Radiofrequency Ablation versus Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma within Milan Criteria: Prognostic Role of Tumor Burden Score
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Definition
2.3. Definition of TBS
2.4. Albumin-Bilirubin (ALBI) Score
2.5. Treatments
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
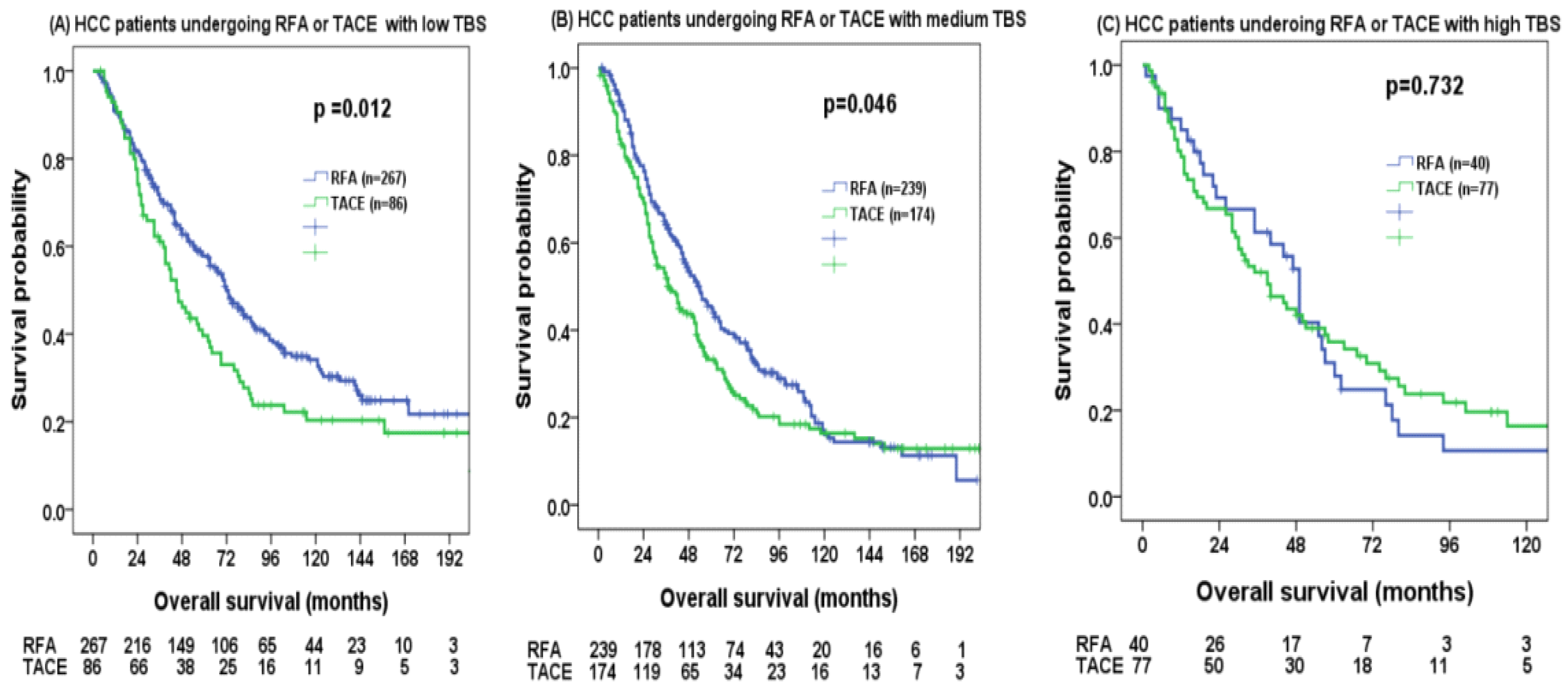
3.2. Kaplan–Meier Survival Analysis
3.3. Univariate and Multivariate Survival Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulik, L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology and management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 477–491.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimbach, J.K.; Kulik, L.M.; Finn, R.S.; Sirlin, C.B.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Zhu, A.X.; Murad, M.H.; Marrero, J.A. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 358–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, S.; Eso, Y.; Okada, H.; Takai, A.; Takahashi, K.; Seno, H. Recent advances in immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makary, M.S.; Khandpur, U.; Cloyd, J.M.; Mumtaz, K.; Dowell, J.D. Locoregional therapy approaches for hepatocellular carcinoma: Recent advances and management strategies. Cancers 2020, 12, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargellini, I.; Sacco, R.; Bozzi, E.; Bertini, M.; Ginanni, B.; Romano, A.; Cicorelli, A.; Tumino, E.; Federici, G.; Cioni, R.; et al. Transarterial chemoembolization in very early and early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients excluded from curative treatment: A prospective cohort study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayasu, K.; Arii, S.; Kudo, M.; Ichida, T.; Matsui, O.; Izumi, N.; Matsuyama, Y.; Sakamoto, M.; Nakashima, O.; Ku, Y.; et al. Superselective transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Validation of treatment algorithm proposed by Japanese guidelines. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golfieri, R.; Cappelli, A.; Cucchetti, A.; Piscaglia, F.; Carpenzano, M.; Peri, E.; Ravaioli, M.; D’Errico-Grigioni, A.; Pinna, A.D.; Bolondi, L. Efficacy of selective transarterial chemoembolization in inducing tumor necrosis in small (<5 cm) hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Chun, Y.S.; Poon, R.T.; Schwartz, M.E.; Yao, F.Y.; Marsh, J.W.; Bhoori, S.; Lee, S.G. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Llovet, J.M.; Miceli, R.; Bhoori, S.; Schiavo, M.; Mariani, L.; Camerini, T.; Roayaie, S.; Schwartz, M.E.; Grazi, G.L.; et al. Predicting survival after liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the Milan criteria: A retrospective, exploratory analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Morioka, D.; Conci, S.; Margonis, G.A.; Sawada, Y.; Ruzzenente, A.; Kumamoto, T.; Iacono, C.; Andreatos, N.; Guglielmi, A.; et al. The tumor burden score: A new “metro-ticket” prognostic tool for colorectal liver metastases based on tumor size and number of tumors. Ann. Surg. 2018, 267, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilimigras, D.I.; Moris, D.; Hyer, J.M.; Bagante, F.; Sahara, K.; Moro, A.; Paredes, A.Z.; Mehta, R.; Ratti, F.; Marques, H.P.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma tumour burden score to stratify prognosis after resection. Br. J. Surg. 2020, 107, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moris, D.; Shaw, B.I.; McElroy, L.; Barbas, A.S. Using hepatocellular carcinoma tumor burden score to stratify prognosis after liver transplantation. Cancers 2020, 12, 3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, S.Y.; Liu, P.H.; Hsu, C.Y.; Ko, C.C.; Huang, Y.H.; Su, C.W.; Lee, R.C.; Tsai, P.H.; Hou, M.C.; Huo, T.I. Tumor burden score as a new prognostic marker for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing transarterial chemoembolization. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 3196–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Hsia, C.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Su, C.W.; Lin, H.C.; Lee, R.C.; Chiou, Y.Y.; Lee, F.Y.; Huo, T.I. Performance status in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Determinants, prognostic impact, and ability to improve the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer system. Hepatology 2013, 57, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.H.; Hsu, C.Y.; Hsia, C.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Su, C.W.; Huang, Y.H.; Lee, F.Y.; Lin, H.C.; Huo, T.I. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: Assessment of eleven staging systems. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, A.; Lai, Q.; Farinati, F.; Bucci, L.; Giannini, E.G.; Napoli, L.; Ciccarese, F.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Di Marco, M.; Caturelli, E.; et al. Utility of tumor burden score to stratify prognosis of patients with hepatocellular cancer: Results of 4759 cases from ITA.LI.CA Study Group. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2018, 22, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.J.; Berhane, S.; Kagebayashi, C.; Satomura, S.; Teng, M.; Reeves, H.L.; O’Beirne, J.; Fox, R.; Skowronska, A.; Palmer, D.; et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.Y.; Hsu, C.Y.; Liu, P.H.; Hsia, C.Y.; Lei, H.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Ko, C.C.; Su, C.W.; Lee, R.C.; Hou, M.C.; et al. Albumin-bilirubin grade-based nomogram of the BCLC system for personalized prognostic prediction in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescure, C.; Estrade, F.; Pedrono, M.; Campillo-Gimenez, B.; Le Sourd, S.; Pracht, M.; Palard, X.; Bourien, H.; Muzellec, L.; Uguen, T.; et al. ALBI Score is a strong predictor of toxicity following SIRT for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Chiou, Y.Y.; Su, C.W.; Lin, H.C.; Lee, R.C.; Chiang, J.H.; Huo, T.I.; Lee, F.Y.; Lee, S.D. Comparison of radiofrequency ablation and transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria: A propensity score analysis. Liver Transpl. 2011, 17, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Liu, P.H.; Hsia, C.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Nagaria, T.S.; Lee, R.C.; Lin, H.C.; Huo, T.I. Surgical resection is better than transarterial chemoembolization for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the Milan criteria: A prognostic nomogram study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manini, M.A.; Sangiovanni, A.; Martinetti, L.; Viganò, D.; La Mura, V.; Aghemo, A.; Iavarone, M.; Crespi, S.; Nicolini, A.; Colombo, M. Transarterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads is effective for the maintenance of the Milan-in status in patients with a small hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Transpl. 2015, 21, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.Y.; Ferrell, L.; Bass, N.M.; Watson, J.J.; Bacchetti, P.; Venook, A.; Ascher, N.L.; Roberts, J.P. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Expansion of the tumor size limits does not adversely impact survival. Hepatology 2001, 33, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toso, C.; Meeberg, G.; Hernandez-Alejandro, R.; Dufour, J.F.; Marotta, P.; Majno, P.; Kneteman, N.M. Total tumor volume and alpha-fetoprotein for selection of transplant candidates with hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective validation. Hepatology 2015, 62, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, T.I.; Hsu, C.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Su, C.W.; Lin, H.C.; Lee, R.C.; Chiou, Y.Y.; Chiang, J.H.; Lee, P.C.; Lee, S.D. Prognostic prediction across a gradient of total tumor volume in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing locoregional therapy. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010, 10, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsilimigras, D.I.; Pawlik, T.M. Prognostication in hepatocellular carcinoma: Is it a burden or a ticket? Br. J. Surg. 2021, 108, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilimigras, D.I.; Mehta, R.; Paredes, A.Z.; Moris, D.; Sahara, K.; Bagante, F.; Ratti, F.; Marques, H.P.; Silva, S.; Soubrane, O.; et al. Overall tumor burden dictates outcomes for patients undergoing resection of multinodular hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the Milan criteria. Ann. Surg. 2020, 272, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Hsu, C.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Chiou, Y.Y.; Lin, H.C.; Huo, T.I. Survival advantage of radiofrequency ablation over transarterial chemoembolization for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and good performance status within the Milan criteria. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 3835–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Hsia, C.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Su, C.W.; Lin, H.C.; Pai, J.T.; Loong, C.C.; Chiou, Y.Y.; Lee, R.C.; Lee, F.Y.; et al. Comparison of surgical resection and transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the Milan criteria: A propensity score analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinato, D.J.; Sharma, R.; Allara, E.; Yen, C.; Arizumi, T.; Kubota, K.; Bettinger, D.; Jang, J.W.; Smirne, C.; Kim, Y.W.; et al. The ALBI grade provides objective hepatic reserve estimation across each BCLC stage of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, T.I. ALBI grade as a new player in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2019, 82, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galle, P.R.; Foerster, F.; Kudo, M.; Chan, S.L.; Llovet, J.M.; Qin, S.; Schelman, W.R.; Chintharlapalli, S.; Abada, P.B.; Sherman, M.; et al. Biology and significance of alpha-fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 2214–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Liu, P.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Hsia, C.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Lin, H.C.; Chiou, Y.Y.; Lee, F.Y.; Huo, T.I. Using serum alpha-fetoprotein for prognostic prediction in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: What is the most optimal cutoff? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118825. [Google Scholar]

| Variables | RFA Patients (n = 546) | TACE Patients (n = 337) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | 67 ± 11 | 67 ± 11 | 0.510 |
| Male/Female, n (%) | 351/195 (64/36) | 225/112 (67/33) | 0.452 |
| Etiologies of liver disease, n (%) | 0.065 | ||
| HBV | 234 (43) | 115 (34) | |
| HCV | 191 (35) | 140 (21) | |
| HBV + HCV | 24 (4) | 19 (6) | |
| Others | 97 (18) | 63 (19) | |
| Performance status (0/1/2), n (%) | 423/64/59 (77/12/11) | 233/67/37 (69/20/11) | 0.004 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 157 (29) | 99 (29) | 0.843 |
| Tumor nodules (single/multiple) | 454/92 (83/17) | 236/101 (70/30) | <0.001 |
| Tumor diameter > 3 cm, n (%) | 94 (17) | 115 (34) | <0.001 |
| Tumor diameter, mean ± SD | 2.29 ± 0.9 | 2.75 ± 1.1 | <0.001 |
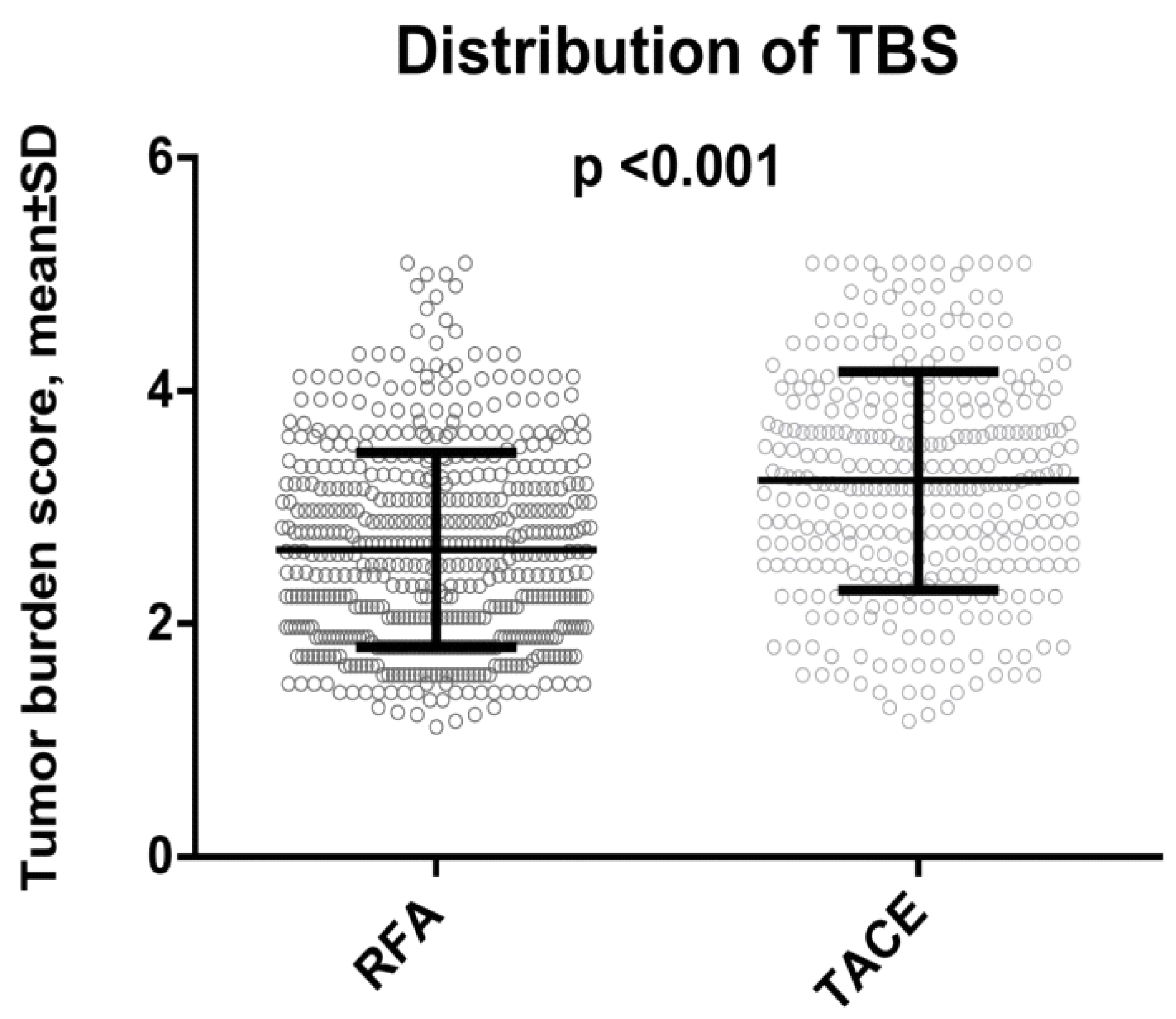
| Tumor burden score (TBS) | <0.001 | ||
| Low | 267 (49) | 86 (26) | |
| Medium | 239 (43) | 174 (51) | |
| High | 40 (8) | 77 (23) | |
| Serum AFP (ng/mL), median (IQR) | 6 (16–65) | 21 (7–112) | 0.142 |
| Serum AFP ≥ 20 ng/mL, n (%) | 247 (45) | 171 (51) | 0.112 |
| Laboratory values, median (IQR) | |||
| Alanine transaminase (U/L) | 44 (28–74) | 57 (27–74) | 0.039 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.8 (3.4–4.1) | 3.6 (3.2–4.1) | 0.744 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.8 (0.5–1.2) | 0.9 (0.6–1.4) | 0.242 |
| Platelets (1000/μL) | 114 (86–163) | 100 (71–151) | 0.469 |
| INR of prothrombin time | 1.08 (1.06–1.13) | 1.08 (1.01–1.16) | 0.056 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.9 (0.8–1.2) | 1.0 (0.8–1.2) | 0.881 |
| CTP class (A/B) | 463/83 (85/15) | 265/72 (79/21) | 0.019 |
| ALBI grade (1/2/3), n (%) | 242/281/23 (44/52/4) | 106/217/14 (31/64/4) | 0.001 |
| BCLC stage (0/A/others), n (%) | 136/290/10 (25/53/22) | 32/196/109 (10/58/32) | <0.001 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall Survival | HR | CI | p | HR | CI | p |
| Age (≤67/>67 years) | 1.518 | 1.294–1.780 | <0.001 | |||
| Sex (male/female) | 0.936 | 0.794–1.103 | 0.432 | |||
| HBsAg (negative/positive) | 1.347 | 1.148–1.581 | <0.001 | |||
| Anti-HCV (negative/positive) | 0.881 | 0.753–1.032 | 0.116 | |||
| Albumin level (≥3.5/<3.5 g/dL) | 1.546 | 1.310–1.825 | <0.001 | |||
| Bilirubin level (≤1.1/>1.1 mg/dL) | 1.418 | 1.197–1.679 | <0.001 | |||
| ALT (≤40/>40 IU/L) | 1.265 | 1.078–1.484 | 0.004 | |||
| Platelet (≥150,000/<150,000/μL) | 1.385 | 1.152–1.665 | 0.001 | |||
| INR of PT (≤1.0/>1.0) | 1.329 | 1.129–1.565 | <0.001 | |||
| AFP (≤20/>20 ng/mL) | 1.497 | 1.297–1.752 | <0.001 | 1.435 | 1.221–1.687 | <0.001 |
| Performance status 0/1–2 | 1.673 | 1.401–1.997 | <0.001 | 1.565 | 1.304–1.878 | <0.001 |
| Tumor burden score | ||||||
| Low | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Medium | 1.392 | 1.173–1.653 | <0.001 | 1.372 | 1.156–1.630 | <0.001 |
| High | 1.623 | 1.271–2.073 | <0.001 | 1.512 | 1.181–1.937 | <0.001 |
| ALBI grade | ||||||
| Grade 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Grade 2 | 1.821 | 1.536–2.158 | <0.001 | 1.611 | 1.355–1.916 | <0.001 |
| Grade 3 | 2.812 | 1.915–4.129 | <0.001 | 2.297 | 1.555–3.394 | <0.001 |
| RFA vs. TACE | 1.368 | 1.166–1.605 | <0.001 | |||
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall Survival | HR | CI | p | HR | CI | p |
| Age (≤67/>67 years) | 1.736 | 1.335–2.257 | <0.001 | 1.774 | 1.360–2.314 | <0.001 |
| Sex (male/female) | 0.952 | 0.730–1.243 | 0.719 | |||
| HBsAg (negative/positive) | 1.589 | 1.219–2.072 | 0.001 | |||
| Anti-HCV (negative/positive) | 0.824 | 0.635–1.069 | 0.145 | |||
| Albumin level (≥3.5/<3.5 g/dL) | 1.639 | 1.242–2.163 | <0.001 | |||
| Bilirubin level (≤1.1/>1.1 mg/dL) | 1.455 | 1.102–1.922 | 0.008 | |||
| ALT (≤40/>40 IU/L) | 1.457 | 1.111–1.911 | 0.006 | |||
| Platelet (≥150,000/<150,000/μL) | 1.912 | 1.338–2.730 | 0.001 | 1.466 | 1.010–2.129 | 0.044 |
| INR of PT (≤1.0/>1.0) | 1.558 | 1.192–2.037 | 0.001 | |||
| AFP (≤20/>20 ng/mL) | 1.297 | 1.001–1.681 | 0.049 | |||
| Performance status 0/1–2 | 1.475 | 1.081–2.012 | 0.014 | |||
| ALBI grade | ||||||
| Grade 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Grade 2 | 1.983 | 1.496–2.628 | <0.001 | 1.738 | 1.293–2.336 | <0.001 |
| Grade 3 | 2.329 | 1.122–4.835 | <0.001 | 2.505 | 1.186–5.288 | 0.016 |
| RFA vs. TACE | 1.436 | 1.078–1.913 | 0.013 | 1.372 | 1.025–1.836 | 0.034 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall Survival | HR | CI | p | HR | CI | p |
| Age (≤67/>67 years) | 1.335 | 1.062–1.677 | 0.013 | 1.521 | 1.199–1.930 | <0.001 |
| Sex (male/female) | 0.955 | 0.750–1.217 | 0.711 | |||
| HBsAg (negative/positive) | 0.826 | 0.658–1.037 | 0.100 | |||
| Anti-HCV (negative/positive) | 0.957 | 0.763–1.199 | 0.710 | |||
| Albumin level (≥3.5/<3.5 g/dL) | 1.507 | 1.190–1.907 | <0.001 | |||
| Bilirubin level (≤1.1/>1.1 mg/dL) | 1.403 | 1.099–1.791 | 0.007 | |||
| ALT (≤40/>40 IU/L) | 0.839 | 0.669–1.053 | 0.130 | |||
| Platelet (≥150,000/<150,000/μL) | 0.791 | 0.616–1.015 | 0.066 | |||
| INR of PT (≤1.0/>1.0) | 0.842 | 0.665–1.066 | 0.153 | |||
| AFP (≤20/>20 ng/mL) | 1.526 | 1.218–1.913 | <0.001 | 1.497 | 1.189–1.885 | 0.001 |
| Performance status 0/1–2 | 2.024 | 1.573–2.605 | <0.001 | 1.828 | 1.408–2.373 | <0.001 |
| ALBI grade | ||||||
| Grade 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Grade 2 | 1.732 | 1.360–2.204 | <0.001 | 1.657 | 1.295–2.119 | <0.001 |
| Grade 3 | 3.022 | 1.848–4.940 | <0.001 | 2.705 | 1.602–4.570 | <0.001 |
| RFA vs. TACE | 1.257 | 1.002–1.576 | 0.048 | |||
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall Survival | HR | CI | p | HR | CI | p |
| Tumor size ≤ 3 cm (n = 674) | ||||||
| Age (≤67/>67 years) | 1.603 | 1.332–1.929 | <0.001 | 1.657 | 1.374–1.998 | <0.001 |
| Sex (male/female) | 0.998 | 0.826–1.208 | 0.987 | |||
| HBsAg(negative/positive) | 1.405 | 1.166–1.692 | <0.001 | 1.298 | 1.076–1.565 | 0.006 |
| Anti-HCV (negative/positive) | 0.854 | 0.711–1.025 | 0.091 | |||
| Albumin level (≥3.5/<3.5 g/dL) | 1.521 | 1.254–1.844 | <0.001 | |||
| Bilirubin level (≤1.1/>1.1 mg/dL) | 1.395 | 1.146–1.699 | 0.001 | |||
| ALT (≤40/>40 IU/L) | 1.353 | 1.119–1.635 | 0.002 | |||
| Platelet (≥150,000/<150,000/μL) | 1.453 | 1.160–1.819 | 0.001 | |||
| INR of PT (≤1.0/>1.0) | 1.324 | 1.097–1.599 | 0.004 | |||
| AFP (≤20/>20 ng/mL) | 1.464 | 1.219–1.758 | <0.001 | 1.378 | 1.144–1.661 | 0.001 |
| Performance status 0/1–2 | 1.733 | 1.403–2.139 | <0.001 | 1.668 | 1.347–2.065 | <0.001 |
| Tumor burden score | ||||||
| Low | 1 | |||||
| Medium-high | 1.365 | 1.137–1.639 | 0.001 | 1.319 | 1.098–1.584 | 0.003 |
| ALBI grade | ||||||
| Grade 1 | 1 | |||||
| Grade 2 | 1.886 | 1.528–2.278 | <0.001 | 1.738 | 1.419–2.128 | <0.001 |
| Grade 3 | 3.215 | 2.068–4.999 | <0.001 | 3.455 | 2.204–5.416 | <0.001 |
| RFA vs. TACE | 1.389 | 1.148–1.680 | 0.001 | |||
| Tumor size > 3 cm (n = 209) | ||||||
| Age (≤67/>67 years) | 0.861 | 0.627–1.182 | 0.335 | |||
| Sex (male/female) | 1.492 | 1.075–2.070 | 0.017 | |||
| HBsAg(negative/positive) | 0.894 | 0.652–1.225 | 0.485 | |||
| Anti-HCV (negative/positive) | 0.910 | 0.663–1.248 | 0.557 | |||
| Albumin level (≥3.5/<3.5 g/dL) | 1.650 | 1.190–2.287 | 0.003 | |||
| Bilirubin level (≤1.1/>1.1 mg/dL) | 1.477 | 1.060–2.057 | 0.021 | |||
| ALT (≤40/>40 IU/L) | 0.847 | 0.623–1.151 | 0.289 | |||
| Platelet (≥150,000/<150,000/μL) | 1.396 | 1.005–1.941 | 0.047 | |||
| INR of PT (≤1.0/>1.0) | 1.470 | 1.053–2.051 | 0.023 | |||
| AFP (≤20/>20 ng/mL) | 1.717 | 1.261–2.339 | 0.001 | 1.680 | 1.233–2.290 | 0.001 |
| Performance status 0/1–2 | 1.434 | 1.031–1.996 | 0.032 | |||
| Tumor burden score | ||||||
| medium | 1 | |||||
| high | 0.959 | 0.705–1.303 | 0.787 | |||
| ALBI grade | ||||||
| Grade 1 | ||||||
| Grade 2–3 | 1.761 | 1.274–2.433 | 0.001 | 1.725 | 1.247–2.386 | 0.001 |
| RFA vs. TACE | 0.894 | 0.657–1.218 | 0.478 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, S.-Y.; Liu, P.-H.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Huang, Y.-H.; Liao, J.-I.; Su, C.-W.; Hou, M.-C.; Huo, T.-I. Radiofrequency Ablation versus Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma within Milan Criteria: Prognostic Role of Tumor Burden Score. Cancers 2022, 14, 4207. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174207
Ho S-Y, Liu P-H, Hsu C-Y, Huang Y-H, Liao J-I, Su C-W, Hou M-C, Huo T-I. Radiofrequency Ablation versus Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma within Milan Criteria: Prognostic Role of Tumor Burden Score. Cancers. 2022; 14(17):4207. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174207
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Shu-Yein, Po-Hong Liu, Chia-Yang Hsu, Yi-Hsiang Huang, Jia-I Liao, Chien-Wei Su, Ming-Chih Hou, and Teh-Ia Huo. 2022. "Radiofrequency Ablation versus Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma within Milan Criteria: Prognostic Role of Tumor Burden Score" Cancers 14, no. 17: 4207. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174207
APA StyleHo, S.-Y., Liu, P.-H., Hsu, C.-Y., Huang, Y.-H., Liao, J.-I., Su, C.-W., Hou, M.-C., & Huo, T.-I. (2022). Radiofrequency Ablation versus Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma within Milan Criteria: Prognostic Role of Tumor Burden Score. Cancers, 14(17), 4207. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174207





