Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific CAR-T Cells in the Suppression of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Western Blotting
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. Lentivirus Production
2.4. Human CD3+ T Cell Enrichment, Activation, and Multiplication
2.5. Construction of Anti-EGFR CARs
2.6. Preparation of Anti-EGFR CAR-T Cells
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. Luciferase-Based Cytolysis Assay
2.9. Cytokine ELISA
2.10. CAR-T Cell Antitumor Function in a Mouse Xenograft Model
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
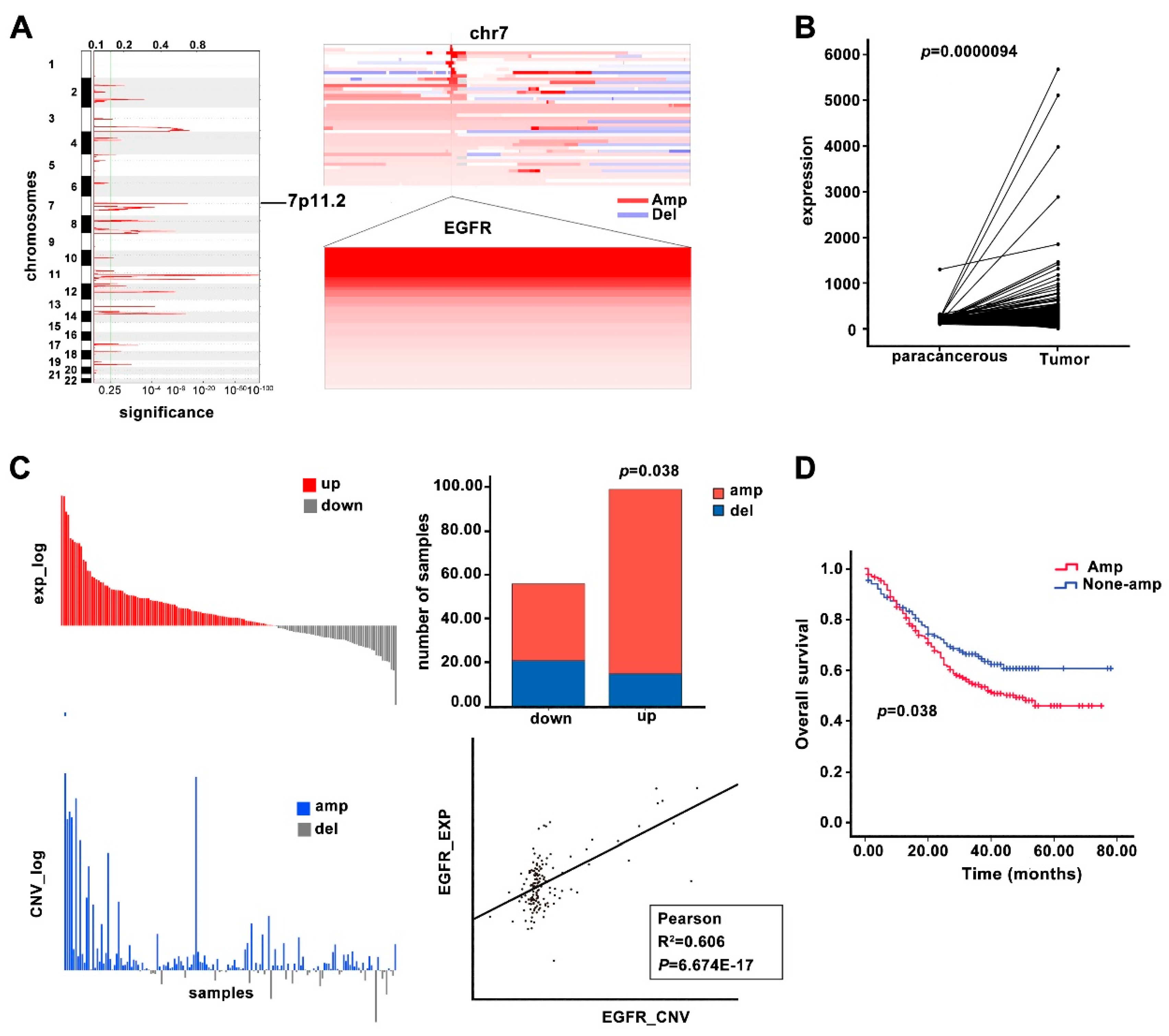
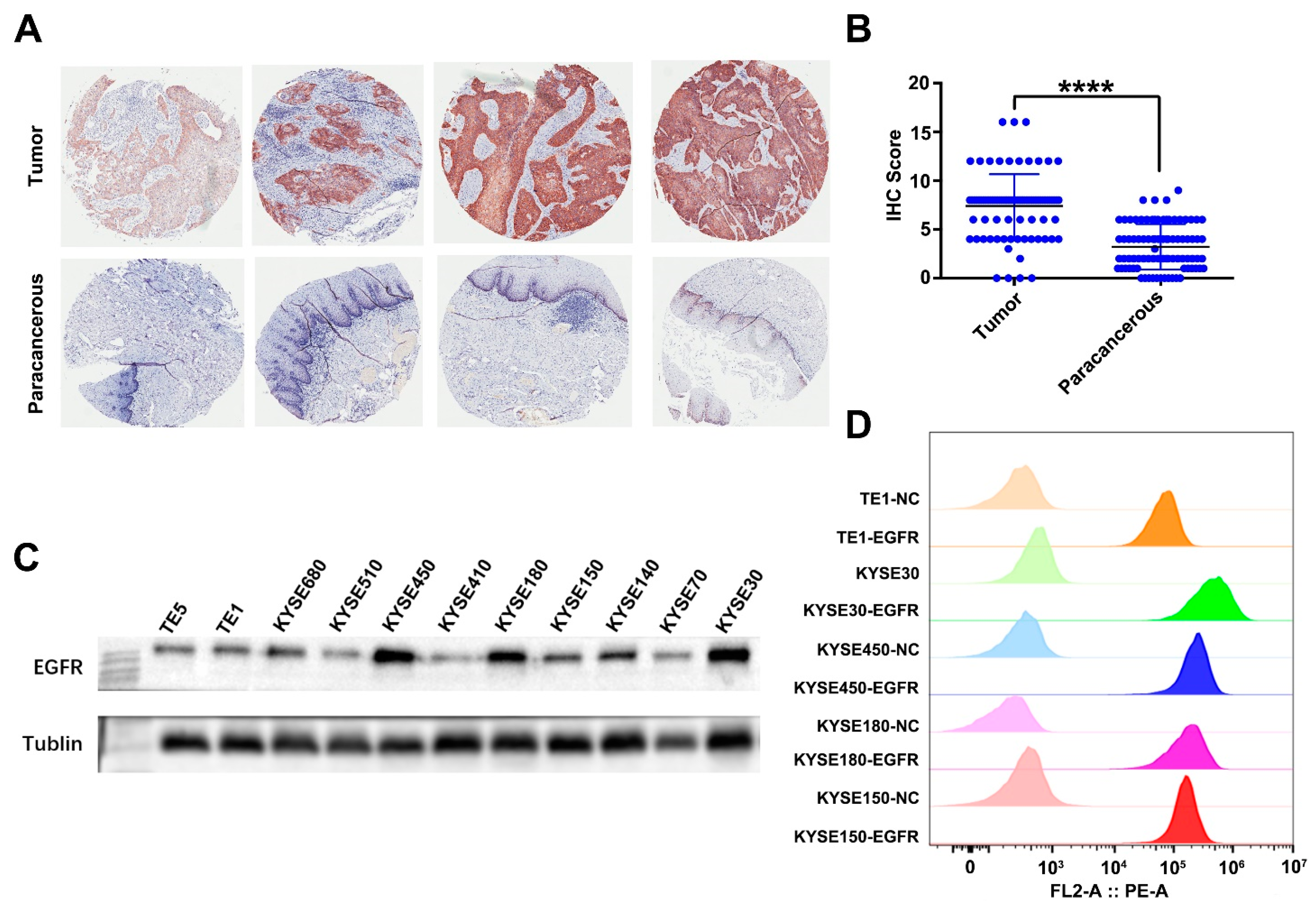
3.1. EGFR Is Overexpressed in ESCC Tissue Samples and Cell Lines
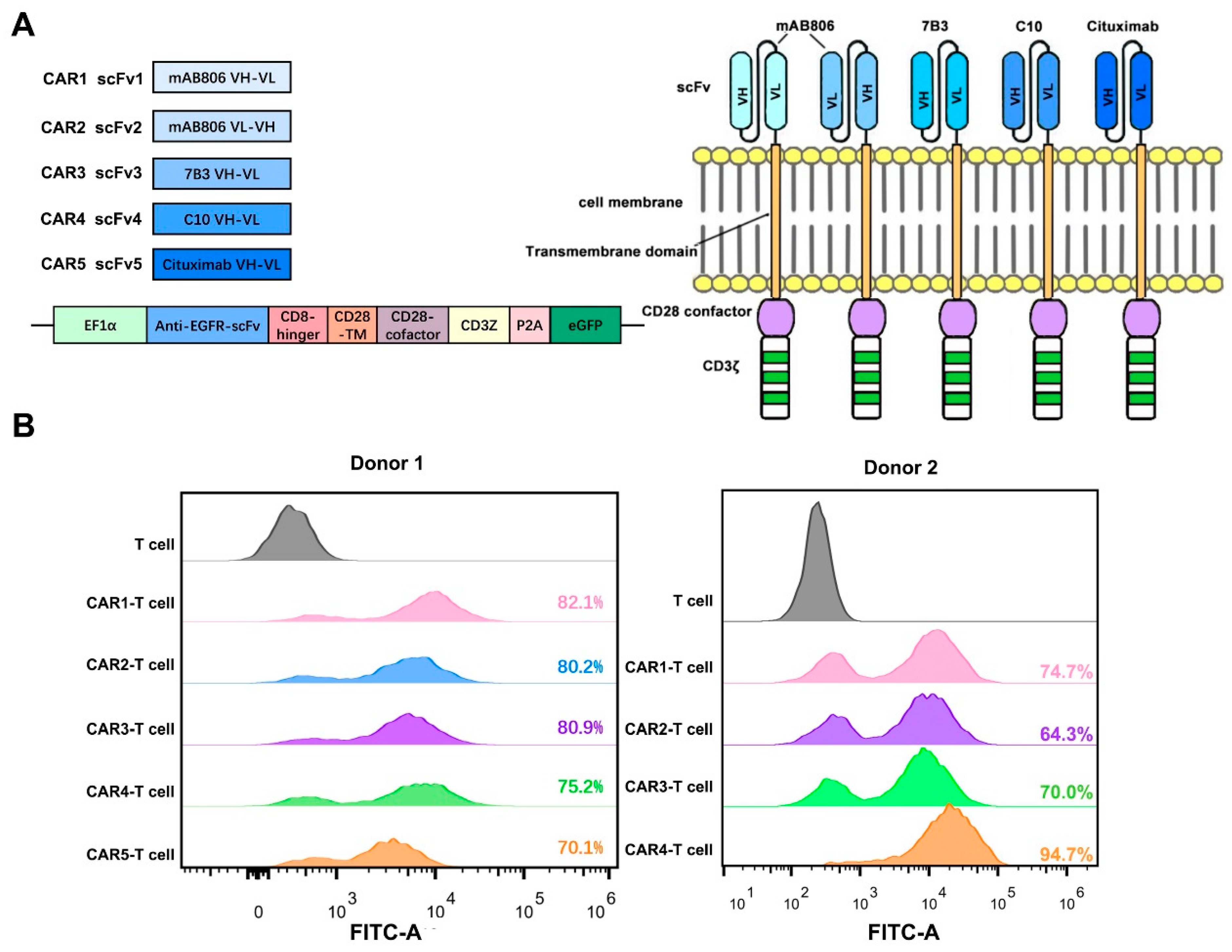
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of Anti-EGFR CAR-T Cells
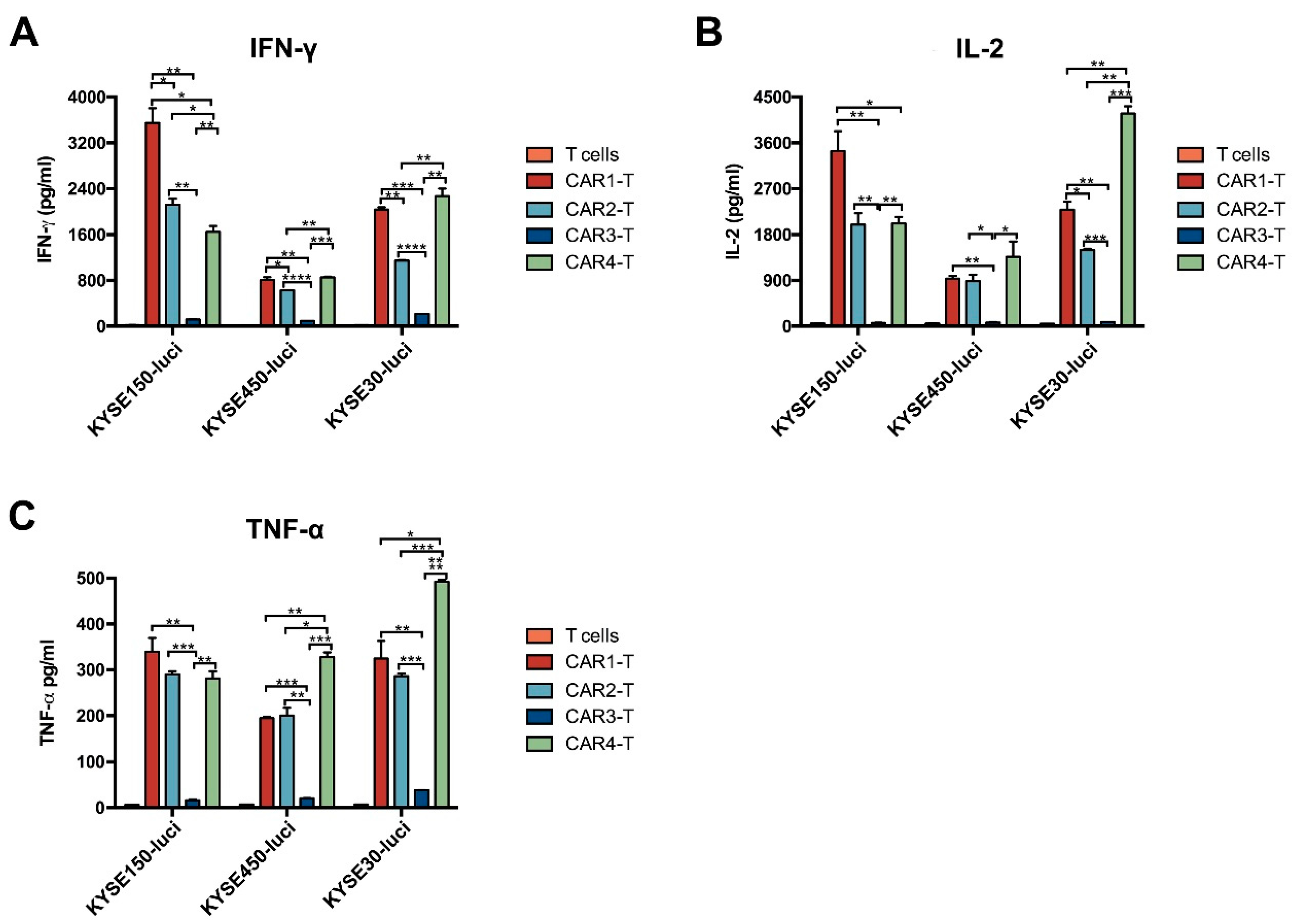
3.3. Anti-EGFR CAR-T Cells Are Cytotoxic for ESCC Cells In Vitro
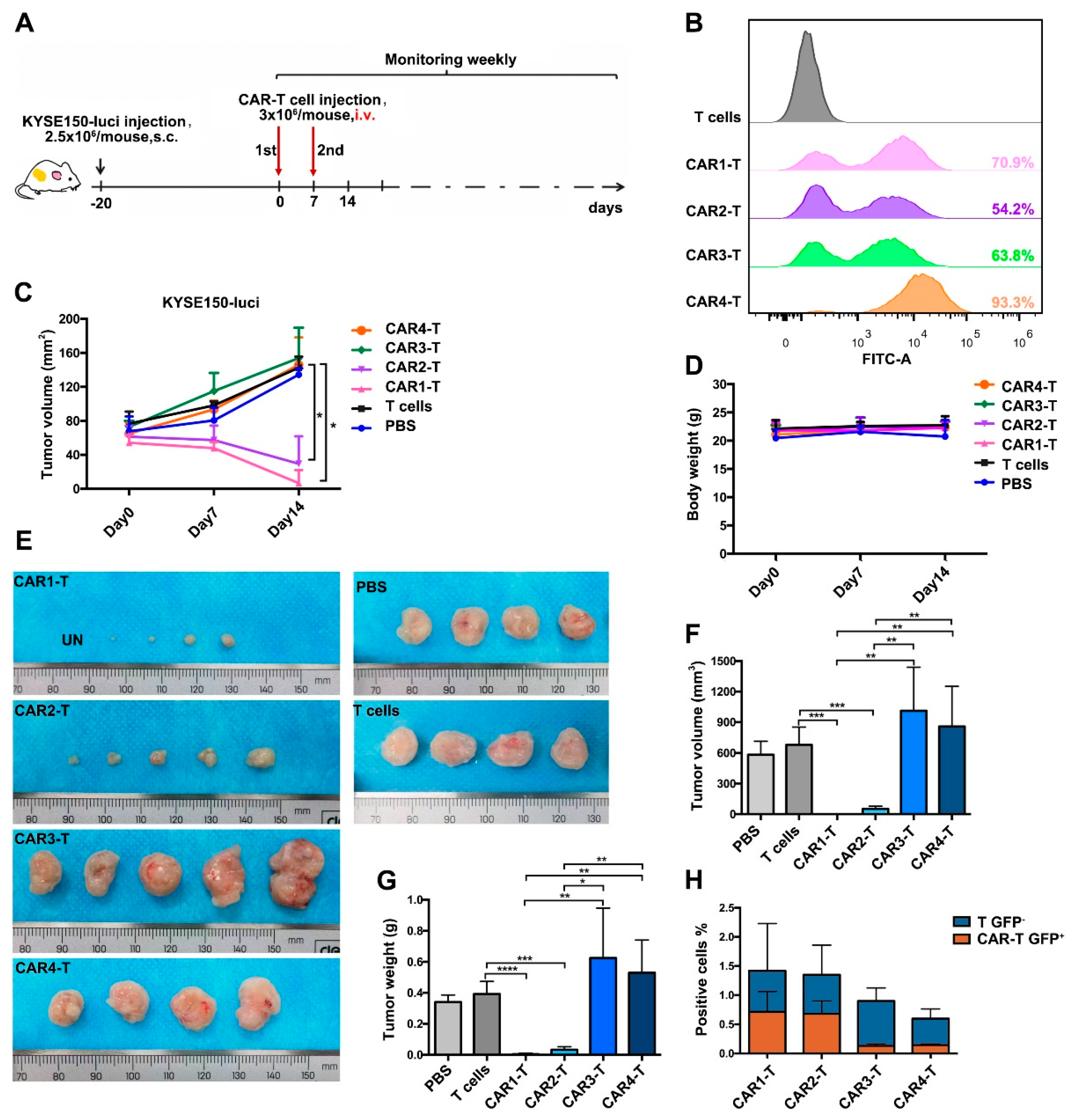
3.4. Anti-EGFR CAR-T Cells Effectively Eliminate ESCC Tumors in a Mouse Xenograft Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morgan, E.; Soerjomataram, I.; Rumgay, H.; Coleman, H.G.; Thrift, A.P.; Vignat, J.; Laversanne, M.; Ferlay, J.; Arnold, M. The Global landscape of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence and mortality in 2020 and projections to 2040: New estimates from GLOBOCAN 2020. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 649–658.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Chen, W.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, S.; Ji, J.S.; Zou, X.; Xia, C.; Sun, K.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; et al. Changing cancer survival in China during 2003–15: A pooled analysis of 17 population-based cancer registries. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e555–e567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doki, Y.; Ajani, J.A.; Kato, K.; Xu, J.; Wyrwicz, L.; Motoyama, S.; Ogata, T.; Kawakami, H.; Hsu, C.H.; Adenis, A.; et al. Nivolumab combination therapy in advanced esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhuang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Niu, Z.; Fan, Q.; et al. Camrelizumab versus investigator’s choice of chemotherapy as second-line therapy for advanced or metastatic oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCORT): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, T.; Shah, M.A.; Muro, K.; Francois, E.; Adenis, A.; Hsu, C.H.; Doi, T.; Moriwaki, T.; Kim, S.B.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Randomized phase III KEYNOTE-181 study of Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy in advanced esophageal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 4138–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shergold, A.L.; Millar, R.; Nibbs, R.J.B. Understanding and overcoming the resistance of cancer to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 145, 104258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.H.; Rodriguez, B.L.; Diao, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Byers, L.A.; Wei, Y.; Chapman, H.A.; Yamauchi, M.; Behrens, C.; et al. Collagen promotes anti-PD-1/PD-L1 resistance in cancer through LAIR1-dependent CD8+ T cell exhaustion. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicki, T.S.; Hu-Lieskovan, S.; Ribas, A. Mechanisms of resistance to PD-1 and PD-L1 blockade. Cancer J. 2018, 24, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Wang, D.; Sun, K.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Resistance mechanisms of anti-PD1/PDL1 therapy in solid tumors. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, J.S.; Long, G.V.; Scolyer, R.A.; Teng, M.W.L.; Smyth, M.J. Resistance to PD1/PDL1 checkpoint inhibition. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 52, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maude, S.L.; Frey, N.; Shaw, P.A.; Aplenc, R.; Barrett, D.M.; Bunin, N.J.; Chew, A.; Gonzalez, V.E.; Zheng, Z.; Lacey, S.F.; et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T cells for sustained remissions in leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Han, W. New development in CAR-T cell therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haslauer, T.; Greil, R.; Zaborsky, N.; Geisberger, R. CAR T-cell therapy in hematological malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davila, M.L.; Riviere, I.; Wang, X.; Bartido, S.; Park, J.; Curran, K.; Chung, S.S.; Stefanski, J.; Borquez-Ojeda, O.; Olszewska, M.; et al. Efficacy and toxicity management of 19-28z CAR T cell therapy in B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 224ra25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Chen, H.; Xi, R.; Cui, H.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, E.; Yan, T.; Lu, X.; Huang, F.; Kong, P.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing of 508 patients identifies key molecular features associated with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Shi, Y.; Xu, C.; Lu, S.; Huang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Su, J.; et al. The prognostic value of EGFR overexpression and amplification in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvari, K.; Sima, H.R.; Toussi, M.S.; Anvari, A.; Shahidsales, S.; Memar, B.; Aledavoud, S.A.; Forghani, M.N.; Abdollahi, A.; Ghaffarzadegan, K. EGFR expression in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its association with pathologic response to preoperative chemoradiotherapy: A study in northeastern Iran. Arch. Iran. Med. 2017, 20, 240–245. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; He, J.; Sun, K.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, N.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor is a prognosis predictor in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 98, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; He, J.; Sun, K.; Wang, L.; Xu, N. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor is an independent prognostic factor for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 11, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelson, J.; Baselga, J. The EGF receptor family as targets for cancer therapy. Oncogene 2000, 19, 6550–6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, H.; Zhang, D.; Bartholomeusz, C.; Doihara, H.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Ueno, N.T. Role of epidermal growth factor receptor in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 136, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wang, P.; Chu, W.; Jin, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Lou, J.; et al. Phase I clinical trial of EGFR-specific CAR-T cells generated by the piggyBac transposon system in advanced relapsed/refractory non-small cell lung cancer patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 3725–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Guo, Y.; Dai, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Jia, H.; Han, W. Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells for the immunotherapy of patients with EGFR-expressing advanced relapsed/refractory non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. China Life Sci. 2016, 59, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Feng, K.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Dai, H.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Jia, H.; Han, W. Phase I study of chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells in patients with EGFR-positive advanced biliary tract cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, J.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Ding, J.; Hu, G.S.; Hu, Y.H.; Liu, S.; Luo, W.X.; Xia, N.S.; et al. Targeting triple-negative breast cancer with combination therapy of EGFR CAR T cells and CDK7 inhibition. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2021, 9, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Zheng, Z.Z.; Liu, J.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Ding, J.C.; Xia, N.S.; Luo, W.X.; Liu, W. EGFR-targeted CAR-T cells are potent and specific in suppressing triple-negative breast cancer both in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2020, 9, e01135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Liu, J.Y.; Zheng, Z.Z.; Chen, Y.J.; Ding, J.C.; Hu, Y.H.; Hu, G.S.; Xia, N.S.; Liu, W. BRD4 inhibition boosts the therapeutic effects of epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted chimeric antigen receptor T cells in glioblastoma. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 3011–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanpay, A.C.; Gust, J.; Johnson, A.J.; Rolczynski, L.S.; Cecchini, M.; Chang, C.A.; Hoglund, V.J.; Mukherjee, R.; Vitanza, N.A.; Orentas, R.J.; et al. EGFR806-CAR T cells selectively target a tumor-restricted EGFR epitope in glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 7080–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramello, M.C.; Benzaïd, I.; Kuenzi, B.M.; Lienlaf-Moreno, M.; Kandell, W.M.; Santiago, D.N.; Pabón-Saldaña, M.; Darville, L.; Fang, B.; Rix, U.; et al. An immunoproteomic approach to characterize the CAR interactome and signalosome. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungbluth, A.A.; Stockert, E.; Huang, H.J.S.; Collins, V.P.; Coplan, K.; Iversen, K.; Kolb, D.; Johns, T.J.; Scott, A.M.; Gullick, W.J.; et al. A monoclonal antibody recognizing human cancers with amplification/overexpression of the human epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.K.; Burgess, A.W.; Clayton, A.H.A.; Scott, A.M. Targeting of a conformationally exposed, tumor-specific epitope of EGFR as a strategy for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2924–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Gao, H.; Kong, J.; Song, B.; Wang, P.; Shi, B.; Wang, H.; Li, Z. Selective targeting of glioblastoma with EGFRvIII/EGFR bitargeted chimeric antigen receptor T cell. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 1314–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Drummond, D.C.; Zou, H.; Hayes, M.E.; Adams, G.P.; Kirpotin, D.B.; Marks, J.D. Impact of single-chain aFv antibody fragment affinity on nanoparticle targeting of epidermal growth factor receptor-expressing tumor cells. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 371, 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Dai, J.; Hou, S.; Kou, G.; Zhao, J.; Li, B.; Wang, H. A High-Affinity Anti-EGFR Monoclonal Antibody. Chinese Patent CN102219855B, 16 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, W.; Sun, R.; Zhang, L.; Bi, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Characterization of somatic structural variations in 528 Chinese individuals with Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Hong, R.; Xue, L.; Ou, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Xiao, W.; Dong, D.; Dong, L.; Fu, M.; et al. Piccolo mediates EGFR signaling and acts as a prognostic biomarker in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3890–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Mamon, H.J.; Hong, T.S.; Choi, N.C.; Fidias, P.M.; Kwak, E.L.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Ryan, D.P.; Bueno, R.; Donahue, D.M.; et al. Preoperative cetuximab, irinotecan, cisplatin, and radiation therapy for patients with locally advanced esophageal cancer. Oncologist 2013, 18, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntharalingam, M.; Winter, K.; Ilson, D.; Dicker, A.P.; Kachnic, L.; Konski, A.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Anker, C.J.; Thakrar, H.; Horiba, N.; et al. Effect of the addition of Cetuximab to Paclitaxel, Cisplatin, and radiation therapy for patients with esophageal cancer: The NRG oncology RTOG 0436 phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebbutt, N.C.; Price, T.J.; Ferraro, D.A.; Wong, N.; Veillard, A.S.; Hall, M.; Sjoquist, K.M.; Pavlakis, N.; Strickland, A.; Varma, S.C.; et al. Panitumumab added to docetaxel, cisplatin and fluoropyrimidine in oesophagogastric cancer: ATTAX3 phase II trial. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, S.J.; Ferry, D.R.; Blazeby, J.M.; Abbas, H.; Dahle-Smith, A.; Mansoor, W.; Thompson, J.; Harrison, M.; Chatterjee, A.; Falk, S.; et al. Gefitinib for oesophageal cancer progressing after chemotherapy (COG): A phase 3, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ji, Q.; Li, Q. Resistance to anti-EGFR therapies in metastatic colorectal cancer: Underlying mechanisms and reversal strategies. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Ye, Y.; Diao, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Green, M.R.; Mills, M.R.; Mills, G.B.; et al. Expression of chimeric antigen receptor therapy targets detected by single-cell sequencing of normal cells may contribute to off-tumor toxicity. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1558–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterner, R.C.; Sterner, R.M. CAR-T cell therapy: Current limitations and potential strategies. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, J.; Wickman, E.; DeRenzo, C.; Gottschalk, S. CAR T cell therapy for solid tumors: Bright future or dark reality? Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 2320–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Rui, W.; Zhao, X.; Lin, X. Enhancing CAR-T cell efficacy in solid tumors by targeting the tumor microenvironment. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, C.; Cui, H.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Ding, N.; Weng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cui, Y. Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific CAR-T Cells in the Suppression of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 6021. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246021
Cheng C, Cui H, Liu H, Wu Y, Ding N, Weng Y, Zhang W, Cui Y. Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific CAR-T Cells in the Suppression of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers. 2022; 14(24):6021. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246021
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Chen, Heyang Cui, Huijuan Liu, Yueguang Wu, Ning Ding, Yongjia Weng, Weimin Zhang, and Yongping Cui. 2022. "Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific CAR-T Cells in the Suppression of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Cancers 14, no. 24: 6021. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246021
APA StyleCheng, C., Cui, H., Liu, H., Wu, Y., Ding, N., Weng, Y., Zhang, W., & Cui, Y. (2022). Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific CAR-T Cells in the Suppression of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers, 14(24), 6021. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14246021




