Emerging Therapeutic RNAs for the Targeting of Cancer Associated Fibroblasts
Abstract
1. Introduction
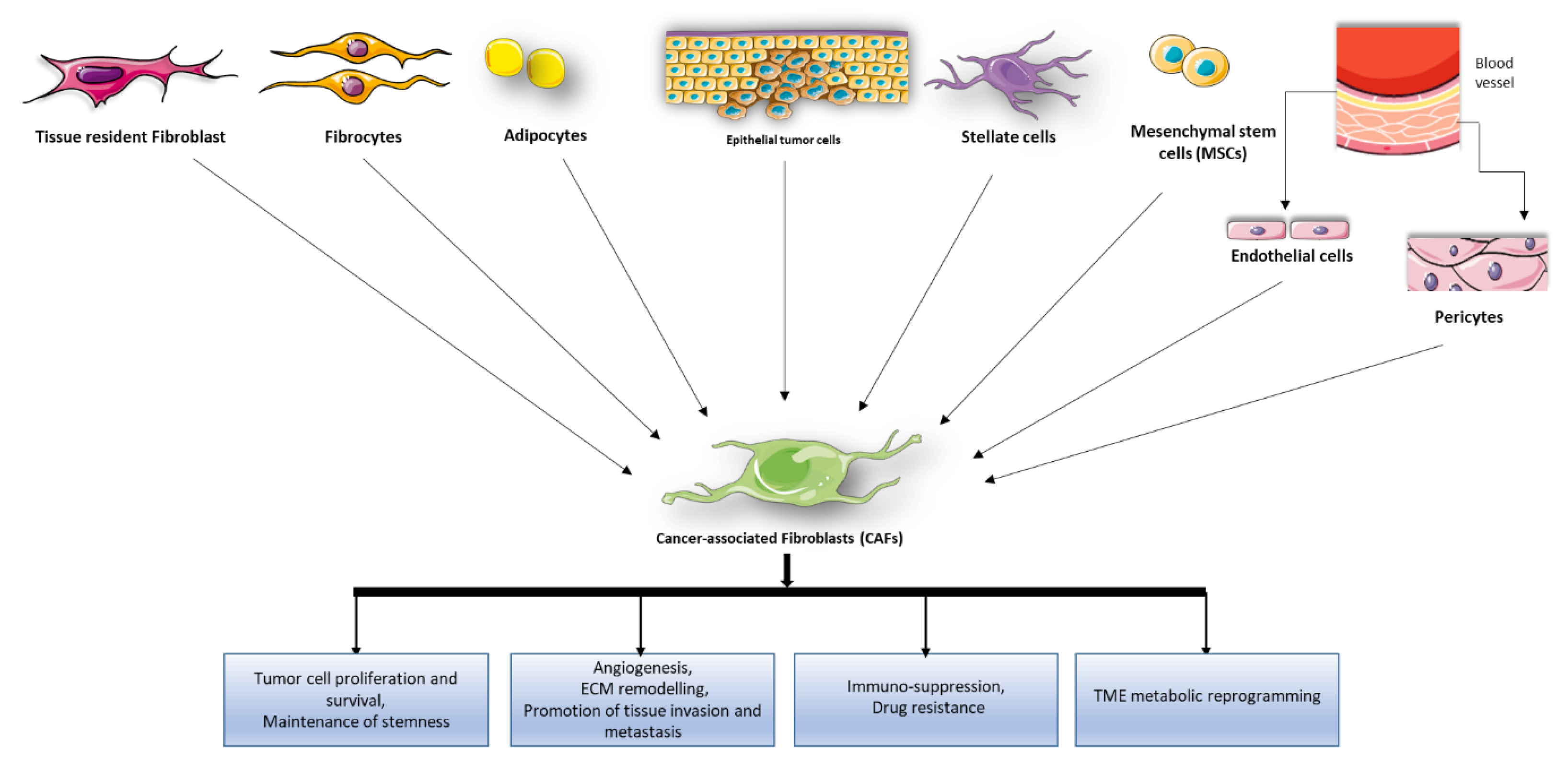
2. Role of CAFs in Tumor Development and Progression
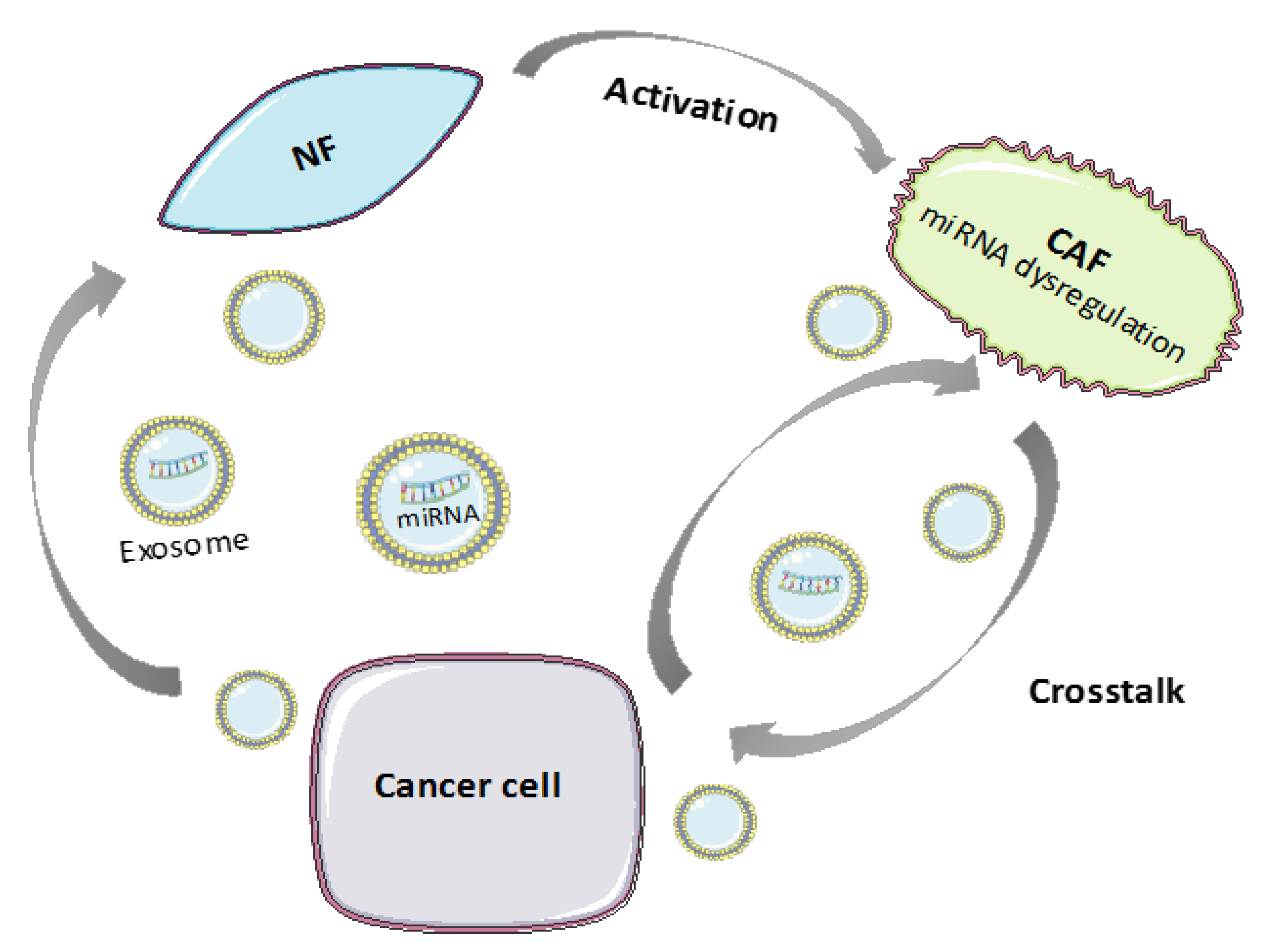
3. Role of Endogenous ncRNAs in CAFs
3.1. MicroRNAs in CAFs
3.1.1. miRNA Deregulation in CAF Activation and Tumor-Promoting Functions
3.1.2. MiRNA Transfer between CAFs and Tumor Cells through Extracellular Vesicles
3.2. lncRNAs in CAFs
4. Synthetic RNA-Based Therapeutic Approaches for CAF Targeting
4.1. SiRNA Therapeutics in CAFs
4.2. ASOs in CAFs
4.3. mRNAs Therapeutics in CAFs
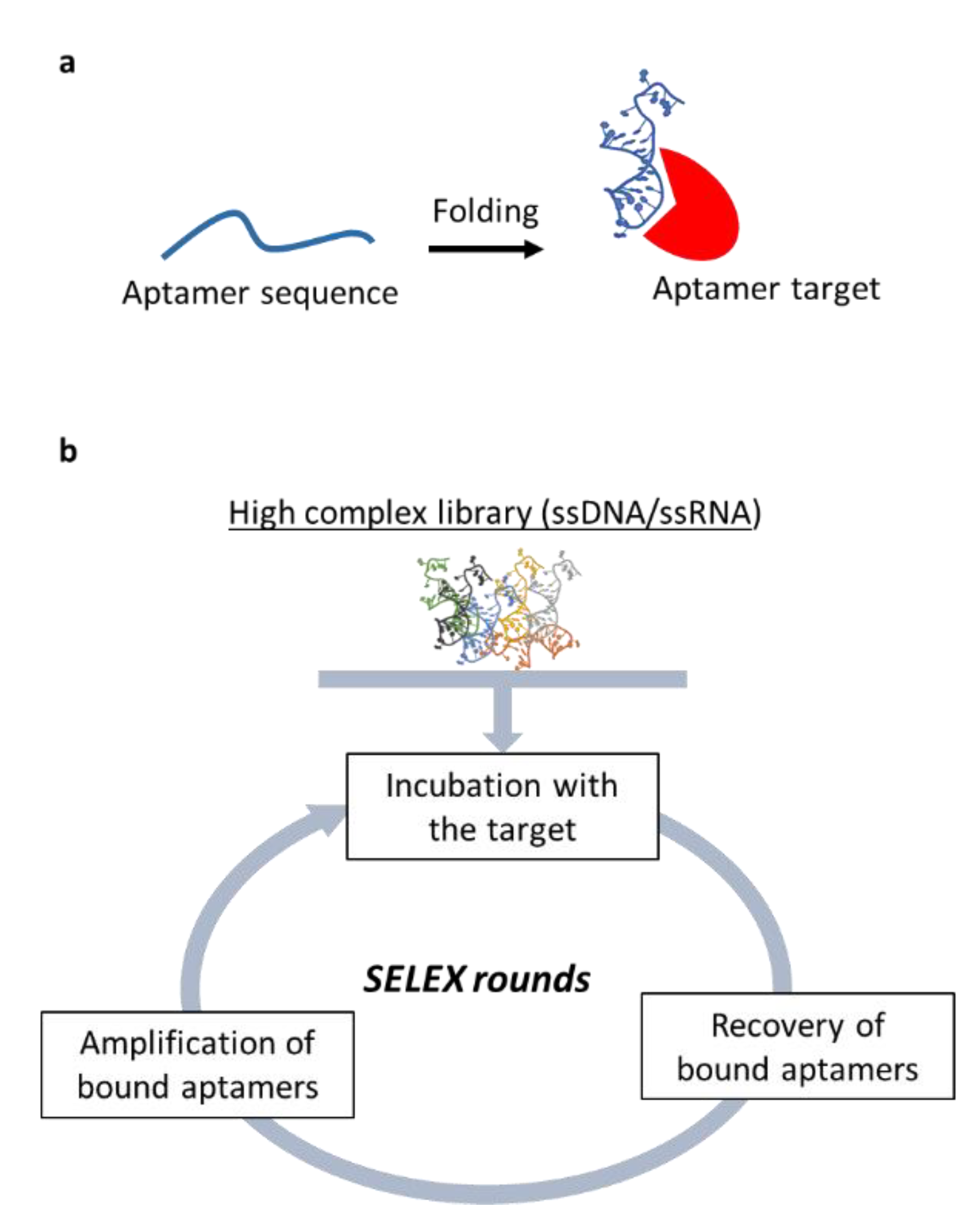
4.4. Nucleic Acid-Based Aptamers in CAFs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hinshaw, D.C.; Shevde, L.A. The Tumor Microenvironment Innately Modulates Cancer Progression. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4557–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Wei, F.; Lian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, J.; Cao, K.; et al. Role of tumor microenvironment in tumorigenesis. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holohan, C.; Van Schaeybroeck, S.; Longley, D.B.; Johnston, P.G. Cancer drug resistance: An evolving paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, G.; Ochiai, A.; Neri, S. Phenotypic and functional heterogeneity of cancer-Associated fibroblast within the tumor microenvironment. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R. The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderton, G. Tumour microenvironment: Driving relapse. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, A.R.; Crooke, S.T. RNA Therapeutics in Oncology: Advances, Challenges, and Future Directions. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 57, S43–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichelmann, A.-K.; Matuszcak, C.; Hummel, R.; Haier, J. Role of miRNAs in cell signaling of cancer associated fibroblasts. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 101, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Lu, T.; Tan, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Wei, L. Long Non-coding RNAs as Communicators and Mediators between the Tumor Microenvironment and Cancer Cells. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devoldere, J.; Dewitte, H.; De Smedt, S.C.; Remaut, K. Evading innate immunity in nonviral mRNA delivery: Don’t shoot the messenger. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Y. Nanoscale platforms for messenger RNA delivery. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 11, e1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabbe, S.; Haas, H.; Diken, M.; Kranz, L.M.; Langguth, P.; Sahin, U. Translating nanoparticulate-personalized cancer vaccines into clinical applications: Case study with RNA-Lipoplexes for the treatment of melanoma. Nanomedicine (Lond.) 2016, 11, 2723–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, C.L.; Catuogno, S.; De Franciscis, V.; Cerchia, L. New insight into clinical development of nucleic acid aptamers. Discov. Med. 2011, 11, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keefe, A.D.; Pai, S.; Ellington, A.D. Aptamers as therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.S. Cancer associated fibroblasts phenotypic and functional heterogeneity. Front. Biosci. 2020, 25, 961–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascard, P.; Tlsty, T.D. Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts: Orchestrating the composition of malignancy. Genome Res. 2016, 30, 1002–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Han, C.; Wang, S.; Fang, P.; Ma, Z.; Xu, L.; Yin, R. Cancer-Associated fibroblasts: An emerging target of anti-cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, L.; Goumas, F.A.; Affeldt, M.; Sandtner, S.; Gehling, U.M.; Brilloff, S.; Walter, J.; Karnatz, N.; Lamszus, K.; Rogiers, X.; et al. Stromal Fibroblasts in Colorectal Liver Metastases Originate From Resident Fibroblasts and Generate an Inflammatory Microenvironment. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, P.G.; Bao, Y.; Prorock, A.; Zigrino, P.; Nischt, R.; Politi, V.; Mauch, C.; Dragulev, B.; Fox, J.W. Gene Expression Profiling Reveals Cross-Talk between Melanoma and Fibroblasts: Implications for Host-Tumor Interactions in Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4134–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F.R.; Capasso, M.; Hagemann, T. The tumor microenvironment at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 5591–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, E.; Astsaturov, I.; Cukierman, E.; DeNardo, D.G.; Egeblad, M.; Evans, R.M.; Fearon, D.; Greten, F.R.; Hingorani, S.R.; Hunter, T.; et al. A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-Associated fibroblasts. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhou, L.; Li, D.; Andl, T.; Zhang, Y. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Build and Secure the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orimo, A.; Gupta, P.B.; Sgroi, D.C.; Arenzana-Seisdedos, F.; Delaunay, T.; Naeem, R.; Carey, V.J.; Richardson, A.L.; Weinberg, R.A. Stromal Fibroblasts Present in Invasive Human Breast Carcinomas Promote Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis through Elevated SDF-1/CXCL12 Secretion. Cell 2005, 121, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wald, O.; Uzi, I.; Amir, G.; Kirshberg, S.; Shlomai, Z.; Zamir, G.; Peled, A.; Shapira, O.M. Interaction between neoplastic cells and cancer-Associated fibroblasts through the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis: Role in non–Small cell lung cancer tumor proliferation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 141, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumi, D.; Ishimoto, T.; Miyake, K.; Sugihara, H.; Eto, K.; Sawayama, H.; Yasuda, T.; Kiyozumi, Y.; Kaida, T.; Kurashige, J.; et al. CXCL12/CXCR4 activation by cancer-Associated fibroblasts promotes integrin β1 clustering and invasiveness in gastric cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 138, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Kim, J.K.; Shiozawa, Y.; Wang, J.; Mishra, A.; Joseph, J.; Berry, J.E.; McGee, S.; Lee, E.; Sun, H.; et al. Recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells into prostate tumours promotes metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bu, W.; Meng, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Ren, M.; Fan, Y.; Sun, H. CXCL12/CXCR4 pathway orchestrates CSC-Like properties by CAF recruited tumor associated macrophage in OSCC. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 378, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobe, N.P.; Rosel, D.; Dvorankova, B.; Kodet, O.; Lacina, L.; Mateu, R.; Smetana, K.; Brábek, A.J.; Smetana, K. Simultaneous blocking of IL-6 and IL-8 is sufficient to fully inhibit CAF-induced human melanoma cell invasiveness. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 146, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, K. Cancer-Associated fibroblasts enhance metastatic potential of lung cancer cells through IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 76116–76128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Zhang, H.; Wen, Z.; Gu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Jia, C.; Lu, Z.; Chen, J. Retinoic acid inhibits pancreatic cancer cell migration and EMT through the downregulation of IL-6 in cancer associated fibroblast cells. Cancer Lett. 2014, 345, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwa, M.Q.; Herum, K.M.; Brakebusch, C. Cancer-Associated fibroblasts: How do they contribute to metastasis? Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2019, 36, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford-Crane, H.; Abrego, J.; Sherman, M.H. Fibroblasts as Modulators of Local and Systemic Cancer Metabolism. Cancers 2019, 11, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Zou, L.; Zhu, Z. Role of Exosomes in Crosstalk Between Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Cancer Cells. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, H.; Zhu, L.; Deng, W.; Li, Q. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Drug Resistance: Role, Molecular Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Strategies. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2014, 37, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.T.; Mani, S.A. Sheep, wolf, or werewolf: Cancer stem cells and the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 2013, 341, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Carstens, J.; Kim, J.; Scheible, M.; Kaye, J.; Sugimoto, H.; Wu, C.-C.; LeBleu, V.S.; Kalluri, R. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal transition is dispensable for metastasis but induces chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 527, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, F. Cancer associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in tumor microenvironment. Front. Biosci. 2010, 15, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieniec, K.A.; Butler, L.M.; Worthley, D.L.; Woods, S.L. Cancer-Associated fibroblasts-heroes or villains? Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, G.; Felsani, A.; D’Agnano, I. Signaling by exosomal microRNAs in cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 34, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ning, Z.; Ma, L.; Liu, W.; Shao, C.; Shu, Y.; Shen, H. Exosomal miRNAs and miRNA dysregulation in cancer-Associated fibroblasts. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.K.; Zillhardt, M.; Hua, Y.; Tiwari, P.; Murmann, A.E.; Peter, M.E.; Lengyel, E. MicroRNAs reprogram normal fibroblasts into cancer-Associated fibroblasts in ovarian cancer. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoepp, M.; Ströse, A.J.; Haier, J. Dysregulation of miRNA Expression in Cancer Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) and Its Consequences on the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2017, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Sun, Y.; Hou, Y.; Peng, Q.; Wang, L.; Luo, H.; Tang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, M. MiRNA expression analysis of cancer-Associated fibroblasts and normal fibroblasts in breast cancer. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 2051–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Hou, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, X.; Tang, S.; Du, Y.-E.; Yang, L.; Yu, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, M.; et al. Stromal miR-200s contribute to breast cancer cell invasion through CAF activation and ECM remodeling. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 23, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enkelmann, A.; Heinzelmann, J.; Von Eggeling, F.; Walter, M.; Berndt, A.; Wunderlich, H.; Junker, K. Specific protein and miRNA patterns characterise tumour-associated fibroblasts in bladder cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 137, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Sun, P.; Hou, X.; Larner, J.; Xiong, W.; Mi, J. MiR-21/Smad 7 signaling determines TGF-beta1-induced CAF formation. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Cao, S.; Li, C.; Mengesha, A.; Kong, B.; Wei, M.Q. Micro-RNA-21 regulates TGF-β-induced myofibroblast differentiation by targeting PDCD4 in tumor-stroma interaction. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 128, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, M.D.; Pickard, K.M.; Nielsen, B.S.; Sayan, A.E.; Jenei, V.; Mellone, M.; Mitter, R.; Primrose, J.N.; Thomas, G.J.; Packham, G.K.; et al. Pleiotropic actions of miR-21 highlight the critical role of deregulated stromal microRNAs during colorectal cancer progression. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunita, A.; Morita, S.; Irisa, T.U.; Goto, A.; Niki, T.; Takai, D.; Nakajima, J.; Fukayama, M. MicroRNA-21 in cancer-Associated fibroblasts supports lung adenocarcinoma progression. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Shan, T.; Ma, J.; Lin, W.; Li, W.; Kang, Y. MiR-21-mediated Metabolic Alteration of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Its Effect on Pancreatic Cancer Cell Behavior. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josson, S.; Gururajan, M.; Sung, S.Y.; Hu, P.; Shao, C.; Zhau, H.E.; Liu, C.; Lichterman, J.; Duan, P.; Li, Q.; et al. Stromal fibroblast-derived miR-409 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and prostate tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2014, 34, 2690–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taddei, M.L.; Cavallini, L.; Comito, G.; Giannoni, E.; Folini, M.; Marini, A.; Gandellini, P.; Morandi, A.; Pintus, G.; Raspollini, M.R.; et al. Senescent stroma promotes prostate cancer progression: The role of miR-210. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 1729–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doldi, V.; Callari, M.; Giannoni, E.; D’Aiuto, F.; Maffezzini, M.; Valdagni, R.; Chiarugi, P.; Gandellini, P.; Zaffaroni, N. Integrated gene and miRNA expression analysis of prostate cancer associated fibroblasts supports a prominent role for interleukin-6 in fibroblast activation. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31441–31460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musumeci, S.; Coppola, V.; Addario, A.; Patrizii, M.; Maugeri, M.; Memeo, L.; Colarossi, C.; Francescangeli, F.; Biffoni, M.; Collura, D.; et al. Control of tumor and microenvironment cross-talk by miR-15a and miR-16 in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 4231–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.-S.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Hua, J.; Zhou, D.-L.; Zhou, B.; Song, Z.-S. MicroRNA-106b in cancer-Associated fibroblasts from gastric cancer promotes cell migration and invasion by targeting PTEN. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 2162–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Shan, J.-X.; Chen, X.-H.; Zhang, D.; Su, L.-P.; Huang, X.-Y.; Yu, B.-Q.; Zhi, Q.-M.; Li, C.-L.; Wang, Y.-Q.; et al. Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-149 in cancer-Associated fibroblasts mediates prostaglandin E2/interleukin-6 signaling in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 588–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprelikova, O.; Yu, X.; Palla, J.; Wei, B.-R.; John, S.; Yi, M.; Stephens, R.; Simpson, R.M.; Risinger, J.I.; Jazaeri, A.; et al. The role of miR-31 and its target gene SATB2 in cancer-Associated fibroblasts. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 4387–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprelikova, O.; Palla, J.; Hibler, B.; Yu, X.; Greer, Y.E.; Yi, M.; Stephens, R.; Maxwell, G.L.; Jazaeri, A.; Risinger, J.I.; et al. Silencing of miR-148a in cancer-Associated fibroblasts results in WNT10B-Mediated stimulation of tumor cell motility. Oncogene 2012, 32, 3246–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xu, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Xing, C.; Cao, J.; Zhu, H.; et al. miR-31 affects colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting autophagy in cancer-Associated fibroblasts. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 79617–79628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Yu, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, J.; Sun, J.; Choksi, S.; Jitkaew, S.; Shu, Y. Reprogramming of Normal Fibroblasts into Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts by miRNAs-Mediated CCL2/VEGFA Signaling. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Miyata, H.; Sugimura, K.; Fukuda, S.; Kanemura, T.; Yamashita, K.; Miyazaki, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Kurokawa, Y.; Yamasaki, M.; et al. miR-27 is associated with chemoresistance in esophageal cancer through transformation of normal fibroblasts to cancer-Associated fibroblasts. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhome, R.; Goh, R.W.; Bullock, M.D.; Pillar, N.; Thirdborough, S.M.; Mellone, M.; Mirnezami, R.; Galea, D.; Veselkov, K.; Gu, Q.; et al. Exosomal microRNAs derived from colorectal cancer-Associated fibroblasts: Role in driving cancer progression. Aging 2017, 9, 2666–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnarumma, E.; Fiore, D.; Nappa, M.; Roscigno, G.; Adamo, A.; Iaboni, M.; Russo, V.; Affinito, A.; Puoti, I.; Quintavalle, C.; et al. Cancer-Associated fibroblasts release exosomal microRNAs that dictate an aggressive phenotype in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 19592–19608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wei, H.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Chen, A.; Li, Z. MicroRNA-181d-5p-Containing Exosomes Derived from CAFs Promote EMT by Regulating CDX2/HOXA5 in Breast Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, T.L.; Peng, B.; Zhang, D.X.; Ma, V.; Mathey-Andrews, C.A.; Lam, C.K.; Kiomourtzis, T.; Jin, J.; McReynolds, L.; Huang, L.; et al. Tumor-secreted extracellular vesicles promote the activation of cancer-Associated fibroblasts via the transfer of microRNA-125b. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1599680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xu, K.; Cui, J.; Yuan, D.; Zou, B.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Li, K.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, B. Cancer-Associated fibroblast-Derived exosomal miR-382-5p promotes the migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, C.L.A.; Co, N.-N.; Tsuruga, T.; Yeung, T.-L.; Kwan, S.Y.; Leung, C.S.; Li, Y.; Lu, E.S.; Kwan, K.; Wong, K.K.; et al. Exosomal transfer of stroma-derived miR21 confers paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells through targeting APAF1. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, K.E.; Zeleniak, A.E.; Fishel, M.; Wu, J.; Littlepage, L.E.; Hill, R. Cancer-Associated fibroblast exosomes regulate survival and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene 2016, 36, 1770–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Rong, Y.; Kuang, T.; Xu, X.; Wu, W.; Wang, D.; Lou, W. Exosomal miRNA-106b from cancer-Associated fibroblast promotes gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 383, 111543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Yan, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, Q.; Shi, J.; Lu, E.; Chen, W.; et al. Exosomal miR-196a derived from cancer-Associated fibroblasts confers cisplatin resistance in head and neck cancer through targeting CDKN1B and ING5. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.L.; Wang, W.; Lan, X.L.; Zeng, Z.C.; Liang, Y.S.; Yan, Y.R.; Song, F.Y.; Wang, F.F.; Zhu, X.H.; Liao, W.; et al. CAFs secreted exosomes promote metastasis and chemotherapy resistance by enhancing cell stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, H.; Dai, B.; Li, J.; Shang, L.; Huang, J.; Shi, X. Hepatocellular carcinoma-derived exosomal miRNA-21 contributes to tumor progression by converting hepatocyte stellate cells to cancer-Associated fibroblasts. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.; Lv, H.; Lv, G.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; Han, Q.; Yu, L.; Su, B.; Guo, L.; Huang, S.; et al. Tumor-Derived exosomal miR-1247-3p induces cancer-Associated fibroblast activation to foster lung metastasis of liver cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aprelikova, O.; Green, J.E. MicroRNA regulation in cancer-Associated fibroblasts. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2011, 61, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Sun, Y.-Q.; Yu, W.; Yan, Y.; Qiao, M.; Jiang, R.; Guan, W.; Wang, L. Downregulation of miRNA-214 in cancer-Associated fibroblasts contributes to migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells through targeting FGF9 and inducing EMT. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, J.J.; Chang, H. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 17, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, D.-H.; Lee, S.K. Long noncoding RNAs in cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2018, 419, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Vecchio, F.; Lee, G.H.; Hawezi, J.; Bhome, R.; Pugh, S.; Sayan, A.E.; Thomas, G.; Packham, G.; Primrose, J.; Pichler, M.; et al. Long non-Coding RNAs within the tumour microenvironment and their role in tumour-Stroma cross-Talk. Cancer Lett. 2018, 421, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Lu, Q.; Shen, B.; Huang, X.; Shen, L.; Zheng, X.; Huang, R.; Yan, J.; Guo, H. TGFβ1 secreted by cancer-Associated fibroblasts induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition of bladder cancer cells through lncRNA-ZEB2NAT. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Jia, H.-H.; Xu, Y.-Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, X.-H.; Wang, Y.-F.; Song, X.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; Sun, T.; Dou, Y.; et al. Paracrine and epigenetic control of CAF-induced metastasis: The role of HOTAIR stimulated by by TGF-ss1 secretion. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ding, L.; Li, Y.; Ren, J.; Shi, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Ni, Y.; Hou, Y. Midkine derived from cancer-Associated fibroblasts promotes cisplatin-resistance via up-regulation of the expression of lncRNA ANRIL in tumour cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Hua, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Yue, J.; Shi, M.; Zhen, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Zhou, R.; Wu, S.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblast–promoted LncRNA DNM3OS Confers Radioresistance by Regulating DNA Damage Response in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 25, 1989–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Ren, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Hu, Q.-G.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Ni, Y.; Hou, Y. A novel stromal lncRNA signature reprograms fibroblasts to promote the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma via LncRNA-CAF/interleukin-33. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Ji, G.; Le, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, L.; Feng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Xuan, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA LINC00092 Acts in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts to Drive Glycolysis and Progression of Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Ding, L.; Zhang, D.; Shi, G.; Xu, Q.; Shen, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Hou, Y. Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts promote the stemness and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer by transferring exosomal lncRNA H19. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3932–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Fougerolles, A.; Vornlocher, H.-P.; Maraganore, J.; Lieberman, J. Interfering with disease: A progress report on siRNA-based therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagani, H.; Rao, J.V.; Palanimuthu, V.R.; Chandrashekar, H.R.; Gang, S. A nanoformulation of siRNA and its role in cancer therapy: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2012, 18, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soutschek, J.; Akinc, A.; Bramlage, B.; Charisse, K.; Constien, R.; Donoghue, M.; Elbashir, S.; Geick, A.; Hadwiger, P.; Harborth, J.; et al. Therapeutic silencing of an endogenous gene by systemic administration of modified siRNAs. Nature 2004, 432, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptasznik, A.; Nakata, Y.; Kalota, A.; Emerson, S.G.; Gewirtz, A.M. Short interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting the Lyn kinase induces apoptosis in primary, and drug-resistant, BCR-ABL1(+) leukemia cells. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 1187–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.W.; Park, T.G. Local and systemic delivery of VEGF siRNA using polyelectrolyte complex micelles for effective treatment of cancer. J. Control. Release 2008, 129, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Zhang, Z.-T.; Qu, X.; Han, W.; Ma, X. Sensitization of breast cancer cells to taxol by inhibition of taxol resistance gene 1. Oncol. Lett. 2011, 3, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.-Y.; Ye, Q.-F.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Peng, X.-Q.; Long, Z.; Ming, Y.-Z. Silencing Notch-1 induces apoptosis and increases the chemosensitivity of prostate cancer cells to docetaxel through Bcl-2 and Bax. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 3, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, T.-L.; Leung, C.S.; Mok, S.C. CAF reprogramming inhibits ovarian cancer progression. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 3783–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.S.; Yeung, T.-L.; Yip, K.-P.; Pradeep, S.; Balasubramanian, L.; Liu, J.; Wong, K.K.; Mangala, L.S.; Armaiz-Pena, G.N.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; et al. Calcium-dependent FAK/CREB/TNNC1 signalling mediates the effect of stromal MFAP5 on ovarian cancer metastatic potential. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Achreja, A.; Yeung, T.-L.; Mangala, L.S.; Jiang, D.; Han, C.; Baddour, J.; Marini, J.; Ni, J.; Nakahara, R.; et al. Targeting Stromal Glutamine Synthetase in Tumors Disrupts Tumor Microenvironment-Regulated Cancer Cell Growth. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.S.K.; Sng, M.K.; Teo, Z.Q.; Chong, H.C.; Twang, J.S.; Tan, N.S. Targeting nuclear receptors in cancer-Associated fibroblasts as concurrent therapy to inhibit development of chemoresistant tumors. Oncogene 2017, 37, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, Z.; Pan, T.; Li, Z.; Chang, X.; Jin, Z.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z.; et al. The reciprocal interaction between tumor cells and activated fibroblasts mediated by TNF-α/IL-33/ST2L signaling promotes gastric cancer metastasis. Oncogene 2019, 39, 1414–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, K.; Hanley, C.J.; Mellone, M.; Szyndralewiez, C.; Heitz, F.; Wiesel, P.; Wood, O.; Machado, M.; Lopez, M.-A.; Ganesan, A.-P.; et al. NOX4 Inhibition Potentiates Immunotherapy by Overcoming Cancer-Associated Fibroblast-Mediated CD8 T-cell Exclusion from Tumors. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 1846–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacheck, V.; Zangemeister-Wittke, U. Antisense molecules for targeted cancer therapy. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2006, 59, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calon, A.; Tauriello, D.V.F.; Batlle, E. TGF-Beta in CAF-Mediated tumor growth and metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2014, 25, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, B.T.; Raguraman, P.; Kosbar, T.R.; Fletcher, S.; Wilton, S.D.; Veedu, R.N. Antisense Oligonucleotides Targeting Angiogenic Factors as Potential Cancer Therapeutics. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 14, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netzer, P.; Domek, M.; Pai, R.; Halter, F.; Tarnawski, A. Inhibition of human colon cancer cell growth by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides targeted at basic fibroblast growth factor. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 15, 1673–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.; Porter, F.W.; Weissman, D. mRNA vaccines—A new era in vaccinology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Wilson, G.; Hebbard, L.; Duan, W.; Liddle, C.; George, J.; Qiao, L. Aptamers: A promising chemical antibody for cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13446–13463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catuogno, S.; Esposito, C.L. Aptamer Cell-Based Selection: Overview and Advances. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, Y.; Leslie, M.; Kameyama, H.; Volk, D.E.; Tanaka, T. Aptamer Therapeutics in Cancer: Current and Future. Cancers 2018, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Rossi, J.J. Aptamers as targeted therapeutics: Current potential and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 16, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, F.; Berraondo, P.; Etxeberria, I.; Frederick, J.; Sahin, U.; Gilboa, E.; Melero, I. An RNA toolbox for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camorani, S.; Hill, B.S.; Fontanella, R.; Greco, A.; Gramanzini, M.; Auletta, L.; Gargiulo, S.; Albanese, S.; Lucarelli, E.; Cerchia, L.; et al. Inhibition of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Homing Towards Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Microenvironment Using an Anti-PDGFRβ Aptamer. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3595–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camorani, S.; Esposito, C.; Rienzo, A.; Catuogno, S.; Iaboni, M.; Condorelli, G.; De Franciscis, V.; Cerchia, L. Inhibition of Receptor Signaling and of Glioblastoma-derived Tumor Growth by a Novel PDGFRβ Aptamer. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 828–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, S.; Roscigno, G.; Affinito, A.; Ingenito, F.; Quintavalle, C.; Condorelli, G. Potential and Challenges of Aptamers as Specific Carriers of Therapeutic Oligonucleotides for Precision Medicine in Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.-Y.; Yuan, W.-F.; Ai, W.-B.; Ai, Y.-W.; Wang, J.-J.; Chu, L.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Wu, J.-F. An exploration of aptamer internalization mechanisms and their applications in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, K.A.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D.G. Knocking down barriers: Advances in siRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catuogno, S.; Esposito, C.L.; Condorelli, G.; De Franciscis, V. Nucleic acids delivering nucleic acids. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 134, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Huang, X.; Min, J.; Le, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Dogan, A.A.; Liu, X.; Zhang, P.; Draz, M.S.; et al. Nanoparticle Delivery Systems for DNA/RNA and their Potential Applications in Nanomedicine. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 2507–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, J.C.; Kowalski, P.; Anderson, D.G. Advances in the delivery of RNA therapeutics: From concept to clinical reality. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Bobbin, M.L.; Burnett, J.; Rossi, J.J. Current Progress of RNA Aptamer-Based Therapeutics. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Operating Mode | MiRNA | De-Regulation Direction | Mechanism of Action | Cancer Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRNA deregulation in CAF activation and tumor-promoting functions | miR-221-5p, miR-31-3p, miR-221-3p | Up-regulation | Differentiation, adhesion, migration, proliferation, and cell–cell interaction | Breast cancer [43,44] |
| miR-205, miR-200b, miR-200c, miR-141, miR-101, miR-342-3p, let-7g, miR-26b | Down-regulation | |||
| miRs-200 family, miR-141 | Down-regulation | Conversion of normal fibroblasts (NFs) into CAFs | ||
| miR-16, miR-320 | Up-regulation | Tumor development and progression | Bladder cancer [45] | |
| miR-243, miR-145 and miR-130 | Down-regulation | |||
| miR-155 | Up-regulation | Conversion of NFs into CAFs | Ovarian cancer [41] | |
| miR-31, miR-214 | Down-regulation | |||
| miR-21 | Up-regulation | CAF activation | Colorectal cancer, lung adenocarcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma [46,47,48,49] | |
| Up-regulation | Metabolic alterations of CAFs | Pancreatic cancer [50] | ||
| miR-409, miR-210, miR-133b | Up-regulation | Conversion of NFs into CAFs Tumor induction and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) | Prostate carcinoma [51,52,53,54] | |
| miR-15, miR-16 | Down-regulation | Tumor growth and progression | ||
| miR-106 | Up-regulation | Proliferation, migration and invasion of tumor cells | Gastric cancer [55,56] | |
| miR-149 | Down-regulation | Transformation of NFs into CAFs | ||
| miR-214 | Down-regulation | EMT | ||
| miR-31 | Down-regulation | Cell invasion, migration and scattering | Endometrial cancer [57,58] | |
| miR-148 | Down-regulation | Activation of the WNT/b-catenin pathway | ||
| miR-31 | Up-regulation | Cancer development | Colorectal cancer [59,60] | |
| miR-1, miR-206 | Down-regulation | Conversion of NFs into CAFs Migration, colony formation, and tumor growth Recruitment of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) | ||
| miR-27a/b | Up-regulation | Poor response to chemotherapy | Esophageal cancer [61] | |
| MiRNA transfer between CAFs and tumor cells through extracellular vesicles | miR-329, miR-181a, miR-199b, miR-382, miR-215, miR-21 | Over-expression | Cancer proliferation and chemoresistance | Colorectal cancer [62] |
| miR-21, miR-378e, miR-143 | Induction of the stemness and EMT phenotype of cancer cells | Breast Cancer [63,64,65] | ||
| miR-125b | Development of CAFs from NFs | |||
| miR-181d-5p | Cell proliferation, invasion, migration, EMT and apoptosis | |||
| miR-382-5p | Cell migration and invasion | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [66] | ||
| miR-21 | Chemoresistance | Ovarian cancer [67] | ||
| miR-146a, miR-106b | Gemcitabine (GEM) resistance | Pancreatic cancer [68,69] | ||
| miR-196a | Cisplatin resistance | Head and neck cancer [70] | ||
| miR-92a-3p | Cell stemness, EMT, metastasis and 5-FU/L-OHP resistance | Colorectal cancer [71] | ||
| miR-21 | CAF activation | Hepatocellular carcinoma [72,73] | ||
| miR-1247-3p |
| lncRNA | Mechanisms of Action | Cancer Type |
|---|---|---|
| ZEB2NAT | CAF-secreted TGFβ1 induces EMT and invasion via lncRNA-ZEB2NAT | Bladder cancer [79] |
| HOTAIR | CAF-secreted TGFβ1 induces EMT and metastasis via LncRNA-HOTAIR | Breast cancer [80] |
| ANRIL | MK released by CAFs enhances cisplatin resistance via the induction of lncRNA-ANRIL. | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [81] |
| DNM3OS | CAFs confer radioresistance promoting the expression lncRNA-DNM3OS via PDGFβ/PDGFRβ/FOXO1 signaling pathway | Esophageal cancer cells [82] |
| Lnc-CAF | Lnc-CAF increase IL-33 expression inducing CAF transformation | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [83] |
| LINC00092 | LINC00092 maintains CAF-phenotype and is simultaneously induced in cancer cells by CAFs-secreted CXCL14 promoting cancer metastasis | Ovarian cancer [84] |
| H19 | LncRNA-H19 carried by CAF-derived exosomes can promote stemness and chemoresistance | Colorectal cancer [85] |
| siRNA Target | Mechanisms of Action | Cancer Type |
|---|---|---|
| MFAP5 | Silencing of MFAP5 expression in CAFs, inhibited ovarian tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis | high-grade serous ovarian cancer [94] |
| Stromal glutamine synthetase and cancer cell glutaminase | The simultaneous silencing of glutamine synthetase in the stroma and glutaminase in cancer cells, disrupts CAFs/cancer cells metabolic crosstalk, inducing tumor regression | high-grade serous ovarian adenocarcinoma [95] |
| RARβ, PPARβ/δ, VDR, GR and AR | knockdown in CAFs leads to attenuation of SCC invasiveness, proliferation, energy metabolism, ROS production and response to chemotherapy | Squamous cell carcinoma [96] |
| IL-33 ior ST2L | Targeting IL-33 expression in CAFs or ST2L expression in gastric cancer (GC) cells inhibits the metastatic capacity of GC cells in nude mice. | Gastric cancer [97] |
| NOX4 | NOX4 inhibition suppresses CAF-mediated immunotherapy resistance | lung, colorectal and breast cancers [98] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santana-Viera, L.; Ibba, M.L.; Rotoli, D.; Catuogno, S.; Esposito, C.L. Emerging Therapeutic RNAs for the Targeting of Cancer Associated Fibroblasts. Cancers 2020, 12, 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061365
Santana-Viera L, Ibba ML, Rotoli D, Catuogno S, Esposito CL. Emerging Therapeutic RNAs for the Targeting of Cancer Associated Fibroblasts. Cancers. 2020; 12(6):1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061365
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantana-Viera, Laura, Maria L. Ibba, Deborah Rotoli, Silvia Catuogno, and Carla L. Esposito. 2020. "Emerging Therapeutic RNAs for the Targeting of Cancer Associated Fibroblasts" Cancers 12, no. 6: 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061365
APA StyleSantana-Viera, L., Ibba, M. L., Rotoli, D., Catuogno, S., & Esposito, C. L. (2020). Emerging Therapeutic RNAs for the Targeting of Cancer Associated Fibroblasts. Cancers, 12(6), 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061365






