Hybrid Clustered Nanoparticles for Chemo-Antibacterial Combinatorial Cancer Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
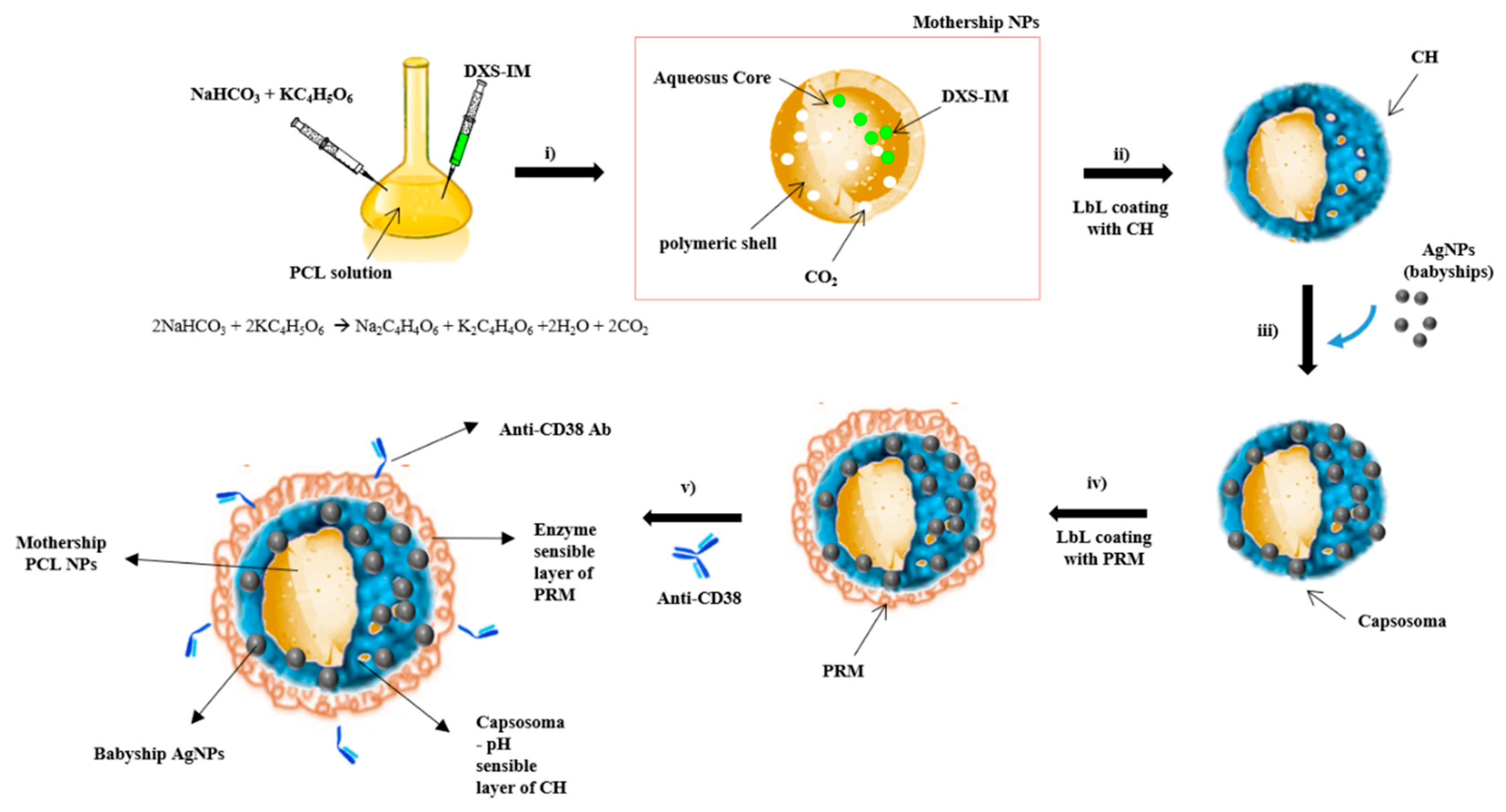
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Hybrid Cluster NPs
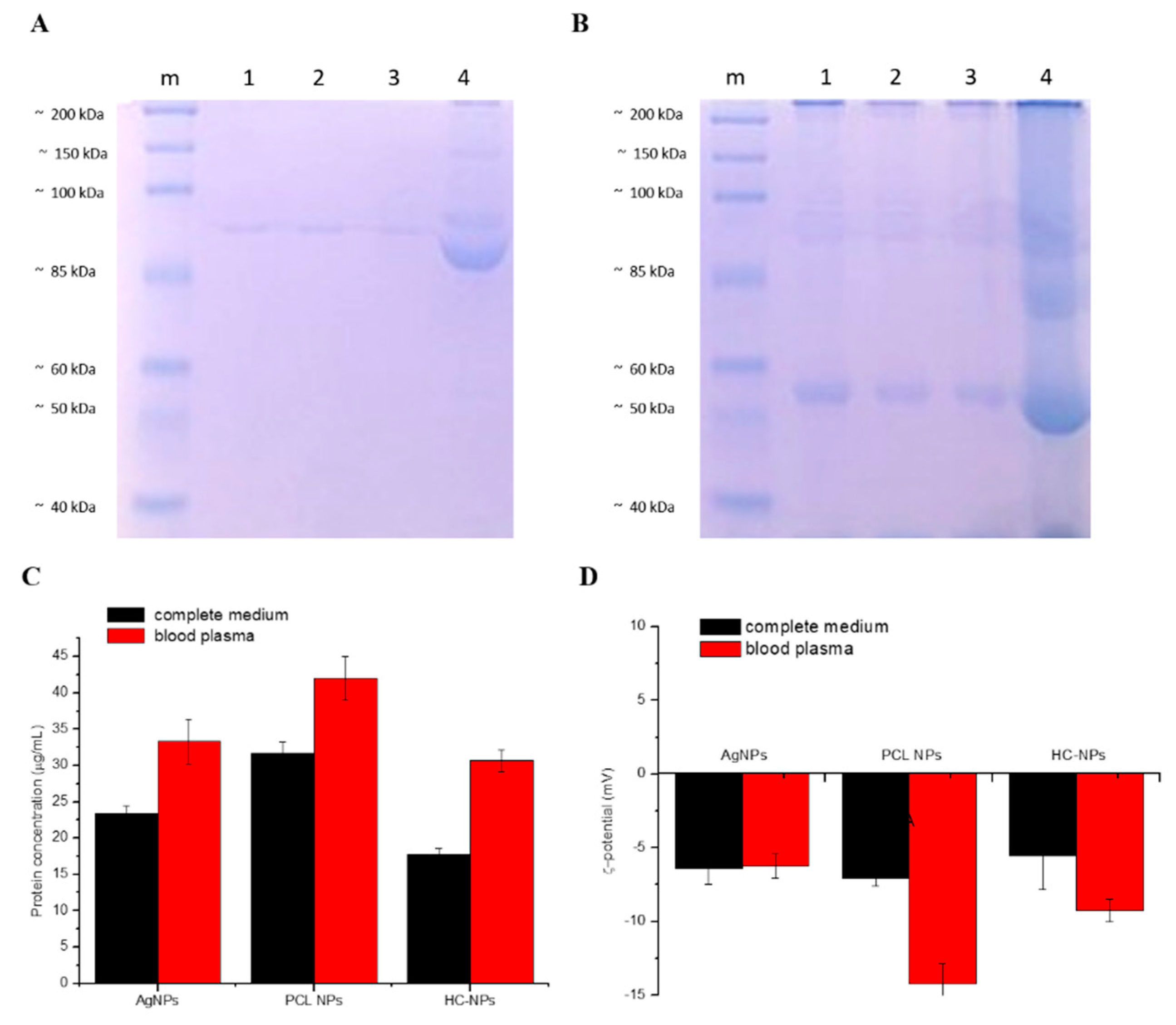
2.2. Protein Corona Analysis
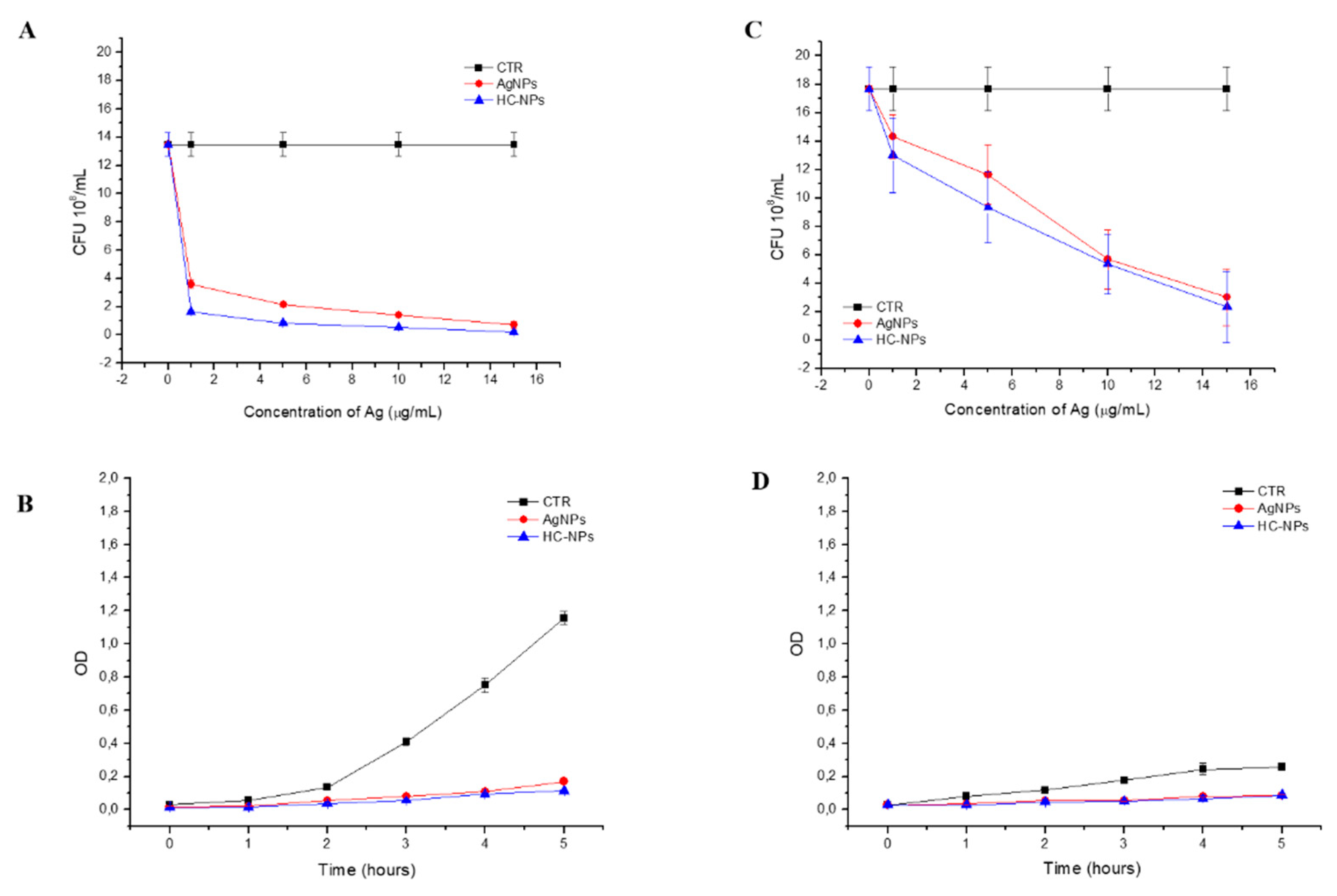
2.3. Antibacterial Action
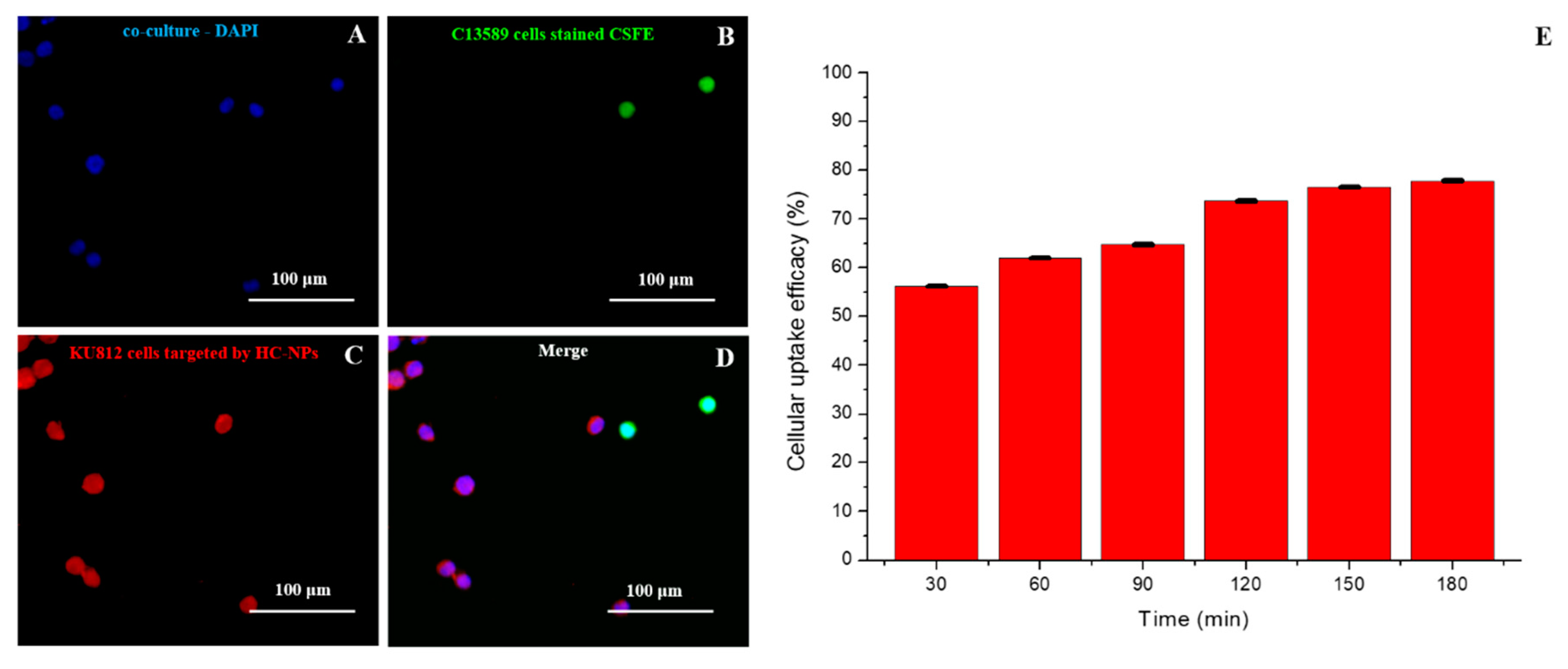
2.4. Targeting and Cellular Uptake Analysis
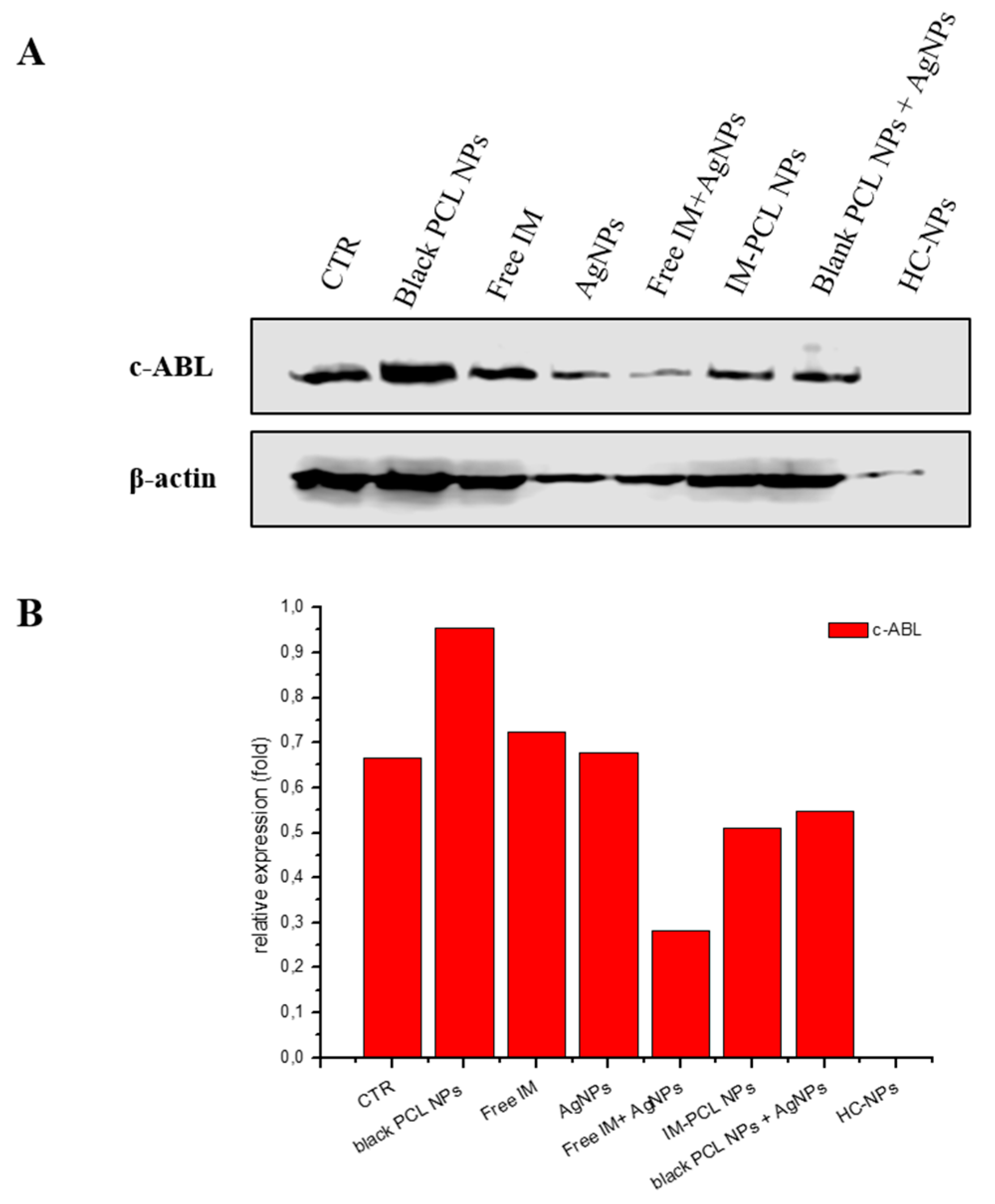
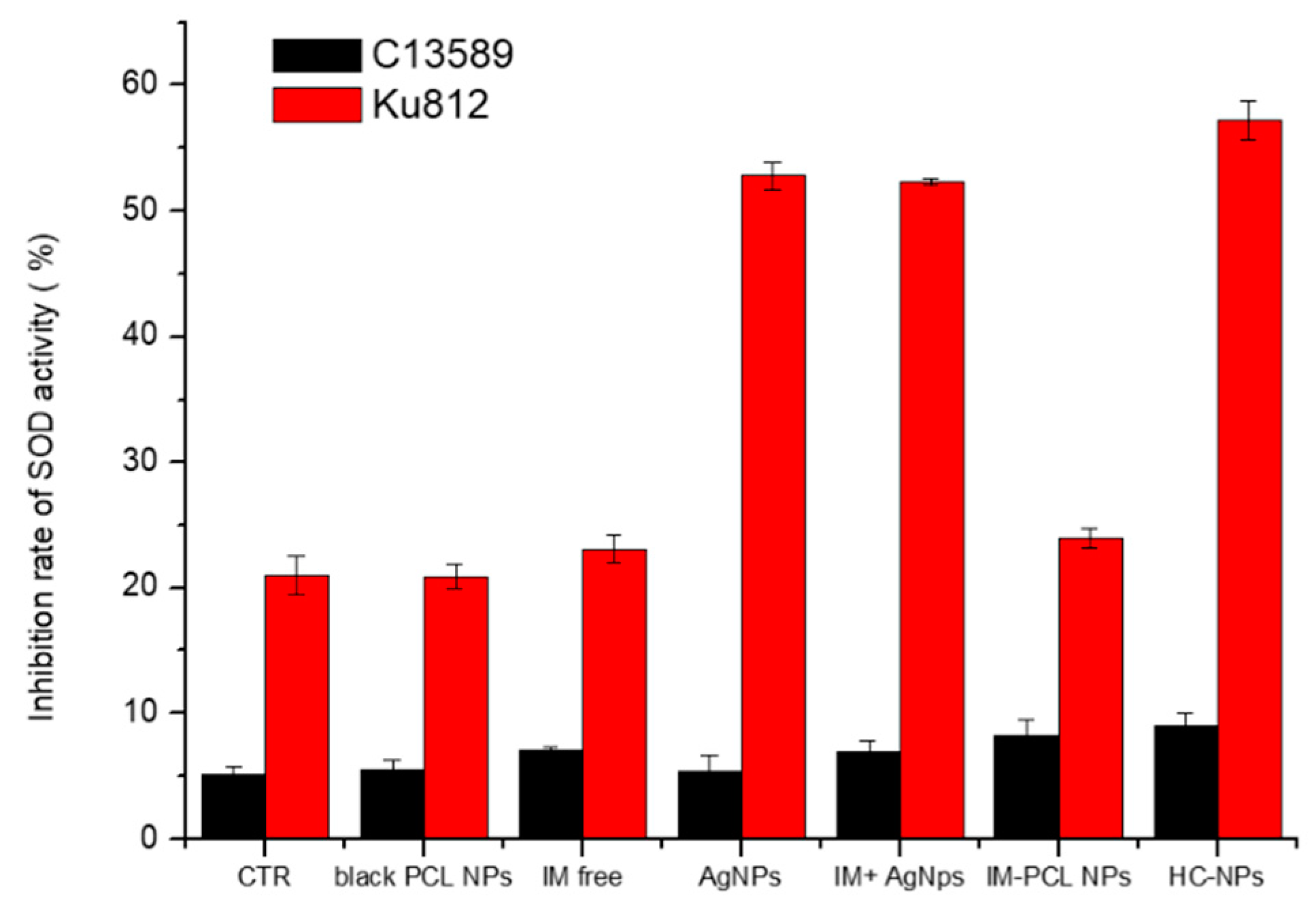
2.5. Anti-Cancer Efficacy of HC-NPs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis and Characterization of AgNPs
4.2. Synthesis of HC-NPs
4.2.1. Synthesis of IM Loaded PCL NPs
4.2.2. Synthesis of HC-NPs
4.2.3. HC-NPs Functionalization with Anti-CD38 Antibody
4.3. Characterization of NPs
4.3.1. Dynamic Light Scattering
4.3.2. UV-VIS Spectroscopy
4.3.3. Scanning and Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.3.4. FT-IR Spectroscopy
4.3.5. Flow Cytometry and SDS-PAGE Assay
4.3.6. Protein Corona
4.3.7. Hemolytic Activity
4.4. Targeting and HC-NP Cellular Uptake
4.5. In Vitro Cancer Efficacy
4.5.1. Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Analysis
4.5.2. Western Blotting for BCR-ABL Inhibition Analysis
4.5.3. Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Assay
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yap, T.A.; Omlin, A.; Bono, J.S.D. Development of Therapeutic Combinations Targeting Major Cancer Signaling Pathways. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1592–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabner, B.A.; Roberts, T.G. Chemotherapy and the war on cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partridge, A.H.; Winer, E.P.; Burstein, H.J. Side Effects of Chemotherapy and Combined Chemohormonal Therapy in Women with Early-Stage Breast Cancer. JNCI Monogr. 2001, 2001, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianni, L.; Salvatorelli, E.; Minotti, G. Anthracycline cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients: Synergism with trastuzumab and taxanes. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2007, 7, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, S.; Merry, S. Tumor-Cell Resistance to Anthracyclines—A Review. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1985, 14, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunbar, A.; Tai, E.; Nielsen, D.B.; Shropshire, S.; Richardson, L.C. Preventing Infections During Cancer Treatment: Development of an Interactive Patient Education Website. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2014, 18, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sanna, V.; Pala, N.; Sechi, M. Targeted therapy using nanotechnology: Focus on cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhzad, O.C.; Langer, R. Impact of Nanotechnology on Drug Delivery. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.E.; Chen, Z.; Shin, D.M. Nanoparticle therapeutics: An emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, B.; D’Amone, S.; Palama, I.E. Wool-Like Hollow Polymeric Nanoparticles for CML Chemo-Combinatorial Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.; La, W.-G.; Hwang, S.; Ha, Y.S.; Park, N.; Won, N.; Jung, S.; Bhang, S.H.; Ma, Y.-J.; Cho, Y.-M.; et al. pH-Responsive Assembly of Gold Nanoparticles and “Spatiotemporally Concerted” Drug Release for Synergistic Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3388–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Cao, D.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Gaines, J.W.; Bozdemir, O.A.; Ambrogio, M.W.; Frasconi, M.; Botros, Y.Y.; Zink, J.I.; et al. Stimulated Release of Size-Selected Cargos in Succession from Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5460–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorthi, C.; Manavalan, R.; Kathiresan, K. Nanotherapeutics to Overcome Conventional Cancer Chemotherapy Limitations. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 14, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostad, S.N.; Dehnad, S.; Nazari, Z.E.; Fini, S.T.; Mokhtari, N.; Shakibaie, M.; Shahverdi, A.R. Cytotoxic Activities of Silver Nanoparticles and Silver Ions in Parent and Tamoxifen-Resistant T47D Human Breast Cancer Cells and Their Combination Effects with Tamoxifen against Resistant Cells. Avicenna J. Med Biotechnol. 2010, 2, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Kudgus, R.A.; Bhattacharya, R.; Mukherjee, P. Inorganic Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 237–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz, N.M.; Ziko, L.; Siam, R.; Mamdouh, W. Core-Shell Silver/Polymeric Nanoparticles-Based Combinatorial Therapy against Breast Cancer In-vitro. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palama, I.E.; Pollini, M.; Paladini, F.; Accorsi, G.; Sannino, A.; Gigli, G.; Palama, I. Inhibiting Growth or Proliferation of a Cancer Cell e.g., Myeloid Leukemia Cell, Comprises Contacting the Cancer Cell with Silver Nanoparticles. WO2015015301-A2 WOIB001895, 31 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Zhu, L.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Ge, Y.; Ma, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Anti-leukemia activity of PVP-coated silver nanoparticles via generation of reactive oxygen species and release of silver ions. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7884–7894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heravi, R.E.; Zakeri, S.; Nazari, P. Anticancer activity evaluation of green synthesised gold-silver alloy nanoparticles on colourectal HT-29 and prostate DU-145 carcinoma cell lines. Micro Nano Lett. 2018, 13, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Matteis, V.; Malvindi, M.A.; Galeone, A.; Brunetti, V.; De Luca, E.; Kote, S.; Kshirsagar, P.; Sabella, S.; Bardi, G.; Pompa, P.P. Negligible particle-specific toxicity mechanism of silver nanoparticles: The role of Ag+ ion release in the cytosol. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richa, S.; Dimple, S.C. Regulatory Approval of Silver Nanoparticles. Appl. Clin. Res. Clin. Trials Regul. Aff. 2018, 5, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardiman, J.W. Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia, BCR-ABL1+. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 132, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcintepe, L.; Halis, E.; Ulku, S. Effect of CD38 on the multidrug resistance of human chronic myelogenous leukemia K562 cells to doxorubicin. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palamà, I.E.; Leporatti, S.; Luca, E.D.; Renzo, N.D.; Maffia, M.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Rinaldi, R.; Gigli, G.; Cingolani, R.; Coluccia, A.M. Imatinib-loaded polyelectrolyte microcapsules for sustained targeting of BCR-ABL+ leukemia stem cells. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelbary, A.A.; Li, X.L.; El-Nabarawi, M.; Elassasy, A.; Jasti, B. Effect of fixed aqueous layer thickness of polymeric stabilizers on zeta potential and stability of aripiprazole nanosuspensions. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2013, 18, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadzuka, Y.; Nakade, A.; Hirama, R.; Miyagishima, A.; Nozawa, Y.; Hirota, S.; Sonobe, T. Effects of mixed polyethyleneglycol modification on fixed aqueous layer thickness and antitumor activity of doxorubicin containing liposome. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 238, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.-H.; Qasim, M.; Kim, J.-H. Nanoparticle-Mediated Combination Therapy: Two-in-One Approach for Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugan, C.; Rayappan, K.; Thangam, R.; Bhanumathi, R.; Shanthi, K.; Vivek, R.; Thirumurugan, R.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Sivasubramanian, S.; Gunasekaran, P.; et al. Combinatorial nanocarrier based drug delivery approach for amalgamation of anti-tumor agents in breast cancer cells: An improved nanomedicine strategy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palamà, I.E.; Coluccia, A.M.; Gigli, G. Uptake of imatinib-loaded polyelectrolyte complexes by BCR-ABL+ cells: A long-acting drug-delivery strategy for targeting oncoprotein activity. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 2087–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, B.; D’Amone, S.; Gigli, G.; Palama, I.E. Sustained anti-BCR-ABL activity with pH responsive imatinib mesylate loaded PCL nanoparticles in CML cells. MedChemComm 2015, 6, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujrati, M.; Malamas, A.; Shin, T.; Jin, E.; Sun, Y.; Lu, Z.-R. Multifunctional Cationic Lipid-Based Nanoparticles Facilitate Endosomal Escape and Reduction-Triggered Cytosolic siRNA Release. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 2734–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, I.; Dawson, K.A. Protein-nanoparticle interactions. Nano Today 2008, 3, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, E.; Kar, M.; Calderón, M. Interactions of organic nanoparticles with proteins in physiological conditions. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 4393–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbo, C.; Molinaro, R.; Taraballi, F.; Toledano Furman, N.E.; Hartman, K.A.; Sherman, M.B.; De Rosa, E.; Kirui, D.K.; Salvatore, F.; Tasciotti, E. Unveiling the in Vivo Protein Corona of Circulating Leukocyte-like Carriers. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3262–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Ouay, B.; Stellacci, F. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: A surface science insight. Nano Today 2015, 10, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, C.-N.; Ho, C.-M.; Chen, R.; He, Q.-Y.; Yu, W.-Y.; Sun, H.; Tam, P.K.-H.; Chiu, J.-F.; Che, C.-M. Proteomic Analysis of the Mode of Antibacterial Action of Silver Nanoparticles. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, M.; Ghourchian, H.; Yazdian, F.; Bagherifam, S.; Bekhradnia, S.; Nyström, B. Anti-cancerous effect of albumin coated silver nanoparticles on MDA-MB 231 human breast cancer cell line. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-C.; Talalay, P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 1984, 22, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | ζ Potential (mV) | Size (nm) | PdI | FALT (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag NPs | −27.9 ± 0.96 | 32.02 ± 0.69 | 0.6 ± 0.06 | - |
| PCL NPs | −11.5 ± 0.24 | 228.1 ± 0.3 | 0.36 ± 0.03 | - |
| PCL-Ag NPs | −25.4 ± 0.15 | 274.8 ± 0.25 | 0.57 ± 0.01 | 1.82 ± 0.02 |
| HC-NPs | 10.8 ± 0.88 | 286.5 ± 0.56 | 0.62 ± 0.05 | 2.55 ± 0.03 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cortese, B.; D’Amone, S.; Testini, M.; Ratano, P.; Palamà, I.E. Hybrid Clustered Nanoparticles for Chemo-Antibacterial Combinatorial Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091338
Cortese B, D’Amone S, Testini M, Ratano P, Palamà IE. Hybrid Clustered Nanoparticles for Chemo-Antibacterial Combinatorial Cancer Therapy. Cancers. 2019; 11(9):1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091338
Chicago/Turabian StyleCortese, Barbara, Stefania D’Amone, Mariangela Testini, Patrizia Ratano, and Ilaria Elena Palamà. 2019. "Hybrid Clustered Nanoparticles for Chemo-Antibacterial Combinatorial Cancer Therapy" Cancers 11, no. 9: 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091338
APA StyleCortese, B., D’Amone, S., Testini, M., Ratano, P., & Palamà, I. E. (2019). Hybrid Clustered Nanoparticles for Chemo-Antibacterial Combinatorial Cancer Therapy. Cancers, 11(9), 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091338