Germline Aberrations in Pancreatic Cancer: Implications for Clinical Care
Abstract
:1. Introduction
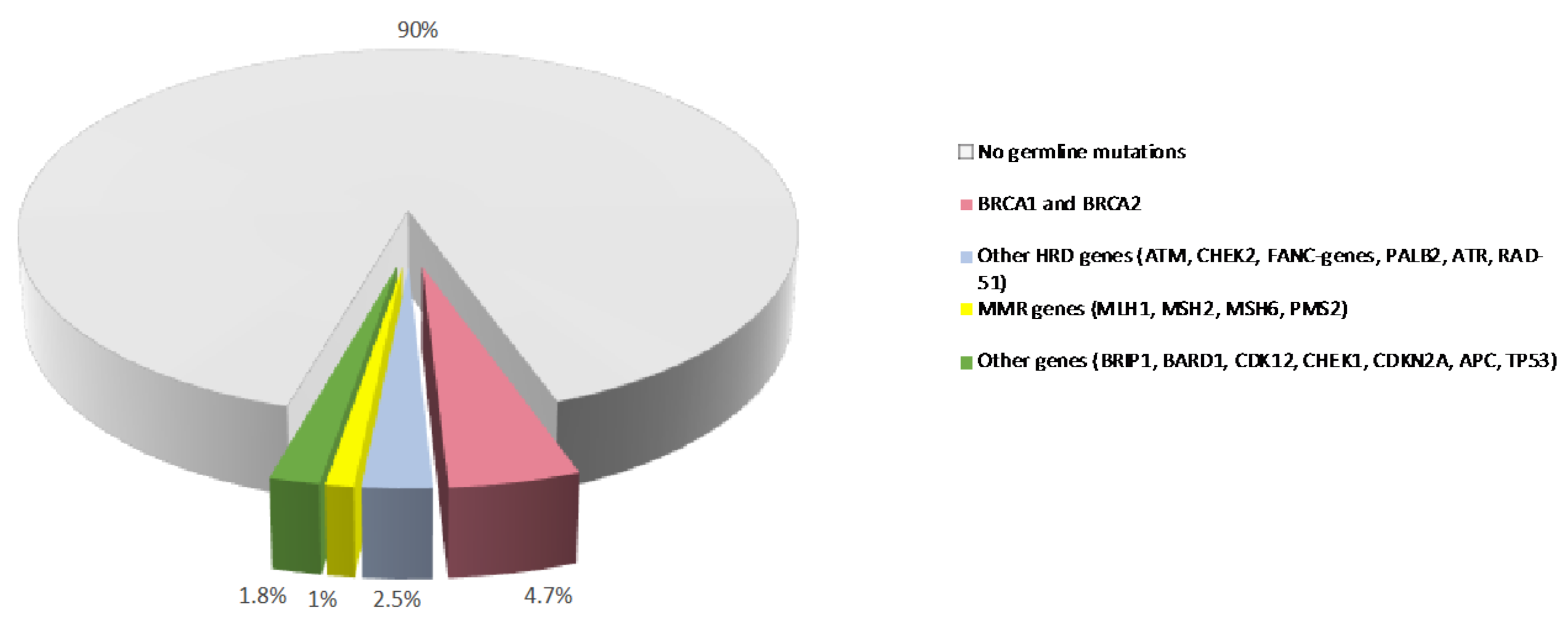
2. Germline Variants and PDAC Susceptibility
3. Implications of Germline Variants Identified in PDAC Patients
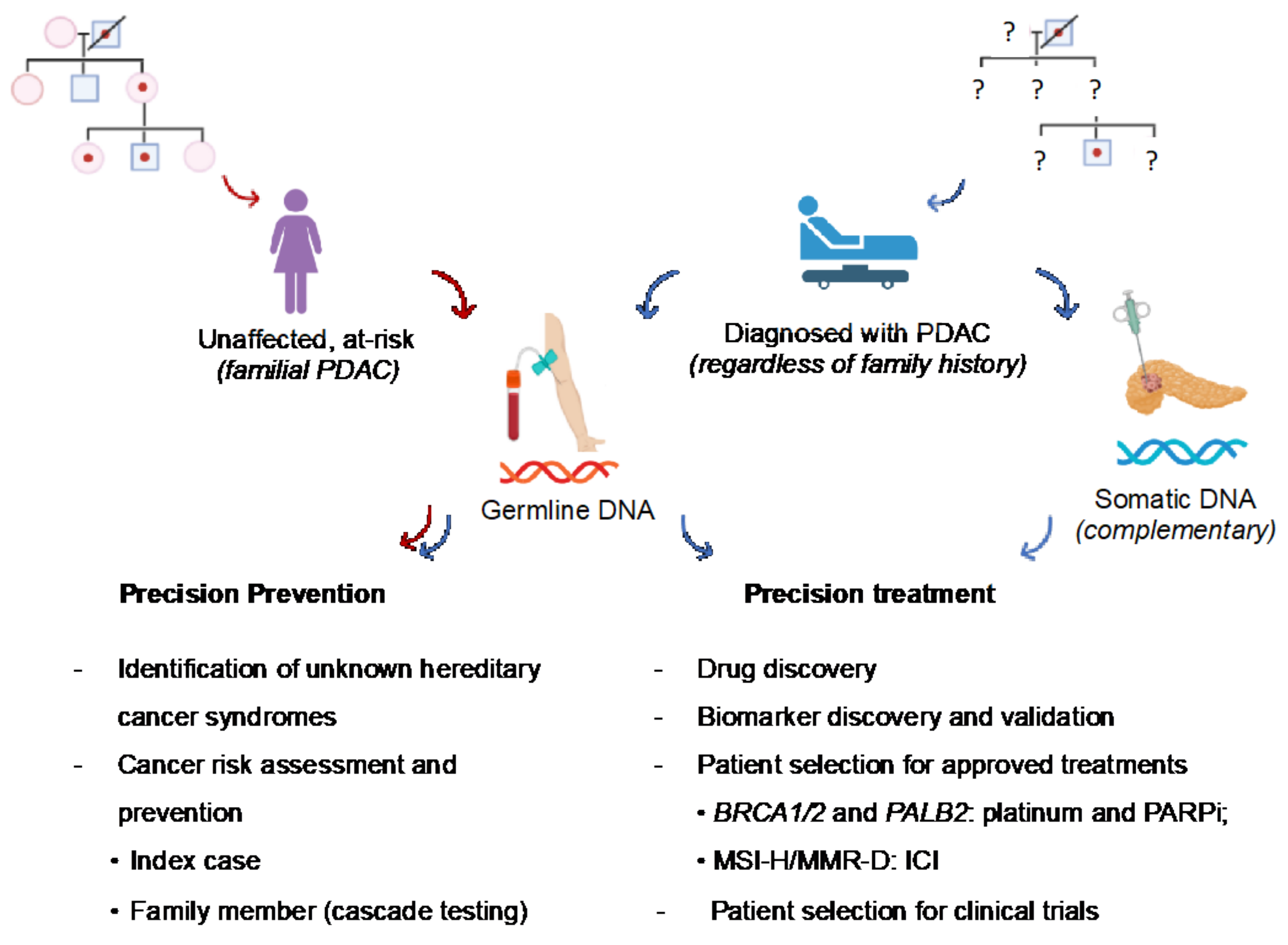
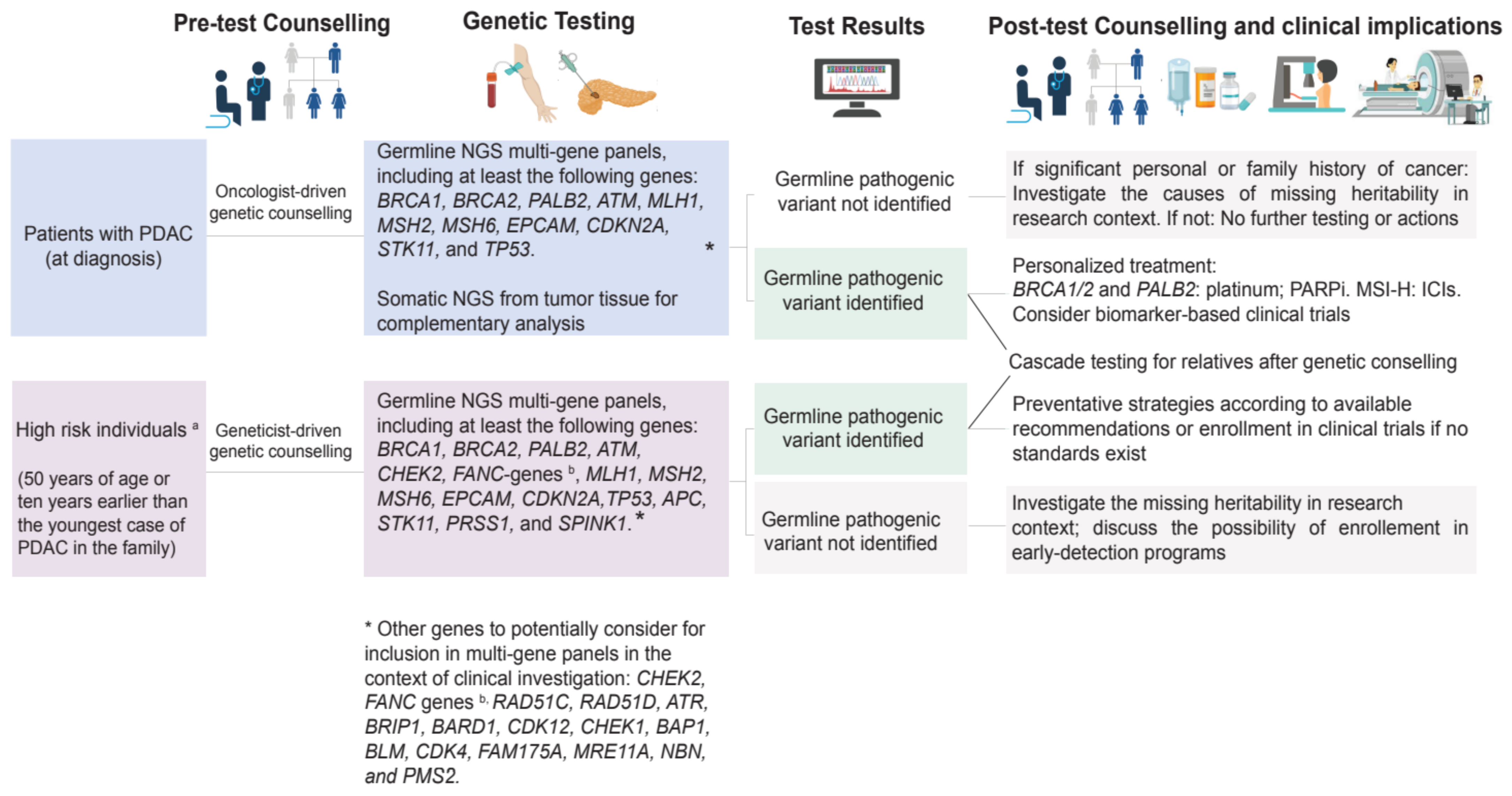
3.1. Preventative Implications
3.2. Therapeutic Implications
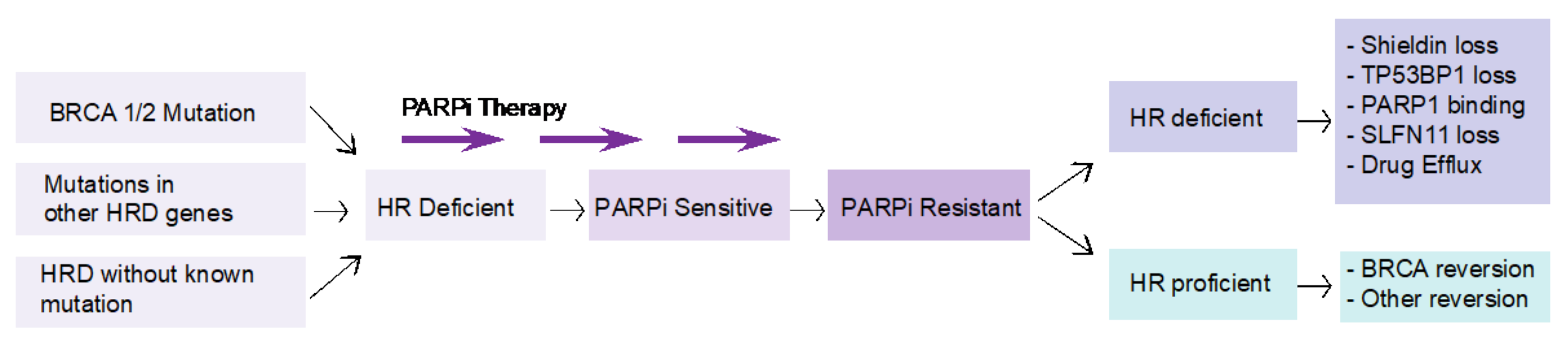
4. Challenges in Targeting BRCA Mutations in PDAC
5. Preclinical and Translational Research in Hereditary PDAC
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Landman, A.; Feetham, L.; Stuckey, D. Working together to reduce the burden of pancreatic cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 334–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lok, V.; Ngai, C.H.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, J.; Lao, X.Q.; Ng, K.; Chong, C.; Zheng, Z.J.; Wong, M.C.S. Worldwide Burden of, Risk Factors for, and Trends in Pancreatic Cancer. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahib, L.; Wehner, M.R.; Matrisian, L.M.; Nead, K.T. Estimated Projection of US Cancer Incidence and Death to 2040. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e214708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddam, S.; Abboud, Y.; Oh, J.; Samaan, J.S.; Nissen, N.N.; Lu, S.C.; Lo, S.K. Incidence of Pancreatic Cancer by Age and Sex in the US, 2000–2018. JAMA 2021, 326, 2075–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillen, S.; Schuster, T.; Meyer Zum Buschenfelde, C.; Friess, H.; Kleeff, J. Preoperative/neoadjuvant therapy in pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of response and resection percentages. PLoS Med. 2010, 7, e1000267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nevala-Plagemann, C.; Hidalgo, M.; Garrido-Laguna, I. From state-of-the-art treatments to novel therapies for advanced-stage pancreatic cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, T.; Hammel, P.; Hebbar, M.; Ben Abdelghani, M.; Wei, A.C.; Raoul, J.L.; Chone, L.; Francois, E.; Artru, P.; Biagi, J.J.; et al. FOLFIRINOX or Gemcitabine as Adjuvant Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2395–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, T.; Desseigne, F.; Ychou, M.; Bouche, O.; Guimbaud, R.; Becouarn, Y.; Adenis, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Gourgou-Bourgade, S.; de la Fouchardiere, C.; et al. FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Hoff, D.D.; Ervin, T.; Arena, F.P.; Chiorean, E.G.; Infante, J.; Moore, M.; Seay, T.; Tjulandin, S.A.; Ma, W.W.; Saleh, M.N.; et al. Increased survival in pancreatic cancer with nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oettle, H.; Riess, H.; Stieler, J.M.; Heil, G.; Schwaner, I.; Seraphin, J.; Gorner, M.; Molle, M.; Greten, T.F.; Lakner, V.; et al. Second-line oxaliplatin, folinic acid, and fluorouracil versus folinic acid and fluorouracil alone for gemcitabine-refractory pancreatic cancer: Outcomes from the CONKO-003 trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 2423–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang-Gillam, A.; Li, C.P.; Bodoky, G.; Dean, A.; Shan, Y.S.; Jameson, G.; Macarulla, T.; Lee, K.H.; Cunningham, D.; Blanc, J.F.; et al. Nanoliposomal irinotecan with fluorouracil and folinic acid in metastatic pancreatic cancer after previous gemcitabine-based therapy (NAPOLI-1): A global, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, T.; Hammel, P.; Reni, M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Macarulla, T.; Hall, M.J.; Park, J.O.; Hochhauser, D.; Arnold, D.; Oh, D.Y.; et al. Maintenance Olaparib for Germline BRCA-Mutated Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.J.; Goldstein, D.; Hamm, J.; Figer, A.; Hecht, J.R.; Gallinger, S.; Au, H.J.; Murawa, P.; Walde, D.; Wolff, R.A.; et al. Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: A phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1960–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempero, M.A.; Malafa, M.P.; Al-Hawary, M.; Behrman, S.W.; Benson, A.B.; Cardin, D.B.; Chiorean, E.G.; Chung, V.; Czito, B.; Del Chiaro, M.; et al. Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma, Version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 439–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, P.; Chang, D.K.; Nones, K.; Johns, A.L.; Patch, A.M.; Gingras, M.C.; Miller, D.K.; Christ, A.N.; Bruxner, T.J.; Quinn, M.C.; et al. Genomic analyses identify molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2016, 531, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biankin, A.V.; Waddell, N.; Kassahn, K.S.; Gingras, M.C.; Muthuswamy, L.B.; Johns, A.L.; Miller, D.K.; Wilson, P.J.; Patch, A.M.; Wu, J.; et al. Pancreatic cancer genomes reveal aberrations in axon guidance pathway genes. Nature 2012, 491, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froeling, F.E.M.; Casolino, R.; Pea, A.; Biankin, A.V.; Chang, D.K. Molecular Subtyping and Precision Medicine for Pancreatic Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddell, N.; Pajic, M.; Patch, A.M.; Chang, D.K.; Kassahn, K.S.; Bailey, P.; Johns, A.L.; Miller, D.; Nones, K.; Quek, K.; et al. Whole genomes redefine the mutational landscape of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 518, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casolino, R.; Paiella, S.; Azzolina, D.; Beer, P.A.; Corbo, V.; Lorenzoni, G.; Gregori, D.; Golan, T.; Braconi, C.; Froeling, F.E.M.; et al. Homologous Recombination Deficiency in Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review and Prevalence Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2617–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, A.; Kidd, J.; Elias, M.C.; Young, K.; Mabey, B.; Taherian, N.; Cummings, S.; Malafa, M.; Rosenthal, E.; Permuth, J.B. Pancreatic Ductal Carcinoma Risk Associated with Hereditary Cancer-Risk Genes. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2022, djac069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Hruban, R.H.; Kamiyama, M.; Borges, M.; Zhang, X.; Parsons, D.W.; Lin, J.C.; Palmisano, E.; Brune, K.; Jaffee, E.M.; et al. Exomic sequencing identifies PALB2 as a pancreatic cancer susceptibility gene. Science 2009, 324, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roberts, N.J.; Jiao, Y.; Yu, J.; Kopelovich, L.; Petersen, G.M.; Bondy, M.L.; Gallinger, S.; Schwartz, A.G.; Syngal, S.; Cote, M.L.; et al. ATM mutations in patients with hereditary pancreatic cancer. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grant, R.C.; Selander, I.; Connor, A.A.; Selvarajah, S.; Borgida, A.; Briollais, L.; Petersen, G.M.; Lerner-Ellis, J.; Holter, S.; Gallinger, S. Prevalence of germline mutations in cancer predisposition genes in patients with pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhen, D.B.; Rabe, K.G.; Gallinger, S.; Syngal, S.; Schwartz, A.G.; Goggins, M.G.; Hruban, R.H.; Cote, M.L.; McWilliams, R.R.; Roberts, N.J.; et al. BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, and CDKN2A mutations in familial pancreatic cancer: A PACGENE study. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macklin, S.K.; Kasi, P.M.; Jackson, J.L.; Hines, S.L. Incidence of Pathogenic Variants in Those with a Family History of Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocci, E.; Guillen-Ponce, C.; Earl, J.; Marquez, M.; Solera, J.; Salazar-Lopez, M.T.; Calcedo-Arnaiz, C.; Vazquez-Sequeiros, E.; Montans, J.; Munoz-Beltran, M.; et al. PanGen-Fam: Spanish registry of hereditary pancreatic cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardiello, F.M.; Brensinger, J.D.; Tersmette, A.C.; Goodman, S.N.; Petersen, G.M.; Booker, S.V.; Cruz-Correa, M.; Offerhaus, J.A. Very high risk of cancer in familial Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, N.J.; Norris, A.L.; Petersen, G.M.; Bondy, M.L.; Brand, R.; Gallinger, S.; Kurtz, R.C.; Olson, S.H.; Rustgi, A.K.; Schwartz, A.G.; et al. Whole Genome Sequencing Defines the Genetic Heterogeneity of Familial Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Childs, E.J.; Mocci, E.; Bracci, P.; Gallinger, S.; Li, D.; Neale, R.E.; Olson, S.H.; Scelo, G.; Bamlet, W.R.; et al. Analysis of Heritability and Genetic Architecture of Pancreatic Cancer: A PanC4 Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rebours, V.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Schnee, M.; Ferec, C.; Maire, F.; Hammel, P.; Ruszniewski, P.; Levy, P. Risk of pancreatic adenocarcinoma in patients with hereditary pancreatitis: A national exhaustive series. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; Shelton, C.A.; Greer, P.J.; Brand, R.E.; Whitcomb, D.C. Germline Variants and Risk for Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review and Emerging Concepts. Pancreas 2018, 47, 924–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Silvestri, V.; Leslie, G.; Rebbeck, T.R.; Neuhausen, S.L.; Hopper, J.L.; Nielsen, H.R.; Lee, A.; Yang, X.; McGuffog, L.; et al. Cancer Risks Associated with BRCA1 and BRCA2 Pathogenic Variants. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, JCO2102112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, M.B.; Pal, T.; Berry, M.P.; Buys, S.S.; Dickson, P.; Domchek, S.M.; Elkhanany, A.; Friedman, S.; Goggins, M.; Hutton, M.L.; et al. Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Breast, Ovarian, and Pancreatic, Version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 77–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, G.M. Familial pancreatic cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2016, 43, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klein, A.P.; Brune, K.A.; Petersen, G.M.; Goggins, M.; Tersmette, A.C.; Offerhaus, G.J.; Griffin, C.; Cameron, J.L.; Yeo, C.J.; Kern, S.; et al. Prospective risk of pancreatic cancer in familial pancreatic cancer kindreds. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2634–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shindo, K.; Yu, J.; Suenaga, M.; Fesharakizadeh, S.; Cho, C.; Macgregor-Das, A.; Siddiqui, A.; Witmer, P.D.; Tamura, K.; Song, T.J.; et al. Deleterious Germline Mutations in Patients with Apparently Sporadic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3382–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; LaDuca, H.; Shimelis, H.; Polley, E.C.; Lilyquist, J.; Hart, S.N.; Na, J.; Thomas, A.; Lee, K.Y.; Davis, B.T.; et al. Multigene Hereditary Cancer Panels Reveal High-Risk Pancreatic Cancer Susceptibility Genes. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, R.; Borazanci, E.; Speare, V.; Dudley, B.; Karloski, E.; Peters, M.L.B.; Stobie, L.; Bahary, N.; Zeh, H.; Zureikat, A.; et al. Prospective study of germline genetic testing in incident cases of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2018, 124, 3520–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaffee, K.G.; Oberg, A.L.; McWilliams, R.R.; Majithia, N.; Allen, B.A.; Kidd, J.; Singh, N.; Hartman, A.R.; Wenstrup, R.J.; Petersen, G.M. Prevalence of germ-line mutations in cancer genes among pancreatic cancer patients with a positive family history. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, C.; Hart, S.N.; Polley, E.C.; Gnanaolivu, R.; Shimelis, H.; Lee, K.Y.; Lilyquist, J.; Na, J.; Moore, R.; Antwi, S.O.; et al. Association Between Inherited Germline Mutations in Cancer Predisposition Genes and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer. JAMA 2018, 319, 2401–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentiluomo, M.; Canzian, F.; Nicolini, A.; Gemignani, F.; Landi, S.; Campa, D. Germline genetic variability in pancreatic cancer risk and prognosis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 79, 105–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.D.; Hurson, A.N.; Zhang, H.; Choudhury, P.P.; Easton, D.F.; Milne, R.L.; Simard, J.; Hall, P.; Michailidou, K.; Dennis, J.; et al. Assessment of polygenic architecture and risk prediction based on common variants across fourteen cancers. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Chen, H.T.; Na, R.; Jiang, D.K.; Lin, X.L.; Yang, F.; Jin, C.; Fu, D.L.; Xu, J.F. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms based genetic risk score in the prediction of pancreatic cancer risk. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 3076–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Yuan, C.; Babic, A.; Bao, Y.; Clish, C.B.; Pollak, M.N.; Amundadottir, L.T.; Klein, A.P.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Pandharipande, P.V.; et al. Genetic and Circulating Biomarker Data Improve Risk Prediction for Pancreatic Cancer in the General Population. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galeotti, A.A.; Gentiluomo, M.; Rizzato, C.; Obazee, O.; Neoptolemos, J.P.; Pasquali, C.; Nentwich, M.; Cavestro, G.M.; Pezzilli, R.; Greenhalf, W.; et al. Polygenic and multifactorial scores for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma risk prediction. J. Med. Genet. 2021, 58, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. What Is Cascade Testing for Hereditary Cancer Syndromes? August 2018. Available online: https://blog.dana-farber.org/insight/2018/08/cascade-testing-hereditary-cancer-syndromes/ (accessed on 19 May 2021).
- Vasen, H.; Ibrahim, I.; Ponce, C.G.; Slater, E.P.; Matthai, E.; Carrato, A.; Earl, J.; Robbers, K.; van Mil, A.M.; Potjer, T.; et al. Benefit of Surveillance for Pancreatic Cancer in High-Risk Individuals: Outcome of Long-Term Prospective Follow-Up Studies From Three European Expert Centers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2010–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinivasan, S.; Won, N.Y.; Dotson, W.D.; Wright, S.T.; Roberts, M.C. Barriers and facilitators for cascade testing in genetic conditions: A systematic review. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 28, 1631–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, M.B.; Pilarski, R.; Yurgelun, M.B.; Berry, M.P.; Buys, S.S.; Dickson, P.; Domchek, S.M.; Elkhanany, A.; Friedman, S.; Garber, J.E.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Breast, Ovarian, and Pancreatic, Version 1.2020. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto, M.I.; Harinck, F.; Hruban, R.H.; Offerhaus, G.J.; Poley, J.W.; Kamel, I.; Nio, Y.; Schulick, R.S.; Bassi, C.; Kluijt, I.; et al. International Cancer of the Pancreas Screening (CAPS) Consortium summit on the management of patients with increased risk for familial pancreatic cancer. Gut 2013, 62, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goggins, M.; Overbeek, K.A.; Brand, R.; Syngal, S.; Del Chiaro, M.; Bartsch, D.K.; Bassi, C.; Carrato, A.; Farrell, J.; Fishman, E.K.; et al. Management of patients with increased risk for familial pancreatic cancer: Updated recommendations from the International Cancer of the Pancreas Screening (CAPS) Consortium. Gut 2020, 69, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoffel, E.M.; McKernin, S.E.; Brand, R.; Canto, M.; Goggins, M.; Moravek, C.; Nagarajan, A.; Petersen, G.M.; Simeone, D.M.; Yurgelun, M.; et al. Evaluating Susceptibility to Pancreatic Cancer: ASCO Provisional Clinical Opinion. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stjepanovic, N.; Moreira, L.; Carneiro, F.; Balaguer, F.; Cervantes, A.; Balmana, J.; Martinelli, E. Hereditary gastrointestinal cancers: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-updagger. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1558–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pujol, P.; Barberis, M.; Beer, P.; Friedman, E.; Piulats, J.M.; Capoluongo, E.D.; Garcia Foncillas, J.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Foulkes, W.D.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines for BRCA1 and BRCA2 genetic testing. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 146, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiella, S.; Salvia, R.; De Pastena, M.; Pollini, T.; Casetti, L.; Landoni, L.; Esposito, A.; Marchegiani, G.; Malleo, G.; De Marchi, G.; et al. Screening/surveillance programs for pancreatic cancer in familial high-risk individuals: A systematic review and proportion meta-analysis of screening results. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canto, M.I.; Almario, J.A.; Schulick, R.D.; Yeo, C.J.; Klein, A.; Blackford, A.; Shin, E.J.; Sanyal, A.; Yenokyan, G.; Lennon, A.M.; et al. Risk of Neoplastic Progression in Individuals at High Risk for Pancreatic Cancer Undergoing Long-Term Surveillance. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 740–751.E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Overbeek, K.A.; Levink, I.J.M.; Koopmann, B.D.M.; Harinck, F.; Konings, I.; Ausems, M.; Wagner, A.; Fockens, P.; van Eijck, C.H.; Groot Koerkamp, B.; et al. Long-term yield of pancreatic cancer surveillance in high-risk individuals. Gut 2021, 71, 1152–1160.e774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeek, K.A.; Goggins, M.G.; Dbouk, M.; Levink, I.J.M.; Koopmann, B.D.M.; Chuidian, M.; Konings, I.; Paiella, S.; Earl, J.; Fockens, P.; et al. Timeline of Development of Pancreatic Cancer and Implications for Successful Early Detection in High-Risk Individuals. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhoda, A.; Vodusek, Z.; Wattamwar, K.; Mukherjee, E.; Gunderson, C.; Grimshaw, A.; Sharma, A.; Ahuja, N.; Kastrinos, F.; Farrell, J.J. Late-Stage Pancreatic Cancer Detected During High-Risk Individual Surveillance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonda, T.A.; Everett, J.N.; Wallace, M.; Simeone, D.M.; Consortium, P. Recommendations for a More Organized and Effective Approach to the Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer from the PRECEDE (Pancreatic Cancer Early Detection) Consortium. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1751–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principe, D.R. Precision Medicine for BRCA/PALB2-Mutated Pancreatic Cancer and Emerging Strategies to Improve Therapeutic Responses to PARP Inhibition. Cancers 2022, 14, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milella, M.; Luchini, C.; Lawlor, R.T.; Johns, A.L.; Casolino, R.; Yoshino, T.; Biankin, A.V. ICGC-ARGO precision medicine: Familial matters in pancreatic cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 25–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marabelle, A.; Le, D.T.; Ascierto, P.A.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; De Jesus-Acosta, A.; Delord, J.P.; Geva, R.; Gottfried, M.; Penel, N.; Hansen, A.R.; et al. Efficacy of Pembrolizumab in Patients with Noncolorectal High Microsatellite Instability/Mismatch Repair-Deficient Cancer: Results From the Phase II KEYNOTE-158 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, V.; Kaestner, V.; Mailankody, S. Cancer Drugs Approved Based on Biomarkers and Not Tumor Type-FDA Approval of Pembrolizumab for Mismatch Repair-Deficient Solid Cancers. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 157–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, H.E.; Schultz, N.; Thomas, H.D.; Parker, K.M.; Flower, D.; Lopez, E.; Kyle, S.; Meuth, M.; Curtin, N.J.; Helleday, T. Specific killing of BRCA2-deficient tumours with inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Nature 2005, 434, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, H.; McCabe, N.; Lord, C.J.; Tutt, A.N.; Johnson, D.A.; Richardson, T.B.; Santarosa, M.; Dillon, K.J.; Hickson, I.; Knights, C.; et al. Targeting the DNA repair defect in BRCA mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature 2005, 434, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouleau, M.; Patel, A.; Hendzel, M.J.; Kaufmann, S.H.; Poirier, G.G. PARP inhibition: PARP1 and beyond. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fong, P.C.; Boss, D.S.; Yap, T.A.; Tutt, A.; Wu, P.; Mergui-Roelvink, M.; Mortimer, P.; Swaisland, H.; Lau, A.; O’Connor, M.J.; et al. Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in tumors from BRCA mutation carriers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Connor, M.J. Targeting the DNA damage response in cancer. Mol. Cell. 2015, 60, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashworth, A. A synthetic lethal therapeutic approach: Poly(ADP) ribose polymerase inhibitors for the treatment of cancers deficient in DNA double-strand break repair. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3785–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, A.; Oltra, S.S.; Moreno-Bueno, G. Insight updating of the molecular hallmarks in ovarian carcinoma. EJC Suppl. 2020, 15, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, T.; Kanji, Z.S.; Epelbaum, R.; Devaud, N.; Dagan, E.; Holter, S.; Aderka, D.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Kaufman, B.; Gershoni-Baruch, R.; et al. Overall survival and clinical characteristics of pancreatic cancer in BRCA mutation carriers. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golan, T.; Barenboim, A.; Lahat, G.; Nachmany, I.; Goykhman, Y.; Shacham-Shmueli, E.; Halpern, N.; Brazowski, E.; Geva, R.; Wolf, I.; et al. Increased rate of complete pathologic response after neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX for BRCA mutation carriers with borderline resectable pancreatic cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 3963–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Agarwal, P.; Mamtani, R.; Symecko, H.; Spielman, K.; O’Hara, M.; O’Dwyer, P.J.; Schneider, C.; Teitelbaum, U.; Nathanson, K.L.; et al. Retrospective survival analysis of patients with resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and a germline BRCA or PALB2 mutation. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casolino, R.; Braconi, C.; Malleo, G.; Paiella, S.; Bassi, C.; Milella, M.; Dreyer, S.B.; Froeling, F.E.M.; Chang, D.K.; Biankin, A.V.; et al. Reshaping preoperative treatment of pancreatic cancer in the era of precision medicine. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 32, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, K.A.; Mick, R.; O’Hara, M.H.; Teitelbaum, U.; Karasic, T.B.; Schneider, C.; Cowden, S.; Southwell, T.; Romeo, J.; Izgur, N.; et al. Phase II Study of Maintenance Rucaparib in Patients with Platinum-Sensitive Advanced Pancreatic Cancer and a Pathogenic Germline or Somatic Variant in BRCA1, BRCA2, or PALB2. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2497–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, B.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Schmutzler, R.K.; Audeh, M.W.; Friedlander, M.; Balmana, J.; Mitchell, G.; Fried, G.; Stemmer, S.M.; Hubert, A.; et al. Olaparib monotherapy in patients with advanced cancer and a germline BRCA1/2 mutation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shroff, R.T.; Hendifar, A.; McWilliams, R.R.; Geva, R.; Epelbaum, R.; Rolfe, L.; Goble, S.; Lin, K.K.; Biankin, A.V.; Giordano, H.; et al. Rucaparib Monotherapy in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer and a Known Deleterious BRCA Mutation. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, E.M.; Lee, J.W.; Zalupski, M.; Capanu, M.; Park, J.; Golan, T.; Tahover, E.; Lowery, M.A.; Chou, J.F.; Sahai, V.; et al. Randomized, Multicenter, Phase II Trial of Gemcitabine and Cisplatin with or without Veliparib in Patients with Pancreas Adenocarcinoma and a Germline BRCA/PALB2 Mutation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchini, C.; Brosens, L.A.A.; Wood, L.D.; Chatterjee, D.; Shin, J.I.; Sciammarella, C.; Fiadone, G.; Malleo, G.; Salvia, R.; Kryklyva, V.; et al. Comprehensive characterisation of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with microsatellite instability: Histology, molecular pathology and clinical implications. Gut 2021, 70, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiricny, J. The multifaceted mismatch-repair system. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germano, G.; Amirouchene-Angelozzi, N.; Rospo, G.; Bardelli, A. The Clinical Impact of the Genomic Landscape of Mismatch Repair-Deficient Cancers. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grant, R.C.; Denroche, R.; Jang, G.H.; Nowak, K.M.; Zhang, A.; Borgida, A.; Holter, S.; Topham, J.T.; Wilson, J.; Dodd, A.; et al. Clinical and genomic characterisation of mismatch repair deficient pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Gut 2021, 70, 1894–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyraud, F.; Italiano, A. Combined PARP Inhibition and Immune Checkpoint Therapy in Solid Tumors. Cancers 2020, 12, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, P.; Bandlamudi, C.; Cheng, M.L.; Srinivasan, P.; Chavan, S.S.; Friedman, N.D.; Rosen, E.Y.; Richards, A.L.; Bouvier, N.; Selcuklu, S.D.; et al. Tumour lineage shapes BRCA-mediated phenotypes. Nature 2019, 571, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, W.; Hu, Z.; Yuan, J.; Pi, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, L.; Tang, Z.; Li, C.; et al. Repression of BET activity sensitizes homologous recombination-proficient cancers to PARP inhibition. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, A.L.; Fehling, S.C.; Garcia, P.L.; Gamblin, T.L.; Council, L.N.; van Waardenburg, R.; Yang, E.S.; Bradner, J.E.; Yoon, K.J. The BET inhibitor JQ1 attenuates double-strand break repair and sensitizes models of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma to PARP inhibitors. EBioMedicine 2019, 44, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogiwara, H.; Ui, A.; Shiotani, B.; Zou, L.; Yasui, A.; Kohno, T. Curcumin suppresses multiple DNA damage response pathways and has potency as a sensitizer to PARP inhibitor. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2486–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muvarak, N.E.; Chowdhury, K.; Xia, L.; Robert, C.; Choi, E.Y.; Cai, Y.; Bellani, M.; Zou, Y.; Singh, Z.N.; Duong, V.H.; et al. Enhancing the Cytotoxic Effects of PARP Inhibitors with DNA Demethylating Agents—A Potential Therapy for Cancer. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen, R.D.; Gajjar, M.K.; Jensen, K.E.; Hamerlik, P. Enhanced efficacy of combined HDAC and PARP targeting in glioblastoma. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, J.; Peng, Y.; Wei, L.; Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; Lan, L.; Kapoor, P.; Ju, Z.; Mo, Q.; Shih, I.M.; et al. ARID1A Deficiency Impairs the DNA Damage Checkpoint and Sensitizes Cells to PARP Inhibitors. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 752–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brenner, J.C.; Ateeq, B.; Li, Y.; Yocum, A.K.; Cao, Q.; Asangani, I.A.; Patel, S.; Wang, X.; Liang, H.; Yu, J.; et al. Mechanistic rationale for inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in ETS gene fusion-positive prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 664–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campbell, P.J.; Yachida, S.; Mudie, L.J.; Stephens, P.J.; Pleasance, E.D.; Stebbings, L.A.; Morsberger, L.A.; Latimer, C.; McLaren, S.; Lin, M.L.; et al. The patterns and dynamics of genomic instability in metastatic pancreatic cancer. Nature 2010, 467, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yachida, S.; Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.A. Evolution and dynamics of pancreatic cancer progression. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5253–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yachida, S.; Jones, S.; Bozic, I.; Antal, T.; Leary, R.; Fu, B.; Kamiyama, M.; Hruban, R.H.; Eshleman, J.R.; Nowak, M.A.; et al. Distant metastasis occurs late during the genetic evolution of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2010, 467, 1114–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, K.K.; Harrell, M.I.; Oza, A.M.; Oaknin, A.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Tinker, A.V.; Helman, E.; Radke, M.R.; Say, C.; Vo, L.T.; et al. BRCA Reversion Mutations in Circulating Tumor DNA Predict Primary and Acquired Resistance to the PARP Inhibitor Rucaparib in High-Grade Ovarian Carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edwards, S.L.; Brough, R.; Lord, C.J.; Natrajan, R.; Vatcheva, R.; Levine, D.A.; Boyd, J.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Ashworth, A. Resistance to therapy caused by intragenic deletion in BRCA2. Nature 2008, 451, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, W.; Swisher, E.M.; Karlan, B.Y.; Agarwal, M.K.; Higgins, J.; Friedman, C.; Villegas, E.; Jacquemont, C.; Farrugia, D.J.; Couch, F.J.; et al. Secondary mutations as a mechanism of cisplatin resistance in BRCA2-mutated cancers. Nature 2008, 451, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhargava, R.; Onyango, D.O.; Stark, J.M. Regulation of Single-Strand Annealing and its Role in Genome Maintenance. Trends Genet. 2016, 32, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swisher, E.M.; Kwan, T.T.; Oza, A.M.; Tinker, A.V.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Oaknin, A.; Coleman, R.L.; Aghajanian, C.; Konecny, G.E.; O’Malley, D.M.; et al. Molecular and clinical determinants of response and resistance to rucaparib for recurrent ovarian cancer treatment in ARIEL2 (Parts 1 and 2). Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Somyajit, K.; Narita, T.; Maskey, E.; Stanlie, A.; Kremer, M.; Typas, D.; Lammers, M.; Mailand, N.; Nussenzweig, A.; et al. DNA Repair Network Analysis Reveals Shieldin as a Key Regulator of NHEJ and PARP Inhibitor Sensitivity. Cell 2018, 173, 972–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirman, Z.; Lottersberger, F.; Takai, H.; Kibe, T.; Gong, Y.; Takai, K.; Bianchi, A.; Zimmermann, M.; Durocher, D.; de Lange, T. 53BP1-RIF1-shieldin counteracts DSB resection through CST- and Polalpha-dependent fill-in. Nature 2018, 560, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, M.P.; Moser, S.C.; Ganesan, S.; Jonkers, J. Understanding and overcoming resistance to PARP inhibitors in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 773–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; George, E.; Ragland, R.; Rafail, S.; Zhang, R.; Krepler, C.; Morgan, M.; Herlyn, M.; Brown, E.; Simpkins, F. Targeting the ATR/CHK1 Axis with PARP Inhibition Results in Tumor Regression in BRCA-Mutant Ovarian Cancer Models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3097–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davies, H.; Glodzik, D.; Morganella, S.; Yates, L.R.; Staaf, J.; Zou, X.; Ramakrishna, M.; Martin, S.; Boyault, S.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; et al. HRDetect is a predictor of BRCA1 and BRCA2 deficiency based on mutational signatures. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castroviejo-Bermejo, M.; Cruz, C.; Llop-Guevara, A.; Gutierrez-Enriquez, S.; Ducy, M.; Ibrahim, Y.H.; Gris-Oliver, A.; Pellegrino, B.; Bruna, A.; Guzman, M.; et al. A RAD51 assay feasible in routine tumor samples calls PARP inhibitor response beyond BRCA mutation. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, e9172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deer, E.L.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, J.; Coursen, J.D.; Shea, J.E.; Ngatia, J.; Scaife, C.L.; Firpo, M.A.; Mulvihill, S.J. Phenotype and genotype of pancreatic cancer cell lines. Pancreas 2010, 39, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Heijden, M.S.; Brody, J.R.; Gallmeier, E.; Cunningham, S.C.; Dezentje, D.A.; Shen, D.; Hruban, R.H.; Kern, S.E. Functional defects in the fanconi anemia pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 165, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hingorani, S.R.; Petricoin, E.F.; Maitra, A.; Rajapakse, V.; King, C.; Jacobetz, M.A.; Ross, S.; Conrads, T.P.; Veenstra, T.D.; Hitt, B.A.; et al. Preinvasive and invasive ductal pancreatic cancer and its early detection in the mouse. Cancer Cell 2003, 4, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olive, K.P.; Jacobetz, M.A.; Davidson, C.J.; Gopinathan, A.; McIntyre, D.; Honess, D.; Madhu, B.; Goldgraben, M.A.; Caldwell, M.E.; Allard, D.; et al. Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling enhances delivery of chemotherapy in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Science 2009, 324, 1457–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerra, C.; Barbacid, M. Genetically engineered mouse models of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Mol. Oncol. 2013, 7, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulidis, F.; Cassidy, L.D.; Pisupati, V.; Jonasson, J.G.; Bjarnason, H.; Eyfjord, J.E.; Karreth, F.A.; Lim, M.; Barber, L.M.; Clatworthy, S.A.; et al. Germline Brca2 heterozygosity promotes Kras(G12D) -driven carcinogenesis in a murine model of familial pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drosos, Y.; Escobar, D.; Chiang, M.Y.; Roys, K.; Valentine, V.; Valentine, M.B.; Rehg, J.E.; Sahai, V.; Begley, L.A.; Ye, J.; et al. ATM-deficiency increases genomic instability and metastatic potential in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.I.; Boj, S.F.; Clevers, H.; Tuveson, D.A. Preclinical models of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Pathol. 2016, 238, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boj, S.F.; Hwang, C.I.; Baker, L.A.; Chio, I.I.C.; Engle, D.D.; Corbo, V.; Jager, M.; Ponz-Sarvise, M.; Tiriac, H.; Spector, M.S.; et al. Organoid models of human and mouse ductal pancreatic cancer. Cell 2015, 160, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| NCT Number | Title | Condition(s) | Interventions | Phase | Start Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04493060 | Niraparib and Dostarlimab for the Treatment of Germline or Somatic BRCA1/2 and PALB2 Mutated Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer | Metastatic Pancreatic cancer | Drug: Niraparib |Biological: Dostarlimab | 2 | December 2020 |
| NCT04548752 | Testing the Addition of Pembrolizumab, an Immunotherapy Cancer Drug to Olaparib Alone as Therapy for Patients With Pancreatic Cancer That Has Spread With Inherited BRCA Mutations | Metastatic Pancreatic cancer | Drug: Olaparib|Biological: Pembrolizumab | 2 | December 2020 |
| NCT03553004 | Niraparib in Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer After Previous Chemotherapy (NIRA-PANC): a Phase 2 Trial | Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer | Drug: Niraparib | 2 | January 2019 |
| NCT04858334 | A Randomized Study of Olaparib or Placebo in Patients With Surgically Removed Pancreatic Cancer Who Have a BRCA1, BRCA2 or PALB2 Mutation, The APOLLO Trial | Resected Pancreatic Cancer (Adjuvant setting) | Drug: Olaparib|Drug: Placebo Administration | 2 | April 2021 |
| NCT04890613 | Study of CX-5461 in Patients With Solid Tumours and BRCA1/2, PALB2 or Homologous Recombination Deficiency (HRD) Mutation | Advanced Solid Tumor | Drug: CX-5461 | 1 | September 2021 |
| NCT04171700 | A Study to Evaluate Rucaparib in Patients With Solid Tumors and With Deleterious Mutations in HRR Genes(LODESTAR trial) | Advanced Solid Tumor | Drug: Rucaparib | 2 | November 2019 |
| NCT04673448 | Niraparib and TSR-042 for the Treatment of BRCA-Mutated Unresectable or Metastatic Breast, Pancreas, Ovary, Fallopian Tube, or Primary Peritoneal Cancer | Advanced Unresectable or Metastatic Breast, Pancreas, Ovary, Fallopian Tube, or Primary Peritoneal Cancer | Biological: Dostarlimab|Drug: Niraparib | 1 | November 2021 |
| NCT04300114 | A Study of Maintenance Treatment With Fluzoparib in gBRCA/PALB2 Mutated Pancreatic Cancer Whose Disease Has Not Progressed on First Line Platinum-Based Chemotherapy | Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer | Drug: Fluzoparib|Drug: Placebo | 3 | August 2020 |
| NCT04150042 | A Study of Melphalan, BCNU, Vitamin B12b, Vitamin C, and Stem Cell Infusion in People With Advanced Pancreatic Cancer and BRCA Mutations | Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer | Drug: Melphalan|Drug: BCNU|Drug: Vitamin B12B|Drug: Vitamin C|Drug: Ethanol|Device: Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cells | 1 | January 2021 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Casolino, R.; Corbo, V.; Beer, P.; Hwang, C.-i.; Paiella, S.; Silvestri, V.; Ottini, L.; Biankin, A.V. Germline Aberrations in Pancreatic Cancer: Implications for Clinical Care. Cancers 2022, 14, 3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133239
Casolino R, Corbo V, Beer P, Hwang C-i, Paiella S, Silvestri V, Ottini L, Biankin AV. Germline Aberrations in Pancreatic Cancer: Implications for Clinical Care. Cancers. 2022; 14(13):3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133239
Chicago/Turabian StyleCasolino, Raffaella, Vincenzo Corbo, Philip Beer, Chang-il Hwang, Salvatore Paiella, Valentina Silvestri, Laura Ottini, and Andrew V. Biankin. 2022. "Germline Aberrations in Pancreatic Cancer: Implications for Clinical Care" Cancers 14, no. 13: 3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133239
APA StyleCasolino, R., Corbo, V., Beer, P., Hwang, C.-i., Paiella, S., Silvestri, V., Ottini, L., & Biankin, A. V. (2022). Germline Aberrations in Pancreatic Cancer: Implications for Clinical Care. Cancers, 14(13), 3239. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14133239





