Oncostatin M: From Intracellular Signaling to Therapeutic Targets in Liver Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction to Liver Cancer
1.1. Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1.2. Cholangiocarcinoma
2. Oncostatin M: ID Card
3. Biological Activity of Oncostatin M
3.1. Role of OSM in Inflammation
3.2. Role of OSM in Cell Proliferation and Tumor Growth
3.3. OSM and Cancer Progression: Cancer Stem Cell Features, Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition, and Angiogenesis
4. Oncostatin M and Liver Stromal Cells
5. OSM and Therapeutic Strategies for HCC and CCA
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ringelhan, M.; Pfister, D.; O’Connor, T.; Pikarsky, E.; Heikenwalder, M. The immunology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razumilava, N.; Gores, G.J. Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet 2014, 383, 2168–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, E.; Sarkar, D. Emerging Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). Cancers 2022, 14, 2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderaro, J.; Couchy, G.; Imbeaud, S.; Amaddeo, G.; Letouzé, E.; Blanc, J.F.; Laurent, C.; Hajji, Y.; Azoulay, D.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; et al. Histological subtypes of hepatocellular carcinoma are related to gene mutations and molecular tumour classification. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucarull, B.; Tutusaus, A.; Rider, P.; Hernáez-Alsina, T.; Cuño, C.; García de Frutos, P.; Colell, A.; Marí, M.; Morales, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Molecular Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Advances. Cancers 2022, 14, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.; Tacke, F.; Arrese, M.; Chander Sharma, B.; Mostafa, I.; Bugianesi, E.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Yilmaz, Y.; George, J.; Fan, J.; et al. Global Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2672–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, K.; Nault, J.C.; Villanueva, A. Genetic profiling of hepatocellular carcinoma using next-generation sequencing. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sas, Z.; Cendrowicz, E.; Weinhäuser, I.; Rygiel, T.P. Tumor Microenvironment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Challenges and Opportunities for New Treatment Options. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabris, L.; Perugorria, M.J.; Mertens, J.; Björkström, N.K.; Cramer, T.; Lleo, A.; Solinas, A.; Sänger, H.; Lukacs-Kornek, V.; Moncsek, A.; et al. The tumour microenvironment and immune milieu of cholangiocarcinoma. Liver Int. 2019, 39 (Suppl. 1), 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banales, J.M.; Marin, J.J.G.; Lamarca, A.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Khan, S.A.; Roberts, L.R.; Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G.; Andersen, J.B.; Braconi, C.; et al. Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: The next horizon in mechanisms and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 557–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastore, M.; Lori, G.; Gentilini, A.; Taddei, M.L.; Di Maira, G.; Campani, C.; Recalcati, S.; Invernizzi, P.; Marra, F.; Raggi, C. Multifaceted Aspects of Metabolic Plasticity in Human Cholangiocarcinoma: An Overview of Current Perspectives. Cells 2020, 9, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinale, V.; Wang, Y.; Carpino, G.; Reid, L.M.; Gaudio, E.; Alvaro, D. Mucin-producing cholangiocarcinoma might derive from biliary tree stem/progenitor cells located in peribiliary glands. Hepatology 2012, 55, 2041–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, J.W.; Kelley, R.K.; Nervi, B.; Oh, D.Y.; Zhu, A.X. Biliary tract cancer. Lancet 2021, 397, 428–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgewater, J.; Galle, P.R.; Khan, S.A.; Llovet, J.M.; Park, J.W.; Patel, T.; Pawlik, T.M.; Gores, G.J. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 1268–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.; Ma, J.; Zou, Z.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Clements, O.; Kim, J.U.; Eliahoo, J. Reply to: ‘Letter regarding [Risk factors for intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis]’. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondossola, D.; Ghidini, M.; Grossi, F.; Rossi, G.; Foschi, D. Practical review for diagnosis and clinical management of perihilar cholangiocarcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 3542–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, T.; Verheij, J.; Gaudio, E.; Evert, M.; Guido, M.; Goeppert, B.; Carpino, G. Anatomical, histomorphological and molecular classification of cholangiocarcinoma. Liver Int. 2019, 39 (Suppl. 1), 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadamuro, M.; Stecca, T.; Brivio, S.; Mariotti, V.; Fiorotto, R.; Spirli, C.; Strazzabosco, M.; Fabris, L. The deleterious interplay between tumor epithelia and stroma in cholangiocarcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabris, L.; Sato, K.; Alpini, G.; Strazzabosco, M. The Tumor Microenvironment in Cholangiocarcinoma Progression. Hepatology 2021, 73 (Suppl. 1), 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caligiuri, A.; Pastore, M.; Lori, G.; Raggi, C.; Di Maira, G.; Marra, F.; Gentilini, A. Role of Chemokines in the Biology of Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilini, A.; Pastore, M.; Marra, F.; Raggi, C. The Role of Stroma in Cholangiocarcinoma: The Intriguing Interplay between Fibroblastic Component, Immune Cell Subsets and Tumor Epithelium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentilini, A.; Caligiuri, A.; Raggi, C.; Rombouts, K.; Pinzani, M.; Lori, G.; Correnti, M.; Invernizzi, P.; Rovida, E.; Navari, N.; et al. CXCR7 contributes to the aggressive phenotype of cholangiocarcinoma cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 2246–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentilini, A.; Rombouts, K.; Galastri, S.; Caligiuri, A.; Mingarelli, E.; Mello, T.; Marra, F.; Mantero, S.; Roncalli, M.; Invernizzi, P.; et al. Role of the stromal-derived factor-1 (SDF-1)-CXCR4 axis in the interaction between hepatic stellate cells and cholangiocarcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, R.S.P.E.; Faria, J.L.R.; Pavão, D.M. Letter to the Editor Regarding the Article: “Radiographic Evaluation of Postoperative Alignment in Total Knee Arthroplasty”-Thomaz LDG, Geist JGB, De Lucena RDL, Schwartsmann CR, Freitas GLS, Spinelli LF. Rev. Bras. Ortop. 2021, 56, 819–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, K.; Boeing, H.; Nöthlings, U.; Jenab, M.; Fedirko, V.; Kaaks, R.; Lukanova, A.; Trichopoulou, A.; Trichopoulos, D.; Boffetta, P.; et al. Inflammatory and metabolic biomarkers and risk of liver and biliary tract cancer. Hepatology 2014, 60, 858–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.L.T.; Bui, K.C.; Scholta, T.; Xing, J.; Bhuria, V.; Sipos, B.; Wilkens, L.; Nguyen Linh, T.; Velavan, T.P.; Bozko, P.; et al. Targeting interleukin 6 signaling by monoclonal antibody siltuximab on cholangiocarcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 1334–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masjedi, A.; Hajizadeh, F.; Beigi Dargani, F.; Beyzai, B.; Aksoun, M.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Zekiy, A.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F. Oncostatin M: A mysterious cytokine in cancers. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 90, 107158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Miyajima, A. Oncostatin M, a multifunctional cytokine. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 149, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, J.M.; Elks, C.M. Oncostatin M: Potential Implications for Malignancy and Metabolism. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 3645–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermanns, H.M. Oncostatin M and interleukin-31: Cytokines, receptors, signal transduction and physiology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, L.; Patel, M.R.; Horvath, E.B.; Tawara, K.; Jorcyk, C.L. IL-6 and ovarian cancer: Inflammatory cytokines in promotion of metastasis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 6685–6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, C.D. The enigmatic cytokine oncostatin m and roles in disease. ISRN Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 512103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, S.L.; Begley, C.G. The oncostatin M signalling pathway: Reversing the neoplastic phenotype? Mol. Med. Today 1999, 5, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintzen, C.; Evers, C.; Lippok, B.E.; Volkmer, R.; Heinrich, P.C.; Radtke, S.; Hermanns, H.M. Box 2 region of the oncostatin M receptor determines specificity for recruitment of Janus kinases and STAT5 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 19465–19477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, D.K.; Kerr, C.; Tong, L.; Smyth, D.; Richards, C.D. Oncostatin-M up-regulates VCAM-1 and synergizes with IL-4 in eotaxin expression: Involvement of STAT6. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 4352–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böing, I.; Stross, C.; Radtke, S.; Lippok, B.E.; Heinrich, P.C.; Hermanns, H.M. Oncostatin M-induced activation of stress-activated MAP kinases depends on tyrosine 861 in the OSM receptor and requires Jak1 but not Src kinases. Cell Signal. 2006, 18, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Robledo, O.; Kinzie, E.; Blanchard, F.; Richards, C.; Miyajima, A.; Baumann, H. Receptor subunit-specific action of oncostatin M in hepatic cells and its modulation by leukemia inhibitory factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 25273–25285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, D.C.; Kerr, C.; Richards, C.D. Oncostatin M-induced IL-6 expression in murine fibroblasts requires the activation of protein kinase Cdelta. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 8740–8747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallace, P.M.; MacMaster, J.F.; Rouleau, K.A.; Brown, T.J.; Loy, J.K.; Donaldson, K.L.; Wahl, A.F. Regulation of inflammatory responses by oncostatin M. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 5547–5555. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wahl, A.F.; Wallace, P.M. Oncostatin M in the anti-inflammatory response. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2001, 60 (Suppl. 3), iii75–iii80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.H.; Han, S.K.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, W.K. Potential of oncostatin M to accelerate diabetic wound healing. Int. Wound J. 2014, 11, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawski, L.; Trojanowska, M. Oncostatin M and its role in fibrosis. Connect. Tissue Res. 2019, 60, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.I.; Guihard, P.; Danger, Y.; Noel, G.; Le Seyec, J.; Boutet, M.A.; Richards, C.D.; L’Helgoualc’h, A.; Genet, V.; Lucas-Clerc, C.; et al. Oncostatin M induces IL-33 expression in liver endothelial cells in mice and expands ST2+CD4+ lymphocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G542–G553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Nonaka, H.; Saito, H.; Tanaka, M.; Miyajima, A. Hepatocyte proliferation and tissue remodeling is impaired after liver injury in oncostatin M receptor knockout mice. Hepatology 2004, 39, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, M.; Tsurusaki, S.; Miyata, N.; Saijou, E.; Okochi, H.; Miyajima, A.; Tanaka, M. Oncostatin M causes liver fibrosis by regulating cooperation between hepatic stellate cells and macrophages in mice. Hepatology 2018, 67, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohin, M.; Guesdon, W.; Mekouo, A.A.; Rabeony, H.; Paris, I.; Atanassov, H.; Favot, L.; Mcheik, J.; Bernard, F.X.; Richards, C.D.; et al. Oncostatin M overexpression induces skin inflammation but is not required in the mouse model of imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 1737–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinca, S.C.; Greiner, D.; Weidenfeld, K.; Bond, L.; Barkan, D.; Jorcyk, C.L. Novel mechanism for OSM-promoted extracellular matrix remodeling in breast cancer: LOXL2 upregulation and subsequent ECM alignment. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.T.; Trojanowska, M.; Reuben, A. Oncostatin M: A cytokine upregulated in human cirrhosis, increases collagen production by human hepatic stellate cells. J. Hepatol. 2000, 32, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.A.; Jenkins, B.J. Recent insights into targeting the IL-6 cytokine family in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 773–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen-Tran, H.H.; Nguyen, T.N.; Chen, C.Y.; Hsu, T. Endothelial Reprogramming Stimulated by Oncostatin M Promotes Inflammation and Tumorigenesis in. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 5060–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.Y.; Hogg, E.K.J.; Below, C.R.; Kononov, A.; Blanco-Gomez, A.; Heider, F.; Xu, J.; Hutton, C.; Zhang, X.; Scheidt, T.; et al. Heterocellular OSM-OSMR signalling reprograms fibroblasts to promote pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, C.; Tewari, B.N.; Kanchan, R.K.; Baghel, K.S.; Nautiyal, N.; Shrivastava, R.; Kaur, H.; Bhatt, M.L.; Bhadauria, S. Macrophages are recruited to hypoxic tumor areas and acquire a pro-angiogenic M2-polarized phenotype via hypoxic cancer cell derived cytokines Oncostatin M and Eotaxin. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 5350–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, A.M.; Abaurrea, A.; Azcoaga, P.; López-Velazco, J.I.; Manzano, S.; Rodriguez, J.; Rezola, R.; Egia-Mendikute, L.; Valdés-Mora, F.; Flores, J.M.; et al. Stromal oncostatin M cytokine promotes breast cancer progression by reprogramming the tumor microenvironment. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Znoyko, I.; Sohara, N.; Spicer, S.S.; Trojanowska, M.; Reuben, A. Expression of oncostatin M and its receptors in normal and cirrhotic human liver. J. Hepatol. 2005, 43, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shao, C.; Duan, L.; Hou, X.; Huang, Y.; Gao, L.; Zong, C.; Liu, W.; Jiang, J.; Ye, F.; et al. Oncostatin M promotes hepatic progenitor cell activation and hepatocarcinogenesis via macrophage-derived tumor necrosis factor-α. Cancer Lett. 2021, 517, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Block, T.M.; Wang, M.; Nefsky, B.; Long, R.; Hafner, J.; Mehta, A.S.; Marrero, J.; Gish, R.; Norton, P.A. Interleukin-6 and oncostatin M are elevated in liver disease in conjunction with candidate hepatocellular carcinoma biomarker GP73. Cancer Biomark. 2012, 11, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maira, G.; Foglia, B.; Napione, L.; Turato, C.; Maggiora, M.; Sutti, S.; Novo, E.; Alvaro, M.; Autelli, R.; Colombatto, S.; et al. Oncostatin M is overexpressed in NASH-related hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cancer cell invasiveness and angiogenesis. J. Pathol. 2022, 257, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, P.; Sun, R.; Li, J.; Hu, Z.; Xin, H.; Luo, C.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J.; Zhou, S. Tumor-associated neutrophils and macrophages interaction contributes to intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma progression by activating STAT3. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Lan, T.; Song, Y.; Cai, J.; Yu, X.; Chen, W. Oncostatin M expression and TP53 mutation status regulate tumor-infiltration of immune cells and survival outcomes in cholangiocarcinoma. Aging 2020, 12, 21518–21543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, S.L.; Hammacher, A.; Douglas, A.M.; Goss, G.A.; Mansfield, R.K.; Heath, J.K.; Begley, C.G. An unexpected biochemical and functional interaction between gp130 and the EGF receptor family in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2002, 21, 460–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Ahlborn, T.E.; Kraemer, F.B.; Liu, J. Oncostatin M-induced growth inhibition and morphological changes of MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells are abolished by blocking the MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2001, 66, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, M.; Höss, N.; Stögbauer, F.; Senner, V.; Paulus, W.; Ringelstein, E.B.; Halfter, H. Complete inhibition of in vivo glioma growth by oncostatin M. J. Neurochem. 2001, 76, 1589–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacreusette, A.; Lartigue, A.; Nguyen, J.M.; Barbieux, I.; Pandolfino, M.C.; Paris, F.; Khammari, A.; Dréno, B.; Jacques, Y.; Blanchard, F.; et al. Relationship between responsiveness of cancer cells to Oncostatin M and/or IL-6 and survival of stage III melanoma patients treated with tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes. J. Pathol. 2008, 216, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, E.; Guihard, P.; Brounais, B.; Riet, A.; Charrier, C.; Battaglia, S.; Gouin, F.; Ponsolle, S.; Bot, R.L.; Richards, C.D.; et al. Direct anti-cancer effect of oncostatin M on chondrosarcoma. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 1822–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, N.; Zhang, X.M.; Wang, H.T.; Mu, X.P.; Han, H.Z.; Yan, W.Q. Inhibition of growth and induction of differentiation of SMMC-7721 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by Oncostatin M. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Che, Q.; Liao, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Dai, C.; Wan, X. Oncostatin M activates STAT3 to promote endometrial cancer invasion and angiogenesis. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Tundidor, S.; Cavarretta, I.T.; Fuchs, D.; Fiechtl, M.; Steiner, H.; Friedbichler, K.; Bartsch, G.; Hobisch, A.; Culig, Z. Interleukin-6 and oncostatin M stimulation of proliferation of prostate cancer 22Rv1 cells through the signaling pathways of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Prostate 2005, 64, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, S.; Wong, S.; Cutz, J.C.; Tanaka, M.; Barra, N.; Lhoták, S.; Ashkar, A.; Richards, C.D. Novel function of Oncostatin M as a potent tumour-promoting agent in lung. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilja, A.; Nordborg, C.; Brun, A.; Salford, L.G.; Aman, P. Expression of the IL-6 family cytokines in human brain tumors. Int. J. Oncol. 2001, 19, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurluler, E.; Tumay, L.V.; Guner, O.S.; Kucukmetin, N.T.; Hizli, B.; Zorluoglu, A. Oncostatin-M as a novel biomarker in colon cancer patients and its association with clinicopathologic variables. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 2042–2047. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koskela, K.; Pelliniemi, T.T.; Rajamäki, A.; Pulkki, K.; Remes, K. Serum oncostatin M in multiple myeloma: Impact on disease severity and prognosis. Eur. J. Haematol. 2000, 65, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, C.; Perales, S.; Alejandre, M.J.; Iglesias, J.; Palomino, R.J.; Martin, M.; Caba, O.; Prados, J.C.; Aránega, A.; Delgado, J.R.; et al. Serum cytokine profile in patients with pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2014, 43, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewangan, J.; Srivastava, S.; Rath, S.K. Salinomycin: A new paradigm in cancer therapy. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Honda, M.; Nio, K.; Nakamoto, Y.; Takamura, H.; Tani, T.; Zen, Y.; Kaneko, S. Oncostatin m renders epithelial cell adhesion molecule-positive liver cancer stem cells sensitive to 5-Fluorouracil by inducing hepatocytic differentiation. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 4687–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamboa, C.M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Kalemba, K.; Wondisford, F.E.; Sabaawy, H.E. Optimized 3D Culture of Hepatic Cells for Liver Organoid Metabolic Assays. Cells 2021, 10, 3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, S.; Haan, C.; Behrmann, I. Oncostatin M up-regulates the ER chaperone Grp78/BiP in liver cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 2066–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holub, M.C.; Hegyesi, H.; Igaz, P.; Polgár, A.; Toth, S.; Falus, A. Soluble interleukin-6 receptor enhanced by oncostatin M induces major changes in gene expression profile of human hepatoma cells. Immunol. Lett. 2002, 82, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatting, M.; Spannbauer, M.; Peng, J.; Al Masaoudi, M.; Sellge, G.; Nevzorova, Y.A.; Gassler, N.; Liedtke, C.; Cubero, F.J.; Trautwein, C. Lack of gp130 expression in hepatocytes attenuates tumor progression in the DEN model. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smigiel, J.M.; Parameswaran, N.; Jackson, M.W. Potent EMT and CSC Phenotypes Are Induced By Oncostatin-M in Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.C.; Yeh, C.T.; Lin, K.H. Cancer Stem Cell Functions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Comprehensive Therapeutic Strategies. Cells 2020, 9, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaks, V.; Kong, N.; Werb, Z. The cancer stem cell niche: How essential is the niche in regulating stemness of tumor cells? Cell Stem Cell 2015, 16, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junk, D.J.; Bryson, B.L.; Smigiel, J.M.; Parameswaran, N.; Bartel, C.A.; Jackson, M.W. Oncostatin M promotes cancer cell plasticity through cooperative STAT3-SMAD3 signaling. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4001–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawara, K.; Bolin, C.; Koncinsky, J.; Kadaba, S.; Covert, H.; Sutherland, C.; Bond, L.; Kronz, J.; Garbow, J.R.; Jorcyk, C.L. OSM potentiates preintravasation events, increases CTC counts, and promotes breast cancer metastasis to the lung. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichy, J.; Pure, E. Oncostatin M and transforming growth factor-beta 1 induce post-translational modification and hyaluronan binding to CD44 in lung-derived epithelial tumor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 18061–18069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Pan, T.; Chang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Oncostatin M receptor, positively regulated by SP1, promotes gastric cancer growth and metastasis upon treatment with Oncostatin M. Gastric Cancer 2019, 22, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffarel, M.M.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Araujo, A.M.; Bauer, J.; Scarpini, C.G.; Coleman, N. Tissue transglutaminase mediates the pro-malignant effects of oncostatin M receptor over-expression in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2013, 231, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, V.; Migliavacca, M.; Bazan, V.; Macaluso, M.; Buscemi, M.; Gebbia, N.; Russo, A. STAT proteins: From normal control of cellular events to tumorigenesis. J. Cell Physiol. 2003, 197, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winder, D.M.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Muralidhar, B.; Bauer, J.; English, W.R.; Zhang, X.; Karagavriilidou, K.; Roberts, I.; Pett, M.R.; Murphy, G.; et al. Overexpression of the oncostatin M receptor in cervical squamous cell carcinoma cells is associated with a pro-angiogenic phenotype and increased cell motility and invasiveness. J. Pathol. 2011, 225, 448–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossey, S.L.; Bear, M.D.; Kisseberth, W.C.; Pennell, M.; London, C.A. Oncostatin M promotes STAT3 activation, VEGF production, and invasion in osteosarcoma cell lines. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, S.; Kappler, V.; Kaczor, J.; Flügel, D.; Rolvering, C.; Kato, N.; Kietzmann, T.; Behrmann, I.; Haan, C. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is up-regulated by oncostatin M and participates in oncostatin M signaling. Hepatology 2009, 50, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, M.K.; Kim, H.S.; Chung, Y.H. Clinical aspects of tumor necrosis factor-α signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 2799–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henkel, J.; Gärtner, D.; Dorn, C.; Hellerbrand, C.; Schanze, N.; Elz, S.R.; Püschel, G.P. Oncostatin M produced in Kupffer cells in response to PGE2: Possible contributor to hepatic insulin resistance and steatosis. Lab. Invest. 2011, 91, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Shen, H.; Yu, H.; Fu, J.; Dong, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H. F4/80. Molecules 2021, 26, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foglia, B.; Sutti, S.; Pedicini, D.; Cannito, S.; Bocca, C.; Maggiora, M.; Bevacqua, M.R.; Rosso, C.; Bugianesi, E.; Albano, E.; et al. Oncostatin M, A Profibrogenic Mediator Overexpressed in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Stimulates Migration of Hepatic Myofibroblasts. Cells 2019, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Seki, E. Inflammation and Liver Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Semin Liver Dis. 2019, 39, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, D.; Rizvi, S.; Razumilava, N.; Bronk, S.F.; Davila, J.I.; Champion, M.D.; Borad, M.J.; Bezerra, J.A.; Chen, X.; Gores, G.J. IL-33 facilitates oncogene-induced cholangiocarcinoma in mice by an interleukin-6-sensitive mechanism. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1627–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Razumilava, N.; Gores, G.J.; Walters, S.; Mizuochi, T.; Mourya, R.; Bessho, K.; Wang, Y.H.; Glaser, S.S.; Shivakumar, P.; et al. Biliary repair and carcinogenesis are mediated by IL-33-dependent cholangiocyte proliferation. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3241–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, E.H.; Bendit, M.; McAleer, D.; Liu, F.; Feeney, M.; Brett, S.; Zamuner, S.; Campanile, A.; Toso, J. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of an anti- oncostatin M monoclonal antibody in rheumatoid arthritis: Results from phase II randomized, placebo-controlled trials. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kucia-Tran, J.A.; Tulkki, V.; Scarpini, C.G.; Smith, S.; Wallberg, M.; Paez-Ribes, M.; Araujo, A.M.; Botthoff, J.; Feeney, M.; Hughes, K.; et al. Anti-oncostatin M antibody inhibits the pro-malignant effects of oncostatin M receptor overexpression in squamous cell carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2018, 244, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswanadhapalli, S.; Dileep, K.V.; Zhang, K.Y.J.; Nair, H.B.; Vadlamudi, R.K. Targeting LIF/LIFR signaling in cancer. Genes Dis. 2022, 9, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Liu, T.; Wu, J.C.; Luo, S.Z.; Chen, R.; Lu, L.G.; Xu, M.Y. STAT3 aggravates TGF-β1-induced hepatic epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and migration. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 98, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Lin, H.; Wu, G.; Zhu, M.; Li, M. IL-6/STAT3 Is a Promising Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 760971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Song, Y.; Shakoor, K.; Yi, W.; Peng, C.; Liu, S. Insights into the role of STAT3 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
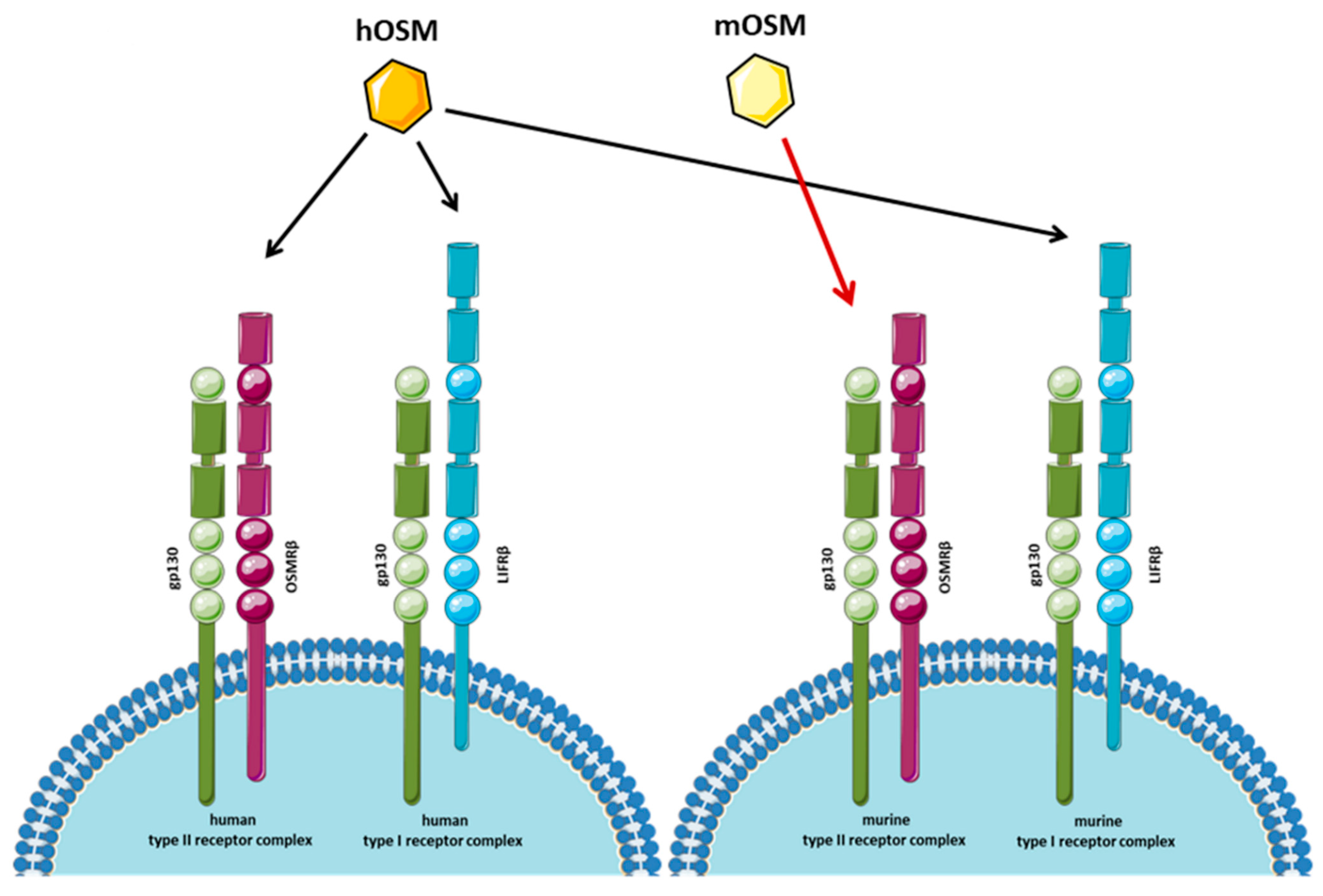
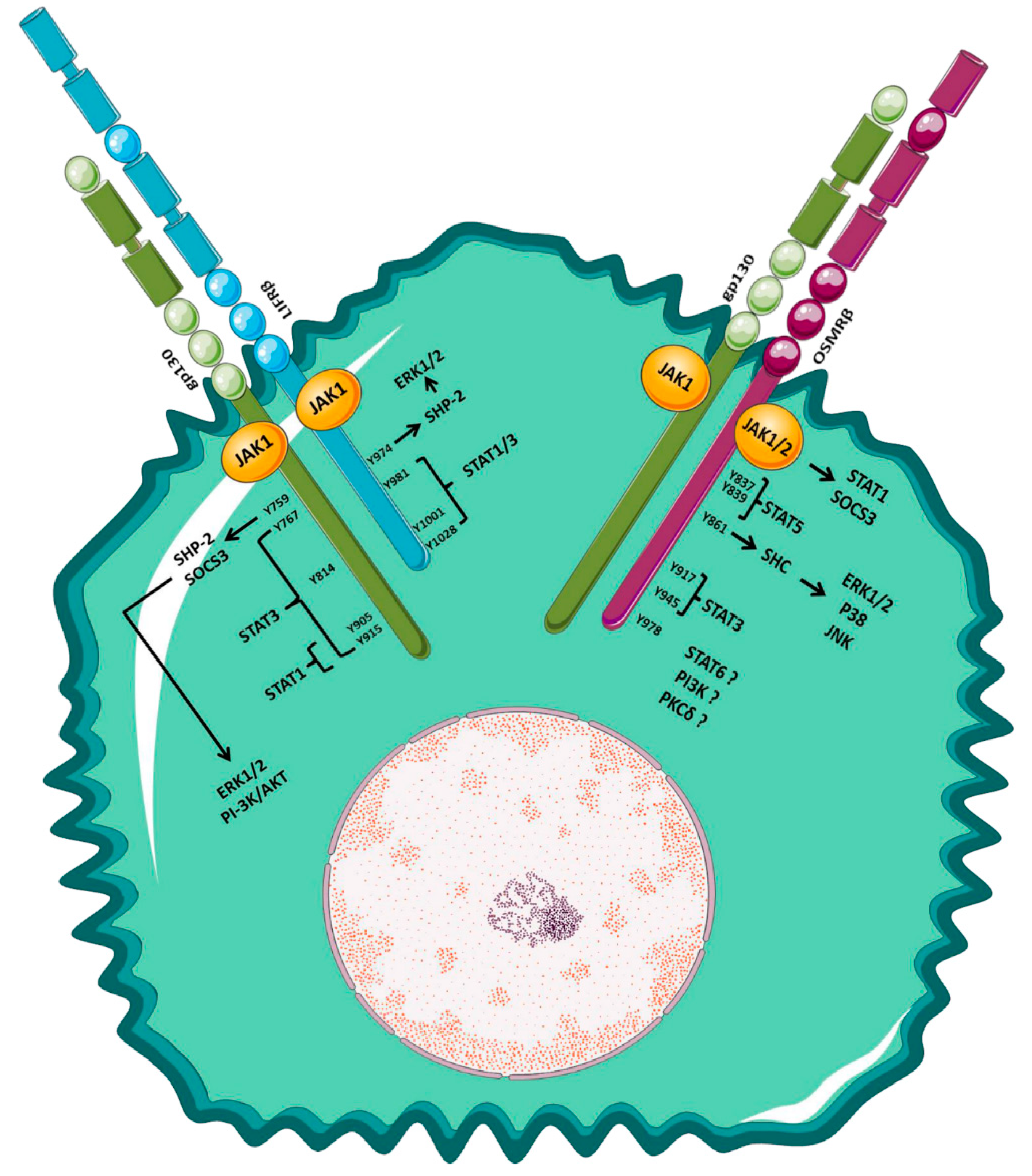
| Tumor Type | Inflammation | Cancer Cell Proliferation/Tumor Growth | CSCs’ Features and EMT | Angiogenesis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCC | Induces macrophage recruitment and TNFα secretion [93] | Decreases proliferation and increases apoptosis in SMMC-7721 and CD133+ HepG2 cells [67]. Induces Grp78 expression in HepG2 and Huh-7 cells [78]. Induces cell proliferation in EpCAM+ HCC cells [75]. | Induces a decrease of stemness markers in EpCAM+ HuH1 and HuH7 cells. Increases the chemosensitivity of EpCAM+ HCC cells in xenograft mice [76]. Induces the expression of CSCs’ differentiation-related markers in CD133+ HepG2 cells and inhibits cell invasion [75]. | Induces HIF1 upregulation and VEGF gene overexpression. Xenograft mice injected with OSM-overexpressing HepG2 cells show a more extensive tumor vascularization [59]. |
| CCA | Secreted by co-cultured TANs and TAMs [60]. | Promotes proliferation in iCCA cells via STAT3 [60]. | Induces iCCA cell invasion via STAT3. Xenograft mice co-injected with TANs, TAMs, and iCCA cells show less metastasis when STAT3 is knocked down in iCCA cells [60]. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caligiuri, A.; Gitto, S.; Lori, G.; Marra, F.; Parola, M.; Cannito, S.; Gentilini, A. Oncostatin M: From Intracellular Signaling to Therapeutic Targets in Liver Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 4211. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174211
Caligiuri A, Gitto S, Lori G, Marra F, Parola M, Cannito S, Gentilini A. Oncostatin M: From Intracellular Signaling to Therapeutic Targets in Liver Cancer. Cancers. 2022; 14(17):4211. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174211
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaligiuri, Alessandra, Stefano Gitto, Giulia Lori, Fabio Marra, Maurizio Parola, Stefania Cannito, and Alessandra Gentilini. 2022. "Oncostatin M: From Intracellular Signaling to Therapeutic Targets in Liver Cancer" Cancers 14, no. 17: 4211. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174211
APA StyleCaligiuri, A., Gitto, S., Lori, G., Marra, F., Parola, M., Cannito, S., & Gentilini, A. (2022). Oncostatin M: From Intracellular Signaling to Therapeutic Targets in Liver Cancer. Cancers, 14(17), 4211. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174211









