Abstract
The WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway controls stem and progenitor cell proliferation, survival and differentiation in epithelial tissues. Aberrant stimulation of this pathway is therefore frequently observed in cancers from epithelial origin. For instance, colorectal and hepatic cancers display activating mutations in the CTNNB1 gene encoding β-catenin, or inactivating APC and AXIN gene mutations. However, these mutations are uncommon in breast and pancreatic cancers despite nuclear β-catenin localization, indicative of pathway activation. Notably, the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6), an indispensable co-receptor for WNT, is frequently overexpressed in colorectal, liver, breast and pancreatic adenocarcinomas in association with increased WNT/β -catenin signaling. Moreover, LRP6 is hyperphosphorylated in KRAS-mutated cells and in patient-derived colorectal tumours. Polymorphisms in the LRP6 gene are also associated with different susceptibility to developing specific types of lung, bladder and colorectal cancers. Additionally, recent observations suggest that LRP6 dysfunction may be involved in carcinogenesis. Indeed, reducing LRP6 expression and/or activity inhibits cancer cell proliferation and delays tumour growth in vivo. This review summarizes current knowledge regarding the biological function and regulation of LRP6 in the development of epithelial cancers—especially colorectal, liver, breast and pancreatic cancers.
1. Introduction
Cell proliferation and differentiation are finely regulated during epithelial tissue development and renewal. One of the most important signaling pathways involved in this regulation is the ubiquitous WNT/β-catenin pathway due to its crucial role in adult stem cell regulation [1]. Accordingly, abnormal WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway activation is therefore involved in the pathogenesis of various human diseases, particularly cancer.
β-catenin protein, encoded by CTNNB1, acts as the main signal transducer. In the absence of WNT factors, β-catenin cytoplasmic concentrations are kept low because of active degradation through the proteasome (Figure 1A). Indeed, in the cytoplasm, β-catenin is associated with a “destruction complex” that includes casein kinase 1 (CK1α), glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3), AXIN and adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) proteins. Within this complex, β-catenin is phosphorylated by CK1α at serine 45. This event leads to subsequent phosphorylations on residues 41, 37 and 33 by GSK3, which mark β-catenin for ubiquitin-mediated degradation in the proteasome [2,3]. WNT ligands bind to the seven-pass transmembrane receptor Frizzled (FZD) and the single-pass low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 or 6 (LRP5/6) (Figure 1B). The WNT–FZD–LRP5/6 trimeric complex recruits the scaffold protein Dishevelled (DVL) which itself polymerizes to bind AXIN [4]. This structure promotes LRP6 aggregation, leading to the formation of LRP6 signalosomes [5]. LRP5/6 is then phosphorylated by both CK1γ and GSK3, releasing free β-catenin in the cytoplasm. LRP6 phosphorylations allow the recruitment of more AXIN and GSK3, acting as an inhibitor of this kinase, amplifying WNT signal activation and allowing sustained activation of the pathway [6]. β-catenin then accumulates in the cytoplasm and translocates in the nucleus, where β-catenin binds to T-cell factor (TCF) or lymphoid enhancer-binding protein factor (LEF). The fully active transcription factor induces the transcription of genes involved in the control of cell cycle, survival and differentiation.
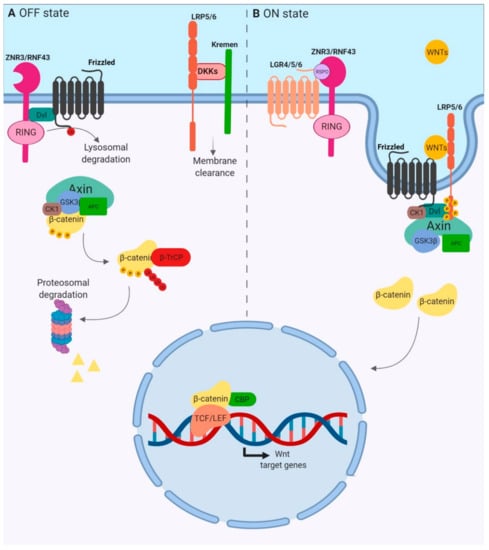
Figure 1.
Overview of canonical WNT signaling. (A) OFF State. The absence of WNT ligands and the presence of antagonists such as DKK family members are associated with the inactive state of the pathway. The β-catenin destruction complex, formed by the scaffolding proteins AXIN and APC, and the kinases CK1α and GSK3, promotes the β-catenin phosphorylation, triggering its ubiquitination by the E3 ubiquitin ligase β-TrCP and its proteosomal degradation. (B) ON State. R-spondin (RSPO) and WNT ligands activate the pathway. RSPO binds both the ring finger proteins RNF43/ZNRF3 and the LGR receptor to form a ternary complex which is rapidly endocytosed. WNT glycoproteins are then able to bind Frizzled and LRP5/6 coreceptors, forming the WNT–FZD–LRP5/6 trimeric complex which recruits the scaffold protein Dishevelled (DVL) which itself polymerizes to bind AXIN. This promotes the formation of LRP6 signalosomes in which LRP6 is phosphorylated by CK1 and GSK3 kinases, releasing β-catenin, which accumulates and translocates into the nucleus to form an active transcription complex with TCF/LEF proteins.
Mutations in WNT/β-catenin pathway coding genes such as CTNNB1, AXIN and APC are found in colorectal and hepatic cancers, as described below, and are known to drive tumorigenesis. However, overexpression of these genes is not reported in all carcinomas, suggesting the involvement of other key components of this pathway in carcinogenesis. In this signaling cascade, coreceptors LRP5/6 are instrumental for downstream signal transduction. Indeed, the expression of non-phosphorylatable LRP5/6 mutants abrogates β-catenin-TCF/LEF transcriptional activity [7]. Herein, we focus on the specific roles of LRP6 in the control of the WNT/β-catenin pathway and in the regulation of tissue homeostasis and carcinoma development.
2. LRP6 Structure, Regulation and Role in Tissue Homeostasis
2.1. Structure
LRP5 and LRP6 proteins are 70% identical [4]. These receptors consist of an extracellular domain with four YWTD (Tyr–Trp–Thr–Asp)-type β-propeller motifs (P1–P4), four EGF-like domains (E1–E4) and three LDLR type A domains (L1–L3) close to the transmembrane (Figure 2A) [8]. One EGF-like domain following each YWTD motif form together the functional module for ligand recognition which are part of two functional units, namely, P1E1P2E2 and P3E3P4E4. While the P1E1P2E2 unit binds specifically WNT1, WNT2, WNT2b, WNT6 and WNT9b, P3E3P4E4 binds WNT3 and WNT3a [4,8,9,10]. Interestingly, LRP6 dimerization mediated by LDLR domains is required for WNT3a activation of β-catenin signaling [11]. Additionally, LRP6 mutant lacking the extracellular domain (named LRP6ΔN mutant) is a constitutively active form of LRP6 that increases β-catenin-TCF/LEF transcriptional activity. This suggests that the LRP6 extracellular domain exerts a negative control on β-catenin-dependent transcriptional activity, probably due to folding rearrangement (Figure 2B) [12]. In contrast, deletion of the cytoplasmic domain of LRP6 (named LRP6ΔC mutant) induces a dominant-negative effect, abrogating β-catenin-dependent transcriptional activity [13].
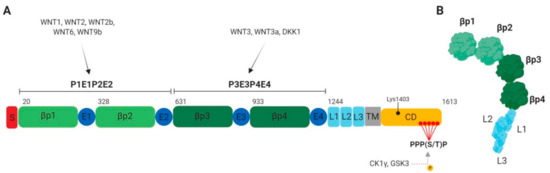
Figure 2.
LRP6 structure. (A) Schematic representation of human LRP6 domains: βp, YWTD β-propeller domains; CD, cytoplasmic domain; E, EGF-like domains; L, LDLR type A repeats; S, signal peptide; TM, transmembrane domain. The five PPP(S/T)P phosphorylation motifs are shown in red. (B) LRP6 ectodomain in its resting state. In absence of ligands, LRP6 undergoes a large bending/unbending motion, preventing homodimer and signalosome formation [14].
2.2. Post-Translational Maturation and Regulation
LRP6 maturation involves several post-translational modifications to ensure correct folding. Palmitoylation of Cys-1394 and Cys-1399 residues is essential for LRP6 exit from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Indeed, palmitoylation-deficient LRP6 mutants are retained in the ER due to Lys-1403 mono-ubiquitination, resulting in defective WNT/β-catenin pathway activation [15]. Conversely, Lys-1403 mono-ubiquitination is needed for correct folding, allowing LRP6 to interact with a chaperone-acting ubiquitin-binding protein, therefore providing time to correctly fold [16]. If misfolding occurs, LRP6 is poly-ubiquitinated on other lysines and then targeted for ER-associated degradation (ERAD) [16].
Like many membrane-anchored proteins, LRP6 folds inefficiently. LRP6’s folding and membrane targeting require the assistance of chaperones and enzymes. For example, the mesoderm development LRP chaperone (MESD) is a specialized chaperone preventing intermolecular disulfide bond formation in the extracellular domain which induces LRP6 aggregation in the ER [17]. Moreover, the membrane targeting of LRP6 is dependent on the cell-surface glycoprotein CD44 binding to F-actin via Ezrin, suggesting the involvement of actin polymerization in the transport of vesicles [18]. Consequently, CD44 silencing induces abnormal LRP6 folding and ER retention [19].
On the cell surface, the presence of large LRP5/6-containing complexes suggests that the monomeric mode of an FZD-LRP6 coreceptor complex is not privileged. In fact, FZD receptors (FZDs) and LRP5/6 undergo multiple polymerizations on the cell surface upon WNT ligand binding, to form oligomers. WNT ligands selectively bind different states of LRP5/6-FZD receptor oligomerization [20]. For instance, WNT1 subfamily ligands (WNT1, WNT2, WNT2b, WNT6 and WNT9b) preferentially bind receptor complexes with predominant LRP5/6 abundance, while WNT3 subfamily ligands (WNT3 and WNT3a) bind to predominant FZD-containing complexes. Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) is a secreted protein that antagonizes canonical WNT signaling by competitive binding to the P3E3P4E4 domain of the LRP6 coreceptor. This leads to LRP6 extracellular domain compaction, resulting in the inhibition of both receptor oligomerization and signaling activation [10,14,21]. Conversely, loss of APC—a negative regulator of WNT signaling—induces the formation of large LRP5/6 signalosomes in a ligand-independent manner [20].
Several groups have reported a crucial role for the five proline-rich PPP(S/T)P motifs, containing serine or threonine residues (Ser1490, Thr1530, Thr1572, Ser1590, Ser1607) in LRP6, in the activation of downstream signaling (Figure 2A) [6]. Phosphorylation of these residues by CK1 and GSK3 kinases leads to β-catenin-dependent pathway activation by releasing β-catenin from the destruction complex, and stabilizing β-catenin. When a dominant-negative mutant of CK1γ is expressed, LRP6 phosphorylation is blocked but signalosomes still form, suggesting that LRP6 phosphorylation is a consequence and not the cause of LRP6 aggregation [5]. Mutations of serines or threonines into alanine in the proline-rich motifs also inhibit subsequent binding of AXIN and GSK3 observed during the amplification phase. Therefore, these mutations inhibit sustained activation of the pathway after WNT binding [22,23,24]. In addition to CK1γ and GSK3, LRP6 can be phosphorylated in the proline-rich PPP(S/T)P motifs by mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK, p38 and JNK, resulting in WNT/β-catenin pathway activation [25,26,27]. Finally, direct interaction between the tight junction transmembrane protein BVES/POPDC1 and the LRP6 transmembrane domain leads to LRP6 dephosphorylation by the PP2A phosphatase, thus inducing a negative feedback regulation of WNT signaling pathway stimulation [28]. Therefore, LRP6 may also represent a point of convergence between the WNT pathway and other signaling pathways.
2.3. Endocytosis
Endocytosis is required for sustained WNT/β-catenin signal activation. Indeed, endocytosis of the LRP5/6-FZD receptor complex occurs quickly after WNT binding [29]. Interestingly, single amino acid substitutions of LDLR repeat residues inhibit LRP6 internalization and WNT signaling activity. It has been suggested that clathrin- and caveolin-dependent pathways mediate receptor complex endocytosis, depending on the cellular context and the WNT subtype [30,31]. By down-regulating transmembrane receptors, clathrin-mediated endocytosis is frequently involved in signal termination [32]. However, it was recently reported that APC inactivation can induce ligand-independent LRP6 signalosome formation via clathrin-mediated endocytosis [33]. This suggests that, without WNT ligands, APC inhibits receptor activation via the clathrin pathway.
Caveolin-dependent internalization occurs mostly at lipid rafts, a platform for receptor-mediated signaling, which facilitates the sequestration of receptors and signaling molecules within caveolae [34]. In fact, the cytoplasmic tail of LRP6 exhibits two tyrosine-based motifs (YXXY and YXXF) that can constitute an endocytic signal [35]. Mutation of these tyrosines impairs LRP6 endocytosis and induces LRP6 association with caveolin in lipid rafts. It has been proposed that in the absence of WNT signal, LRP6 is distributed between lipid raft and non-lipid-raft domains. Upon binding of WNT glycoproteins, LRP6 and FZD coreceptors are translocated to lipid rafts and aggregate in LRP6 signalosomes [5]. LRP6 is then phosphorylated and internalized by caveolin-dependent mechanisms, an event required for downstream β-catenin pathway activation. Therefore, disruption of the tyrosine-based motifs promotes LRP6 caveolin-mediated endocytosis at the expanse of clathrin-mediated endocytosis [35]. Notably, by phosphorylating these tyrosine residues, SRC and FER kinases reduce LRP6 cell surface distribution and inhibit the WNT/β-catenin pathway after WNT3a stimulation. Thus, LRP6 tyrosine phosphorylation acts as a negative feedback to avoid uncontrolled activation of the WNT pathway [36].
2.4. Tissue Homeostasis
2.4.1. Embryonic Development
Mouse models lacking Lrp6 have been developed in order to determine the role of LRP6 during development. Global Lrp6 deletion in mice induces a severe phenotype with developmental defects in eye, limb and neural tube [37,38]. Moreover, mice die at birth, indicating a crucial role for LRP6 in embryogenesis, organ formation and function. Notably, the phenotype of Lrp6 knockout mice is less severe than the phenotype observed in Ctnnb1 knockout mice, which die during gastrulation, and the phenotype observed in Wnt3a, Wnt1 and Wnt7a knockout mice, which also exhibit early embryonic lethality [37,39].
2.4.2. Intestinal Epithelial Development and Homeostasis
The WNT/β-catenin pathway is critical for intestinal epithelial homeostasis and development. Mice overexpressing DKK1, a WNT pathway inhibitor, exhibit reduced numbers of crypts and villi, decreased villus size [40], as well as proliferation and differentiation defects—especially of secretory cell types including Paneth cells, goblet cells and enteroendocrine cells. This indicates that active WNT signaling controls intestinal epithelial cell proliferation, differentiation and renewal. In this regard, both LRP5 and LRP6 are expressed in epithelial cells at the bottom of adult intestinal crypts, where proliferation and differentiation are tightly regulated [41]. Notably, while conditional LRP5 or LRP6 deletion in intestinal epithelial cells does not alter intestinal architecture during late embryonic stages, conditional deletion of both LRP5 and LRP6 significantly perturbs the crypt–villus architecture, with decreased cell proliferation, reduced enteroendocrine cell numbers and altered enterocyte distribution along the crypt–villus axis [42]. These data suggest that LRP5 and LRP6 play compensatory roles during embryonic intestinal development. Interestingly, however, LRP5/6 and WNT/β-catenin are nonessential for the development of pseudostratified epithelium (E13.5, E14.5), the stage before the formation of columnar epithelium in typical villi [43].
3. LRP6 and Carcinoma Development
Given the importance of the WNT/β-catenin pathway in development, proliferation and differentiation, disruption of this pathway leads to the development of many diseases, including cancer. Deregulation of the pathway occurs at different levels, and mutations in genes encoding components of the destruction complex are central to tumor formation [44]. Additionally, some polymorphisms identified in the LRP6 gene have been associated with different susceptibility to the development of cancers (Table 1).

Table 1.
LRP6 functional variants and expression status in distinct cancers. Some single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and mutations in the LRP6 gene have been associated with increased or decreased risk of cancer development.
The following sections provide an overview of current knowledge on the role and regulation of LRP6 in the development of epithelial cancers, including colorectal, liver, breast and pancreatic (as summarized in Figure 3).
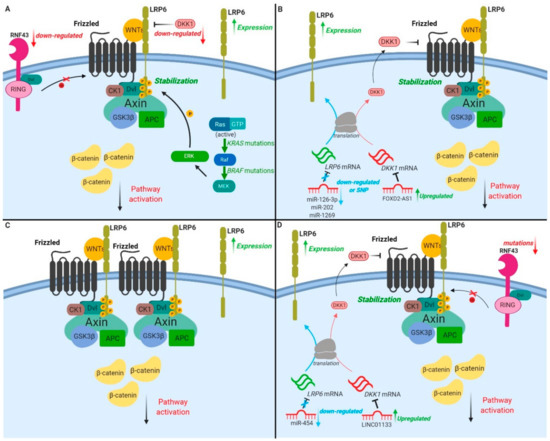
Figure 3.
LRP6 and WNT/β-catenin pathway alterations in epithelial cancers. (A) In colorectal cancer (CRC), LRP6 overexpression is observed in 61% of malignant tissues isolated from patients. (i) Mutations in the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF43, (ii) downregulation of the antagonist DKK1 and (iii) overactivation of the RAS/MAPK pathway result in the recruitment of degradation complex components at the membrane and WNT/β-catenin pathway overactivation. (B) In hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs), LRP6 is overexpressed in 45%–75% of HCC tumours. Downregulation of miR-126-3p, miR-202 and single-nucleotide polymorphism of miR-1269 result in increased LRP6 mRNA stability and protein levels. The long non-coding RNA FOX2-ASI, upregulated in HCC, targets and downregulates DKK1 mRNA (LRP6 inhibitor), thus increasing LRP6 membrane levels. (C) In breast cancers (BCs), LRP6 overexpression is observed in 20%–36% of carcinomas, and β-catenin nuclear accumulation is reported in 40%–60% of cases. (D) In pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), (i) mutations of RNF43 are observed in 5%–10% of PDAC patients, (ii) down-regulation of miR-454 and (iii) upregulation of LINC01133—a long non-coding RNA which induces DKK1 promoter methylation (decreasing DKK1 expression)—all explain increased LRP6 expression and subsequent increased β-catenin-dependent signaling.
3.1. Colorectal Cancer
3.1.1. Molecular Biomarkers
With more than 1.8 million new cases and 881,000 deaths in 2018, colorectal cancers (CRCs) represent the third most diagnosed cancer worldwide and the second leading cause of death by cancer [55]. CRC incidence is higher in developed countries, and is increasing in transition countries. CRC is a heterogenous disease with distinct CRC subtypes identified and associated with unique clinical and molecular features [56]. Most sporadic CRCs arise in a multistep process, from mucosal hyperplasia to adenomas and carcinomas. Of these cancers, 70%–80% develop via conventional adenomatous polyps initiated by mutations activating the WNT/β-catenin pathway, commonly in the APC gene [57]. Mutually exclusive to APC, other common mutations of WNT pathway components include CTNNB1, AXIN2, SOX9 and RNF43 [58]. However, dysregulation of β-catenin signaling is not sufficient to generate the CRC phenotype. Chromosomal instability and additional somatic mutations in KRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA and/or inactivation of the TP53, SMAD4 and FBXW7 tumor suppressor genes collaborate to promote the progression of APC-mutant adenomatous lesions to CRC. Serrated adenocarcinomas, accounting for 20%–30% of CRCs, follow an alternative pathway independent of APC mutations, in which serrated polyps replace the traditional adenoma as the CRC precursor lesion [59]. This pathway involves early BRAF mutations, excess CpG island methylation and DNA microsatellite instability (MSI). Interestingly, increased WNT pathway activation is frequently observed in BRAF-mutated tumours due to loss-of-function mutations in RNF43 [60]—an E3 ubiquitin ligase which mediates ubiquitination and degradation of the WNT receptor complex (Figure 1).
3.1.2. Deregulation of LRP6 Expression and Function
Using whole-genome sequencing, three functional variants of LRP6 have been identified as novel candidate risk factors of early-onset CRC patients (Table 1) [47]. Besides that, in a systematic review of 11 publications, using sequence data from 863 familial CRC cases and 1604 individuals without CRC, Broderick et al. (2017) found no significant enrichment of LRP6 mutations in CRC [61,62]. Nevertheless, LRP6 is overexpressed in many CRC cell lines in comparison to normal epithelial cells, and 61% of malignant tissues isolated from sporadic CRC patients harbor higher LRP6 levels (Table 1) [53]. This increased LRP6 expression in CRC may result from hypermethylation of the Necdin promoter—a transcriptional repressor of the LRP6 gene [63]. Aside from these observations, reduced expression of the LRP6 antagonist DKK1 has also been observed in CRC patients, and is inversely correlated with tumour grade and metastatic potential [64,65,66].
LRP6 phosphorylation is also increased in human colorectal tumours in comparison to healthy adjacent normal tissues (Table 1) [27,54]. This increased LRP6 phosphorylation correlates with tumour malignancy and staging as well as with poor prognosis of CRC, suggesting an important contribution of LRP6 activation in CRC progression and disease outcome [54]. In this regard, it has been shown that by inhibiting LRP6 expression, miR-195 down-regulates β-catenin signaling and transcription of target genes such as RUNX2 and VEGFa, which in turn decrease CRC metastasis [67]. Additionally, the lncRNA-MALAT1, which is highly expressed in recurrent CRC, reduces the levels of miR-195, abrogating its inhibitory effect on LRP6 expression. Hence, MALAT1 was recently proposed to be a biomarker for predicting the recurrence and metastasis of CRC patients [67].
3.1.3. Targeting LRP6 in CRC Models
Not surprisingly, LRP6 overexpression in CRC cells induces WNT/β-catenin activation, actin and microtubule remodeling and cell migration [54]. Conversely, LRP6 silencing—even in CRC cells with APC mutations—inhibits constitutive WNT pathway activation, indicating that LRP6 at least partially mediates the positive effect of APC inactivation on the WNT pathway [33]. These results were recently challenged by Chen and He (2019), who did not detect any modulation of WNT signaling activation and β-catenin levels in cell lines in which APC and LRP6 and/or LRP5 were knocked out by CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing [68]. However, single-cell analyses performed in isogenic human colonic epithelial cell lines confirmed that total and nuclear levels of β-catenin were increased upon LRP6 silencing, hence confirming an important role for LRP6 in WNT signaling of APC-mutated cells [69]. In this respect, LRP6 monoclonal antibodies targeting the WNT3 binding site significantly reduce proliferation and growth of tumorigenic ApcMin/+ organoids (Table 2) [33]. Furthermore, a bispecific antibody (GSK3178022) to LRP6 that is capable of blocking stimulation by a range of WNT and R-spondin (RSPO) ligands in vitro potently delayed tumor growth in a patient-derived RSPO fusion model of CRC (Table 2) [70]. More recently, single-domain antibody fragments (VHH) against the WNT3-binding site have been shown to block Rnf43 mutant intestinal organoid growth and survival, by depleting stem-like tumor cells (Table 2) [71]. Overall, these studies clearly indicate that LRP6 may represent a promising therapeutic target for CRC, in particular for WNT-hypersensitive tumours.

Table 2.
List of therapeutic reagents targeting LRP6 in various cancers. Different antibodies, small molecules and peptides have been shown to exert anticancer properties by directly or indirectly inhibiting LRP6 function.
KRAS is the most commonly mutated oncogene in CRC. KRAS is mutated on codons 12, 13, 61, 117 or 146 in about 30–60% of patients with adenocarcinomas of the colon or rectum [72,73]. Our group has demonstrated in cellulo that the nuclear transcriptional activity of β-catenin is enhanced upon sustained oncogenic stimulation of normal intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) by KRAS (G12D) or its downstream effectors BRAF (V600E) and MEK1 (S218/222D) [27]. Importantly, the expression of a dominant-negative TCF4 mutant which inhibits β-catenin/TCF4 transactivation severely attenuated the IEC transformation induced by oncogenic MEK1 and reduced tumorigenic potential in mice [27]. These data suggest that KRAS/MAPK signaling uses the β-catenin pathway to induce IEC transformation. This is consistent with the recent observation that WNT signaling components were significantly enriched in KRAS-dependent CRC cells compared to KRAS-independent cells, even though comparable APC mutations occurred in both [74]. Notably, we recently observed that LRP6 was phosphorylated on serine-1490 and threonine-1572 in an MEK-dependent manner, in IEC transformed by oncogenic KRAS or BRAF, thus providing a mechanism integrating KRAS/MAPK and canonical WNT/β-catenin signaling during intestinal transformation (Figure 3A and Table 1) [27].
3.2. Liver Cancer
3.2.1. Molecular Biomarkers
Liver cancer incidence is higher in the least-developed countries. Environmental risk factors for liver cancer include viral infections, alcohol intake, obesity and type 2 diabetes [55]. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) represents 75–85% of liver cancers, with 50–83% of these cancers characterized by abnormal accumulation and distribution of β-catenin [75]. By contrast to CRC, HCC rarely exhibits APC mutations. However, CTNNB1 or AXIN1 mutations are frequently observed respectively in 20% and 55–100% of HCCs (100% of poorly differentiated HCCs) [75,76,77,78,79,80]. Thus, aberrant WNT/β-catenin pathway activation is likely involved in HCC tumorigenesis.
3.2.2. Deregulation of LRP6 Expression and Function
Although no mutation has been reported in LRP6, 45–75% of HCC tumour samples harbor increased LRP6 expression in comparison to normal liver tissue. This increased LRP6 expression is associated with malignancy, poor prognosis and chemoresistance (Table 1) [48,49,50]. Accordingly, ectopic expression of a constitutively activated form of LRP6 in HCC cells promotes proliferation, invasion and migration, and increases tumour formation in immunodeficient mice [48]. Aside from these observations, it has recently been reported that high expression of LncRNA FOXD2-AS1, which targets the LRP6 inhibitor DKK1 mRNA, predicts poor prognosis in HCC patients. Mechanistically, by downregulating DKK1 expression, FOXD2-AS1 promotes the activation of WNT/β-catenin in HCC cell lines and enhances their tumorigenic properties (Figure 3B) [81]. Interestingly, LRP6 expression is also regulated by various miRNAs in HCC. MiR-202 and miR-126-3p expression is decreased in HCC tumour tissues, inversely correlating with LRP6 expression [82,83]. MiR-202 or miR-126-3p overexpression in HCC cells suppresses LRP6 expression, and dramatically inhibits HCC cell proliferative, angiogenic and invasive properties (Figure 2B) [82,83]. Moreover, by targeting LRP6, miR-1269a inhibits proliferation while inducing apoptosis of human HCC cells. Interestingly, a single nucleotide variant in miR-1269a, associated with increased susceptibility to HCC, was recently identified [84].
Hepatitis B (HB) viral infection is one of the major etiological factors for HCC, with chronic infection occurring in 50% of HCCs [85]. The HBV-expressed HBx protein is necessary not only for HBV infection but also for HCC development [86]. Intriguingly, a C-terminal truncated Hbx protein (HBx∆C) is found in 46–80% of HBV-infected HCCs [87,88]. A recent study reported that HBx∆C increased the expression of the lipid raft-associated protein caveolin-1, resulting in the activation of the WNT/β-catenin pathway [50]. More specifically, caveolin-1 acts by enhancing LRP6 protein stability, leading to the activation of the WNT pathway. Given the high incidence of HBV in HCC development, targeting LRP6 could be an efficient therapeutic strategy to limit tumour development in this context.
3.3. Breast Cancer
3.3.1. Molecular Biomarkers
Breast cancers are a leading cause of cancer deaths, with a higher incidence in industrialized countries. Three main subtypes have been described, namely, luminal estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, HER2-enriched and triple negative breast carcinomas (TNBCs) that do not express ER, PR and HER2 [89]. Consequently, TNBC patients are unresponsive to targeted therapies, and treatment is limited to conventional chemotherapy. Therefore, there is an urgent need for new therapeutic targets specifically for these patients. Notably, nuclear β-catenin levels are increased in 40–60% of breast cancers, notably in TNBC subtypes associated with poor prognosis [90]. Interestingly, mice expressing an active form of β-catenin in the mammary gland develop basal-like tumours, suggesting a role for the WNT signaling pathway in breast tumour development. However, in contrast to what is observed in HCC or CRC, mutations of genes encoding components of the WNT/β-catenin pathway are rarely found in breast cancer [91,92]. Interestingly, expression of LRP6, but not LRP5, has been shown to define a new class of breast cancer subtypes, as LRP6 is overexpressed in 20–36% of breast carcinomas (Figure 3C and Table 1) [51].
3.3.2. Targeting the Expression and Function of LRP6
LRP6 silencing in breast cancer cell lines impairs proliferation, anchorage-independent cell growth and tumorigenesis in xenograft assays. In addition, LRP6 is able to initiate mammary tumorigenesis, as seen with MMTV-LRP6 mice that develop mammary gland hyperplasia [93]. Notably, exogenous administration of a MESD peptide in a MMTV-WNT1 tumour mouse model suppressed tumor growth in vivo, likely through peptide binding to mature LRP6 at the cell surface and interference with ligand binding [51]. As discussed previously, LRP5/6-FZD receptor complexes are found in lipid rafts enriched with cholesterol and sphingolipids. Therefore, cholesterol depletion with methyl-β-cyclodextrins disrupts lipid rafts and decreases both LRP6 and β-catenin expression in TNBC-derived cells [94]. Finally, natural compounds isolated from plants (e.g., prodigiosin, silibinin, rottlerin, salinomycin and gigantol) all inhibit WNT/β-catenin activity and growth in TNBC cells by suppressing LRP6 expression and phosphorylation (Table 2) [95,96,97,98,99]. Moreover, niclosamide, a teniacide of the antihelminthic family, induces LRP6 degradation in breast cancer cell lines, resulting in increased cell apoptosis and decreased cell proliferation (Table 2) [100]. This emphasizes the possibility that LRP6 can represent a potential therapeutic target for breast cancers.
3.4. Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
3.4.1. Molecular Biomarkers
Pancreatic cancer is among the most devastating cancers, with a five-year survival rate less than 10% [55,101]. Pancreatic cancer incidence is explained by many risk factors, including smoking, alcohol intake, family history and genetic susceptibility with germline mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2 and mismatch repair genes [101,102]. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), the most common and aggressive form of pancreatic cancer, is mainly associated with the presence of oncogenic KRASG12V mutation [103,104]. Some studies highlight the promoting role of the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway in KRAS-dependent PDAC initiation and progression [105,106]. Interestingly, 65% of PDAC tumor samples display increased β-catenin protein levels, which are associated with decreased serine 75/threonine 41 phosphorylation and β-catenin stabilization, but not with CTNNB1 gene mutation [107]. Notably, most patient tumors exhibit enhanced β-catenin levels without modification of phosphorylation state, suggesting that other mechanisms are involved. That said, genomic analysis has revealed that 5–10% of PDAC patients harbor mutations in the RNF43 gene [108,109,110,111]. Notably, these pancreatic tumours are highly dependent on WNT signaling (Figure 3D [112,113].
3.4.2. Deregulation of LRP6 Expression and Function
LRP6 expression and activity are tightly regulated in PDAC. Increased LRP6 expression and phosphorylation associated with β-catenin nuclear accumulation have been observed in human-derived PDAC as well as murine KRAS-dependent pancreatic cancers (KPCs) [52]. More specifically, the microRNA miR-454, which targets LRP6 mRNA, is downregulated in PDAC (Figure 3D) and therefore its overexpression in pancreatic cancer cells impairs proliferation, angiogenic activity and metastatic potential [114,115]. Expression profiles of miRNA expressed in pancreatic cancers have correlated reduced miR-29c expression with poor prognosis [116]. Using TargetScan, LRP6, as well as FRAT2, FZD4 and FZD5, were identified as potential miR-29c targets. Not surprisingly, overexpression of miR-29c inhibits PDAC cell tumorigenicity and invasion, likely by direct inhibition of these WNT signaling proteins. On the other hand, LRP6 activity is also controlled by LINC01133, a long non-coding RNA upregulated in pancreatic cancers. Indeed, LINC01133 decreases DKK1 expression by inducing DKK1 promoter methylation (Figure 3D) [117]. Therefore, LINCO1133 overexpression in pancreatic cancer cell lines increases β-catenin transcriptional activity and promotes proliferative, tumoral and invasive properties.
3.4.3. Targeting the Expression and Function of LRP6
Interestingly, the vitamin D receptor gene has been recently identified as a determinant of survival in patients with pancreatic cancer [118]. In this regard, a negative correlation between patient’s vitamin D serum levels and pancreatic cancer has been observed, with vitamin D insufficiency associated with pancreatic cancer progression [118,119]. Notably, the vitamin D analogue calcipotriol, which displays anticancer properties in advanced pancreatic tumours, likely acts by reducing LRP6 protein levels (Table 2) [120,121]. In fact, treatment of pancreatic cancer cells with calcipotriol induces the expression of low-density lipoprotein receptor adaptor protein 1 (LDLRAP1), which interacts with tyrosine motifs of the LRP6 cytoplasmic tail, thereby inducing LRP6 clathrin-dependent endocytosis and subsequent lysosome-dependent degradation. Hence, by targeting LRP6 expression, vitamin D analogs act as therapeutic WNT inhibitors to inhibit PDAC tumor growth. In line with that, LRP6 silencing in human pancreatic cancer cell lines inhibits β-catenin/TCF transcriptional activity and cell proliferation [52].
3.5. Other Epithelial Cancers
Some evidence also suggests a role for LRP6 in the development of other epithelial cancers, including prostate, gastric, bladder, non-small-cell lung (NSCL) and papillary thyroid cancers. For instance, androgen-dependent LRP6 expression is necessary for prostate cancer cell growth [122]. As observed in breast cancer cells, silibinin, rottlerin, salinomycin and niclosamide were demonstrated to inhibit WNT/β-catenin activity and pancreatic cancer cell growth by suppressing LRP6 expression or phosphorylation (Table 2) [95,96,97,100]. Interestingly, treatment with recombinant MESD protein, a LRP5/6 chaperone protein able to bind to mature LRP5 and LRP6 on the cell surface, decreases LRP6 phosphorylation in prostate cancer cells, inhibiting their proliferation and tumorigenic potential (Table 2) [123,124]. On the other hand, infection of gastric epithelial cells with Helicobacter pylori or Mycoplasma hyorhinis induced rapid phosphorylation of LRP6 and downstream activation of Wnt/β -catenin signaling [125,126]. Additionally, curcumin and pantoprazole (a proton pump inhibitor) have demonstrated promising inhibitory effects on the growth of gastric adenocarcinoma (Table 2) [127,128]. In papillary thyroid carcinoma, miR126 and miR381-3p expression inhibits cell proliferation, migration/invasion and reduces tumour growth by decreasing LRP6 expression [129,130]. Regarding bladder cancer, ectopic expression of LRP6 in T24 cells promotes viability and invasion, while knockdown of LRP6 induces cell apoptosis [131]. Interestingly, the single-nucleotide polymorphism of LRP6 rs10743980 was recently associated with a decreased risk of developing bladder cancer [46]. Likewise, in a cohort of 500 non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, LRP6 rs10845498 was associated with a reduced risk of NSCLC and LRP6 rs6488507 with increased risk of NSCLC in tobacco smokers (Table 1) [45]. Further studies are however needed to elucidate the functional impact of LRP6 expression and activity in NSCLC.
4. LRP6: A Candidate for Targeted Therapy
Until now, the clinical trials that were conducted to inhibit the Wnt/β-catenin pathway mostly involved the use of porcupine inhibitors to block WNT secretion or the use of adenoviruses to overexpress DKK3, an antagonist of LRP5/6 (Table 3). Inhibitors of porcupine have demonstrated promising results in phase I clinical trials, inducing tumor regression in BRAF-mutant CRC, TNBC and pancreatic cancer patients (Table 3) [136,137,138]. However, given the crucial role of WNT signaling in the regulation of tissue homeostasis, global WNT inhibition may result in adverse or toxic effects. Interestingly, LRP6 alterations belong to inclusion criteria in clinical trials using inhibitors of porcupine in various cancers, highlighting the presumed critical role of LRP6 in cancer development [139]. Indeed, as mentioned in this review, upregulated LRP6 function in tumours is frequently associated with cell malignancy, poor prognosis and/or chemoresistance. Therefore, LRP6 protein clearly represents a pertinent actionable target for cancer therapy. In this regard, modified antibodies specifically targeting the extracellular domain of LRP6 were previously generated, and some of them seem very promising [9,33,70,71,132]. For instance, LRP6 monoclonal antibodies targeting the WNT3 binding site potently reduced the proliferation and growth of Apc-mutant intestinal tumoroids [33]. Nonetheless, the LPR6 extracellular domain is divided into two functional entities, P1E1P2E2 and P3E3P4E4, which respectively bind WNT1 and WNT3 glycoproteins. Therefore, the use of an antibody targeting the WNT3 binding site of LRP6 can sensitize cells to WNT1 ligands and vice versa, probably due to antibody-mediated LRP6 dimerization. Consequently, it becomes necessary to develop specific domain antibodies to selectively inhibit LRP6 activation by certain classes of WNTs while leaving the binding of other WNT ligands unchanged, limiting potential side effects. In this respect, Fenderico et al. (2019) recently used CIS display technology to identify single-domain antibody fragments (VHH) that bind the P3E3P4E4 region (WNT3-binding site). By inhibiting cellular responses to WNT3a but not those to WNT1, these anti-LRP5/6 VHHs efficiently block Rnf43 mutant intestinal organoid growth and survival [71]. Thus, targeting specific regions of LRP6 ectodomain, especially the P3E3P4E4 region, may represent a promising strategy to reduce β-catenin-dependent signaling in tumours, without altering other WNT functions.

Table 3.
Clinical trials targeting effectors of WNT/β-catenin pathway. Given the importance of the WNT/β-catenin pathway in cancer development, effectors of this pathway such as porcupine and LRP6 are specifically targeted in Phase 1 and 2 clinical trials in various cancers. Ad: adenovirus, DKK3: Dickkopf-related protein 3, RAF: rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma, PD-1: Programmed cell death 1, EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor.
5. Conclusions
From these previous studies, it is clear that LRP6 is a key player in the activation of the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway and, consequently, in the regulation of tissue homeostasis under physiological and pathological conditions. However, β-catenin-independent roles of WNT/LRP6 signaling have recently been reported [140]. How exactly these β-catenin-independent WNT/LRP6 signaling pathways contribute to tumour development remains to be determined. Furthermore, LRP6 is phosphorylated by mitogen-activated protein kinases such as ERK1/2, which transduce signals from the cell surface to the nucleus, thus affecting cell proliferation, differentiation and survival [25]. Notably, increased phosphorylation of LRP6 was observed in KRAS-transformed intestinal epithelial cells [27]. Hence, it will be relevant to determine whether inhibiting LRP6 function interferes with tumoral properties of human KRAS-mutated cancer cells. This would be a very important finding since KRAS is mutated in 80% of human PDAC, 40–50% of CRC and 30–50% of lung carcinomas and is very difficult to target. In the future, it will be necessary to fully characterize LRP6 activators and downstream effectors under specific cellular contexts. The elucidation of the LRP6 interactome may be one additional step to further understand LRP6 functions in cancer development.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, J.R.; writing—review and editing, J.R., A.C.-B., N.R.; supervision, N.R.
Funding
This research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research Grant to Nathalie Rivard (MOP, 119593). Nathalie Rivard is a recipient of a Canadian Research Chair in colorectal cancer and inflammatory cell signalling.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to acknowledge Claude Asselin for critical reading and review of the manuscript. The figures have been created with Biorender.com.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tan, S.H.; Barker, N. Chapter Two—Wnt Signaling in Adult Epithelial Stem Cells and Cancer. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Larraín, J., Olivares, G., Eds.; WNT Signaling in Health and Disease; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 153, pp. 21–79. [Google Scholar]
- Yost, C.; Torres, M.; Miller, J.R.; Huang, E.; Kimelman, D.; Moon, R.T. The axis-inducing activity, stability, and subcellular distribution of beta-catenin is regulated in Xenopus embryos by glycogen synthase kinase 3. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 1443–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Semenov, M.; Han, C.; Baeg, G.H.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, X.; He, X. Control of beta-catenin phosphorylation/degradation by a dual-kinase mechanism. Cell 2002, 108, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Semenov, M.; Tamai, K.; Zeng, X. LDL receptor-related proteins 5 and 6 in Wnt/β-catenin signaling: Arrows point the way. Development 2004, 131, 1663–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilic, J.; Huang, Y.-L.; Davidson, G.; Zimmermann, T.; Cruciat, C.-M.; Bienz, M.; Niehrs, C. Wnt induces LRP6 signalosomes and promotes dishevelled-dependent LRP6 phosphorylation. Science 2007, 316, 1619–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niehrs, C.; Shen, J. Regulation of Lrp6 phosphorylation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 2551–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, J.; Palmby, T.R.; Gavard, J.; Williams, B.O.; Gutkind, J.S. Multiple PPPS/TP motifs act in a combinatorial fashion to transduce Wnt signaling through LRP6. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Bubeck, D.; MacDonald, B.T.; Liang, W.-X.; Mao, J.-H.; Malinauskas, T.; Llorca, O.; Aricescu, A.R.; Siebold, C.; He, X.; et al. Structural and Functional Studies of LRP6 Ectodomain Reveal a Platform for Wnt Signaling. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettenberg, S.A.; Charlat, O.; Daley, M.P.; Liu, S.; Vincent, K.J.; Stuart, D.D.; Schuller, A.G.; Yuan, J.; Ospina, B.; Green, J.; et al. Inhibition of tumorigenesis driven by different Wnt proteins requires blockade of distinct ligand-binding regions by LRP6 antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15473–15478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourhis, E.; Tam, C.; Franke, Y.; Bazan, J.F.; Ernst, J.; Hwang, J.; Costa, M.; Cochran, A.G.; Hannoush, R.N. Reconstitution of a Frizzled8·Wnt3a·LRP6 Signaling Complex Reveals Multiple Wnt and Dkk1 Binding Sites on LRP6. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 9172–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yan, H.; Ren, D.; Yin, Y.; Li, Z.; He, Q.; Wo, D.; Ho, M.S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. LRP6 dimerization through its LDLR domain is required for robust canonical Wnt pathway activation. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, K.; Gonzalez-Sancho, J.M.; Castelo-Soccio, L.A.; Howe, L.R.; Brown, A.M.C. Truncated mutants of the putative Wnt receptor LRP6/Arrow can stabilize beta-catenin independently of Frizzled proteins. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4873–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamai, K.; Semenov, M.; Kato, Y.; Spokony, R.; Liu, C.; Katsuyama, Y.; Hess, F.; Saint-Jeannet, J.P.; He, X. LDL-receptor-related proteins in Wnt signal transduction. Nature 2000, 407, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matoba, K.; Mihara, E.; Tamura-Kawakami, K.; Miyazaki, N.; Maeda, S.; Hirai, H.; Thompson, S.; Iwasaki, K.; Takagi, J. Conformational Freedom of the LRP6 Ectodomain Is Regulated by N-glycosylation and the Binding of the Wnt Antagonist Dkk1. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrami, L.; Kunz, B.; Iacovache, I.; van der Goot, F.G. Palmitoylation and ubiquitination regulate exit of the Wnt signaling protein LRP6 from the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5384–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrody, E.; Abrami, L.; Feldman, M.; Kunz, B.; Urbé, S.; van der Goot, F.G. Ubiquitin-dependent folding of the Wnt signaling coreceptor LRP6. Elife 2016, 5, e19083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, J.-C.; Lee, L.; Zhang, L.; Wefer, S.; Brown, K.; DeRossi, C.; Wines, M.E.; Rosenquist, T.; Holdener, B.C. Mesd Encodes an LRP5/6 Chaperone Essential for Specification of Mouse Embryonic Polarity. Cell 2003, 112, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamnes, M. Regulating the actin cytoskeleton during vesicular transport. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2002, 14, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M.; Metzger, M.; Gradl, D.; Davidson, G.; Orian-Rousseau, V. CD44 functions in Wnt signaling by regulating LRP6 localization and activation. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; He, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, J.; Gan, X. Oligomerization of Frizzled and LRP5/6 protein initiates intracellular signaling for the canonical WNT/β-catenin pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 19710–19724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niida, A.; Hiroko, T.; Kasai, M.; Furukawa, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Sugano, S.; Akiyama, T. DKK1, a negative regulator of Wnt signaling, is a target of the β-catenin/TCF pathway. Oncogene 2004, 23, 8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Pan, W.; Farr, G.H.; Flynn, C.; Yuan, H.; Takada, S.; Kimelman, D.; Li, L.; et al. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-5 binds to Axin and regulates the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Bafico, A.; Harris, V.K.; Aaronson, S.A. A Novel Mechanism for Wnt Activation of Canonical Signaling through the LRP6 Receptor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 5825–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamai, K.; Zeng, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Harada, Y.; Chang, Z.; He, X. A mechanism for Wnt coreceptor activation. Mol. Cell 2004, 13, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Červenka, I.; Wolf, J.; Mašek, J.; Krejci, P.; Wilcox, W.R.; Kozubík, A.; Schulte, G.; Gutkind, J.S.; Bryja, V. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases Promote WNT/β-Catenin Signaling via Phosphorylation of LRP6. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krejci, P.; Aklian, A.; Kaucka, M.; Sevcikova, E.; Prochazkova, J.; Masek, J.K.; Mikolka, P.; Pospisilova, T.; Spoustova, T.; Weis, M.; et al. Receptor tyrosine kinases activate canonical WNT/β-catenin signaling via MAP kinase/LRP6 pathway and direct β-catenin phosphorylation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemieux, E.; Cagnol, S.; Beaudry, K.; Carrier, J.; Rivard, N. Oncogenic KRAS signalling promotes the Wnt/β-catenin pathway through LRP6 in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4914–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.J.; Short, S.P.; Parang, B.; Brown, R.E.; Li, C.; Ng, V.H.; Saito-Diaz, K.; Choksi, Y.A.; Washington, M.K.; Smith, J.J.; et al. Blood vessel epicardial substance (BVES) reduces LRP6 receptor and cytoplasmic-catenin levels to modulate Wnt signaling and intestinal homeostasis. Carcinogenesis 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, M.; Hernandez, A.; McGough, I.J.; Vincent, J.-P. Inhibitors of endocytosis prevent Wnt/Wingless signalling by reducing the level of basal β-catenin/Armadillo. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 4918–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Gao, N. Keeping Wnt Signalosome in Check by Vesicular Traffic. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Pan, W.; Jones, S.A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Wu, D. Clathrin and AP2 are required for PtdIns(4,5)P2-mediated formation of LRP6 signalosomes. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymkiewicz, I.; Shupliakov, O.; Dikic, I. Cargo- and compartment-selective endocytic scaffold proteins. Biochem. J. 2004, 383, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito-Diaz, K.; Benchabane, H.; Tiwari, A.; Tian, A.; Li, B.; Thompson, J.J.; Hyde, A.S.; Sawyer, L.M.; Jodoin, J.N.; Santos, E.; et al. APC Inhibits Ligand-Independent Wnt Signaling by the Clathrin Endocytic Pathway. Dev. Cell 2018, 44, 566–581.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razani, B.; Wang, X.B.; Engelman, J.A.; Battista, M.; Lagaud, G.; Zhang, X.L.; Kneitz, B.; Hou, H.; Christ, G.J.; Edelmann, W.; et al. Caveolin-2-Deficient Mice Show Evidence of Severe Pulmonary Dysfunction without Disruption of Caveolae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 2329–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-C.; Kanekiyo, T.; Roth, B.; Bu, G. Tyrosine-based signal mediates LRP6 receptor endocytosis and desensitization of Wnt/β-catenin pathway signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27562–27570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Su, Y.; Wesslowski, J.; Hagemann, A.I.; Ramialison, M.; Wittbrodt, J.; Scholpp, S.; Davidson, G. Tyrosine phosphorylation of LRP6 by Src and Fer inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signalling. EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 1254–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinson, K.I.; Brennan, J.; Monkley, S.; Avery, B.J.; Skarnes, W.C. An LDL-receptor-related protein mediates Wnt signalling in mice. Nature 2000, 407, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.J.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Yamagami, T.; Zhao, T.; Song, L.; Wang, K. Generation of Lrp6 conditional gene-targeting mouse line for modeling and dissecting multiple birth defects/congenital anomalies. Dev. Dyn. 2010, 239, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haegel, H.; Larue, L.; Ohsugi, M.; Fedorov, L.; Herrenknecht, K.; Kemler, R. Lack of beta-catenin affects mouse development at gastrulation. Development 1995, 121, 3529–3537. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, D.; Gregorieff, A.; Begthel, H.; Clevers, H. Canonical Wnt signals are essential for homeostasis of the intestinal epithelium. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 1709–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorieff, A.; Pinto, D.; Begthel, H.; Destrée, O.; Kielman, M.; Clevers, H. Expression Pattern of Wnt Signaling Components in the Adult Intestine. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Baker, J.J.; Zylstra-Diegel, C.R.; Williams, B.O. Lrp5 and Lrp6 play compensatory roles in mouse intestinal development. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, A.M.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Finkbeiner, S.R.; Nagy, M.S.; Walker, E.M.; Ethen, N.J.; Williams, B.O.; Battle, M.A.; Spence, J.R. A Dynamic WNT/β-CATENIN Signaling Environment Leads to WNT-Independent and WNT-Dependent Proliferation of Embryonic Intestinal Progenitor Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2016, 7, 826–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastas, J.N.; Moon, R.T. WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, W.; Kong, X. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6) rs10845498 polymorphism is associated with a decreased risk of non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierzynski, J.A.; Hildebrandt, M.A.; Kamat, A.M.; Lin, J.; Ye, Y.; Dinney, C.P.N.; Wu, X. Genetic Variants in the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway as Indicators of Bladder Cancer Risk. J. Urol. 2015, 194, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Voer, R.M.; Hahn, M.-M.; Weren, R.D.A.; Mensenkamp, A.R.; Gilissen, C.; van Zelst-Stams, W.A.; Spruijt, L.; Kets, C.M.; Zhang, J.; Venselaar, H.; et al. Identification of Novel Candidate Genes for Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer Susceptibility. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, E.K.-K.; Wong, B.Y.-C.; Yau, T.-O.; Ng, I.O.-L. Upregulation of the Wnt co-receptor LRP6 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis and enhances cell invasion. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Bu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, S.; Liu, Q. Maintenance of stemness is associated with the interation of LRP6 and heparin-binding protein CCN2 autocrined by hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Tey, S.K.; Ko, F.C.F.; Kwong, E.M.L.; Gao, Y.; Ng, I.O.-L.; Cheung, S.T.; Guan, X.-Y.; Yam, J.W.P. C-terminal truncated HBx protein activates caveolin-1/LRP6/β-catenin/FRMD5 axis in promoting hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2019, 444, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-C.; Prior, J.; Piwnica-Worms, D.; Bu, G. LRP6 overexpression defines a class of breast cancer subtype and is a target for therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5136–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, B.; Giri, B.; Majumder, K.; Dudeja, V.; Banerjee, S.; Saluja, A. Modulation of post-translational modifications in β-catenin and LRP6 inhibits Wnt signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 388, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rismani, E.; Fazeli, M.S.; Mahmoodzadeh, H.; Movassagh, A.; Azami, S.; Karimipoor, M.; Teimoori-Toolabi, L. Pattern of LRP6 gene expression in tumoral tissues of colorectal cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2017, 19, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; An, Y.; Hou, W.; Cao, Y.-N.; Yao, M.-F.; Ma, N.-N.; Hou, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.-J.; Zhang, B. LRP6 promotes invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer through cytoskeleton dynamics. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 109632–109645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Sierra, M.S.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut 2017, 66, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearon, E.R.; Vogelstein, B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell 1990, 61, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segditsas, S.; Tomlinson, I. Colorectal cancer and genetic alterations in the Wnt pathway. Oncogene 2006, 25, 7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.C. Pathogenesis and Management of Serrated Polyps: Current Status and Future Directions. Gut Liver 2014, 8, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, C.E.; McKeone, D.M.; Kalimutho, M.; Bettington, M.L.; Pearson, S.-A.; Dumenil, T.D.; Wockner, L.F.; Burge, M.; Leggett, B.A.; Whitehall, V.L.J. RNF43 and ZNRF3 are commonly altered in serrated pathway colorectal tumorigenesis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 70589–70600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, P.; Dobbins, S.E.; Chubb, D.; Kinnersley, B.; Dunlop, M.G.; Tomlinson, I.; Houlston, R.S. Validation of Recently Proposed Colorectal Cancer Susceptibility Gene Variants in an Analysis of Families and Patients-a Systematic Review. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 75–77.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraweera, N.; Robinson, J.; Volikos, E.; Guenther, T.; Talbot, I.; Tomlinson, I.; Silver, A. Mutations within Wnt pathway genes in sporadic colorectal cancers and cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 1837–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-H.; Chen, Q.; Lu, Y.-X.; Zhang, J.-M.; Lin, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, W.-J.; Li, X.-M.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.-N. Hypermethylation of NDN promotes cell proliferation by activating the Wnt signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 46191–46203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Sancho, J.M.; Aguilera, O.; García, J.M.; Pendás-Franco, N.; Peña, C.; Cal, S.; García de Herreros, A.; Bonilla, F.; Muñoz, A. The Wnt antagonist DICKKOPF-1 gene is a downstream target of beta-catenin/TCF and is downregulated in human colon cancer. Oncogene 2005, 24, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.; Sun, B.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Gao, J.; Leng, X. Dickkopf-1 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colon cancer cells and contributes to colon cancer suppression. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, B.; Qi, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y. Dickkopf-1 expression is down-regulated during the colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence and correlates with reduced microvessel density and VEGF expression. Histopathology 2015, 67, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Q.; Cai, G.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Sui, H.; Li, Q. MALAT1 regulates the transcriptional and translational levels of proto-oncogene RUNX2 in colorectal cancer metastasis. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; He, X. APC Deficiency Leads to β-Catenin Stabilization and Signaling Independent of LRP5/6. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 825–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabel, C.R.; Alizadeh, E.; Robbins, D.J.; Ahmed, Y.; Lee, E.; Thorne, C.A. Single-Cell Analyses Confirm the Critical Role of LRP6 for Wnt Signaling in APC-Deficient Cells. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 827–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, H.; Granger, D.; Jones, G.; Anderson, L.; Friel, S.; Rycroft, D.; Fieles, W.; Tunstead, J.; Steward, M.; Wattam, T.; et al. Novel Bispecific Domain Antibody to LRP6 Inhibits Wnt and R-spondin Ligand-Induced Wnt Signaling and Tumor Growth. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenderico, N.; van Scherpenzeel, R.C.; Goldflam, M.; Proverbio, D.; Jordens, I.; Kralj, T.; Stryeck, S.; Bass, T.Z.; Hermans, G.; Ullman, C.; et al. Anti-LRP5/6 VHHs promote differentiation of Wnt-hypersensitive intestinal stem cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.L.; Zhao, W.; Project, C.G.; Leung, S.Y.; Yuen, S.T. BRAF and KRAS Mutations in Colorectal Hyperplastic Polyps and Serrated Adenomas. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 4878–4881. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Normanno, N.; Tejpar, S.; Morgillo, F.; De Luca, A.; Van Cutsem, E.; Ciardiello, F. Implications for KRAS status and EGFR-targeted therapies in metastatic CRC. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 6, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Sweeney, M.F.; Yu, M.; Burger, A.; Greninger, P.; Benes, C.; Haber, D.A.; Settleman, J. TAK1 (MAP3K7) inhibition promotes apoptosis in KRAS-dependent colon cancers. Cell 2012, 148, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, K.J.; Han, W.C.; Choi, S.C.; Kim, T.H. Immunohistochemical Study of beta-catenin Expression between Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Res. Treat. 2002, 34, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Park, W.S.; Nam, S.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Yoo, N.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, C.K. Mutations of beta-catenin and AXIN I genes are a late event in human hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Liver Int. 2005, 25, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Coste, A.; Romagnolo, B.; Billuart, P.; Renard, C.A.; Buendia, M.A.; Soubrane, O.; Fabre, M.; Chelly, J.; Beldjord, C.; Kahn, A.; et al. Somatic mutations of the beta-catenin gene are frequent in mouse and human hepatocellular carcinomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8847–8851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Roberts, L.R.; Aderca, I.N.; Dong, X.; Qian, C.; Murphy, L.M.; Nagorney, D.M.; Burgart, L.J.; Roche, P.C.; Smith, D.I.; et al. Mutational spectrum of beta-catenin, AXIN1, and AXIN2 in hepatocellular carcinomas and hepatoblastomas. Oncogene 2002, 21, 4863–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, S.; Daigo, Y.; Furukawa, Y.; Kato, T.; Miwa, N.; Nishiwaki, T.; Kawasoe, T.; Ishiguro, H.; Fujita, M.; Tokino, T.; et al. AXIN1 mutations in hepatocellular carcinomas, and growth suppression in cancer cells by virus-mediated transfer of AXIN1. Nat. Genet. 2000, 24, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-D.; Park, C.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Choi, S.-K.; Rew, J.-S.; Kim, D.-Y.; Koh, Y.-S.; Jeung, K.-W.; Lee, K.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; et al. Genetic alterations of Wnt signaling pathway–associated genes in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, K.; Jia, F.; Li, S. EGR1-induced upregulation of lncRNA FOXD2-AS1 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via epigenetically silencing DKK1 and activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Lv, Z.; Cao, L.; Ding, C.; Gyabaah, O.-A.K.; Xie, H.; Zhou, L.; Wu, J.; Zheng, S. MiR-126-3p suppresses tumor metastasis and angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting LRP6 and PIK3R2. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, D.; Xiong, Y.; Xue, C.; Chen, G.; Yan, B.; Ye, Q. miR-202 suppresses cell proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma by downregulating LRP6 post-transcriptionally. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, P.; Li, W.; Zeng, D.; Ma, Y.; Xu, D.; Zheng, W.; Tang, F.; Chen, J.; Shi, J.; Hu, H.; et al. A single nucleotide variant in microRNA-1269a promotes the occurrence and process of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting to oncogenes SPATS2L and LRP6. Bull. Cancer 2017, 104, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Viral Hepatitis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1264–1273.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.-A.; Lee, C. Hepatitis B virus X gene and hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 974–990.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sze, K.M.F.; Chu, G.K.Y.; Lee, J.M.F.; Ng, I.O.L. C-terminal truncated hepatitis B virus x protein is associated with metastasis and enhances invasiveness by c-jun/matrix metalloproteinase protein 10 activation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2013, 57, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, N.-F.; Lau, S.H.; Hu, L.; Xie, D.; Wu, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M.-C.; Fung, J.; Bai, X.; et al. COOH-Terminal Truncated HBV X Protein Plays Key Role in Hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5061–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turashvili, G.; Brogi, E. Tumor Heterogeneity in Breast Cancer. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, F.C.; Lacroix-Triki, M.; Savage, K.; Arnedos, M.; Lambros, M.B.; MacKay, A.; Natrajan, R.; Reis-Filho, J.S. β-Catenin pathway activation in breast cancer is associated with triple-negative phenotype but not with CTNNB1 mutation. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 209–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.M. Wnt signaling in breast cancer: Have we come full circle? Breast Cancer Res. 2001, 3, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-Y.; Xia, W.; Wang, J.C.; Kwong, K.Y.; Spohn, B.; Wen, Y.; Pestell, R.G.; Hung, M.-C. β-Catenin, a novel prognostic marker for breast cancer: Its roles in cyclin D1 expression and cancer progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4262–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Lu, W.; Bu, G. Wnt signaling activation and mammary gland hyperplasia in MMTV–LRP6 transgenic mice: Implication for breast cancer tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2010, 29, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badana, A.K.; Chintala, M.; Gavara, M.M.; Naik, S.; Kumari, S.; Kappala, V.R.; Iska, B.R.; Malla, R.R. Lipid rafts disruption induces apoptosis by attenuating expression of LRP6 and survivin in triple negative breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Lin, C.; King, T.D.; Chen, H.; Reynolds, R.C.; Li, Y. Silibinin inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling by suppressing Wnt co-receptor LRP6 expression in human prostate and breast cancer cells. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 2291–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Li, Y. Salinomycin suppresses LRP6 expression and inhibits both Wnt/β-catenin and mTORC1 signaling in breast and prostate cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 115, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Lin, C.; Li, Y. Rottlerin induces Wnt co-receptor LRP6 degradation and suppresses both Wnt/β-catenin and mTORC1 signaling in prostate and breast cancer cells. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wang, Z.; Su, Z.; Song, J.; Zhou, L.; Sun, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. Gigantol inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling and exhibits anticancer activity in breast cancer cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, B.; Zhou, L.; Yu, S.; Su, Z.; Song, J.; Sun, Q.; Sha, O.; Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; et al. Prodigiosin inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling and exerts anticancer activity in breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13150–13155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Lin, C.; Roberts, M.J.; Waud, W.R.; Piazza, G.A.; Li, Y. Niclosamide Suppresses Cancer Cell Growth by Inducing Wnt Co-Receptor LRP6 Degradation and Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Gaduputi, V. Epidemiology of Pancreatic Cancer: Global Trends, Etiology and Risk Factors. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.P. Genetic Susceptibility to Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2012, 51, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almoguera, C.; Shibata, D.; Forrester, K.; Martin, J.; Arnheim, N.; Perucho, M. Most human carcinomas of the exocrine pancreas contain mutant c-K-ras genes. Cell 1988, 53, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Dey, P.; Yao, W.; Kimmelman, A.C.; Draetta, G.F.; Maitra, A.; DePinho, R.A. Genetics and biology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 355–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Morris, J.P.; Yan, W.; Schofield, H.K.; Gurney, A.; Simeone, D.M.; Millar, S.E.; Hoey, T.; Hebrok, M.; di Magliano, M.P. Canonical Wnt signaling Is required for pancreatic carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 4909–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arensman, M.D.; Kovochich, A.N.; Kulikauskas, R.M.; Lay, A.R.; Yang, P.-T.; Li, X.; Donahue, T.; Major, M.B.; Moon, R.T.; Chien, A.J.; et al. WNT7B mediates autocrine Wnt/β-catenin signaling and anchorage-independent growth in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2014, 33, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, G.; Germinaro, M.; Micsenyi, A.; Monga, N.K.; Bell, A.; Sood, A.; Malhotra, V.; Sood, N.; Midda, V.; Monga, D.K.; et al. Aberrant Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Neoplasia 2006, 8, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.; Zhang, X.; Parsons, D.W.; Lin, J.C.-H.; Leary, R.J.; Angenendt, P.; Mankoo, P.; Carter, H.; Kamiyama, H.; Jimeno, A.; et al. Core Signaling Pathways in Human Pancreatic Cancers Revealed by Global Genomic Analyses. Science 2008, 321, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddell, N.; Pajic, M.; Patch, A.-M.; Chang, D.K.; Kassahn, K.S.; Bailey, P.; Johns, A.L.; Miller, D.; Nones, K.; Quek, K.; et al. Whole genomes redefine the mutational landscape of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 518, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, P.; Chang, D.K.; Nones, K.; Johns, A.L.; Patch, A.-M.; Gingras, M.-C.; Miller, D.K.; Christ, A.N.; Bruxner, T.J.C.; Quinn, M.C.; et al. Genomic analyses identify molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2016, 531, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network Integrated Genomic Characterization of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 185–203.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.-K.; Spit, M.; Jordens, I.; Low, T.Y.; Stange, D.E.; van de Wetering, M.; van Es, J.H.; Mohammed, S.; Heck, A.J.R.; Maurice, M.M.; et al. Tumour suppressor RNF43 is a stem-cell E3 ligase that induces endocytosis of Wnt receptors. Nature 2012, 488, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Hao, H.-X.; Growney, J.D.; Woolfenden, S.; Bottiglio, C.; Ng, N.; Lu, B.; Hsieh, M.H.; Bagdasarian, L.; Meyer, R.; et al. Inactivating mutations of RNF43 confer Wnt dependency in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12649–12654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Xu, L.-L.; Shi, C.-Y.; Wei, W.; Wang, D.-S.; Cai, D.-F. MicroRNA-454 regulates stromal cell derived factor-1 in the control of the growth of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Shi, C.; Li, T.; Kuang, T. microRNA-454 shows anti-angiogenic and anti-metastatic activity in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by targeting LRP6. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Yu, C.; Chen, M.; Zhang, H.; Tian, S.; Sun, C. Reduction of miR-29c enhances pancreatic cancer cell migration and stem cell-like phenotype. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 2767–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Y.-C.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.-C. Long non-coding RNA LINC01133 silencing exerts antioncogenic effect in pancreatic cancer through the methylation of DKK1 promoter and the activation of Wnt signaling pathway. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innocenti, F.; Owzar, K.; Jiang, C.; Etheridge, A.S.; Gordân, R.; Sibley, A.B.; Mulkey, F.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Glubb, D.; Neel, N.; et al. The vitamin D receptor gene as a determinant of survival in pancreatic cancer patients: Genomic analysis and experimental validation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Loon, K.; Owzar, K.; Jiang, C.; Kindler, H.L.; Mulcahy, M.F.; Niedzwiecki, D.; O’Reilly, E.M.; Fuchs, C.; Innocenti, F.; Venook, A.P.; et al. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D levels and survival in advanced pancreatic cancer: Findings from CALGB 80303 (Alliance). J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, M.H.; Yu, R.T.; Engle, D.D.; Ding, N.; Atkins, A.R.; Tiriac, H.; Collisson, E.A.; Connor, F.; Van Dyke, T.; Kozlov, S.; et al. Vitamin D receptor-mediated stromal reprogramming suppresses pancreatitis and enhances pancreatic cancer therapy. Cell 2014, 159, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arensman, M.D.; Nguyen, P.; Kershaw, K.M.; Lay, A.R.; Ostertag-Hill, C.A.; Sherman, M.H.; Downes, M.; Liddle, C.; Evans, R.M.; Dawson, D.W. Calcipotriol Targets LRP6 to Inhibit Wnt Signaling in Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Kim, E.K.; Kim, M.; Ha, J.M.; Kim, Y.W.; Jin, S.Y.; Shin, H.K.; Ha, H.K.; Lee, J.Z.; Bae, S.S. Androgen Receptor-dependent Expression of Low-density Lipoprotein Receptor-related Protein 6 is Necessary for Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 19, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Lu, W.; Zhai, L.; Bethea, T.; Berry, K.; Qu, Z.; Waud, W.R.; Li, Y. Mesd Is A General Inhibitor of Different Wnt Ligands in Wnt/LRP Signaling and Inhibits PC-3 Tumor Growth In Vivo. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 3120–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Liu, C.-C.; Thottassery, J.V.; Bu, G.; Li, Y. Mesd Is a Universal Inhibitor of Wnt Coreceptors LRP5 and LRP6 and Blocks Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Cancer Cells. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 4635–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnad, T.; Feoktistova, M.; Leverkus, M.; Lendeckel, U.; Naumann, M. Helicobacter pylori-induced activation of beta-catenin involves low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 and Dishevelled. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Rong, Z.; Shou, C. Mycoplasma hyorhinis infection promotes gastric cancer cell motility via β-catenin signaling. Cancer Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.; Deng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, P. Curcumin Inhibits Gastric Carcinoma Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis by Suppressing the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Zou, X.; Chen, M.; Shen, Y.; Huang, S.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, P. Effect of pantoprazole on human gastric adenocarcinoma SGC7901 cells through regulation of phospho-LRP6 expression in Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Zhao, J.; Bai, L.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Q. miR-126 inhibits papillary thyroid carcinoma growth by targeting LRP6. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 2202–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kong, W.; Yang, L.; Li, P.-P.; Kong, Q.-Q.; Wang, H.-Y.; Han, G.-X.; Wang, Q.-B. MiR-381-3p inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting LRP6 in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 3804–3811. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Qi, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Fan, L. lncRNA PEG10 promotes cell survival, invasion and migration by sponging miR-134 in human bladder cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Bourhis, E.; Chiu, C.; Stawicki, S.; DeAlmeida, V.I.; Liu, B.Y.; Phamluong, K.; Cao, T.C.; Carano, R.A.D.; Ernst, J.A.; et al. Wnt Isoform-Specific Interactions with Coreceptor Specify Inhibition or Potentiation of Signaling by LRP6 Antibodies. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.; Choi, M.Y.; Yu, J.; Castro, J.E.; Kipps, T.J.; Carson, D.A. Salinomycin inhibits Wnt signaling and selectively induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13253–13257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arend, R.C.; Londoño-Joshi, A.I.; Samant, R.S.; Li, Y.; Conner, M.; Hidalgo, B.; Alvarez, R.D.; Landen, C.N.; Straughn, J.M.; Buchsbaum, D.J. Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin pathway by niclosamide: A therapeutic target for ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 134, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, G.; Huang, Y.; Mao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin by anthelmintic drug niclosamide effectively targets growth, survival, and angiogenesis of retinoblastoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 3776–3786. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Pan, S.; Hsieh, M.H.; Ng, N.; Sun, F.; Wang, T.; Kasibhatla, S.; Schuller, A.G.; Li, A.G.; Cheng, D.; et al. Targeting Wnt-driven cancer through the inhibition of Porcupine by LGK974. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20224–20229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proffitt, K.D.; Madan, B.; Ke, Z.; Pendharkar, V.; Ding, L.; Lee, M.A.; Hannoush, R.N.; Virshup, D.M. Pharmacological Inhibition of the Wnt Acyltransferase PORCN Prevents Growth of WNT-Driven Mammary Cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, N.; Kurzrock, R. Targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in cancer: Update on effectors and inhibitors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 62, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LRP6—My Cancer Genome. Available online: https://www.mycancergenome.org/content/gene/lrp6/#ref-3 (accessed on 31 July 2019).
- Acebron, S.P.; Niehrs, C. β-Catenin-Independent Roles of Wnt/LRP6 Signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 956–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).