A Novel Platform to Test In Vivo Single Gene Dependencies in t(8,21) and t(15,17) AML Confirms Zeb2 as Leukemia Target
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
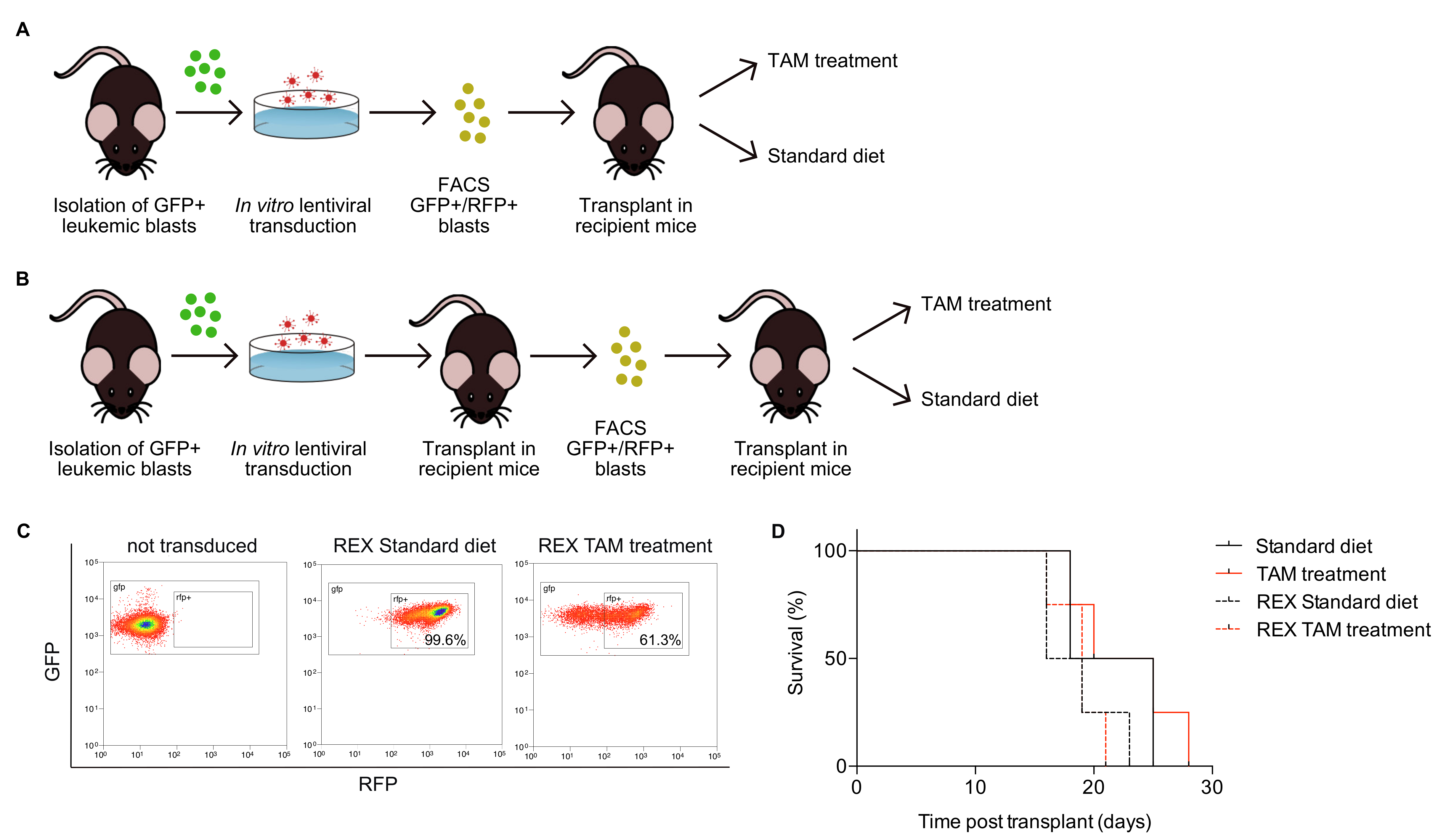
2.1. Design of a Novel Mouse Model System to Investigate Oncogene Addiction
2.2. Generation of Leukemia Expressing High Levels of GFP and Cre Recombinase
2.3. Generation of Leukemia Co-Expressing GFP and RFP and Carrying Integrated shRNAs of Interest
2.4. Monitoring of Inducible shRNA Expression in the In Vivo Growing Leukemia
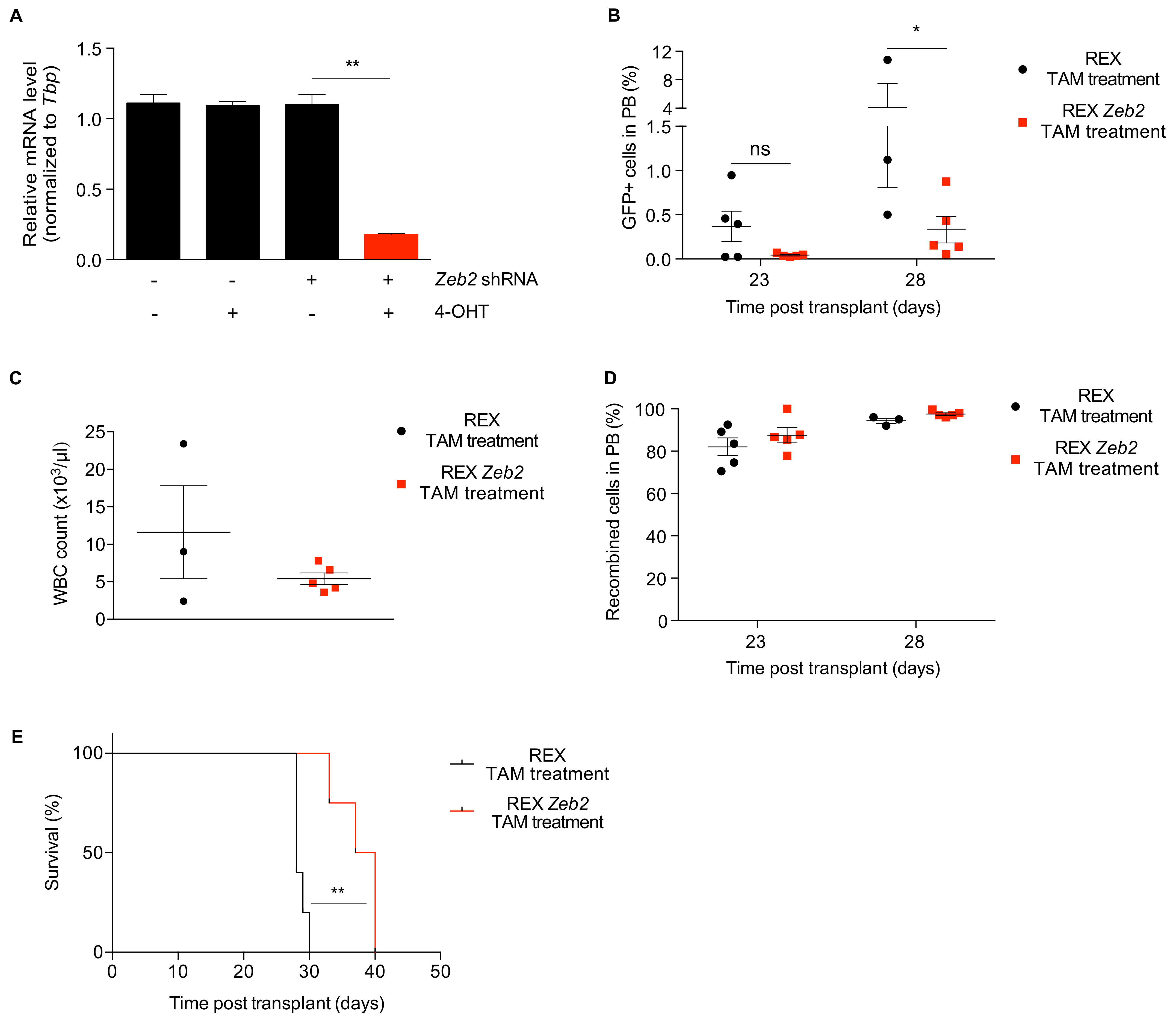
2.5. Proof of Concept: Zeb2 Contributes to the Maintenance and Expansion of t(8;21) In Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mouse-Model Generation and Characterization
4.2. Cell Lines
4.3. REX Lentiviral Vector Construction
4.4. Lentiviral Transduction of Leukemic Blasts
4.5. Gene Expression Analysis of Murine LT-HSCs
4.6. Zeb2 Expression Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tyner, J.W.; Tognon, C.E.; Bottomly, D.; Wilmot, B.; Kurtz, S.E.; Savage, S.L.; Long, N.; Schultz, A.R.; Traer, E.; Abel, M.; et al. Functional genomic landscape of acute myeloid leukaemia. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 562, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.F.; Mardis, E.R. The emerging clinical relevance of genomics in cancer medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haley, B.; Roudnicky, F. Functional Genomics for Cancer Drug Target Discovery. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.T.; Asthana, S.; Gao, S.P.; Lee, B.H.; Chapman, J.S.; Kandoth, C.; Gao, J.; Socci, N.D.; Solit, D.B.; Olshen, A.B.; et al. Identifying recurrent mutations in cancer reveals widespread lineage diversity and mutational specificity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunen, D.; Bernards, R. Drug therapy: Exploiting synthetic lethality to improve cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, D.; Cicalese, A.; Dellino, G.I.; Luzi, L.; Riva, L.; D#x2019;Alesio, C.; Diaferia, G.R.; Carugo, A.; Cavallaro, E.; Piccioni, R.; et al. In Vivo Genetic Screens of Patient-Derived Tumors Revealed Unexpected Frailty of the Transformed Phenotype. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westervelt, P.; Lane, A.A.; Pollock, J.L.; Oldfather, K.; Holt, M.S.; Zimonjic, D.B.; Popescu, N.C.; DiPersio, J.F.; Ley, T.J. High-penetrance mouse model of acute promyelocytic leukemia with very low levels of PML-RARα expression. Blood 2003, 102, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, M.; O’Brien, D.; Kumaravelu, P.; Lenny, N.; Yeoh, E.-J.; Downing, J.R. Expression of a conditional AML1-ETO oncogene bypasses embryonic lethality and establishes a murine model of human t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 2002, 1, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, A.; Meissner, A.; Dillon, C.P.; McManus, M.; Sharp, P.A.; Van Parijs, L.; Jaenisch, R.; Jacks, T. Cre-lox-regulated conditional RNA interference from transgenes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10380–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, S.; Watanabe, T.; Lin, C.S.; William, C.M.; Tanabe, Y.; Jessell, T.M.; Costantini, F. Cre reporter strains produced by targeted insertion of EYFP and ECFP into the ROSA26 locus. BMC Dev. Biol. 2001, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, A.Y.; Ikawa, T.; Muramatsu, M.; Economides, A.N.; Niwa, A.; Okuda, T.; Murphy, A.J.; Rojas, J.; Heike, T.; Nakahata, T.; et al. Direct Hematological Toxicity and Illegitimate Chromosomal Recombination Caused by the Systemic Activation of CreERT2. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5633–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandewalle, C.; Roy, F.V.; Berx, G. The role of the ZEB family of transcription factors in development and disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 66, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Riedt, T.; Goossens, S.; García, C.C.; Szczepanski, S.; Brandes, M.; Pieters, T.; Dobrosch, L.; Gütgemann, I.; Farla, N.; et al. The EMT transcription factor Zeb2 controls adult murine hematopoietic differentiation by regulating cytokine signaling. Blood 2017, 129, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, J.; Li, Y.; Fang, N.; Liu, B.; Zu, L.; Chang, R.; Li, X.; Zhou, Q. MiR-132 Suppresses the Migration and Invasion of Lung Cancer Cells via Targeting the EMT Regulator ZEB2. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denecker, G.; Vandamme, N.; Akay, O.; Koludrovic, D.; Taminau, J.; Lemeire, K.; Gheldof, A.; De Craene, B.; Van Gele, M.; Brochez, L.; et al. Identification of a ZEB2-MITF-ZEB1 transcriptional network that controls melanogenesis and melanoma progression. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 1250–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudell, D.; Harper, D.P.; Novak, R.L.; Pierce, R.M.; Slape, C.; Wolff, L.; Aplan, P.D. Retroviral insertional mutagenesis identifies Zeb2 activation as a novel leukemogenic collaborating event in CALM-AF10 transgenic mice. Blood 2010, 115, 1194–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, S.; Radaelli, E.; Blanchet, O.; Durinck, K.; Meulen, J.V.D.; Peirs, S.; Taghon, T.; Tremblay, C.S.; Costa, M.; Ghahremani, M.F.; et al. ZEB2 drives immature T-cell lymphoblastic leukaemia development via enhanced tumour-initiating potential and IL-7 receptor signalling. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Mar, B.G.; Zhang, H.; Puram, R.V.; Vazquez, F.; Weir, B.A.; Hahn, W.C.; Ebert, B.; Pellman, D. The EMT regulator ZEB2 is a novel dependency of human and murine acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saia, M.; Termanini, A.; Rizzi, N.; Mazza, M.; Barbieri, E.; Valli, D.; Ciana, P.; Gruszka, A.M.; Alcalay, M. AML1/ETO accelerates cell migration and impairs cell-to-cell adhesion and homing of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoletti, M.; Texido, G. In Vivo Target Validation by Inducible RNAi in Human Xenograft Mouse Models. In Advanced Structural Safety Studies; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Now York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 986, pp. 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Kumar, A.R.; Hudson, W.A.; Li, Q.; Wu, B.; Staggs, R.A.; Lund, E.A.; Sam, T.N.; Kersey, J.H. Malignant Transformation Initiated by Mll-AF9: Gene Dosage and Critical Target Cells. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallardo, M.; Caronno, A.; Pruneri, G.; Raviele, P.R.; Viale, A.; Pelicci, P.G.; Colombo, E. NPMc+ and FLT3_ITD mutations cooperate in inducing acute leukaemia in a novel mouse model. Leukemia 2013, 27, 2248–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, T.J.; Miller, C.; Ding, L.; Raphael, B.J.; Mungall, A.J.; Robertson, G.; Hoadley, K.; Triche, T.J.; Laird, P.W.; Baty, J.D.; et al. Genomic and Epigenomic Landscapes of Adult De Novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2059–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapin, N.; Bagger, F.O.; Jendholm, J.; Mora-Jensen, H.; Krogh, A.; Kohlmann, A.; Thiede, C.; Borregaard, N.; Bullinger, L.; Winther, O.; et al. Comparing cancer vs normal gene expression profiles identifies new disease entities and common transcriptional programs in AML patients. Blood 2014, 123, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandewalle, C.; Comijn, J.; De Craene, B.; Vermassen, P.; Bruyneel, E.; Andersen, H.; Tulchinsky, E.; Van Roy, F.; Berx, G. SIP1/ZEB2 induces EMT by repressing genes of different epithelial cell-cell junctions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 6566–6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-C.; Liao, T.-T.; Yang, M.-H. Emerging roles of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hematological malignancies. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, B.; Shim, J.S. Targeting Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) to Overcome Drug Resistance in Cancer. Molecules 2016, 21, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santamaria, P.G.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Portillo, F.; Cano, A. EMT: Present and future in clinical oncology. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Conti, G.; Gruszka, A.M.; Valli, D.; Cammarata, A.U.; Righi, M.; Mazza, M.; Pelicci, P.G. A Novel Platform to Test In Vivo Single Gene Dependencies in t(8,21) and t(15,17) AML Confirms Zeb2 as Leukemia Target. Cancers 2020, 12, 3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123768
De Conti G, Gruszka AM, Valli D, Cammarata AU, Righi M, Mazza M, Pelicci PG. A Novel Platform to Test In Vivo Single Gene Dependencies in t(8,21) and t(15,17) AML Confirms Zeb2 as Leukemia Target. Cancers. 2020; 12(12):3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123768
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Conti, Giulia, Alicja M. Gruszka, Debora Valli, Andrea Umberto Cammarata, Matteo Righi, Massimiliano Mazza, and Pier Giuseppe Pelicci. 2020. "A Novel Platform to Test In Vivo Single Gene Dependencies in t(8,21) and t(15,17) AML Confirms Zeb2 as Leukemia Target" Cancers 12, no. 12: 3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123768
APA StyleDe Conti, G., Gruszka, A. M., Valli, D., Cammarata, A. U., Righi, M., Mazza, M., & Pelicci, P. G. (2020). A Novel Platform to Test In Vivo Single Gene Dependencies in t(8,21) and t(15,17) AML Confirms Zeb2 as Leukemia Target. Cancers, 12(12), 3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123768





