Ultrasound-Assisted Urea-Water Solution (AdBlue) Droplets Vaporization: A Mathematical Model for Film and Volumetric Regimes with Implications in NOx Emission Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
- When the AdBlue solution is injected onto the hot surfaces of the exhaust system, a phase transformation occurs after reaching saturation temperature, i.e., vaporization. If the surface temperature is too low (below the vaporization temperature) only partial phase transformation occurs. If the surface temperature is much above the saturation temperature, pseudo-sublimation occurs when AdBlue is injected onto the surface.
- In the case of AdBlue micro-droplets entrained in motion by the hot flue gas stream, vaporization proceeds convectively in volume, in which case the phenomena are characterized by mass transport and enhanced thermal diffusion.
- Following the injection of the AdBlue solution, the liquid droplets undergo a biphasic transformation through a continuous mass transfer cycle until they enter the SCR honeycomb.
2. Methodology and Mathematical Framework
2.1. Research Method: Thermal Operating Context and Assumptions
2.2. Ultrasonic Device and Operating-Frequency Treatment
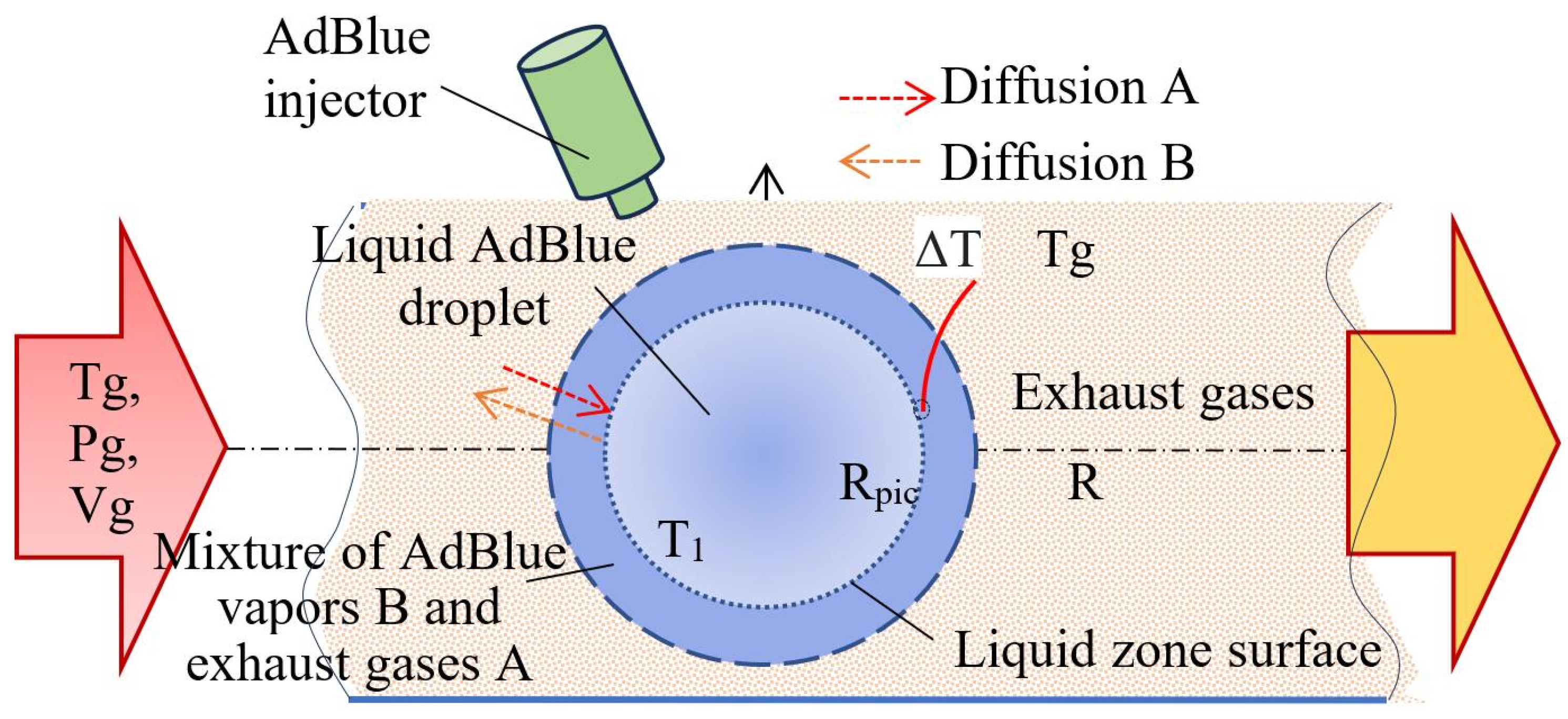
2.3. Convective Vaporization of AdBlue Droplets Evolving in a Hot Gaseous Medium with or Without Calefaction
- Vapour formation is when AdBlue droplets are injected onto a surface subject to a magnetostrictive effect; a phenomenon known as calefaction may occur if atomized droplets detached from the surface move into a volume of hot gas. The phenomenon must take place in the immediate vicinity of the solid surface without intimate contact with it, and the droplets are agitated by ultrasonic waves obtained by the magnetostrictive effect. Thermal diffusion can also be taken into account in the calculations. This regime involves a complex volume interaction, where the velocity and temperature of the gaseous medium directly influence the evaporation process.
- Evaporation on contact with hot surfaces is a scenario that simulates direct injection on hot components of the exhaust manifold or catalyst structure when the droplet jet hits the walls of the exhaust duct of the diesel engine. In this case, the heat transfer is conductive and radiative and takes a significant part in vaporization.
- The mechanism of formation of solid deposits is directly related to the operating temperature and is characterized by the appearance of solid deposits of AdBlue salts either on the injector nozzle or on the front surface of the catalyst nozzle. This phenomenon is mainly caused by high temperatures, temperature inhomogeneities, and the unfinished evaporation process of the AdBlue droplets.
3. Determination of the Diameter of the AdBlue Droplets Injected into the Exhaust Gas Volume of the SCR, Considering the Diffusion Phenomenon
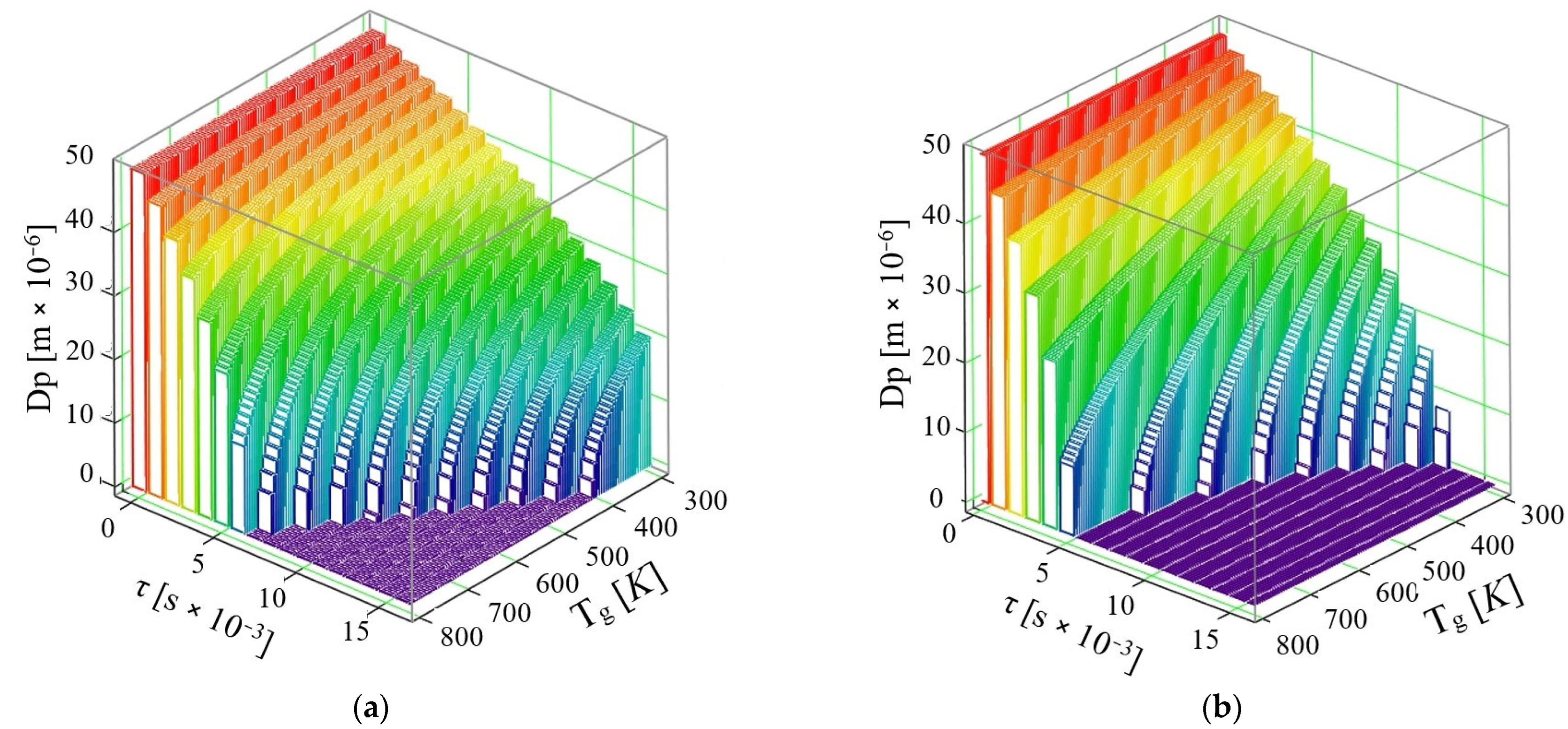
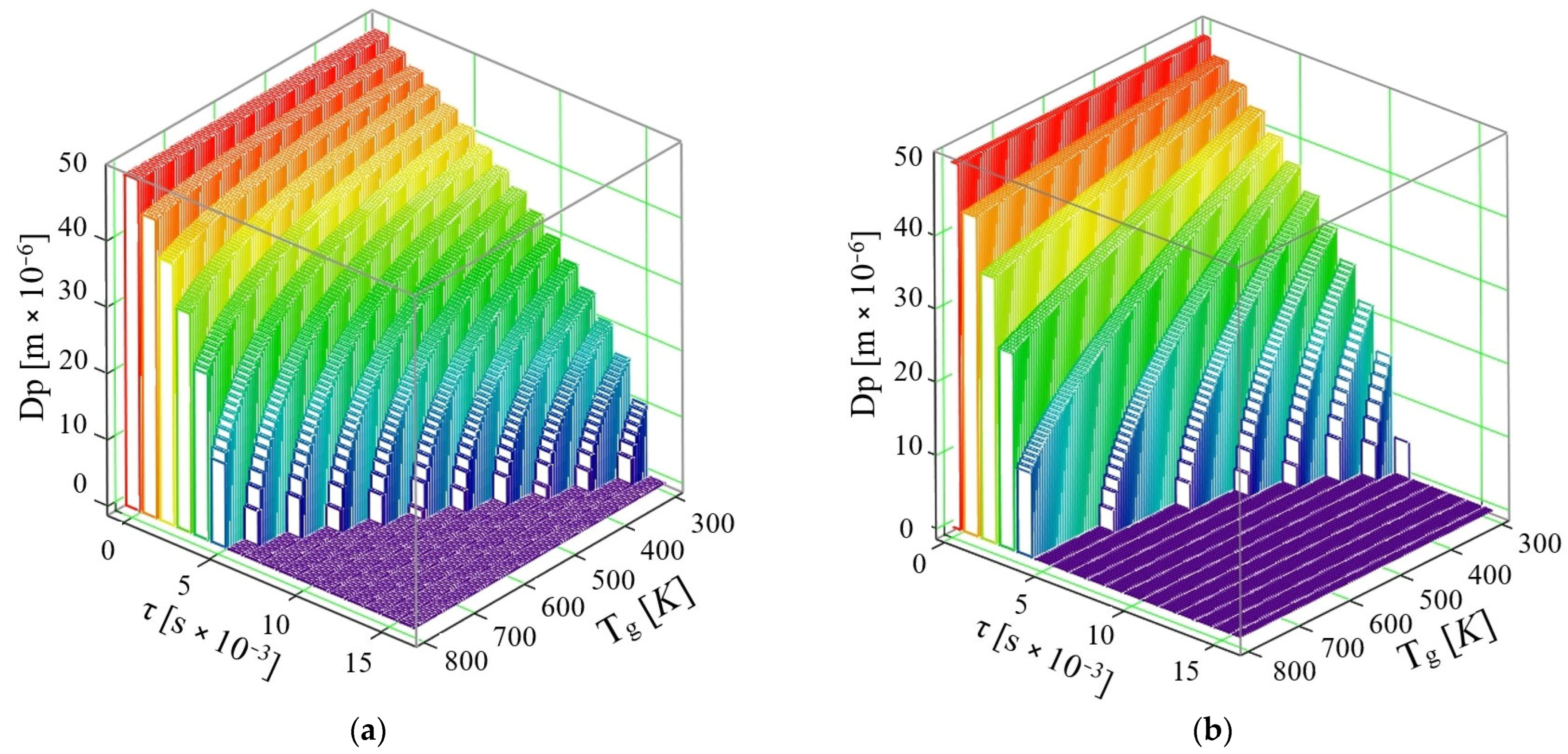
- If the phenomenon of thermal diffusion is not taken into account, the calculations show that a drop of AdBlue with diameter dPAD = 50 × 10−6 m at a velocity u = 10 m/s can completely vaporize in time τ = 9 × 10−3 s at the maximum exhaust gas temperature required for vaporization is Tg = 800 K, while at Tg = 600 K the time required for complete vaporization is τ = 16 × 10−3 s. So, the complete vaporization of the AdBlue droplets occurs faster for higher exhaust gas temperatures.
- If the phenomenon of thermal diffusion is taken into account, at the same initial droplet diameter dPAD = 50 × 10−6 m and the same exhaust gas velocity u = 10 m/s, it is found that the AdBlue droplets vaporize much faster than in the previous case (when thermal diffusion is not taken into account). Thus, the vaporization takes place completely in a time τ = 7 × 10−3 s at a maximum required flue gas temperature Tg = 767 K, while at temperature Tg = 367 K the minimum required time is τ = 16 × 10−3 s.
- If the phenomenon of thermal diffusion is not taken into account, at a velocity u = 30 m/s, it can be easily observed that a drop of AdBlue completely vaporizes at the maximum temperature Tg = 800 K in the time τ = 6 × 10−3 s, while at temperature Tg = 400 K a vaporization time τ = 16 × 10−3 s is required.
- If the thermal diffusion phenomenon is taken into account, at the velocity u = 30 m/s, the vaporization proceeds completely in a time τ = 5 × 10−3 s at a maximum flue gas temperature Tg = 800 K, while at temperature Tg = 366 K, the minimum time required for vaporization decreases to τ = 11 × 10−3 s. In this model for the gaseous medium velocity u = 30 m/s, it is found that already all the droplets are completely vaporized by the end of the travelled path, which is the case corresponding to good functioning of the SCR.
- If the phenomenon of thermal diffusion is not taken into account, it can be observed that droplets of AdBlue completely vaporize at a maximum temperature Tg = 800 K, in τ = 5 × 10−3 s, and at a temperature Tg = 330 K in τ = 14 × 10−3 s.
- If the phenomenon of thermal diffusion is taken into account, at the velocity u = 50 m/s, vaporization proceeds completely in a time τ = 4 × 10−3 s at a maximum flue gas temperature Tg = 530 K, while at a temperature Tg = 333 K the time required for complete vaporization is τ = 9 × 10−3 s.
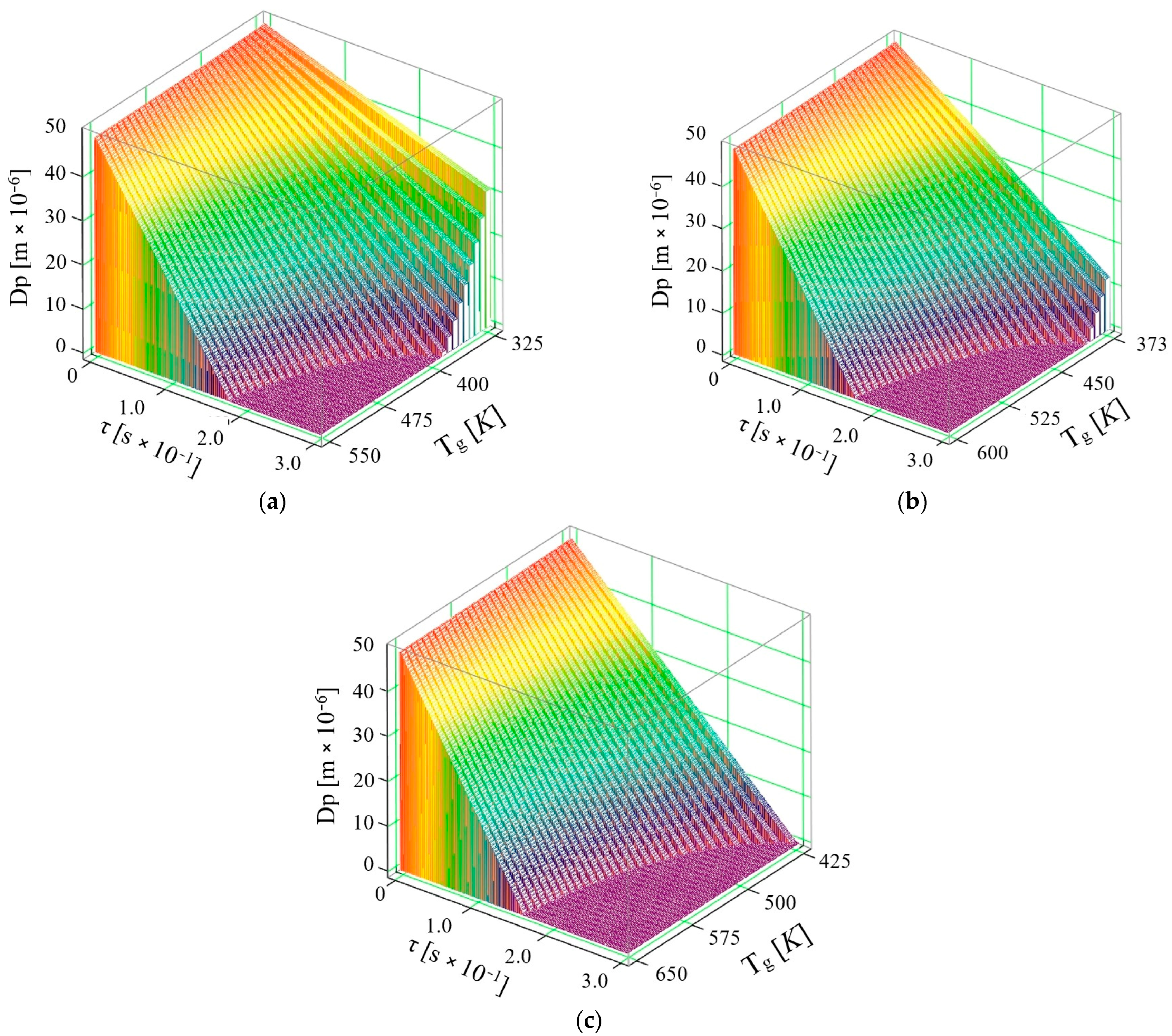
4. Considerations on the Vaporization of AdBlue Solution in the Pellicular Regime and the Influence of Ultrasound on This Process
- temperatures below the saturation value of the AdBlue droplets
- AdBlue saturation (boiling) temperatures
- temperatures above boiling temperature when vapors are produced (at which the decomposition of urea in the SCR catalyst takes place)
- superheated temperatures well above saturation when urea can decompose into solid salts and deposit on SCR system components.
- the temperature of the vaporization surface corresponds to the values of the exhaust manifold heated by the exhaust gases, in which case it obviously has lower values than those of the heat source (exhaust gases)
- the exhaust duct is thin-walled, in which case convective heat exchange with the outside environment is favored, leading to rapid cooling, especially at negative outside temperature values
- the heating process of the exhaust pipe is particularly slow when the diesel engine is running cold, a phenomenon which is maintained until the operating temperature is reached
- when vaporizing on surfaces, the droplets injected form a thin film of liquid at high flow rates, in which case this corresponds to a process that no longer involves only AdBlue droplets floating in a hot gaseous medium as in volume vaporization
- the velocity of the droplets moving in a gaseous medium is much higher than in the case of the liquid film flow formed during surface injection
- convective and radiative phenomena can no longer be taken into account in surface vaporization, the phenomenon being rather conductive
- thermal diffusion can be considered as zero since the phenomenon of the interpenetration of the molecules of one body (very fine droplets of AdBlue) between the molecules of another body (exhaust gases) no longer occurs, since the process takes place without the intervention of an external force; when the temperature of the surface onto which the AdBlue jet is injected is close to that of the droplet, the rate of regression of the droplet diameter is attenuated, suggesting that the evaporation process is slower.
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Numerical Results and Comparison with the Literature
5.2. Discussion of Figures (Trends)
5.3. Algorithmic Shortcomings and Limitations
- Single-droplet scope. An isolated droplet was analyzed; spray-scale interactions (breakup, coalescence, vapor shielding) were not modeled.
- Near-surface idealization (pellicular regime). Wall micro-roughness, wettability dynamics, and transient wetting transitions were not resolved.
- Ultrasound representation. Ultrasonic action was incorporated at system level (enhanced atomization/interfacial renewal); the spatio–temporal acoustic/cavitation field was not explicitly solved.
- Gas-side transport closure. Heat and mass transfer on the gas side used analytical correlations; 3D non-uniformities and turbulence in the exhaust line were not computed.
- Property ranges. Results relied on temperature/pressure-dependent correlations within the ranges shown; extrapolation beyond these bounds should be done cautiously.
- Validation breadth. Comparison employed a limited literature set; experiments under matched boundary conditions would further strengthen validation.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Picus, C.M.; Mihai, I.; Suciu, C. Experimental Investigations upon Ultrasound Influence on Calefaction of AdBlue in Selective Catalytic Reduction Systems (SCR). Micromachines 2023, 14, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission, Joint Research Centre. Real Driving Emissions Testing: A Game-Changer for NOx to Promote Cleaner Vehicles in the EU; Brief No. 1/2023; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2023; Available online: https://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/bitstream/JRC134453/JRC134453_01.pdf (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- European Environment Agency (EEA). Emissions of Air Pollutants from Transport (Indicator); 3 March 2025 (Modified 8 May 2025). Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/european-zero-pollution-dashboards/indicators/emissions-of-air-pollutants-from-transport-indicator (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Majewski, W.A.; Jääskeläinen, H. Diesel Emissions and Their Control, 2nd ed.; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2023; ISBN 978-1-46860-569-3. [Google Scholar]
- de Ruiter, J.M.; van Mensch, P. Analysis of the Emission Performance of the Vehicles Tested for the Green Vehicle Index (GVI) Project; TNO Report TNO 2022 R10798; TNO: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2022; Available online: https://publications.tno.nl/publication/34639479/2iENph/TNO-2022-R10798.pdf (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Bakhshmand, S.K.; Mulholland, E.; Tietge, U.; Rodríguez, F. Remote Sensing of Heavy-Duty Vehicle Emissions in Europe; ICCT Working Paper 2022-25; International Council on Clean Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; Available online: https://theicct.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/remote-sensing-hdvs-europe-aug22.pdf (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Nishad, K.; Sadiki, A.; Janicka, J. Numerical Investigation of AdBlue Droplet Evaporation and Thermal Decomposition in the Context of NOx-SCR Using a Multi Component Evaporation Model. Energies 2018, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnathpur, C.; Apewokin, S.L.; Holl, S.; Burke, J.F.; Heichelbech, J. System, Method, and Apparatus for Delivering Highly Atomized Diesel Exhaust Fluid to an Exhaust Aftertreatment System. US8888017B2, 18 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, R.; Pandit, A.B. Correlations to Predict Droplet Size in Ultrasonic Atomisation. Ultrasonics 2001, 39, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakosi, E.; Manolache, G. Procese și Caracteristici ale Motoarelor cu Ardere Internă; Universitatea Tehnică Gh. Asachi din Iași, Facultatea de Mecanică: Iasi, Romania, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Boriboonsomsin, K.; Durbin, T. Real-World Exhaust Temperature Profiles of On-Road Heavy-Duty Diesel Vehicles Equipped with Selective Catalytic Reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amuzescu, A.; Popovici, D. Curs de Electrotehnică; Editura Printech: Bucharest, Romania, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Asif, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, W. Urea-SCR Temperature Investigation for NOx Control of Diesel Engine. MATEC Web. Conf. 2015, 26, 03002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joon, H.B.; Sung, D.Y. Control of NOx Emissions from Diesel Engine by Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) with Urea. Catalysis 2004, 30, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.H.; Paratore, M.; Gonze, E. Electrically Heated Catalysts for Cold-Start Emissions in Diesel Aftertreatment; SAE Technical Paper No. 2012-01-1092; General Motors Company: Detroit, MI, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, C.; Fabrice, L. Heat and Mass Transfer in Evaporating Droplets in Interaction: Influence of the Fuel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 53, 3495–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.H.; Lim, H.C.; Lee, H.W. Evaporation-Induced Saline Rayleigh Convection Inside a Colloidal Droplet. Phys. Fluids 2013, 25, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapan, K.P.; Pradipta, K.; Kumar, P. Evaporation Induced Natural Convection Inside a Droplet of Aqueous Solution Placed on a Superhydrophobic Surface. Colloids Surf. A 2017, 530, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Langenberg, S.; Carstens, T.; Hupperich, T. Determination of Binary Gas-Phase Diffusion Coefficients of Unstable and Adsorbing Atmospheric Trace Gases at Low Temperature. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 3669–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisenko, S.P.; Brin, A.A.; Petruchik, A.I. Evaporative Cooling of Water in a Mechanical Draft Cooling Tower. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2004, 47, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brin, A.A.; Fisenko, S.P.; Khodyko, Y.A. Characteristic Features of Evaporative Cooling of Droplets in High-Temperature Flows. J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys. 2011, 84, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Sun, D.; Guo, X.; Li, N.; Li, C.; Wei, J.; Zang, Z. Investigation of in situ high temperature sensor based on the direct absorption spectroscopy signal of ammonia gas for coal-fired power plant. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2019, 51, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihai, I. Modelul Fizico-Matematic al Motorului Diesel Alimentat cu Adaos de apă. Ph.D. Thesis, Institutul Politehnic Gh. Asachi din Iași, Iași, Romania, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Chedli, M. Contribuții la Cercetarea Influenței Organizării Mișcărilor Aerului Asupra Repartiției Combustibilului în Camere de Ardere Unitare ale Motoarelor cu Aprindere prin Comprimare Rapide. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitatea Politehnica din Timișoara, Timișoara, Romania, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lieber, C.; Koch, R.; Bauer, H.J. Spray Evaporation of Urea–Water Solution: Experiments and Modelling. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2020, 116, 110108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Youtong, Z.; Asif, M. Investigation on UWS Evaporation for Vehicle SCR Applications. AIChE J. 2016, 62, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkhold, F.; Meingast, U.; Wassermann, P. Modeling and Simulation of the Injection of Urea-Water-Solution for Automotive SCR DeNOx-Systems. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 70, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontin, S.; Höfler, A.; Koch, R.; Bauer, H.J. Heat and Mass Transfer Accompanied by Crystallisation of Single Particles Containing Urea-Water-Solution. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Brno, Czech Republic, 6–8 September 2010; p. 11. [Google Scholar]





| Solution | Initial Droplet Diameter | Evaporation Time | Normalized Evaporation Time | Gas Temperature | Gas Velocity | Evaporation Medium | Authors | Relative Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | [µm] | [s] | [s/mm2] | [K] | [m/s] | [%] | ||
| Urea solution | 750–1240 | 140 | 141.41 | 323 | 1.1 | Hot air | (Lieber et al., 2020) [24] | 4.40 |
| 860–1300 | 18 | 15.43 | 523 | 2.8 | Hot air | 6.41 | ||
| 570–1310 | 10 | 11.32 | 673 | 4.3 | Hot air | 6.41 | ||
| 10 | 0.003 | 30.00 | 873 | 250 | Hot air | (Wei et al., 2016) [25] | 2.18 | |
| 8 | 0.002 | 31.25 | 1.14 | |||||
| 900 | 21 | 25.93 | 473 | 0 | Hot air | (Birkhold et al., 2007) [26] | 6.40 | |
| 892 | 8 | 10.05 | 673 | 0 | Hot air | 6.41 | ||
| 893 | 7.5 | 9.40 | 773 | 0 | Hot air | 2.80 | ||
| 70 | 0.78 | 159.18 | 673 | 0 | Hot air | (Kontin et al., 2010) [27] | 6.53 | |
| 0.04 | 8.16 | 900 | 100 | Hot air | 3.20 | |||
| AdBlue | 50 | 0.016 | 6.40 | 600 | 10 | Exhaust gases | Present study | 0 |
| 0.009 | 3.60 | 800 | 10.29 | |||||
| 0.016 | 6.40 | 367 | 0 | |||||
| 0.007 | 2.80 | 767 | 0 | |||||
| 0.005 | 2.00 | 800 | 30 | Exhaust gases | 8.00 | |||
| 0.011 | 4.40 | 366 | 0 | |||||
| 0.016 | 6.40 | 400 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Picus, C.M.; Mihai, I.; Suciu, C. Ultrasound-Assisted Urea-Water Solution (AdBlue) Droplets Vaporization: A Mathematical Model for Film and Volumetric Regimes with Implications in NOx Emission Control. Micromachines 2025, 16, 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090996
Picus CM, Mihai I, Suciu C. Ultrasound-Assisted Urea-Water Solution (AdBlue) Droplets Vaporization: A Mathematical Model for Film and Volumetric Regimes with Implications in NOx Emission Control. Micromachines. 2025; 16(9):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090996
Chicago/Turabian StylePicus, Claudiu Marian, Ioan Mihai, and Cornel Suciu. 2025. "Ultrasound-Assisted Urea-Water Solution (AdBlue) Droplets Vaporization: A Mathematical Model for Film and Volumetric Regimes with Implications in NOx Emission Control" Micromachines 16, no. 9: 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090996
APA StylePicus, C. M., Mihai, I., & Suciu, C. (2025). Ultrasound-Assisted Urea-Water Solution (AdBlue) Droplets Vaporization: A Mathematical Model for Film and Volumetric Regimes with Implications in NOx Emission Control. Micromachines, 16(9), 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090996






