Causes for Frequent Pathogenic BRCA1 Variants Include Low Penetrance in Fertile Ages, Recurrent De-Novo Mutations and Genetic Drift
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients and ethics
2.2. Material and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tharmaratnam, K.; Hagen, A.I.; Moller, P. MRI screening of women with hereditary predisposition to breast cancer: Diagnostic performance and survival analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 148, 687–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finch, A.P.; Lubinski, J.; Moller, P.; Singer, C.F.; Karlan, B.; Senter, L.; Rosen, B.; Maehle, L.; Ghadirian, P.; Cybulski, C.; et al. Impact of oophorectomy on cancer incidence and mortality in women with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, A.; Dorum, A.; Heimdal, K.; Maehle, L.; Hovig, E.; Moller, P. BRCA1 1675delA and 1135insA account for one third of Norwegian familial breast-ovarian cancer and are associated with later disease onset than less frequent mutations. Dis. Mark. 1999, 15, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, P.; Maehle, L.; Engebretsen, L.F.; Ludvigsen, T.; Jonsrud, C.; Apold, J.; Vabo, A.; Clark, N. High penetrances of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations confirmed in a prospective series. Hered. Cancer Clin. Pract. 2010, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, P.; Maehle, L.; Vabo, A.; Clark, N.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A. Age-specific incidence rates for breast cancer in carriers of BRCA1 mutations from Norway. Clin. Genet. 2013, 83, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, P.; Hagen, A.I.; Apold, J.; Maehle, L.; Clark, N.; Fiane, B.; Lovslett, K.; Hovig, E.; Vabo, A. Genetic epidemiology of BRCA mutations--family history detects less than 50% of the mutation carriers. Eur. J. Cancer 2007, 43, 1713–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimdal, K.; Maehle, L.; Apold, J.; Pedersen, J.C.; Moller, P. The Norwegian founder mutations in BRCA1: High penetrance confirmed in an incident cancer series and differences observed in the risk of ovarian cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2003, 39, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudkin, T.M.; Hamel, N.; Galvez, M.; Hogervorst, F.; Gille, J.J.; Moller, P.; Apold, J.; Foulkes, W.D. The frequent BRCA1 mutation 1135insA has multiple origins: A haplotype study in different populations. BMC Med. Genet. 2006, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, P.; Seppala, T.T.; Bernstein, I.; Holinski-Feder, E.; Sala, P.; Gareth Evans, D.; Lindblom, A.; Macrae, F.; Blanco, I.; Sijmons, R.H.; et al. Cancer risk and survival in path_MMR carriers by gene and gender up to 75 years of age: A report from the Prospective Lynch Syndrome Database. Gut 2018, 67, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchenbaecker, K.B.; Hopper, J.L.; Barnes, D.R.; Phillips, K.A.; Mooij, T.M.; Roos-Blom, M.J.; Jervis, S.; van Leeuwen, F.E.; Milne, R.L.; Andrieu, N.; et al. Risks of Breast, Ovarian, and Contralateral Breast Cancer for BRCA1 and BRCA2. JAMA 2017, 317, 2402–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, P.; Heimdal, K.; Apold, J.; Fredriksen, A.; Borg, A.; Hovig, E.; Hagen, A.; Hagen, B.; Pedersen, J.C.; Maehle, L.; et al. Genetic epidemiology of BRCA1 mutations in Norway. Eur. J. Cancer 2001, 37, 2428–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, K.J.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Kalager, M.; Zahl, P.H. Breast Cancer Screening in Denmark. Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 167, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
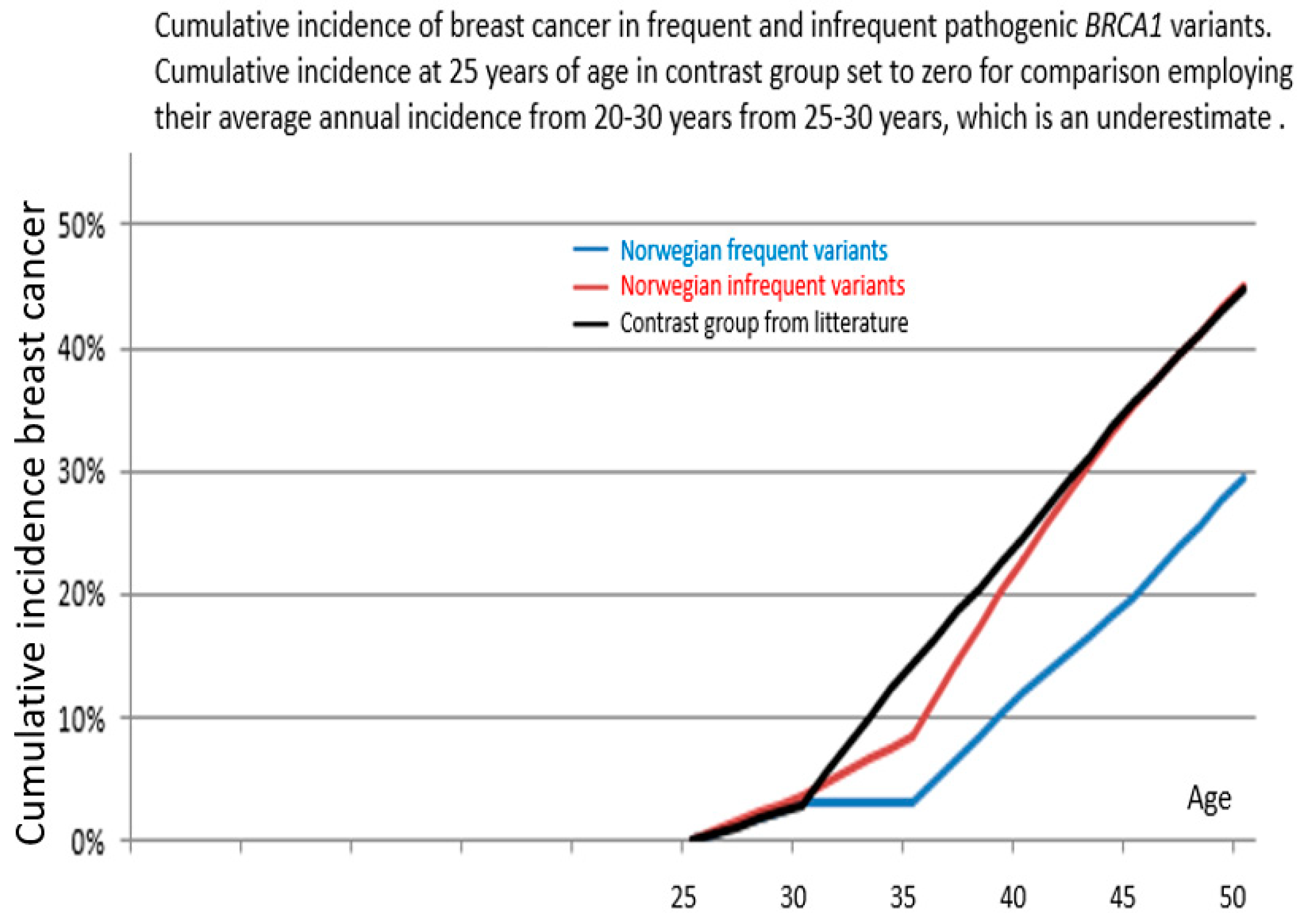

| Cancer Type | Path_BRCA1 Variant | 25yrs | 25ca | AIR25 (95%CI) | 30yrs | 30ca | AIR30 (95%CI) | 35yrs | 35ca | AIR35 (95%CI) | 40yrs | 40ca | AIR40 (95%CI) | 45yrs | 45ca | AIR45 (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ovarian cancer | Frequent | 48 | 0 | 0 | 161 | 0 | 0 | 173 | 1 | 0.0058 | 115 | 5 | 0.0435 | 33 | 1 | 0.0303 |
| Infrequent | 36 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 107 | 0 | 0 | 80 | 1 | 0.0125 | 28 | 2 | 0.0714 | |
| Breast cancer | Frequent | 165 | 1 | 0.006 (0–0.034) | 463 | 0 | 0 (0–0.008) | 414 | 8 | 0.019 (0.008–0.038) | 219 | 4 | 0.018 (0.005–0.047) | 80 | 2 | 0.025 (0.003–0.090) |
| Infrequent | 134 | 1 | 0.008 (0–0.041) | 299 | 3 | 0.010 (0.002–0.029) | 297 | 10 | 0.034 (0.016–0.062) | 173 | 6 | 0.034 (0.013–0.076) | 95 | 3 | 0.032 (0.006–0.093) |
| Path_BRCA1 Variant | From 25 Years of Age to | Cumulative Incidence | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value Versus Infrequent | p-Value Versus Kuchenbaeker et al. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequent | 40 years | 12% | 4–20% | 0.05 | 0.0001 |
| 45 years | 20% | 10–30% | 0.02 | 0.0001 | |
| 50 years | 29% | 14–45% * | 0.09 * | 0.01 * | |
| Infrequent | 40 years | 23% | 12–34% | ||
| 45 years | 35% | 22–48% | |||
| 50 years | 45% | 30–60% * | |||
| Kuchenbaeker et al. | 40 years | 24% | 21–28% | ||
| 45 years | 35% | 32–39% | |||
| 50 years | 45% | 41–49% |
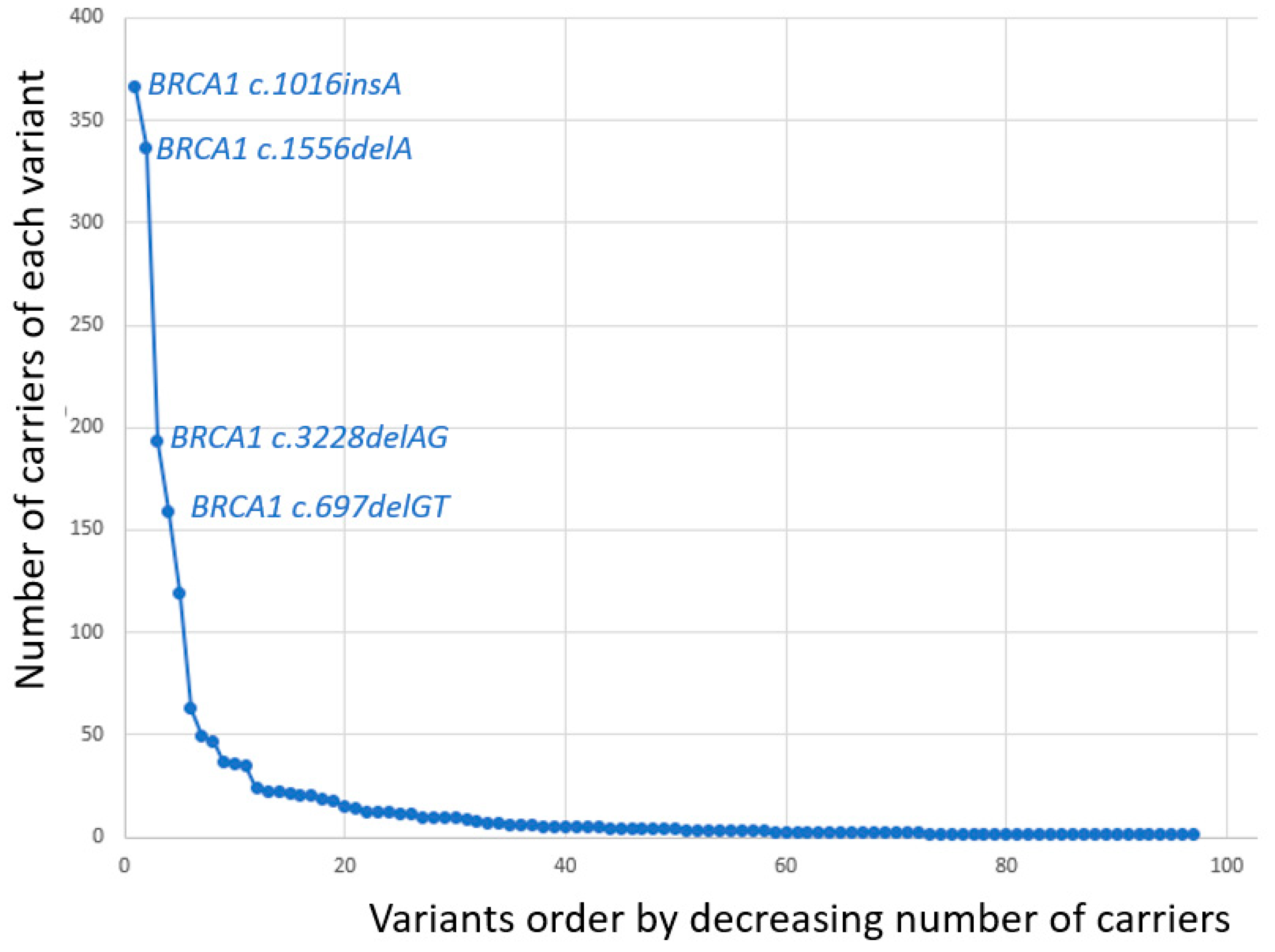
| BRCA1 Variant | Number of Carriers |
|---|---|
| c.1016dupA | 366 |
| c.1556delA | 337 |
| c.3228_3229delAG | 193 |
| c.697_698delGT | 159 |
| c.3178G>T | 119 |
| c.4745delA | 63 |
| c.1A>G | 49 |
| c.2351_2357delCGTTACT | 47 |
| c.5075-2A>C | 37 |
| c.3084_3094delTAATAACATTA | 36 |
| c.5047G>T | 35 |
| del exon 8–13 | 24 |
| c.3607C>T | 22 |
| dup exon 13 | 22 |
| c.3048_3052dupTGAGA | 21 |
| c.3331_3334delCAAG | 20 |
| c.5266dupC | 20 |
| del exon 22 | 19 |
| c.1072delC | 18 |
| c.5511G>A | 15 |
| c.1450G>T | 14 |
| c.3319G>T | 14 |
| c.2869C>T | 13 |
| c.5513T>G | 12 |
| c.66dupA | 12 |
| del exon 3-16 | 12 |
| c.2475delC | 11 |
| c.3966delA | 11 |
| c.1058G>A | 10 |
| c.2591C>G | 10 |
| c.4065_4068delTCAA | 9 |
| c.5407-25T>A | 8 |
| c.1292dupT | 7 |
| c.2558ins356 | 7 |
| c.3874delT | 6 |
| c.457_458ins21 | 6 |
| c.5251C>T | 6 |
| c.68_69delAG | 6 |
| c.1687C>T | 5 |
| c.3710delT | 5 |
| c.5503C>T | 5 |
| c.5534delA | 5 |
| c.794_795delCT | 5 |
| del exon 1–13 | 5 |
| c.4689C>G | 5 |
| c.115T>G | 4 |
| c.2989_2990dupAA | 4 |
| c.4035delA | 4 |
| c.4300delA | 4 |
| c.5213G>A | 4 |
| c.3770_3771delAG | 3 |
| c.4612C>T | 3 |
| c.5153G>C | 3 |
| c.848T>A | 3 |
| del exon 1–3 | 3 |
| c.1287delA | 2 |
| c.1695dupG | 2 |
| c.2389G>T | 2 |
| c.2438dupG | 2 |
| c.2681_2682delAA | 2 |
| c.3477_3479delAAAinsC | 2 |
| c.3700_3704delGTAAA | 2 |
| c.3835delG | 2 |
| c.386delG | 2 |
| c.4932_4933dupAA | 2 |
| c.4972delA | 2 |
| c.65T>C | 2 |
| del exon 18–24 | 2 |
| del exon 5–7 | 2 |
| c.1059G>A | 1 |
| c.130T>A | 1 |
| c.140G>T | 1 |
| c.1674dupA | 1 |
| c.1961dupA | 1 |
| c.2185G>T | 1 |
| c.241C>T | 1 |
| c.2722G>T | 1 |
| c.2727_2730delTCAA | 1 |
| c.3005delA | 1 |
| c.3817C>T | 1 |
| c.3937C>T | 1 |
| c.5075A>C | 1 |
| c.514C>T | 1 |
| c.5212G>A | 1 |
| c.5434C>G | 1 |
| c.929delA | 1 |
| del exon 13 | 1 |
| del exon 16 | 1 |
| del exon 20–24 | 1 |
| Sum | 1914 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Møller, P.; Dominguez-Valentin, M.; Rødland, E.A.; Hovig, E. Causes for Frequent Pathogenic BRCA1 Variants Include Low Penetrance in Fertile Ages, Recurrent De-Novo Mutations and Genetic Drift. Cancers 2019, 11, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11020132
Møller P, Dominguez-Valentin M, Rødland EA, Hovig E. Causes for Frequent Pathogenic BRCA1 Variants Include Low Penetrance in Fertile Ages, Recurrent De-Novo Mutations and Genetic Drift. Cancers. 2019; 11(2):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11020132
Chicago/Turabian StyleMøller, Pål, Mev Dominguez-Valentin, Einar Andreas Rødland, and Eivind Hovig. 2019. "Causes for Frequent Pathogenic BRCA1 Variants Include Low Penetrance in Fertile Ages, Recurrent De-Novo Mutations and Genetic Drift" Cancers 11, no. 2: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11020132
APA StyleMøller, P., Dominguez-Valentin, M., Rødland, E. A., & Hovig, E. (2019). Causes for Frequent Pathogenic BRCA1 Variants Include Low Penetrance in Fertile Ages, Recurrent De-Novo Mutations and Genetic Drift. Cancers, 11(2), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11020132





