Step-Double-Zone-JTE for SiC Devices with Increased Tolerance to JTE Dose and Surface Charges
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Device Structure
2.2. Fabrication Procedure
3. Results
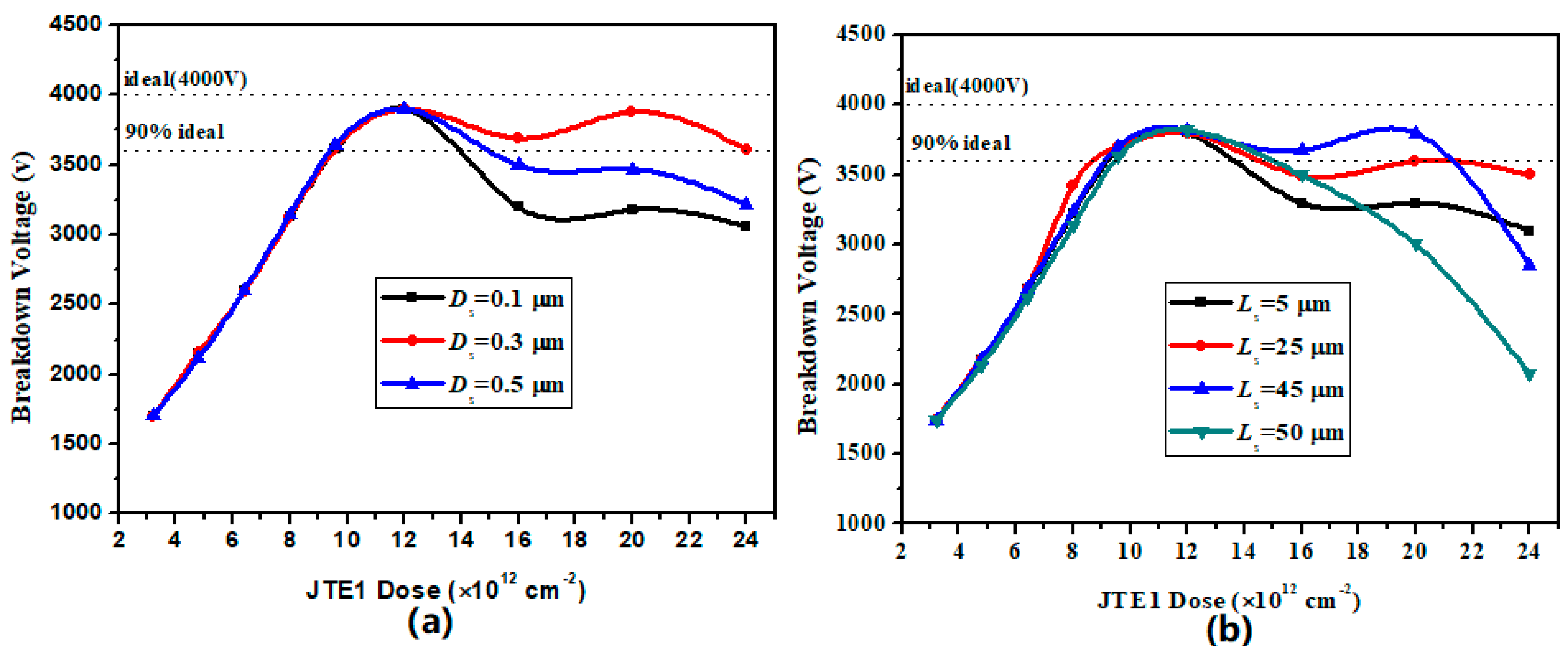
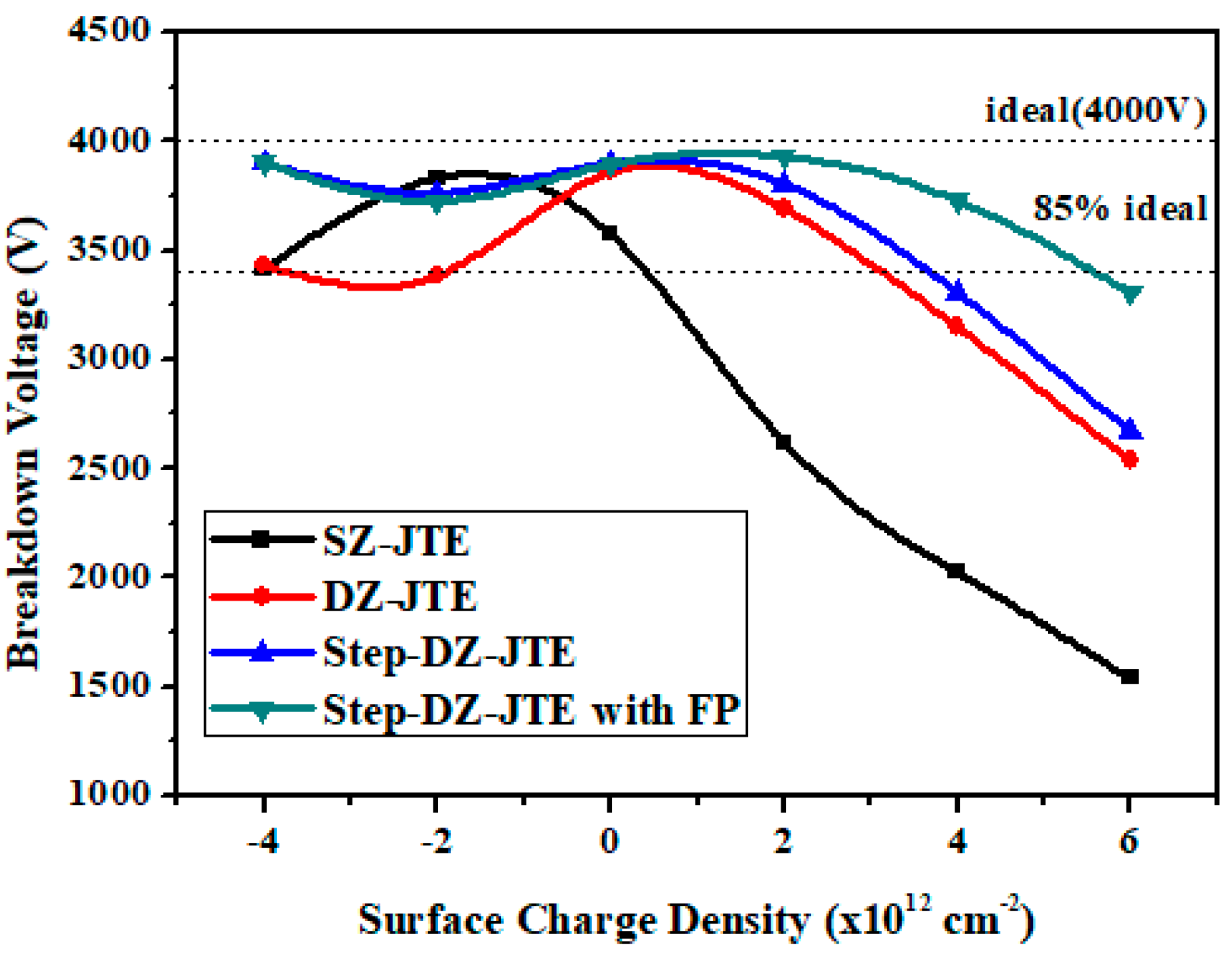
3.1. Simulation Optimization of the DZ-JTE
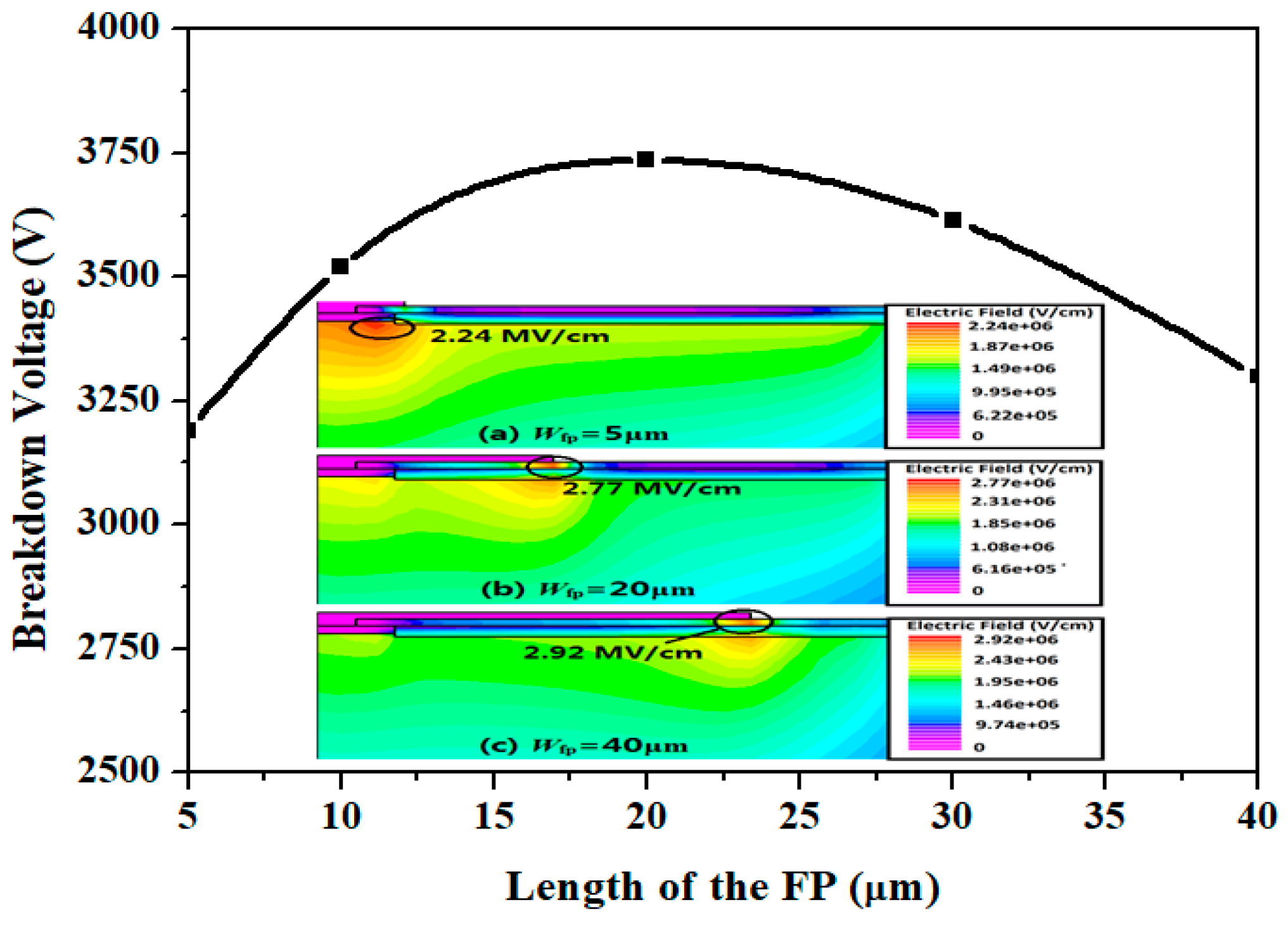
3.2. Simulation Optimization of the Step-DZ-JTE with FP
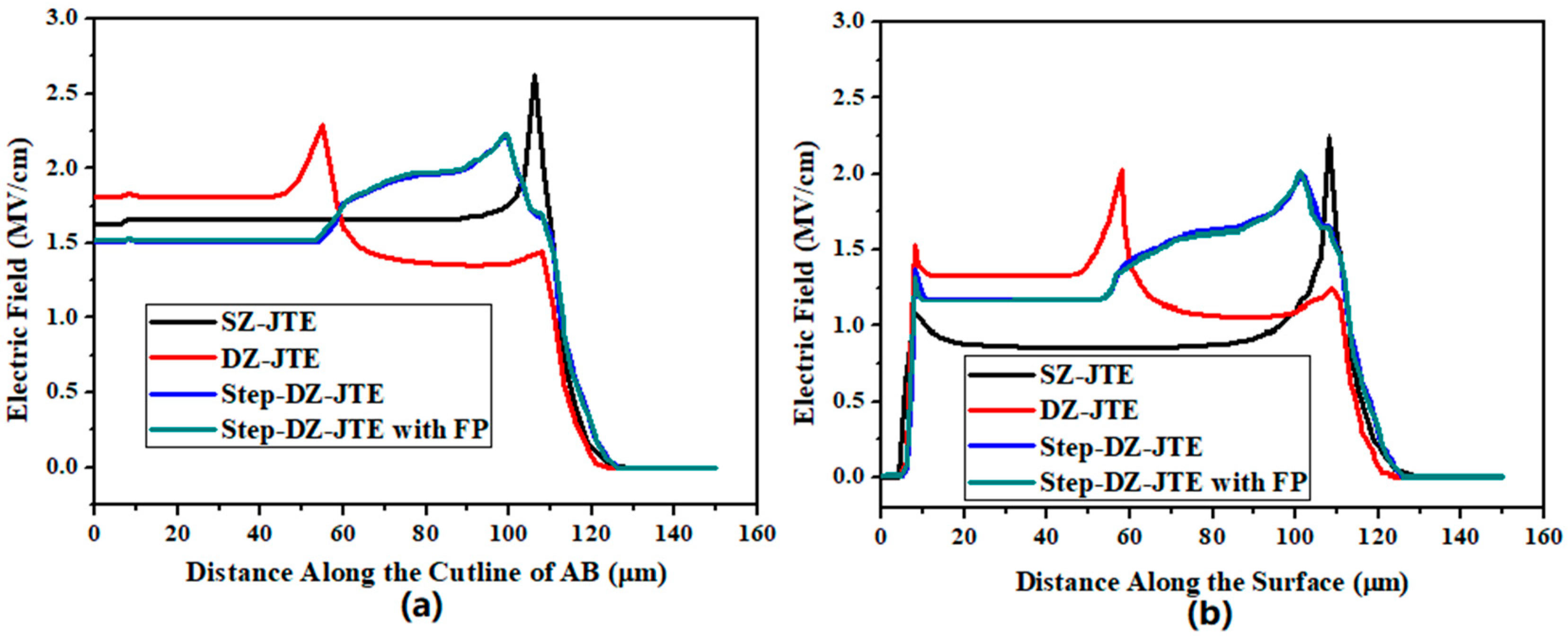
3.3. Compare Electric Field Distribution
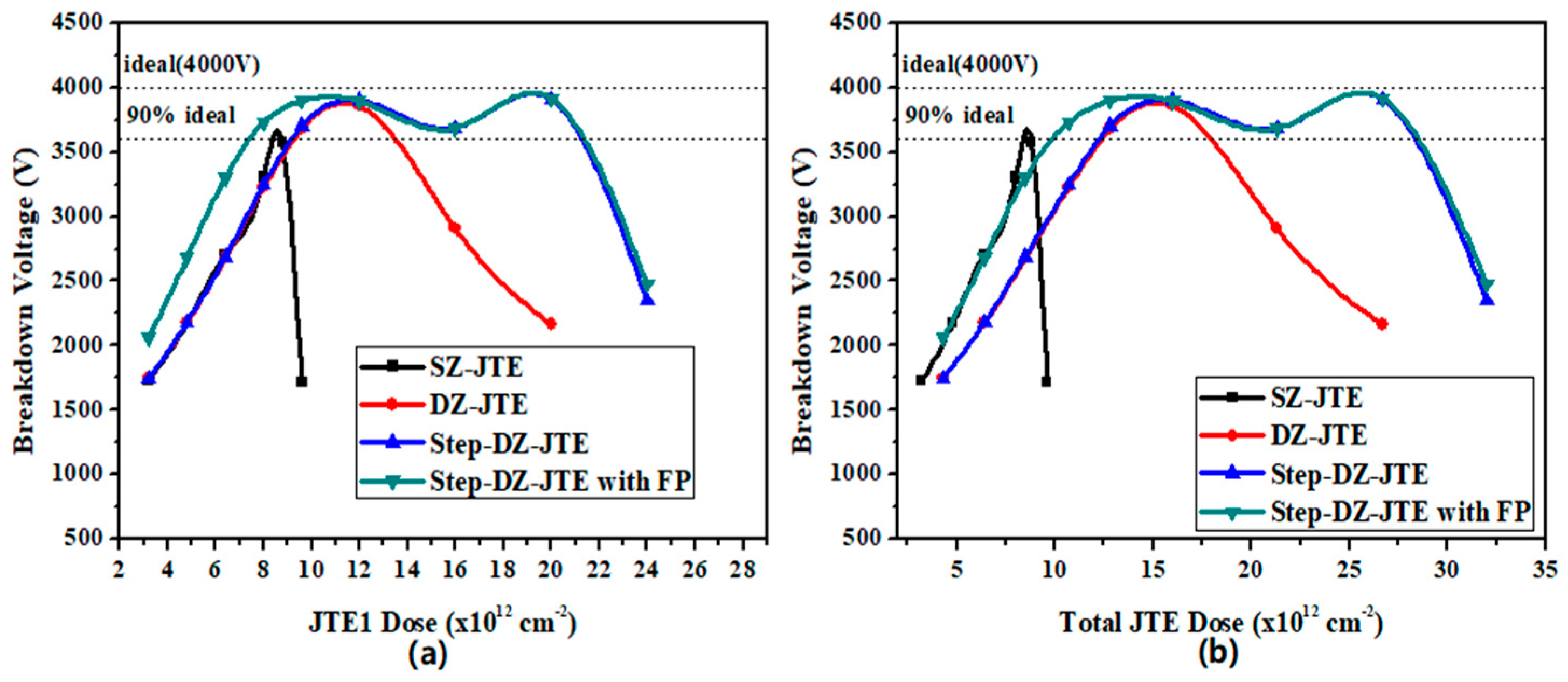
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shenai, K.; Scott, R.S.; Baliga, B.J. Optimum semiconductors for high-power electronics. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 1989, 36, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elasser, A.; Chow, T.P. Silicon carbide benefits and advantages for power electronics circuits and systems. Proc. IEEE 2002, 90, 969–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimoto, T. Ultrahigh-voltage SiC devices for future power infrastructure. In Proceedings of the 2013 Proceedings of the European Solid-State Device Research Conference, Bucharest, Romania, 16–20 September 2013; pp. 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casady, J.B.; Johnson, R.W. Status of silicon carbide (SiC) as a wide-bandgap semiconductor for high-temperature applications: A review. Solid-State Electron. 1996, 39, 1409–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttay, C.; Raynaud, C.; Morel, H.; Civrac, G.; Locatelli, M.L.; Morel, F. Thermal stability of silicon carbide power diodes. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2012, 59, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, B.; Gupta, S.K.; Taube, W.R.; Akhtar, J. High-k dielectrics based field plate edge termination engineering in 4H-SiC Schottky diode. Int. J. Electron. 2016, 103, 2064–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarplee, M.C.; Madangarli, V.P.; Zhang, Q.; Sudarshan, T.S. Design rules for field plate edge termination in SiC Schottky diodes. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2001, 48, 2659–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, E.V.; Cheng, L.; O’Loughlin, M.; Capell, C. 22 kV, 1 cm2, 4H-SiC n-IGBTs with improved conductivity modulation. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices & Ic’s, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 15–19 June 2014; pp. 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamor-Baliarda, A.; Vanmeerbeek, P.; Roig, J.; Moens, P. Electric field unbalance for robust floating ring termination. Microelectron. Reliab. 2011, 51, 1959–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, W.; Baliga, B.J. A Near Ideal Edge Termination Technique for 4500V 4H-SiC Devices: The Hybrid Junction Termination Extension (Hybrid-JTE). IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2016, 37, 1609–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Skromme, B.J. Design and optimization of junction termination extension (JTE) for 4H SiC high voltage Schottky diodes. Solid State Electron. 2005, 49, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okayama, T.; Arthur, S.D.; Rao, R.R.; Kishore, K.; Rao, M.V. Stability and 2-D Simulation Studies of Avalanche Breakdown in 4H-SiC DMOSFETS with JTE. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices. 2008, 55, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xing-Hua, F.U. Simulation study on 4H-SiC Schottky diode with JTE structure. In Proceedings of the 2014 16th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Lappeenranta, Finland, 26–28 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, G.; Suda, J.; Kimoto, T. Space-Modulated Junction Termination Extension for Ultrahigh-Voltage p-i-n Diodes in 4H-SiC. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2012, 59, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Li, L.; Wu, J.; Li, C.; Chen, W. A Multiple-Ring-Modulated JTE Technique for 4H-SiC Power Device with Improved JTE-Dose Window. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2017, 64, 5042–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.; Tournier, D.; Perez-Tomas, A.; Godignon, P.; Mestres, N. Planar edge termination design and technology considerations for 1.7-kV 4H-SiC PiN diodes. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2005, 52, 2309–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.; Mestres, N.; Tournier, D. A highly effective edge termination design for SiC planar high power devices. Mater. Sci. Forum 2014, 457–460, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, X. Research on high-voltage 4H-SiC P-i-N diode with planar edge junction termination techniques. Chin. Phys. B 2011, 20, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Tao, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, G.; Bai, S. Development of g10kv 4H-SiC SBD junction extension termination. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Electronic Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China, 19–21 August 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, D.C.; Niu, G.; Cressler, J.D. Design of single and multiple zone junction termination extension structures for SiC power devices. Solid-State Electron. 2001, 45, 1659–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, W.; Brunt, E.V.; Baliga, B.J.; Huang, A.Q. A new edge termination technique for high-voltage devices in 4H-SiC–multiple-floating-zone junction termination extension. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2011, 32, 880–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandi, R.; Buono, B.; Domeij, M.; Zetterling, C.M. High-Voltage 4H-SiC PiN Diodes with Etched Junction Termination Extension. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2009, 30, 1170–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pâques, G.; Dheilly, N.; Planson, D.; Scharnholz, S. Graded Etched Junction Termination for SiC Thyristors. Mater. Sci. Forum 2011, 679–680, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.F.; Hsu, H.C.; Chu, K.W.; Lee, L.H.; Tsai, M.J. Counter-Doped JTE, an Edge Termination for HV SiC Devices with Increased Tolerance to the Surface Charge. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2015, 62, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, N.; Niwa, H.; Suda, J.; Kimoto, T. Ultrahigh-Voltage SiC p-i-n Diodes with Improved Forward Characteristics. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2015, 62, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Shen, H.; Zhang, J. Numerical and experimental study of the mesa configuration in high-voltage 4H–SiC PiN rectifiers. Chin. Phys. B 2016, 25, 087201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliga, B.J. Fundamentals of Power Semiconductor Devices; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Chapter 3; pp. 91–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Bahng, W.; Kang, I.H. Fabrication characteristics of 1.2 kV SiC JBS diode. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Microelectronics, Nis, Serbia & Montenegro, 11–14 May 2008; pp. 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- Hiyoshi, T.; Hori, T.; Suda, J. Simulation and Experimental Study on the Junction Termination Structure for High-Voltage 4H-SiC PiN Diodes. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2008, 55, 1841–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yuan, H.; Song, Q. Fabrication of 3.1 kV/10 A 4H-SiC Junction Barrier Schottky Diodes. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 11th International Conference on ASIC (ASICON), Chengdu, China, 3–6 November 2015; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.Y.; Yen, C.T.; Chu, K.W.; Chen, Y.S. A novel 4H-SiC Trench MOS Barrier Schottky rectifier fabricated by a two-mask process. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and ICS, Kanazawa, Japan, 26–30 May 2013; pp. 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
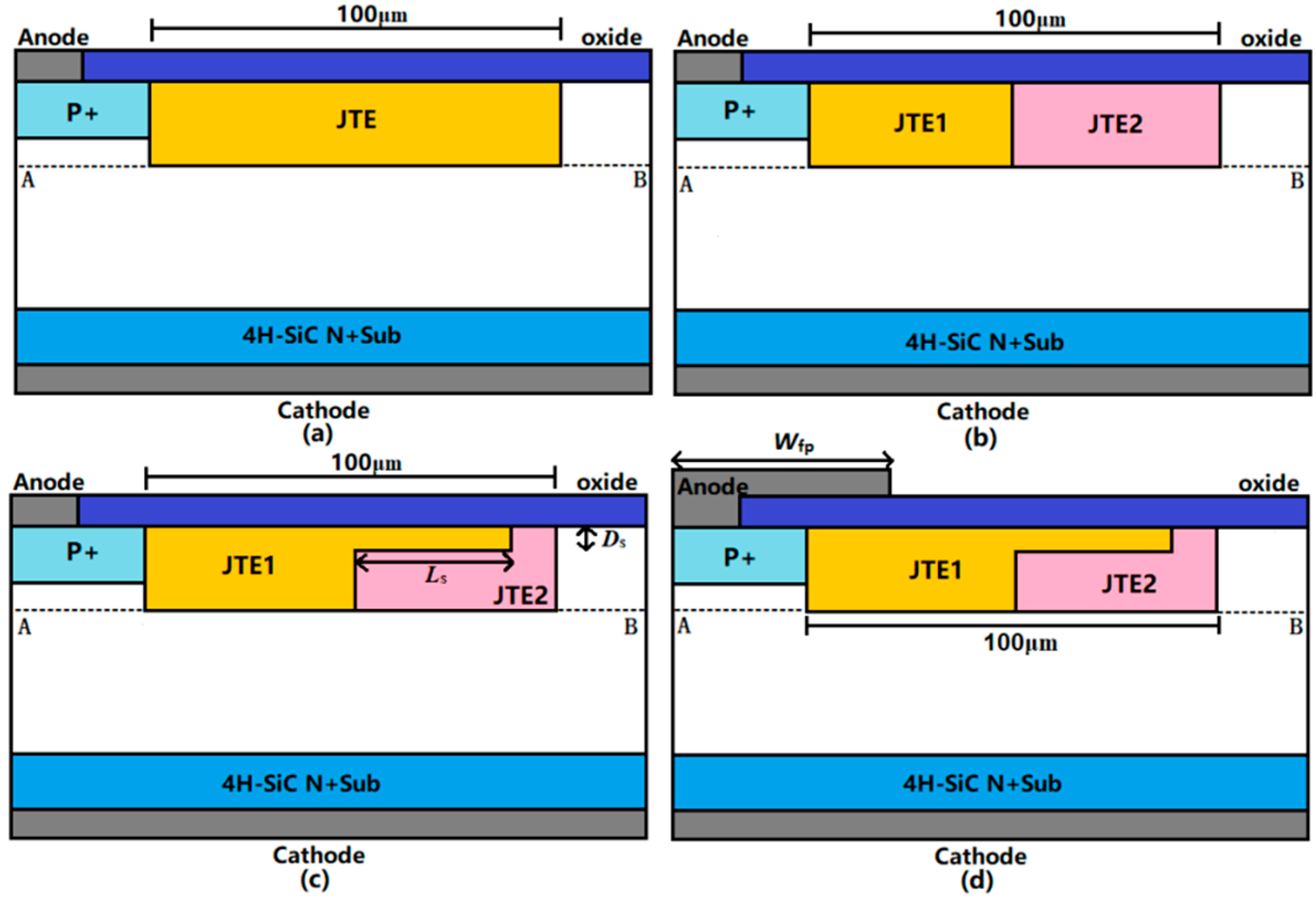
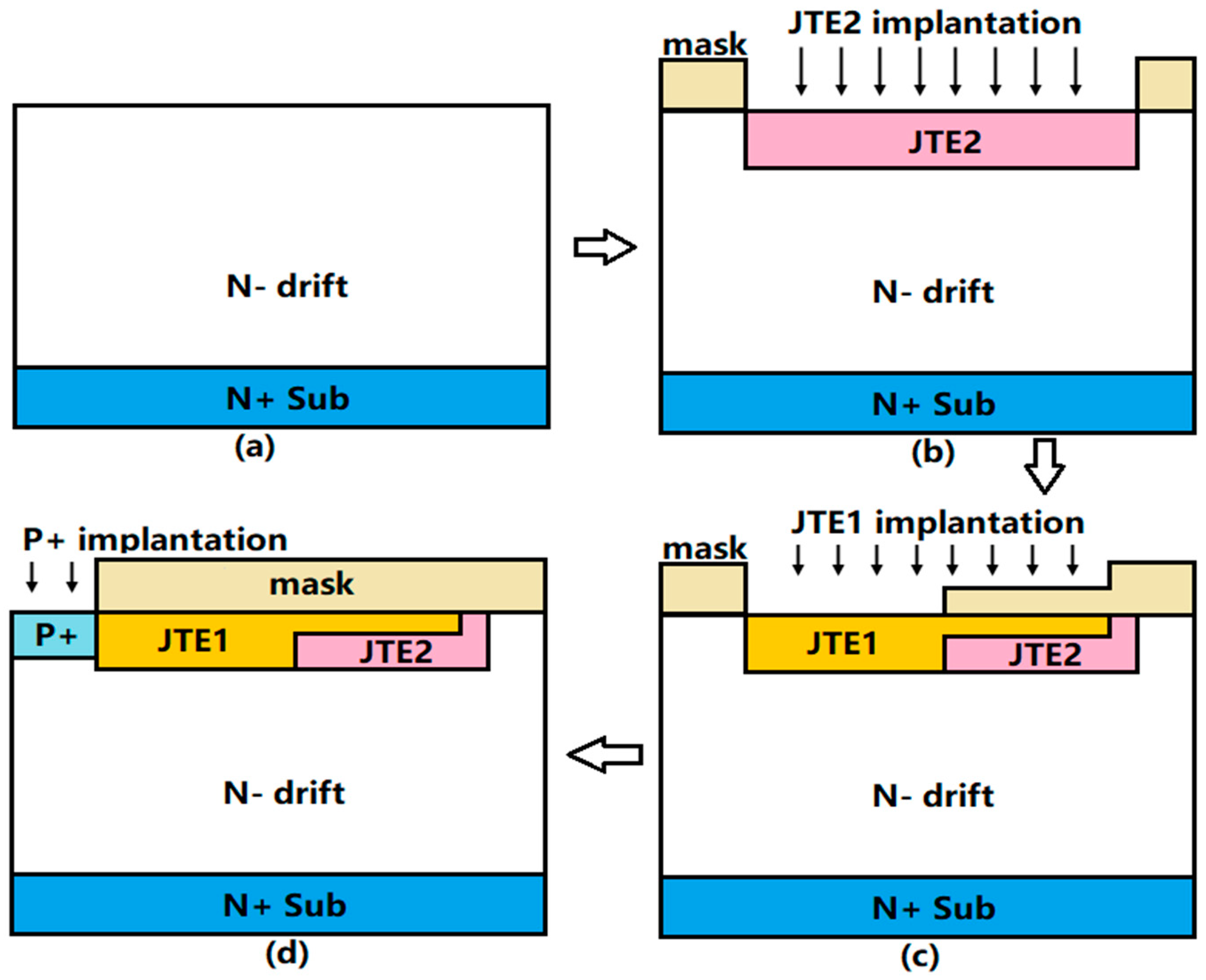
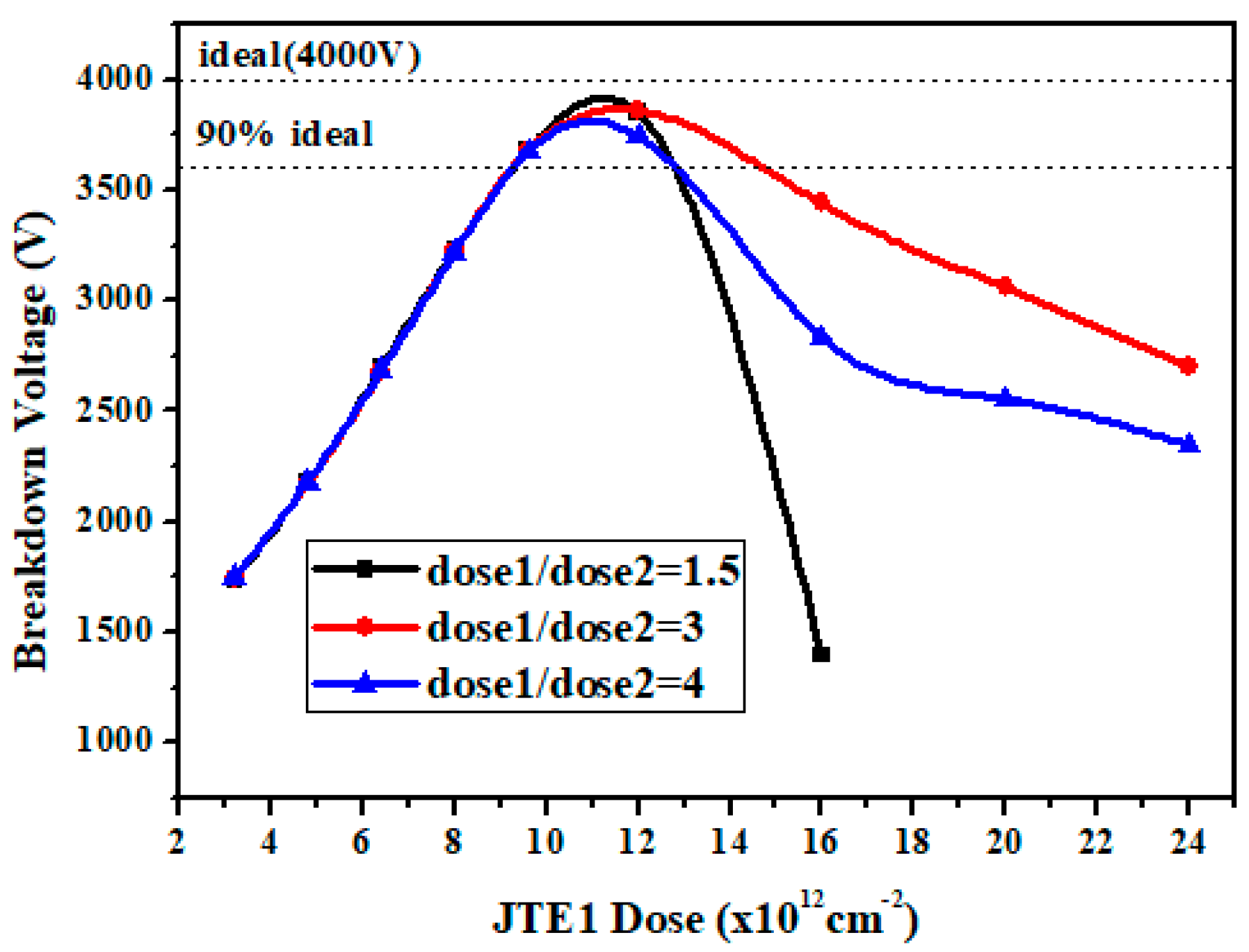
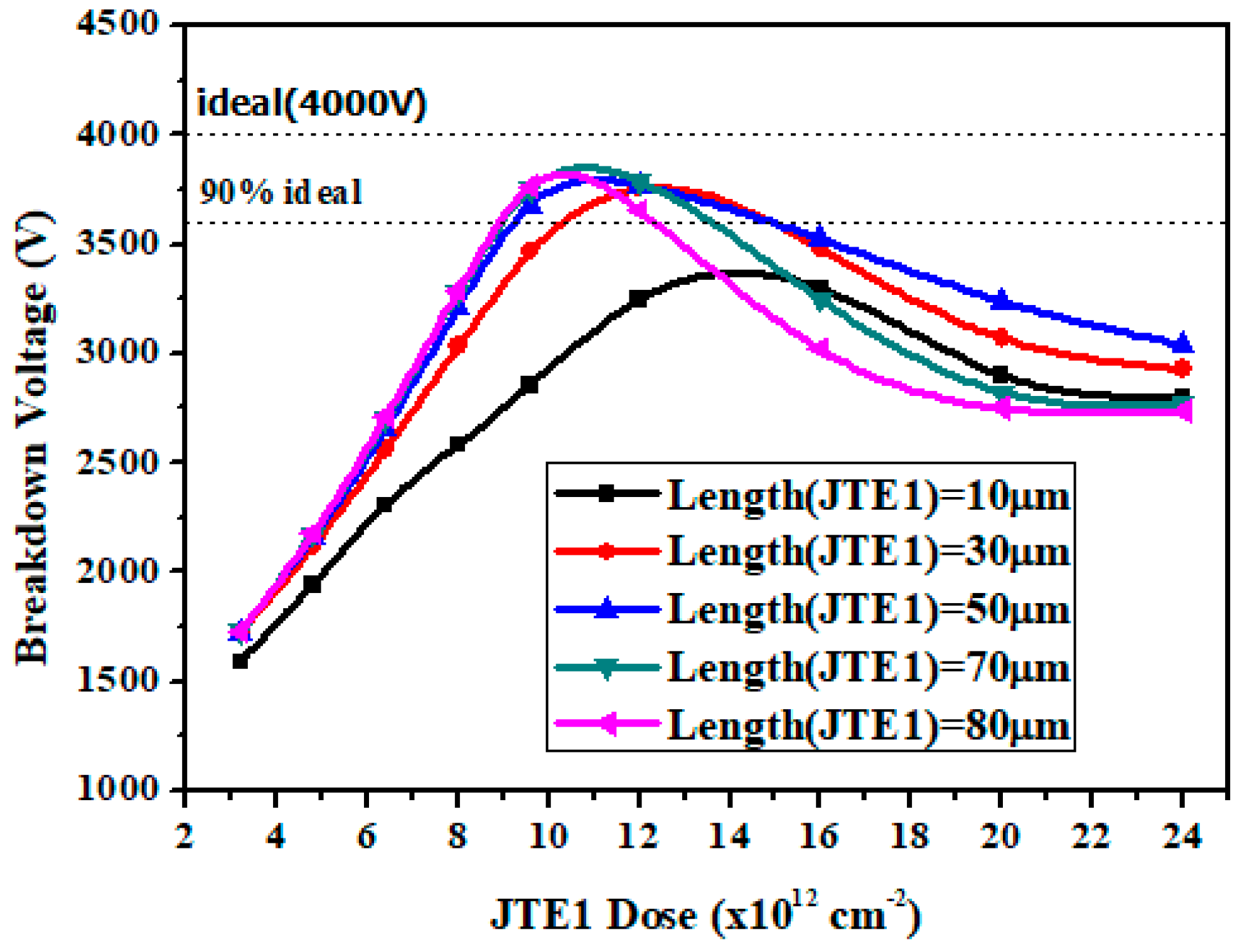
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| P+ anode junction depth | 0.6 μm |
| Junction termination extension (JTE) junction depth | 0.8 μm |
| Depth of the step JTE (Ds) | 0.3 μm |
| Length of the step JTE (Ls) | 45 μm |
| Length of the anode FP (Wfp) | 20 μm |
| Thickness of drift | 30 μm |
| n- drift dopant concentration (ND) | 3.0 × 1015 cm−3 |
| p+ anode dopant concentration (NA) | 1.0 × 1019 cm−3 |
| Structures | SZ-JTE | DZ-JTE | Step-DZ-JTE | Step-DZ-JTE with FP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JTE total length (μm) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Number of p-type implant | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| JTE1 dose tolerance for 90% BV (× 1012 cm−2) | 0.4 | 4.1 | 12.2 | 13.8 |
| Total JTE dose tolerance for 90% BV ((× 1012 cm−2) | 0.4 | 5.6 | 16.3 | 18.4 |
| The percentage of positive and negative variation | (+2.2%, −2.2%) | (+17.5%, −17.0%) | (+75%, −18.4%) | (+75%, −35%) |
| Max. positive SC density for 85% BV (× 1012 cm−2) | 0.5 | 3.2 | 3.7 | 5.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kuang, X.; Wang, W.; Tang, J.; Sun, Y. Step-Double-Zone-JTE for SiC Devices with Increased Tolerance to JTE Dose and Surface Charges. Micromachines 2018, 9, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9120610
Huang Y, Wang Y, Kuang X, Wang W, Tang J, Sun Y. Step-Double-Zone-JTE for SiC Devices with Increased Tolerance to JTE Dose and Surface Charges. Micromachines. 2018; 9(12):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9120610
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yifei, Ying Wang, Xiaofei Kuang, Wenju Wang, Jianxiang Tang, and Youlei Sun. 2018. "Step-Double-Zone-JTE for SiC Devices with Increased Tolerance to JTE Dose and Surface Charges" Micromachines 9, no. 12: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9120610
APA StyleHuang, Y., Wang, Y., Kuang, X., Wang, W., Tang, J., & Sun, Y. (2018). Step-Double-Zone-JTE for SiC Devices with Increased Tolerance to JTE Dose and Surface Charges. Micromachines, 9(12), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9120610




