Immunotherapy for Aggressive and Metastatic Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumors (PitNETs): State-of-the Art
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
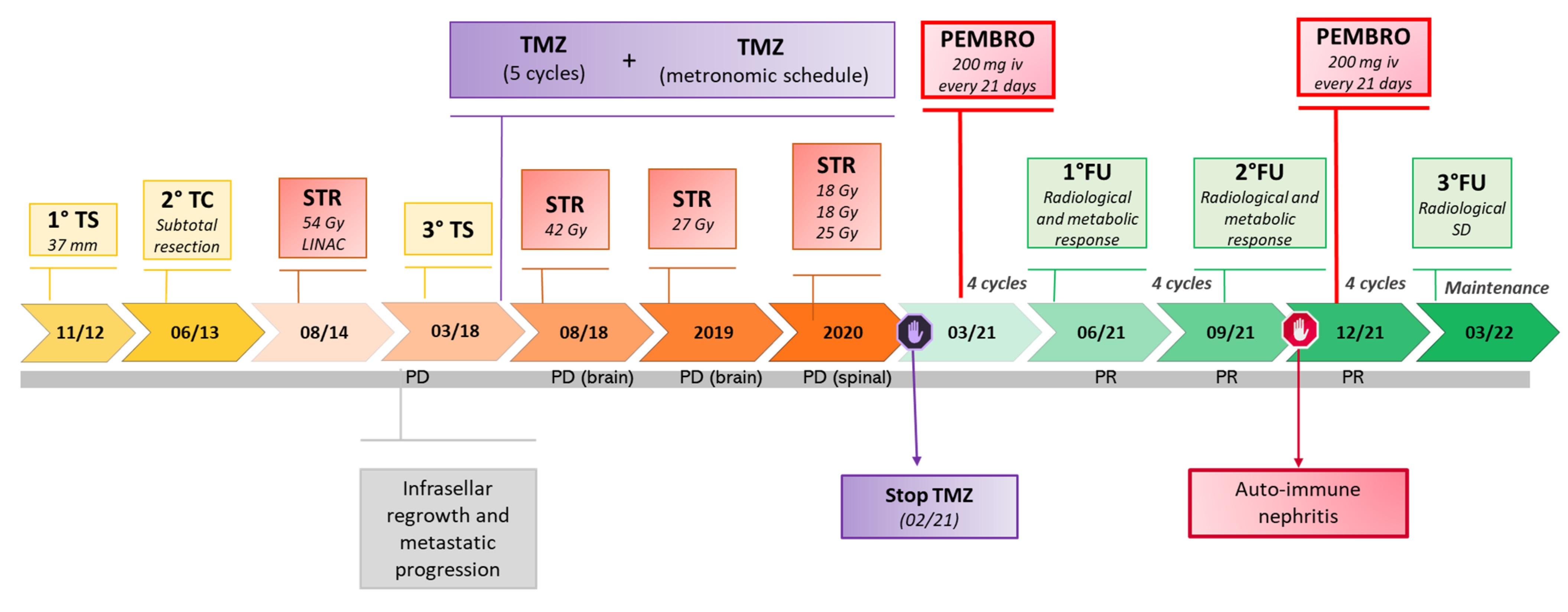
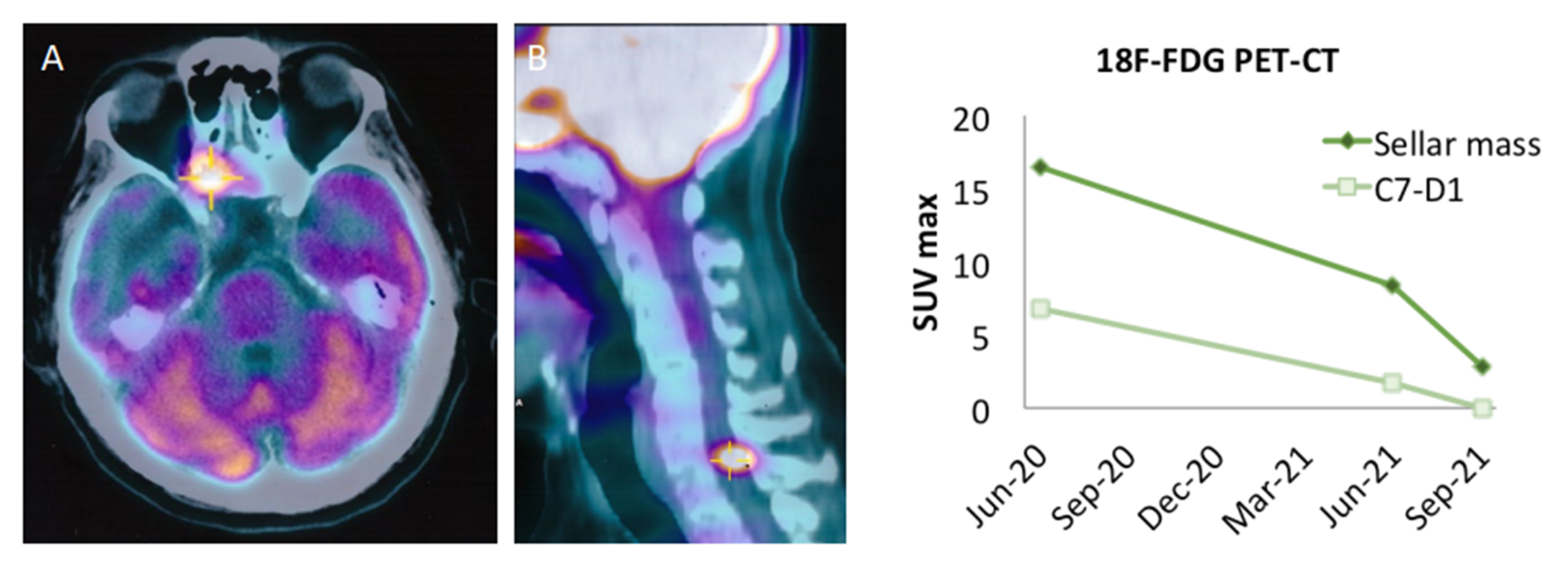
2. Clinical Observation: Efficacy of Pembrolizumab in A Metastatic Non-Functioning PitNET
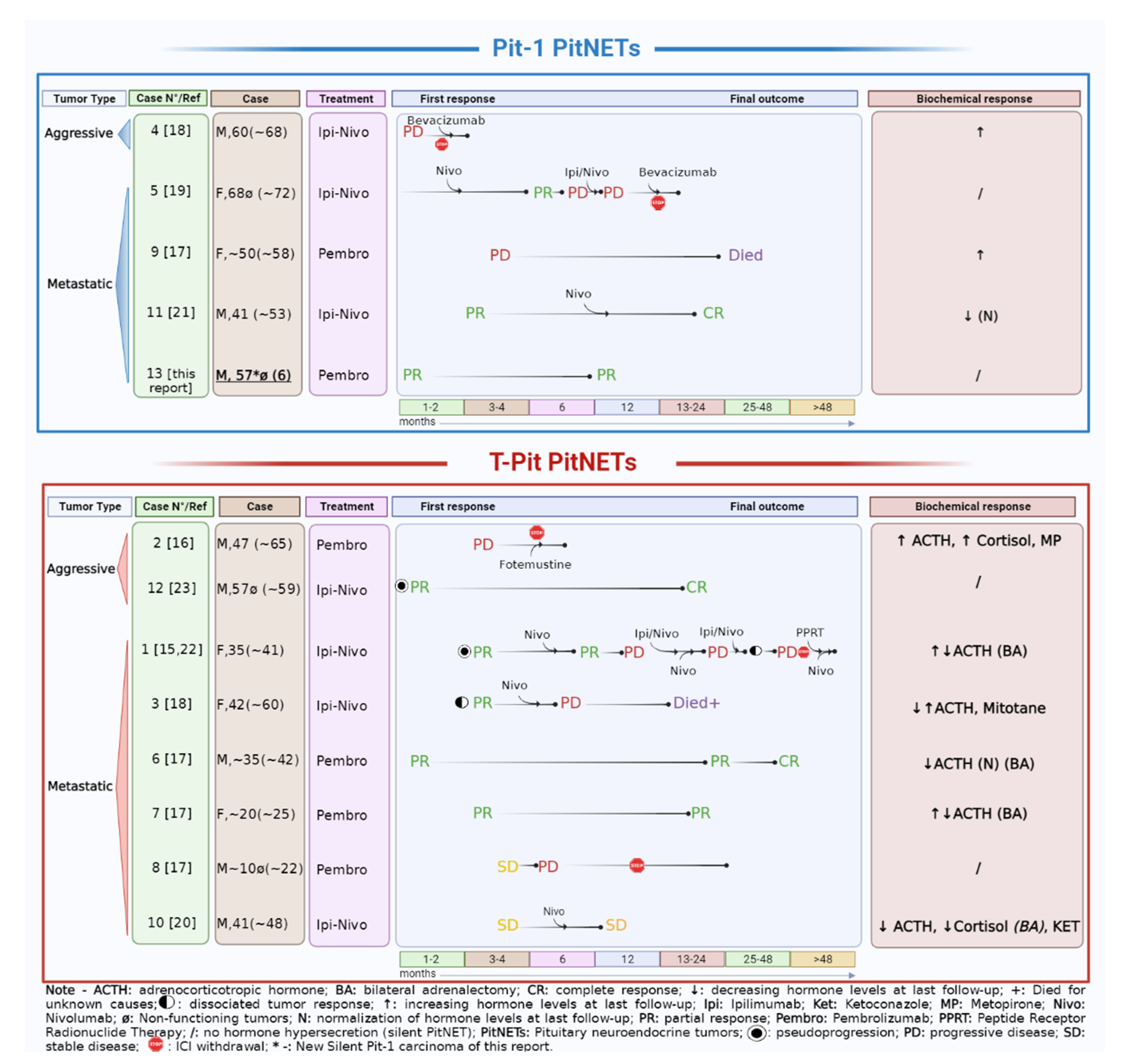
3. Analysis of PitNETs Response to ICIs according to Their Functional and Aggressive/Metastatic Behavior
4. Molecular Characterization of PitNETs and Potential Relationship with the Clinical Response to ICIs
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raverot, G.; Ilie, M.D.; Lasolle, H.; Amodru, V.; Trouillas, J.; Castinetti, F.; Brue, T. Aggressive Pituitary Tumours and Pituitary Carcinomas. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormack, A.; Dekkers, O.M.; Petersenn, S.; Popovic, V.; Trouillas, J.; Raverot, G.; Burman, P.; ESE survey collaborators. Treatment of Aggressive Pituitary Tumours and Carcinomas: Results of a European Society of Endocrinology (ESE) Survey 2016. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C. A Decade of Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidel, J.A.; Otsuka, A.; Kabashima, K. Anti-PD-1 and Anti-CTLA-4 Therapies in Cancer: Mechanisms of Action, Efficacy, and Limitations. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardoll, D.M. The Blockade of Immune Checkpoints in Cancer Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilky, B.A. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: The Linchpins of Modern Immunotherapy. Immunol. Rev. 2019, 290, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kockx, M.M.; McCleland, M.; Koeppen, H. Microenvironmental Regulation of Tumour Immunity and Response to Immunotherapy. J. Pathol. 2021, 254, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H. The Role of DNA Mismatch Repair in Immunotherapy of Human Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 2821–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Horn, M.; Magee, G.; Hodges, K.; Evers, M.; Arnold, S.; Anthony, L. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Single Institution Experience with Review of Literature. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 8801–8809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-Toubah, T.; Cives, M.; Strosberg, J. Novel Immunotherapy Strategies for Treatment of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanciulli, G.; Di Molfetta, S.; Dotto, A.; Florio, T.; Feola, T.; Colao, A.; Faggiano, A.; NIKE Group; Albertelli, M.; Altieri, B.; et al. Commentary: Case Report: Abdominal Lymph Node Metastases of Parathyroid Carcinoma: Diagnostic Workup, Molecular Diagnosis, and Clinical Management. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 700806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Molfetta, S.; Dotto, A.; Fanciulli, G.; Florio, T.; Feola, T.; Colao, A.; Faggiano, A. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: New Weapons Against Medullary Thyroid Cancer? Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 667784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanciulli, G.; Di Molfetta, S.; Dotto, A.; Florio, T.; Feola, T.; Rubino, M.; de Cicco, F.; Colao, A.; Faggiano, A.; Nike Group, null. Emerging Therapies in Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in the Starting Blocks. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 10, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Molfetta, S.; Feola, T.; Fanciulli, G.; Florio, T.; Colao, A.; Faggiano, A.; Nike Group, null. Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Lung Carcinoids with Aggressive Behaviour: One More Arrow in Our Quiver? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.L.; Jonsson, P.; Tabar, V.; Yang, T.J.; Cuaron, J.; Beal, K.; Cohen, M.; Postow, M.; Rosenblum, M.; Shia, J.; et al. Marked Response of a Hypermutated ACTH-Secreting Pituitary Carcinoma to Ipilimumab and Nivolumab. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 3925–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caccese, M.; Barbot, M.; Ceccato, F.; Padovan, M.; Gardiman, M.P.; Fassan, M.; Denaro, L.; Emanuelli, E.; D’Avella, D.; Scaroni, C.; et al. Rapid Disease Progression in Patient with Mismatch-Repair Deficiency Pituitary ACTH-Secreting Adenoma Treated with Checkpoint Inhibitor Pembrolizumab. Anticancer Drugs 2020, 31, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majd, N.; Waguespack, S.G.; Janku, F.; Fu, S.; Penas-Prado, M.; Xu, M.; Alshawa, A.; Kamiya-Matsuoka, C.; Raza, S.M.; McCutcheon, I.E.; et al. Efficacy of Pembrolizumab in Patients with Pituitary Carcinoma: Report of Four Cases from a Phase II Study. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duhamel, C.; Ilie, M.D.; Salle, H.; Nassouri, A.S.; Gaillard, S.; Deluche, E.; Assaker, R.; Mortier, L.; Cortet, C.; Raverot, G. Immunotherapy in Corticotroph and Lactotroph Aggressive Tumors and Carcinomas: Two Case Reports and a Review of the Literature. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, L.S.; Sim, H.-W.; McCormack, A.I. Case Report: A Case of Pituitary Carcinoma Treated With Sequential Dual Immunotherapy and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibition Therapy. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 576027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sol, B.; de Filette, J.M.K.; Awada, G.; Raeymaeckers, S.; Aspeslagh, S.; Andreescu, C.E.; Neyns, B.; Velkeniers, B. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy for ACTH-Secreting Pituitary Carcinoma: A New Emerging Treatment? Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 184, K1–K5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goichot, B.; Taquet, M.-C.; Baltzinger, P.; Baloglu, S.; Gravaud, M.; Malouf, G.G.; Noël, G.; Imperiale, A. Should Pituitary Carcinoma Be Treated Using a NET-like Approach? A Case of Complete Remission of a Metastatic Malignant Prolactinoma with Multimodal Therapy Including Immunotherapy. Clin. Endocrinol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.L.; Tabar, V.; Young, R.J.; Cohen, M.; Cuaron, J.; Yang, T.J.; Rosenblum, M.; Rudneva, V.A.; Geer, E.B.; Bodei, L. Synergism of Checkpoint Inhibitors and Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy in the Treatment of Pituitary Carcinoma. J. Endocr. Soc. 2021, 5, bvab133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Manzoor, S.; Rothman, Y.; Hagen, M.; Pater, L.; Golnik, K.; Mahammedi, A.; Lin, A.L.; Bhabhra, R.; Forbes, J.A.; et al. Complete Response of a Patient With a Mismatch Repair Deficient Aggressive Pituitary Adenoma to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy: A Case Report. Neurosurgery 2022, 91, e51–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzoubi, H.; Minasi, S.; Gianno, F.; Antonelli, M.; Belardinilli, F.; Giangaspero, F.; Jaffrain-Rea, M.-L.; Buttarelli, F.R. Alternative Lengthening of Telomeres (ALT) and Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Promoter Methylation in Recurrent Adult and Primary Pediatric Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumors. Endocr. Pathol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, A.M.; Kato, S.; Bazhenova, L.; Patel, S.P.; Frampton, G.M.; Miller, V.; Stephens, P.J.; Daniels, G.A.; Kurzrock, R. Tumor Mutational Burden as an Independent Predictor of Response to Immunotherapy in Diverse Cancers. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 2598–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raverot, G.; Burman, P.; McCormack, A.; Heaney, A.; Petersenn, S.; Popovic, V.; Trouillas, J.; Dekkers, O.M. European Society of Endocrinology European Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Aggressive Pituitary Tumours and Carcinomas. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, G1–G24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouillas, J.; Jaffrain-Rea, M.-L.; Vasiljevic, A.; Dekkers, O.; Popovic, V.; Wierinckx, A.; McCormack, A.; Petersenn, S.; Burman, P.; Raverot, G.; et al. Are Aggressive Pituitary Tumors and Carcinomas Two Sides of the Same Coin? Pathologists Reply to Clinician’s Questions. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 21, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Gao, Q.; Han, A.; Zhu, H.; Yu, J. The Potential Mechanism, Recognition and Clinical Significance of Tumor Pseudoprogression after Immunotherapy. Cancer Biol. Med. 2019, 16, 655–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, L.; Bogaerts, J.; Perrone, A.; Ford, R.; Schwartz, L.H.; Mandrekar, S.; Lin, N.U.; Litière, S.; Dancey, J.; Chen, A.; et al. IRECIST: Guidelines for Response Criteria for Use in Trials Testing Immunotherapeutics. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e143–e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodi, F.S.; Ballinger, M.; Lyons, B.; Soria, J.-C.; Nishino, M.; Tabernero, J.; Powles, T.; Smith, D.; Hoos, A.; McKenna, C.; et al. Immune-Modified Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors (ImRECIST): Refining Guidelines to Assess the Clinical Benefit of Cancer Immunotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persigehl, T.; Lennartz, S.; Schwartz, L.H. IRECIST: How to Do It. Cancer Imaging 2020, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibney, G.T.; Weiner, L.M.; Atkins, M.B. Predictive Biomarkers for Checkpoint Inhibitor-Based Immunotherapy. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e542–e551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Bi, W.L.; Greenwald, N.F.; Du, Z.; Agar, N.Y.R.; Kaiser, U.B.; Woodmansee, W.W.; Reardon, D.A.; Freeman, G.J.; Fecci, P.E.; et al. Increased Expression of Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Human Pituitary Tumors. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 76565–76576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.-F.; Wang, T.-J.; Yang, Y.-K.; Yao, K.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.M.; Yan, C.-X. The Expression Profile of PD-L1 and CD8+ Lymphocyte in Pituitary Adenomas Indicating for Immunotherapy. J. Neurooncol. 2018, 139, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suteau, V.; Collin, A.; Menei, P.; Rodien, P.; Rousselet, M.-C.; Briet, C. Expression of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Human Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumor. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 2053–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchini, J.; Sioson, L.; Clarkson, A.; Sheen, A.; Gill, A.J. PD-L1 Is Preferentially Expressed in PIT-1 Positive Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumours. Endocr. Pathol. 2021, 32, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, D.P.; Levine, K.K.; Betensky, R.A.; Codd, P.J.; Romany, C.A.; Reavie, L.B.; Batchelor, T.T.; Futreal, P.A.; Stratton, M.R.; Curry, W.T.; et al. Loss of the Mismatch Repair Protein MSH6 in Human Glioblastomas Is Associated with Tumor Progression during Temozolomide Treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2038–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, F.A.; Veldwijk, M.R.; Herskind, C.; Wenz, F. Radiotherapy, Tumor Mutational Burden, and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Time to Do the Math. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2018, 194, 873–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-Q.; Adam, B.; Jack, A.S.; Lam, A.; Broad, R.W.; Chik, C.L. Immune Cell Infiltrates in Pituitary Adenomas: More Macrophages in Larger Adenomas and More T Cells in Growth Hormone Adenomas. Endocr. Pathol. 2015, 26, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Tamura, R.; Tamura, H.; Mase, T.; Kosugi, K.; Morimoto, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Toda, M. Analysis of Tumor Angiogenesis and Immune Microenvironment in Non-Functional Pituitary Endocrine Tumors. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagnik, G.; Rutowski, M.J.; Shah, S.S.; Aghi, M.K. Stratifying Nonfunctional Pituitary Adenomas into Two Groups Distinguished by Macrophage Subtypes. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 2212–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.R.; Martinez, A.; Stahl, J.M.; Logan, S.J.; Perricone, A.J.; Ferris, M.J.; Buchwald, Z.S.; Chowdhary, M.; Delman, K.A.; Monson, D.K.; et al. Increase in PD-L1 Expression after Pre-Operative Radiotherapy for Soft Tissue Sarcoma. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1442168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minniti, G.; Paolini, S.; Jaffrain-Rea, M.L.; Isidori, A.; Scaringi, C.; Russo, I.; Osti, M.F.; Cavallo, L.; Esposito, V. Stereotactic Reirradiation with Temozolomide in Patients with Recurrent Aggressive Pituitary Tumors and Pituitary Carcinomas. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 149, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, M.; Chi, Y.; Wang, Z. The Adverse Events Associated with Combination Immunotherapy in Cancers: Challenges and Chances. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 16, e154–e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldea, M.; Orillard, E.; Mansi, L.; Marabelle, A.; Scotte, F.; Lambotte, O.; Michot, J.-M. How to Manage Patients with Corticosteroids in Oncology in the Era of Immunotherapy? Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 141, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caturegli, P.; Di Dalmazi, G.; Lombardi, M.; Grosso, F.; Larman, H.B.; Larman, T.; Taverna, G.; Cosottini, M.; Lupi, I. Hypophysitis Secondary to Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-Associated Protein 4 Blockade: Insights into Pathogenesis from an Autopsy Series. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 3225–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.P.; Othus, M.; Chae, Y.K.; Giles, F.J.; Hansel, D.E.; Singh, P.P.; Fontaine, A.; Shah, M.H.; Kasi, A.; Baghdadi, T.A.; et al. A Phase II Basket Trial of Dual Anti-CTLA-4 and Anti-PD-1 Blockade in Rare Tumors (DART SWOG 1609) in Patients with Nonpancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ref | Sex, Age (years), Case Number | Histotype, Functional Status | Metastases | Previous Treatments * | ICI Drugs (Schedule) | Proliferative Markers | Potential Predictive Markers/Genetics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lin A.L., 2018 [15] | F, 35, Case 1 | Corticotroph metastatic PitNET, CD/Nelson’s syndrome | Liver | NS (4 times); RT (2 times sellar); Pas, Ket, Cab/Ket, Mif, Met; BA; CAPTEM (4 + 2 cycles); Systemic chemotherapy (2 cycles) *. | Ipi (3 mg/kg) + Nivo (1 mg/kg) every 3 weeks (5 cycles). Maintenance with Nivo (6 months). | Metastasis: Ki-67 up to 50% | Primary: No variant of interest (°) MSH6 IHC pos. no MSH6 mutation Metastasis: MGMT IHC pos. PDL1 < 1% MMRd (MSH6 IHC neg. MSH6 mutation) TMB: 93 mut/Mb (high) Both: No USP8 mutation. |
| Left adnexa | RT (sellar) Metastasis surgery | Ipi + Nivo (4 cycles). Maintenance with Nivo. | N/A | TMB: 3.5 m/Mb (low) | |||
| 2021 [22] | Brain (1) Brain (2) | RT (metastasis) RT (metastasis) PPRT | Ipi + Nivo (4 cycles). Nivo (6 months). | N/A | N/A | ||
| Caccese M, 2019 [16] | M, 47 Case 2 | Corticotroph PitNET, silent→CD | / | -NS (3 times); -RT; -Pas; -TMZ (2 years) | Pembro (200 mg) (4 cycles). | Ki-67 3%, p53 pos (NS1/2) Ki-67 > 3%, p53 pos (NS 3) | PDL-1 IHC 0%. MMRd (MSH2, MSH6 IHC neg) |
| Duhamel C, 2020 [18] | F, 42 Case 3 | Corticotroph metastatic PitNET, CD | Liver (5), suspected bone | NS (3 times); RT (3 sellar); Pas, Cab, Ket, Met, Mitotane; TMZ (10 + 3 cycles); Hydroxyurea (3 months). | Ipi (1 mg/kg) + Nivo (3 mg/kg) every 3 weeks (5 cycles). Maintenance with Nivo (every 2 weeks for 12 cycles). | Primary: Ki-67 2%, M = 0, p53 neg (NS 1); Ki-67 5%, M = 5/10 HPFs, p53 2% (NS 3). Liver metastasis: Ki-67 10%, p53 7%. | Liver metastasis: PDL-1 IHC neg. |
| M, 60 Case 4 | Aggressive Lactotroph PitNET | / | NS (3 times); RT; Cab, Pas; TMZ (6 cycles). | Ipi (1 mg/kg) + Nivo (3 mg/kg) every 3 weeks (2 cycles)—(withdrawal for severe toxicity and PD). | Ki-67 10%, M = 5/10 HPFs (NS 1); Ki-67 10–11%, M = 1/10 HPFs (NS 2); Ki-67 25%, M > 20/10 HPFs (NS 3). | MGMT promoter partially methylated 9–12%; MMS. TMB: 1 mut/Mb (low) Single gene abnormalities reported (°°); | |
| Lamb L.S, 2020 [19] | F, 72 Case 5 | Lactotroph (Pit-1+, PRL+) metastatic PitNET, silent | Dural/spinal | NS (3 times); RT (2 times sellar + metastasis); Metastasis surgery; TMZ (3 cycles). | Ipi (3 mg/kg) + Nivo (1 mg/kg) every 3 weeks (2 cycles). Nivo (3 mg/kg, twice weekly—17 cycles). Ipi + Nivo (4 cycles) − (withdrawal for severe toxicity and PD). | Primary: Ki-67 10%, M = 5/10 HPFs (NS1) Metastasis: Ki-67 20%. | Primary (?): PDL-1 IHC < 1%; “MMR proficient”; TMB: 6.8 mut/Mb (intermediate). Metastasis: MGMT IHC pos. |
| Majd N, 2020 [17] | M, mid-30 s Case 6 | Corticotroph metastatic PitNET, CD | Liver, retroperitoneal lymphnodes, SNC | NS (3 times); RT (3 times sellar + metastases); BA; TMZ (16 + 8 cycles); CAPTEM (1 + 4 cycles); Local treatment of metastasis including surgery; FGFR inhibitor (2 cycles); CCNU + Bvz (1 cycle) | Pembro (200 mg) for 29 cycles. | N/A | Orbital localization MMRd.: “Hypermutated” phenotype, including MSH2, MSH6 and FGFR4 mutations. Liver metastasis (IHC): PDL-1 neg; TIL score 2 |
| F, early 20 Case 7 | Corticotroph metastatic PitNET, CD | SNC, Bone, liver, pleura | NS (2 times); RT (sellar); BA; Pas; TMZ (7 cycles); CAPTEM (7 cycles) | Pembro (200 mg) for 15 cycles. | N/A | Primary before TMZ: PDL-1 IHC neg; MSS. | |
| M, late teens Case 8 | Corticotroph metastatic PitNET, silent (ACTH+) | Dural, bone | NS (4 times); RT (2 times sellar + metastases); TMZ (12 + 7 + 2 cycles); IDO1 pathway inhibitor (11 cycles). | Pembro (200 mg) for 6 cycles. | N/A | Primary: PDL-1 IHC neg. MSS. TMB: “low” TIL negative. | |
| F, early 50 Case 9 | Lactotroph metastatic PitNET | Bone, liver | NS; RT (sellar + metastases); Cab; Systemic chemotherapy (1 cycle) **; TMZ (12 + 2 cycles); CAPTEM (2 cycles). | Pembro (200 mg) for 6 cycles. | N/A | Tumor (Primary?): PDL-1 IHC neg; TIL score 2. Metastases: No mutation (bone) MSS (liver); TMB: “intermediate” (liver). | |
| Sol B, 2021 [20] | 41, M Case 10 | Corticotroph metastatic PitNET, CD | SNC and spine | NS (2 times); RT (2 times sellar); Ket, Pas, Cab; BA; TMZ (3 + 9 cycles). | Ipi (3 mg/kg) + Nivo (1 mg/kg) every 3 weeks (4 cycles). Maintenance with Nivo (240 mg) every 2 weeks. | Ki-67 < 1%, p53 pos (1+) (NS 1) | N/A |
| Goichot B, 2021 [21] | 41, M Case 11 | PRL-secreting metastatic PitNET | Lung, pancreas, SNC | NS (2 times); RT (3 sellar + metastases); Cab; TMZ (43 cycles); Metastases surgery (2). | Ipi (3 mg/kg) + Nivo (1 mg/kg) every 3 weeks (4 cycles). Maintenance with Nivo every 2 weeks. | Primary: Ki-67 40% (NS 1). Lung metastasis: Ki-67 40–50%. | PDL-1 IHC 95% (sphenoid). |
| Shah, 2022 [23] | 57, M Case 12 | Sparsely granulated corticotroph aggressive PitNET–No CD (ACTH+) | / | NS; RT (sellar); TMZ (3 cycles). | Ipi (3 mg/kg)+ Nivo (1 mg/kg) every 3 weeks for 4 cycles. Maintenance Nivo (480 mg every 4 weeks) for 10 cycles. | Focal Ki-67 75–80%, moderate p53 pos. (NS1) | MGMT promoter methylation; MMRd: MLH1 and PMS2 IHC neg; MSH2 and MSH6 IHC pos; MLH1 and TP53 mutations; TMB: 8.8 mut/Mb (intermediate) |
| Feola, 2022 [this report] | 57, M Case 13 | Pit-1 non-functioning metastatic PitNET (Hormone negative) | SNC and dural | NS (3 times); RT (2 times sellar + metastases); TMZ (5 cycles+ metronomic schedule). | Pembro (200 mg) every 21 days. | Ki-67 10%, p53 < 5% (NS 1/2); Ki67 20%, p53 10%, M = 1/10 HPFs (NS 3). | Primary: MGMT promoter unmethylated; PDL1 IHC pos (95%); MSH2/6 IHC pos; CD68 > CD4 > CD8 IHC pos. TIL 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feola, T.; Carbonara, F.; Verrico, M.; Di Crescenzo, R.M.; Gianno, F.; Colonnese, C.; Arcella, A.; de Alcubierre, D.; Tomao, S.; Esposito, V.; et al. Immunotherapy for Aggressive and Metastatic Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumors (PitNETs): State-of-the Art. Cancers 2022, 14, 4093. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174093
Feola T, Carbonara F, Verrico M, Di Crescenzo RM, Gianno F, Colonnese C, Arcella A, de Alcubierre D, Tomao S, Esposito V, et al. Immunotherapy for Aggressive and Metastatic Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumors (PitNETs): State-of-the Art. Cancers. 2022; 14(17):4093. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174093
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeola, Tiziana, Francesca Carbonara, Monica Verrico, Rosa Maria Di Crescenzo, Francesca Gianno, Claudio Colonnese, Antonietta Arcella, Dario de Alcubierre, Silverio Tomao, Vincenzo Esposito, and et al. 2022. "Immunotherapy for Aggressive and Metastatic Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumors (PitNETs): State-of-the Art" Cancers 14, no. 17: 4093. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174093
APA StyleFeola, T., Carbonara, F., Verrico, M., Di Crescenzo, R. M., Gianno, F., Colonnese, C., Arcella, A., de Alcubierre, D., Tomao, S., Esposito, V., Giangaspero, F., Minniti, G., & Jaffrain-Rea, M.-L. (2022). Immunotherapy for Aggressive and Metastatic Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumors (PitNETs): State-of-the Art. Cancers, 14(17), 4093. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14174093








