HDAC Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
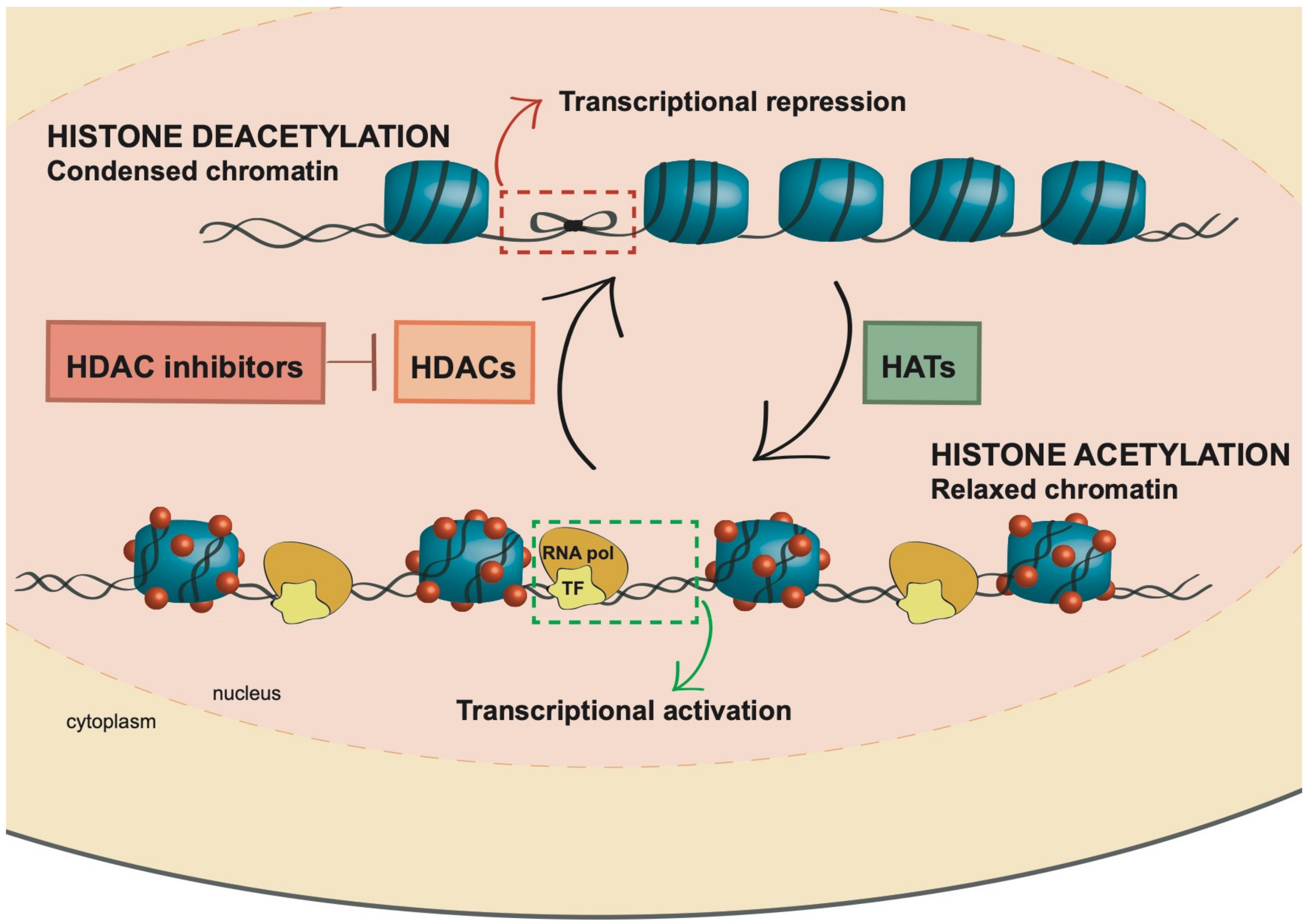
2. Histone Acetylation
2.1. HDAC Classes
2.2. HDACs: More Than Histone Deacetylases
2.3. Implication of HDACs in Cancer
3. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDACi): Mechanism of Action and Role in AML
3.1. Hydroximates
3.1.1. Trichostatin A
3.1.2. Vorinostat
3.1.3. Panobinostat
3.1.4. Belinostat
3.2. Benzamides
3.2.1. Entinostat
3.2.2. Mocetinostat
3.3. Cyclic Peptides
3.3.1. Romidepsin
3.3.2. Apicidin
3.3.3. Trapoxin A
3.4. Aliphatic Acids
3.5. Electrophilic Ketones
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wrighton, K.H. Regulatory networks in AML. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, S.A.; Imperato, M.R.; Coleman, D.J.L.; Pickin, A.; Potluri, S.; Ptasinska, A.; Chin, P.S.; Blair, H.; Cauchy, P.; James, S.R.; et al. Subtype-specific regulatory network rewiring in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallman, M.S.; Gilliland, D.G.; Rowe, J.M. Drug therapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2005, 106, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estey, E.; Döhner, H. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet 2006, 368, 1894–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saultz, J.; Garzon, R. Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Concise Review. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döhner, H.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Bloomfield, C.D. Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1136–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kouchkovsky, I.; Abdul-Hay, M. Acute myeloid leukemia: A comprehensive review and 2016 update. Blood Cancer J. 2016, 6, e441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, J.; Nimer, S. Recent advances in the understanding and treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. F1000Research 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukyurt, S.; Eskazan, A.E. New drugs approved for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in 2018. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenberg, B.; Rowe, J.M. Blood; American Society of Hematology: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Plass, C.; Oakes, C.; Blum, W.; Marcucci, G. Epigenetics in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Semin. Oncol. 2008, 35, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagunas-Rangel, F.A.; Chávez-Valencia, V.; Gómez-Guijosa, M.Á.; Cortes-Penagos, C. Acute Myeloid Leukemia-Genetic Alterations and Their Clinical Prognosis. Int. J. Hematol. Stem Cell Res. 2017, 11, 328–339. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, S.F.; Levine, R.L. Genetic and epigenetic determinants of AML pathogenesis. Semin. Hematol. 2019, 56, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, S.L.; Kouzarides, T.; Shiekhattar, R.; Shilatifard, A. An operational definition of epigenetics. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 781–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baylin, S.B.; Jones, P.A. A decade of exploring the cancer epigenome-biological and translational implications. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, M.A.; Kouzarides, T. Cancer epigenetics: From mechanism to therapy. Cell 2012, 150, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.M.; Walsh, L.A.; Chan, T.A. Driver mutations of cancer epigenomes. Protein Cell 2014, 5, 265–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Jia, L.; Lv, W.; Wang, L.; Cui, W. Epigenetic enzyme mutations: Role in tumorigenesis and molecular inhibitors. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardin, C.; Dombret, H. Hypomethylating Agents as a Therapy for AML. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2017, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohl, S.R.; Bullinger, L.; Rücker, F.G. Epigenetic therapy: Azacytidine and decitabine in acute myeloid leukemia. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2018, 11, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, P.A. A tale of histone modifications. Genome Biol. 2001, 2, REVIEWS0003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biterge, B.; Schneider, R. Histone variants: Key players of chromatin. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 356, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucchetti, B.; Shimada, A.K.; Katz, A.; Curigliano, G. The role of histone deacetylase inhibitors in metastatic breast cancer. Breast 2019, 43, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heintzman, N.D.; Stuart, R.K.; Hon, G.; Fu, Y.; Ching, C.W.; Hawkins, R.D.; Barrera, L.O.; Van Calcar, S.; Qu, C.; Ching, K.A.; et al. Distinct and predictive chromatin signatures of transcriptional promoters and enhancers in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zang, C.; Rosenfeld, J.A.; Schones, D.E.; Barski, A.; Cuddapah, S.; Cui, K.; Roh, T.-Y.; Peng, W.; Zhang, M.Q.; et al. Combinatorial patterns of histone acetylations and methylations in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverna, S.D.; Li, H.; Ruthenburg, A.J.; Allis, C.D.; Patel, D.J. How chromatin-binding modules interpret histone modifications: Lessons from professional pocket pickers. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 1025–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, E.; Yoshida, M. Erasers of histone acetylation: The histone deacetylase enzymes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a018713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberland, M.; Montgomery, R.L.; Olson, E.N. The many roles of histone deacetylases in development and physiology: Implications for disease and therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmorstein, R.; Roth, S.Y. Histone acetyltransferases: Function, structure, and catalysis. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2001, 11, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräff, J.; Tsai, L.H. Histone acetylation: Molecular mnemonics on the chromatin. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropero, S.; Esteller, M. The role of histone deacetylases (HDACs) in human cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2007, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, N.G.; Ozdag, H.; Caldas, C. p300/CBP and cancer. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4225–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Packman, K.; Jeffrey, R.; Tenniswood, M. Histone deacetylase inhibitors differentially stabilize acetylated p53 and induce cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Seto, E. Deacetylation of nonhistone proteins by HDACs and the implications in cancer. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2011, 206, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Iyer, M.; Mceachin, R.; Zhao, M.; Wu, Y.M.; Cao, X.; Oravecz-Wilson, K.; Zajac, C.; Mathewson, N.; Wu, S.R.J.; et al. Genome-Wide STAT3 Binding Analysis after Histone Deacetylase Inhibition Reveals Novel Target Genes in Dendritic Cells. J. Innate Immun. 2017, 9, 126–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Harikumar, K.B.; Gupta, S.R.; Tharakan, S.T.; Koca, C.; Dey, S.; Sung, B. Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3, inflammation, and cancer: How intimate is the relationship. In Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences; Blackwell Publishing Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 1171, pp. 59–76. [Google Scholar]
- Glozak, M.A.; Sengupta, N.; Zhang, X.; Seto, E. Acetylation and deacetylation of non-histone proteins. Gene 2005, 363, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hull, E.E.; Montgomery, M.R.; Leyva, K.J. HDAC Inhibitors as Epigenetic Regulators of the Immune System: Impacts on Cancer Therapy and Inflammatory Diseases. Biomed Res. Int. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckschlager, T.; Plch, J.; Stiborova, M.; Hrabeta, J. Histone deacetylase inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Seto, E. HDACs and HDAC inhibitors in cancer development and therapy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichert, W.; Röske, A.; Gekeler, V.; Beckers, T.; Ebert, M.P.; Pross, M.; Dietel, M.; Denkert, C.; Röcken, C. Association of patterns of class I histone deacetylase expression with patient prognosis in gastric cancer: A retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.C.; Johnstone, R.W. New and emerging HDAC inhibitors for cancer treatment. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichert, W.; Röske, A.; Niesporek, S.; Noske, A.; Buckendahl, A.C.; Dietel, M.; Gekeler, V.; Boehm, M.; Beckers, T.; Denkert, C. Class I histone deacetylase expression has independent prognostic impact in human colorectal cancer: Specific role of class I histone deacetylases in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weichert, W.; Röske, A.; Gekeler, V.; Beckers, T.; Stephan, C.; Jung, K.; Fritzsche, F.R.; Niesporek, S.; Denkert, C.; Dietel, M.; et al. Histone deacetylases 1, 2 and 3 are highly expressed in prostate cancer and HDAC2 expression is associated with shorter PSA relapse time after radical prostatectomy. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamiya, Y.; Ono, T.; Saito, H.; Takahashi, N.; Ito, M.; Mitsui, M.; Motoyama, S.; Ogawa, J. Expression of histone deacetylase 1 correlates with a poor prognosis in patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer 2011, 74, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osada, H.; Tatematsu, Y.; Saito, H.; Yatabe, Y.; Mitsudomi, T.; Takahashi, T. Reduced expression of class II histone deacetylase genes is associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 112, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkidou, K.; Gaughan, L.; Cook, S.; Leung, H.Y.; Neal, D.E.; Robson, C.N. Upregulation and Nuclear Recruitment of HDACl in Hormone Refractory Prostate Cancer. Prostate 2004, 59, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.F.; Lawrence, M.S.; Demichelis, F.; Drier, Y.; Cibulskis, K.; Sivachenko, A.Y.; Sboner, A.; Esgueva, R.; Pflueger, D.; Sougnez, C.; et al. The genomic complexity of primary human prostate cancer. Nature 2011, 470, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropero, S.; Fraga, M.F.; Ballestar, E.; Hamelin, R.; Yamamoto, H.; Boix-Chornet, M.; Caballero, R.; Alaminos, M.; Setien, F.; Paz, M.F.; et al. A truncating mutation of HDAC2 in human cancers confers resistance to histone deacetylase inhibition. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöblom, T.; Jones, S.; Wood, L.D.; Parsons, D.W.; Lin, J.; Barber, T.D.; Mandelker, D.; Leary, R.J.; Ptak, J.; Silliman, N.; et al. The consensus coding sequences of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science 2006, 314, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanigan, C.L.; van Engeland, M.; De Bruine, A.P.; Wouters, K.A.; Weijenberg, M.P.; Eshleman, J.R.; Herman, J.G. An Inactivating Mutation in HDAC2 Leads to Dysregulation of Apoptosis Mediated by APAF1. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1654–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, R.W.; Licht, J.D. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy: Is transcription the primary target? Cancer Cell 2003, 4, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licht, J.D. AML1 and the AML1-ETO fusion protein in the pathogenesis of t (8; 21) AML. Oncogene 2001, 20, 5660–5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cheney, M.D.; Gaudet, J.J.; Chruszcz, M.; Lukasik, S.M.; Sugiyama, D.; Lary, J.; Cole, J.; Dauter, Z.; Minor, W.; et al. The tetramer structure of the Nervy homology two domain, NHR2, is critical for AML1/ETO’s activity. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, L.F.; Zhang, D.-E. The 8; 21 translocation in leukemogenesis. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4255–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minucci, S.; Pelicci, P.G. Histone deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more) treatments for cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Croce, L.; Raker, V.A.; Corsaro, M.; Fazi, F.; Fanelli, M.; Faretta, M.; Fuks, F.; Lo Coco, F.; Kouzarides, T.; Nervi, C.; et al. Methyltransferase recruitment and DNA hypermethylation of target promoters by an oncogenic transcription factor. Science 2002, 295, 1079–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego, E.M.; He, L.Z.; Warrell, R.P.; Wang, Z.G.; Pandolfi, P.P. Retinoic acid (RA) and As2O3 treatment in transgenic models of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) unravel the distinct nature of the leukemogenic process induced by the PML-RARa and PLZF-RARα oncoproteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10173–10178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereshchenko, O.R.; Gu, W.; Dalla-Favera, R. Acetylation inactivates the transcriptional repressor BCL6. Nat. Genet. 2002, 32, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun-Chung, K.; Suk-Chul, B. HDAC inhibitors as anti-cancer drugs. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2011, 3, 166–179. [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand, P. Inside HDAC with HDAC inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 2095–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottamal, M.; Zheng, S.; Huang, T.L.; Wang, G. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in clinical studies as templates for new anticancer agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 3898–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Song, W. Zinc binding groups for histone deacetylase inhibitors. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.T.T.; Kim, H.N.; Lee, I.K.; Nguyen-Pham, T.N.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, J.J.; Park, K.S.; Kook, H.; Kim, H.J. Improved therapeutic effect against leukemia by a combination of the histone methyltransferase inhibitor chaetocin and the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2013, 28, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momparler, R.L.; Côté, S.; Momparler, L.F.; Idaghdour, Y. Epigenetic therapy of acute myeloid leukemia using 5-aza-2’-deoxycytidine (decitabine) in combination with inhibitors of histone methylation and deacetylation. Clin. Epigenet. 2014, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, H.M.; Saeed, S.; Alkan, S. Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce caspase-dependent apoptosis and downregulation of daxx in acute promyelocytic leukaemia with t (15; 17). Br. J. Haematol. 2001, 115, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.-Z.; Tolentino, T.; Grayson, P.; Zhong, S.; Warrell, R.P.; Rifkind, R.A.; Marks, P.A.; Richon, V.M.; Pandolfi, P.P. Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce remission in transgenic models of therapy-resistant acute promyelocytic leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Rahmani, M.; Almenara, J.; Subler, M.; Krystal, G.; Conrad, D.; Varticovski, L.; Dent, P.; Grant, S. Histone deacetylase inhibitors promote STI571-mediated apoptosis in STI571-sensitive and -resistant Bcr/Abl+ human myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 2118–2126. [Google Scholar]
- Fiskus, W.; Wang, Y.; Joshi, R.; Rao, R.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Kolhe, R.; Balusu, R.; Eaton, K.; Lee, P.; et al. Cotreatment with vorinostat enhances activity of MK-0457 (VX-680) against acute and chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6106–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.P.; Rudra, S.; Keating, M.J.; Wierda, W.G.; Palladino, M.; Chandra, J. Caspase-8 dependent histone acetylation by a novel proteasome inhibitor, NPI-0052: A mechanism for synergy in leukemia cells. Blood 2009, 113, 4289–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozawa, K.; Nakanishi, T.; Tan, M.; Fang, H.B.; Wang, W.C.; Edelman, M.J.; Carlton, D.; Gojo, I.; Sausville, E.A.; Ross, D.D. Preclinical studies of vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid) combined with cytosine arabinoside and etoposide for treatment of acute leukemias. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 1698–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Kadia, T.; Tong, W.; Zhang, M.; Jia, Y.; Yang, H.; Hu, Y.; Viallet, J.; O’Brien, S.; Garcia-Manero, G. The combination of a histone deacetylase inhibitor with the BH3-mimetic GX15-070 has synergistic antileukemia activity by activating both apoptosis and autophagy. Autophagy 2010, 6, 976–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Kmieciak, M.; Leng, Y.; Lin, H.; Rizzo, K.A.; Dumur, C.I.; Ferreira-Gonzalez, A.; Dai, Y.; et al. A regimen combining the Wee1 inhibitor AZD1775 with HDAC inhibitors targets human acute myeloid leukemia cells harboring various genetic mutations. Leukemia 2015, 29, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.H.; Yeh, T.K.; Jiaang, W.T.; Yen, K.J.; Chen, C.H.; Huang, C.T.; Yen, S.C.; Hsieh, S.Y.; Chou, L.H.; Chen, C.P.; et al. Evaluation of the antitumor effects of BPR1J-340, a potent and selective FLT3 inhibitor, alone or in combination with an HDAC inhibitor, vorinostat, in AML cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e83160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Niu, X.; Chen, B.; Edwards, H.; Xu, L.; Xie, C.; Lin, H.; Polin, L.; Taub, J.W.; Ge, Y.; et al. Synthesis and Antileukemic Activities of Piperlongumine and HDAC Inhibitor Hybrids against Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 7974–7990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschbaum, M.; Gojo, I.; Goldberg, S.L.; Bredeson, C.; Kujawski, L.A.; Yang, A.; Marks, P.; Frankel, P.; Sun, X.; Tosolini, A.; et al. A phase 1 clinical trial of vorinostat in combination with decitabine in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia or myelodysplastic syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 167, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- How, J.; Minden, M.D.; Brian, L.; Chen, E.X.; Brandwein, J.; Schuh, A.C.; Schimmer, A.D.; Gupta, V.; Webster, S.; Degelder, T.; et al. A phase i trial of two sequence-specific schedules of decitabine and vorinostat in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 2793–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadia, T.M.; Yang, H.; Ferrajoli, A.; Maddipotti, S.; Schroeder, C.; Madden, T.L.; Holleran, J.L.; Egorin, M.J.; Ravandi, F.; Thomas, D.A.; et al. A phase i study of vorinostat in combination with idarubicin in relapsed or refractory leukaemia: Research paper. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 150, 72–82. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Manero, G.; Tambaro, F.P.; Bekele, N.B.; Yang, H.; Ravandi, F.; Jabbour, E.; Borthakur, G.; Kadia, T.M.; Konopleva, M.Y.; Faderl, S.; et al. Phase II trial of vorinostat with idarubicin and cytarabine for patients with newly diagnosed acute myelogenous leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2204–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holkova, B.; Supko, J.G.; Ames, M.M.; Reid, J.M.; Shapiro, G.I.; Perkins, E.B.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Tombes, M.B.; Honeycutt, C.; McGovern, R.M.; et al. A phase I trial of vorinostat and alvocidib in patients with relapsed, refractory, or poor prognosis acute leukemia, or refractory anemia with excess blasts-2. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1873–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, R.B.; Medeiros, B.C.; Gardner, K.M.; Orlowski, K.F.; Gallegos, L.; Scott, B.L.; Hendrie, P.C.; Estey, E.H. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin in combination with vorinostat and azacitidine in older patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia: A phase I/II study. Haematologica 2014, 99, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, R.B.; Medeiros, B.C.; Powell, B.L.; Schiffer, C.A.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Estey, E.H. Phase II trial of vorinostat and gemtuzumab ozogamicin as induction and post-remission therapy in older adults with previously untreated acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2012, 97, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayar, H.; Cripe, L.D.; Saliba, A.N.; Abu Zaid, M.; Konig, H.; Boswell, H.S. Combination of sorafenib, vorinostat and bortezomib for the treatment of poor-risk AML: Report of two consecutive clinical trials. Leuk. Res. 2019, 77, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blagitko-Dorfs, N.; Schlosser, P.; Greve, G.; Pfeifer, D.; Meier, R.; Baude, A.; Brocks, D.; Plass, C.; Lübbert, M. Combination treatment of acute myeloid leukemia cells with DNMT and HDAC inhibitors: Predominant synergistic gene downregulation associated with gene body demethylation. Leukemia 2019, 33, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiskus, W.; Buckley, K.; Rao, R.; Mandawat, A.; Yang, Y.; Joshi, R.; Wang, Y.; Balusu, R.; Chen, J.; Koul, S.; et al. Panobinostat treatment depletes EZH2 and DNMT1 levels and enhances decitabine mediated de-repression of JunB and loss of survival of human acute leukemia cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalakrishnapillai, A.; Kolb, E.A.; McCahan, S.M.; Barwe, S.P. Epigenetic drug combination induces remission in mouse xenograft models of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2017, 58, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.; Niu, X.; Walton, E.; Hurley, L.; Lin, H.; Edwards, H.; Taub, J.W.; Wang, Z.; Ge, Y. Synergistic anti-leukemic interactions between ABT-199 and panobinostat in acute myeloid leukemia ex vivo. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 3893–3902. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, W.; Zhang, W.; Edwards, H.; Chu, R.; Madlambayan, G.J.; Taub, J.W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Lin, H.; et al. Synergistic anti-leukemic interactions between panobinostat and MK-1775 in acute myeloid leukemia ex vivo. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1784–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiskus, W.; Sharma, S.; Saha, S.; Shah, B.; Devaraj, S.G.T.; Sun, B.; Horrigan, S.; Leveque, C.; Zu, Y.; Iyer, S.; et al. Pre-clinical efficacy of combined therapy with novel β-catenin antagonist BC2059 and histone deacetylase inhibitor against AML cells. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiskus, W.; Sharma, S.; Shah, B.; Portier, B.P.; Devaraj, S.G.T.; Liu, K.; Iyer, S.P.; Bearss, D.; Bhalla, K.N. Highly effective combination of LSD1 (KDM1A) antagonist and pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor against human AML cells. Leukemia 2014, 28, 2155–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiskus, W.; Sharma, S.; Qi, J.; Valenta, J.A.; Schaub, L.J.; Shah, B.; Peth, K.; Portier, B.P.; Rodriguez, M.; Devaraj, S.G.T.; et al. Highly active combination of BRD4 antagonist and histone deacetylase inhibitor against human acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 1142–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietschmann, K.; Bolck, H.A.; Buchwald, M.; Spielberg, S.; Polzer, H.; Spiekermann, K.; Bug, G.; Heinzel, T.; Bohmer, F.D.; Krämer, O.H. Breakdown of the FLT3-ITD/STAT5 axis and synergistic apoptosis induction by the histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat and FLT3-specific inhibitors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 2373–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.J.; Huang, K.K.; Yang, M.; Qiao, L.; Wang, Q.; Ye, J.Y.; Zhou, H.S.; Yi, Z.S.; Wu, F.Q.; Wang, Z.X.; et al. Synergistic effect of panobinostat and bortezomib on chemoresistant acute myelogenous leukemia cells via AKT and NF-κB pathways. Cancer Lett. 2012, 326, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandawat, A.; Fiskus, W.; Buckley, K.M.; Robbins, K.; Rao, R.; Balusu, R.; Navenot, J.M.; Wang, Z.X.; Ustun, C.; Chong, D.G.; et al. Pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat depletes CXCR4 levels and signaling and exerts synergistic antimyeloid activity in combination with CXCR4 antagonists. Blood 2010, 116, 5306–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiso, P.; Colado, E.; Ocio, E.M.; Garayoa, M.; Martín, J.; Atadja, P.; Pandiella, A.; San-Miguel, J.F. The synergy of panobinostat plus doxorubicin in acute myeloid leukemia suggests a role for HDAC inhibitors in the control of DNA repair. Leukemia 2009, 23, 2265–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiskus, W.; Wang, Y.; Sreekumar, A.; Buckley, K.M.; Shi, H.; Jillella, A.; Ustun, C.; Rao, R.; Fernandez, P.; Chen, J.; et al. Combined epigenetic therapy with the histone methyltransferase EZH2 inhibitor 3-deazaneplanocin A and the histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat against human AML cells. Blood 2009, 114, 2733–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Manero, G.; Sekeres, M.A.; Egyed, M.; Breccia, M.; Graux, C.; Cavenagh, J.D.; Salman, H.; Illes, A.; Fenaux, P.; Deangelo, D.J.; et al. A phase 1b/2b multicenter study of oral panobinostat plus azacitidine in adults with MDS, CMML or AML with ≤30% blasts. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2799–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewersdorf, J.P.; Shallis, R.; Stahl, M.; Zeidan, A.M. Epigenetic therapy combinations in acute myeloid leukemia: What are the options? Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2019, 10, 2040620718816698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocio, E.M.; Herrera, P.; Olave, M.-T.; Castro, N.; Pérez-Simón, J.A.; Brunet, S.; Oriol, A.; Mateo, M.; Sanz, M.-Á.; López, J.; et al. Panobinostat as part of induction and maintenance for elderly patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia: Phase Ib/II panobidara study. Haematologica 2015, 100, 1294–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieduwilt, M.J.; Pawlowska, N.; Thomas, S.; Olin, R.; Logan, A.C.; Damon, L.E.; Martin, T.; Kang, M.; Sayre, P.H.; Boyer, W.; et al. Histone Deacetylase Inhibition with Panobinostat Combined with Intensive Induction Chemotherapy in Older Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Phase I Study Results. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4917–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlenk, R.F.; Krauter, J.; Raffoux, E.; Kreuzer, K.A.; Schaich, M.; Noens, L.; Pabst, T.; Vusirikala, M.; Bouscary, D.; Spencer, A.; et al. Panobinostat monotherapy and combination therapy in patients with acute myeloid leukemia: Results from two clinical trials. Haematologica 2018, 103, E25–E28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiuliene, G.; Stirblyte, I.; Cicenaite, D.; Kaupinis, A.; Valius, M.; Navakauskiene, R. Belinostat, a potent HDACi, exerts antileukaemic effect in human acute promyelocytic leukaemia cells via chromatin remodelling. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 1742–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savickiene, J.; Treigyte, G.; Valiuliene, G.; Stirblyte, I.; Navakauskiene, R. Epigenetic and molecular mechanisms underlying the antileukemic activity of the histone deacetylase inhibitor belinostat in human acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Anticancer. Drugs 2014, 25, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valiulienė, G.; Stirblytė, I.; Jasnauskaitė, M.; Borutinskaitė, V.; Navakauskienė, R. Anti-leukemic effects of HDACi Belinostat and HMTi 3-Deazaneplanocin A on human acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 799, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valiuliene, G.; Treigyte, G.; Savickiene, J.; Matuzevičius, D.; Alksne, M.; Jarašiene-Burinskaja, R.; Bukelskiene, V.; Navakauskas, D.; Navakauskiene, R. Histone modifications patterns in tissues and tumours from acute promyelocytic leukemia xenograft model in response to combined epigenetic therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 79, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Pei, X.Y.; Kramer, L.B.; Dent, P.; Grant, S. Bortezomib interacts synergistically with belinostat in human acute myeloid leukaemia and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells in association with perturbations in NF-κB and Bim. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 153, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Kmieciak, M.; Leng, Y.; Li, L.; Lin, H.; Rizzo, K.A.; Dumur, C.I.; Ferreira-Gonzalez, A.; et al. The NAE inhibitor pevonedistat interacts with the HDAC inhibitor belinostat to target AML cells by disrupting the DDR. Blood 2016, 127, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny-Diermayr, V.; Hart, S.; Goh, K.C.; Cheong, A.; Ong, L.-C.; Hentze, H.; Pasha, M.K.; Jayaraman, R.; Ethirajulu, K.; Wood, J.M. The oral HDAC inhibitor pracinostat (SB939) is efficacious and synergistic with the JAK2 inhibitor pacritinib (SB1518) in preclinical models of AML. Blood Cancer J. 2012, 2, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaza, Y.M.; Kadia, T.M.; Jabbour, E.J.; Konopleva, M.Y.; Borthakur, G.; Ferrajoli, A.; Estrov, Z.; Wierda, W.G.; Alfonso, A.; Chong, T.H.; et al. Phase 1 dose escalation multicenter trial of pracinostat alone and in combination with azacitidine in patients with advanced hematologic malignancies. Cancer 2017, 123, 4851–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Manero, G.; Montalban-Bravo, G.; Berdeja, J.G.; Abaza, Y.; Jabbour, E.; Essell, J.; Lyons, R.M.; Ravandi, F.; Maris, M.; Heller, B.; et al. Phase 2, randomized, double-blind study of pracinostat in combination with azacitidine in patients with untreated, higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer 2017, 123, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Manero, G.; Fong, C.Y.; Venditti, A.; Mappa, S.; Spezia, R.; Ades, L. A phase 3, randomized study of pracinostat (PRAN) in combination with azacitidine (AZA) versus placebo in patients ≥18 years with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) unfit for standard induction chemotherapy (IC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, TPS7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, C.; Ikezoe, T.; Yang, J.; Koeffler, H.P.; Yokoyama, A. Inhibition of MEK/ERK signaling synergistically potentiates histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced growth arrest, apoptosis and acetylation of histone H3 on p21waf1 promoter in acute myelogenous leukemia cell. Leukemia 2008, 22, 1449–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, C.; Ikezoe, T.; Yang, J.; Koeffler, H.P.; Yokoyama, A. Blockade of mTOR signaling potentiates the ability of histone deacetylase inhibitor to induce growth arrest and differentiation of acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Leukemia 2008, 22, 2159–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishioka, C.; Ikezoe, T.; Yang, J.; Udaka, K.; Yokoyama, A. Simultaneous inhibition of DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase induces p53-independent apoptosis via down-regulation of Mcl-1 in acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Leuk. Res. 2011, 35, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fandy, T.E.; Herman, J.G.; Kerns, P.; Jiemjit, A.; Sugar, E.A.; Choi, S.H.; Yang, A.S.; Aucott, T.; Dauses, T.; Odchimar-Reissig, R.; et al. Early epigenetic changes and DNA damage do not predict clinical response in an overlapping schedule of 5-azacytidine and entinostat in patients with myeloid malignancies. Blood 2009, 114, 2764–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prebet, T.; Sun, Z.; Figueroa, M.E.; Ketterling, R.; Melnick, A.; Greenberg, P.L.; Herman, J.; Juckett, M.; Wang, E.S.; Smith, M.R.; et al. Prolonged administration of azacitidine with or without entinostat for myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia with myelodysplasia-related changes: Results of the US Leukemia intergroup trial E1905. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, H.; Ito, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Towatari, M.; Ito, M.; Ueda, R.; Saito, H.; Naoe, T. In vivo effects of a histone deacetylase inhibitor, FK228, on human acute promyelocytic leukemia in NOD/Shi-scid/scid mice. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 2001, 92, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klisovic, D.D.; Katz, S.E.; Effron, D.; Klisovic, M.I.; Wickham, J.; Parthun, M.R.; Guimond, M.; Marcucci, G. Depsipeptide (FR901228) inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in primary and metastatic human uveal melanoma cell lines. investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 2390–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shaker, S.; Bernstein, M.; Momparler, L.F.; Momparler, R.L. Preclinical evaluation of antineoplastic activity of inhibitors of DNA methylation (5-aza-2’-deoxycytidine) and histone deacetylation (trichostatin A, depsipeptide) in combination against myeloid leukemic cells. Leuk. Res. 2003, 27, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, H.; Towatari, M.; Hatano, S.; Kitamura, K.; Kiyoi, H.; Kinoshita, T.; Tanimoto, M.; Murate, T.; Kawashima, K.; Saito, H.; et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors are the potent inducer/enhancer of differentiation in acute myeloid leukemia: A new approach to anti-leukemia therapy. Leukemia 1999, 13, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredly, H.; Gjertsen, B.T.; Bruserud, Ø. Histone deacetylase inhibition in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia: The effects of valproic acid on leukemic cells, and the clinical and experimental evidence for combining valproic acid with other antileukemic agents. Clin. Epigenet. 2013, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trus, M.R.; Yang, L.; Suarez Saiz, F.; Bordeleau, L.; Jurisica, I.; Minden, M.D. The histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid alters sensitivity towards all trans retinoic acid in acute myeloblastic leukemia cells. Leukemia 2005, 19, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, J.P.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Huang, X.; Cortes, J.; Ravandi, F.; Jabbour, E.; Borthakur, G.; Brandt, M.; Pierce, S.; Kantarjian, H.M. Results of phase 2 randomized study of low-dose decitabine with or without valproic acid in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer 2015, 121, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, W.; Klisovic, R.B.; Hackanson, B.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Devine, H.; Vukosavljevic, T.; Huynh, L.; Lozanski, G.; Kefauver, C.; et al. Phase I study of decitabine alone or in combination with valproic acid in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 3884–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Manero, G.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, B.; Yang, H.; Rosner, G.; Verstovsek, S.; Rytting, M.; Wierda, W.G.; Ravandi, F.; Koller, C.; et al. Phase 1/2 study of the combination of 5-aza-2’-deoxycytidine with valproic acid in patients with leukemia. Blood 2006, 108, 3271–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten Cate, B.; Samplonius, D.F.; Bijma, T.; De Leij, L.F.M.H.; Helfrich, W.; Bremer, E. The histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid potently augments gemtuzumab ozogamicin-induced apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemic cells. Leukemia 2007, 21, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano, A.O.; Yang, H.; Faderl, S.; Estrov, Z.; Giles, F.; Ravandi, F.; Cortes, J.; Wierda, W.G.; Ouzounian, S.; Quezada, A.; et al. Safety and clinical activity of the combination of 5-azacytidine, valproic acid, and all-trans retinoic acid in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2007, 110, 2302–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolini, G.; Orlandi, M.; Papi, A.; Ammar, K.; Tonelli, R.; Franzoni, M.; Pession, A.; Rocchi, P.; Ferreri, A.M. Growth inhibition and proapoptotic activity induction by IIF and valproic acid on RA-resistant leukemia cells. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, O.; Provaznikova, D.; Marinov, I.; Kuzelova, K.; Spicka, I. Antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects of proteasome inhibitors and their combination with histone deacetylase inhibitors on leukemia cells. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord. Drug Targets 2009, 9, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Kang, J.; Wang, J. Curcumin p38-dependently enhances the anticancer activity of valproic acid in human leukemia cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 41, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredly, H.; Stapnes Bjørnsen, C.; Gjertsen, B.T.; Bruserud, Ø. Combination of the histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid with oral hydroxyurea or 6-mercaptopurin can be safe and effective in patients with advanced acute myeloid leukaemia–a report of five cases. Hematology 2010, 15, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.-K.; Noh, E.-K.; Yoon, D.-J.; Jo, J.-C.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, H. Dasatinib accelerates valproic acid-induced acute myeloid leukemia cell death by regulation of differentiation capacity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, D.; Huang, K.; Yin, S.; Li, Y.; Xie, S.; Ma, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, J. Synergistic/additive interaction of valproic acid with bortezomib on proliferation and apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Leuk. Lymphoma 2012, 53, 2487–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.-H.; Wei, L.; Chen, L.; Zhao, S.-Q.; Wu, W.-L.; Shen, Z.-X.; Li, J.-M. Synergistic effect of bortezomib and valproic acid treatment on the proliferation and apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome cells. Ann. Hematol. 2011, 90, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Gao, L.; Cheng, H.; Tang, G.; Hu, X.; Wang, J. Valproic acid enhances the antileukemic effect of cytarabine by triggering cell apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- McCormack, E.; Haaland, I.; Venås, G.; Forthun, R.B.; Huseby, S.; Gausdal, G.; Knappskog, S.; Micklem, D.R.; Lorens, J.B.; Bruserud, O.; et al. Synergistic induction of p53 mediated apoptosis by valproic acid and nutlin-3 in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2012, 26, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuendgen, A.; Schmid, M.; Schlenk, R.; Knipp, S.; Hildebrandt, B.; Steidl, C.; Germing, U.; Haas, R.; Dohner, H.; Gattermann, N. The histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor valproic acid as monotherapy or in combination with all-trans retinoic acid in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 2006, 106, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuendgen, A.; Knipp, S.; Fox, F.; Strupp, C.; Hildebrandt, B.; Steidl, C.; Germing, U.; Haas, R.; Gattermann, N. Results of a phase 2 study of valproic acid alone or in combination with all-trans retinoic acid in 75 patients with myelodysplastic syndrome and relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Ann. Hematol. 2005, 84, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffoux, E.; Chaibi, P.; Dombret, H.; Degos, L. Valproic acid and all-trans retinoic acid for the treatment of elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2005, 90, 986–988. [Google Scholar]
- Bug, G.; Ritter, M.; Wassmann, B.; Schoch, C.; Heinzel, T.; Schwarz, K.; Romanski, A.; Kramer, O.H.; Kampfmann, M.; Hoelzer, D.; et al. Clinical trial of valproic acid and all-trans retinoic acid in patients with poor-risk acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 2005, 104, 2717–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassara, M.; Döhner, K.; Brossart, P.; Held, G.; Götze, K.; Horst, H.-A.; Ringhoffer, M.; Köhne, C.-H.; Kremers, S.; Raghavachar, A.; et al. Valproic acid in combination with all-trans retinoic acid and intensive therapy for acute myeloid leukemia in older patients. Blood 2014, 123, 4027–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsetti, M.T.; Salvi, F.; Perticone, S.; Baraldi, A.; De Paoli, L.; Gatto, S.; Pietrasanta, D.; Pini, M.; Primon, V.; Zallio, F.; et al. Hematologic improvement and response in elderly AML/RAEB patients treated with valproic acid and low-dose Ara-C. Leuk. Res. 2011, 35, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, S.; Gill, D.; McMillan, N.A.J.; Saunders, N.; Murphy, R.; Spurr, T.; Keane, C.; Fan, H.M.; Mollee, P. Valproic acid combined with cytosine arabinoside in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia has in vitro but limited clinical activity. Leuk. Lymphoma 2012, 53, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradner, J.E.; West, N.; Grachan, M.L.; Greenberg, E.F.; Haggarty, S.J.; Warnow, T.; Mazitschek, R. Chemical phylogenetics of histone deacetylases. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrales-Medina, F.F.; Manton, C.A.; Orlowski, R.Z.; Chandra, J. Efficacy of panobinostat and marizomib in acute myeloid leukemia and bortezomib-resistant models. Leuk. Res. 2015, 39, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Iglesias, O.; Ruiz-Llorente, L.; Sánchez-Martínez, R.; García, L.; Zambrano, A.; Aranda, A. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Mechanism of action and therapeutic use in cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2008, 10, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, J.J.; Li, X.; Chou, C.J. Advances and Challenges of HDAC Inhibitors in Cancer Therapeutics. In Advances in Cancer Research; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 138, pp. 183–211. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.Q.; Zhang, Y.Z. Histone deacetylase inhibition: An important mechanism in the treatment of lymphoma. Cancer Biol. Med. 2012, 9, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Vigushin, D.M.; Ali, S.; Pace, P.E.; Mirsaidi, N.; Ito, K.; Adcock, I.; Coombes, R.C. Trichostatin A is a histone deacetylase inhibitor with potent antitumor activity against breast cancer in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 971–976. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, J.; Malta-Vacas, J.; Louis, M.; Brault, L.; Bagrel, D.; Monteiro, C.; Brito, M. Modulation of translation factor’s gene expression by histone deacetylase inhibitors in breast cancer cells. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2005, 43, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hrgovic, I.; Doll, M.; Kleemann, J.; Wang, X.-F.; Zoeller, N.; Pinter, A.; Kippenberger, S.; Kaufmann, R.; Meissner, M. The histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin a decreases lymphangiogenesis by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest via p21-dependent pathways. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, N.; Maruyama, T.; Sakurai, R.; Masuda, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Shimizu, A.; Kishi, I.; Asada, H.; Yamagoe, S.; Yoshimura, Y. Involvement of histone acetylation in ovarian steroid-induced decidualization of human endometrial stromal cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 16675–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, H.; Maruyama, T.; Nagashima, T.; Asada, H.; Yoshimura, Y. Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce differentiation of human endometrial adenocarcinoma cells through up-regulation of glycodelin. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 5365–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, P.A.; Richon, V.M.; Rifkind, R.A. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Inducers of differentiation or apoptosis of transformed cells. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Nagaria, P.K.; Pawar, N.; Adewuyi, A.; Gojo, I.; Meyers, D.J.; Cole, P.A.; Rassool, F.V. Histone deacetylase inhibitors decrease NHEJ both by acetylation of repair factors and trapping of PARP1 at DNA double-strand breaks in chromatin. Leuk. Res. 2016, 45, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, G.; Cardoso, B.A.; Belo, H.; Almeida, A.M. Vorinostat Induces Apoptosis and Differentiation in Myeloid Malignancies: Genetic and Molecular Mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubna, A.K. Vorinostat-An overview. Indian J. Dermatol. 2015, 60, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalban-Bravo, G.; Garcia-Manero, G. Novel drugs for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2015, 29, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Eom, G.H. HDAC and HDAC Inhibitor: From Cancer to Cardiovascular Diseases. Chonnam Med. J. 2016, 52, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suraweera, A.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Richard, D.J. Combination therapy with histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) for the treatment of cancer: Achieving the full therapeutic potential of HDACi. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruccelli, L.A.; Dupéré-Richer, D.; Pettersson, F.; Retrouvey, H.; Skoulikas, S.; Miller, W.H. Vorinostat induces reactive oxygen species and dna damage in acute myeloid leukemia cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, E.W.; Loaiza-Bonilla, A.; Juckett, M.; DiPersio, J.F.; Roy, V.; Slack, J.; Wu, W.; Laumann, K.; Espinoza-Delgado, I.; Gore, S.D. A phase 2 study of vorinostat in acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Qiu, S.; Ge, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wei, H.; Guo, D.; Chen, S.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Xing, H.; et al. A novel SAHA-bendamustine hybrid induces apoptosis of leukemia cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20121–20131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, C.; Jin, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Ma, Z.; Huang, X.; He, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.; et al. High PARP-1 expression predicts poor survival in acute myeloid leukemia and PARP-1 inhibitor and SAHA-bendamustine hybrid inhibitor combination treatment synergistically enhances anti-tumor effects. EBioMedicine 2018, 38, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craddock, C.F.; Houlton, A.E.; Quek, L.S.; Ferguson, P.; Gbandi, E.; Roberts, C.; Metzner, M.; Garcia-Martin, N.; Kennedy, A.; Hamblin, A.; et al. Outcome of azacitidine therapy in acute myeloid leukemia is not improved by concurrent vorinostat therapy but is predicted by a diagnostic molecular signature. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6430–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mims, A.S.; Mishra, A.; Orwick, S.; Blachly, J.; Klisovic, R.B.; Garzon, R.; Walker, A.R.; Devine, S.M.; Walsh, K.J.; Vasu, S.; et al. A novel regimen for relapsed/refractory adult acute myeloid leukemia using a KMT2A partial tandem duplication targeted therapy: Results of phase 1 study NCI 8485. Haematologica 2018, 103, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, J.M.; Hackanson, B.; Lübbert, M.; Jung, M. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors in recent clinical trials for cancer therapy. Clin. Epigenet. 2010, 1, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas-Zornoza, A.; Agirre, X.; Abizanda, G.; Moreno, C.; Segura, V.; De Martino Rodriguez, A.; José-Eneriz, E.S.; Miranda, E.; Martín-Subero, J.I.; Garate, L.; et al. Preclinical activity of LBH589 alone or in combination with chemotherapy in a xenogeneic mouse model of human acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Veggel, M.; Westerman, E.; Hamberg, P. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Panobinostat. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2018, 57, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anne, M.; Sammartino, D.; Barginear, M.F.; Budman, D. Profile of panobinostat and its potential for treatment in solid tumors: An update. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2013, 6, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.; Wei, A.; Mithraprabhu, S.; Cummings, N.; Liu, H.B.; Perugini, M.; Reed, K.; Avery, S.; Patil, S.; Walker, P.; et al. Dual epigenetic targeting with panobinostat and azacitidine in acute myeloid leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood Cancer J. 2014, 4, e170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Z.; Kwitkowski, V.E.; Del Valle, P.L.; Ricci, M.S.; Saber, H.; Habtemariam, B.A.; Bullock, J.; Bloomquist, E.; Shen, Y.L.; Chen, X.H.; et al. FDA approval: Belinostat for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2666–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, R.M. Belinostat: First global approval. Drugs 2014, 74, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beleodaq approved for rare lymphomas. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 978.
- Kirschbaum, M.H.; Foon, K.A.; Frankel, P.; Ruel, C.; Pulone, B.; Tuscano, J.M.; Newman, E.M. A phase 2 study of belinostat (PXD101) in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia or patients over the age of 60 with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia: A California Cancer Consortium Study. Leuk. Lymphoma 2014, 55, 2301–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finazzi, G.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Martinelli, V.; Ruggeri, M.; Nobile, F.; Specchia, G.; Pogliani, E.M.; Olimpieri, O.M.; Fioritoni, G.; Musolino, C.; et al. A phase II study of Givinostat in combination with hydroxycarbamide in patients with polycythaemia vera unresponsive to hydroxycarbamide monotherapy. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 161, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlan, A.; Monzani, V.; Reznikov, L.L.; Leoni, F.; Fossati, G.; Modena, D.; Mascagni, P.; Dinarello, C.A. Pharmacokinetics, safety and inducible cytokine responses during a phase 1 trial of the oral histone deacetylase inhibitor ITF2357 (givinostat). Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaldi, A.; Dellacasa, C.M.; Finazzi, G.; Carobbio, A.; Ferrari, M.L.; Guglielmelli, P.; Gattoni, E.; Salmoiraghi, S.; Finazzi, M.C.; Di Tollo, S.; et al. A pilot study of the Histone-Deacetylase inhibitor Givinostat in patients with JAK2V617F positive chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 150, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganai, S.A. Histone deacetylase inhibitor givinostat: The small-molecule with promising activity against therapeutically challenging haematological malignancies. J. Chemother. 2016, 28, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetto, A.T.; Ang, J.E.; Lal, R.; Olmos, D.; Molife, L.R.; Kristeleit, R.; Parker, A.; Casamayor, I.; Olaleye, M.; Mais, A.; et al. First-in-human, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic phase i study of resminostat, an oral histone deacetylase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5494–5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribrag, V.; Kim, W.S.; Bouabdallah, R.; Lim, S.T.; Coiffier, B.; Illes, A.; Lemieux, B.; Dyer, M.J.S.; Offner, F.; Felloussi, Z.; et al. Safety and efficacy of abexinostat, a pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor, in non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Results of a phase II study. Haematologica 2017, 102, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vey, N.; Prebet, T.; Thalamas, C.; Charbonnier, A.; Rey, J.; Kloos, I.; Liu, E.; Luan, Y.; Vezan, R.; Graef, T.; et al. Phase 1 dose-escalation study of oral abexinostat for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes, acute myeloid leukemia, or acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 58, 1880–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evens, A.M.; Balasubramanian, S.; Vose, J.M.; Harb, W.; Gordon, L.I.; Langdon, R.; Sprague, J.; Sirisawad, M.; Mani, C.; Yue, J.; et al. A phase I/II multicenter, open-label study of the oral histone deacetylase inhibitor abexinostat in relapsed/refractory lymphoma. In Proceedings of the Clinical Cancer Research; American Association for Cancer Research Inc.: Denver, CO, USA, 2016; Volume 22, pp. 1059–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Morschhauser, F.; Terriou, L.; Coiffier, B.; Bachy, E.; Varga, A.; Kloos, I.; Lelièvre, H.; Sarry, A.L.; Depil, S.; Ribrag, V. Phase 1 study of the oral histone deacetylase inhibitor abexinostat in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, or chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, B.; Baird, R.; Kristeleit, R.S.; Plummer, R.; Cowan, R.; Stewart, A.; Fourneau, N.; Hellemans, P.; Elsayed, Y.; McClue, S.; et al. A phase I study of quisinostat (JNJ-26481585), an oral hydroxamate histone deacetylase inhibitor with evidence of target modulation and antitumor activity, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4262–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbetti, V.; Gozzini, A.; Rovida, E.; Morandi, A.; Spinelli, E.; Fossati, G.; Mascagni, P.; Lübbert, M.; Dello Sbarba, P.; Santini, V. Selective anti-leukaemic activity of low-dose histone deacetylase inhibitor ITF2357 on AML1/ETO-positive cells. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Golay, J.; Cuppini, L.; Leoni, F.; Micò, C.; Barbui, V.; Domenghini, M.; Lombardi, L.; Neri, A.; Barbui, A.M.; Salvi, A.; et al. The histone deacetylase inhibitor ITF2357 has anti-leukemic activity in vitro and in vivo and inhibits IL-6 and VEGF production by stromal cells. Leukemia 2007, 21, 1892–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novotny-Diermayr, V.; Sausgruber, N.; Loh, Y.K.; Pasha, M.K.; Jayaraman, R.; Hentze, H.; Yong, W.P.; Goh, B.C.; Toh, H.C.; Ethirajulu, K.; et al. Pharmacodynamic evaluation of the target efficacy of SB939, an oral HDAC inhibitor with selectivity for tumor tissue. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabkiewicz, J.; Gilmour, M.; Hills, R.; Vyas, P.; Bone, E.; Davidson, A.; Burnett, A.; Knapper, S. The targeted histone deacetylase inhibitor tefinostat (CHR-2845) shows selective in vitro efficacy in monocytoid-lineage leukaemias. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 16650–16662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Lowenberg, B.; Zachee, P.; Vey, N.; Breems, D.; Van de Loosdrecht, A.A.; Davidson, A.H.; Wells, G.; Needham, L.; Bawden, L.; et al. A phase I first-in-human study with tefinostat–a monocyte/macrophage targeted histone deacetylase inhibitor–in patients with advanced haematological malignancies. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 162, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffat, D.; Patel, S.; Day, F.; Belfield, A.; Donald, A.; Rowlands, M.; Wibawa, J.; Brotherton, D.; Stimson, L.; Clark, V.; et al. Discovery of 2-(6-{[(6-fluoroquinolin-2-yl)methyl]amino}bicyclo [3.1.0]hex-3-yl)-N-hydroxypyrimidine-5-carboxamide (CHR-3996), a class I selective orally active histone deacetylase inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 8663–8678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerji, U.; van Doorn, L.; Papadatos-Pastos, D.; Kristeleit, R.; Debnam, P.; Tall, M.; Stewart, A.; Raynaud, F.; Garrett, M.D.; Toal, M.; et al. A phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of CHR-3996, an oral class I selective histone deacetylase inhibitor in refractory solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 2687–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wightman, F.; Lu, H.K.; Solomon, A.E.; Saleh, S.; Harman, A.N.; Cunningham, A.L.; Gray, L.; Churchill, M.; Cameron, P.U.; Dear, A.E.; et al. Entinostat is a histone deacetylase inhibitor selective for class 1 histone deacetylases and activates HIV production from latently infected primary T cells. AIDS 2013, 27, 2853–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, R.M.; Rudek, M.A.; Piekarz, R. Entinostat: A promising treatment option for patients with advanced breast cancer. Futur. Oncol. 2017, 13, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, C.; Ikezoe, T.; Yang, J.; Takeuchi, S.; Phillip Koeffler, H.; Yokoyama, A. MS-275, a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor with selectivity against HDAC1, induces degradation of FLT3 via inhibition of chaperone function of heat shock protein 90 in AML cells. Leuk. Res. 2008, 32, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsey, J.M.; Kettyle, L.M.J.; Sharpe, D.J.; Mulgrew, N.M.; Dickson, G.J.; Bijl, J.J.; Austin, P.; Mayotte, N.; Cellot, S.; Lappin, T.R.J.; et al. Entinostat prevents leukemia maintenance in a collaborating oncogene-dependent model of cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 1434–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gojo, I.; Jiemjit, A.; Trepel, J.B.; Sparreboom, A.; Figg, W.D.; Rollins, S.; Tidwell, M.L.; Greer, J.; Chung, E.J.; Lee, M.-J.; et al. Phase 1 and pharmacologic study of MS-275, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in adults with refractory and relapsed acute leukemias. Blood 2007, 109, 2781–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillico, R.; Lawrence, C.K.; Lakowski, T.M. Selective DOT1L, LSD1, and HDAC Class i Inhibitors Reduce HOXA9 Expression in MLL-AF9 Rearranged Leukemia Cells, but Dysregulate the Expression of Many Histone-Modifying Enzymes. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2657–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Manero, G.; Assouline, S.; Cortes, J.; Estrov, Z.; Kantarjian, H.; Yang, H.; Newsome, W.M.; Miller, W.H.; Rousseau, C.; Kalita, A.; et al. Phase 1 study of the oral isotype specific histone deacetylase inhibitor MGCD0103 in leukemia. Blood 2008, 112, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piekarz, R.L.; Frye, R.; Prince, H.M.; Kirschbaum, M.H.; Zain, J.; Allen, S.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Ling, A.; Turner, M.; Peer, C.J.; et al. Phase 2 trial of romidepsin in patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2011, 117, 5827–5834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campàs-Moya, C. Romidepsin for the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Drugs Today 2009, 45, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, H.; Singh, A.; Dewangan, P.K.; Patel, V.; Jain, D.K.; Tiwari, S.K.; Veerasamy, R.; Sharma, P.C. Peptide Based Macrocycles: Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors with Antiproliferative Activity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 1887–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Chen, Q.; Shimada, K.; Tang, M.; Li, H.; Gurumurthy, A.; Khoury, J.D.; Xu, B.; Huang, S.; Qiu, Y. Histone deacetylase inhibitor targets CD123/CD47-positive cells and reverse chemoresistance phenotype in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Marcucci, G.; Parthun, M.R.; Xiao, J.J.; Klisovic, R.B.; Moran, M.; Lin, T.S.; Liu, S.; Sklenar, A.R.; Davis, M.E.; et al. A phase 1 and pharmacodynamic study of depsipeptide (FK228) in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2005, 105, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek, V.M.; Fircanis, S.; Maslak, P.; Guernah, I.; Baum, M.; Wu, N.; Panageas, K.; Wright, J.J.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Nimer, S.D. Tolerability, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics studies of depsipeptide (Romidepsin) in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia or advanced myelodysplastic syndromes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, D.M.; Leng, Y.; Marinova, Z.; Kim, H.J.; Chiu, C.T. Multiple roles of HDAC inhibition in neurodegenerative conditions. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Bae, G.-U.; Yoon, J.W.; Hong, S.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, Y.-W.; Lee, H.-W.; Han, J.-W. Apicidin, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, induces apoptosis and Fas/Fas ligand expression in human acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 2073–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, N.J.; Christianson, D.W. Binding of the Microbial Cyclic Tetrapeptide Trapoxin A to the Class i Histone Deacetylase HDAC8. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 2281–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, T.; Towatari, M.; Kosugi, H.; Saito, H. Up-regulation of costimulatory/adhesion molecules by histone deacetylase inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood 2000, 96, 3847–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Faussat, A.-M.; Majdak, P.; Perrot, J.-Y.; Chaoui, D.; Legrand, O.; Marie, J.-P. Valproic acid inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells expressing P-gp and MRP1. Leukemia 2004, 18, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Klisovic, R.B.; Vukosavljevic, T.; Yu, J.; Paschka, P.; Huynh, L.; Pang, J.; Neviani, P.; Liu, Z.; Blum, W.; et al. Targeting AML1/ETO-histone deacetylase repressor complex: A novel mechanism for valproic acid-mediated gene expression and cellular differentiation in AML1/ETO-positive acute myeloid leukemia cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 321, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.C.; Lin, H.; Huang, M.J.; Chow, J.M.; Lin, S.; Liu, H.E. Downregulation of c-Myc is critical for valproic acid-induced growth arrest and myeloid differentiation of acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2007, 31, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göttlicher, M.; Minucci, S.; Zhu, P.; Krämer, O.H.; Schimpf, A.; Giavara, S.; Sleeman, J.P.; Lo Coco, F.; Nervi, C.; Pelicci, P.G.; et al. Valproic acid defines a novel class of HDAC inhibitors inducing differentiation of transformed cells. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 6969–6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozzini, A.; Rovida, E.; Dello Sbarba, P.; Galimberti, S.; Santini, V.; Galimbert, S. Butyrates, as a single drug, induce histone acetylation and granulocytic maturation: Possible selectivity on core binding factor-acute myeloid leukemia blasts. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8955–8961. [Google Scholar]
- Maslak, P.; Chanel, S.; Camacho, L.H.; Soignet, S.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Guernah, I.; Warrell, R.; Nimer, S. Pilot study of combination transcriptional modulation therapy with sodium phenylbutyrate and 5-azacytidine in patients with acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia 2006, 20, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.A.; Witter, D.J.; Belvedere, S. Histone deacetylase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 5097–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, R.R.; Wada, C.K.; Garland, R.B.; Curtin, M.L.; Michaelides, M.R.; Li, J.; Pease, L.J.; Glaser, K.B.; Marcotte, P.A.; Bouska, J.J.; et al. Trifluoromethyl ketones as inhibitors of histone deacetylase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 3443–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| HDAC Classes | HDAC Members | Cofactor |
|---|---|---|
| Class I | HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3, and HDAC8 | Zn2+-dependent |
| Class IIa | HDAC4, HDAC5, HDAC7, and HDAC9 | Zn2+-dependent |
| Class IIb | HDAC6 and HDAC10 | Zn2+-dependent |
| Class III (Sirtuins) | SIRT1-7 | NAD+-dependent |
| Class IV | HDAC11 | Zn2+-dependent |
| HDACi Classes | HDAC Inhibitor | Target HDAC Class | Preclinical Combinations | Clinical Trials Combinations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroximates | Trichostatin A | pan * | Chaetocin [64] Decitabine + DZNep [65] | |
| Vorinostat (SAHA) | pan * | ATRA [66,67,68] MK-0457 [69] NPI-0052 [70] Cytarabine [71] Etoposide [71] GX15-070 [72] AZD1775 [73] BPR1J-340 [74] BMN673 [75] | Decitabine [76,77] Idarubicin [78] Idarubicin + Cytarabine [79] Alvocidib [80] GO + AZA [81,82] Sorafenib + Bortezomib [83] | |
| Panobinostat (LBH589) | pan * | Decitabine [84,85] AZA [86] ABT-199 [87] MK-1775 [88] BC2059 [89] SP2509 [90] JQ1 [91] AC220 [92] Bortezomib [93] CXCR4 antagonist [94] Doxorubicin [95] DZNep [96] | AZA [97] GSK2879552 [98] Cytarabine + Idarubicin [99] Daunorubicin + Cytarabine [100] Cytarabine + Mitoxantrane [101] | |
| Belinostat (PXD101) | pan * | ATRA [102,103] DZNep + ATRA [104,105] DZNep + ATRA + Idarubicin [104,105] Bortezomib [106] Pevenedistat [107] | ||
| Givinostat (ITF2357) | pan * | |||
| Resminostat (4SC201) | pan | |||
| Abexinostat (PCI-24781) | pan | |||
| Quisinostat (JNJ-26481585) | pan | |||
| Pracinostat (SB939) | pan | SB1518 [108] | AZA [109,110,111] | |
| Tefinostat (CHR-2845) | pan | |||
| CHR-3996 | I | |||
| Benzamides | Entinostat | I | AZD6244 [112] RAD001 [113] Decitabine [114] | AZA [115,116] |
| Mocetinostat | I, IV | |||
| Cyclic peptides | Romidepsin | I | ATRA [117] Decitabine [118] AZA [119] | |
| Apicidin | I | |||
| Trapoxin A | I, II | ATRA [120] | ||
| Aliphatic acids | Valproic acid | I, IIa | ATRA [121,122] Decitabine [123,124,125] GO [126] AZA [127] Retinoid IIF [128] NPI-0052 [129] PR-171 [129] Curcumin [130] Hydroxiurea [131] 6-mercaptopurine [131] Dasatinib [132] Bortezomib [133,134] Cytarabine [135] Nutlin-3 [136] | ATRA [137,138,139,140,141] Cytarabine [142,143] Hydroxiurea [131] 6-mercaptopurine [131] Decitabine [123,124,125] AZA [127] |
| Butyric acid | I, II | |||
| Phenylbutyric acid | I, II |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
San José-Enériz, E.; Gimenez-Camino, N.; Agirre, X.; Prosper, F. HDAC Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2019, 11, 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111794
San José-Enériz E, Gimenez-Camino N, Agirre X, Prosper F. HDAC Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers. 2019; 11(11):1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111794
Chicago/Turabian StyleSan José-Enériz, Edurne, Naroa Gimenez-Camino, Xabier Agirre, and Felipe Prosper. 2019. "HDAC Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia" Cancers 11, no. 11: 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111794
APA StyleSan José-Enériz, E., Gimenez-Camino, N., Agirre, X., & Prosper, F. (2019). HDAC Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers, 11(11), 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111794





