P3H4 Promotes Malignant Progression of Lung Adenocarcinoma via Interaction with EGFR
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gene Expression Datasets
2.2. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
2.3. Reverse Transcription-Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.4. Construction of P3H4 RNA Interference Lentiviral Vector
2.5. Western Blotting Analysis
2.6. Cell Proliferation
2.7. Cellular Apoptosis Assay
2.8. Colony Formation Assays
2.9. Wound Healing Assay
2.10. Transwell Assay
2.11. Animal Experiments
2.12. Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Construction
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. P3H4 Showed Increased Expression in LUAD
3.2. The Malignant Progression of LUAD Was Suppressed by P3H4 Knockdown In Vitro
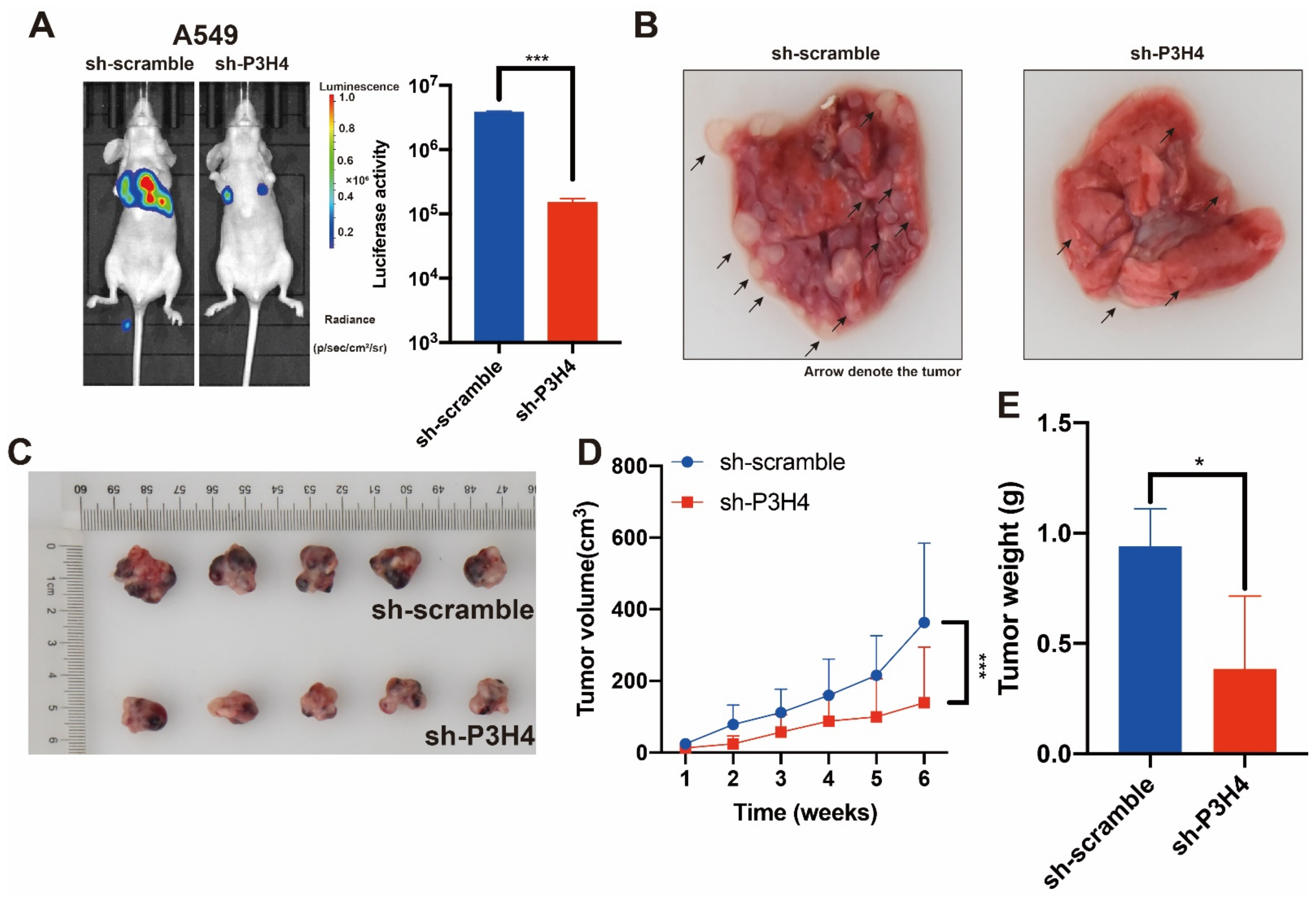
3.3. P3H4 Knockdown Suppressed the Malignant Progression of LUAD In Vivo
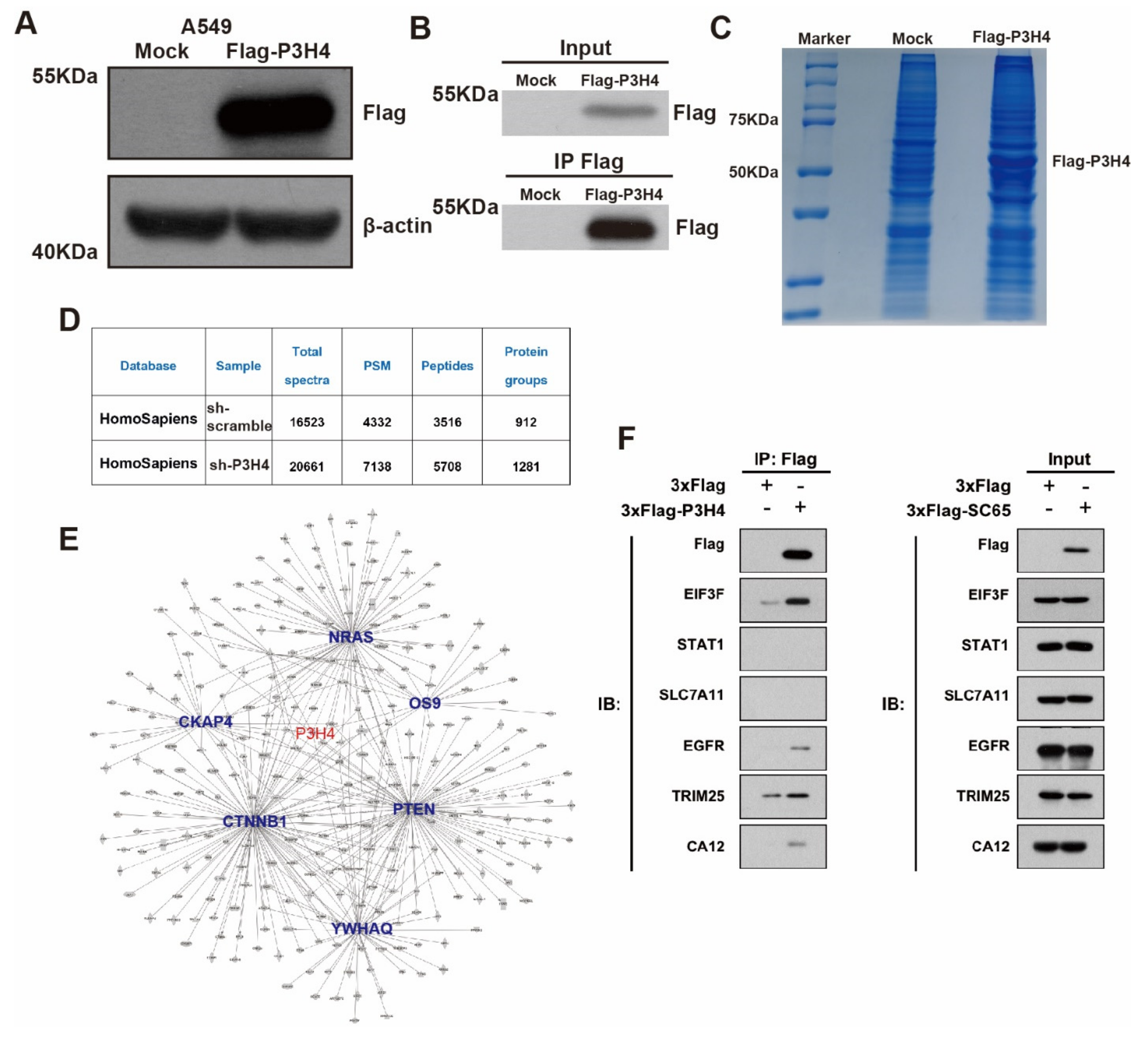
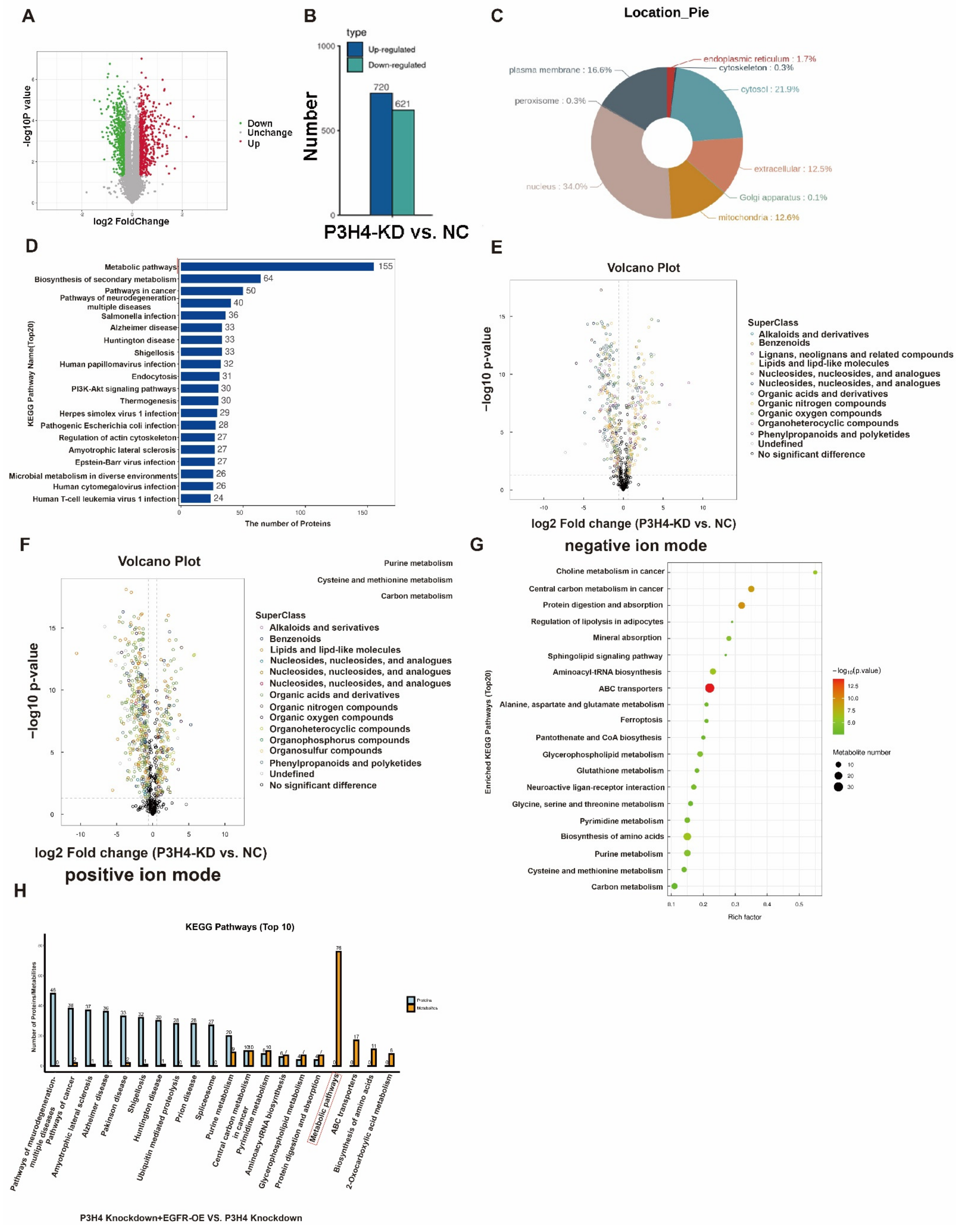
3.4. P3H4 Interacts with EGFR to Promote Malignant LUAD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, A.A.; Solomon, B.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Gainor, J.F.; Heist, R.S. Lung cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duma, N.; Santana-Davila, R.; Molina, J.R. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Epidemiology, Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Yatabe, Y.; Austin, J.H.M.; Beasley, M.B.; Chirieac, L.R.; Dacic, S.; Duhig, E.; Flieder, D.B.; et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Genetic, Clinical and Radiologic Advances Since the 2004 Classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Burke, A.P.; Marx, A.; Nicholson, A.G. Introduction to the 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus, and Heart. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1240–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudkerk, M.; Liu, S.; Heuvelmans, M.A.; Walter, J.E.; Field, J.K. Lung cancer LDCT screening and mortality reduction—Evidence, pitfalls and future perspectives. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.D.; Nogueira, L.; Mariotto, A.B.; Rowland, J.H.; Yabroff, K.R.; Alfano, C.M.; Jemal, A.; Kramer, J.L.; Siegel, R.L. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 363–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarakulasinghe, N.B.; van Zanwijk, N.; Soo, R.A. Molecular targeted therapy in the treatment of advanced stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Respirology 2015, 20, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochs, R.L.; Stein, T.W., Jr.; Chan, E.K.; Ruutu, M.; Tan, E.M. cDNA cloning and characterization of a novel nucleolar protein. Mol. Biol. Cell 1996, 7, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gruenwald, K.; Castagnola, P.; Besio, R.; Dimori, M.; Chen, Y.; Akel, N.S.; Swain, F.L.; Skinner, R.A.; Eyre, D.R.; Gaddy, D.; et al. Sc65 is a novel endoplasmic reticulum protein that regulates bone mass homeostasis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heard, M.E.; Besio, R.; Weis, M.; Rai, J.; Hudson, D.M.; Dimori, M.; Zimmerman, S.M.; Kamykowski, J.A.; Hogue, W.R.; Swain, F.L.; et al. Sc65-Null Mice Provide Evidence for a Novel Endoplasmic Reticulum Complex Regulating Collagen Lysyl Hydroxylation. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Pang, K.; Pang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; He, H.; Zhou, R.; Shi, Z.; Han, C. Knockdown of P3H4 inhibits proliferation and invasion of bladder cancer. Aging 2020, 12, 2156–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dong, Y.; Shi, Z.; He, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Han, C.; Hao, L. P3H4 and PLOD1 expression associates with poor prognosis in bladder cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2022. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comtesse, N.; Zippel, A.; Walle, S.; Monz, D.; Backes, C.; Fischer, U.; Mayer, J.; Ludwig, N.; Hildebrandt, A.; Keller, A.; et al. Complex humoral immune response against a benign tumor: Frequent antibody response against specific antigens as diagnostic targets. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9601–9606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhou, H.; Song, J.; Cui, H.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, H. P3H4 Overexpression Serves as a Prognostic Factor in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Comput. Math Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 9971353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlessinger, J. Receptor tyrosine kinases: Legacy of the first two decades. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2014, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigismund, S.; Avanzato, D.; Lanzetti, L. Emergi.ing functions of the EGFR in cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi-Montalcini, R.; Booker, B. Excessive Growth of the Sympathetic Ganglia Evoked by a Protein Isolated from Mouse Salivary Glands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1960, 46, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearden, S.; Stevens, J.; Wu, Y.L.; Blowers, D. Mutation incidence and coincidence in non small-cell lung cancer: Meta-analyses by ethnicity and histology (mutMap). Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2371–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, R.; Moran, T.; Queralt, C.; Porta, R.; Cardenal, F.; Camps, C.; Majem, M.; Lopez-Vivanco, G.; Isla, D.; Provencio, M.; et al. Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarden, Y.; Sliwkowski, M.X. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotow, J.; Bivona, T.G. Understanding and targeting resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 637–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.R.; Sibilia, M.; Erben, R.G. The EGFR network in bone biology and pathology. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, K.S.; Rohatgi, N.; Halldorsson, S.; Briem, E.; Gudjonsson, T.; Gudmundsson, S.; Rolfsson, O. EGFR Signal-Network Reconstruction Demonstrates Metabolic Crosstalk in EMT. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Wu, S.; Jiao, J.; Tran, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, R.; Zhang, L.; et al. TRIM21 and PHLDA3 negatively regulate the crosstalk between the PI3K/AKT pathway and PPP metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosios, A.M.; Manning, B.D. Cancer Signaling Drives Cancer Metabolism: AKT and the Warburg Effect. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 4896–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Reyes, I.; Chandel, N.S. Cancer metabolism: Looking forward. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; DeBerardinis, R.J. Understanding the Intersections between Metabolism and Cancer Biology. Cell 2017, 168, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghergurovich, J.M.; Lang, J.D.; Levin, M.K.; Briones, N.; Facista, S.J.; Mueller, C.; Cowan, A.J.; McBride, M.J.; Rodriguez, E.S.R.; Killian, A.; et al. Local production of lactate, ribose phosphate, and amino acids within human triple-negative breast cancer. Med 2021, 2, 736–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, R.A.; Mak, T.W. An Alternative Sugar Fuels AML. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, X.G.; Chudnovskiy, A.; Baudrier, L.; Prizer, B.; Liu, Y.; Ostendorf, B.N.; Yamaguchi, N.; Arab, A.; Tavora, B.; Timson, R.; et al. Functional Genomics In Vivo Reveal Metabolic Dependencies of Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 211–221.e216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancur, D.E.; Kapner, K.S.; Yamamoto, K.; Banh, R.S.; Neggers, J.E.; Sohn, A.S.W.; Wu, W.; Manguso, R.T.; Brown, A.; Root, D.E.; et al. Functional Genomics Identifies Metabolic Vulnerabilities in Pancreatic Cancer. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 199–210.e198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, C.; Liang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Li, J.; Ma, H.; Guo, L.; Jiang, W.; Feng, Y. P3H4 Promotes Malignant Progression of Lung Adenocarcinoma via Interaction with EGFR. Cancers 2022, 14, 3243. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133243
Fang C, Liang Y, Huang Y, Jiang D, Li J, Ma H, Guo L, Jiang W, Feng Y. P3H4 Promotes Malignant Progression of Lung Adenocarcinoma via Interaction with EGFR. Cancers. 2022; 14(13):3243. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133243
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Chen, Yingkuan Liang, Yong Huang, Dong Jiang, Jiaxi Li, Haitao Ma, Lingchuan Guo, Wei Jiang, and Yu Feng. 2022. "P3H4 Promotes Malignant Progression of Lung Adenocarcinoma via Interaction with EGFR" Cancers 14, no. 13: 3243. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133243
APA StyleFang, C., Liang, Y., Huang, Y., Jiang, D., Li, J., Ma, H., Guo, L., Jiang, W., & Feng, Y. (2022). P3H4 Promotes Malignant Progression of Lung Adenocarcinoma via Interaction with EGFR. Cancers, 14(13), 3243. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133243





