Involving the microRNA Targetome in Esophageal-Cancer Development and Behavior
Abstract
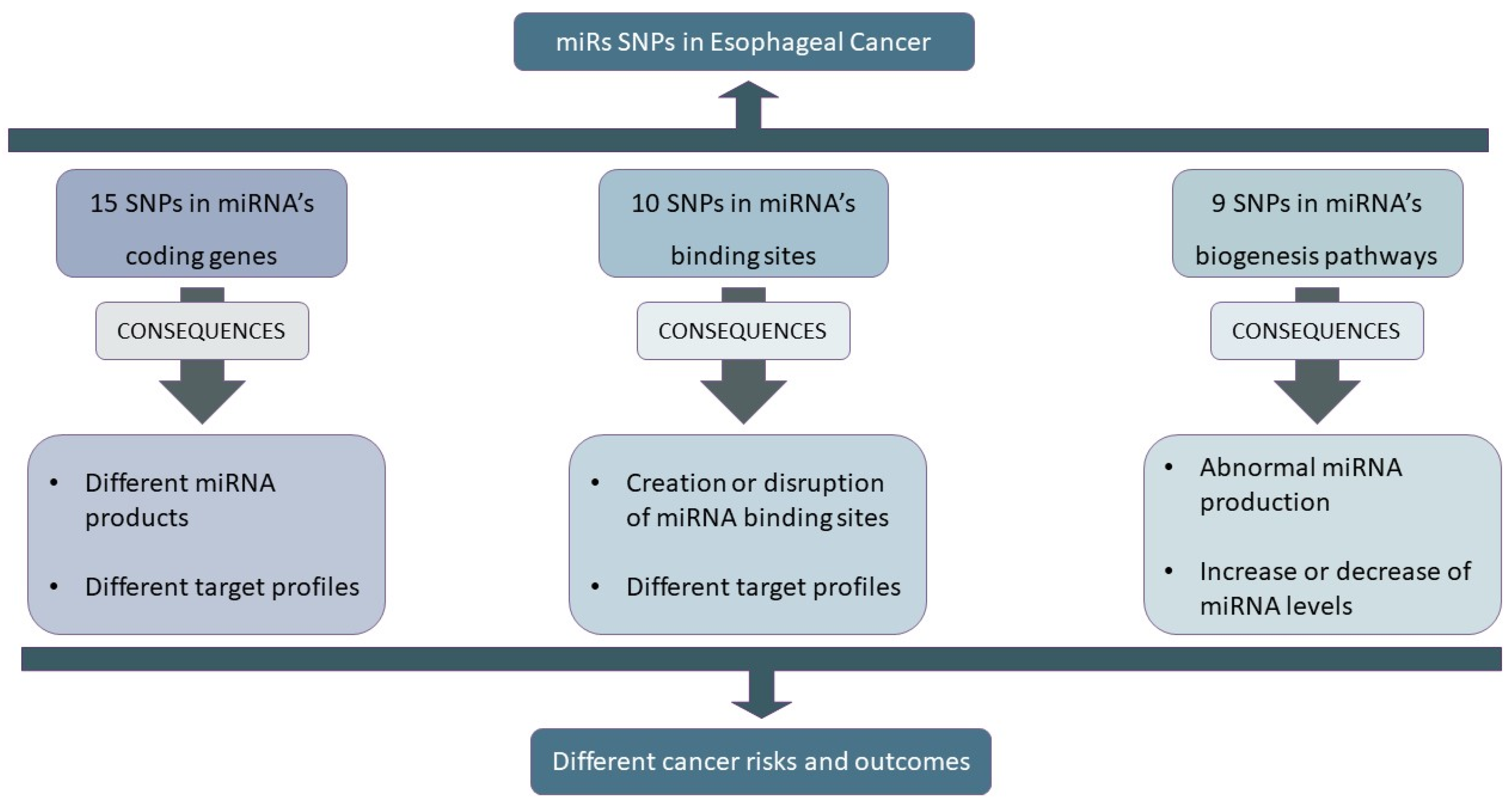
:1. Introduction
2. Evidence Acquisition
3. Evidence Synthesis
3.1. SNPs in miRNA Loci
3.2. SNPs in miRNA-Binding Sites
3.3. SNPs in miRNA Processing Machinery
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohashi, S.; Miyamoto, S.; Kikuchi, O.; Goto, T.; Amanuma, Y.; Muto, M. Recent Advances from Basic and Clinical Studies of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1700–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 359–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweigert, M.; Dubecz, A.; Stein, H.J. Oesophageal cancer—An overview. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamangar, F.; Dores, G.M.; Anderson, W.F. Patterns of Cancer Incidence, Mortality, and Prevalence Across Five Continents: Defining Priorities to Reduce Cancer Disparities in Different Geographic Regions of the World. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2137–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, C.; Bosetti, C.; Malvezzi, M.; Bertuccio, P.; Levi, F.; Negri, E.; La Vecchia, C.; Lunet, N. Patterns and trends in esophageal cancer mortality and incidence in Europe (1980–2011) and predictions to 2015. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arnold, M.; Laversanne, M.; Brown, L.M.; Devesa, S.S.; Bray, F. Predicting the Future Burden of Esophageal Cancer by Histological Subtype: International Trends in Incidence up to 2030. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, C.; Peleteiro, B.; Bento, M.J.; Lunet, N. Trends in gastric and esophageal cancer incidence in northern Portugal (1994-2009) by subsite and histology, and predictions for 2015. Tumori 2017, 103, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buas, M.F.; Onstad, L.; Levine, D.M.; Risch, H.A.; Chow, W.-H.; Liu, G.; Fitzgerald, R.C.; Bernstein, L.; Ye, W.; Bird, N.C.; et al. MiRNA-Related SNPs and Risk of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma and Barrett’s Esophagus: Post Genome-Wide Association Analysis in the BEACON Consortium. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cariati, A.; Casano, A.; Campagna, A.; Cariati, E.; Pescio, G. Prognostic factors influencing morbidity and mortality in esophageal carcinoma. Rev. Hosp. Clín. 2002, 57, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cijs, T.M.; Verhoef, C.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Koppert, L.B.; Tran, T.C.K.; Wijnhoven, B.P.L.; Tilanus, H.W.; de Jonge, J. Outcome of esophagectomy for cancer in elderly patients. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 90, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Bo, Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, E.; Yuan, L. Concurrent neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy could improve survival outcomes for patients with esophageal cancer: a meta-analysis based on random clinical trials. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 20410–20417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Hagen, P.; Hulshof, M.C.C.M.; van Lanschot, J.J.B.; Steyerberg, E.W.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Wijnhoven, B.P.L.; Richel, D.J.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.P.; Hospers, G.A.P.; Bonenkamp, J.J.; et al. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- x2019 Sullivan, K.E.; Hurley, E.T.; Hurley, J.P. Understanding Complete Pathologic Response in Oesophageal Cancer: Implications for Management and Survival. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2015, 2015, e9. [Google Scholar]
- Nariman-Saleh-Fam, Z.; Bastami, M.; Somi, M.H.; Samadi, N.; Abbaszadegan, M.R.; Behjati, F.; Ghaedi, H.; Tavakkoly-Bazzaz, J.; Masotti, A. In silico dissection of miRNA targetome polymorphisms and their role in regulating miRNA-mediated gene expression in esophageal cancer. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 74, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiam, K.; Mayne, G.C.; Watson, D.I.; Woodman, R.J.; Bright, T.F.; Michael, M.Z.; Karapetis, C.S.; Irvine, T.; Phillips, W.A.; Hummel, R.; et al. Identification of microRNA Biomarkers of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Using Next Generation Sequencing. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, M.; Kim, V.N. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Dong, H.; Fan, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, G. Genetic polymorphisms of microRNA machinery genes predict overall survival of esophageal squamous carcinoma. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2018, 32, e22170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pipan, V.; Zorc, M.; Kunej, T. MicroRNA Polymorphisms in Cancer: A Literature Analysis. Cancers 2015, 7, 1806–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, G.; Yan, J.; Noltner, K.; Feng, J.; Li, H.; Sarkis, D.A.; Sommer, S.S.; Rossi, J.J. SNPs in human miRNA genes affect biogenesis and function. RNA 2009, 15, 1640–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moszyńska, A.; Gebert, M.; Collawn, J.F.; Bartoszewski, R. SNPs in microRNA target sites and their potential role in human disease. Open Biol. 2017, 7, e170019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, P.; Krek, A.; Zavolan, M.; Macino, G.; Rajewsky, N. Cell-type-specific signatures of microRNAs on target mRNA expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2746–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Ashurst, J.L.; Bradley, A. Identification of mammalian microRNA host genes and transcription units. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Sevignani, C.; Dumitru, C.D.; Hyslop, T.; Noch, E.; Yendamuri, S.; Shimizu, M.; Rattan, S.; Bullrich, F.; Negrini, M.; et al. Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2999–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, M.; Miao, J.; Guo, Y.; Gao, W.; Cui, Q. An analysis of human microRNA and disease associations. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, H.-M.; Wang, K.; Hu, T.; Shan, G.; Sun, J.; Guo, A.-Y. Genome-wide identification of SNPs in microRNA genes and the SNP effects on microRNA target binding and biogenesis. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Lee, C.G.L. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Associated with MicroRNA Regulation. Biomolecules 2013, 3, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Zeng, L.; Luo, S.; Bai, F.; Zhong, R.; Wu, L.; Huang, G.-L.; Pu, X. Association of microRNA-423 rs6505162 C>A polymorphism with susceptibility and metastasis of colorectal carcinoma. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018, 97, e9846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, P.; Zhu, X.; Geng, Q.; Xia, L.; Sun, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Xu, D. The microRNA-423-3p-Bim Axis Promotes Cancer Progression and Activates Oncogenic Autophagy in Gastric Cancer. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, X.; Zeng, X.; Huang, Y.; Chen, S.; Lin, F.; Yang, G.; Yang, N. miR-423-5p serves as a diagnostic indicator and inhibits the proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 4723–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Ren, J.; Guleng, B. miRNA423-5p regulates cell proliferation and invasion by targeting trefoil factor 1 in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2014, 347, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Han, Z.; Yang, C. Associations of microRNA single nucleotide polymorphisms and disease risk and pathophysiology. Clin. Genet. 2017, 92, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Guan, S.; Liu, F.; Chen, X.; Han, L.; Wang, D.; Nesa, E.U.; Wang, X.; Bao, C.; Wang, N.; et al. Prognostic and diagnostic potential of miR-146a in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, e290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fendereski, M.; Zia, M.F.; Shafiee, M.; Safari, F.; Saneie, M.H.; Tavassoli, M. MicroRNA-196a as a Potential Diagnostic Biomarker for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Investig. 2017, 35, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, B.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Bao, X.; Bai, M. Inhibition of miR-196a affects esophageal cancer cell growth in vitro. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Li, M.; You, W.; Ji, Y.; Cui, X.; Hu, J.; Chen, Y.; Pang, L.; Li, S.; Wei, Y.; et al. A Genetic Variant in miR-124 Decreased the Susceptibility to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Chinese Kazakh Population. Genet. Test Mol. Biomark. 2018, 22, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faluyi, O.O.; Eng, L.; Qiu, X.; Che, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, D.; Ying, N.; Tse, A.; Kuang, Q.; Dodbiba, L.; et al. Validation of microRNA pathway polymorphisms in esophageal adenocarcinoma survival. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, F.; Chen, J.; Guo, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhao, D.; et al. Genetic variants in miR-196a2 and miR-499 are associated with susceptibility to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese Han population. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 4777–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-J.; Wang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Tu, C.; Feng, T.-B.; Qi, C.-J. MicroRNA-124 rs531564 Polymorphism and Cancer Risk: A Meta-analysis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 7905–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; You, W.; Zhu, J.; Cui, X.; Hu, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Wei, Y.; et al. A Genetic Variant in miRNA-219-1 Is Associated with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Chinese Kazakhs. Dis. Mark. 2015, 2015, e541531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Yang, L.; You, W.; Cui, X.; Chen, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, W.; Li, S.; Song, X.; Wei, Y.; et al. Genetic variation in miR-100 rs1834306 is associated with decreased risk for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Kazakh patients in northwest China. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 7332–7340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Lu, T.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, M.; Kolluri, V.K.; Qiu, L.; et al. miR-449b rs10061133 and miR-4293 rs12220909 polymorphisms are associated with decreased esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in a Chinese population. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 8789–8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Qu, H.; Luo, M.; Wang, P.; Song, C.; Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; Dai, L. MicroRNAs related polymorphisms and genetic susceptibility to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2014, 289, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Yang, S.; Chaugai, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.W. Meta-analysis of Hsa-mir-499 polymorphism (rs3746444) for cancer risk: evidence from 31 case-control studies. BMC Med. Genet. 2014, 15, e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, J.; Xu, J.; Du, J. The genetic association between pri-miR-34b/c polymorphism (rs4938723 T > C) and susceptibility to cancers: evidence from published studies. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 12525–12534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.-W.; Huang, Y.-C.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Hua, K.-T.; Huang, Y.-T.; Chiang, T.-H.; Chen, J.-S.; Huang, P.-M.; Hsu, H.-H.; Kuo, S.-W.; et al. Association of miRNA-related genetic polymorphisms and prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Li, M.; Hu, C.; Duan, H. Prognostic role of microRNA polymorphisms in patients with advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma receiving platinum-based chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 73, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Zhou, R.-M.; Wang, G.-Y.; Wang, C.-M.; Chen, Z.-F.; Liu, W. Hsa-miR-196a2 functional SNP is associated with the risk of ESCC in individuals under 60 years old. Biomarkers 2014, 19, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yang, X.; Ru, G.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xing, C.; Wu, Y.; Cao, J. miR-146a gene polymorphism rs2910164 and the risk of digestive tumors: A meta-analysis of 21 case-control studies. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Wang, X.; Zheng, L.; Shi, Y.; Wang, L.; Shao, A.; Tang, W.; Ding, G.; Liu, C.; Liu, R.; et al. Hsa-miR-34b/c rs4938723 T>C and hsa-miR-423 rs6505162 C>A polymorphisms are associated with the risk of esophageal cancer in a Chinese population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Vogelsang, M.; Schafer, G.; Matejcic, M.; Parker, M.I. MicroRNA polymorphisms and environmental smoke exposure as risk factors for oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Zheng, L.; Liu, S.; Yin, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Shao, A.; Tang, W.; Ding, G.; et al. MiR-196a2 rs11614913 T > C polymorphism and risk of esophageal cancer in a Chinese population. Hum. Immunol. 2013, 74, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Sun, G.-P.; Zou, Y.-F.; Fan, L.-L.; Song, B. Quantitative assessment of the association between miR-196a2 rs11614913 polymorphism and gastrointestinal cancer risk. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umar, M.; Upadhyay, R.; Prakash, G.; Kumar, S.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Mittal, B. Evaluation of common genetic variants in pre-microRNA in susceptibility and prognosis of esophageal cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2013, 52, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Pan, Y.; Cho, W.C.; Xu, Y.; Gu, L.; Nie, Z.; Chen, L.; Song, G.; Gao, T.; Li, R.; et al. The association between four genetic variants in microRNAs (rs11614913, rs2910164, rs3746444, rs2292832) and cancer risk: evidence from published studies. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Wang, K.K.; Gu, J.; Yang, H.; Lin, J.; Ajani, J.A.; Wu, X. Genetic variations in microRNA-related genes are novel susceptibility loci for esophageal cancer risk. Cancer Prev. Res. 2008, 1, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, T.J. Wanted: regulatory SNPs. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 439–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sethupathy, P.; Collins, F.S. MicroRNA target site polymorphisms and human disease. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, C.; Shi, J.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, M.; Lin, D. A functional BRCA1 coding sequence genetic variant contributes to risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2309–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, I.; Ajay, S.S.; Yook, J.I.; Kim, H.S.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, N.H.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Athey, B.D. New class of microRNA targets containing simultaneous 5′-UTR and 3-′UTR interaction sites. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Z. miR-502 medaited histone methyltransferase SET8 expression is associated with outcome of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, e32921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Bai, Y.H.; Sun, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.B.; Cai, B. SNP at miR-483-5p-binding site in the 3’-untranslated region of the BSG gene is associated with susceptibility to esophageal cancer in a Chinese population. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, e15027735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Shao, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Xiao, D.; Huang, F. The Functional Variant in the 3’UTR of PTPRT with the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Chinese Population. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, C.; Li, M.; Tang, X.; Lu, C.; Li, H.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, M. Association of a genetic variation in a miR-191 binding site in MDM4 with risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, J.; Guo, H.; Xu, X.; Xiong, G.; Guan, X.; Liu, B.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, K.; Bai, Y. MiR-196a binding-site SNP regulates RAP1A expression contributing to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma risk and metastasis. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 2147–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mullany, L.E.; Wolff, R.K.; Herrick, J.S.; Buas, M.F.; Slattery, M.L. SNP Regulation of microRNA Expression and Subsequent Colon Cancer Risk. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WeiGang, G.; Di, G.; XuGuang, P.; Dong, X.; YingYong, H. Expression of HER4 in esophageal carcinoma tissues and its clinical significance. Tumor 2009, 29, 673–676. [Google Scholar]
- Patrao, A.S.; Dias, F.; Teixeira, A.L.; Maurício, J.; Medeiros, R. XPO5 genetic polymorphisms in cancer risk and prognosis. Pharmacogenomics 2018, 19, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; He, J.; Pu, W.; Peng, Y. The Role of Exportin-5 in MicroRNA Biogenesis and Cancer. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Larrea, C.F.; Navarro, A.; Tejero, R.; Tovar, N.; Diaz, T.; Cibeira, M.T.; Rosinol, L.; Ferrer, G.; Rovira, M.; Rozman, M.; et al. Impact of MiRSNPs on survival and progression in patients with multiple myeloma undergoing autologous stem cell transplantation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3697–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Zhao, J.; He, J.; Qi, D.; Wang, L.; Ma, X.; Liu, P. Genetic variants in the MicroRNA biosynthetic pathway Gemin3 and Gemin4 are associated with a risk of cancer: a meta-analysis. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Location | SNP | Population | Type of Study | Sample Size | Relevant Genotype | Outcome | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pri-miR-124-1 | rs531564 | Kazach | Case controls | 239 cases/227 controls | CG+GG | ↓ ESCC risk | Wu et al. (2018) [35] |
| Pri-miR-124-1 | rs531564 | Canadian | Cohort | 368 cases | G allele | ↑ EAC OS | Faluyi et al. (2017) [36] |
| Pre-miR-423 | rs6505162 | Iranian | Case control | 200 cases/300 controls | AA | ↓ EC risk | Nariman-Saleh-Fam et al. (2016) [14] |
| Pre-miR-196a2 | rs11614913 | Chinese | Case control | 1400 cases/2185 controls | CC | ↑ ESCC risk | Shen et al. (2016) [37] |
| Pre-miR-499 | rs3746444 | C allele | |||||
| Pre-miR-4467 Pre-miR-3117 | rs12534337 rs7526812 | Mixed ethnicity | Case control | 2515 EA cases 3295 BE cases 3207 controls | A allele C allele | ↑ BE and ↑ EAC risk | Buas et al. (2015) [8] |
| Pri-miR-124-1 | rs531564 | Chinese | Meta analysis | 1738 cases/1961 controls | GG | ↓ ESCC risk | Li et al. (2015) [38] |
| Pre-miR-219-1 | rs107822 | Kazach | Case control | 248 cases/300 controls | AA/A allele | ↓ ESCC risk | Song et al. (2015) [39] |
| rs213210 | T allele | ||||||
| Pre-miR-100 | rs1834306 | Kazach | Case control | 248 cases/300 controls | CC/C allele | ↓ ESCC risk | Zhu et al. (2015) [40] |
| Pre-miR-499b | rs10061133 | Chinese | Case control | 773 cases/882 controls | GG | ↓ ESCC risk | Zhang et al. (2015) [41] |
| Pre-miR-4293 | rs12220909 | C allele | |||||
| Pre-miR-196a-2 | rs11614913 | Chinese | Case control | 381 cases/426 controls | TT | ↓ ESCC risk | Qu et al. (2014) [42] |
| Pre-miR-499 | rs3746444 | Mixed ethnicity | Meta analysis | 12799 cases/14507 controls | TC+CC | ↑ EC risk in the asian population | Chen et al. (2014) [43] |
| Pri-miR-34b/c | rs4938723 | Mixed ethnicity | Meta analysis | 7753 cases/8014 controls | CC | ↓ ESCC risk in the asian population | Li et al. (2014) [44] |
| Pre-miR-608 | rs4919510 | Taiwan | Cohort | 504 cases | GC | ↑ OS and ↑ PFS in ESCC | Yang et al. (2014) [45] |
| Pre-miR-146a | rs2910164 | Chinese | Cohort | 378 cases | CG+GG | ↑ risk of severe hematological toxicity in ESCC | Wu et al. (2014) [46] |
| Pre-miR-196a2 | rs11614913 | TT | ↓ OS ESCC | ||||
| Pre-miR-125a | rs12976445 | TT | ↓ OS ESCC | ||||
| Pre-miR-196a-2 | rs11614913 | Chinese | Case control | 597 cases/597 controls | CT+TT | ↑ ESCC risk | Wang et al. (2014) [47] |
| Pre-miR-146a | rs2910164 | Mixed ethnicity | Meta analysis | 790 cases/814 controls | GC+GG | ↑ EC risk in the asian population | Xu et al. (2014) [48] |
| Pre-miR-423 | rs6505162 | Chinese | Case control | 629 cases/686 controls | AA | ↑ ESCC risk | Yin et al. (2013) [49] |
| Pre-miR-423 | rs6505162 | Black ethnicity | Case control | 368 cases/583 controls | C allele | ↑ ESCC risk | Wang et al. (2013) [50] |
| 5′-UTR miR-26a-1 | rs7372209 | Mixed ethnicity | 197 cases/420 controls | T allele | ↑ ESCC risk | ||
| Pre-miR-196a-2 | rs11614913 | Chinese | Case control | 380 cases/380 controls | CC | ↓ ESCC risk in women | Wei et al. (2013) [51] |
| Pre-miR-196a-2 | rs11614913 | Mixed ethnicity | Meta analysis | 4947 cases and 5642 controls | C allele | ↑ EC risk | Wang et al. (2013) [52] |
| Pre-miR-196a2 | rs11614913 | Indian | Meta analysis | 289 cases/309 controls | T allele | ↓ OS in ESCC | Umar et al. (2013) [53] |
| Pre-miR-146a | rs2910164 | C allele | |||||
| Pre-miR-499 | rs3746444 | C allele | |||||
| Pre-miR-423 | rs6505162 | A allele | |||||
| Pre-miR-146a | rs2910164 | Mixed ethnicity | Meta analysis | 772 cases/779 controls | C allele | ↓ EC risk in the asian population | He et al. (2012) [54] |
| Pre-miR-423 | rs6505162 | Caucasian | Case control | 346 cases/346 controls | AC+AA | ↓ EC risk | Ye et al. (2008) [55] |
| miRNA Binding Site | SNP | Population | Type of Study | Sample Size | Relevant Genotype | Outcome | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3′-UTR of KIAA0423 | rs1053667 | Canadian | Cohort | 368 cases | C allele | ↑ OS in EAC | Faluyi et al. (2017) [36] |
| 3′-UTR of SET8 | rs16917496 | Chinese | Case control | 180 cases/142 controls | CC | ↑ OS and ↑ Post-surgery survival in ESCC | Wang et al. (2016) [60] |
| 3′-UTR of BSG | rs11473 | Chinese | Case control | 624 cases/636 controls | TT/T allele | ↑ risk of ESCC | Li et al. (2016) [61] |
| 3′-UTR of RDH8 | rs1644730 | Mixed ethnicity | Case control | 2515 EA cases 3295 BE cases 3207 controls | A allele | ↓ BE and ↓ EA risk | Buas et al. (2015) [8] |
| 3′-UTR of PTPRT | rs2866943 | Chinese | Case control | 790 cases/749 controls | CT/TT | ↓ risk of ESCC | Yao et al. (2015) [62] |
| rs6029959 | CC/AC | ↑ risk of ESCC | |||||
| 3′-UTR of ErbB4 | rs1595066 | Chinese | Case control | 381 cases/426 controls | AA/A allele | ↓ risk of ESCC | Qu et al. (2014) [42] |
| Coding sequence of BRCA1 | rs799917 | Jinan | Case control | 540 cases/550 controls | CC | ↑ risk of ESCC | Zhang et al. (2013) [58] |
| Huaian | 588 cases/600 controls | ||||||
| 3′-UTR of MDM4 | rs4245739 | Jinan | Case control | 540 cases/550 controls | AC+CC | ↓ risk of ESCC | Zhou et al. (2013) [63] |
| Huaian | 588 cases/600 controls | ||||||
| 3′-UTR of RAP1A | rs6573 | Chinese | Case control | 537 cases and 608 controls | CC | ↑ risk of metastasis in ESCC | Wang et al. (2012) [64] |
| Gene | SNP | Population | Type of Study | Sample Size | Relevant Genotype | Outcome | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XPO5 | rs11077 | Chinese | Cohort | 128 cases | AA | ↑ OS in ESCC | Wang et al. (2018) [17] |
| GEMIN 3 | rs197412 | Canadian | Cohort | 368 cases | C allele | ↑ OS EAC | Faluyi et al. (2017) [36] |
| GEMIN 4 | rs910924 | North American | Case control | 346 cases/346 controls | G allele | Haplotype associated with ↓ EC risk | Ye et al. (2008) [55] |
| rs2740348 | C allele | ||||||
| rs7813 | G allele | ||||||
| rs910925 | G allele | ||||||
| rs3744741 | C allele | ||||||
| rs1062923 | A allele | ||||||
| rs4968104 | T allele |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dias, F.; Morais, M.; Teixeira, A.L.; Medeiros, R. Involving the microRNA Targetome in Esophageal-Cancer Development and Behavior. Cancers 2018, 10, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10100381
Dias F, Morais M, Teixeira AL, Medeiros R. Involving the microRNA Targetome in Esophageal-Cancer Development and Behavior. Cancers. 2018; 10(10):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10100381
Chicago/Turabian StyleDias, Francisca, Mariana Morais, Ana Luísa Teixeira, and Rui Medeiros. 2018. "Involving the microRNA Targetome in Esophageal-Cancer Development and Behavior" Cancers 10, no. 10: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10100381
APA StyleDias, F., Morais, M., Teixeira, A. L., & Medeiros, R. (2018). Involving the microRNA Targetome in Esophageal-Cancer Development and Behavior. Cancers, 10(10), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10100381








