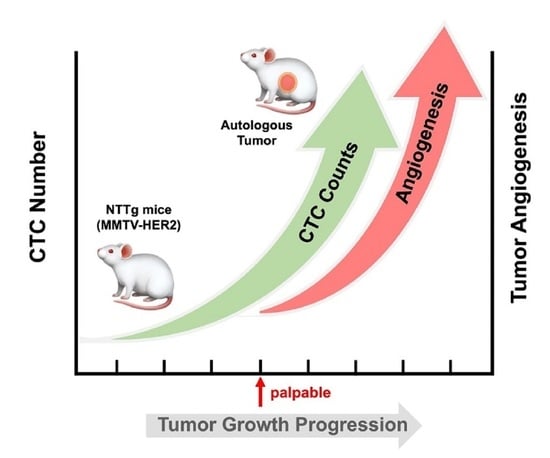
Early Detection and Dynamic Changes of Circulating Tumor Cells in Transgenic NeuN Transgenic (NTTg) Mice with Spontaneous Breast Tumor Development
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model
2.2. Anesthesia
2.3. Measurement of Tumor Size and Vascular Density by Doppler Ultrasonography
2.4. Lumpectomy for Primary Culture of Tumor Cells and Pathology Examination
2.5. Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation (QCM-D) Measurements for Verification of Surface Modification
2.6. mCMx Chip Fabrication
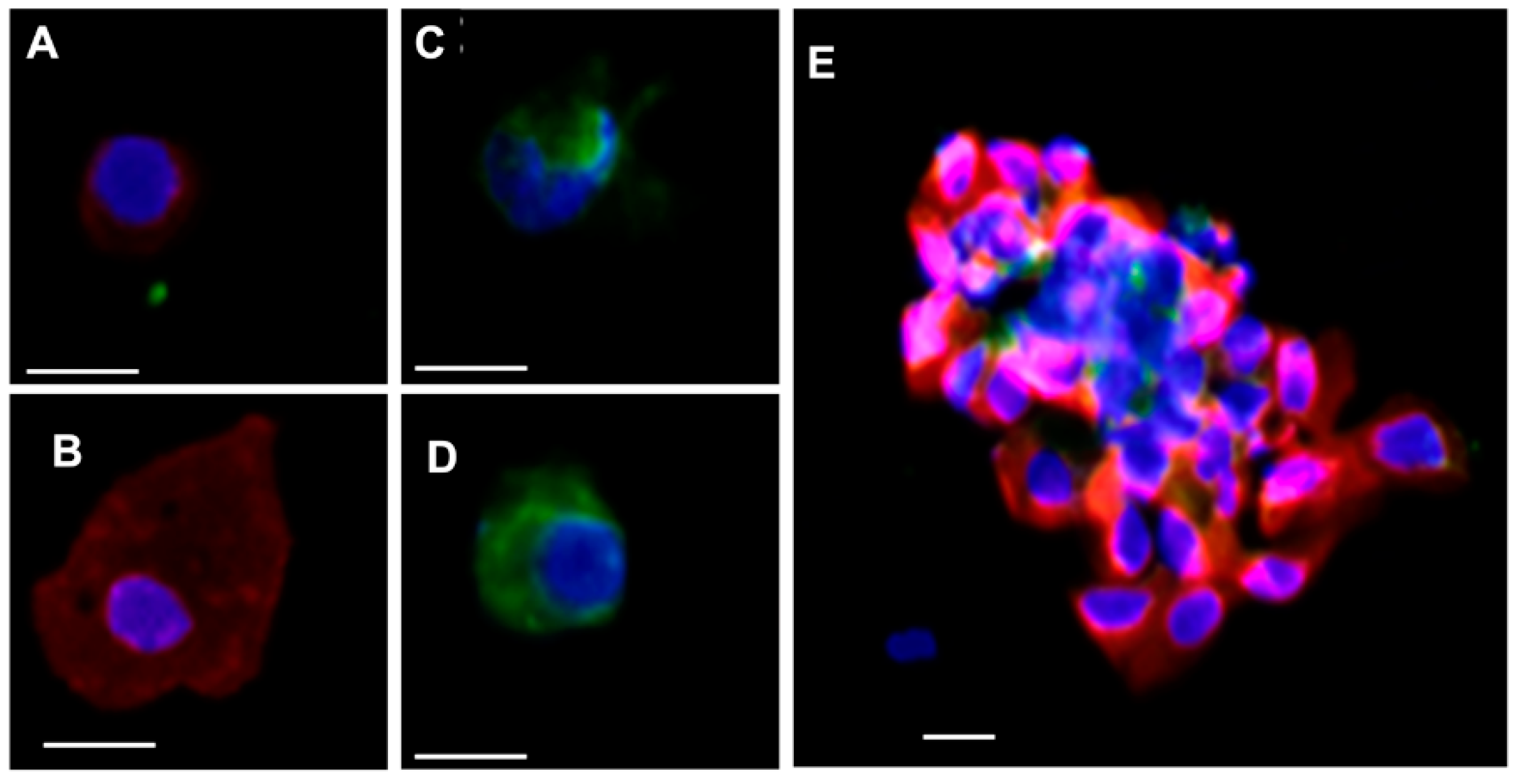
2.7. CTCs Captured by the mCMx Chip and Immunostaining for Enumeration
2.8. Inoculation of Captured CTCs for the Tumorigenesis Test
3. Results
3.1. Modified CMx (mCMx) Chip Construction and Feasibility
3.1.1. Surface Coating of the mCMx Chip
3.1.2. Cell Identification
3.2. CTC in the Early Stage of Tumor Development and during Tumor Progression
3.3. Replanting the CTCs and Tumorigenesis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glaves, D. Correlation Between Circulating Cancer-Cells And Incidence Of Metastases. Br. J. Cancer 1983, 48, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasseur, A.; Kiavue, N.; Bidard, F.C.; Pierga, J.Y.; Cabel, L. Clinical utility of circulating tumor cells: An update. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1647–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, S.; Vogl, F.D.; Naume, B.; Janni, W.; Osborne, M.P.; Coombes, R.C.; Schlimok, G.; Diel, I.J.; Gerber, B.; Gebauer, G. A pooled analysis of bone marrow micrometastasis in breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidard, F.-C.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; Gomme, S.; Nos, C.; de Rycke, Y.; Thiery, J.P.; Sigal-Zafrani, B.; Mignot, L.; Sastre-Garau, X.; Pierga, J.-Y. Disseminated tumor cells of breast cancer patients: A strong prognostic factor for distant and local relapse. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 3306–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartkopf, A.D.; Taran, F.-A.; Wallwiener, M.; Hahn, M.; Becker, S.; Solomayer, E.-F.; Brucker, S.Y.; Fehm, T.N.; Wallwiener, D. Prognostic relevance of disseminated tumour cells from the bone marrow of early stage breast cancer patients–results from a large single-centre analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2550–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucci, A.; Hall, C.S.; Lodhi, A.K.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Anderson, A.E.; Xiao, L.; Bedrosian, I.; Kuerer, H.M.; Krishnamurthy, S. Circulating tumour cells in non-metastatic breast cancer: A prospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rack, B.; Schindlbeck, C.; Jückstock, J.; Andergassen, U.; Hepp, P.; Zwingers, T.; Friedl, T.W.; Lorenz, R.; Tesch, H.; Fasching, P.A. Circulating tumor cells predict survival in early average-to-high risk breast cancer patients. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Cristofanilli, M.; Singh, B.; Reuben, J.; Gao, H.; Cohen, E.N.; Andreopoulou, E.; Hall, C.S.; Lodhi, A.; Jackson, S. Detection of minimal residual disease in blood and bone marrow in early stage breast cancer. Cancer 2010, 116, 3330–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, H.D.; Fu, R.; Cantor, A.; Pappas, M.; Daeges, M.; Humphrey, L. Effectiveness of breast cancer screening: Systematic review and meta-analysis to update the 2009 US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 164, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaseem, A.; Lin, J.S.; Mustafa, R.A.; Horwitch, C.A.; Wilt, T.J. Screening for breast cancer in average-risk women: A guidance statement from the American College of Physicians. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohuchi, N.; Suzuki, A.; Sobue, T.; Kawai, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Zheng, Y.-F.; Shiono, Y.N.; Saito, H.; Kuriyama, S.; Tohno, E. Sensitivity and specificity of mammography and adjunctive ultrasonography to screen for breast cancer in the Japan Strategic Anti-cancer Randomized Trial (J-START): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosse, S.A.; Gorges, T.M.; Pantel, K. Biology, detection, and clinical implications of circulating tumor cells. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Stott, S.; Toner, M.; Maheswaran, S.; Haber, D.A. Circulating tumor cells: Approaches to isolation and characterization. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 192, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huesemann, Y.; Geigl, J.B.; Schubert, F.; Musiani, P.; Meyer, M.; Burghart, E.; Forni, G.; Eils, R.; Fehm, T.; Riethmueller, G.; et al. Systemic spread is an early step in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.-C.; Tseng, P.-Y.; Tsai, W.-S.; Liao, M.-Y.; Lu, S.-H.; Frank, C.W.; Chen, J.-S.; Wu, H.-C.; Chang, Y.-C. Antibody conjugated supported lipid bilayer for capturing and purification of viable tumor cells in blood for subsequent cell culture. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 5191–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Tsai, W.-S.; Shao, H.-J.; Wu, J.-C.; Lai, J.-M.; Lu, S.-H.; Hung, T.-F.; Yang, C.-T.; Wu, L.-C.; Chen, J.-S. Sensitive and specific biomimetic lipid coated microfluidics to isolate viable circulating tumor cells and microemboli for cancer detection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, W.-S.; Chen, J.-S.; Shao, H.-J.; Wu, J.-C.; Lai, J.-M.; Lu, S.-H.; Hung, T.-F.; Chiu, Y.-C.; You, J.-F.; Hsieh, P.-S. Circulating tumor cell count correlates with colorectal neoplasm progression and is a prognostic marker for distant metastasis in non-metastatic patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.-S.; You, J.-F.; Hung, H.-Y.; Hsieh, P.-S.; Hsieh, B.; Lenz, H.-J.; Idos, G.; Friedland, S.; Pan, J.Y.-J.; Shao, H.-J. Novel Circulating Tumor Cell Assay for Detection of Colorectal Adenomas and Cancer. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, C.T.; Webster, M.A.; Schaller, M.; Parsons, T.J.; Cardiff, R.D.; Muller, W.J. Expression of the neu protooncogene in the mammary epithelium of transgenic mice induces metastatic disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 10578–10582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bargmann, C.I.; Hung, M.-C.; Weinberg, R.A. Multiple independent activations of the neu oncogene by a point mutation altering the transmembrane domain of p185. Cell 1986, 45, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torphy, R.J.; Tignanelli, C.J.; Kamande, J.W.; Moffitt, R.A.; Loeza, S.G.H.; Soper, S.A.; Yeh, J.J. Circulating tumor cells as a biomarker of response to treatment in patient-derived xenograft mouse models of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89474. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, M.J.; Wollish, W.S.; Lobo, M.; Esserman, L.J. Epithelial and fibroblast cell lines derived from a spontaneous mammary carcinoma in a MMTV/neu transgenic mouse. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2002, 38, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harouaka, R.A.; Nisic, M.; Zheng, S.-Y. Circulating Tumor Cell Enrichment Based on Physical Properties. J. Lab. Autom. 2013, 18, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Mori, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Takahashi, S.; Kodama, T. Mouse Model of Lymph Node Metastasis via Afferent Lymphatic Vessels for Development of Imaging Modalities. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muthukkaruppan, V.; Kubai, L.; Auerbach, R. Tumor-induced neovascularization in the mouse eye. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1982, 69, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Katoh, M.; Neumaier, M.; Nezam, R.; Izbicki, J.R.; Schumacher, U. Correlation of circulating tumor cells with tumor size and metastatic load in a spontaneous lung metastasis model. Anticancer. Res. 2004, 24, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baluk, P.; Morikawa, S.; Haskell, A.; Mancuso, M.; McDonald, D.M. Abnormalities of basement membrane on blood vessels and endothelial sprouts in tumors. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 1801–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benoy, I.H.; Salgado, R.; Elst, H.; Van Dam, P.; Weyler, J.; Van Marck, E.; Scharpe, S.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Dirix, L.Y. Relative microvessel area of the primary tumour, and not lymph node status, predicts the presence of bone marrow micrometastases detected by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction in patients with clinically non-metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2005, 7, R210–R219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davies, M.M.; Mathur, P.; Carnochan, P.; Saini, S.; Allen-Mersh, T.G. Effect of manipulation of primary tumour vascularity on metastases in an adenocarcinoma model. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dhakal, H.P.; Naume, B.; Synnestvedt, M.; Borgen, E.; Kaaresen, R.; Schlichting, E.; Wiedswang, G.; Bassarova, A.; Giercksky, K.-E.; Nesland, J.M. Vascularization in primary breast carcinomas: Its prognostic significance and relationship with tumor cell dissemination. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2341–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maltoni, R.; Fici, P.; Amadori, D.; Gallerani, G.; Cocchi, C.; Zoli, M.; Rocca, A.; Cecconetto, L.; Folli, S.; Scarpi, E. Circulating tumor cells in early breast cancer: A connection with vascular invasion. Cancer Lett. 2015, 367, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alix-Panabières, C.; Pantel, K. Circulating tumor cells: Liquid biopsy of cancer. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alix-Panabieres, C.; Pantel, K. Clinical Applications of Circulating Tumor Cells and Circulating Tumor DNA as Liquid Biopsy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ilie, M.; Hofman, V.; Long-Mira, E.; Selva, E.; Vignaud, J.-M.; Padovani, B.; Mouroux, J.; Marquette, C.-H.; Hofman, P. “Sentinel” circulating tumor cells allow early diagnosis of lung cancer in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marquette, C.-H.; Boutros, J.; Benzaquen, J.; Ferreira, M.; Pastre, J.; Pison, C.; Padovani, B.; Bettayeb, F.; Fallet, V.; Guibert, N. Circulating tumour cells as a potential biomarker for lung cancer screening: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.-S.; Nimgaonkar, A.; Segurado, O.; Chang, Y.; Hsieh, B.; Shao, H.-J.; Wu, J.; Lai, -.M. Jr.; Javey, M.; Watson, D. Prospective clinical study of circulating tumor cells for colorectal cancer screening. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hundt, S.; Haug, U.; Brenner, H. Comparative evaluation of immunochemical fecal occult blood tests for colorectal adenoma detection. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzaniga, P.; de Berardinis, E.; Raimondi, C.; Gradilone, A.; Busetto, G.M.; De Falco, E.; Nicolazzo, C.; Giovannone, R.; Gentile, V.; Cortesi, E. Circulating tumor cells detection has independent prognostic impact in high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1978–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulze, K.; Gasch, C.; Staufer, K.; Nashan, B.; Lohse, A.W.; Pantel, K.; Riethdorf, S.; Wege, H. Presence of EpCAM-positive circulating tumor cells as biomarker for systemic disease strongly correlates to survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 2165–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashist, Y.K.; Effenberger, K.E.; Vettorazzi, E.; Riethdorf, S.; Yekebas, E.F.; Izbicki, J.R.; Pantel, K. Disseminated tumor cells in bone marrow and the natural course of resected esophageal cancer. Ann. Surg. 2012, 255, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thery, L.; Meddis, A.; Cabel, L.; Proudhon, C.; Latouche, A.; Pierga, J.-Y.; Bidard, F.-C. Circulating tumor cells in early breast cancer. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2019, 3, pkz026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méhes, G.; Witt, A.; Kubista, E.; Ambros, P.F. Circulating breast cancer cells are frequently apoptotic. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wirtz, D.; Konstantopoulos, K.; Searson, P.C. The physics of cancer: The role of physical interactions and mechanical forces in metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jordan, N.V.; Bardia, A.; Wittner, B.S.; Benes, C.; Ligorio, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, M.; Sundaresan, T.K.; Licausi, J.A.; Desai, R. HER2 expression identifies dynamic functional states within circulating breast cancer cells. Nature 2016, 537, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galletti, G.; Sung, M.S.; Vahdat, L.T.; Shah, M.A.; Santana, S.M.; Altavilla, G.; Kirby, B.J.; Giannakakou, P. Isolation of breast cancer and gastric cancer circulating tumor cells by use of an anti HER2-based microfluidic device. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, A.D.; Mirek, E.T.; Aiello, N.M.; Maitra, A.; Bailey, J.M.; McAllister, F.; Reichert, M.; Beatty, G.L.; Rustgi, A.K.; Vonderheide, R.H.; et al. EMT and Dissemination Precede Pancreatic Tumor Formation. Cell 2012, 148, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aceto, N.; Bardia, A.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Donaldson, M.C.; Wittner, B.S.; Spencer, J.A.; Yu, M.; Pely, A.; Engstrom, A.; Zhu, H. Circulating tumor cell clusters are oligoclonal precursors of breast cancer metastasis. Cell 2014, 158, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, J.-M.; Krebs, M.G.; Lancashire, L.; Sloane, R.; Backen, A.; Swain, R.K.; Priest, L.; Greystoke, A.; Zhou, C.; Morris, K. Clinical significance and molecular characteristics of circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor microemboli in patients with small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.-C.; Chang, Y.-T.; Chen, J.-Y.; Jeng, Y.-M.; Yang, C.-Y.; Tien, Y.-W.; Yang, S.-H.; Chen, H.-L.; Liang, T.-Y.; Wang, C.-F. Clinical significance of circulating tumor microemboli as a prognostic marker in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; Bai, F.; Wu, K. Growing trends of contralateral prophylactic mastectomy and reconstruction in young breast cancer. J. Surg. Res. 2019, 239, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.M.; Freedman, R.A.; Sagara, Y.; Aydogan, F.; Barry, W.T.; Golshan, M. Growing use of contralateral prophylactic mastectomy despite no improvement in long-term survival for invasive breast cancer. Ann. Surg. 2017, 265, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valachis, A.; Nearchou, A.D.; Lind, P. Surgical management of breast cancer in BRCA-mutation carriers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 144, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sprundel, T.; Schmidt, M.; Rookus, M.; Brohet, R.; Van Asperen, C.; Rutgers, E.T.; van‘t Veer, L.; Tollenaar, R. Risk reduction of contralateral breast cancer and survival after contralateral prophylactic mastectomy in BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation carriers. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 93, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teoh, V.; Tasoulis, M.-K.; Gui, G. Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy in Women with Unilateral Breast Cancer Who Are Genetic Carriers, Have a Strong Family History or Are just Young at Presentation. Cancers 2020, 12, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Metcalfe, K.A.; Retrouvey, H.; Kerrebijn, I.; Butler, K.; O’Neill, A.C.; Cil, T.; Zhong, T.; Hofer, S.O.; McCready, D.R. Predictors of uptake of contralateral prophylactic mastectomy in women with nonhereditary breast cancer. Cancer 2019, 125, 3966–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, P.J.; Abdulghani, M.; Waljee, J.F.; Kozlow, J.H.; Sabel, M.S.; Newman, L.A.; Chung, K.C.; Momoh, A.O. An analysis of the decisions made for contralateral prophylactic mastectomy and breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 138, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanikou, E.; Markou, A.; Politaki, E.; Koutsopoulos, A.; Psyrri, A.; Mavroudis, D.; Georgoulias, V.; Lianidou, E. PIK 3 CA hotspot mutations in circulating tumor cells and paired circulating tumor DNA in breast cancer: A direct comparison study. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 2515–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bader, A.G.; Kang, S.; Vogt, P.K. Cancer-specific mutations in PIK3CA are oncogenic in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Bardia, A.; Aceto, N.; Bersani, F.; Madden, M.W.; Donaldson, M.C.; Desai, R.; Zhu, H.; Comaills, V.; Zheng, Z. Ex vivo culture of circulating breast tumor cells for individualized testing of drug susceptibility. Science 2014, 345, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, W.-S.; Hung, T.-F.; Chen, J.-Y.; Huang, S.-H.; Chang, Y.-C. Early Detection and Dynamic Changes of Circulating Tumor Cells in Transgenic NeuN Transgenic (NTTg) Mice with Spontaneous Breast Tumor Development. Cancers 2021, 13, 3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133294
Tsai W-S, Hung T-F, Chen J-Y, Huang S-H, Chang Y-C. Early Detection and Dynamic Changes of Circulating Tumor Cells in Transgenic NeuN Transgenic (NTTg) Mice with Spontaneous Breast Tumor Development. Cancers. 2021; 13(13):3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133294
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Wen-Sy, Tsung-Fu Hung, Jia-Yang Chen, Shu-Huan Huang, and Ying-Chih Chang. 2021. "Early Detection and Dynamic Changes of Circulating Tumor Cells in Transgenic NeuN Transgenic (NTTg) Mice with Spontaneous Breast Tumor Development" Cancers 13, no. 13: 3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133294
APA StyleTsai, W.-S., Hung, T.-F., Chen, J.-Y., Huang, S.-H., & Chang, Y.-C. (2021). Early Detection and Dynamic Changes of Circulating Tumor Cells in Transgenic NeuN Transgenic (NTTg) Mice with Spontaneous Breast Tumor Development. Cancers, 13(13), 3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133294