Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor Modulates Multiple Downstream Signaling Pathways in Prostate Cancer Inhibiting Cell Invasiveness
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Collection
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Immunofluorescence
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. CNTF Treatment of LNCaP and 22Rv1 Cell Lines
2.7. Analysis of Glucose Uptake after CNTF Treatment
2.8. Wound Healing Assay
2.9. Transwell Invasion Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
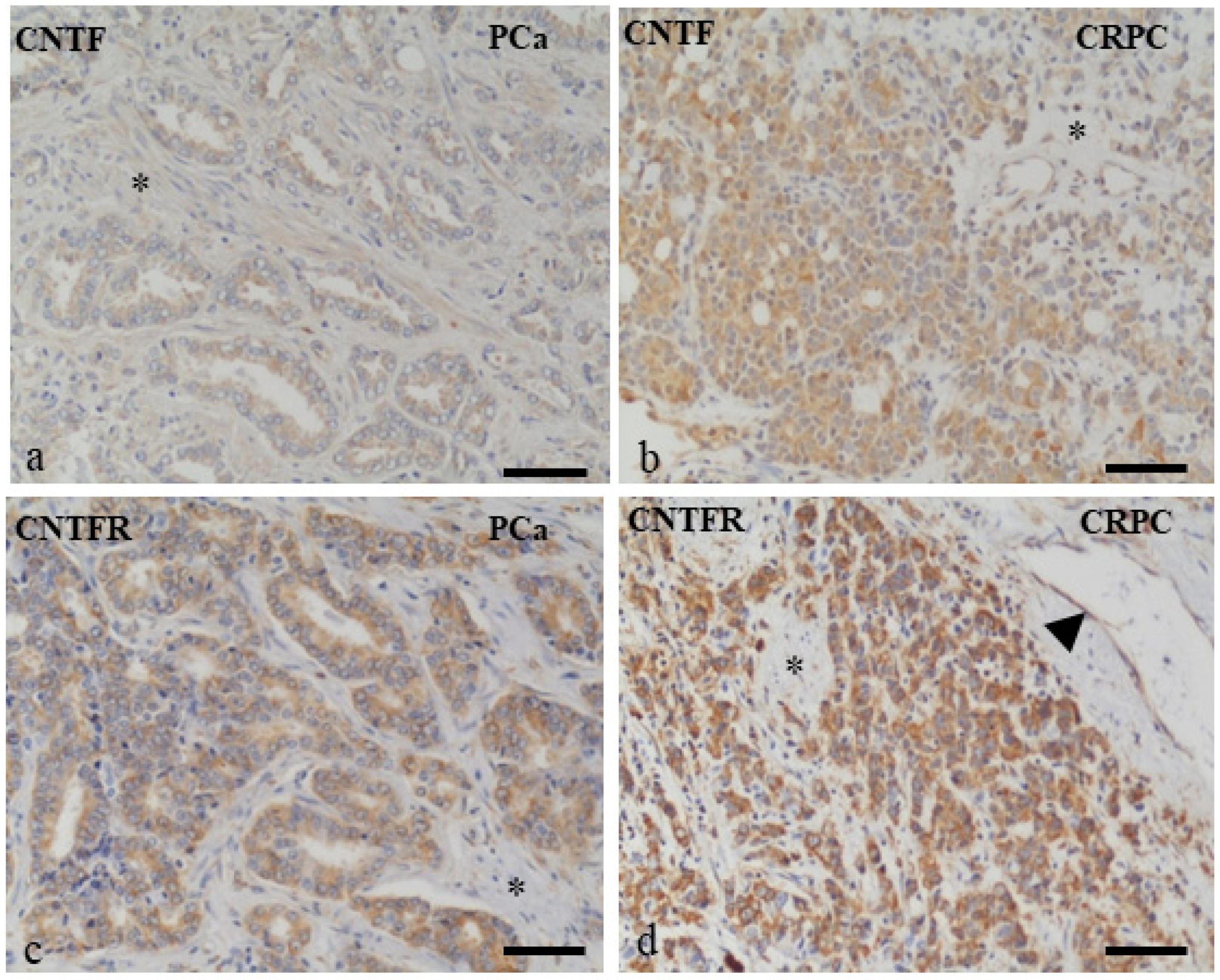
3.1. Human PCa and CRPC Tissues Expressed CNTF and CNTFRα
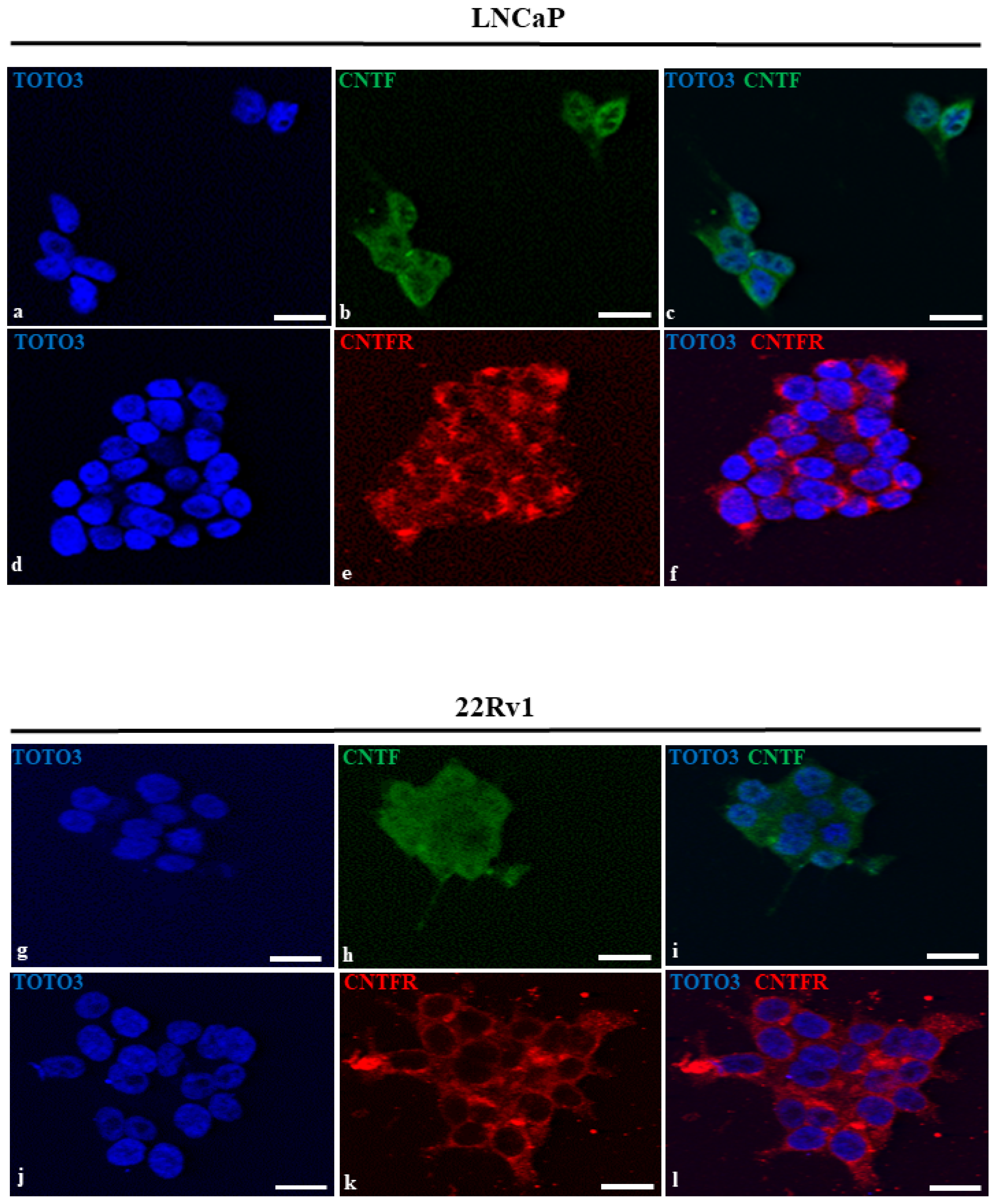
3.2. LNCaP and 22Rv1 Cell Lines Expressed Both CNTF and CNTFRα
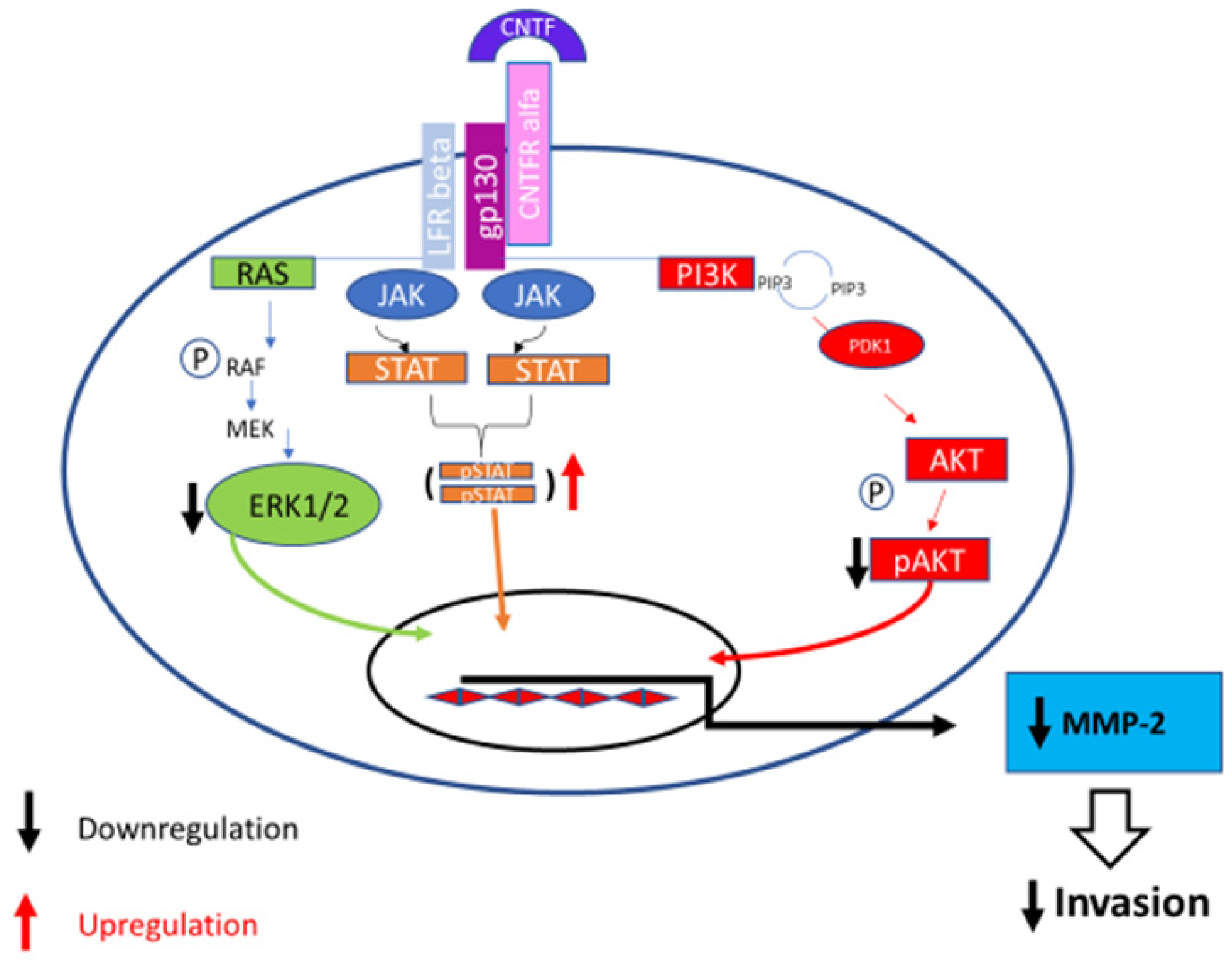
3.3. MAPK/ERK, AKT/PI3K and Jak/STAT Pathways Modulation after CNTF Treatments
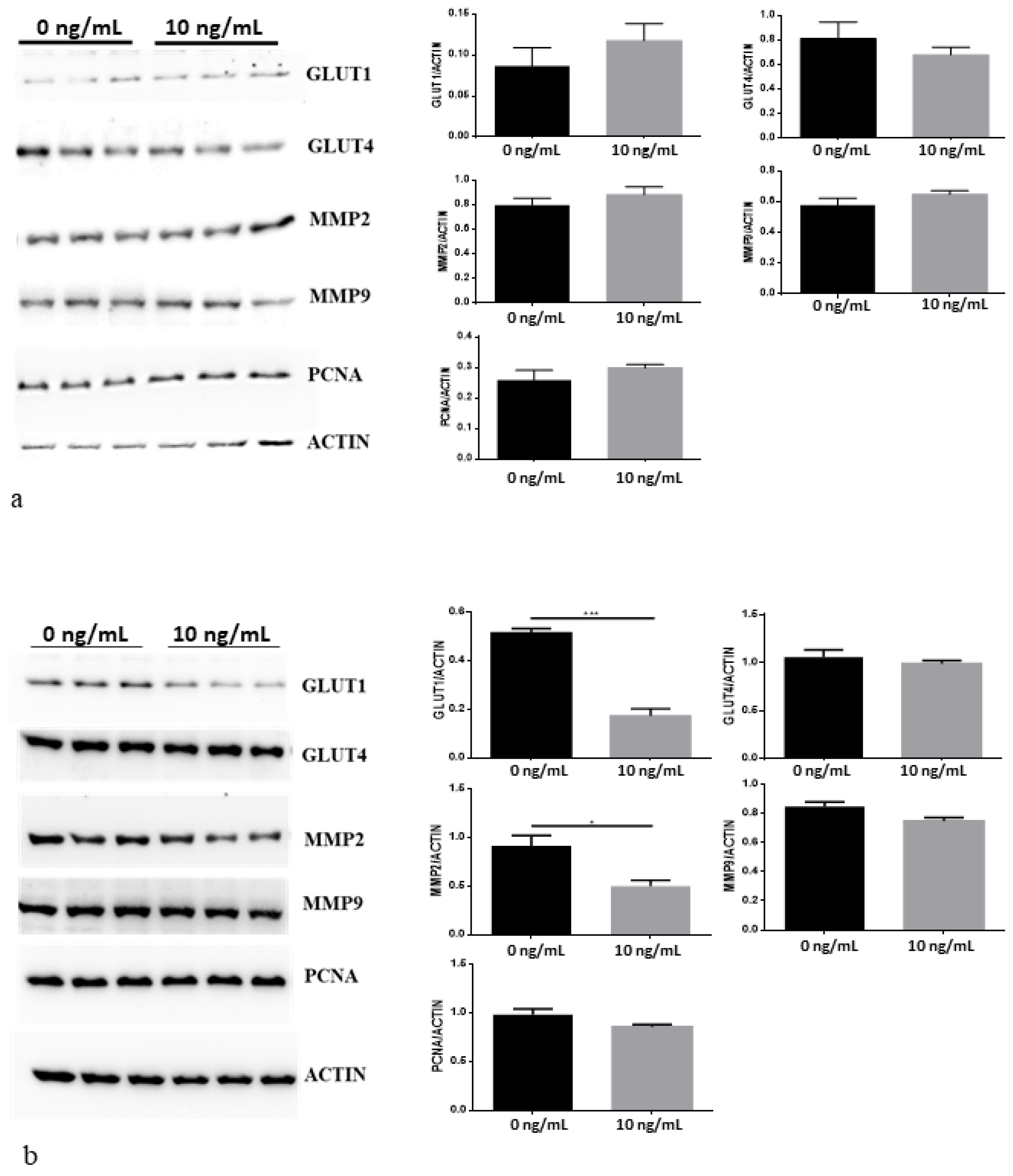
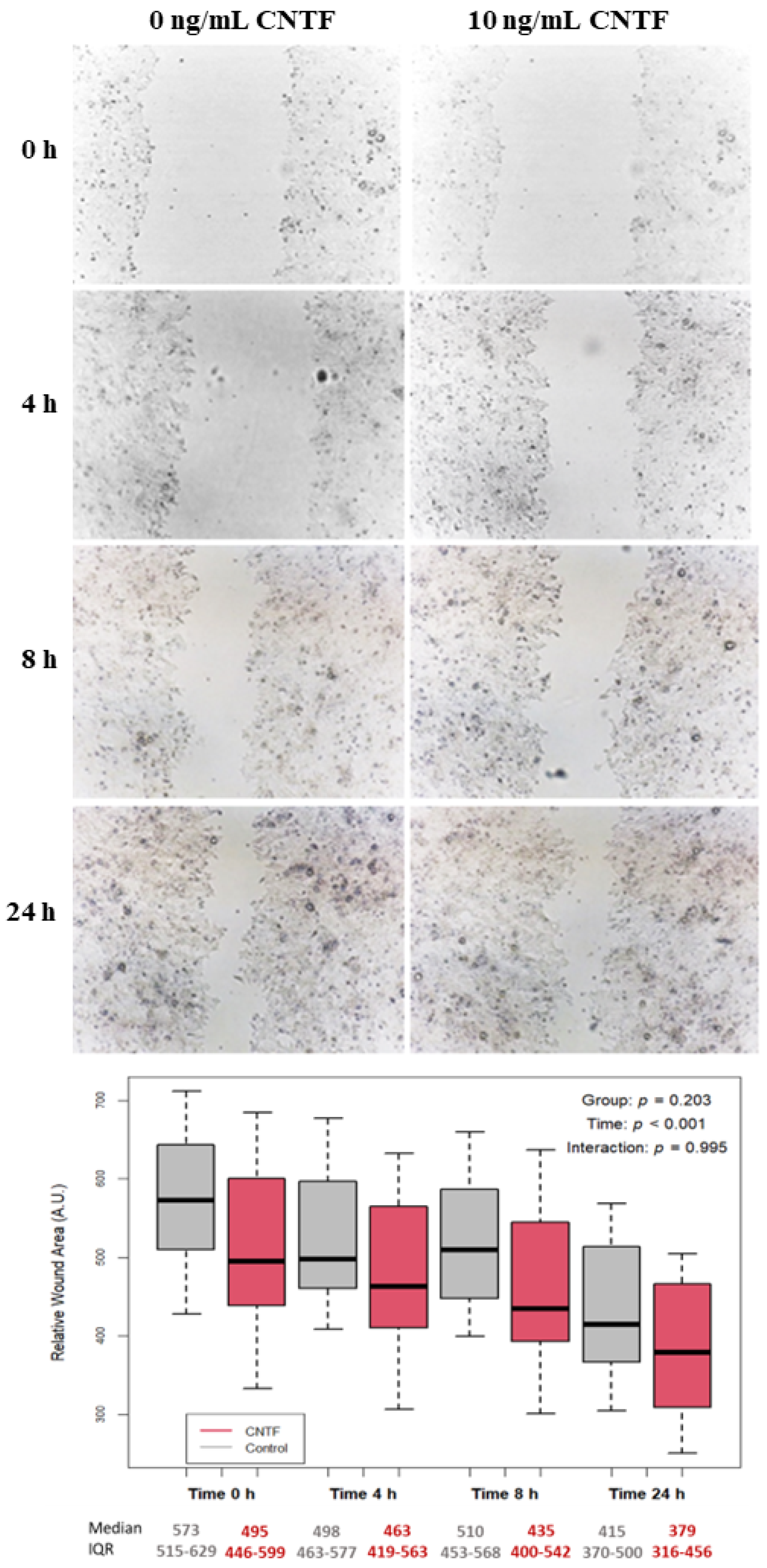
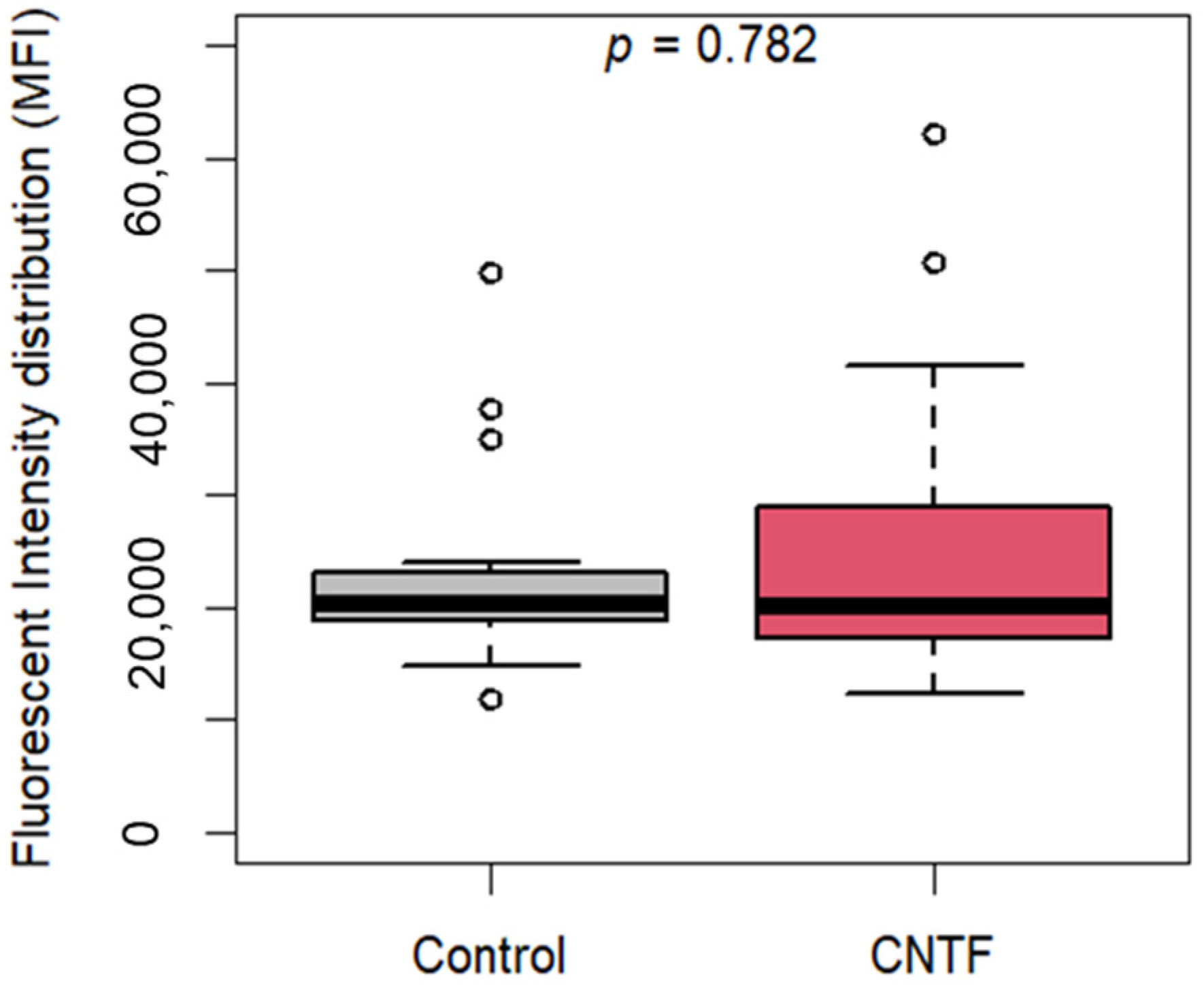
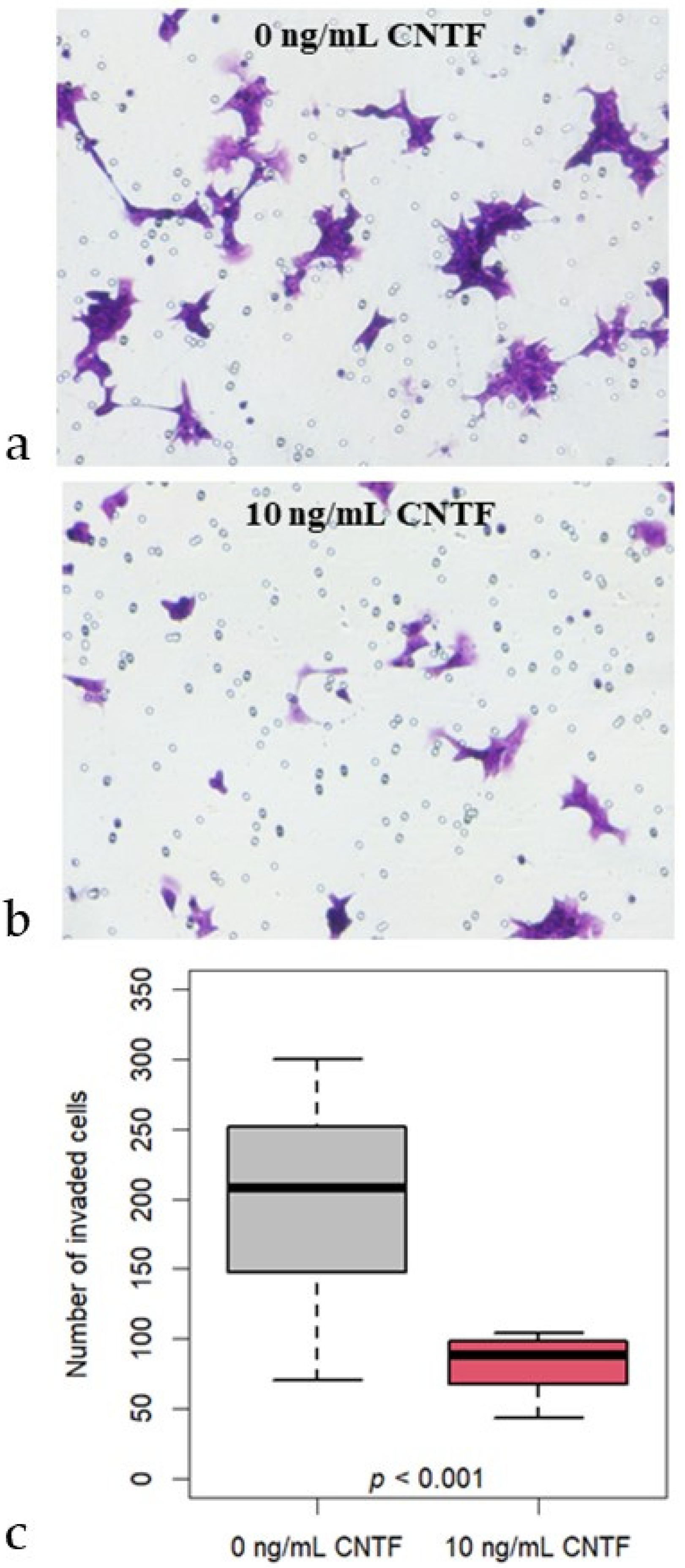
3.4. CNTF Treatments Did Not Affect Cell Migration and Glucose Uptake but Reduce 22Rv1 Cells Invasiveness
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marklund, M.; Schultz, N.; Friedrich, S.; Berglund, E.; Tarish, F.; Tanoglidi, A.; Liu, Y.; Bergenstrahle, L.; Erickson, A.; Helleday, T.; et al. Spatio-temporal analysis of prostate tumors in situ suggests pre-existence of treatment-resistant clones. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culig, Z.; Puhr, M. Interleukin-6 and prostate cancer: Current developments and unsolved questions. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 462, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pencik, J.; Wiebringhaus, R.; Susani, M.; Culig, Z.; Kenner, L. IL-6/STAT3/ARF: The guardians of senescence, cancer progression and metastasis in prostate cancer. Swiss. Med. Wkly. 2015, 145, w14215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Culig, Z. Proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 in prostate carcinogenesis. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Urol. 2014, 2, 231–238. [Google Scholar]
- Fantone, S.; Tossetta, G.; Montironi, R.; Senzacqua, M.; Marzioni, D.; Mazzucchelli, R. Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) and its receptor (CNTFRalpha) signal through MAPK/ERK pathway in human prostate tissues: A morphological and biomolecular study. Eur. J. Histochem. 2020, 64, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.A.; Jenkins, B.J. Recent insights into targeting the IL-6 cytokine family in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 773–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rascio, F.; Spadaccino, F.; Rocchetti, M.T.; Castellano, G.; Stallone, G.; Netti, G.S.; Ranieri, E. The Pathogenic Role of PI3K/AKT Pathway in Cancer Onset and Drug Resistance: An Updated Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.E.; Marlein, C.; Walker, H.F.; Frame, F.M.; Mann, V.M.; Simms, M.S.; Davies, B.R.; Collins, A.T.; Maitland, N.J. Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway activates autophagy and compensatory Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signalling in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 56698–56713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, D.J.; Kobayashi, N.; Ruscetti, M.; Zhi, A.; Tran, L.M.; Huang, J.; Gleave, M.; Wu, H. Pten loss and RAS/MAPK activation cooperate to promote EMT and metastasis initiated from prostate cancer stem/progenitor cells. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1878–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz, C.V.; Alves, M.G.; Marques, R.; Moreira, P.I.; Oliveira, P.F.; Maia, C.J.; Socorro, S. Androgen-responsive and nonresponsive prostate cancer cells present a distinct glycolytic metabolism profile. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 2077–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Menendez, P.; Hevia, D.; Rodriguez-Garcia, A.; Mayo, J.C.; Sainz, R.M. Regulation of GLUT transporters by flavonoids in androgen-sensitive and -insensitive prostate cancer cells. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 3238–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S. Glucose decorated gold nanoclusters: A membrane potential independent fluorescence probe for rapid identification of cancer cells expressing Glut receptors. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 155, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szablewski, L. Expression of glucose transporters in cancers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1835, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, R.A.; Harris, I.S.; Mak, T.W. Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Yu, F.X.; Luo, Y.; Hagen, T. Oncogenic activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway promotes cellular glucose uptake by downregulating the expression of thioredoxin-interacting protein. Cell Signal. 2016, 28, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinoshima, H.; Takita, M.; Saruwatari, K.; Umemura, S.; Obata, Y.; Ishii, G.; Matsumoto, S.; Sugiyama, E.; Ochiai, A.; Abe, R.; et al. Signaling through the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K)/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Axis Is Responsible for Aerobic Glycolysis mediated by Glucose Transporter in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 17495–17504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avanzato, D.; Pupo, E.; Ducano, N.; Isella, C.; Bertalot, G.; Luise, C.; Pece, S.; Bruna, A.; Rueda, O.M.; Caldas, C.; et al. High USP6NL Levels in Breast Cancer Sustain Chronic AKT Phosphorylation and GLUT1 Stability Fueling Aerobic Glycolysis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3432–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macheda, M.L.; Rogers, S.; Best, J.D. Molecular and cellular regulation of glucose transporter (GLUT) proteins in cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 202, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, J.D.; Williams, E.D.; Slavin, J.L.; Best, J.D.; Rogers, S. Expression and localization of GLUT1 and GLUT12 in prostate carcinoma. Cancer 2003, 97, 2035–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantone, S.; Mazzucchelli, R.; Giannubilo, S.R.; Ciavattini, A.; Marzioni, D.; Tossetta, G. AT-rich interactive domain 1A protein expression in normal and pathological pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 154, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tossetta, G.; Fantone, S.; Giannubilo, S.R.; Marinelli Busilacchi, E.; Ciavattini, A.; Castellucci, M.; Di Simone, N.; Mattioli-Belmonte, M.; Marzioni, D. Pre-eclampsia onset and SPARC: A possible involvement in placenta development. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 6091–6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinelli Busilacchi, E.; Costantini, A.; Mancini, G.; Tossetta, G.; Olivieri, J.; Poloni, A.; Viola, N.; Butini, L.; Campanati, A.; Goteri, G.; et al. Nilotinib Treatment of Patients Affected by Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease Reduces Collagen Production and Skin Fibrosis by Downmodulating the TGF-beta and p-SMAD Pathway. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perugini, J.; Di Mercurio, E.; Tossetta, G.; Severi, I.; Monaco, F.; Reguzzoni, M.; Tomasetti, M.; Dani, C.; Cinti, S.; Giordano, A. Biological Effects of Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor on hMADS Adipocytes. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tossetta, G.; Fantone, S.; Busilacchi, E.M.; Di Simone, N.; Giannubilo, S.R.; Scambia, G.; Giordano, A.; Marzioni, D. Modulation of matrix metalloproteases by ciliary neurotrophic factor in human placental development. Cell Tissue Res. 2022, 390, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, K.; Gel, Y.R.; Brunner, E.; Konietschke, F. nparLD: An R Software Package for the Nonparametric Analysis of Longitudinal Data in Factorial Experiments. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 50, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, P.; Backman, L.J.; Zhou, Q.; Danielson, P. Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor Promotes the Migration of Corneal Epithelial Stem/progenitor Cells by Up-regulation of MMPs through the Phosphorylation of Akt. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; He, Z.; Ruan, J.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Gong, C.; Iqbal, K.; Sun, S.; Chen, H. Role of ciliary neurotrophic factor in the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2013, 37, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, N.E.; Poulton, I.J.; Walker, E.C.; Pompolo, S.; Quinn, J.M.; Martin, T.J.; Sims, N.A. Ciliary neurotrophic factor inhibits bone formation and plays a sex-specific role in bone growth and remodeling. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2010, 86, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.W.; White, J.D.; Walker, E.C.; Martin, T.J.; Sims, N.A. Myokines (muscle-derived cytokines and chemokines) including ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) inhibit osteoblast differentiation. Bone 2014, 64, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.J.; Dong, L.L.; Kang, X.L.; Li, Z.M.; Zhang, H.Y. Leptin promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of prostate cancer cells by regulating ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 8341–8348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickols, N.G.; Nazarian, R.; Zhao, S.G.; Tan, V.; Uzunangelov, V.; Xia, Z.; Baertsch, R.; Neeman, E.; Gao, A.C.; Thomas, G.V.; et al. MEK-ERK signaling is a therapeutic target in metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2019, 22, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, A.C.; Vieira, A.S.; Rogerio, F.; Rezende, L.F.; Boschero, A.C.; Negro, A.; Langone, F. Effects of systemic administration of ciliary neurotrophic factor on Bax and Bcl-2 proteins in the lumbar spinal cord of neonatal rats after sciatic nerve transection. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2008, 41, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, X. Nogo receptor knockdown and ciliary neurotrophic factor attenuate diabetic retinopathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 2030–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Lee, H.J.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xiang, Q.; Lee, E.O.; Kim, S.H.; Lu, J. Penta-1,2,3,4,6-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose induces p53 and inhibits STAT3 in prostate cancer cells in vitro and suppresses prostate xenograft tumor growth in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 2681–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tindall, D.J. Androgen action during prostate carcinogenesis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 776, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emonds, K.M.; Swinnen, J.V.; van Weerden, W.M.; Vanderhoydonc, F.; Nuyts, J.; Mortelmans, L.; Mottaghy, F.M. Do androgens control the uptake of 18F-FDG, 11C-choline and 11C-acetate in human prostate cancer cell lines? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 38, 1842–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.S.; Jin, W.J.; Kwak, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Yun, M.J.; Kim, J.W.; Park, S.W.; Kim, K.S. Androgen stimulates glycolysis for de novo lipid synthesis by increasing the activities of hexokinase 2 and 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase 2 in prostate cancer cells. Biochem. J. 2011, 433, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massie, C.E.; Lynch, A.; Ramos-Montoya, A.; Boren, J.; Stark, R.; Fazli, L.; Warren, A.; Scott, H.; Madhu, B.; Sharma, N.; et al. The androgen receptor fuels prostate cancer by regulating central metabolism and biosynthesis. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 2719–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Yu, Z.; Zou, J. LncRNA-SNHG16 Silencing Inhibits Prostate Carcinoma Cell Growth, Downregulate GLUT1 Expression and Reduce Glucose Uptake. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 1751–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Wang, J.; Yan, W.; Cui, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gao, X.; Wen, X.; Chen, J. GLUT1 regulates cell glycolysis and proliferation in prostate cancer. Prostate 2018, 78, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Cao, X.; Lv, X.; Chen, F. Shikonin inhibits prostate cancer cells metastasis by reducing matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 expression via AKT/mTOR and ROS/ERK1/2 pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 21, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stearns, M.E.; Wang, M.; Stearns, M. IL-10 blocks collagen IV invasion by “invasion stimulating factor” activated PC-3 ML cells: Upregulation of TIMP-1 expression. Oncol. Res. 1995, 7, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth, J.A.; Yousif, R.; Herzog, M.; Che, M.; Upadhyay, J.; Shekarriz, B.; Bhagat, S.; Mullins, C.; Fridman, R.; Cher, M.L. Matrix metalloproteinase activity, bone matrix turnover, and tumor cell proliferation in prostate cancer bone metastasis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, C.S.; Shen, K.H.; Huang, J.S.; Ko, S.C.; Shih, Y.W. Antimetastatic potential of fisetin involves inactivation of the PI3K/Akt and JNK signaling pathways with downregulation of MMP-2/9 expressions in prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 333, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudel, D.; Fradet, Y.; Meyer, F.; Harel, F.; Tetu, B. Significance of MMP-2 expression in prostate cancer: An immunohistochemical study. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8511–8515. [Google Scholar]
- Trudel, D.; Fradet, Y.; Meyer, F.; Harel, F.; Tetu, B. Membrane-type-1 matrix metalloproteinase, matrix metalloproteinase 2, and tissue inhibitor of matrix proteinase 2 in prostate cancer: Identification of patients with poor prognosis by immunohistochemistry. Hum. Pathol. 2008, 39, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antibody | IHC | WB | IF | Company |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pAb Rabbit anti-human CNTF (#ab190985) | 1:500 | // | 1:100 | Abcam, Cambridge, UK |
| pAb Rabbit anti-human CNTFRα (#PA5-45053) | // | 1:400 | // | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA |
| mAb Mouse anti-human CNTFRα (#ab89333) | 1:150 | // | 1:100 | Abcam, Cambridge, UK |
| mAb Rabbit anti-human pAKT (#4060) | // | 1:1000 | // | Cell signaling technology, Danvers, MA, USA |
| pAb Rabbit anti-human AKT (#9272) | // | 1:1000 | // | Cell signaling technology, Danvers, MA, USA |
| mAb Rabbit anti-human pERK1/2 (#4377) | // | 1:800 | // | Cell signaling technology, Danvers, MA, USA |
| mAb Rabbit anti-human ERK1/2 (#4695) | // | 1:1000 | // | Cell signaling technology, Danvers, MA, USA |
| mAb Mouse anti-human pSTAT3 (#4113) | // | 1:800 | // | Cell signaling technology, Danvers, MA, USA |
| mAb Rabbit anti-human STAT3 (#4904) | // | 1:1000 | // | Cell signaling technology, Danvers, MA, USA |
| pAb Rabbit anti-human GLUT1 (#PA1-46152) | // | 1:500 | // | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA |
| pAb Rabbit anti-human GLUT4 (#PA5-23052) | // | 1:500 | // | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA |
| pAb Rabbit anti-human MMP-9 (#10375-2-AP) | // | 1:500 | // | Proteintech Group, Manchester, UK |
| mAb Mouse anti-human MMP-2 (#436000) | // | 1:500 | // | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA |
| mAb Mouse anti-human PCNA (#sc-56) | // | 1:250 | // | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc, Dallas, TX, USA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tossetta, G.; Fantone, S.; Gesuita, R.; Goteri, G.; Senzacqua, M.; Marcheggiani, F.; Tiano, L.; Marzioni, D.; Mazzucchelli, R. Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor Modulates Multiple Downstream Signaling Pathways in Prostate Cancer Inhibiting Cell Invasiveness. Cancers 2022, 14, 5917. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235917
Tossetta G, Fantone S, Gesuita R, Goteri G, Senzacqua M, Marcheggiani F, Tiano L, Marzioni D, Mazzucchelli R. Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor Modulates Multiple Downstream Signaling Pathways in Prostate Cancer Inhibiting Cell Invasiveness. Cancers. 2022; 14(23):5917. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235917
Chicago/Turabian StyleTossetta, Giovanni, Sonia Fantone, Rosaria Gesuita, Gaia Goteri, Martina Senzacqua, Fabio Marcheggiani, Luca Tiano, Daniela Marzioni, and Roberta Mazzucchelli. 2022. "Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor Modulates Multiple Downstream Signaling Pathways in Prostate Cancer Inhibiting Cell Invasiveness" Cancers 14, no. 23: 5917. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235917
APA StyleTossetta, G., Fantone, S., Gesuita, R., Goteri, G., Senzacqua, M., Marcheggiani, F., Tiano, L., Marzioni, D., & Mazzucchelli, R. (2022). Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor Modulates Multiple Downstream Signaling Pathways in Prostate Cancer Inhibiting Cell Invasiveness. Cancers, 14(23), 5917. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14235917










