Characterization of PEG-Modified Composite Membranes for Microfluidic Oxygenator Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
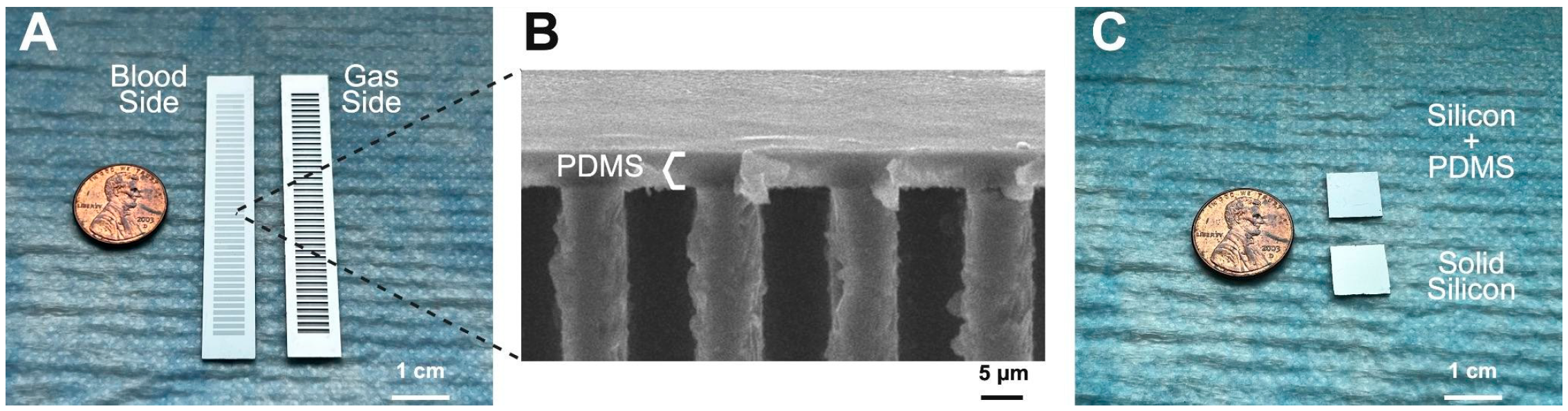
2.1. PDMS Membrane Fabrication
2.2. PEG Coating Procedure
2.3. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Analysis
2.4. Contact Angle Goniometry
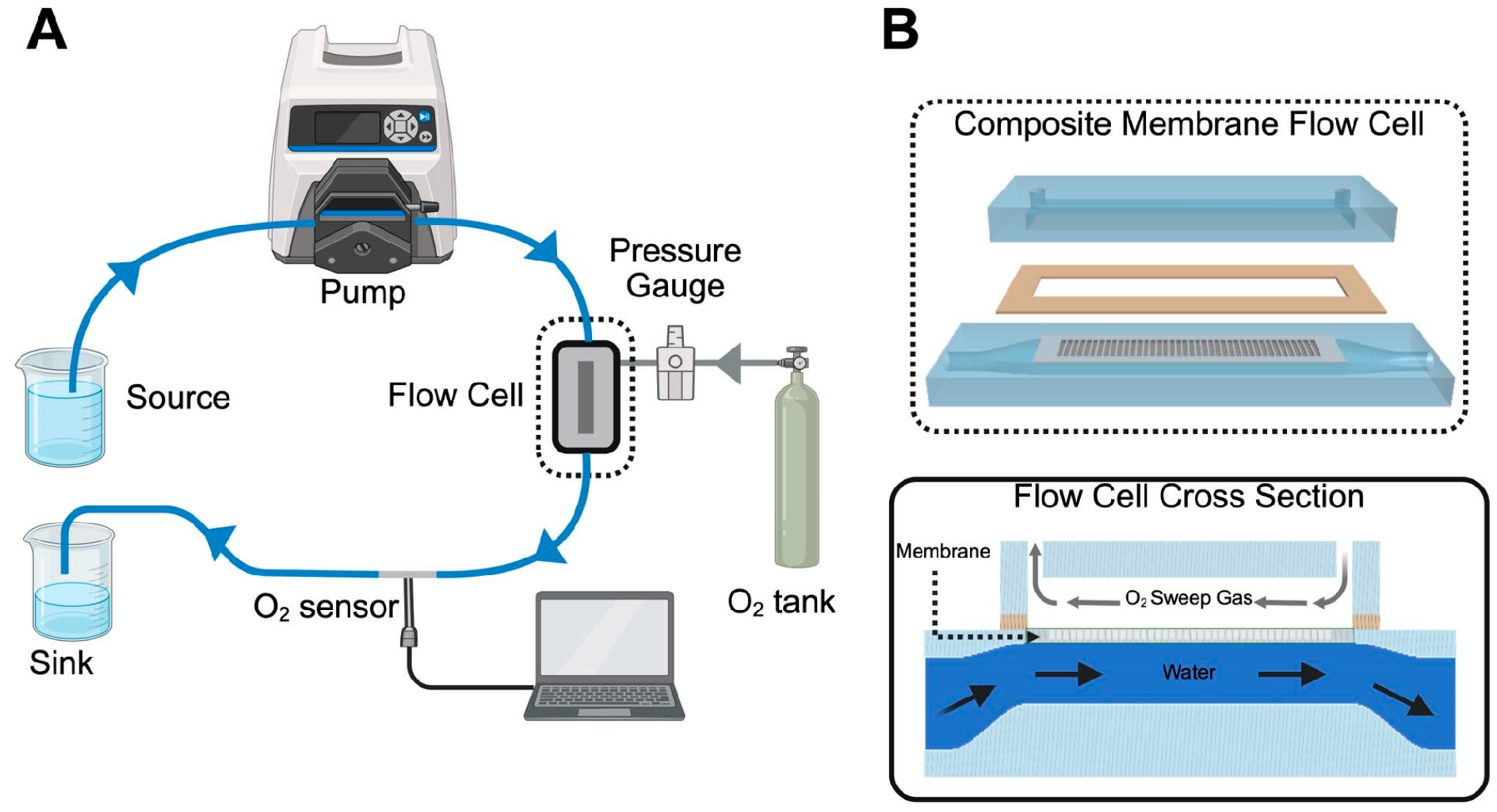
2.5. Oxygen Flux Measurements
2.6. Protein Adsorption Characterization
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
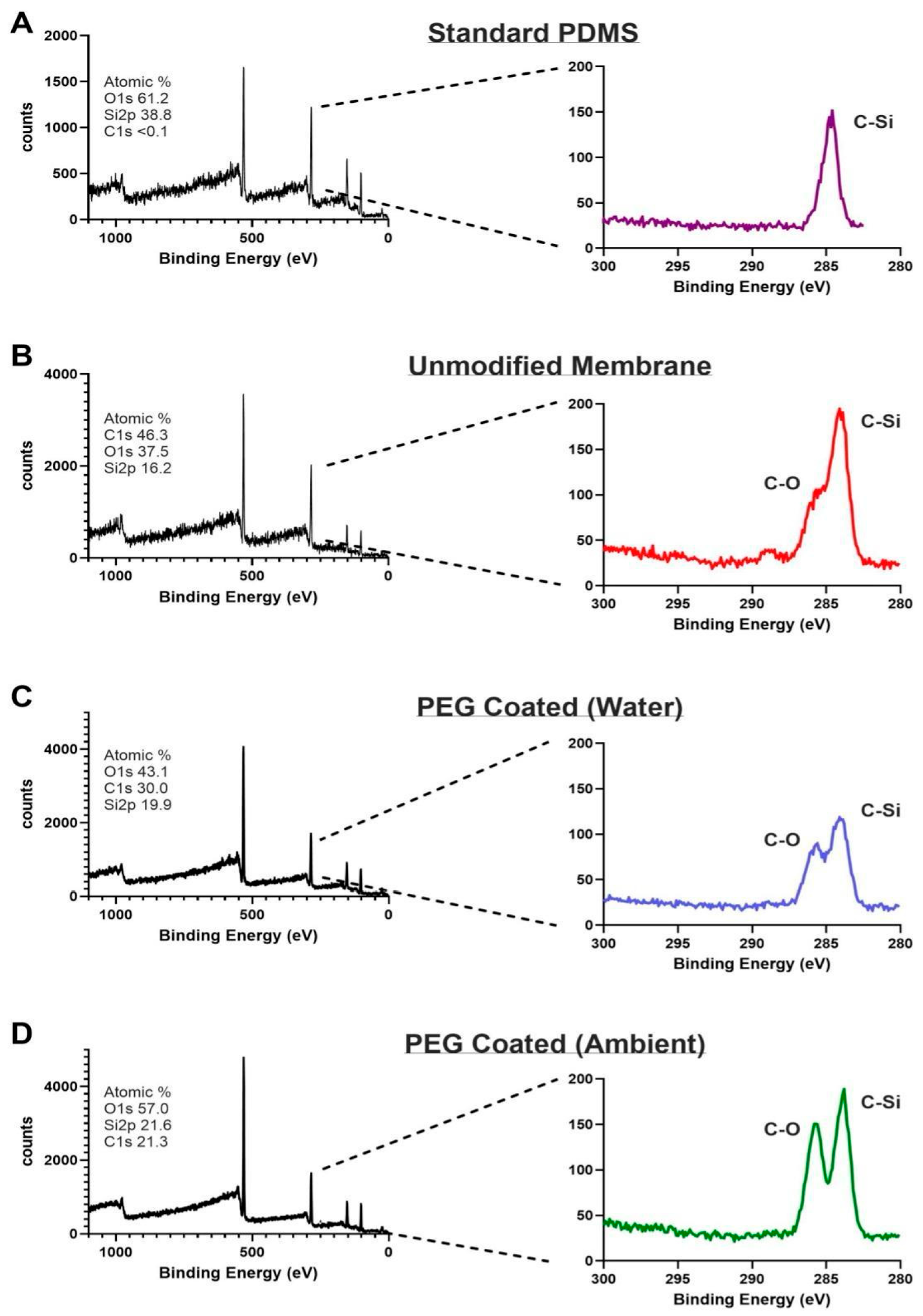
3.1. XPS
3.2. Contact Angles
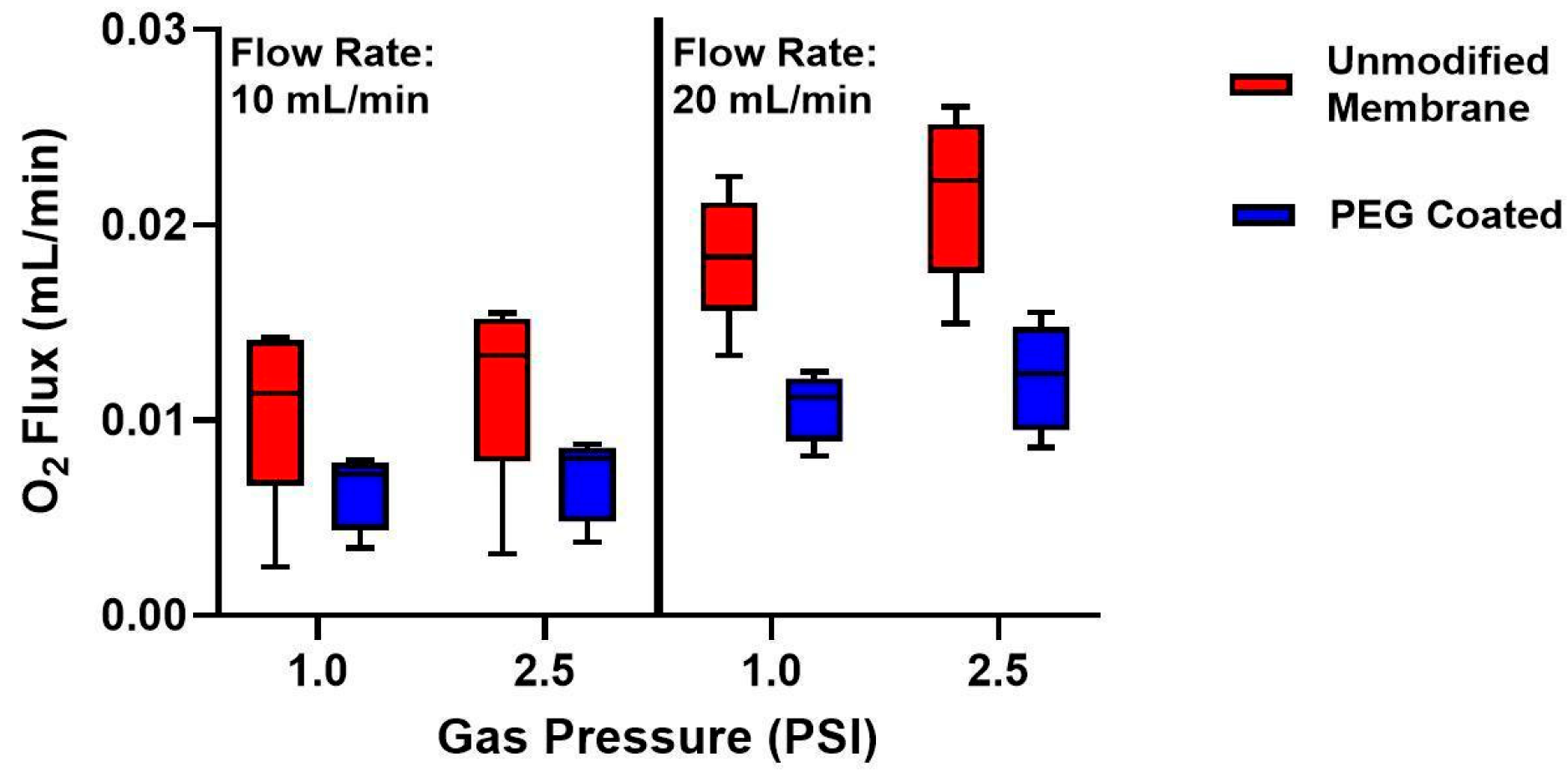
3.3. Oxygen Fluxes
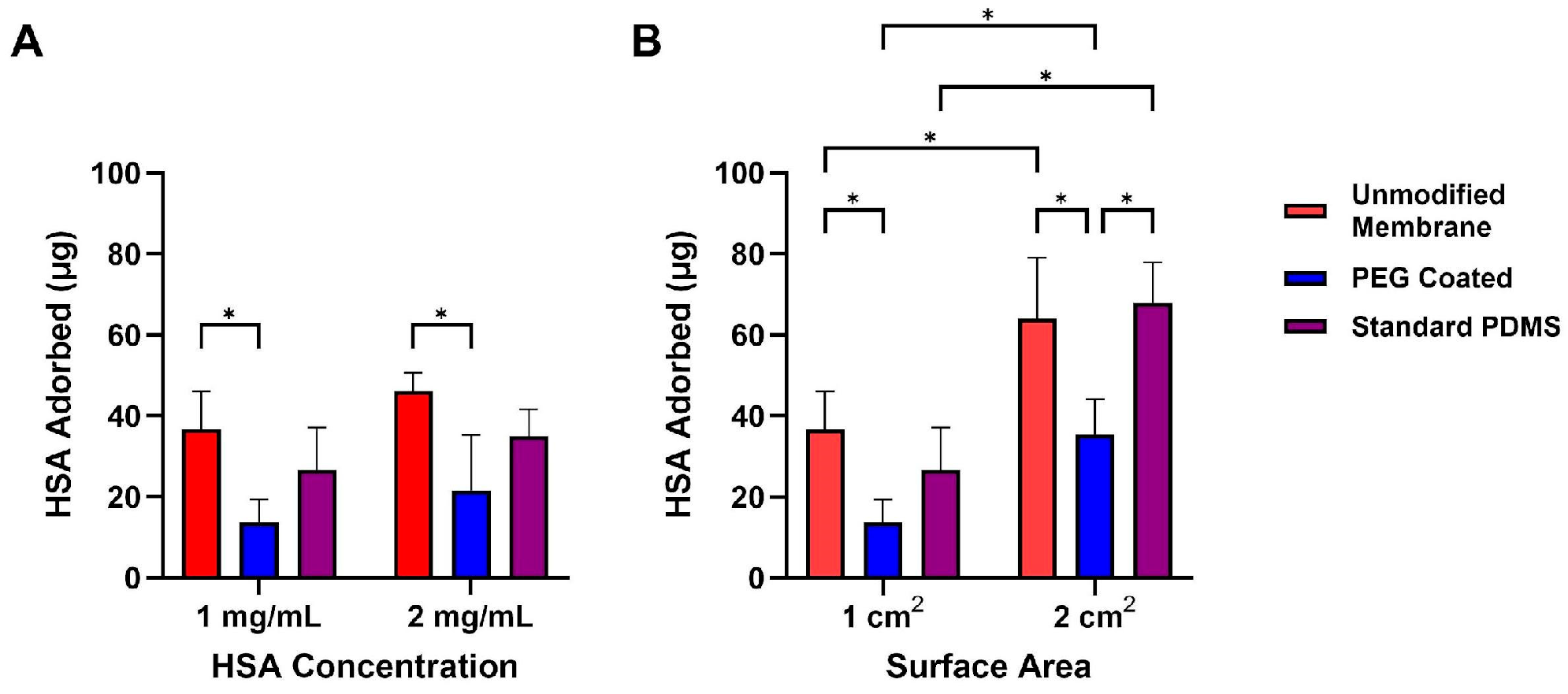
3.4. Protein Adsorption
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ECMO | Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenator |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
| HSA | Human serum albumin |
| PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| PVA | Polyvinyl Alcohol |
| SOI | Silicon-on-insulator |
| IPA | Isopropyl Alcohol |
| BCA | Bicinchoninic Acid assay |
| WCA | Water Contact Angle |
| PMP | Polymethylpentene |
References
- Rabah, H.; Rabah, A. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO): What We Need to Know. Cureus 2022, 14, e26735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.; Khalpey, Z.; Smith, R.; Burkhoff, D.; Kociol, R.D. Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Cardiogenic Shock and Cardiac Arrest: Cardinal Considerations for Initiation and Management. Circ Heart Fail. 2018, 11, e004905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treml, B.; Breitkopf, R.; Bukumirić, Z.; Bachler, M.; Boesch, J.; Rajsic, S. ECMO Predictors of Mortality: A 10-Year Referral Centre Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staessens, S.; Moussa, M.D.; Pierache, A.; Rauch, A.; Rousse, N.; Boulleaux, E.; Ung, A.; Desender, L.; Pradines, B.; Vincentelli, A.; et al. Thrombus formation during ECMO: Insights from a detailed histological analysis of thrombus composition. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 20, 2058–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Themas, K.; Zisis, M.; Kourek, C.; Konstantinou, G.; D’anna, L.; Papanagiotou, P.; Ntaios, G.; Dimopoulos, S.; Korompoki, E. Acute Ischemic Stroke during Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO): A Narrative Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Maskey, A. Anticoagulation in ECMO patients: An overview. Indian J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021, 37, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, S.R.; Murphree, C.R.; Zonies, D.; Meyer, A.D.; Mccarty, O.J.T.; Deloughery, T.G.; Shatzel, J.J. Thrombosis and Bleeding in Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) Without Anticoagulation: A Systematic Review. ASAIO J. 2021, 67, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher-Sandersjöö, A.; Thelin, E.P.; Bartek, J.; Elmi-Terander, A.; Broman, M.; Bellander, B.-M. Management of intracranial hemorrhage in adult patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO): An observational cohort study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0190365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimbel, A.A.; Hsiao, J.C.; Kim, E.S.; Lewis, D.J.; Risoleo, T.F.; Urban, J.N.; Borenstein, J.T. A high gas transfer efficiency microfluidic oxygenator for extracorporeal respiratory assist applications in critical care medicine. Artif. Organs 2021, 45, E247–E264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimbel, A.A.; Flores, E.; Koo, A.; García-Cardeña, G.; Borenstein, J.T. Development of a biomimetic microfluidic oxygen transfer device. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3227–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potkay, J.A. The promise of microfluidic artificial lungs. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 4122–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharia, A.; Abada, E.; Feinberg, B.; Yeager, T.; Moses, W.; Park, J.; Blaha, C.; Wright, N.; Padilla, B.; Roy, S. Silicon Micropore-Based Parallel Plate Membrane Oxygenator. Artif. Organs 2018, 42, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abada, E.N.; Feinberg, B.J.; Roy, S. Evaluation of silicon membranes for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). Biomed. Microdevices 2018, 20, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, W.-H.; Wang, M.-J.; Chang, C.-W.; Wei, T.-C.; Lai, J.-Y.; Tsai, W.-B.; Lee, C. Improvement of hemocompatibility on materials by photoimmobilization of poly(ethylene glycol). J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 9991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yuan, L.; Song, W.; Wu, Z.; Li, D. Biocompatible polymer materials: Role of protein–surface interactions. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 1059–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Estevez, A.M.; Gref, R.; Alonso, M.J. A journey through the history of PEGylated drug delivery nanocarriers. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2024, 14, 2026–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovach, K.M.; Capadona, J.R.; Gupta, A.S.; Potkay, J.A. The effects of PEG-based surface modification of PDMS microchannels on long-term hemocompatibility: PEG-Based Surface Modification of PDMS Microchannels. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2014, 102, 4195–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanei, Z.; Ghanbari, T.; Sharif, A. Polyethylene glycol-grafted graphene oxide nanosheets in tailoring the structure and reverse osmosis performance of thin film composite membrane. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauvelt, D.G.; Higgins, N.C.; Hesek, A.; De, B.N.; Wright, N.; Nithianandam, P.; Blaha, C.; Moyer, J.; Chui, B.W.; Baltazar, F.J.; et al. A silicon membrane microfluidic oxygenator for use as an artificial placenta with minimal anticoagulation. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2025, 10, e70037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusubramaniam, L.; Lowe, R.; Fissell, W.H.; Li, L.; Marchant, R.E.; Desai, T.A.; Roy, S. Hemocompatibility of Silicon-Based Substrates for Biomedical Implant Applications. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 39, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gago, D.; Corvo, M.C.; Chagas, R.; Ferreira, L.M.; Coelhoso, I. Protein Adsorption Performance of a Novel Functionalized Cellulose-Based Polymer. Polymers 2022, 14, 5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlady, V.; Buijs, J.; Jennissen, H.P. [26] Methods for studying protein adsorption. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 309, pp. 402–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Zheng, Z.; Fan, W.; Mao, C.; Shi, J.; Li, L. Surface monofunctionalized polymethyl pentene hollow fiber membranes by plasma treatment and hemocompatibility modification for membrane oxygenators. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 362, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popat, K.C.; Sharma, S.; Desai, T.A. Quantitative XPS Analysis of PEG-Modified Silicon Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 5185–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Yang, F.; Xin, H.; Wang, L.; Gao, C. Oxygen-Rich Polymer Polyethylene Glycol-Functionalized Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Toward Air-Stable n-Type Thermoelectric Materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 26482–26489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gökaltun, A.; Kang, Y.B.; Yarmush, M.L.; Usta, O.B.; Asatekin, A. Simple Surface Modification of Poly(dimethylsiloxane) via Surface Segregating Smart Polymers for Biomicrofluidics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Su, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, A.; Wang, L.; Deng, X.; Chen, Z.; Fan, Y. Comparison of hemodynamic features and thrombosis risk of membrane oxygenators with different structures: A numerical study. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 159, 106907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, B.P.N.; Nguyen, B.T.D.; Jeong, I.-S.; Kim, J.F. Hemocompatibility challenge of membrane oxygenator for artificial lung technology. Acta Biomater. 2022, 152, 19–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachaux, J.; Hwang, G.; Arouche, N.; Naserian, S.; Harouri, A.; Lotito, V.; Casari, C.; Lok, T.; Menager, J.B.; Issard, J.; et al. A compact integrated microfluidic oxygenator with high gas exchange efficiency and compatibility for long-lasting endothelialization. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 4791–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdam, A.S.; Talabazar, F.R.; Jafarpour, M.; Koşar, A.; Cebeci, F.Ç.; Ghorbani, M. New Nanofiber Composition for Multiscale Bubble Capture and Separation. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 39959–39969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Ingole, P.G.; Yun, S.; Choi, W.; Kim, J.; Lee, H. Water vapor removal using CA/PEG blending materials coated hollow fiber membrane. J. Chem. Technol. Amp. Biotech. 2015, 90, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crago, M.; Lee, A.; Hoang, T.P.; Talebian, S.; Naficy, S. Protein adsorption on blood-contacting surfaces: A thermodynamic perspective to guide the design of antithrombogenic polymer coatings. Acta Biomater. 2024, 180, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brash, J.L.; Horbett, T.A.; Latour, R.A.; Tengvall, P. The blood compatibility challenge. Part 2: Protein adsorption phenomena governing blood reactivity. Acta Biomater. 2019, 94, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pflaum, M.; Kühn-Kauffeldt, M.; Schmeckebier, S.; Dipresa, D.; Chauhan, K.; Wiegmann, B.; Haug, R.J.; Schein, J.; Haverich, A.; Korossis, S. Endothelialization and characterization of titanium dioxide-coated gas-exchange membranes for application in the bioartificial lung. Acta Biomater. 2017, 50, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Yin, H.; Fan, W.; Zhang, T.; Li, L.; Mao, C. Polyethylene glycol acrylate-grafted polysulphone membrane for artificial lungs: Plasma modification and haemocompatibility improvement. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 10, 065022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Higgins, N.C.; Blauvelt, D.G.; Roy, S. Characterization of PEG-Modified Composite Membranes for Microfluidic Oxygenator Applications. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16121383
Higgins NC, Blauvelt DG, Roy S. Characterization of PEG-Modified Composite Membranes for Microfluidic Oxygenator Applications. Micromachines. 2025; 16(12):1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16121383
Chicago/Turabian StyleHiggins, Nicholas C., David G. Blauvelt, and Shuvo Roy. 2025. "Characterization of PEG-Modified Composite Membranes for Microfluidic Oxygenator Applications" Micromachines 16, no. 12: 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16121383
APA StyleHiggins, N. C., Blauvelt, D. G., & Roy, S. (2025). Characterization of PEG-Modified Composite Membranes for Microfluidic Oxygenator Applications. Micromachines, 16(12), 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16121383






