A Novel Calcium-Mediated EMT Pathway Controlled by Lipids: An Opportunity for Prostate Cancer Adjuvant Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
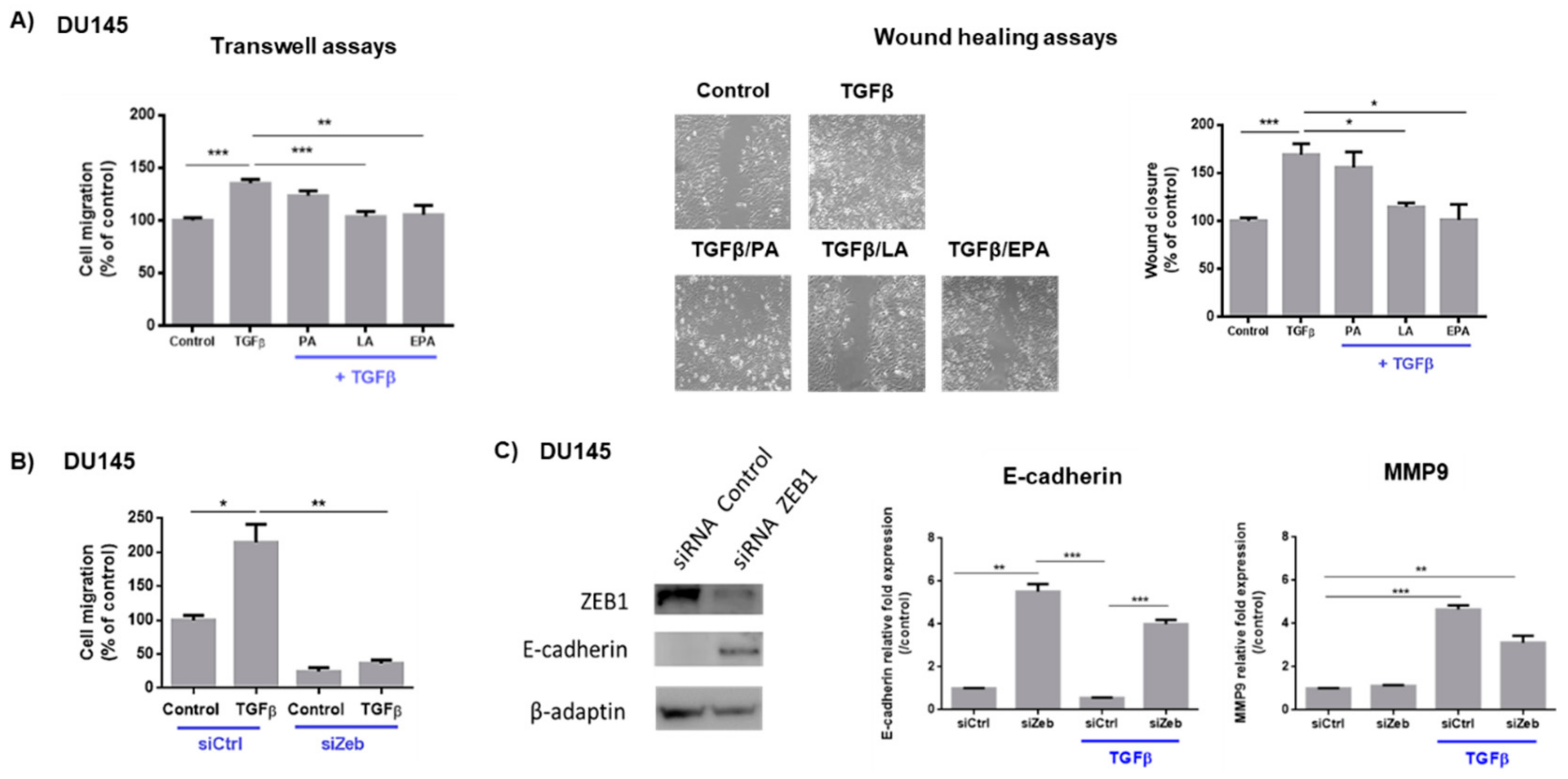
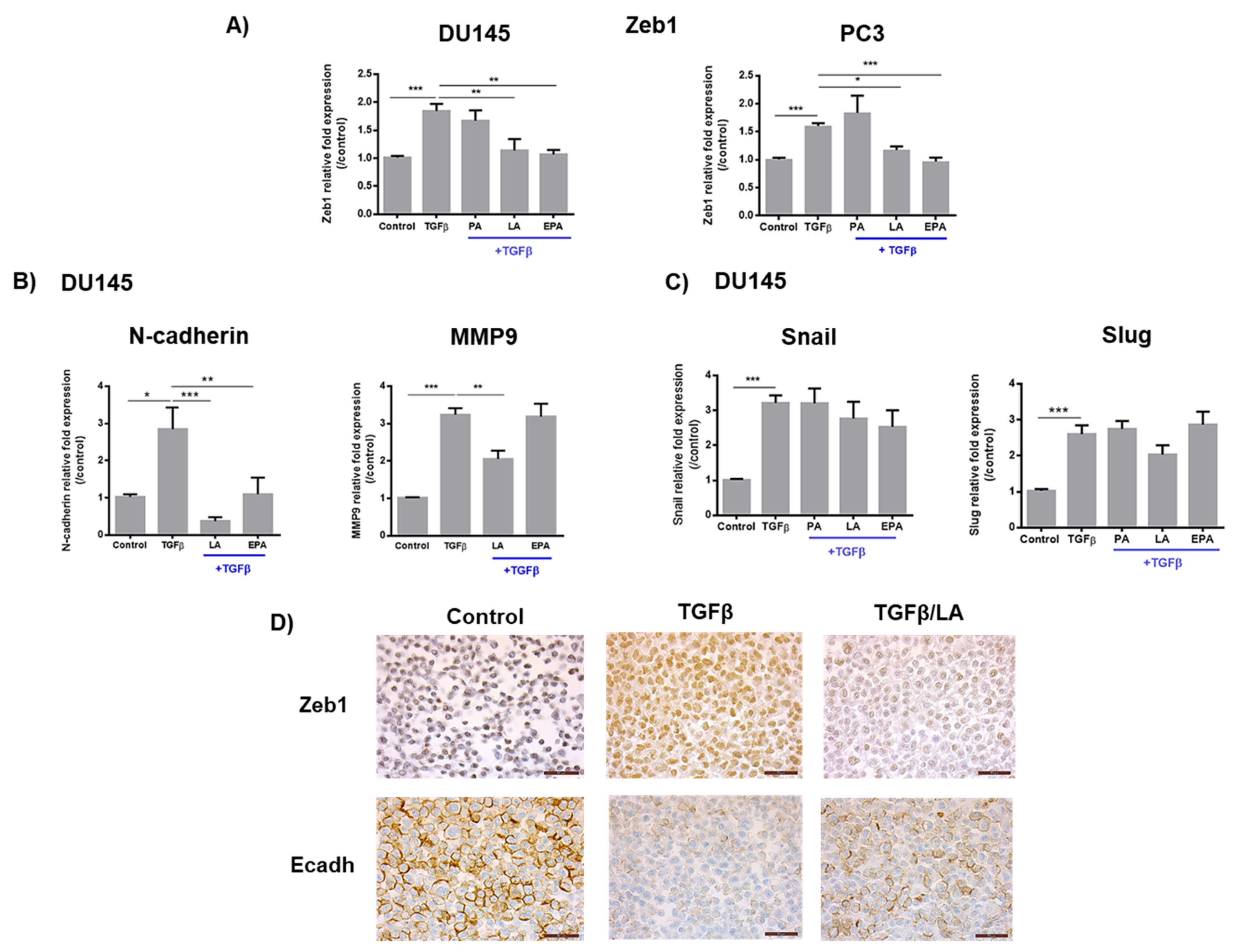
2.1. Linoleic Acid and Eicosapentaenoic Acid Inhibit Cell Migration Induced by TGFβ and the Expression of Zeb1 and Its Target Genes
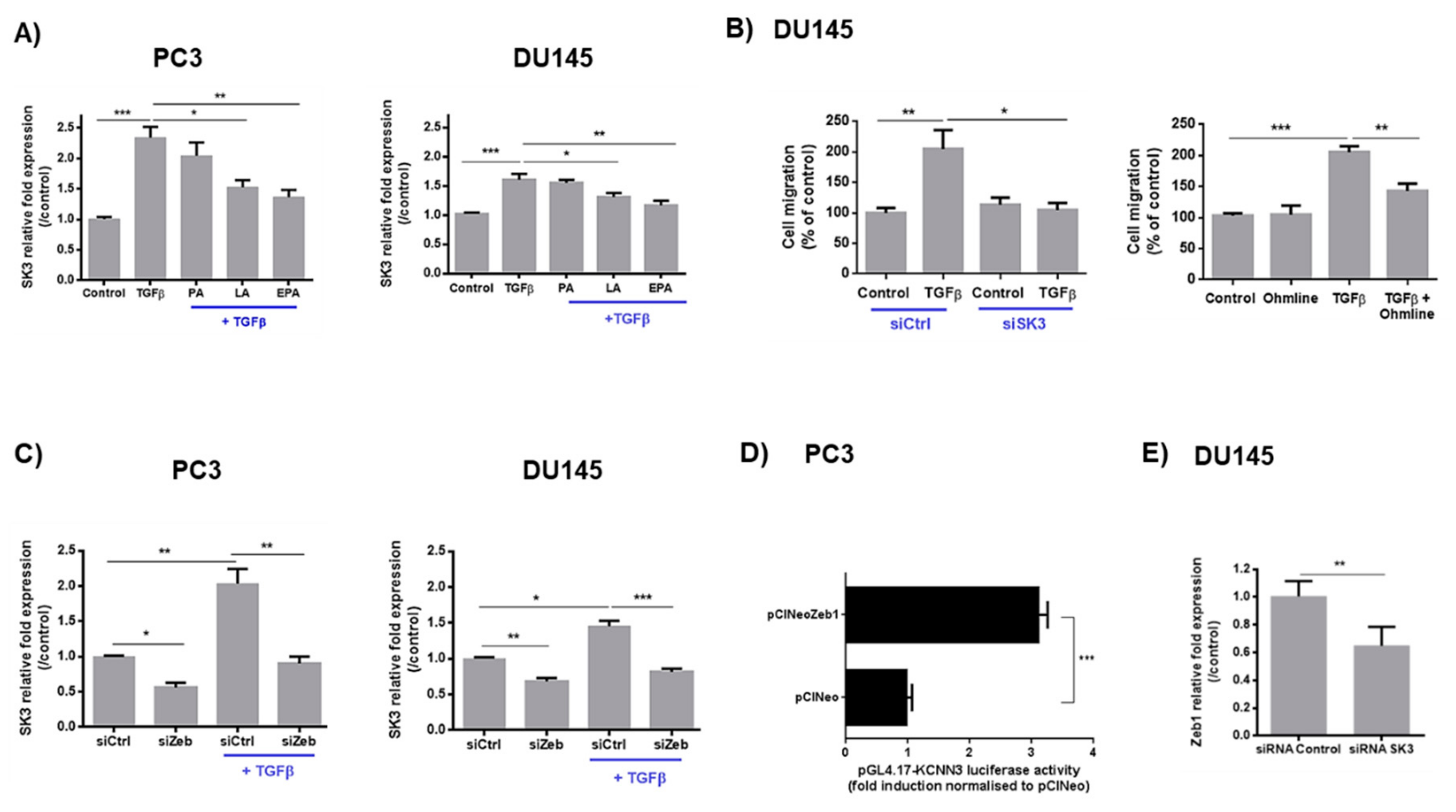
2.2. LA and EPA Inhibit SK3 Expression Induced by TGFβ, and SK3 is Dependent on Zeb1 Expression
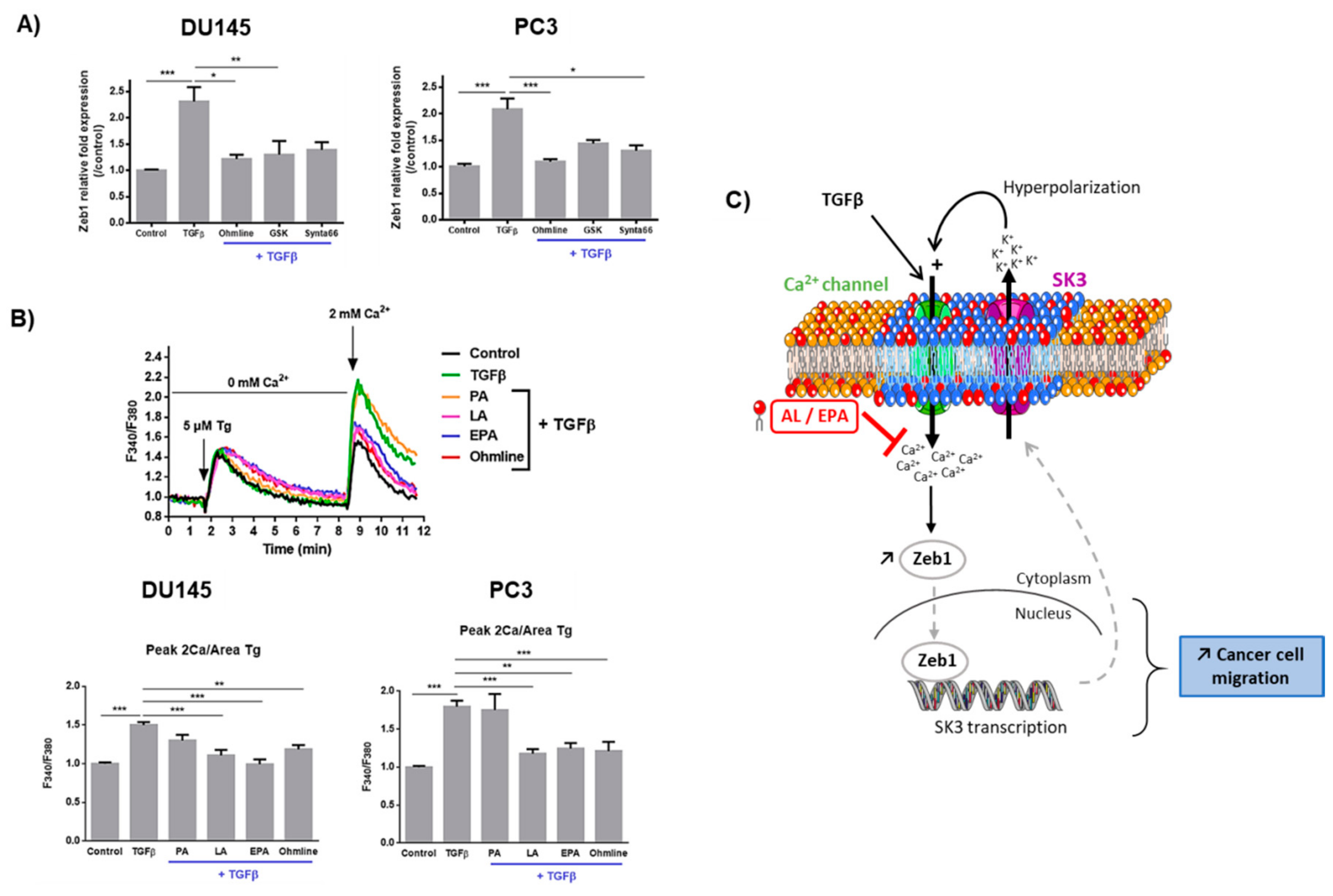
2.3. Ca2+ Entry Is Required for the Upregulation of Zeb1 Expression and Is Inhibited by LA and EPA In Vitro and Ex Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Tissue Slices
4.1.1. Immunohistochemistry
4.1.2. Ex Vivo Intracellular Ca2+ Measurements
4.2. Cell Lines and Products
4.3. Cytosolic Ca2+ Measurements in Cell Lines
4.4. Reporter Gene Constructs and Luciferase Assay
4.5. Migration Assays
4.6. siRNA Assays
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR.
4.8. Western-Blot
4.9. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Fundings
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EMT | Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition |
| EPA | Eicosapentaenoic acid |
| FA | Fatty acid |
| LA | Linoleic acid |
| PA | Palmitic acid |
| AA | Arachidonic acid |
| PPAT | Periprostatic adipose tissue |
| PUFA | Polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| PCa | Prostate cancer |
| SOCE | Store-operated Ca2+ entry |
References
- Damber, J.-E.; Aus, G. Prostate cancer. Lancet 2008, 371, 1710–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finley, D.S.; Calvert, V.S.; Inokuchi, J.; Lau, A.; Narula, N.; Petricoin, E.F.; Zaldivar, F.; Santos, R.; Tyson, D.R.; Ornstein, D.K. Periprostatic adipose tissue as a modulator of prostate cancer aggressiveness. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, V.; Guérard, A.; Mazerolles, C.; Le Gonidec, S.; Toulet, A.; Nieto, L.; Zaidi, F.; Majed, B.; Garandeau, D.; Socrier, Y.; et al. Periprostatic adipocytes act as a driving force for prostate cancer progression in obesity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figiel, S.; Pinault, M.; Domingo, I.; Guimaraes, C.; Guibon, R.; Besson, P.; Tavernier, E.; Blanchet, P.; Multigner, L.; Bruyère, F.; et al. Fatty acid profile in peri-prostatic adipose tissue and prostate cancer aggressiveness in African-Caribbean and Caucasian patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 91, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, T.R.; Zhau, H.E.; Odero-Marah, V.A.; Osunkoya, A.O.; Kimbro, K.S.; Tighiouart, M.; Liu, T.; Simons, J.W.; O’Regan, R.M. Insulin-like growth factor-I-dependent up-regulation of ZEB1 drives epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2479–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figiel, S.; Vasseur, C.; Bruyere, F.; Rozet, F.; Maheo, K.; Fromont, G. Clinical significance of epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in prostate cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 61, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, G.R.; Prevarskaya, N.; Roberts-Thomson, S.J. The calcium-cancer signalling nexus. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, I.; Monteith, G.R. Plasma membrane ion channels and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in cancer cells. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, R517–R525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaar, A.; Sukumaran, P.; Sun, Y.; Dhasarathy, A.; Singh, B.B. TRPC1-STIM1 activation modulates transforming growth factor β-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 80554–80567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapovalov, G.; Skryma, R.; Prevarskaya, N. Calcium channels and prostate cancer. Recent Pat. Anticancer Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevarskaya, N.; Skryma, R.; Shuba, Y. Calcium in tumour metastasis: New roles for known actors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guéguinou, M.; Harnois, T.; Crottes, D.; Uguen, A.; Deliot, N.; Gambade, A.; Chantôme, A.; Haelters, J.P.; Jaffrès, P.A.; Jourdan, M.L.; et al. SK3/TRPC1/Orai1 complex regulates SOCE-dependent colon cancer cell migration: A novel opportunity to modulate anti-EGFR mAb action by the alkyl-lipid Ohmline. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 36168–36184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantôme, A.; Potier-Cartereau, M.; Clarysse, L.; Fromont, G.; Marionneau-Lambot, S.; Guéguinou, M.; Pagès, J.-C.; Collin, C.; Oullier, T.; Girault, A.; et al. Pivotal role of the lipid Raft SK3-Orai1 complex in human cancer cell migration and bone metastases. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 4852–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Wu, J.H.Y. Omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: effects on risk factors, molecular pathways, and clinical events. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 2047–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, J.; Arita, M. Cardioprotective mechanism of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. J. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elinder, F.; Liin, S.I. Actions and Mechanisms of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Voltage-Gated Ion Channels. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.M.; Azimi, I.; Faville, R.A.; Peters, A.A.; Jalink, K.; Putney, J.W.; Goodhill, G.J.; Thompson, E.W.; Roberts-Thomson, S.J.; Monteith, G.R. Induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in breast cancer cells is calcium signal dependent. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2307–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figiel, S.; Pasqualin, C.; Bery, F.; Maupoil, V.; Vandier, C.; Potier-Cartereau, M.; Domingo, I.; Guibon, R.; Bruyere, F.; Maheo, K.; et al. Functional Organotypic Cultures of Prostate Tissues: A Relevant Preclinical Model that Preserves Hypoxia Sensitivity and Calcium Signaling. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Wang, S.; Feng, R. STIM1 plays an important role in TGF-β-induced suppression of breast cancer cell proliferation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 16866–16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, S.H.A.; Cheng, H.; Li, J.; Feng, R. The effect of TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition on the expression of intracellular calcium-handling proteins in T47D and MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 583, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asuthkar, S.; Velpula, K.K.; Elustondo, P.A.; Demirkhanyan, L.; Zakharian, E. TRPM8 channel as a novel molecular target in androgen-regulated prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17221–17236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, S.L.; England, S.K. SK3 channel expression during pregnancy is regulated through estrogen and Sp factor-mediated transcriptional control of the KCNN3 gene. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 299, E640–E646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massagué, J. TGFbeta in Cancer. Cell 2008, 134, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikushima, H.; Miyazono, K. TGFbeta signalling: A complex web in cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudey, S.K.; Sundar, R.; Heldin, C.-H.; Bergh, A.; Landström, M. Pro-invasive properties of Snail1 are regulated by sumoylation in response to TGFβ stimulation in cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 97703–97726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougnoux, P.; Hajjaji, N.; Ferrasson, M.N.; Giraudeau, B.; Couet, C.; Le Floch, O. Improving outcome of chemotherapy of metastatic breast cancer by docosahexaenoic acid: a phase II trial. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornfeld, S.; Goupille, C.; Vibet, S.; Chevalier, S.; Pinet, A.; Lebeau, J.; Tranquart, F.; Bougnoux, P.; Martel, E.; Maurin, A.; et al. Reducing endothelial NOS activation and interstitial fluid pressure with n-3 PUFA offset tumor chemoresistance. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, C.M.; Sparagna, G.C.; Le, C.H.; De Mooy, A.B.; Routh, M.A.; Holmes, M.G.; Hickson-Bick, D.L.; Zarini, S.; Murphy, R.C.; Xu, F.Y.; et al. Dietary linoleate preserves cardiolipin and attenuates mitochondrial dysfunction in the failing rat heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 94, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farvid, M.S.; Ding, M.; Pan, A.; Sun, Q.; Chiuve, S.E.; Steffen, L.M.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Dietary linoleic acid and risk of coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Circulation 2014, 130, 1568–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Dubois, R.N. Eicosanoids and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, T.A.; Yapa, K.T.D.S.; Monteith, G.R. Altered calcium signaling in cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1848, 2502–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Girault, A.; Haelters, J.-P.; Potier-Cartereau, M.; Chantome, A.; Pinault, M.; Marionneau-Lambot, S.; Oullier, T.; Simon, G.; Couthon-Gourvès, H.; Jaffrès, P.-A.; et al. New alkyl-lipid blockers of SK3 channels reduce cancer cell migration and occurrence of metastasis. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2011, 11, 1111–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Tomita, H.; Shakkottai, V.G.; Gargus, J.J. Genomic organization and promoter analysis of human KCNN3 gene. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 46, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Potier, M.; Joulin, V.; Roger, S.; Besson, P.; Jourdan, M.-L.; Leguennec, J.-Y.; Bougnoux, P.; Vandier, C. Identification of SK3 channel as a new mediator of breast cancer cell migration. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 2946–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lacher, M.D.; Shiina, M.; Chang, P.; Keller, D.; Tiirikainen, M.I.; Korn, W.M. ZEB1 limits adenoviral infectability by transcriptionally repressing the coxsackie virus and adenovirus receptor. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Age (y), Median (Range) | 63 (51–75) | |
|---|---|---|
| PSA (ng/mL), Median (Range) | 7.2 (4.5–35) | |
| pTNM stage | pT3 | n = 7 |
| pT2 | n = 7 | |
| ISUP score | 1 | n = 1 |
| 2 | n = 4 | |
| 3 | n = 5 | |
| 4 | n = 2 | |
| 5 | n = 2 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Figiel, S.; Bery, F.; Chantôme, A.; Fontaine, D.; Pasqualin, C.; Maupoil, V.; Domingo, I.; Guibon, R.; Bruyère, F.; Potier-Cartereau, M.; et al. A Novel Calcium-Mediated EMT Pathway Controlled by Lipids: An Opportunity for Prostate Cancer Adjuvant Therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111814
Figiel S, Bery F, Chantôme A, Fontaine D, Pasqualin C, Maupoil V, Domingo I, Guibon R, Bruyère F, Potier-Cartereau M, et al. A Novel Calcium-Mediated EMT Pathway Controlled by Lipids: An Opportunity for Prostate Cancer Adjuvant Therapy. Cancers. 2019; 11(11):1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111814
Chicago/Turabian StyleFigiel, Sandy, Fanny Bery, Aurélie Chantôme, Delphine Fontaine, Côme Pasqualin, Véronique Maupoil, Isabelle Domingo, Roseline Guibon, Franck Bruyère, Marie Potier-Cartereau, and et al. 2019. "A Novel Calcium-Mediated EMT Pathway Controlled by Lipids: An Opportunity for Prostate Cancer Adjuvant Therapy" Cancers 11, no. 11: 1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111814
APA StyleFigiel, S., Bery, F., Chantôme, A., Fontaine, D., Pasqualin, C., Maupoil, V., Domingo, I., Guibon, R., Bruyère, F., Potier-Cartereau, M., Vandier, C., Fromont, G., & Mahéo, K. (2019). A Novel Calcium-Mediated EMT Pathway Controlled by Lipids: An Opportunity for Prostate Cancer Adjuvant Therapy. Cancers, 11(11), 1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111814





