The Intermediate Filament Synemin Regulates Non-Homologous End Joining in an ATM-Dependent Manner
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
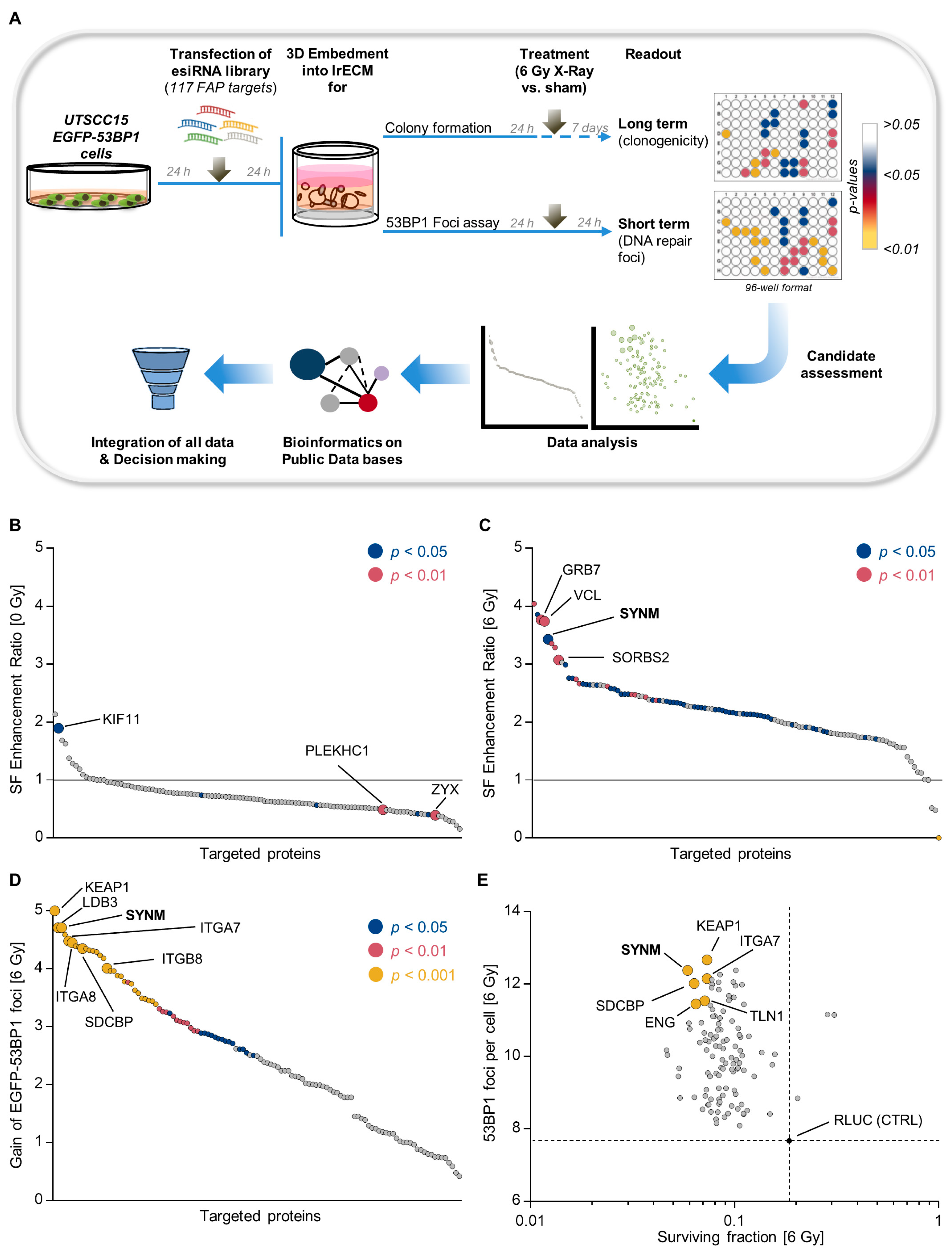
2.1. Identification of Adhesome-Based Key Regulators of Radiation Sensitivity and DNA Double Strand Break Repair in HNSCC
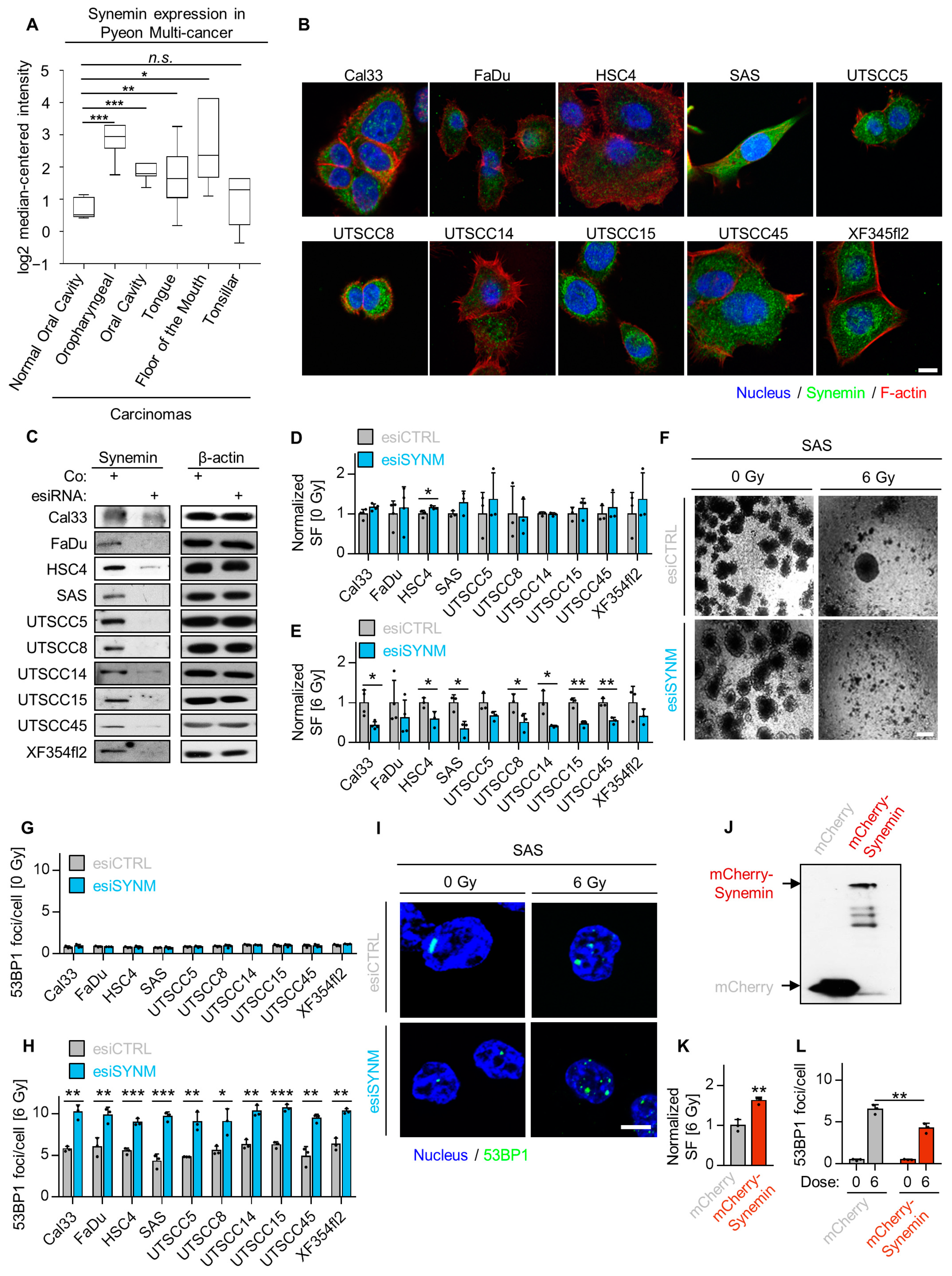
2.2. Synemin Modulates Radiation Sensitivity and DNA Double Strand Break Repair in HNSCC Cells
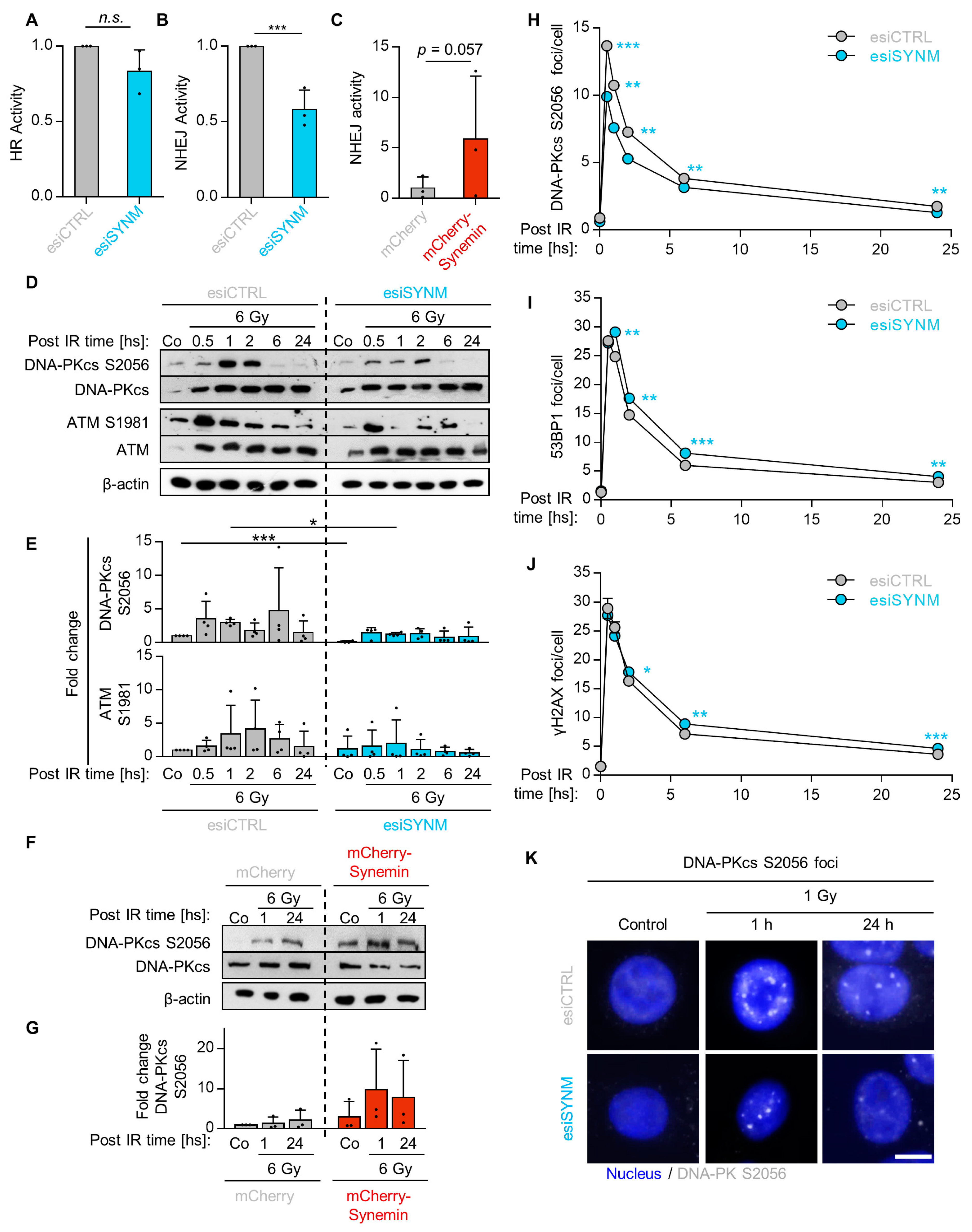
2.3. Synemin Regulates NHEJ by Influencing DNA-PKcs and ATM Phosphorylation
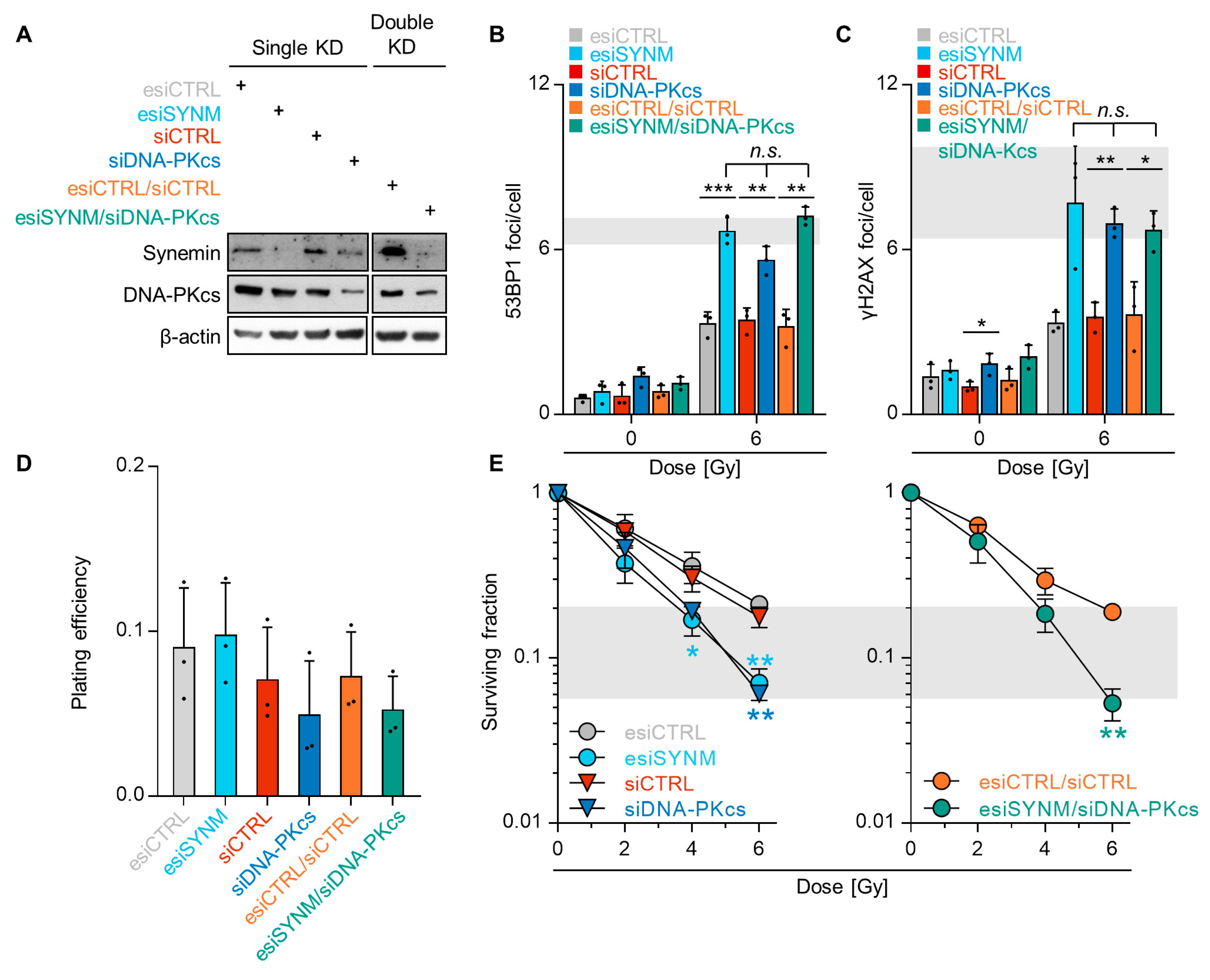
2.4. Synemin Influences DSB Repair Responses by Regulating DNA-PKcs
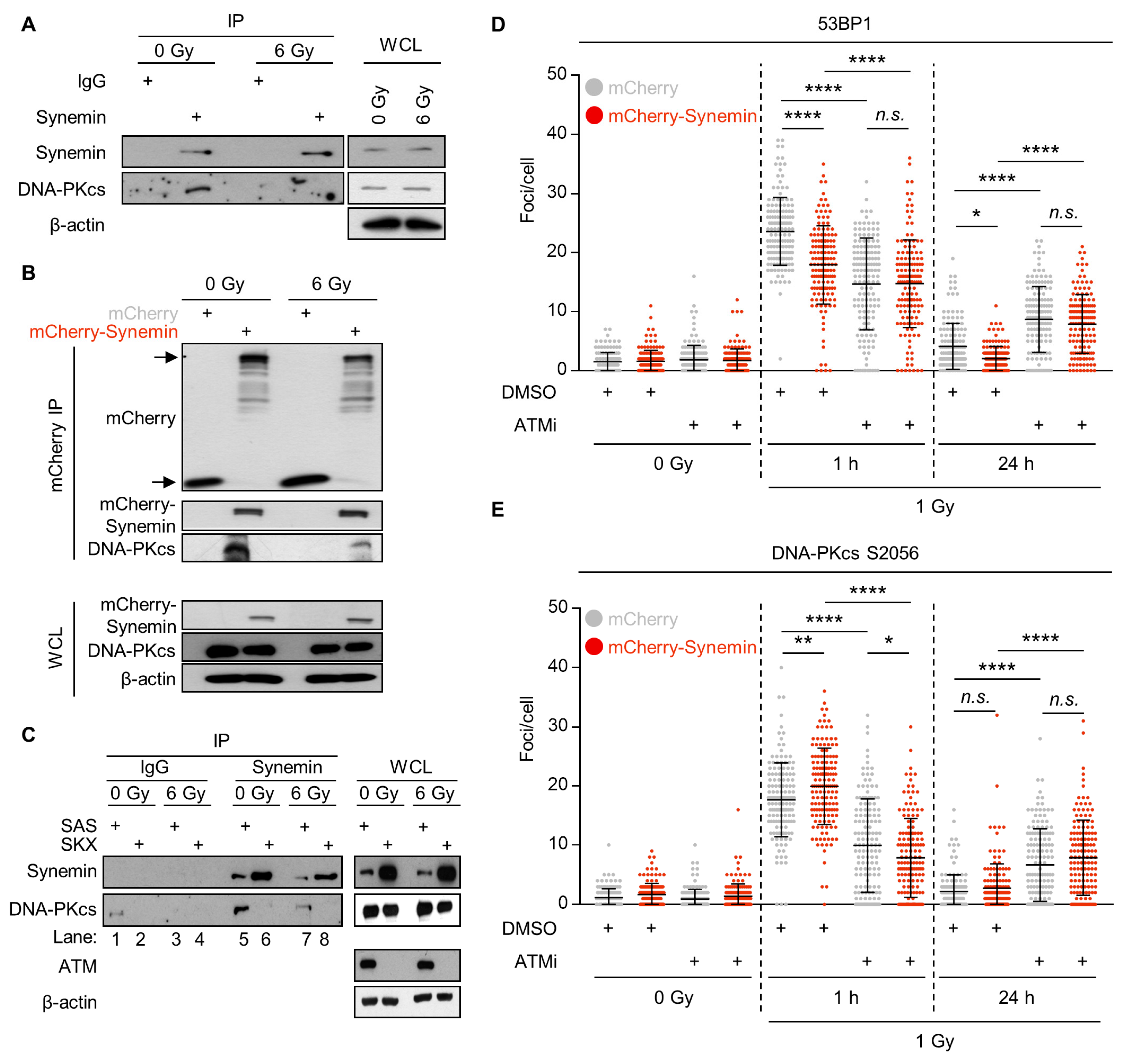
2.5. Synemin Interacts with DNA-PKcs in an ATM-Dependent Manner
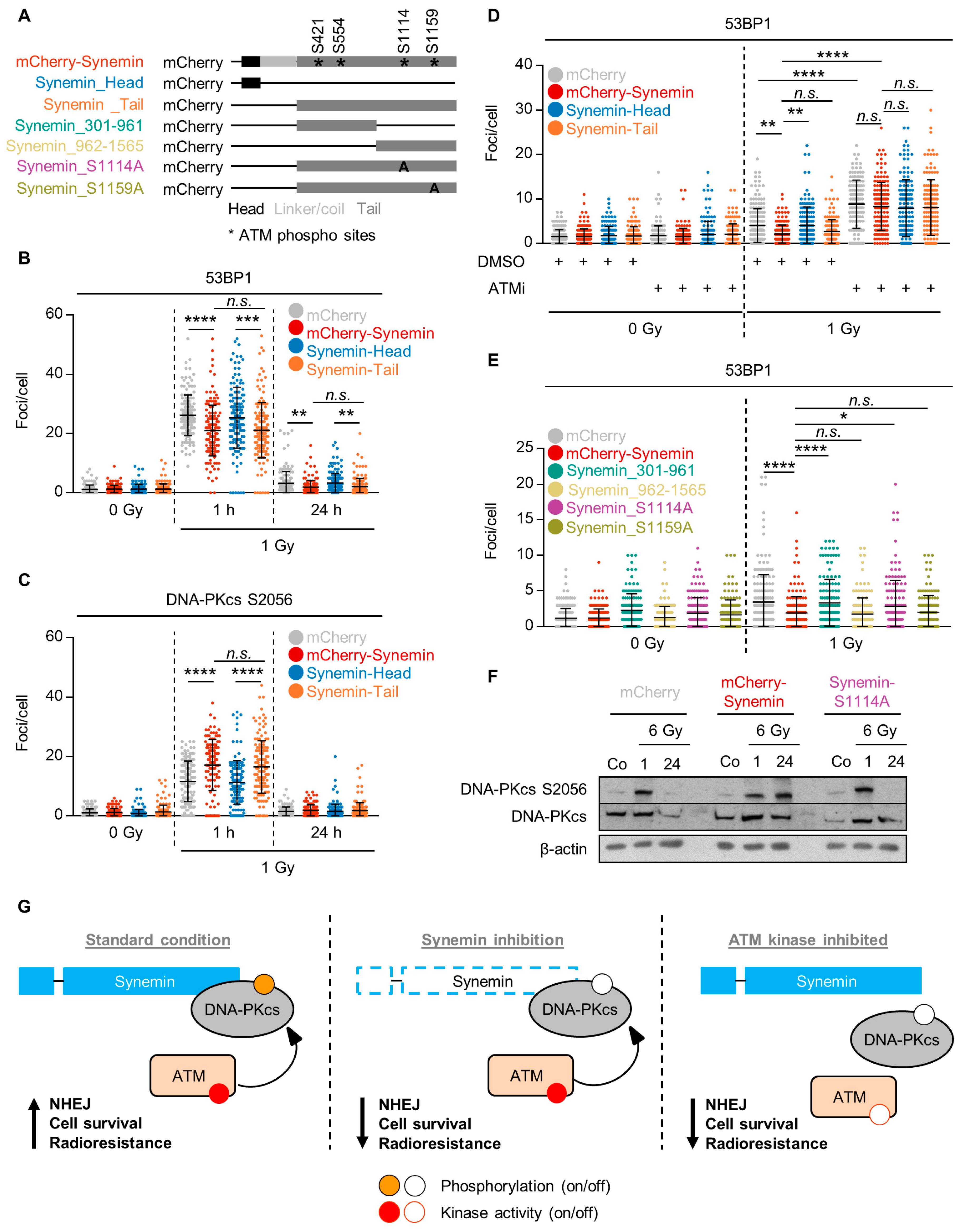
2.6. ATM Phosphorylation of the Synemin Tail Modulates DNA Repair
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and 3D Cell Culture
4.2. X-Ray Irradiation
4.3. Antibodies
4.4. 3D High-Throughput Screen Using esiRNA (3D HTP-RNAi-S)
4.5. esiRNA and siRNA Transfection
4.6. Total Protein Extraction, Western Blotting
4.7. 3D Colony Formation Assay
4.8. Foci Assay
4.9. Synenim Constructs and Stable Transfection
4.10. DRGFP and pimEJ5GFP-Based Chromosomal Break Reporter Assay
4.11. Proximity Ligation Assay (PLA)
4.12. Immunoprecipitation
4.13. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.14. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolderson, E.; Richard, D.J.; Zhou, B.-B.S.; Khanna, K.K. Recent advances in cancer therapy targeting proteins involved in DNA double-strand break repair. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6314–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackford, A.N.; Jackson, S.P. ATM, ATR, and DNA-PK: The trinity at the heart of the dna damage response. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 801–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgmann, K.; Köcher, S.; Kriegs, M.; Mansour, W.Y.; Parplys, A.C.; Rieckmann, T.; Rothkamm, K. DNA repair. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2016, 198, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minten, E.V.; Yu, D.S. DNA repair: Translation to the clinic. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 31, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.H.Y.; Pannunzio, N.R.; Adachi, N.; Lieber, M.R. Non-homologous DNA end joining and alternative pathways to double-strand break repair. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkenist, C.J.; Kastan, M.B. Chromatin perturbations during the DNA damage response in higher eukaryotes. DNA Repair (Amst.) 2015, 36, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissell, M.J.; Weaver, V.M.; Lelièvre, S.A.; Wang, F.; Petersen, O.W.; Schmeichel, K.L. Tissue structure, nuclear organization, and gene expression in normal and malignant breast. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 1757s–1763s. [Google Scholar]
- Eke, I.; Cordes, N. Focal adhesion signaling and therapy resistance in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 31, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienert, E.; Eke, I.; Aust, D.; Cordes, N. LIM-only protein FHL2 critically determines survival and radioresistance of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eke, I.; Zscheppang, K.; Dickreuter, E.; Hickmann, L.; Mazzeo, E.; Unger, K.; Krause, M.; Cordes, N. Simultaneous β1 integrin-EGFR targeting and radiosensitization of human head and neck cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickreuter, E.; Eke, I.; Krause, M.; Borgmann, K.; Van Vugt, M.A.; Cordes, N. Targeting of β1 integrins impairs DNA repair for radiosensitization of head and neck cancer cells. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotula, E.; Faigle, W.; Berthault, N.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Sun, J.S.; Dutreix, M.; Quanz, M. DNA-PK target identification reveals novel links between DNA repair signaling and cytoskeletal regulation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz Osterman, C.J.; Ozmadenci, D.; Kleinschmidt, E.G.; Taylor, K.N.; Barrie, A.M.; Jiang, S.; Bean, L.M.; Sulzmaier, F.J.; Jean, C.; Tancioni, I.; et al. FAK activity sustains intrinsic and acquired ovarian cancer resistance to platinum chemotherapy. Elife 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, K.; Wu, X.; Yang, X.; Song, G.; Zhang, B.; Zhong, L. Integrative PDGF/PDGFR and focal adhesion pathways are downregulated in ERCC1-defective non-small cell lung cancer undergoing sodium glycididazole-sensitized cisplatin treatment. Gene 2019, 691, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Kharbanda, S.; Mayer, B.; Kufe, D.; Weaver, D.T. Binding of Ku and c-Abl at the kinase homology region of DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 24763–24766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérette, D.; Khan, P.A.; Savard, P.E.; Vincent, M. Molecular evolution of type VI intermediate filament proteins. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, R.; Pizzolato, G.; Robson, R.M.; Gabbiani, G.; Skalli, O. Intermediate filament protein synemin is present in human reactive and malignant astrocytes and associates with ruffled membranes in astrocytoma cells. Glia 2005, 50, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Huiatt, T.W.; Paulin, D.; Li, Z.; Robson, R.M. Synemin interacts with the LIM domain protein zyxin and is essential for cell adhesion and migration. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehlgans, S.; Eke, I.; Cordes, N. Targeting FAK radiosensitizes 3-dimensional grown human HNSCC cells through reduced Akt1 and MEK1/2 signaling. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, e669–e676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eke, I.; Koch, U.; Hehlgans, S.; Sandfort, V.; Stanchi, F.; Zips, D.; Baumann, M.; Shevchenko, A.; Pilarsky, C.; Haase, M.; et al. PINCH1 regulates Akt1 activation and enhances radioresistance by inhibiting PP1alpha. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 2516–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eke, I.; Deuse, Y.; Hehlgans, S.; Gurtner, K.; Krause, M.; Baumann, M.; Shevchenko, A.; Sandfort, V.; Cordes, N. β1 Integrin/FAK/cortactin signaling is essential for human head and neck cancer resistance to radiotherapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Network, T.C.G.A. Comprehensive genomic characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Nature 2015, 517, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Ren, J.; Gao, X.; Jin, C.; Wen, L.; Yao, X. GPS 2.0, a tool to predict kinase-specific phosphorylation sites in hierarchy. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 1598–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, W.Y.; Bogdanova, N.V.; Kasten-Pisula, U.; Rieckmann, T.; Köcher, S.; Borgmann, K.; Baumann, M.; Krause, M.; Petersen, C.; Hu, H.; et al. Aberrant overexpression of miR-421 downregulates ATM and leads to a pronounced DSB repair defect and clinical hypersensitivity in SKX squamous cell carcinoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 106, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampietro, D.; Sámano-Sánchez, H.; Davey, N.E.; Sharan, M.; Mészáros, B.; Gibson, T.J.; Kumar, M. Conserved SQ and QS motifs in bacterial effectors suggest pathogen interplay with the ATM kinase family during infection. bioRxiv 2018, 364117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickup, M.W.; Mouw, J.K.; Weaver, V.M. The extracellular matrix modulates the hallmarks of cancer. EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, K.; Mahajan, N.P. Cross talk of tyrosine kinases with the DNA damage signaling pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 10588–10601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabodi, S.; Del Pilar Camacho-Leal, M.; Di Stefano, P.; Defilippi, P. Integrin signalling adaptors: Not only figurants in the cancer story. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.-J.; Constanzo, J.D.; Venkateswaran, N.; Melegari, M.; Ilcheva, M.; Morales, J.C.; Skoulidis, F.; Heymach, J.V.; Boothman, D.A.; Scaglioni, P.P. Focal adhesion kinase regulates the DNA damage response and its inhibition radiosensitizes mutant KRAS lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5851–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehlow, A.; Cordes, N. Invasion as target for therapy of glioblastoma multiforme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1836, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.E.; Bundred, N.J.; Landberg, G.; Clarke, R.B.; Farnie, G. Focal adhesion kinase and Wnt signaling regulate human ductal carcinoma in situ stem cell activity and response to radiotherapy. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Pelagio, K.P.; Chen, L.; Joca, H.C.; Ward, C.; Jonathan Lederer, W.; Bloch, R.J. Absence of synemin in mice causes structural and functional abnormalities in heart. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2018, 114, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parlakian, A.; Paulin, D.; Izmiryan, A.; Xue, Z.; Li, Z. Intermediate filaments in peripheral nervous system: Their expression, dysfunction and diseases. Rev. Neurol. (Paris) 2016, 172, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quick, Q.; Paul, M.; Skalli, O. Roles and potential clinical applications of intermediate filament proteins in brain tumors. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2015, 22, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noetzel, E.; Rose, M.; Sevinc, E.; Hilgers, R.-D.; Hartmann, A.; Naami, A.; Knüchel, R.; Dahl, E. Intermediate filament dynamics and breast cancer: Aberrant promoter methylation of the synemin gene is associated with early tumor relapse. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4814–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitre, A.; Davis, N.; Paul, M.; Orr, A.W.; Skalli, O. Synemin promotes AKT-dependent glioblastoma cell proliferation by antagonizing PP2A. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-H.; Cheng, C.-C.; Lai, Y.-S.; Chao, W.-T.; Pei, R.-J.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Ho, C.-C. Synemin down-regulation in human hepatocellular carcinoma does not destabilize cytoskeletons in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 404, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanamiryan, L.; Li, Z.; Paulin, D.; Xue, Z. Self-assembly incompetence of synemin is related to the property of its head and rod domains. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 9531–9539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilak, S.R.; Sernett, S.W.; Bilak, M.M.; Bellin, R.M.; Stromer, M.H.; Huiatt, T.W.; Robson, R.M. Properties of the novel intermediate filament protein synemin and its identification in mammalian muscle. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1998, 355, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, F.; Leube, R. Epithelial intermediate filaments: Guardians against microbial infection? Cells 2016, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceau, N.; Schutte, B.; Gilbert, S.; Loranger, A.; Henfling, M.E.R.; Broers, J.L.V.; Mathew, J.; Ramaekers, F.C.S. Dual roles of intermediate filaments in apoptosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 2265–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothballer, A.; Kutay, U. The diverse functional LINCs of the nuclear envelope to the cytoskeleton and chromatin. Chromosoma 2013, 122, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spichal, M.; Fabre, E. The emerging role of the cytoskeleton in chromosome dynamics. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lottersberger, F.; Karssemeijer, R.A.; Dimitrova, N.; De Lange, T. 53BP1 and the LINC complex promote microtubule-dependent DSB mobility and DNA repair. Cell 2015, 163, 880–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, N.D.; Stanley, F.K.T.; Moore, S.; Goodarzi, A.A. ATM-dependent pathways of chromatin remodelling and oxidative DNA damage responses. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Cordes, N. ATM controls DNA repair and mitochondria transfer between neighboring cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehlow, A.; Klapproth, E.; Jin, S.; Hannen, R.; Hauswald, M.; Bartsch, J.-W.; Nimsky, C.; Temme, A.; Leitinger, B.; Cordes, N. Interaction of discoidin domain receptor 1 with a 14-3-3-Beclin-1-Akt1 complex modulates glioblastoma therapy sensitivity. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 3672–3683.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittler, R.; Putz, G.; Pelletier, L.; Poser, I.; Heninger, A.K.; Drechsel, D.; Fischer, S.; Konstantinova, I.; Habermann, B.; Grabner, H.; et al. An endoribonuclease-prepared siRNA screen in human cells identifies genes essential for cell division. Nature 2004, 432, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, E.R.; Byron, A.; Askari, J.A.; Ng, D.H.J.; Millon-Frémillon, A.; Robertson, J.; Koper, E.J.; Paul, N.R.; Warwood, S.; Knight, D.; et al. Definition of a consensus integrin adhesome and its dynamics during adhesion complex assembly and disassembly. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, A.J.; Johnson, R.D.; Thompson, L.H.; Jasin, M. XRCC3 promotes homology-directed repair of DNA damage in mammalian cells service XRCC3 promotes homology-directed repair of DNA damage in mammalian cells. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 2633–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, M.; Heijink, A.M.; Bisselink, Y.J.W.M.; Seinstra, R.I.; Silljé, H.H.W.; De Vries, E.G.E.; Van Vugt, M.A.T.M. Forced activation of Cdk1 via wee1 inhibition impairs homologous recombination. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3001–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deville, S.S.; Vehlow, A.; Förster, S.; Dickreuter, E.; Borgmann, K.; Cordes, N. The Intermediate Filament Synemin Regulates Non-Homologous End Joining in an ATM-Dependent Manner. Cancers 2020, 12, 1717. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071717
Deville SS, Vehlow A, Förster S, Dickreuter E, Borgmann K, Cordes N. The Intermediate Filament Synemin Regulates Non-Homologous End Joining in an ATM-Dependent Manner. Cancers. 2020; 12(7):1717. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071717
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeville, Sara Sofia, Anne Vehlow, Sarah Förster, Ellen Dickreuter, Kerstin Borgmann, and Nils Cordes. 2020. "The Intermediate Filament Synemin Regulates Non-Homologous End Joining in an ATM-Dependent Manner" Cancers 12, no. 7: 1717. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071717
APA StyleDeville, S. S., Vehlow, A., Förster, S., Dickreuter, E., Borgmann, K., & Cordes, N. (2020). The Intermediate Filament Synemin Regulates Non-Homologous End Joining in an ATM-Dependent Manner. Cancers, 12(7), 1717. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071717






