Quantification and Phenotypic Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles from Patients with Acute Myeloid and B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Leukemia Patient Samples, Cell Isolation and Primary Cell Culture
2.2. Isolation and Purification of EVs from Platelet-Free Plasma
2.3. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
2.4. Fluorescence Triggering Flow Cytometry (FT-FCM)
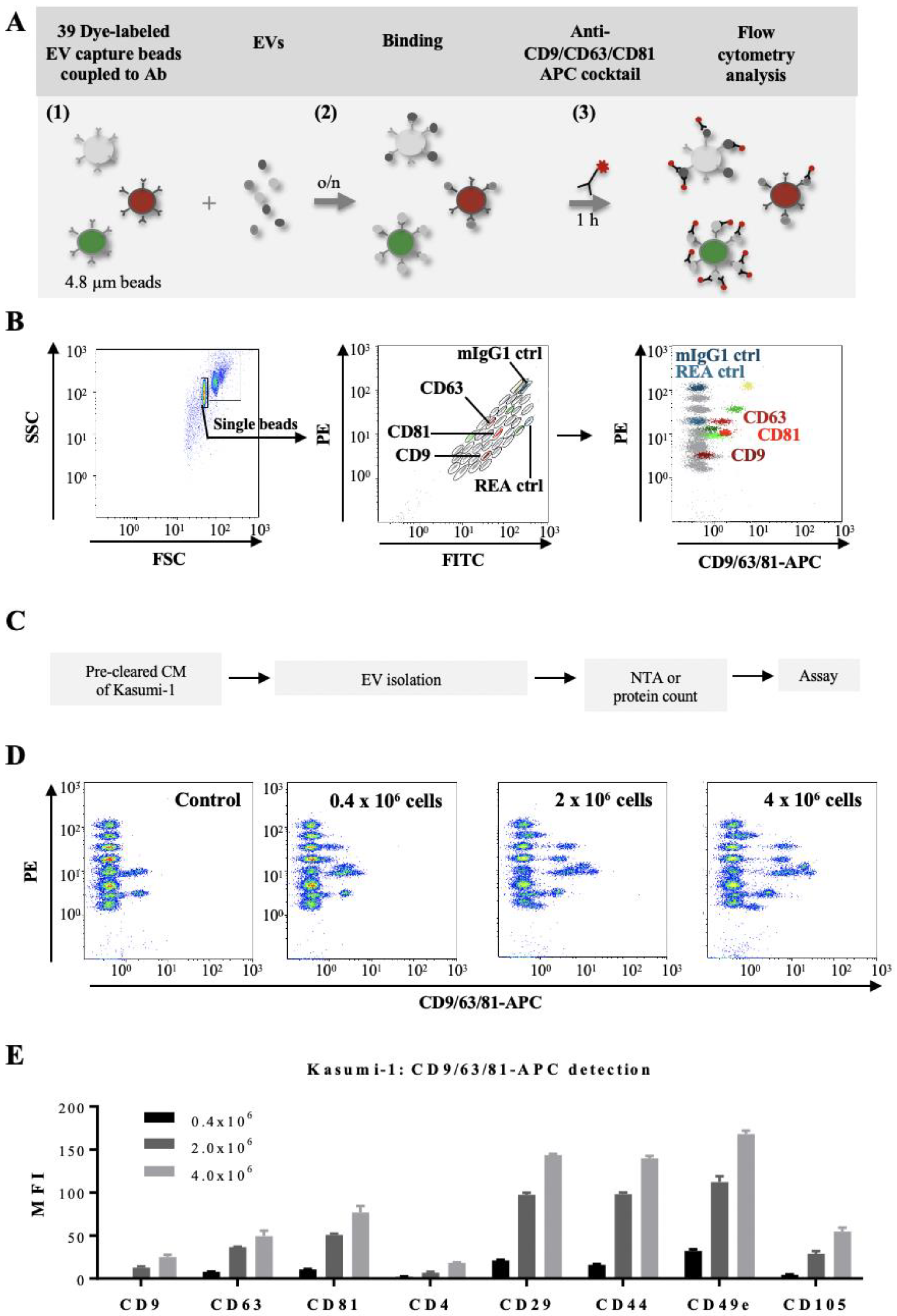
2.5. Multiplex Bead-Based EV Flow Cytometry Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
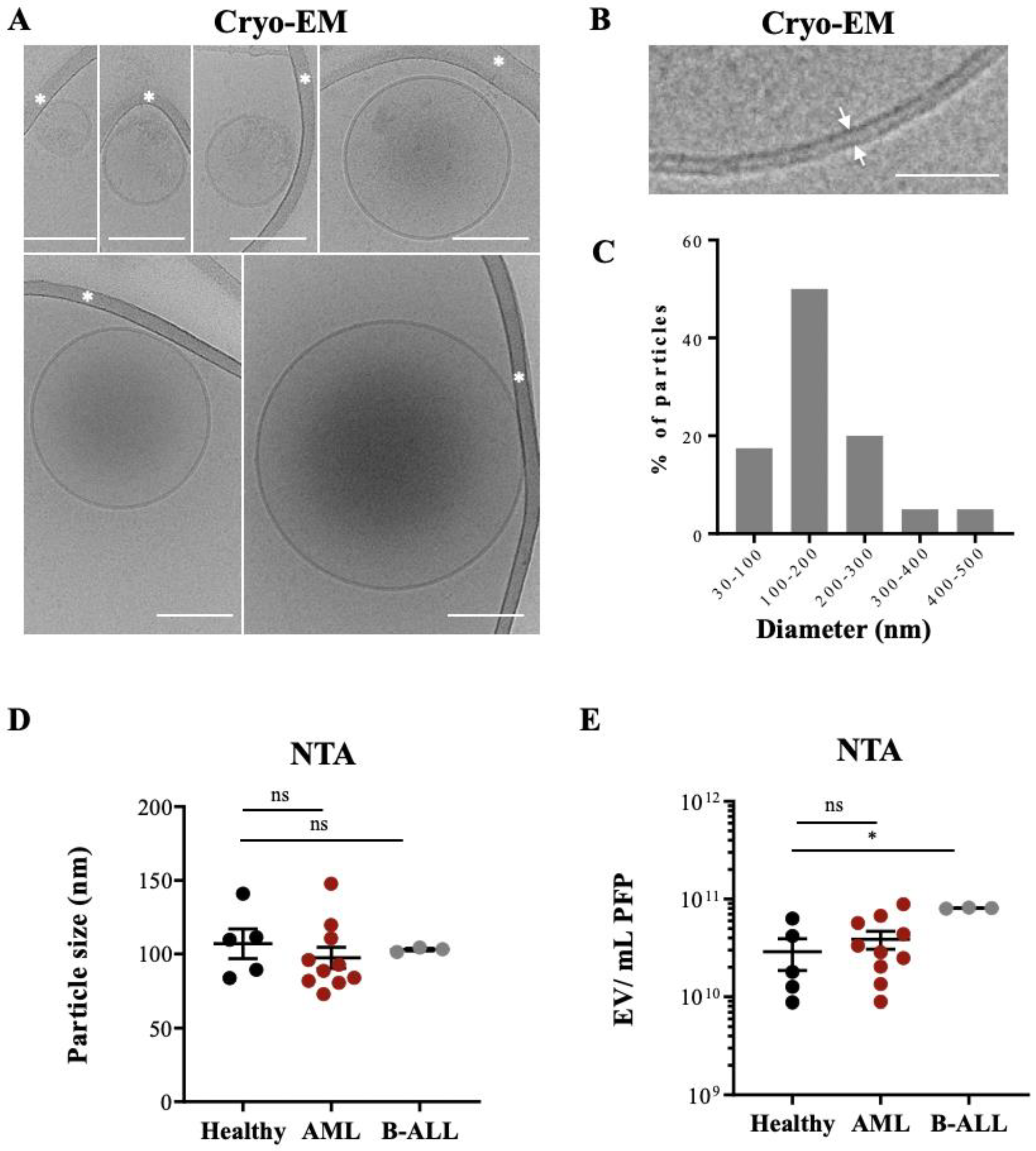
3.1. Characterization of Morphology, Size, and Counts of Leukemia-Derived EVs by Cryo-EM and NTA
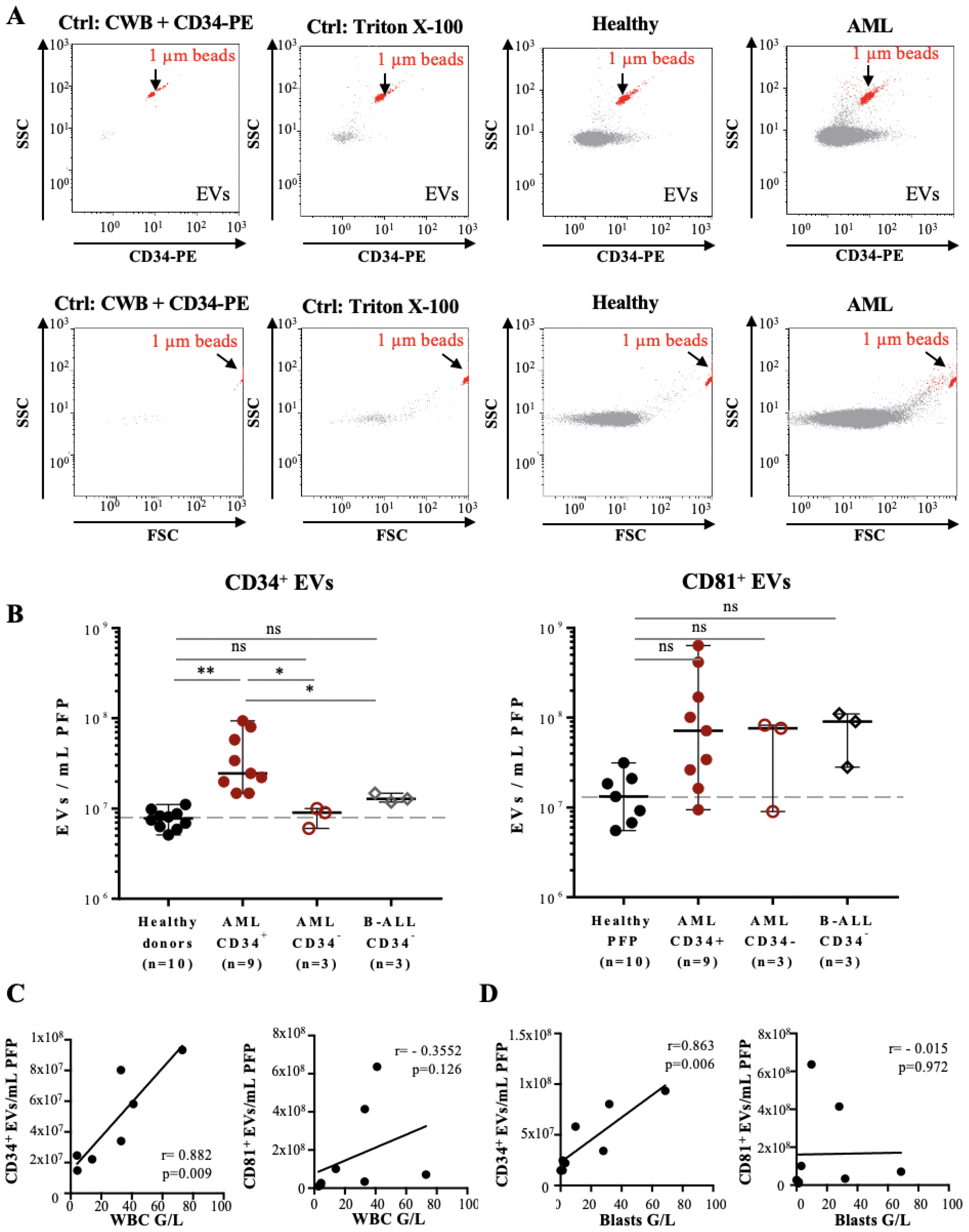
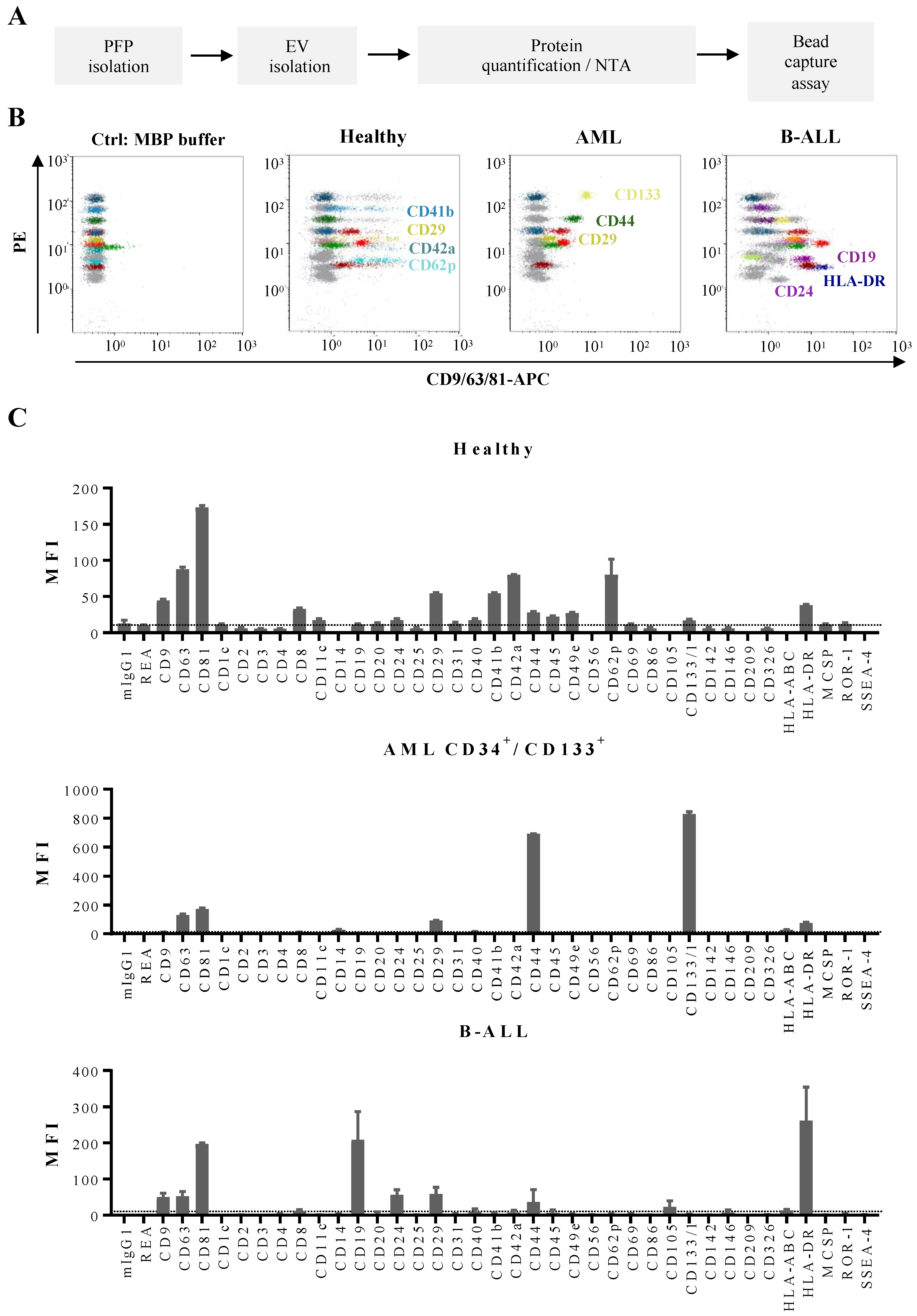
3.2. Quantification and Immunophenotyping of Leukemia-Derived EVs by Fluorescence Triggering Flow Cytometry
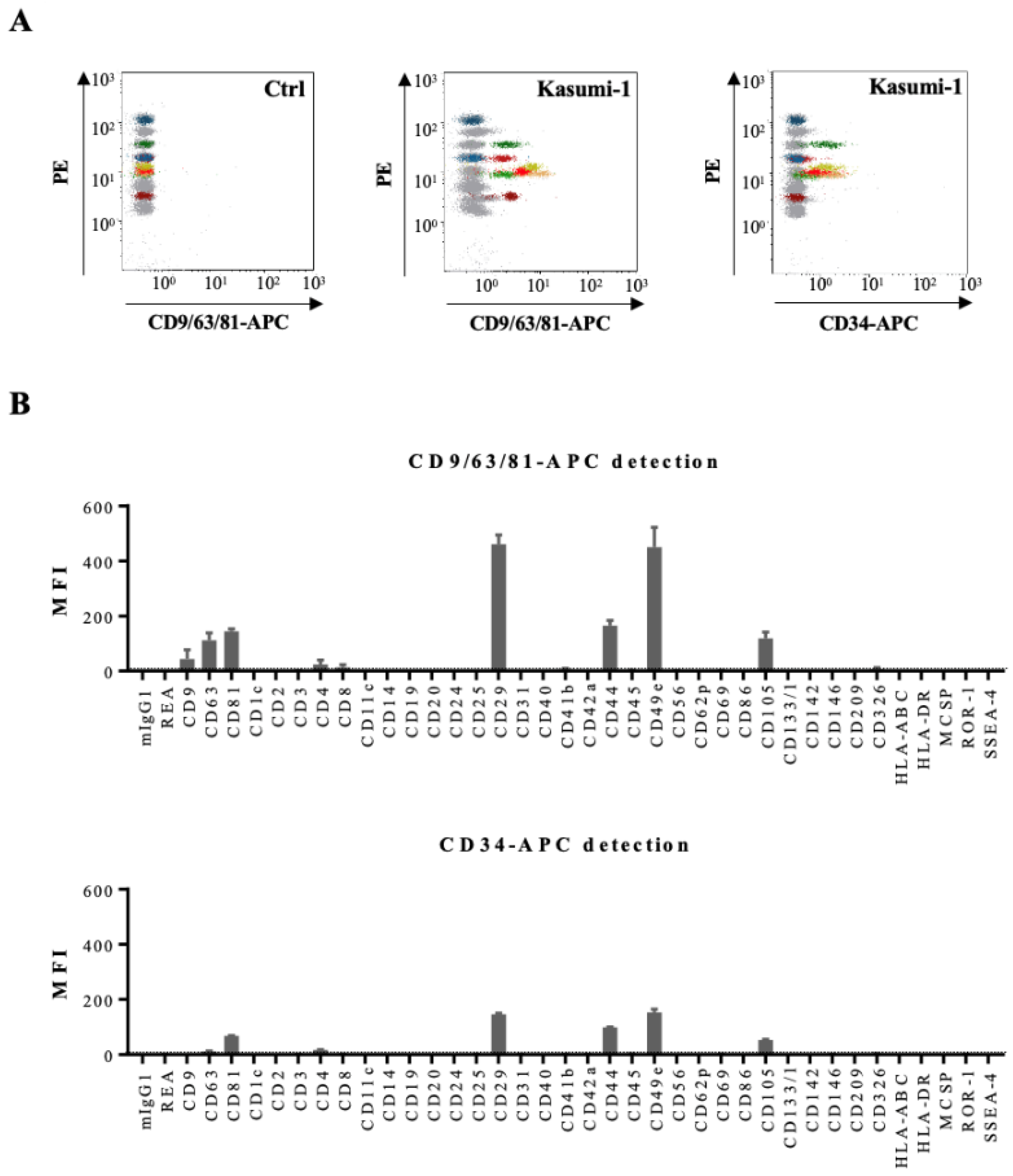
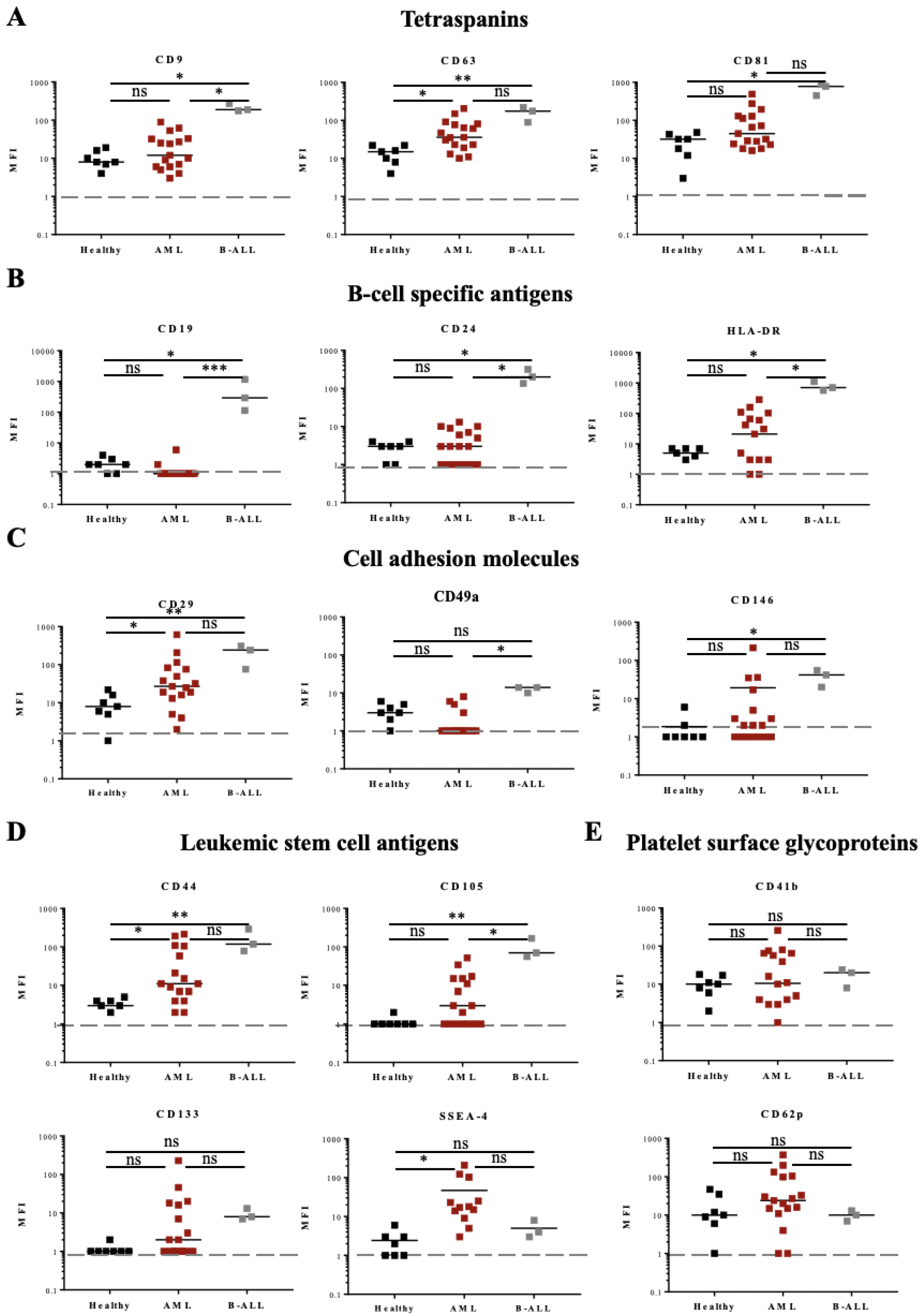
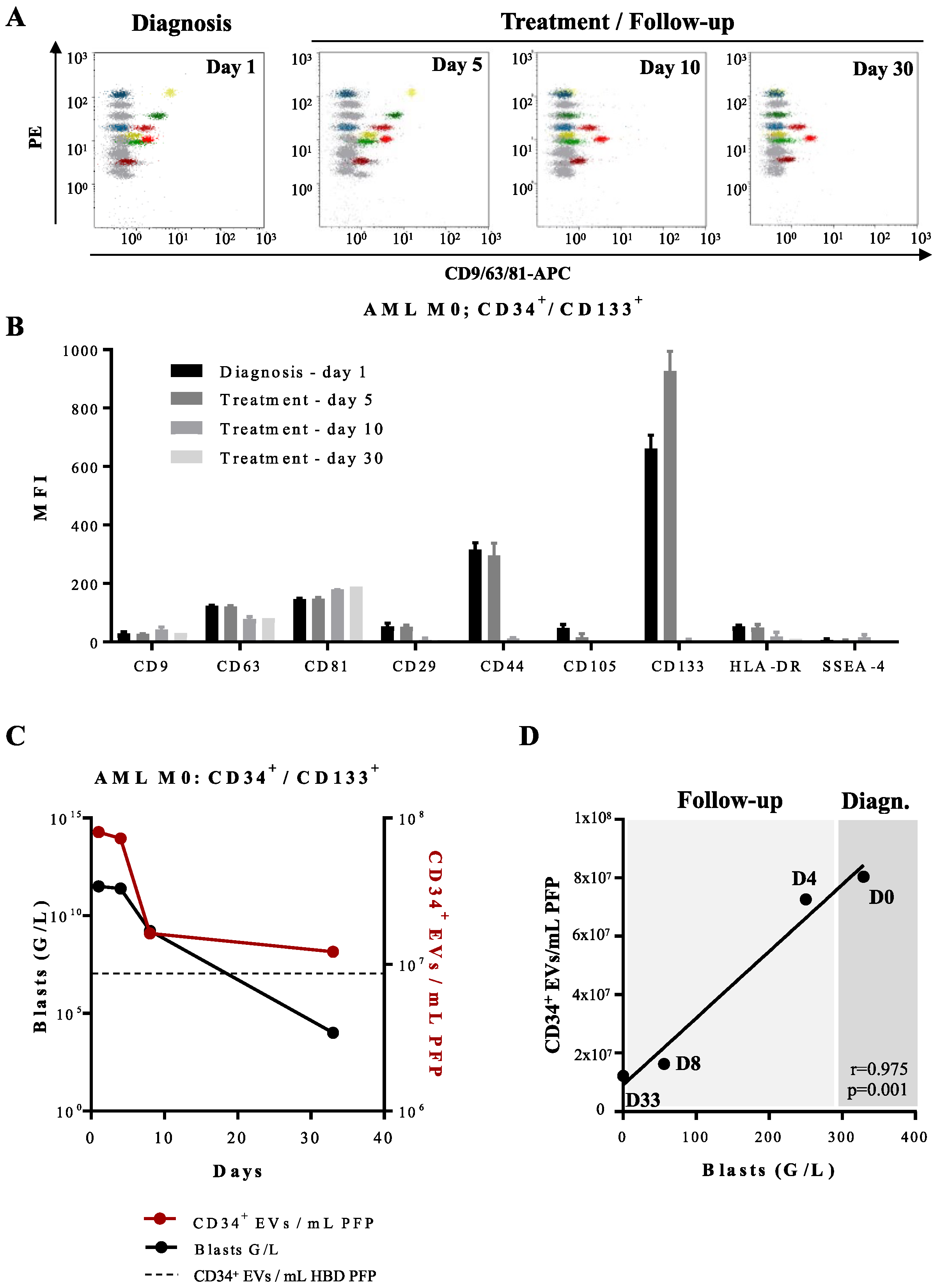
3.3. Determination of Phenotypic Profiles of Leukemia-Derived EVs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ratajczak, M.Z.; Ratajczak, J. Extracellular microvesicles/exosomes: Discovery, disbelief, acceptance, and the future? Leukemia 2020, 34, 3126–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Gould, S.J. Exosomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 487–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Kaslan, M.; Lee, S.H.; Yao, J.; Gao, Z. Progress in Exosome Isolation Techniques. Theranostics 2017, 7, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the Interna-tional Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, J.A.; Tang, V.A.; van Der Pol, E.; Görgens, A. MIFlowCyt-EV: The Next Chapter in the Reporting and Reliability of Single Extracellular Vesicle Flow Cytometry Experiments. Cytom. Part A 2020, 99, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denzer, K.; Van Eijk, M.; Kleijmeer, M.J.; Jakobson, E.; De Groot, C.; Geuze, H.J. Follicular dendritic cells carry MHC class II-expressing microvesicles at their surface. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, D.K.; Franklin, J.L.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Zhang, Q.; Coffey, R.J. Abstract 1985: Reassessment of exosome composition. Cell 2019, 177, 428–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisticò, N.; Maisano, D.; Iaccino, E.; Vecchio, E.; Fiume, G.; Rotundo, S.; Quinto, I.; Mimmi, S. Role of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)-Derived Exosomes in Tumor Progression and Survival. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lei, Q.; Wang, H.; Xu, C.; Liu, T.; Kong, F.; Yang, C.; Yan, G.; Sun, L.; Zhao, A.; et al. Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles inhibit osteogenesis and exacerbate myeloma bone disease. Theranostics 2019, 9, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moloudizargari, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Asghari, M.H.; Zimta, A.A.; Neagoe, I.B.; Nabavi, S.M. The emerging role of exosomes in multiple myeloma. Blood Rev. 2019, 38, 100595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanski, M.J.; Szajnik, M.; Welsh, A.; Whiteside, T.L.; Boyiadzis, M. Blast-derived microvesicles in sera from patients with acute myeloid leukemia suppress natural killer cell function via membrane-associated transforming growth factor-β1. Haematologica 2011, 96, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.S.; Muller, L.; Boyiadzis, M.; Whiteside, T.L. Isolation and Characterization of CD34+ Blast-Derived Exosomes in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Garcia, M.; Weng, L.; Jung, X.; Murakami, J.L.; Hu, X.; McDonald, T.; Lin, A.; Kumar, A.R.; DiGiusto, D.L.; et al. Acute myeloid leukemia transforms the bone marrow niche into a leukemia-permissive microenvironment through exosome secretion. Leukemia 2017, 32, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornick, N.I.; Doron, B.; Abdelhamed, S.; Huan, J.; Harrington, C.A.; Shen, R.; Cambronne, X.A.; Verghese, S.C.; Kurre, P. AML suppresses hematopoiesis by releasing exosomes that contain microRNAs targeting c-MYB. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, ra88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pando, A.; Reagan, J.; Quesenberry, P.; Fast, L.D. Extracellular vesicles in leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2018, 64, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viola, S.; Traer, E.; Huan, J.; Hornick, N.I.; Tyner, J.W.; Agarwal, A.; Loriaux, M.M.; Johnstone, B.; Kurre, P. Alterations in acute myeloid leukaemia bone marrow stromal cell exosome content coincide with gains in tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 172, 983–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, J.; Miękus, K.; Kucia, M.; Zhang, J.; Reca, R.; Dvorak, P.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Embryonic stem cell-derived microvesicles reprogram hematopoietic progenitors: Evidence for horizontal transfer of mRNA and protein delivery. Leukemia 2006, 20, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arraud, N.; Gounou, C.; Linares, R.; Brisson, A.R. A simple flow cytometry method improves the detection of phosphatidylserine-exposing extracellular vesicles. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 13, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arraud, N.; Gounou, C.; Turpin, D.; Brisson, A.R. Fluorescence triggering: A general strategy for enumerating and phenotyping extracellular vesicles by flow cy-tometry. Cytom. Part A 2016, 89, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiklander, O.P.B.; Bostancioglu, R.B.; Welsh, J.A.; Zickler, A.M.; Murke, F.; Corso, G.; Felldin, U.; Hagey, D.W.; Evertsson, B.; Liang, X.-M.; et al. Systematic Methodological Evaluation of a Multiplex Bead-Based Flow Cytometry Assay for Detection of Extracellular Vesicle Surface Signatures. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koliha, N.; Wiencek, Y.; Heider, U.; Jüngst, C.; Kladt, N.; Krauthäuser, S.; Johnston, I.C.D.; Bosio, A.; Schauss, A.; Wild, S. A novel multiplex bead-based platform highlights the diversity of extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 29975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuana, Y.; Koning, R.; Kuil, M.E.; Rensen, P.C.N.; Koster, A.; Bertina, R.M.; Osanto, S. Cryo-electron microscopy of extracellular vesicles in fresh plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 21494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arraud, N.; Linares, R.; Tan, S.; Gounou, C.; Pasquet, J.-M.; Mornet, S.; Brisson, A.R. Extracellular vesicles from blood plasma: Determination of their morphology, size, phenotype and concentration. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, R.; Tan, S.; Gounou, C.; Arraud, N.; Brisson, A.R. High-speed centrifugation induces aggregation of extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 29509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issman, L.; Brenner, B.; Talmon, Y.; Aharon, A. Cryogenic Transmission Electron Microscopy Nanostructural Study of Shed Microparticles. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolba, F.M.; Foda, M.E.; Kamal, H.M.; Elshabrawy, D.A. Expression of CD133 in acute leukemia. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanada, M.; Bachmann, M.; Hardy, J.W.; Frimannson, D.O.; Bronsart, L.; Wang, A.; Sylvester, M.D.; Schmidt, T.L.; Kaspar, R.L.; Butte, M.J.; et al. Differential fates of biomolecules delivered to target cells via extracellular vesicles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1433–E1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado, H.; Alečković, M.; Lavotshkin, S.; Matei, I.; Costa-Silva, B.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Williams, C.; García-Santos, G.; Ghajar, C.M.; et al. Erratum: Corrigendum: Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksvold, M.P.; Kullmann, A.; Forfang, L.; Kierulf, B.; Li, M.; Brech, A.; Vlassov, A.V.; Smeland, E.B.; Neurauter, A.; Pedersen, K.W. Expression of B-Cell Surface Antigens in Subpopulations of Exosomes Released From B-Cell Lymphoma Cells. Clin. Ther. 2014, 36, 847–862.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belov, L.; Matic, K.J.; Hallal, S.; Best, G.; Mulligan, S.P.; Christopherson, R.I. Extensive surface protein profiles of extracellular vesicles from cancer cells may provide diagnostic signatures from blood samples. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 25355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Finger, E.; Gutierrez-Ramos, J.C. Expression of CD34 in endothelial cells, hematopoietic progenitors and nervous cells in fetal and adult mouse tissues. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, D.; Husel, W.; Lewandowska, K. CD34 expression on platelets. Platelets 2003, 14, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguet, L.; Pacaud, K.; Felden, C.; Hugel, B.; Martinez, M.C.; Freyssinet, J.M.; Herbrecht, R.; Potier, N.; van Dorsselaer, A.; Mauvieux, L. Proteomic analysis of malignant lymphocyte membrane microparticles using double ionization coverage optimi-zation. Proteomics 2006, 6, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, A.M.; El-Badawy, O.; Elsayh, K.I.; Mohamed, W.M.Y.; Riad, K.F.; Abdel-Rahim, M.; Rayan, A. Upregulation of CD146 in Pediatric B-Cell Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia and Its Implications on Treatment Outcomes. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 9736159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendall, L.; Bradstock, K.; Gottlieb, D. Expression of CD44 variant exons in acute myeloid leukemia is more common and more complex than that observed in normal blood, bone marrow or CD34+ cells. Leukemia 2000, 14, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chakhachiro, Z.I.; Zuo, Z.; Aladily, T.N.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Cortes, J.E.; AlAyed, K.; Nguyen, M.H.; Medeiros, L.J.; Bueso-Ramos, C. CD105 (Endoglin) Is Highly Overexpressed in a Subset of Cases of Acute Myeloid Leukemias. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 140, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauer, J.; Schwartz, K.; Tandler, C.; Hinterleitner, C.; Roerden, M.; Jung, G.; Salih, H.R.; Heitmann, J.S.; Märklin, M. CD105 (Endoglin) as negative prognostic factor in AML. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannagi, R.; Cochran, N.A.; Ishigami, F.; Hakomori, S.; Andrews, P.W.; Knowles, B.B.; Solter, D. Stage-specific embryonic antigens (SSEA-3 and -4) are epitopes of a unique globo-series ganglioside isolated from human teratocarcinoma cells. EMBO J. 1983, 2, 2355–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, J.A.; Itskovitz-Eldor, J.; Shapiro, S.S.; Waknitz, M.A.; Swiergiel, J.J.; Marshall, V.S.; Jones, J.M. Embryonic Stem Cell Lines Derived from Human Blastocysts. Science 1998, 282, 1145–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reubinoff, B.; Pera, M.F.; Fong, C.-Y.; Trounson, A.; Bongso, A. Embryonic stem cell lines from human blastocysts: Somatic differentiation in vitro. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gang, E.J.; Bosnakovski, D.; Figueiredo, C.A.; Visser, J.W.; Perlingeiro, R.C.R. SSEA-4 identifies mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow. Blood 2006, 109, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappellano, G.; Raineri, D.; Rolla, R.; Giordano, M.; Puricelli, C.; Vilardo, B.; Manfredi, M.; Cantaluppi, V.; Sainaghi, P.P.; Castello, L.; et al. Circulating Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Are a Hallmark of Sars-Cov-2 Infection. Cells 2021, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miljkovic-Licina, M.; Arraud, N.; Zahra, A.D.; Ropraz, P.; Matthes, T. Quantification and Phenotypic Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles from Patients with Acute Myeloid and B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers 2022, 14, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010056
Miljkovic-Licina M, Arraud N, Zahra AD, Ropraz P, Matthes T. Quantification and Phenotypic Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles from Patients with Acute Myeloid and B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers. 2022; 14(1):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010056
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiljkovic-Licina, Marijana, Nicolas Arraud, Aicha Dorra Zahra, Patricia Ropraz, and Thomas Matthes. 2022. "Quantification and Phenotypic Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles from Patients with Acute Myeloid and B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia" Cancers 14, no. 1: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010056
APA StyleMiljkovic-Licina, M., Arraud, N., Zahra, A. D., Ropraz, P., & Matthes, T. (2022). Quantification and Phenotypic Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles from Patients with Acute Myeloid and B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers, 14(1), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010056





