Effects of Antiangiogenetic Drugs on Microcirculation and Macrocirculation in Patients with Advanced-Stage Renal Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Blood Pressure Measurements
2.3. Laboratory Plasma, Serum, and Urine Analysis
2.4. Evaluation of Vascular Parameters (FMD and Carotid Distensibility)
2.5. Echocardiography
2.6. Capillaroscopy
2.7. Radiological Imaging of the Disease
2.8. Statistical Analysis
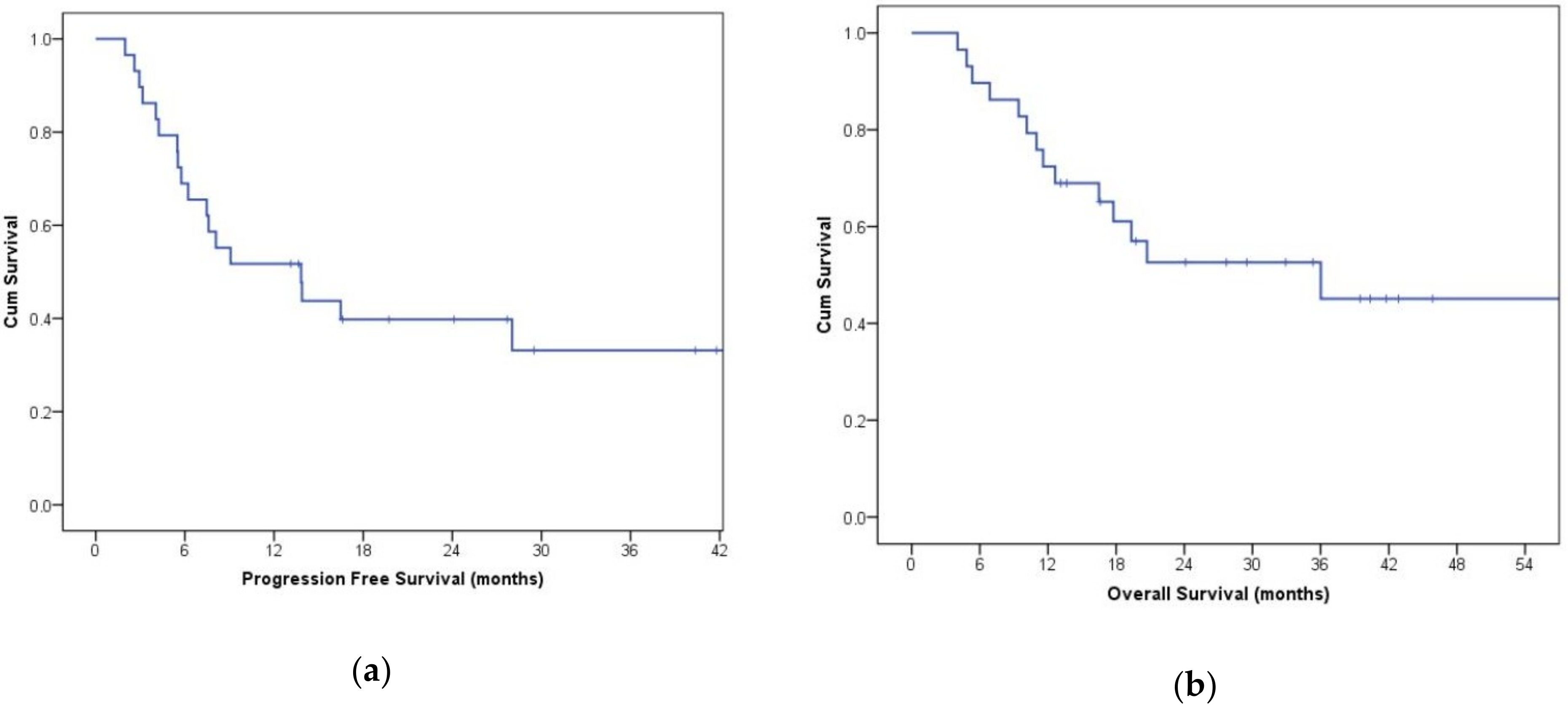
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Population Characteristics
3.2. Blood Pressure Increase
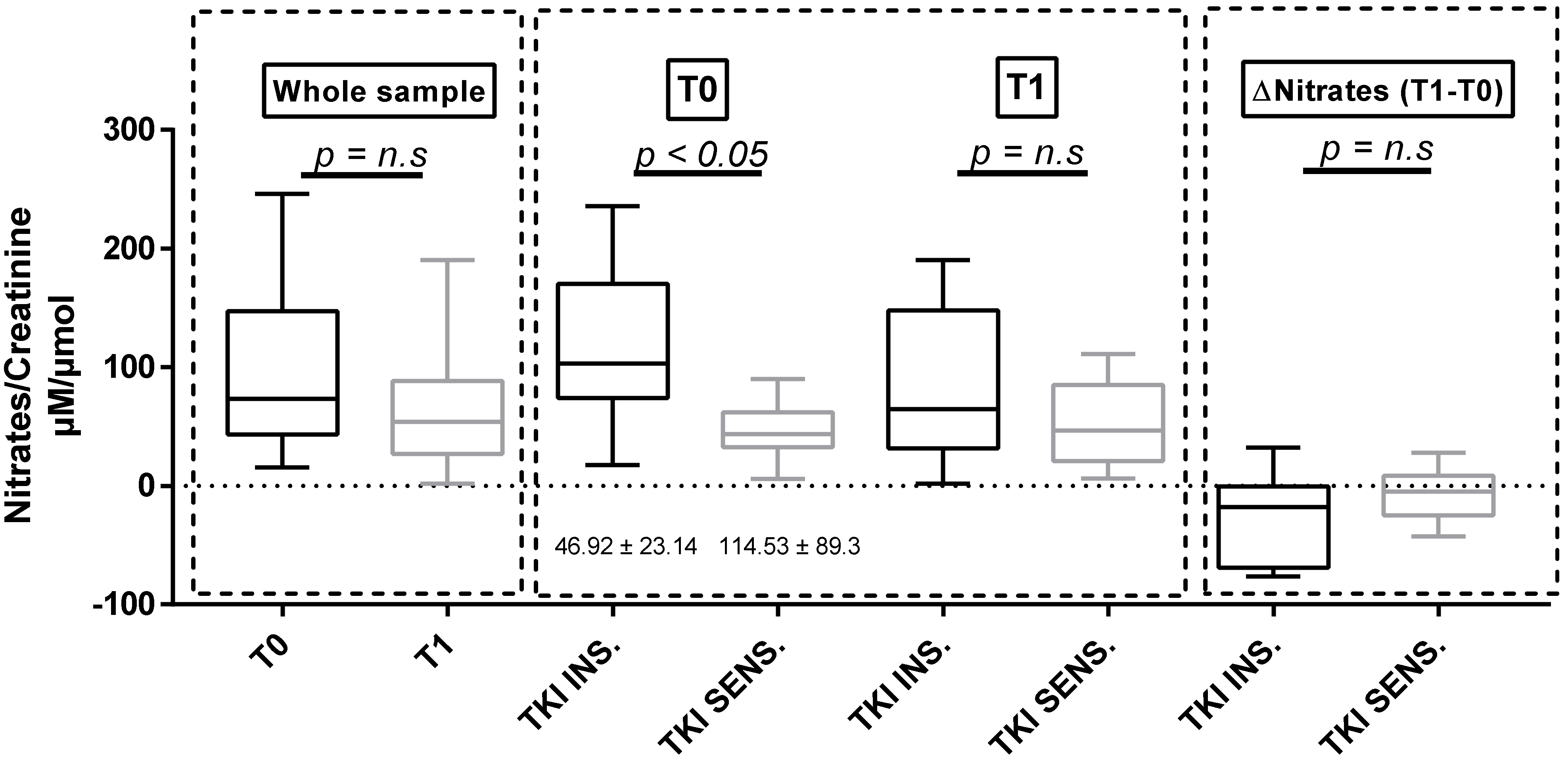
3.3. Urinary Nitrates
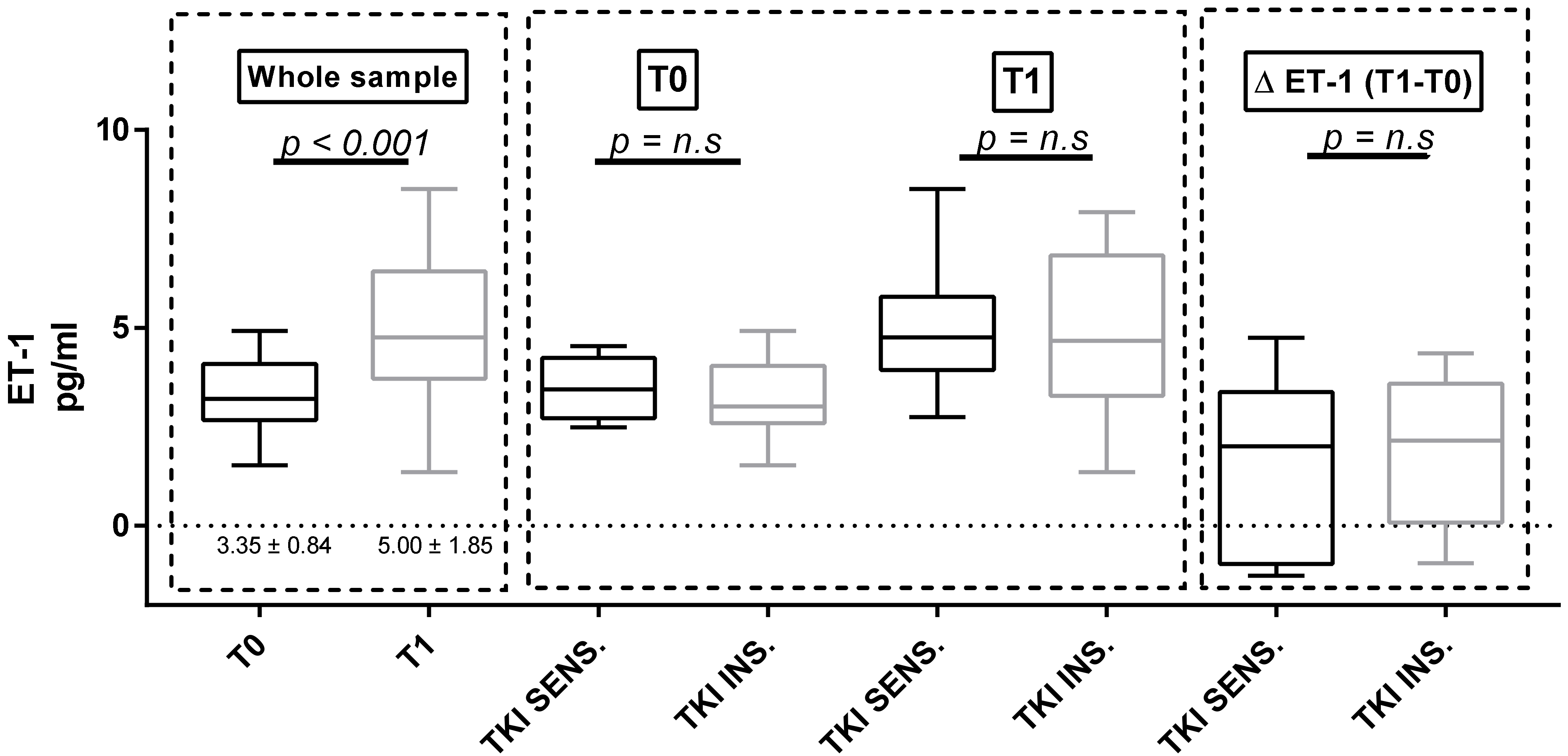
3.4. Proteinuria and ET-1
3.5. Capillaroscopy
3.6. Vascular Parameters and Echocardiography
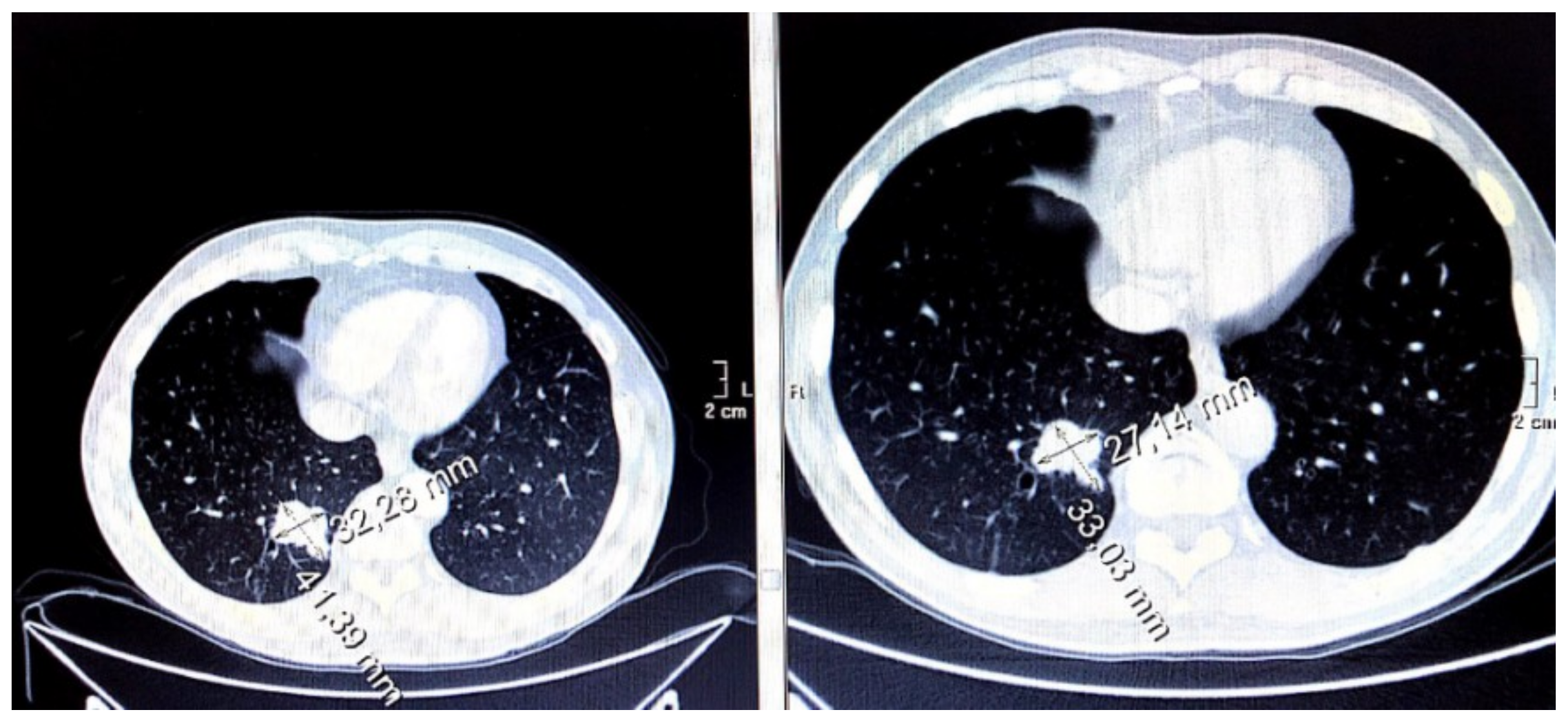
3.7. Evaluation of Disease Wuìith CT Imaging
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arora, A.; Scholar, E.M. Role of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 315, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greef, B.; Eisen, T. Medical treatment of renal cancer: New horizons. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touyz, R.M.; Herrmann, S.M.S.; Herrmann, J. Vascular toxicities with VEGF inhibitor therapies–focus on hypertension and arterial thrombotic events. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2018, 12, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semeniuk-Wojtaś, A.; Lubas, A.; Stec, R.; Szczylik, C.; Niemczyk, S. Influence of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on Hypertension and Nephrotoxicity in Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamnvik, O.P.; Choueiri, T.K.; Turchin, A.; McKay, R.R.; Goyal, L.; Davis, M.; Kaymakcalan, M.D.; Williams, J.S. Clinical risk factors for the development of hypertension in patients treated with inhibitors of the VEGF signaling pathway. Cancer 2015, 121, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappers, M.H.; Smedts, F.M.; Horn, T.; van Esch, J.H.; Sleijfer, S.; Leijten, F.; Wesseling, S.; Strevens, H.; Jan Danser, A.H.; van den Meiracker, A.H.; et al. The Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor Sunitinib Causes a Preeclampsia-Like Syndrome With Activation of the Endothelin System. Hypertension 2011, 58, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankhorst, S.; Kappers, M.H.W.; van Esch, J.H.M.; Danser, A.H.J.; van den Meiracker, A.H. Hypertension During Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibition: Focus on Nitric Oxide, Endothelin-1, and Oxidative Stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facemire, C.S.; Nixon, A.B.; Griffiths, R.; Hurwitz, H.; Coffman, T.M. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 controls blood pressure by regulating nitric oxide synthase expression. Hypertension 2009, 54, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappers, M.H.W.; van Esch, J.H.M.; Sluiter, W.; Sleijfer, S.; Danser, A.H.J.; van den Meiracker, A.H. Hypertension induced by the tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib is associated with increased circulating endothelin-1 levels. Hypertension 2010, 56, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touyz, R.M.; Lang, N.N.; Herrmann, J.; van den Meiracker, A.H.; Danser, A.H.J. Recent Advances in Hypertension and Cardiovascular Toxicities With Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibition. Hypertension 2017, 70, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, M.P.; van der Veldt, A.A.M.; Lankheet, N.A.; Wijnstok, N.J.; van den Eertwegh, A.J.M.; Boven, E.; Serné, E.H. Sunitinib-induced reduction in skin microvascular density is a reversible phenomenon. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2010, 21, 1923–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefe, D.; Bowen, J.; Gibson, R.; Tan, T.; Okera, M.; Stringer, A. Noncardiac vascular toxicities of vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors in advanced cancer: A review. Oncologist 2011, 16, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corretti, M.C.; Anderson, T.J.; Benjamin, E.J.; Celermajer, D.; Charbonneau, F.; Creager, M.A.; Deanfield, J.; Drexler, H.; Gerhard-Herman, M.; Herrington, D.; et al. Guidelines for the ultrasound assessment of endothelial-dependent flow-mediated vasodilation of the brachial artery: A report of the International Brachial Artery Reactivity Task Force. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, D.Y.C.; Xie, W.; Regan, M.M.; Warren, M.A.; Golshayan, A.R.; Sahi, C.; Eigl, B.J.; Ruether, J.D.; Cheng, T.; North, S.; et al. Prognostic Factors for Overall Survival in Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated With Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor–Targeted Agents: Results From a Large, Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5794–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Cella, D.; Reeves, J.; Hawkins, R.; Guo, J.; Nathan, P.; Staehler, M.; de Souza, P.; Merchan, J.R.; et al. Pazopanib versus Sunitinib in Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; Tomczak, P.; Hutson, T.E.; Michaelson, M.D.; Negrier, S.; Oudard, S.; Gore, M.E.; Tarazi, J.; Hariharan, S.; et al. Axitinib versus sorafenib as second-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: Overall survival analysis and updated results from a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2013, 14, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.; Chedid, A.; Oudard, S. Home Blood-Pressure Monitoring in Patients Receiving Sunitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitland, M.L.; Bakris, G.L.; Black, H.R.; Chen, H.X.; Durand, J.-B.; Elliott, W.J.; Ivy, S.P.; Leier, C.V.; Lindenfeld, J.; Liu, G.; et al. Initial assessment, surveillance, and management of blood pressure in patients receiving vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway inhibitors. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ding, F.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, G.; Lin, T.; He, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wei, G. Incidence and risk of hypertension associated with vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer patients: A comprehensive network meta-analysis of 72 randomized controlled trials involving 30013 patients. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 67661–67673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eechoute, K.; van der Veldt, A.A.M.; Oosting, S.; Kappers, M.H.W.; Wessels, J.A.M.; Gelderblom, H.; Guchelaar, H.-J.; Reyners, A.K.L.; van Herpen, C.M.L.; Haanen, J.B.; et al. Polymorphisms in Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase (eNOS) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Predict Sunitinib-Induced Hypertension. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 92, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankhorst, S.; Saleh, L.; Danser, A.J.; van den Meiracker, A.H. Etiology of angiogenesis inhibition-related hypertension. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 21, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smallwood, M.J.; Ble, A.; Melzer, D.; Winyard, P.G.; Benjamin, N.; Shore, A.C.; Gilchrist, M. Relationship Between Urinary Nitrate Excretion and Blood Pressure in the InChianti Cohort. Am. J. Hypertens. 2017, 30, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larochelle, P.; Kollmannsberger, C.; Feldman, R.D.; Schiffrin, E.L.; Poirier, L.; Patenaude, F.; Ruether, D.; Myers, M.; Bjarnason, G. Hypertension management in patients with renal cell cancer treated with anti-angiogenic agents. Curr. Oncol. 2012, 19, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinning, A.R.; Bengtsen, C.; Jensen, N.V.; Bastholt, L.; Jensen, B.L.; Madsen, K. Pazopanib-Induced Hypertension in Patients With Renal Cell Carcinoma Is Associated With Low Urine Excretion of NO Metabolites. Hypertension 2018, 71, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruzliak, P.; Kovacova, G.; Pechanova, O. Therapeutic potential of nitric oxide donors in the prevention and treatment of angiogenesis-inhibitor-induced hypertension. Angiogenesis 2013, 16, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thachil, J. Nitric oxide and adverse events of vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2011, 27, 1503–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Tomczak, P.; Michaelson, M.D.; Bukowski, R.M.; Oudard, S.; Negrier, S.; Szczylik, C.; Pili, R.; Bjarnason, G.A.; et al. Overall Survival and Updated Results for Sunitinib Compared With Interferon Alfa in Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3584–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, G.; Golshayan, A.; Elson, P.; Wood, L.; Garcia, J.; Bukowski, R.; Rini, B. Sunitinib and sorafenib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients with renal insufficiency. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 1618–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandula, P.; Agarwal, R. Proteinuria and hypertension with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steeghs, N.; Gelderblom, H.; Roodt, J.O.; Christensen, O.; Rajagopalan, P.; Hovens, M.; Putter, H.; Rabelink, T.J.; de Koning, E. Hypertension and rarefaction during treatment with telatinib, a small molecule angiogenesis inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 3470–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joannides, R.; Haefeli, W.E.; Linder, L.; Richard, V.; Bakkali, E.H.; Thuillez, C.; Luscher, T.F. Nitric oxide is responsible for flow-dependent dilatation of human peripheral conduit arteries in vivo. Circulation 1995, 91, 1314–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agewall, S.; Hulthe, J.; Fagerberg, B.; Gottfridsson, B.; Wikstrand, J. Post-occlusion brachial artery vasodilatation after ischaemic handgrip exercise is nitric oxide mediated. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2002, 22, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alivon, M.; Giroux, J.; Briet, M.; Goldwasser, F.; Laurent, S.; Boutouyrie, P. Large artery stiffness and hypertension after antiangiogenic drugs: Influence on cancer progression. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Baseline (T0, n = 29) | 1 Month (T1, n = 29) | 3 Months (T2, n = 25) | 6 Months (T3, n = 21) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP (mmHg) | 136.5 ± 14.9 | 145.7 ± 17.3 † | 137.4 ± 11.4 | 133.7 ± 15.1 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 85.3 ± 10. | 87.9 ± 11.3 | 85.7 ± 8.3 | 80.7 ± 11.7 |
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.21 ± 0.25 | 1.27 ± 0.28 | 1.17 ± 0.30 | 1.17 ± 0.30 |
| GFR (mL/min) | 66.06 ± 24.81 | 69.28 ± 26.32 | 63.62 ± 28.39 | 68.73 ± 28.23 |
| Nitrates/Creatinine (µM/µmol of creatinine) | 84.21 ± 73.43 | 70.57 ± 67.84 | 73.95 ± 75.55 | 72.31 ± 52.33 † |
| Platelets (103/µL) | 257.4 ± 103.0 | 190.2 ± 76.4 ‡ | 226.8 ± 129.9 | 225.6 ± 94.3 |
| IMT (mm) | 0.78 ± 0.20 | 0.73 ± 0.12 | 0.75 ± 0.14 | 0.70 ± 0.15 |
| CD (103 kpa) | 19.47 ± 9.10 | 20.71 ± 15.86 | 19.42 ± 8.10 | 17.83 ± 7.73 |
| FMD (%) | 3.75 ± 5.95 | 3.43 ± 5.24 | 3.15 ± 3.73 | 3.33 ± 6.46 |
| IVS (mm) | 0.97 ± 0.15 | 0.99 ± 0.21 | 0.96 ± 0.15 | 0.95 ± 0.19 |
| Indexed LVM (LVM/BSA. g/m2) | 99.78 ± 78.66 | 93.26 ± 44.73 | 97.38 ± 44.73 | 85.18 ± 33.24 |
| EF (%) | 58.90 ± 7.51 | 56.94 ± 7.37 | 56.11 ± 8.60 | 57.63 ± 7.67 |
| E/A | 0.74 ± 0.19 | 1.07 ± 0.62 | 0.94 ± 0.55 | 0.87 ± 0.32 |
| Parameters | TKI-Sensitive (14/29) | TKI-Insensitive (15/29) | TKI-Sensitive (14/29) | TKI-Insensitive (15/29) | TKI-Sensitive (11/25) | TKI-Insensitive (14/25) | TKI-Sensitive (8/21) | TKI-Insensitive (13/21) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline (T0, n = 29) | 1 month (T1, n = 29) | 3 months (T2 n = 25) | 6 months (T3, n = 21) | |||||
| SBP (mmHg) | 129.6 ± 12.8 | 142.1 ± 14.5 § | 154.9 ± 16.6 | 138.2 ± 14.2 † | 136.1 ± 15.5 | 138.3 ± 8.4 | 128.0 ± 21.0 | 136.6 ± 14.3 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 79.7 ± 7.6 | 89.9 ± 10.0 † | 93.4 ± 8.7 | 83.50 ± 11.4 § | 84.6 ± 9.2 | 86.4 ± 7.3 | 75.1 ± 12.9 | 83.4 ± 10.4 |
| Platelets (103/µL) | 363.5 ± 227.3 | 217.6 ± 54.8 § | 236.9 ± 136.2 | 176.0 ± 57.1 | 260.1 ± 192.9 | 206.1 ± 68.1 | 234.5 ± 103.1 | 221.0 ± 93.2 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.36 ± 0.63 | 1.23 ± 0.31 | 1.20 ± 0.74 | 1.29 ± 0.30 | 1.23 ± 0.30 | 1.13 ± 0.33 | 1.04 ± 0.26 | 1.23 ± 0.30 |
| Nitrates/Creatinine(µM/µmol of creatinine) | 46.92 ± 23.14 | 114.53 ± 89.3 § | 51.55 ± 36.49 | 86.02 ± 83.41 | 59.20 ± 90.80 | 84.77 ± 63.30 | 63.95 ± 41.13 | 75.89 ± 57.49 |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 23.64 ± 3.23 | 27.28 ± 4.79 § | 24.09 ± 4.56 | 26.55 ± 4.26 | 23.64 ± 3.65 | 26.67 ± 4.59 | 24.25 ± 4.24 | 26.30 ± 4.67 |
| CD (103/KPa) | 19.07 ± 10.63 | 19.80 ± 10.99 | 21.27 ± 22.14 | 20.26 ± 8.75 | 19.16 ± 7.90 | 19.60 ± 8.50 | 20.74 ± 11.16 | 16.37 ± 5.25 |
| FMD (%) | 2.88 ± 3.87 | 4.32 ± 7.08 | 4.09 ± 3.36 | 3.00 ± 6.27 | 2.61 ± 5.00 | 4.13 ± 5.16 | 1.05 ± 2.08 | 4.63 ± 7.15 |
| cIMT (mm) | 0.79 ± 0.21 | 0.77 ± 0.18 | 0.72 ± 0.13 | 0.74 ± 0.11 | 0.70 ± 0.14 | 0.79 ± 0.14 | 0.68 ± 0.16 | 0.71 ± 0.15 |
| Indexed LVM (LVM/BSA g/m2) | 81.04 ± 23.96 | 94.00 ± 47.38 | 96.02 ± 31.28 | 91.23 ± 53.50 | 98.59 ± 30.31 | 96.60 ± 64.98 | 86.47 ± 31.45 | 84.49 ± 35.23 |
| EF (%) | 58.81 ± 8.04 | 58.98 ± 7.32 | 57.85 ± 5.64 | 56.21 ± 8.64 | 59.08 ± 7.60 | 54.14 ± 8.91 | 57.84±5.68 | 57.52±8.70 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dalbeni, A.; Ciccarese, C.; Bevilacqua, M.; Benati, M.; Caimmi, C.; Cerrito, L.; Famà, F.; Iacovelli, R.; Mantovani, A.; Meneguzzi, F.M.A.; et al. Effects of Antiangiogenetic Drugs on Microcirculation and Macrocirculation in Patients with Advanced-Stage Renal Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11010030
Dalbeni A, Ciccarese C, Bevilacqua M, Benati M, Caimmi C, Cerrito L, Famà F, Iacovelli R, Mantovani A, Meneguzzi FMA, et al. Effects of Antiangiogenetic Drugs on Microcirculation and Macrocirculation in Patients with Advanced-Stage Renal Cancer. Cancers. 2019; 11(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleDalbeni, Andrea, Chiara Ciccarese, Michele Bevilacqua, Marco Benati, Cristian Caimmi, Luca Cerrito, Federico Famà, Roberto Iacovelli, Anna Mantovani, Francesco Massari Alessandra Meneguzzi, and et al. 2019. "Effects of Antiangiogenetic Drugs on Microcirculation and Macrocirculation in Patients with Advanced-Stage Renal Cancer" Cancers 11, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11010030
APA StyleDalbeni, A., Ciccarese, C., Bevilacqua, M., Benati, M., Caimmi, C., Cerrito, L., Famà, F., Iacovelli, R., Mantovani, A., Meneguzzi, F. M. A., Minuz, P., Montagnana, M., Orsolini, G., Rossini, M., Tortora, G., Viapiana, O., & Fava, C. (2019). Effects of Antiangiogenetic Drugs on Microcirculation and Macrocirculation in Patients with Advanced-Stage Renal Cancer. Cancers, 11(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11010030







