Combined Effects of Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Adipocyte Renin–Angiotensin System Inhibition on Breast Cancer Cell Inflammation and Migration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
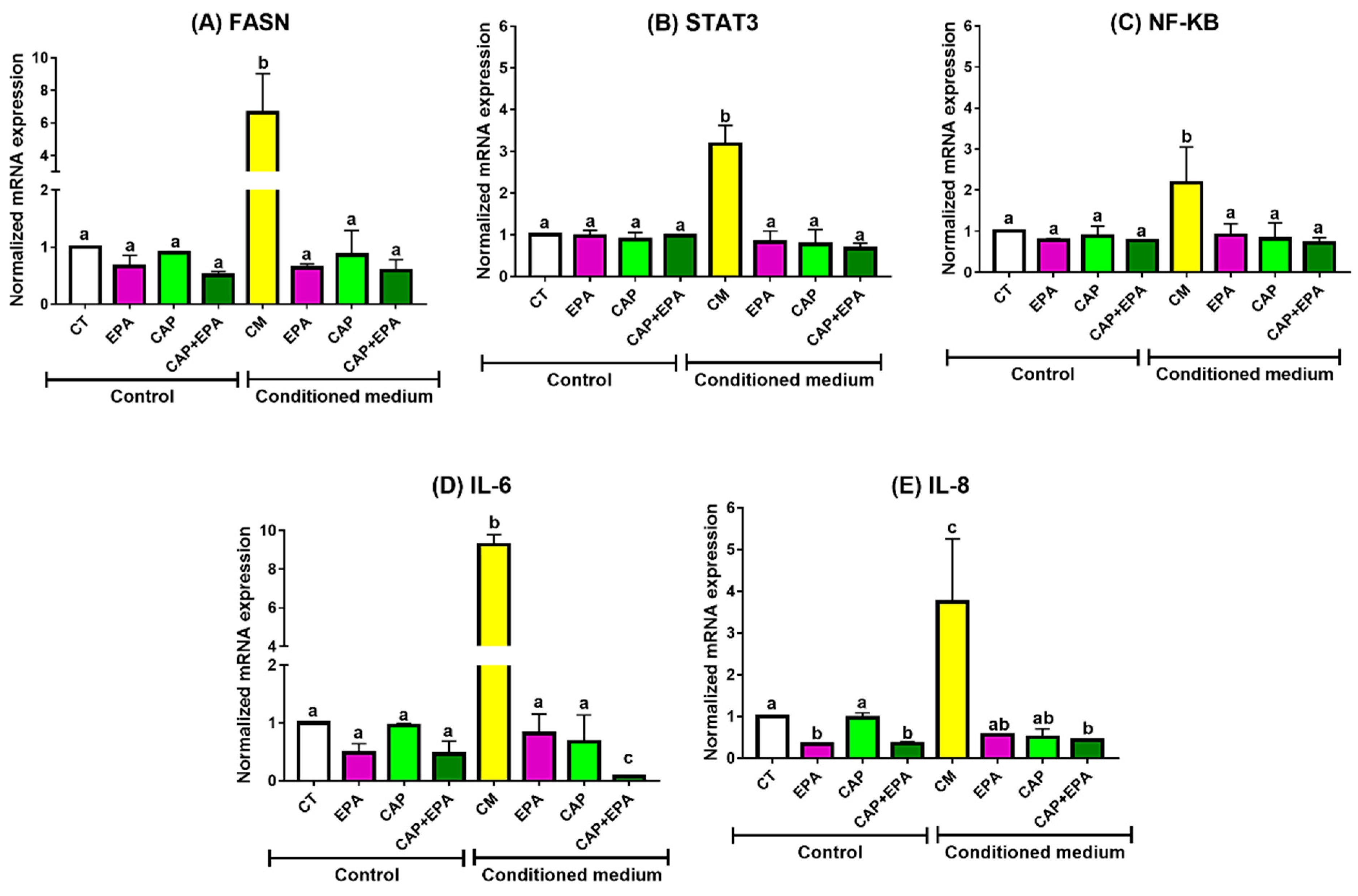
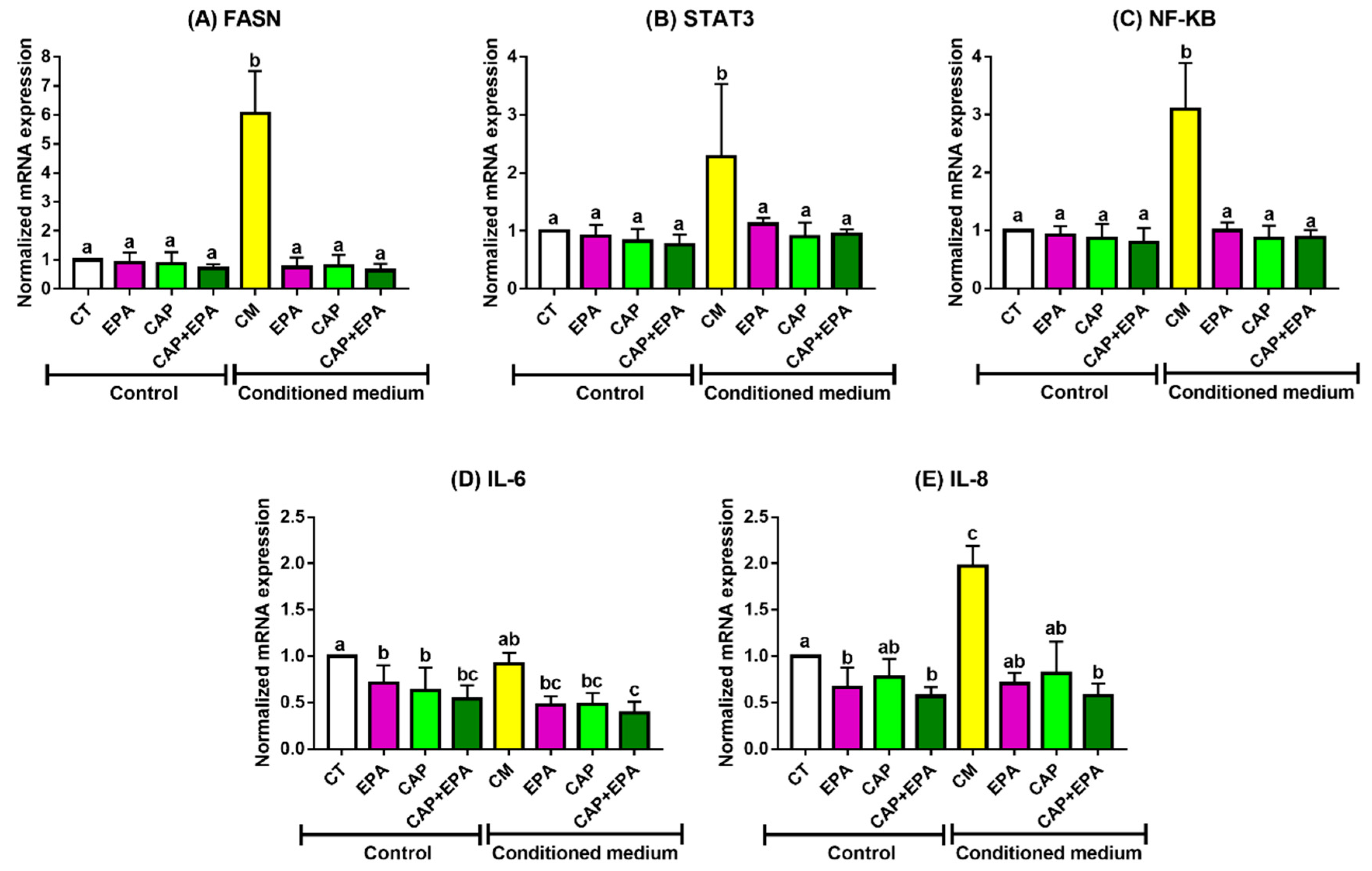
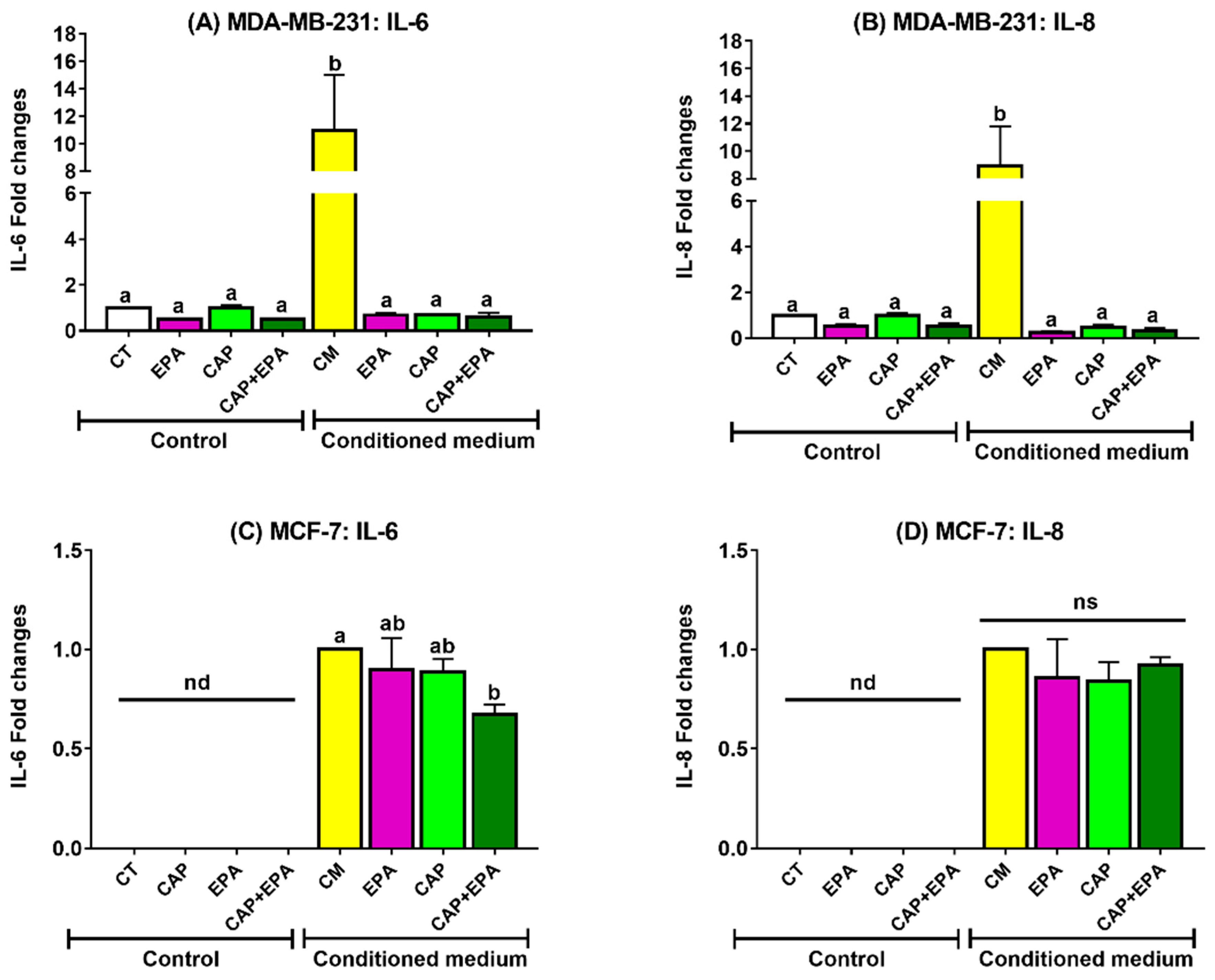
2.1. Effect of Captopril and EPA on Markers of Fatty Acid Synthesis and Inflammation in BC Cells and Role of Human Adipocyte-Conditioned Media (CM)
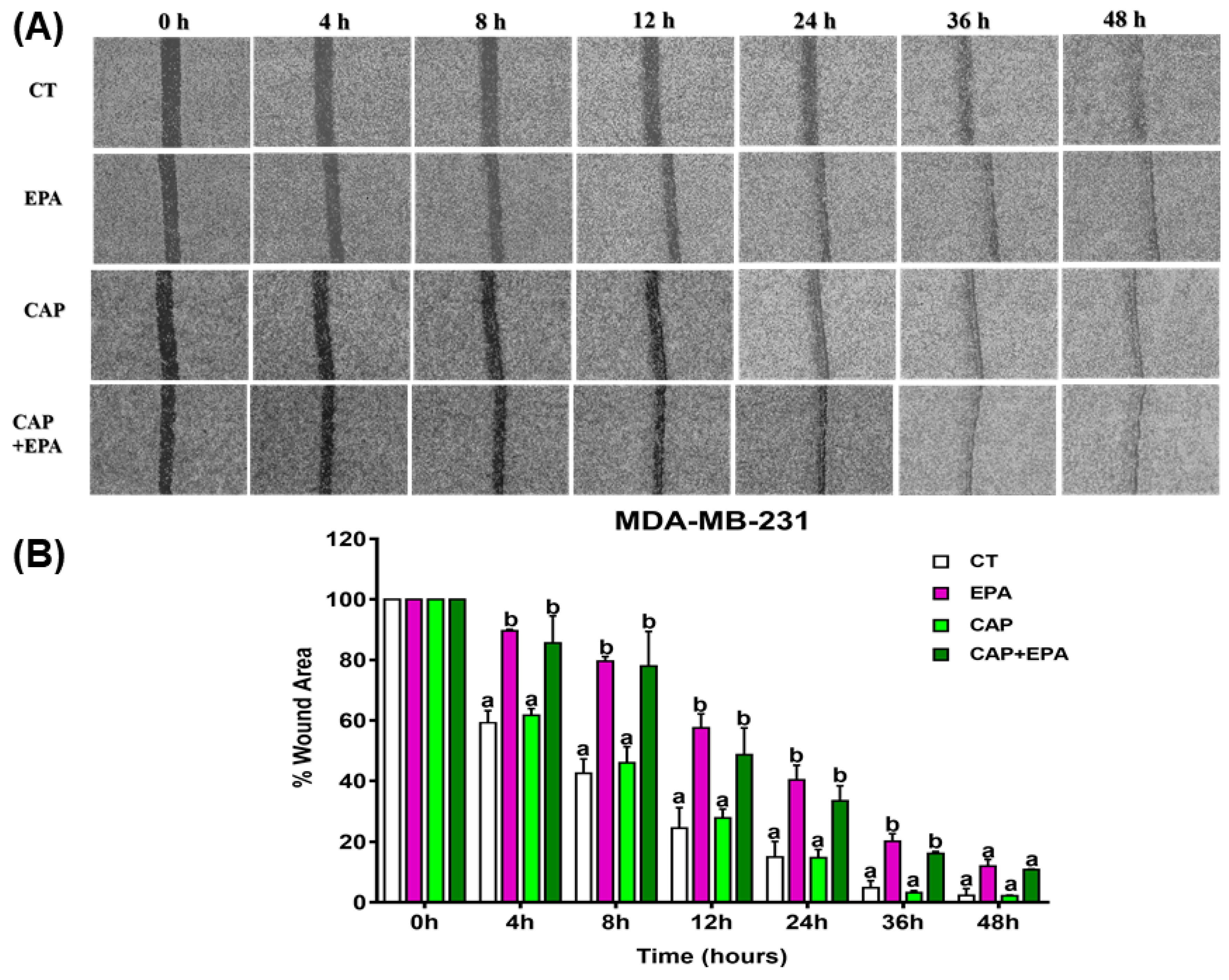
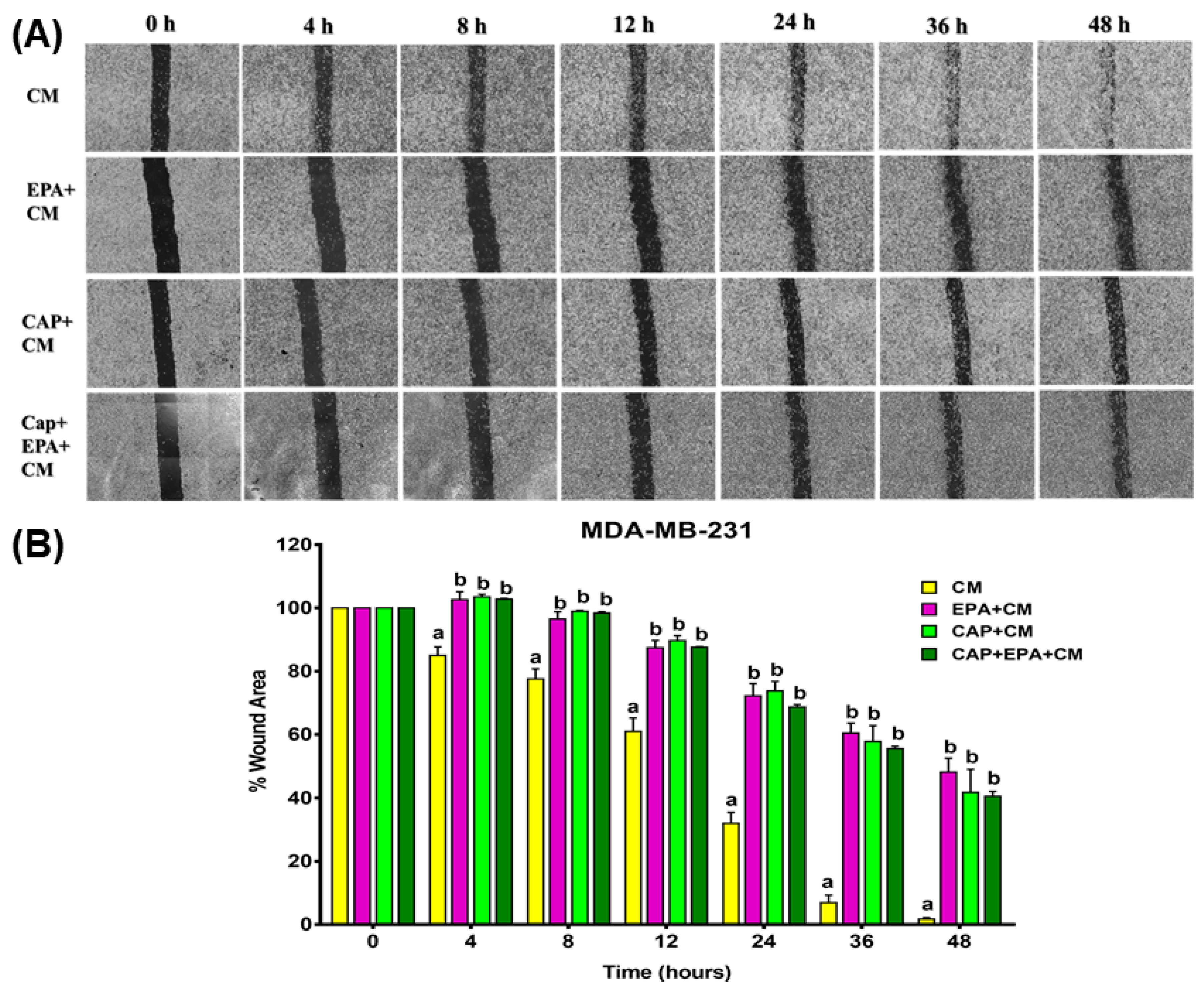
2.2. Combined Effect of Captopril and EPA on Breast Cancer Cell Migration in Response to Treatment with Adipocyte CM, Measured by a Wound Healing Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture Experiments
4.2. Treatment with ACE Inhibitor, Captopril, and Eicosapentaenoic Acid for Conditioned Medium Experiments
4.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.4. RNA Isolation and Real-Time Quatitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
- IL-6 (5′-AGACAGCCACTCACCTCTTCAG-3′, 5′-TTTCTGCCAGTGCCTCTTTGC-3′),
- IL-8 (5′-AGGACAAGAGCCAGGAAGAA-3′, 5′-GGGTGGAAAGGTTTGGAGTATG-3′),
- NF-κB (5′-ATGGCTTCTATGAGGCTGAG-3′, 5′-GTTGTTGTTGGTCTGGATGC-3′),
- STAT3 (5′-AGAAGGACATCAGCGGTAAGA-3′, 5′-GGATAGAGATAGACCAGTGGAGAC-3′),
- FASN (5′-TCGTGGGCTACAGCATGGT-3′, 5′-GCCCTCTGAAGTCGAAGAAGAA-3X),
- 18S (5′-CTACCACATCCAAGGAAGCA-3′, 5’-TTTTTCGTCACTACCTCCCCG-3′), and
- TBP (5′-ATGGTGGTGTTGTGAGAAGATG-3′, 5′-CAGATAGCAGCACGGTATGAG-3′).
4.5. Wound Healing Assay
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Agt | Angiotensinogen |
| Ang I | Angiotensin I |
| Ang II | Angiotensin II |
| ACE | Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| ACE-I | Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor |
| ARB | Angiotensin receptor type I blocker |
| AT1R | Angiotensin receptor type I |
| AT2R | Angiotensin receptor type II |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| BC | Breast cancer |
| CAA | Cancer-associated adipocytes |
| CAP | Captopril |
| CM | Conditioned medium |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| DHA | Docosahexaenoic acid |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| EPA | Eicosapentaenoic acid |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| FASN | Fatty acid synthase |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| ER+ | Estrogen receptor positive |
| ER- | Estrogen receptor negative |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| HER2+ | Human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 positive |
| HMSC | Human mesenchymal stem cells |
| HUVEC | Human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-8 | Interleukin-8 |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| n-3 PUFA | Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PR | Progesterone receptor |
| RAS | Renin–angiotensin system |
| RT-qPCR | Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| TAM | Tumor-associated macrophage |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| TNBC | Triple-negative breast cancer |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Stewart, B.; Wild, C.P. World Cancer Report 2014; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael, A.R. Obesity as a risk factor for development and poor prognosis of breast cancer. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2006, 113, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.; Schatzkin, A.; Lacey, J.V.; Albanes, D.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; Adams, K.F.; Kipnis, V.; Mouw, T.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Leitzmann, M.F. Adiposity, Adult Weight Change, and Postmenopausal Breast Cancer Risk. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simone, V.; D’avenia, M.; Argentiero, A.; Felici, C.; Rizzo, F.M.; De Pergola, G.; Silvestris, F. Obesity and breast cancer: Molecular interconnections and potential clinical applications. Oncologist 2016, 21, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Lyon, C.J.; Bergin, S.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Hsueh, W.A. Obesity, Inflammation, and Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2016, 11, 421–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirat, B.; Bochet, L.; Dabek, M.; Daviaud, D.; Dauvillier, S.; Majed, B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Meulle, A.; Salles, B.; Le Gonidec, S.; et al. Cancer-associated adipocytes exhibit an activated phenotype and contribute to breast cancer invasion. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, V.; Franze, E.; Ronchetti, G.; Colantoni, A.; Fantini, M.C.; Di Fusco, D.; Sica, G.S.; Sileri, P.; MacDonald, T.T.; Pallone, F.; et al. Th17-type cytokines, IL-6 and TNF-alpha synergistically activate STAT3 and NF-kB to promote colorectal cancer cell growth. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3493–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, D.R.; Hurt, E.M.; Farrar, W.L. The role of IL-6 and STAT3 in inflammation and cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 2502–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, K.; Resat, H. Constitutive activation of STAT3 in breast cancer cells: A review. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 2570–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kuhajda, F.P.; Li, J.N.; Pizer, E.S.; Han, W.F.; Sokoll, L.J.; Chan, D.W. Fatty acid synthase (FAS) expression in human breast cancer cell culture supernatants and in breast cancer patients. Cancer Lett. 2001, 167, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, J.; Kovacs, P.; Ruschke, K.; Kloting, N.; Fasshauer, M.; Schon, M.R.; Korner, A.; Stumvoll, M.; Bluher, M. Fatty acid synthase gene expression in human adipose tissue: Association with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Dubois, R.N. Associations between obesity and cancer: The role of fatty acid synthase. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyengar, P.; Combs, T.P.; Shah, S.J.; Gouon-Evans, V.; Pollard, J.W.; Albanese, C.; Flanagan, L.; Tenniswood, M.P.; Guha, C.; Lisanti, M.P.; et al. Adipocyte-secreted factors synergistically promote mammary tumorigenesis through induction of anti-apoptotic transcriptional programs and proto-oncogene stabilization. Oncogene 2003, 22, 6408–6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalupahana, N.S.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. The adipose tissue renin-angiotensin system and metabolic disorders: A review of molecular mechanisms. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 47, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, F.; Mogi, M.; Horiuchi, M. Role of renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system in adipose tissue dysfunction. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 378, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, L.; Menikdiwela, K.; LeMieux, M.; Dufour, J.M.; Kaur, G.; Kalupahana, N.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. The renin angiotensin system, oxidative stress and mitochondrial function in obesity and insulin resistance. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namazi, S.; Rostami-Yalmeh, J.; Sahebi, E.; Jaberipour, M.; Razmkhah, M.; Hosseini, A. The role of captopril and losartan in prevention and regression of tamoxifen-induced resistance of breast cancer cell line MCF-7: An in vitro study. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2014, 68, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscella, A.; Greco, S.; Elia, M.G.; Storelli, C.; Marsigliante, S. Angiotensin II stimulation of Na+/K+ATPase activity and cell growth by calcium-independent pathway in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 173, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, M.; Jain, R.K. Targeting the renin-angiotensin system to improve cancer treatment: Implications for immunotherapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues-Ferreira, S.; Nahmias, C. G-protein coupled receptors of the renin-angiotensin system: New targets against breast cancer? Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Rui, Q.; Zhu, X.; Yu, Z.; Gao, R.; Liu, H. Antihypertensive drug use and breast cancer risk: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 62545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulu, A.; Harris, T.R.; Morisseau, C.; Miyabe, C.; Inoue, H.; Schuster, G.; Dong, H.; Iosif, A.M.; Liu, J.Y.; Weiss, R.H.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors in angiotensin-II-dependent hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 62, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabian, C.J.; Kimler, B.F.; Hursting, S.D. Omega-3 fatty acids for breast cancer prevention and survivorship. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalupahana, N.S.; Claycombe, K.; Newman, S.J.; Stewart, T.; Siriwardhana, N.; Matthan, N.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Eicosapentaenoic Acid Prevents and Reverses Insulin Resistance in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice via Modulation of Adipose Tissue Inflammation. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1915–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalupahana, N.S.; Claycombe, K.J.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. (n-3) Fatty Acids Alleviate Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Insulin Resistance: Mechanistic Insights. Adv. Nutr. 2011, 2, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Jawadi, A.; Moussa, H.; Ramalingam, L.; Dharmawardhane, S.; Gollahon, L.; Gunaratne, P.; Layeequr Rahman, R.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Protective properties of n-3 fatty acids and implications in obesity-associated breast cancer. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Jawadi, A.; Rasha, F.; Ramalingam, L.; Alhaj, S.; Moussa, H.; Gollahon, L.; Dharmawardhane, S.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Protective effects of eicosapentaenoic acid in adipocyte-breast cancer cell cross talk. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 75, 108244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, A.; Jolivel, V.; Durand, S.; Kersual, N.; Chalbos, D.; Chavey, C.; Vignon, F.; Lazennec, G. Mechanisms underlying differential expression of interleukin-8 in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 6105–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardhana, N.; Kalupahana, N.S.; Fletcher, S.; Xin, W.; Claycombe, K.J.; Quignard-Boulange, A.; Zhao, L.; Saxton, A.M.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids differentially regulate adipose angiotensinogen and other inflammatory adipokines in part via NF-κB-dependent mechanisms. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinton, E.A.; Mason, R.P. Prescription omega-3 fatty acid products containing highly purified eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Superko, H.R.; Superko, A.R.; Lundberg, G.P.; Margolis, B.; Garrett, B.C.; Nasir, K.; Agatston, A.S. Omega-3 Fatty Acid Blood Levels Clinical Significance Update. Curr. Cardiovasc. Risk Rep. 2014, 8, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itakura, H.; Yokoyama, M.; Matsuzaki, M.; Saito, Y.; Origasa, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Oikawa, S.; Sasaki, J.; Hishida, H.; Kita, T.; et al. Relationships between plasma fatty acid composition and coronary artery disease. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2011, 18, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braeckman, R.A.; Stirtan, W.G.; Soni, P.N. Pharmacokinetics of Eicosapentaenoic Acid in Plasma and Red Blood Cells After Multiple Oral Dosing With Icosapent Ethyl in Healthy Subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2014, 3, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Li, C.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Amakye, W.K.; Mao, L. DHA increases adiponectin expression more effectively than EPA at relative low concentrations by regulating PPARγ and its phosphorylation at Ser273 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansara, P.P.; Deshpande, R.A.; Vaidya, M.M.; Kaul-Ghanekar, R. Differential Ratios of Omega Fatty Acids (AA/EPA+DHA) Modulate Growth, Lipid Peroxidation and Expression of Tumor Regulatory MARBPs in Breast Cancer Cell Lines MCF7 and MDA-MB-231. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, J.P. Consumer_Captopril_Capoten. Available online: https://www.rxlist.com/consumer_captopril_capoten/drugs-condition.htm (accessed on 3 January 2020).
- Small, W., Jr.; James, J.L.; Moore, T.D.; Fintel, D.J.; Lutz, S.T.; Movsas, B.; Suntharalingam, M.; Garces, Y.I.; Ivker, R.; Moulder, J.; et al. Utility of the ACE Inhibitor Captopril in Mitigating Radiation-associated Pulmonary Toxicity in Lung Cancer: Results From NRG Oncology RTOG 0123. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 41, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglin, M.; Munster, P.; Fink, A.; Krischer, J. Lisinopril or Coreg CR in reducing cardiotoxicity in women with breast cancer receiving trastuzumab: A rationale and design of a randomized clinical trial. Am. Heart J. 2017, 188, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoyama, K.; Hirakata, H.; Iseki, K.; Fujimi, S.; Omae, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Kawahara, Y. Blood concentration and urinary excretion of captopril (SQ 14,225) in patients with chronic renal failure. Hypertension 1981, 3, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, N.M.; Gucalp, A.; Dannenberg, A.J.; Hudis, C.A. Obesity and Cancer Mechanisms: Tumor Microenvironment and Inflammation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4270–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagaradze, G.; Grigorieva, O.; Nimiritsky, P.; Basalova, N.; Kalinina, N.; Akopyan, Z.; Efimenko, A. Conditioned Medium from Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Towards the Clinical Translation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieman, K.M.; Romero, I.L.; Van Houten, B.; Lengyel, E. Adipose tissue and adipocytes support tumorigenesis and metastasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, J.C.; Church, F.C. Mature breast adipocytes promote breast cancer cell motility. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2012, 92, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Martin, A.; Colomer, R.; Brunet, J.; Lupu, R.; Menendez, J.A. Overexpression of fatty acid synthase gene activates HER1/HER2 tyrosine kinase receptors in human breast epithelial cells. Cell Prolif. 2008, 41, 59–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alwarawrah, Y.; Hughes, P.; Loiselle, D.; Carlson, D.A.; Darr, D.B.; Jordan, J.L.; Xiong, J.; Hunter, L.M.; Dubois, L.G.; Thompson, J.W.; et al. Fasnall, a Selective FASN Inhibitor, Shows Potent Anti-tumor Activity in the MMTV-Neu Model of HER2(+) Breast Cancer. Cell Chem. Biol. 2016, 23, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faggioli, L.; Costanzo, C.; Merola, M.; Bianchini, E.; Furia, A.; Carsana, A.; Palmieri, M. Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B), nuclear factor interleukin-6 (NFIL-6 or C/EBP beta) and nuclear factor interleukin-6 beta (NFIL6-beta or C/EBP delta) are not sufficient to activate the endogenous interleukin-6 gene in the human breast carcinoma cell line MCF-7. Comparative analysis with MDA-MB-231 cells, an interleukin-6-expressing human breast carcinoma cell line. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 239, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chavey, C.; Muhlbauer, M.; Bossard, C.; Freund, A.; Durand, S.; Jorgensen, C.; Jobin, C.; Lazennec, G. Interleukin-8 expression is regulated by histone deacetylases through the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in breast cancer. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 74, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravata, V.; Minafra, L.; Forte, G.I.; Cammarata, F.P.; Russo, G.; Di Maggio, F.M.; Augello, G.; Lio, D.; Gilardi, M.C. Cytokine profile of breast cell lines after different radiation doses. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2017, 93, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebble, T.; Arden, N.K.; Stroud, M.A.; Wootton, S.A.; Burdge, G.C.; Miles, E.A.; Ballinger, A.B.; Thompson, R.L.; Calder, P.C. Inhibition of tumour necrosis factor-a and interleukin-6 production by mononuclear cells following dietary fish-oil supplementation in healthy men and response to antioxidant co-supplementation. Br. J. Nutr. 2003, 90, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvall, M.G.; Levy, B. DHA- and EPA-derived resolvins, protectins, and maresins in airway inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 785, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illan-Cabeza, N.A.; Jimenez-Pulido, S.B.; Hueso-Urena, F.; Ramirez-Exposito, M.J.; Sanchez-Sanchez, P.; Martinez-Martos, J.M.; Moreno-Carretero, M.N. Effects on estrogen-dependent and triple negative breast cancer cells growth of Ni(II), Zn(II) and Cd(II) complexes with the Schiff base derived from pyridine-2-carboxaldehyde and 5,6-diamino-1,3-dimethyluracil explored through the renin-angiotensin system (RAS)-regulating aminopeptidases. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2018, 185, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, I.; Lee, J.; Sneddon, A.A.; Cascio, M.G.; Pertwee, R.G.; Wahle, K.W.; Rotondo, D.; Heys, S.D. Anticancer effects of n-3 EPA and DHA and their endocannabinoid derivatives on breast cancer cell growth and invasion. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, W.H.; Leung, W.H.; Pang, Y.J.; Kuo, L.W.; Hsu, H.H. EPA significantly improves anti-EGFR targeted therapy by regulating miR-378 expression in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 6188–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazi, Z.R.; Silva, G.C.; Ribeiro, T.P.; Leon-Gonzalez, A.J.; Kassem, M.; Mirajkar, A.; Alvi, A.; Abbas, M.; Zgheel, F.; Schini-Kerth, V.B.; et al. EPA:DHA 6:1 prevents angiotensin II-induced hypertension and endothelial dysfunction in rats: Role of NADPH oxidase- and COX-derived oxidative stress. Hypertens. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hypertens. 2017, 40, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulu, A.; Stephen Lee, K.S.; Miyabe, C.; Yang, J.; Hammock, B.G.; Dong, H.; Hammock, B.D. An omega-3 epoxide of docosahexaenoic acid lowers blood pressure in angiotensin-II-dependent hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 64, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Bournazou, E.; Sansone, P.; Berishaj, M.; Gao, S.P.; Daly, L.; Wels, J.; Theilen, T.; Granitto, S.; Zhang, X.; et al. The IL-6/JAK/Stat3 Feed-Forward Loop Drives Tumorigenesis and Metastasis. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krusche, B.; Arend, J.; Efferth, T. Synergistic inhibition of angiogenesis by artesunate and captopril in vitro and in vivo. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 454783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel-Carrasco, J.L.; Zambrano, S.; Blanca, A.J.; Mate, A.; Vazquez, C.M. Captopril reduces cardiac inflammatory markers in spontaneously hypertensive rats by inactivation of NF-kB. J. Inflamm. 2010, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Fried, S.K. Optimal protocol for the differentiation and metabolic analysis of human adipose stromal cells. Methods Enzymol. 2014, 538, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortman, P.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kalupahana, N.S.; Kim, S.; Hansen-Petrik, M.; Saxton, A.M.; Claycombe, K.J.; Voy, B.H.; Whelan, J.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. n3 and n6 polyunsaturated fatty acids differentially modulate prostaglandin E secretion but not markers of lipogenesis in adipocytes. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rasha, F.; Kahathuduwa, C.; Ramalingam, L.; Hernandez, A.; Moussa, H.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Combined Effects of Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Adipocyte Renin–Angiotensin System Inhibition on Breast Cancer Cell Inflammation and Migration. Cancers 2020, 12, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010220
Rasha F, Kahathuduwa C, Ramalingam L, Hernandez A, Moussa H, Moustaid-Moussa N. Combined Effects of Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Adipocyte Renin–Angiotensin System Inhibition on Breast Cancer Cell Inflammation and Migration. Cancers. 2020; 12(1):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010220
Chicago/Turabian StyleRasha, Fahmida, Chanaka Kahathuduwa, Latha Ramalingam, Arelys Hernandez, Hanna Moussa, and Naima Moustaid-Moussa. 2020. "Combined Effects of Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Adipocyte Renin–Angiotensin System Inhibition on Breast Cancer Cell Inflammation and Migration" Cancers 12, no. 1: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010220
APA StyleRasha, F., Kahathuduwa, C., Ramalingam, L., Hernandez, A., Moussa, H., & Moustaid-Moussa, N. (2020). Combined Effects of Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Adipocyte Renin–Angiotensin System Inhibition on Breast Cancer Cell Inflammation and Migration. Cancers, 12(1), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010220






