A.; Summerfield, D.D.; Doyle, J.J.; Torok, C.M.; Dietz, H.C.; Pomper, M.G.; Yu, S.M. Targeting Collagen Strands by Photo-Triggered Triple-Helix Hybridization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14767–14772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.P.; Choi, S.-Y.; Kee, Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, Y.; Park, H.-C.; Ro, H. Transgenic Fluorescent Zebrafish Lines That Have Revolutionized Biomedical Research. Lab. Anim. Res. 2021, 37, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandooren, J.; Van den Steen, E.; Opdenakker, G. Biochemistry and molecular biology of gelatinase B or matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9): The next decade. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 222–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacRae, C.A.; Peterson, R.T. Zebrafish as Tools for Drug Discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augoff, K.; Hryniewicz-Jankowska, A.; Tabola, R.; Stach, K. MMP9: A Tough Target for Targeted Therapy for Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, S.; Cavaco, A.; Basso, B.; Mota, J.; Cruz-Duarte, R.; Costa, M.; Carvalho, L.; Lima, A.; Costa, L.; Ferreira, R.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Deflamin against Colorectal Cancer Development and Progression. Cancers 2022, 14, 6182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246182
Silva S, Cavaco A, Basso B, Mota J, Cruz-Duarte R, Costa M, Carvalho L, Lima A, Costa L, Ferreira R, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Deflamin against Colorectal Cancer Development and Progression. Cancers. 2022; 14(24):6182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246182
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Sara, Ana Cavaco, Bianca Basso, Joana Mota, Raquel Cruz-Duarte, Miguel Costa, Lara Carvalho, Ana Lima, Luis Costa, Ricardo Ferreira, and et al. 2022. "Therapeutic Potential of Deflamin against Colorectal Cancer Development and Progression" Cancers 14, no. 24: 6182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246182
APA StyleSilva, S., Cavaco, A., Basso, B., Mota, J., Cruz-Duarte, R., Costa, M., Carvalho, L., Lima, A., Costa, L., Ferreira, R., & Martins, M. (2022). Therapeutic Potential of Deflamin against Colorectal Cancer Development and Progression. Cancers, 14(24), 6182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246182








