Ultrasound Radiomics Nomogram to Diagnose Sub-Centimeter Thyroid Nodules Based on ACR TI-RADS
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
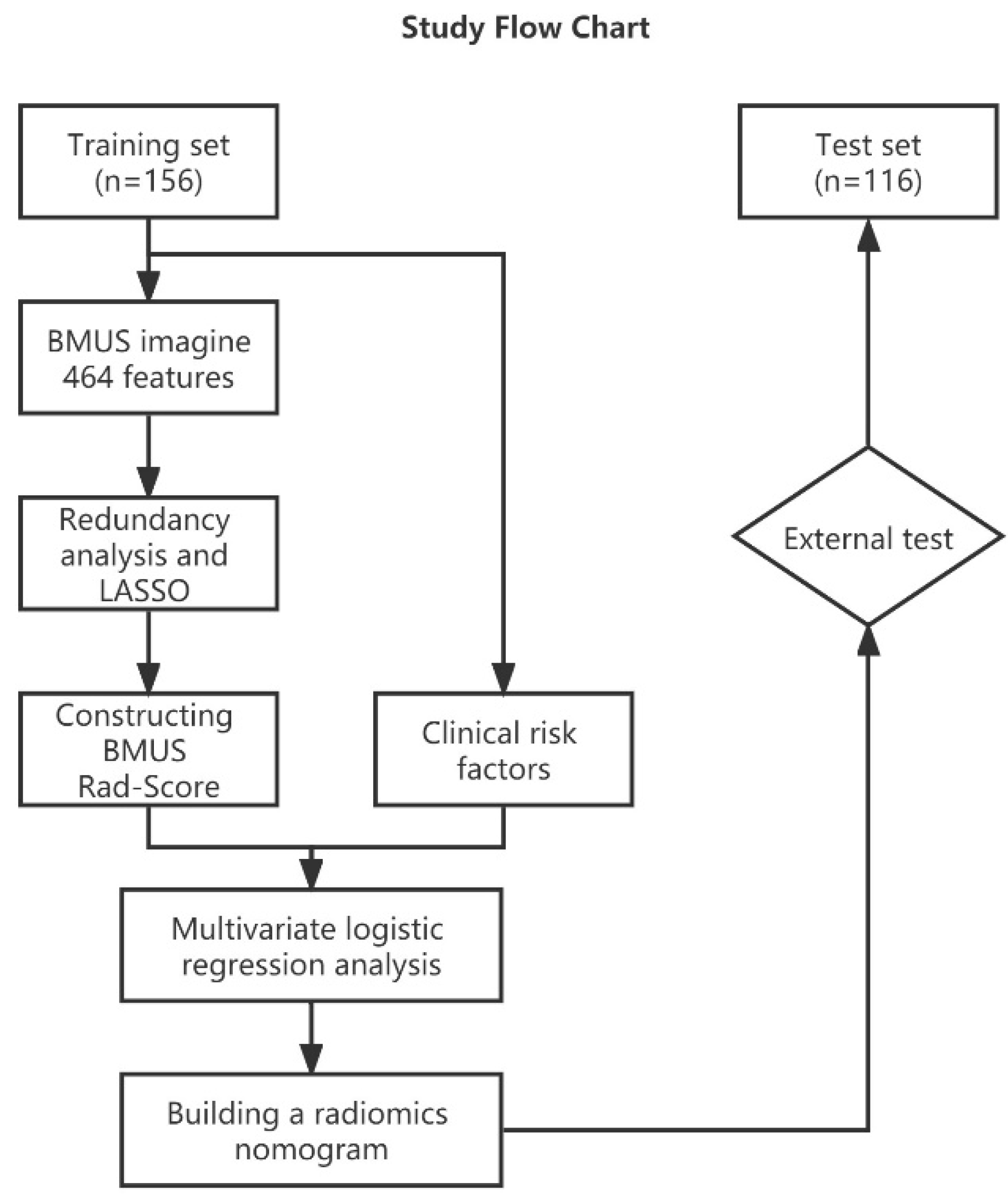
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Groups
2.2. Clinical Data and Ultrasound Images
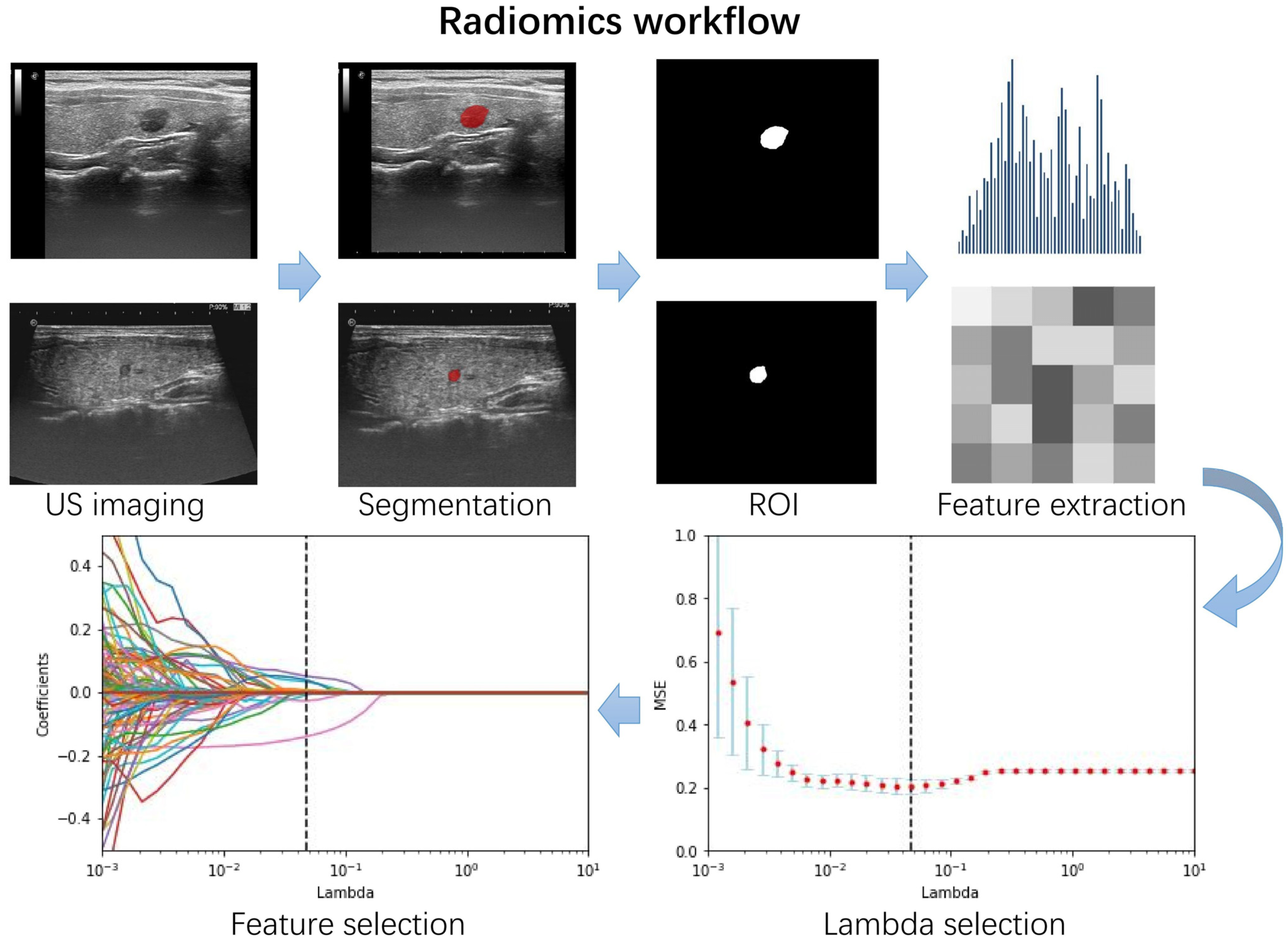
2.3. Region of Interest Segmentation and Radiomics Feature Extraction
2.4. Feature Selection and Rad-Score Building
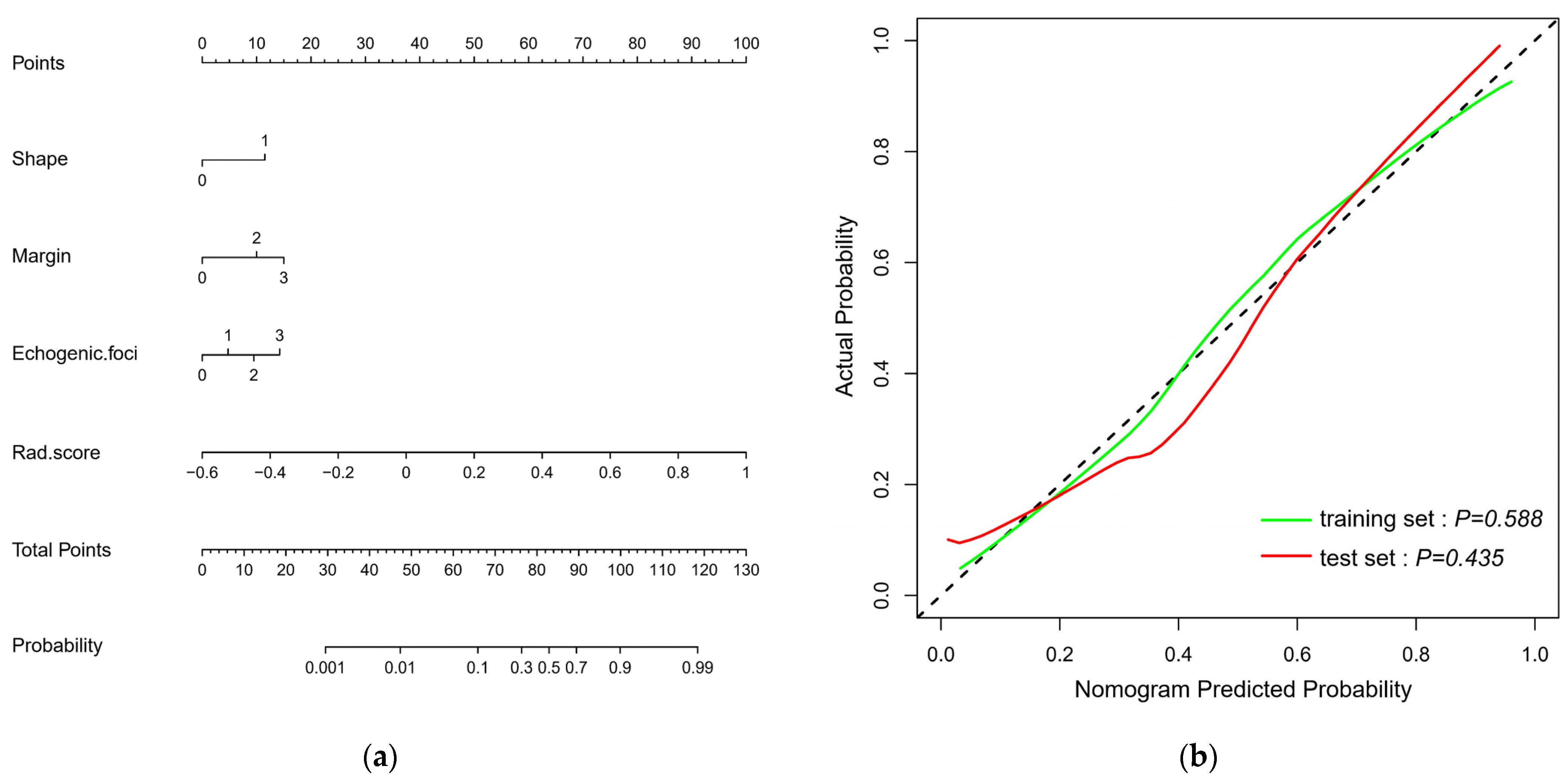
2.5. Constructing Ultrasound Radiomics Nomogram
2.6. The Performance of Ultrasound Radiomics Nomogram
2.7. Statistical Analyses
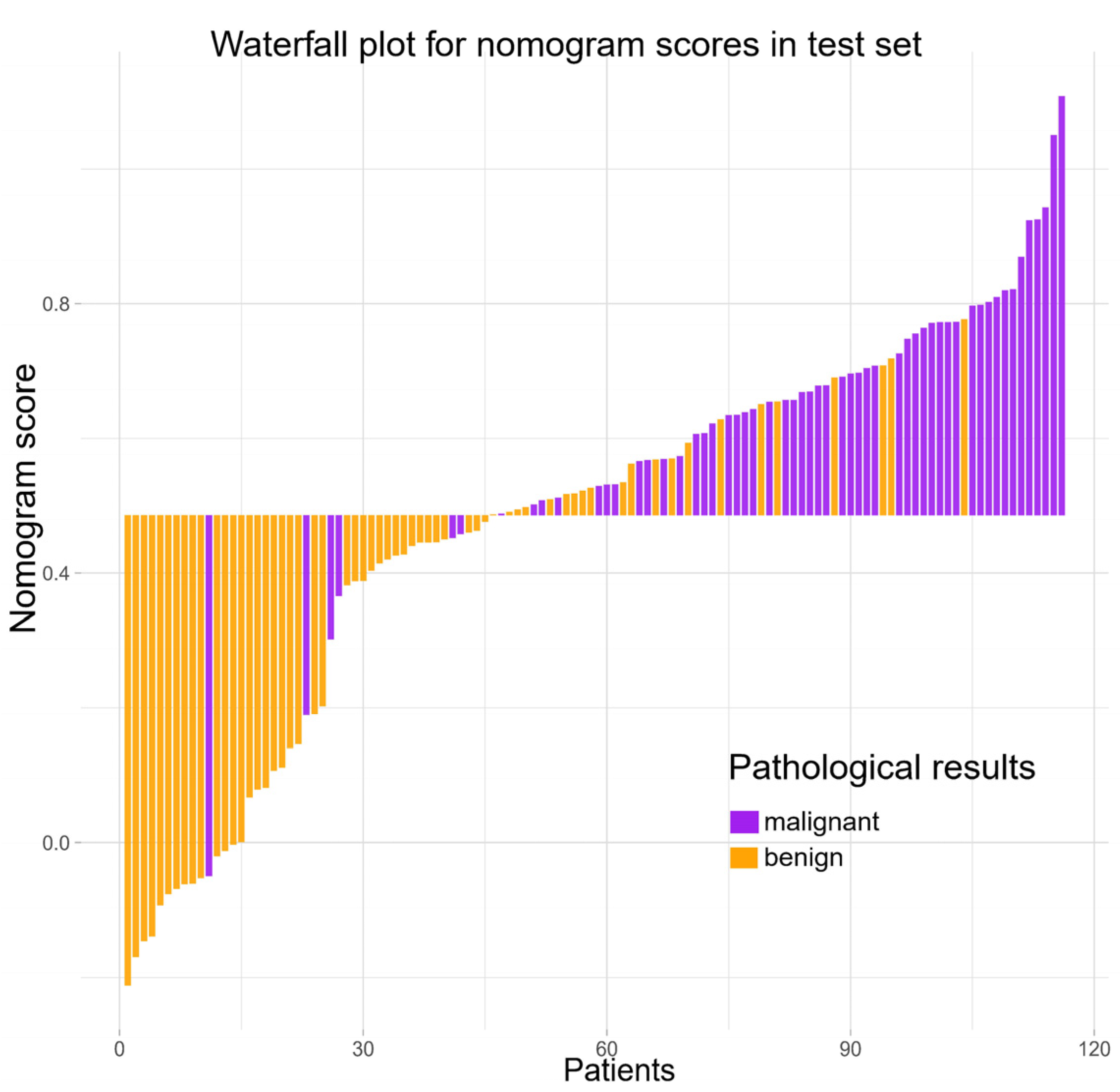
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Information
3.2. Establishment of Radiomics Score
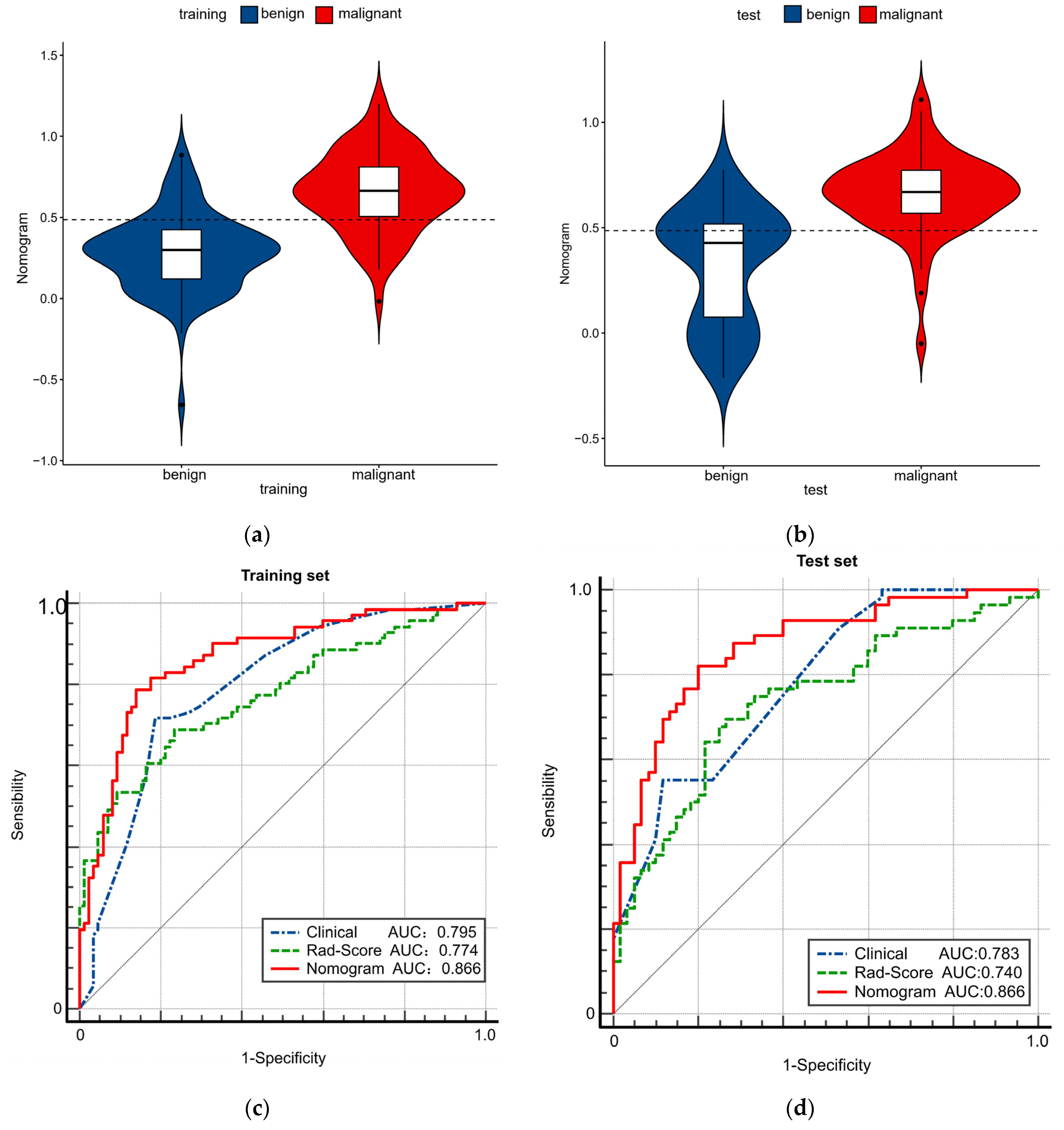
3.3. Constructing and Evaluating Nomogram
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kitahara, C.M.; Sosa, J.A. The changing incidence of thyroid cancer. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharib, H.; Papini, E.; Paschke, R.; Duick, D.S.; Valcavi, R.; Hegedüs, L.; Vitti, P. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, Associazione Medici Endocrinologi, and European Thyroid Association medical guidelines for clinical practice for the diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules: Executive Summary of recommendations. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2010, 33, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.; Farrell, S.G.; Grossmann, M. Thyroid nodules: Diagnosis and management. Med. J. Aust. 2018, 209, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Chai, Y.J.; Park, I.; Woo, J.-W.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, K.E.; Choe, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.S. Nomogram for predicting central node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 115, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrá, J.C.; Picado, O.; Liu, S.; Ouyang, W.; Teo, R.; Franco, A.M.; Lew, J.I. Clinically significant cancer rates in incidentally discovered thyroid nodules by routine imaging. J. Surg. Res. 2017, 219, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, W.-J.; Ji, Q.-H.; Zhu, Y.-X.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, C.-P.; Shen, Q.; Li, D.-S.; Wu, Y. Risk factors for neck nodal metastasis in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: A study of 1066 patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Cho, Y.J.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, J.G.; Ahn, C.J.; Lee, D.H. Analysis of the clinicopathologic features of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma based on 7-mm tumor size. World J. Surg. 2011, 35, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, B. Role of Ultrasound in the Management of Thyroid Nodules and Thyroid Cancer. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2017, 39, 445–450. [Google Scholar]
- Blum, M. Ultrasonography of the Thyroid; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Hershman, J.M., Hofland, J., Kalra, S., et al., Eds.; Endotext: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Tessler, F.N.; Middleton, W.D.; Grant, E.G.; Hoang, J.K.; Berland, L.L.; Teefey, S.A.; Cronan, J.J.; Beland, M.D.; Desser, T.S.; Frates, M.C.; et al. ACR Thyroid Imaging, Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS): White Paper of the ACR TI-RADS Committee. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2017, 14, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, Z.; He, Y.; Mai, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, M.; Li, S.; Yi, W.; Wu, S.; Bai, T.; et al. An Artificial Intelligence Model Based on ACR TI-RADS Characteristics for US Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules. Radiology 2022, 303, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.N.; Zhang, B.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Y.X.; Lai, X.J.; Zhang, X.Y. Logistic Regression Analysis of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound and Conventional Ultrasound Characteristics of Sub-centimeter Thyroid Nodules. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 3102–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, A.; Johnson, D.N.; White, M.; Siddiqui, S.; Antic, T.; Mathew, M.; Grogan, R.H.; Angelos, P.; Kaplan, E.L.; Cipriani, N.A. Thyroid Nodule Size at Ultrasound as a Predictor of Malignancy and Final Pathologic Size. Thyroid 2017, 27, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausei, S.; Dionigi, G.; Frattini, F.; Castano, P.; Leotta, A.; Rovera, F.; Boni, L.; Bartalena, L.; Dionigi, R. Nodule size and fine-needle aspiration biopsy: Diagnostic challenges for thyroid malignancy. Am. J. Surg. 2011, 201, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, S. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI radiomics nomogram for predicting axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer. Cancer Imaging 2022, 22, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, T.; Luo, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, X.; Guo, X. Radiomics predicts the prognosis of patients with locally advanced breast cancer by reflecting the heterogeneity of tumor cells and the tumor microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res. 2022, 24, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zeng, J.; Li, H.; Yu, X. A Deep Learning Radiomics Analysis for Survival Prediction in Esophageal Cancer. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 4034404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Huang, X.; Hu, H.-T.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Cao, Q.; Wang, W.; Liu, B.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Predicting Malignancy in Thyroid Nodules: Radiomics Score Versus 2017 American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging, Reporting and Data System. Thyroid 2018, 28, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Schabath, M.B. Radiomics Improves Cancer Screening and Early Detection. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 2556–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Ma, J.; Duan, S.; Xia, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, L. Preoperative classification of primary and metastatic liver cancer via machine learning-based ultrasound radiomics. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 4576–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Chen, D.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Qiao, G.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. Diagnosis of Ovarian Neoplasms Using Nomogram in Combination With Ultrasound Image-Based Radiomics Signature and Clinical Factors. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 753948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, P.; Du, H.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Wan, L.; Zhao, B.; Ren, J. Ultrasound Radiomics Nomogram Integrating Three-Dimensional Features Based on Carotid Plaques to Evaluate Coronary Artery Disease. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowinska-Klencka, D.; Klencki, M.; Wojtaszek-Nowicka, M.; Wysocka-Konieczna, K.; Wozniak-Osela, E.; Popowicz, B. Validation of Four Thyroid Ultrasound Risk Stratification Systems in Patients with Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis; Impact of Changes in the Threshold for Nodule’s Shape Criterion. Cancers 2021, 13, 4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lu, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, B.; Xu, M.; Xie, X.; Kuang, M.; Wang, W.; Shen, S.; Chen, L. Preoperative Survival Prediction in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Using a Ultrasound-Based Radiographic-Radiomics Signature. J. Ultrasound Med. 2021, 41, 1483–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.-W.; Zhu, F.-P.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Liu, X.-S.; Wu, F.-Y.; Wang, K.; Xia, Y.-X.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Jiang, W.-J.; Li, X.-C.; et al. A radiomics approach to predict lymph node metastasis and clinical outcome of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 3725–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayerhoefer, M.E.; Materka, A.; Langs, G.; Häggström, I.; Szczypiński, P.; Gibbs, P.; Cook, G. Introduction to Radiomics. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, R.; Rosenkrantz, A.; Bennett, G.L.; Dane, B.; Jacobs, J.; Slywotzky, C.; Smereka, P.N.; Tong, A.; Sheth, S. Interreader Concordance of the TI-RADS: Impact of Radiologist Experience. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 214, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Tomoda, C.; Uruno, T.; Takamura, Y.; Miya, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Matsuzuka, F.; Kuma, K.; Miyauchi, A. Papillary microcarcinoma of the thyroid: How should it be treated? World J. Surg. 2004, 28, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.; Tsang, V.; Clifton-Bligh, R.J.; Gild, M.L. Papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: Is active surveillance always enough? Clin. Endocrinol. 2021, 95, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Feng, J.W.; Wu, W.X.; Qi, G.F.; Wang, F.; Hu, J.; Hong, L.Z.; Liu, S.Y.; Jiang, Y. Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Nomogram Based on Clinical and Ultrasound Features to Improve the Prediction of Lymph Node Metastases in the Central Compartment. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 770824. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, S.; Dong, Y.; Kang, H.; Zhan, W. Ultrasonography is valuable in evaluation of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma based on 5 mm tumor size. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2018, 14, S319–S323. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, J.; Xu, D.; Yang, Z.; Sun, J.; Sun, L.; Wu, Y.; Qiao, H. Combination of serum microRNAs and ultrasound profile as predictive biomarkers of diagnosis and prognosis for papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 3611–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Ma, B.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Qu, N.; Gao, Y.; Ji, Q. The impact of presence of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis on diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy in subcentimeter thyroid nodules: A retrospective study from FUSCC. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Li, C.; Kang, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Duo, L.; Tang, W. Clinical predictive model for the 1-year remission probability of IgA vasculitis nephritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101 Pt B, 108341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ye, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, X.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Q.; et al. An Externally Validated Dynamic Nomogram for Predicting Unfavorable Prognosis in Patients With Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 683051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Training Dataset No. (%) | Test Dataset No. (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.826 | ||
| male | 34 (21.8) | 24 (20.7) | |
| female | 122 (78.2) | 92 (79.3) | |
| Age, mean ± SD, years | 45.64 ± 12.00 | 47.47 ± 11.20 | 0.201 |
| Pathology | 0.651 | ||
| benign | 85 (54.5) | 60 (51.7) | |
| malignant | 71 (45.5) | 56 (48.3) | |
| Tumor location | 0.225 | ||
| left | 84 (53.8) | 71 (61.2) | |
| right | 72 (46.2) | 45 (38.8) | |
| Tumor size, mean ± SD, mm | 7.30 ± 1.73 | 7.41 ± 1.66 | 0.609 |
| TI-RADS level | 0.903 | ||
| TR 3 | 1 (0.6) | 6 (5.2) | |
| TR 4 | 36 (23.1) | 21 (18.1) | |
| TR 5 | 119 (76.3) | 89 (76.7) | |
| Composition | 0.119 | ||
| solid | 154 (98.7) | 111 (95.7) | |
| mixed cystic and solid | 2 (0.3) | 5 (4.3) | |
| Echogenicity | <0.001 | ||
| hyperechoic or isoechoic | 7 (4.5) | 21 (18.1) | |
| hypoechoic | 139 (89.1) | 93 (80.2) | |
| very hypoechoic | 10 (6.4) | 2 (1.7) | |
| Shape | 0.005 | ||
| wider-than-tall | 90 (57.7) | 47 (40.5) | |
| taller-than-wide | 66 (42.3) | 69 (59.5) | |
| Margin | <0.001 | ||
| smooth or ill-defined | 82 (52.6) | 23 (19.8) | |
| lobulated or irregular | 65 (41.7) | 83 (71.6) | |
| extra-thyroidal extension | 9 (5.7) | 10 (8.6) | |
| Echogenic foci | 0.206 | ||
| none or large comet-tail artifacts | 68 (43.6) | 64 (55.2) | |
| macrocalcifications | 14 (9.0) | 9 (7.8) | |
| peripheral (rim) calculations | 6 (3.8) | 6 (5.1) | |
| punctate echogenic foci | 68 (43.6) | 37 (31.9) | |
| BMUS Rad-score, median (interquartile range) | 0.40 (0.32–0.52) | 0.41 (0.30–0.51) | 0.358 |
| Characteristic | Training Dataset No. (%) | Test Dataset No. (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malignant | Benign | p-Value | Malignant | Benign | p-Value | |
| Sex | 0.078 | 0.788 | ||||
| male | 20 (28.2) | 14 (16.5) | 11(19.4) | 13 (21.7) | ||
| female | 51 (71.8) | 71 (83.5) | 45 (80.6) | 47 (78.3) | ||
| Age, mean ± SD, years | 44.01 ± 11.57 | 47.00 ± 12.25 | 0.122 | 46.13 ± 10.30 | 48.73 ± 11.92 | 0.211 |
| Tumor location | 0.372 | 0.782 | ||||
| left | 41 (57.7) | 43 (50.6) | 35 (62.5) | 36 (60.0) | ||
| right | 30 (42.3) | 42 (49.4) | 21 (37.5) | 24 (40.0) | ||
| Tumor size, mean ± SD, mm | 7.20 ± 1.79 | 7.39 ± 1.69 | 0.5 | 7.76 ± 1.68 | 7.08 ± 1.59 | 0.027 |
| TI-RADS level | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| TR 3 | 0 | 1 (1.2) | 0 | 6 (10.0) | ||
| TR 4 | 4 (5.6) | 32 (37.6) | 3 (5.4) | 18 (30.0) | ||
| TR 5 | 67 (94.4) | 52 (61.2) | 53 (94.6) | 36 (60.0) | ||
| Composition | 0.193 | 0.196 | ||||
| solid | 71 (100) | 83 (97.6) | 55 (98.2) | 56 (93.3) | ||
| mixed cystic and solid | 0 | 2 (2.4) | 1 (1.8) | 4 (6.7) | ||
| Echogenicity | 0.077 | 0.046 | ||||
| hyperechoic or isoechoic | 3 (4.2) | 4 (4.7) | 5 (8.9) | 16 (26.7) | ||
| hypoechoic | 60 (84.5) | 79 (92.9) | 50 (89.3) | 43 (71.7) | ||
| very hypoechoic | 8 (11.3) | 2 (2.4) | 1 (1.8) | 1 (1.6) | ||
| Shape | 0.01 | 0.076 | ||||
| wider-than-tall | 33 (46.5) | 57 (67.1) | 18 (32.1) | 29 (48.3) | ||
| taller-than-wide | 38 (53.5) | 28 (32.9) | 38 (67.9) | 31 (51.7) | ||
| Margin | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| smooth or ill-defined | 26 (36.6) | 56 (65.9) | 1 (1.8) | 22 (36.7) | ||
| lobulated or irregular | 37 (52.1) | 28 (32.9) | 45 (80.4) | 38 (63.3) | ||
| extra-thyroidal extension | 8 (11.3) | 1 (1.2) | 10 (17.8) | 0 | ||
| Echogenic foci | 0.007 | 0.001 | ||||
| none or large comet-tail artifacts | 24 (33.8) | 44 (51.8) | 30 (53.6) | 34 (56.7) | ||
| macrocalcifications | 3 (4.2) | 11 (12.9) | 1 (1.8) | 8 (13.3) | ||
| peripheral (rim) calculations | 3 (4.2) | 3 (3.5) | 0 | 6 (10.0) | ||
| punctate echogenic foci | 41 (57.8) | 27 (31.8) | 25 (44.6) | 12 (20.0) | ||
| BMUS Rad-score, median (interquartile range) | 0.50 (0.37–0.64) | 0.36 (0.30–0.42) | <0.001 | 0.46 (0.37–0.62) | 0.33 (0.25–0.42) | <0.001 |
| Intercept and Variable | Clinical Model | BMUS Radiomics Nomogram | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | β | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Intercept | −2.606 | −5.867 | ||||
| Shape | 1.493 | 4.452 (2.004–9.890) | <0.001 | 1.489 | 4.431 (1.799–10.913) | 0.001 |
| Margin | 0.842 | 2.322 (1.610–3.349) | <0.001 | 0.646 | 1.909 (1.276–2.854) | 0.002 |
| Echogenic foci | 0.595 | 1.813 (1.364–2.410) | <0.001 | 0.614 | 1.847 (1.342–2.542) | <0.001 |
| TI-RADS level | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| BMUS Rad-score | NA | NA | NA | 8.079 | 2.243 (1.581–3.184) | <0.001 |
| Variable | Clinical Model (95% CI) | Rad-Score (95% CI) | BMUS Radiomics Nomogram (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Cohort | Test Cohort | Training Cohort | Test Cohort | Training Cohort | Test Cohort | |
| Cutoff value | 0.587 | 0.587 | 0.421 | 0.421 | 0.486 | 0.486 |
| AUC | 0.795 (0.723–0.855) | 0.783 (0.697–0.854) | 0.774 (0.700–0.837) | 0.740 (0.651–0.817) | 0.866 (0.802–0.915) | 0.866 (0.790–0.922) |
| PLR | 4.00 (2.57–6.24) | 3.79 (2.25–6.41) | 3.62 (2.35–5.57) | 2.93 (1.84–4.67) | 6.70 (3.83–11.73) | 8.88 (3.82–20.64) |
| NLR | 0.27 (0.17–0.43) | 0.28 (0.17–0.47) | 0.31 (0.20–0.47) | 0.36 (0.22–0.56) | 0.16 (0.09–0.29) | 0.20 (0.11–0.34) |
| Sensitivity, % | 78.26 (66.69–87.29) | 77.19 (64.16–87.26) | 75.71 (63.99–85.17) | 73.21 (59.70–84.17) | 85.71 (75.29–92.93) | 82.26 (70.47–90.80) |
| Specificity, % | 80.46 (70.56–88.18) | 79.66 (67.17–89.02) | 79.07 (68.95–87.10) | 75.00 (62.14–85.28) | 87.21 (78.26–93.44) | 90.74 (79.70–96.92) |
| PPV, % | 76.06 (67.08–83.20) | 78.57 (68.46–86.10) | 74.65 (65.66–81.93) | 73.21 (63.17–81.33) | 84.51 (75.70–90.52) | 91.07 (81.45–95.95) |
| NPV, % | 82.35 (74.67–88.08) | 78.33 (68.79–85.57) | 80.00 (72.28–85.98) | 75.00 (65.51–82.57) | 88.23 (80.77–93.05) | 81.67 (72.14–88.46) |
| Diagnostic accuracy, % | 79.49 (72.29–85.53) | 73.08 (65.40–79.86) | 74.14 (65.18–81.82) | 86.54 (80.16–91.47) | 86.21 (78.57–91.91) | |
| TP | 51 | 31 | 43 | 36 | 54 | 43 |
| TN | 67 | 46 | 71 | 46 | 73 | 48 |
| FP | 18 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 12 | 12 |
| FN | 20 | 25 | 28 | 20 | 17 | 13 |
| Brier score | 0.181 | 0.181 | 0.186 | 0.209 | 0.144 | 0.153 |
| Training Cohort (95% CI) | Test Cohort (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | p-Value | AUC | p-Value | |
| Clinical vs. Rad-score | 0.795 vs. 0.774 | 0.6748 | 0.783 vs. 0.740 | 0.4835 |
| Clinical vs. Nomogram | 0.795 vs. 0.866 | 0.0019 | 0.783 vs. 0.866 | 0.0099 |
| Rad-score vs. Nomogram | 0.774 vs. 0.866 | 0.0053 | 0.740 vs. 0.866 | 0.0006 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, X.; Qian, C.; Wei, Y.; Xia, Z.; Ding, W.; Ni, X. Ultrasound Radiomics Nomogram to Diagnose Sub-Centimeter Thyroid Nodules Based on ACR TI-RADS. Cancers 2022, 14, 4826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194826
Lu W, Zhang D, Zhang Y, Qian X, Qian C, Wei Y, Xia Z, Ding W, Ni X. Ultrasound Radiomics Nomogram to Diagnose Sub-Centimeter Thyroid Nodules Based on ACR TI-RADS. Cancers. 2022; 14(19):4826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194826
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Wenwu, Di Zhang, Yuzhi Zhang, Xiaoqin Qian, Cheng Qian, Yan Wei, Zicong Xia, Wenbo Ding, and Xuejun Ni. 2022. "Ultrasound Radiomics Nomogram to Diagnose Sub-Centimeter Thyroid Nodules Based on ACR TI-RADS" Cancers 14, no. 19: 4826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194826
APA StyleLu, W., Zhang, D., Zhang, Y., Qian, X., Qian, C., Wei, Y., Xia, Z., Ding, W., & Ni, X. (2022). Ultrasound Radiomics Nomogram to Diagnose Sub-Centimeter Thyroid Nodules Based on ACR TI-RADS. Cancers, 14(19), 4826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194826





