Study on Nano-Grinding Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Subsurface Damage in Monocrystalline Silicon
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Nano-Grinding Properties in Monocrystalline Silicon
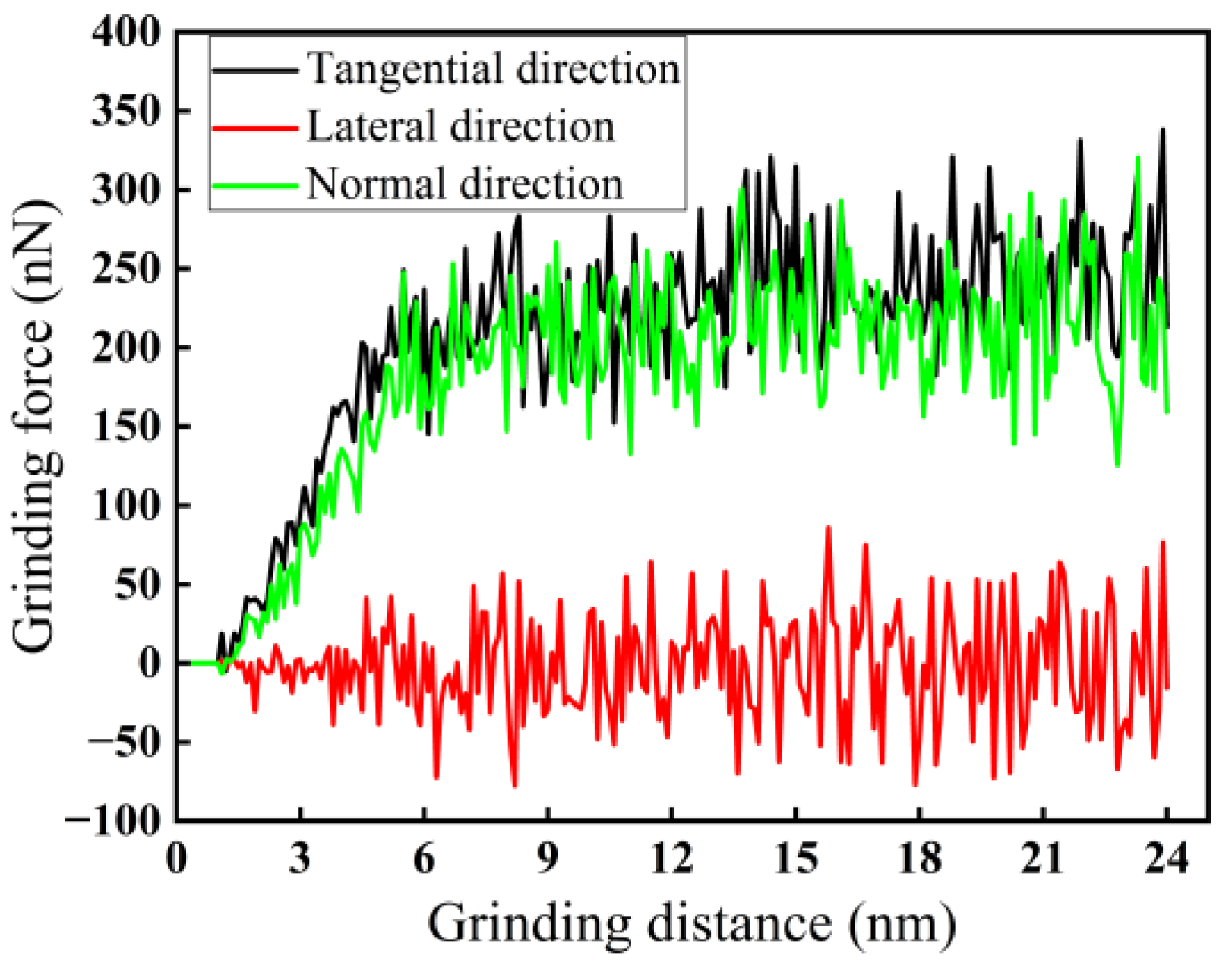
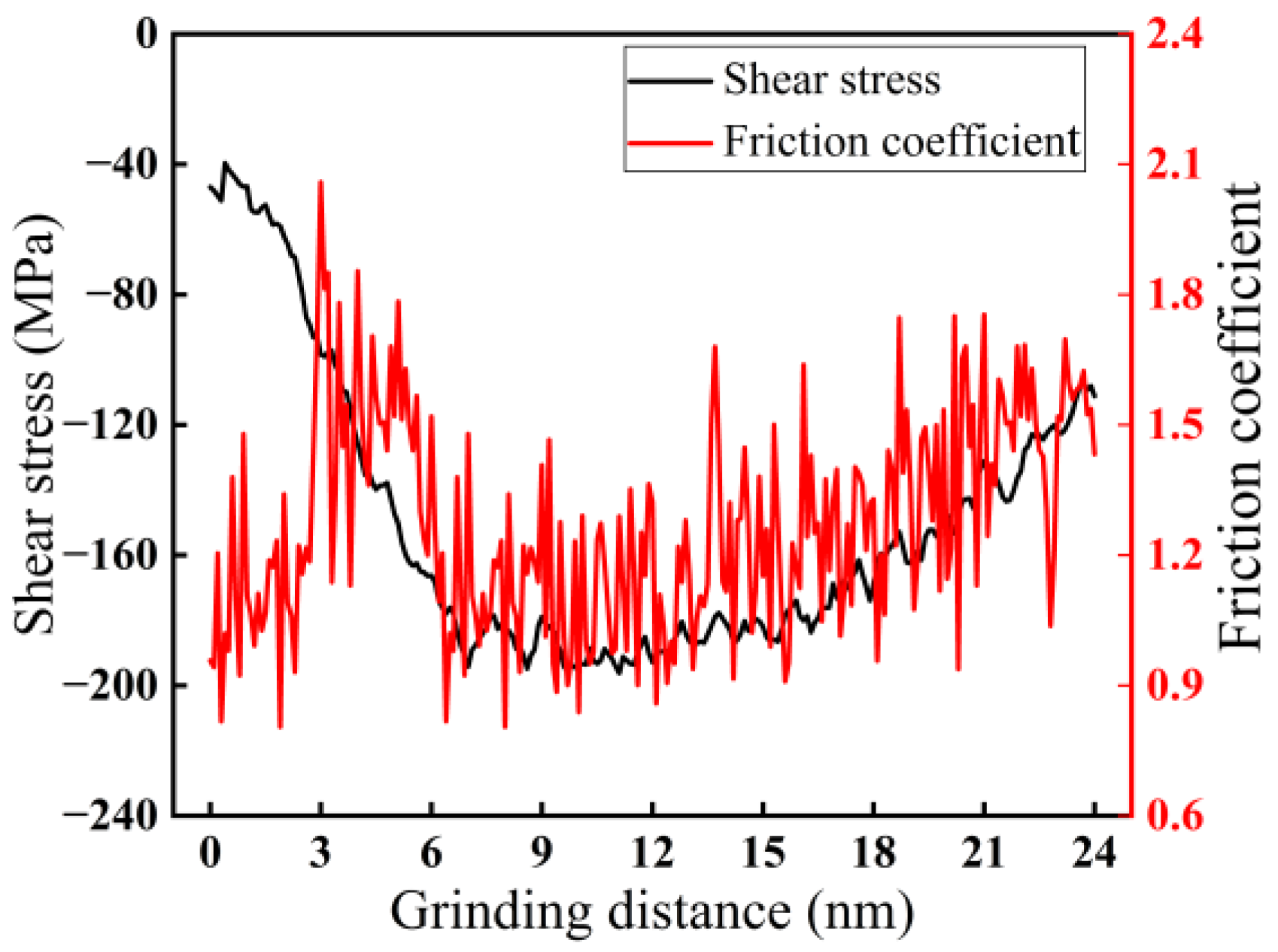
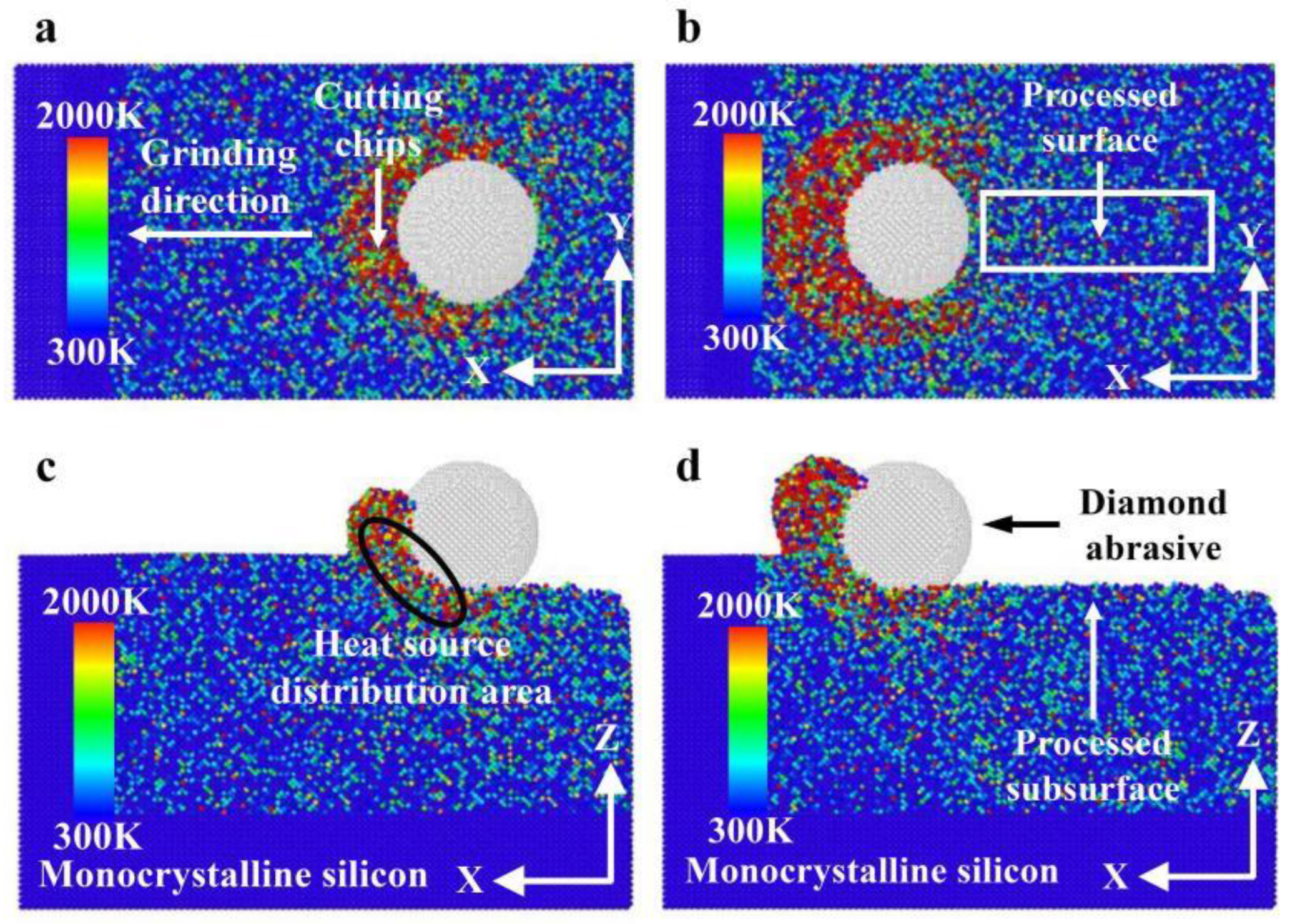
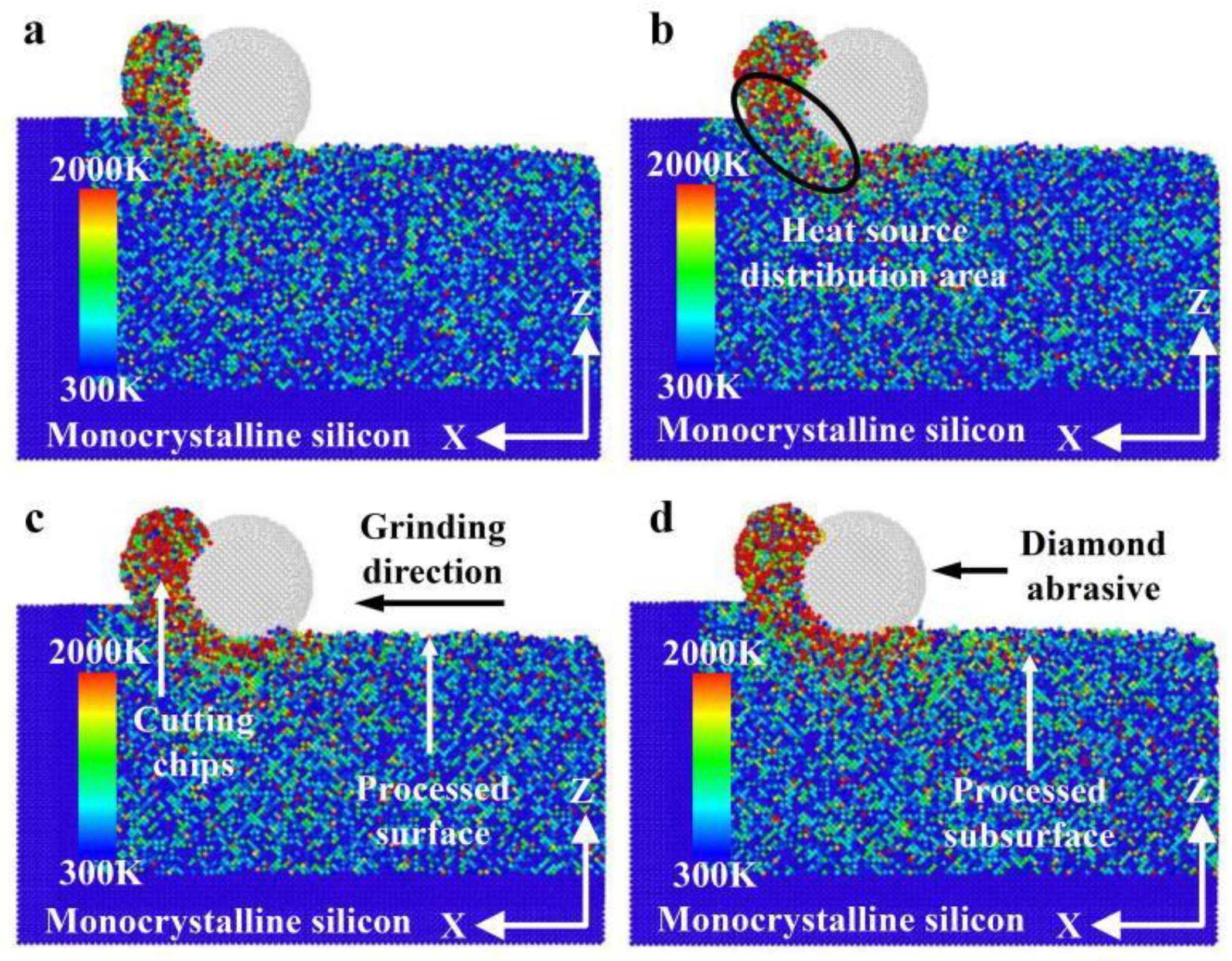
3.1.1. Change in Force–Thermal During Nano-Grinding
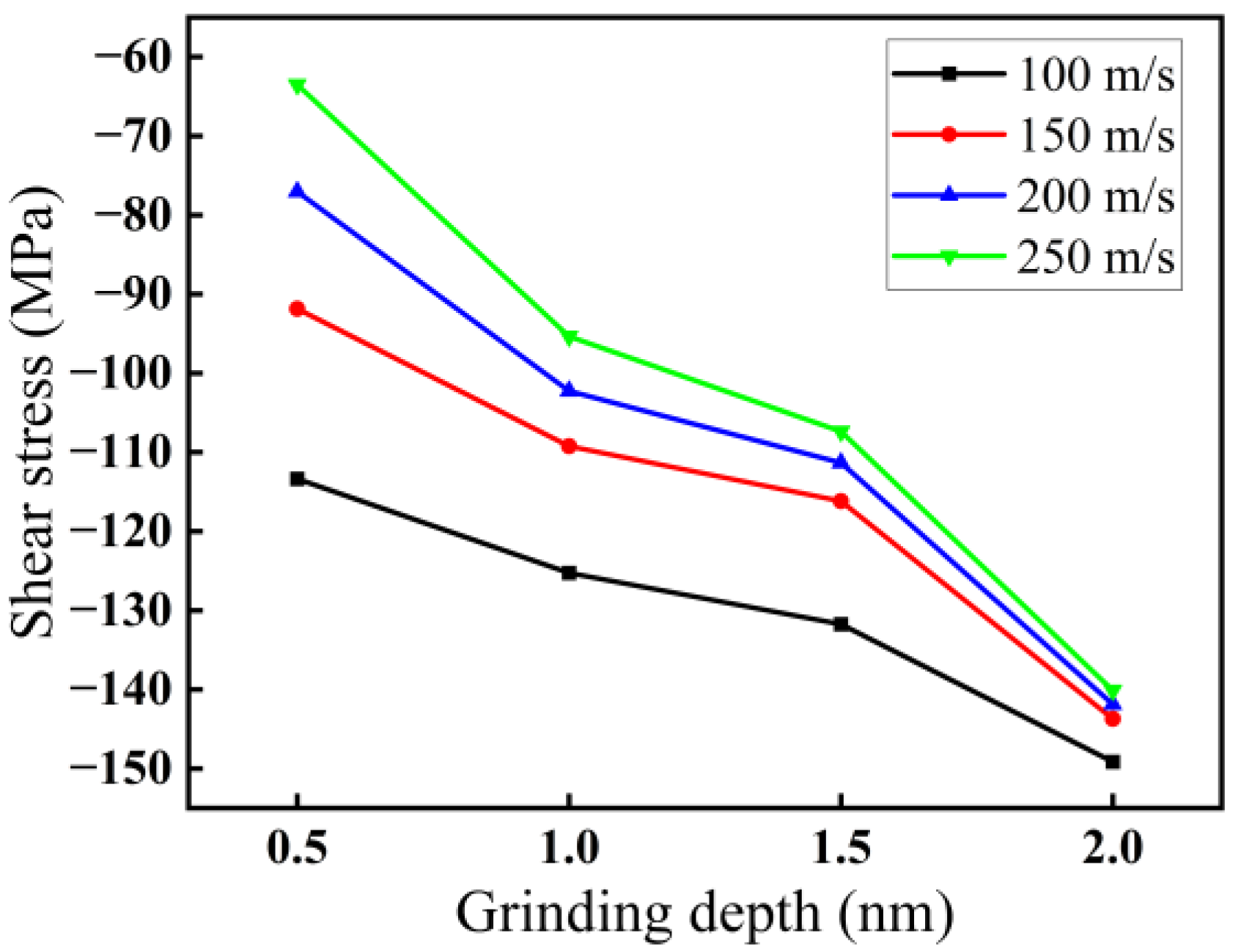
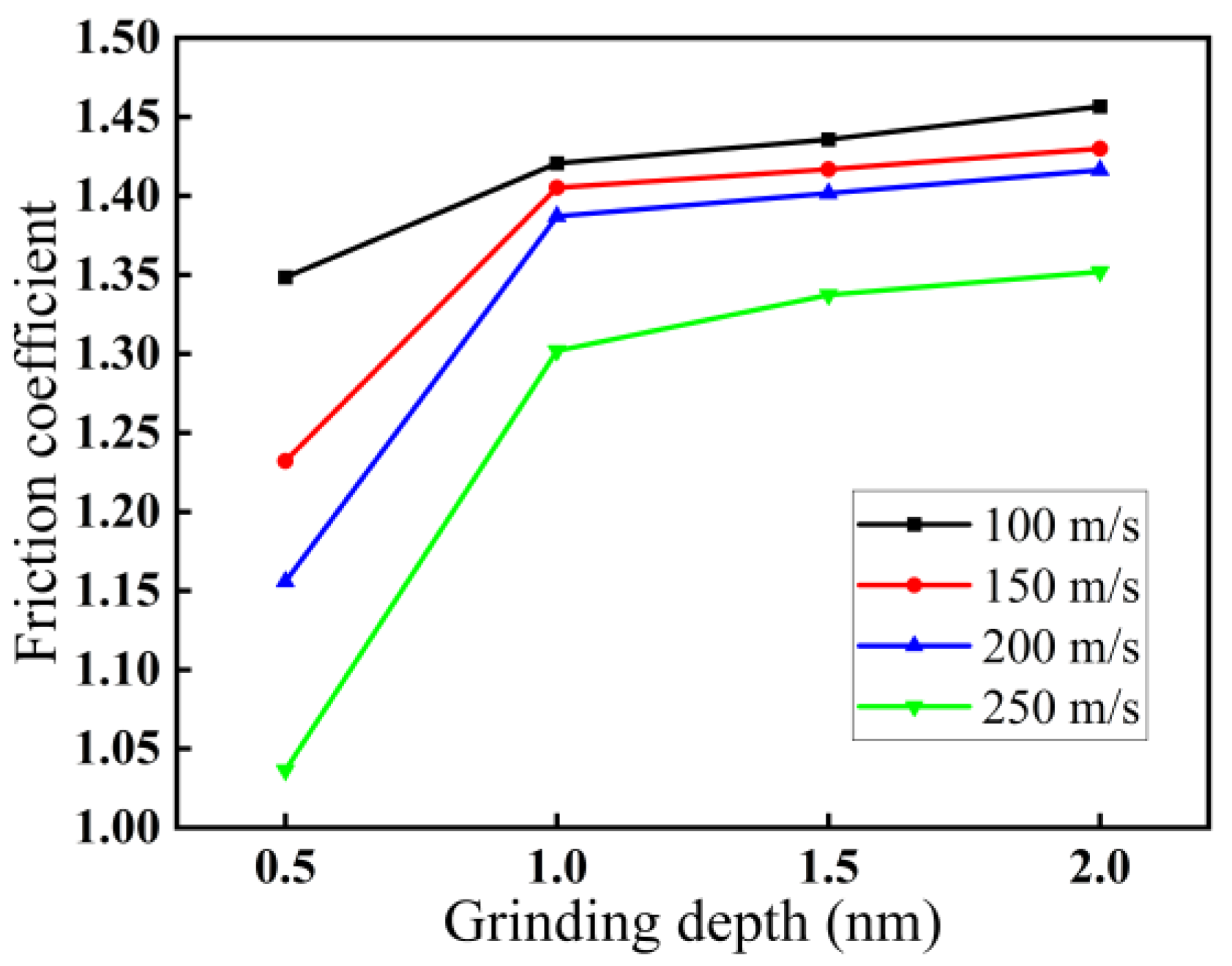
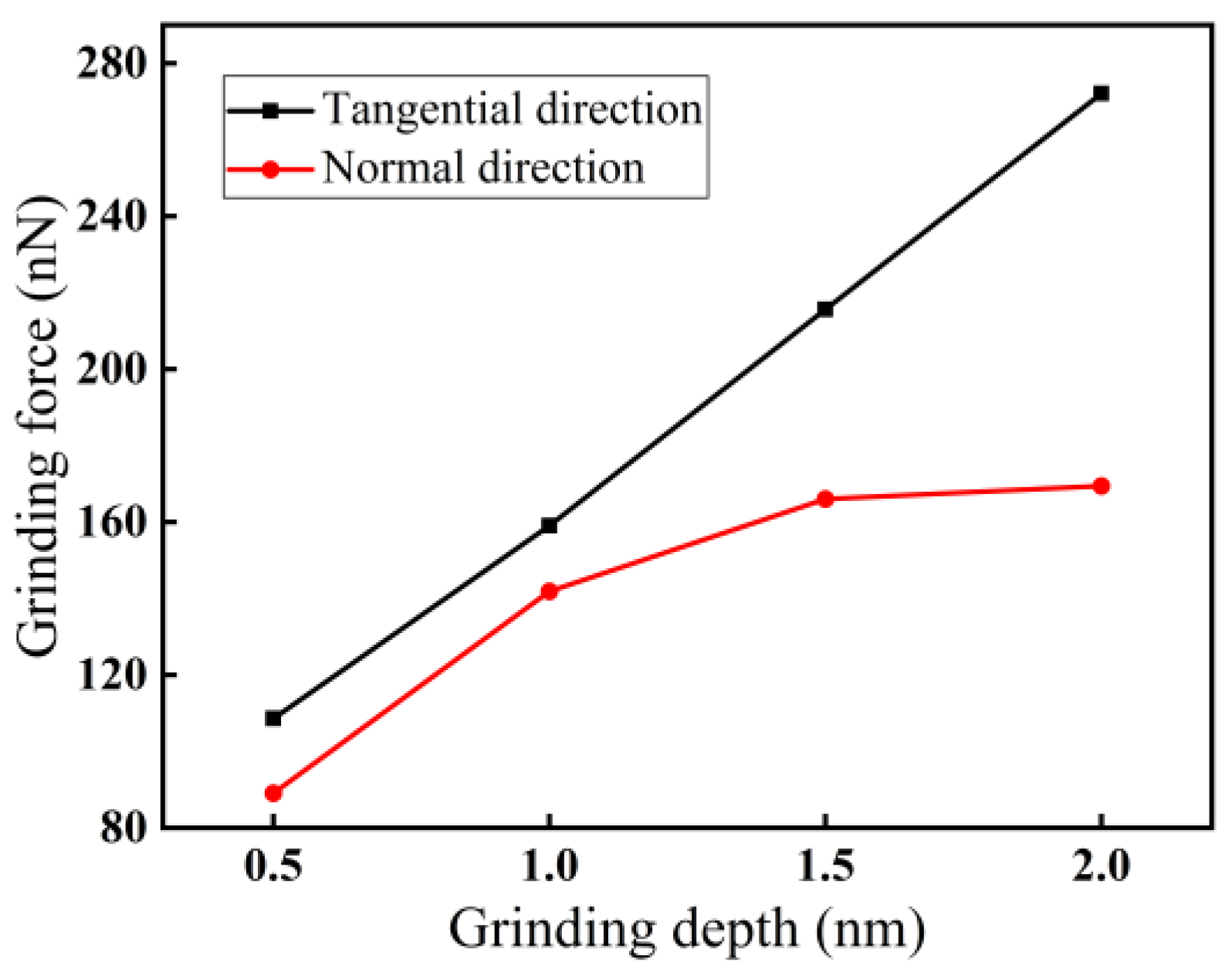
3.1.2. Effect of Grinding Depth on Force–Thermal Behavior
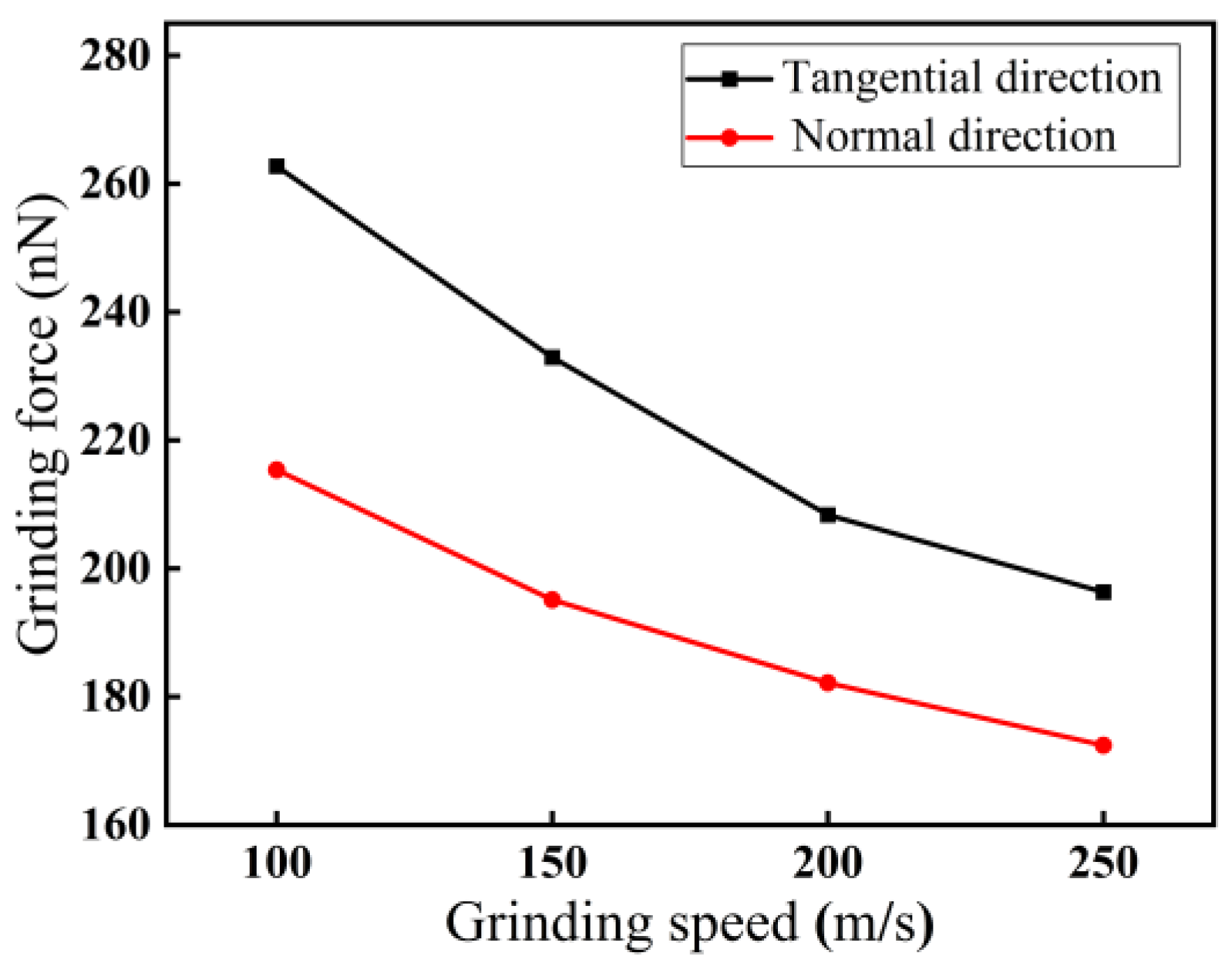
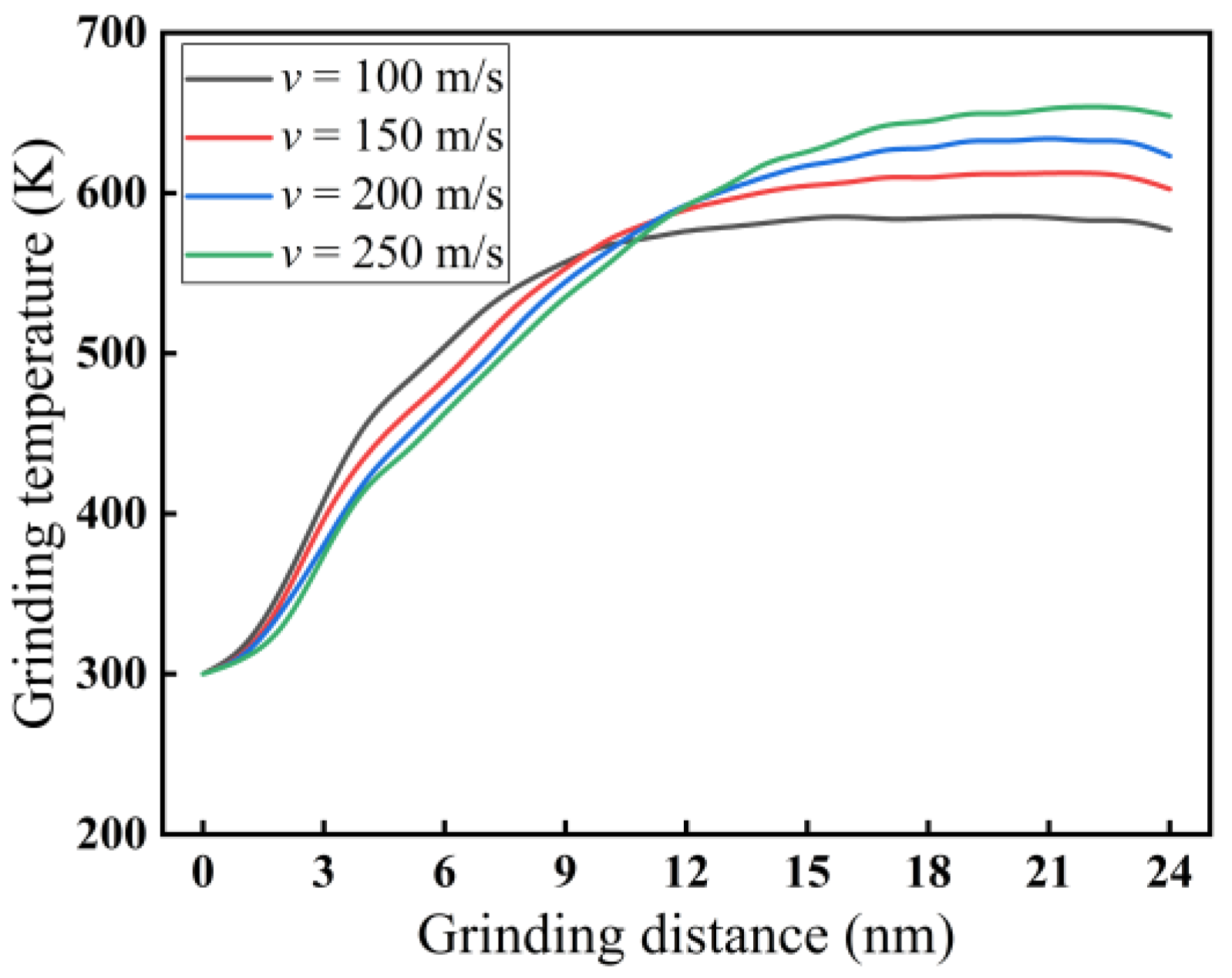
3.1.3. Effect of Grinding Speed on Force–Thermal Behavior
3.2. Analysis of Subsurface Damage for Monocrystalline Silicon in Nano-Grinding
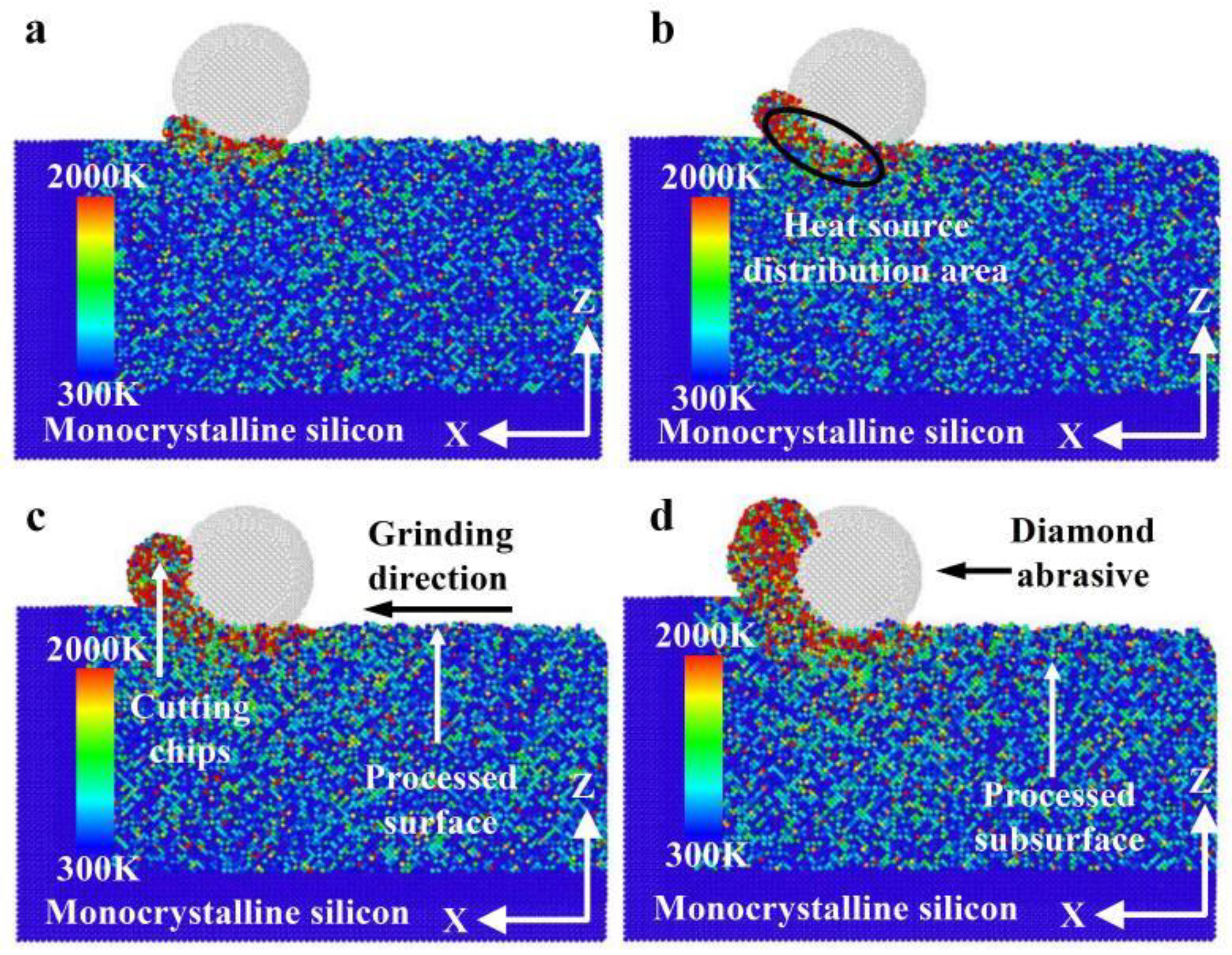
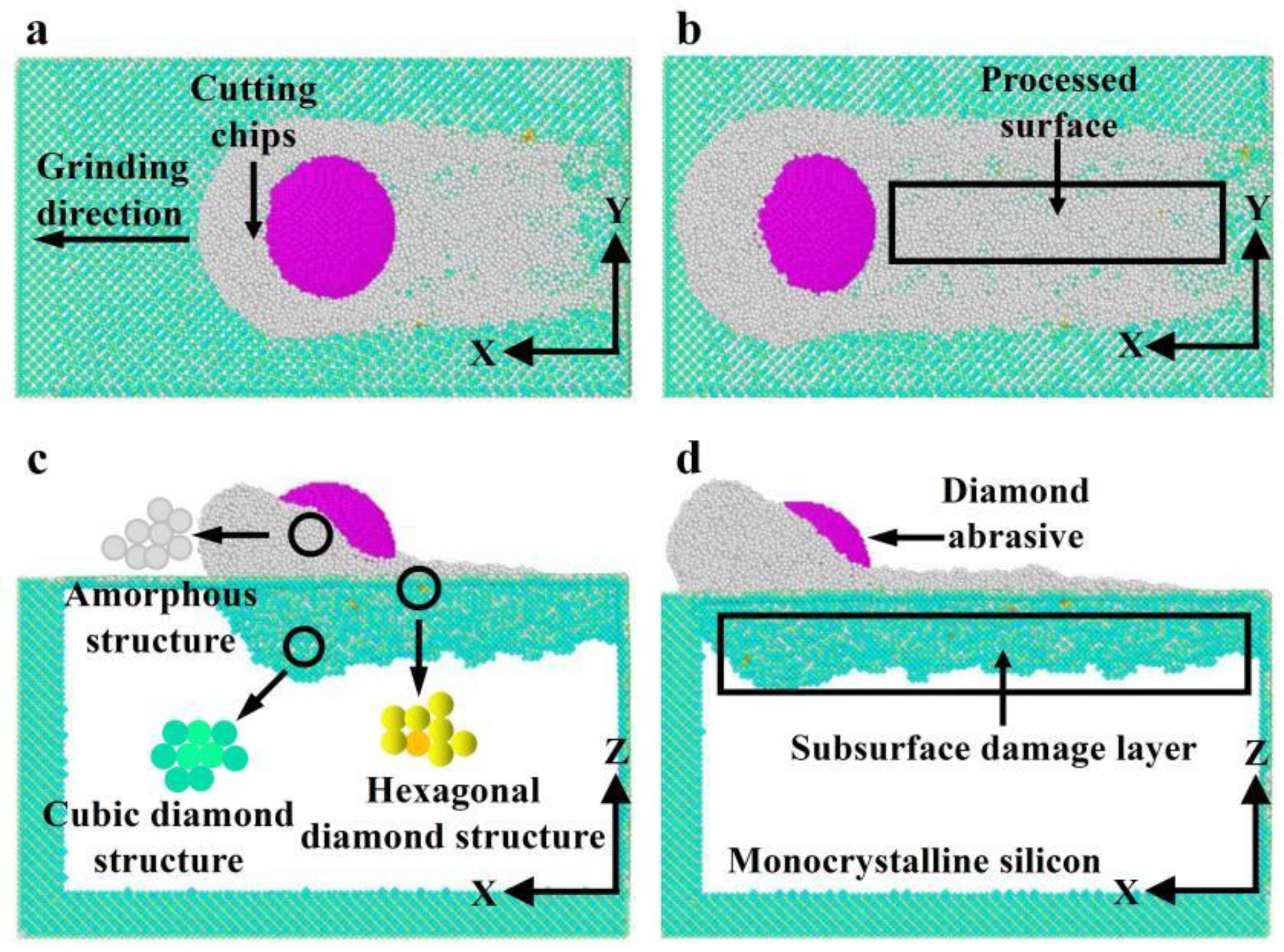
3.2.1. Formation Mechanism for Subsurface Damage
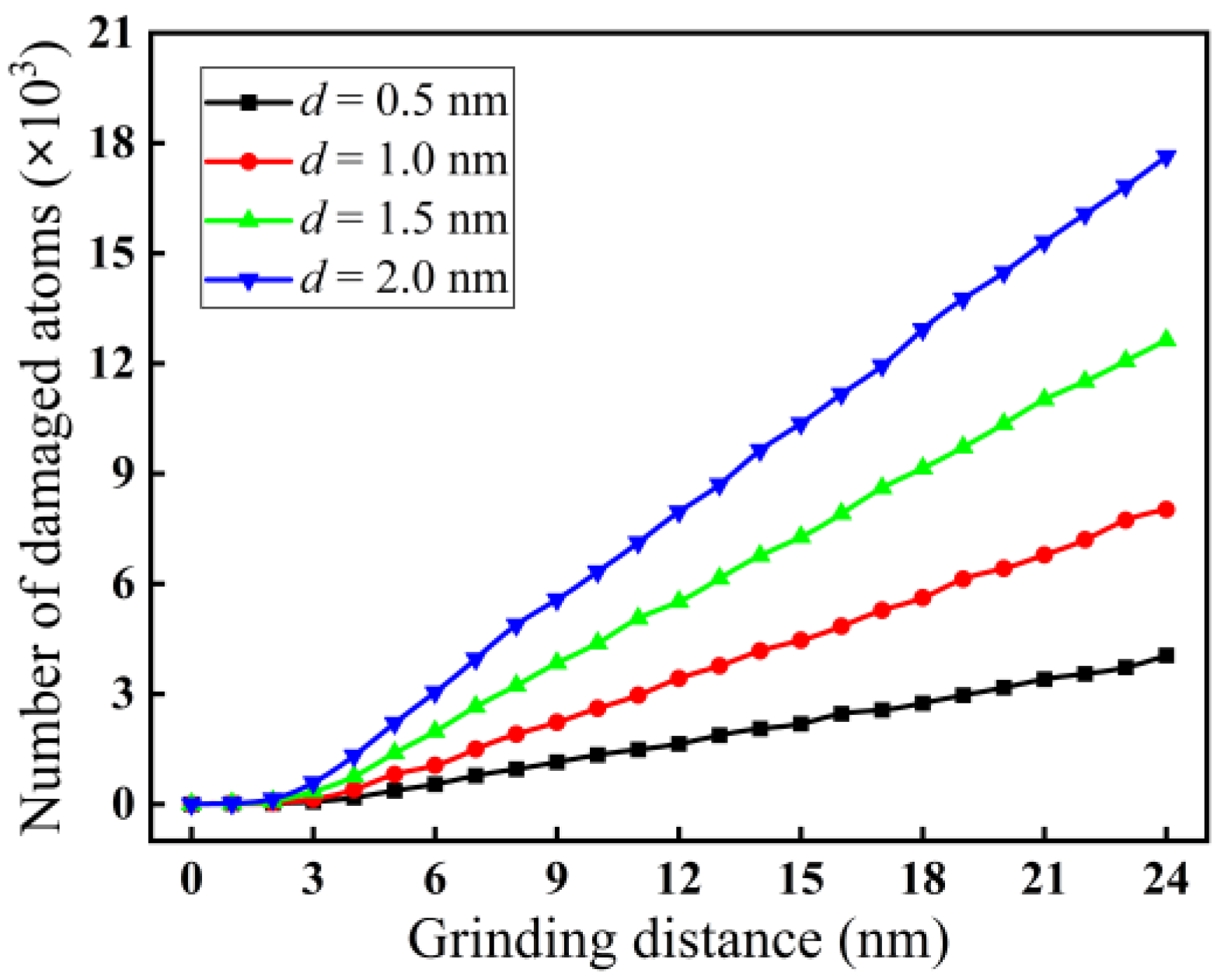
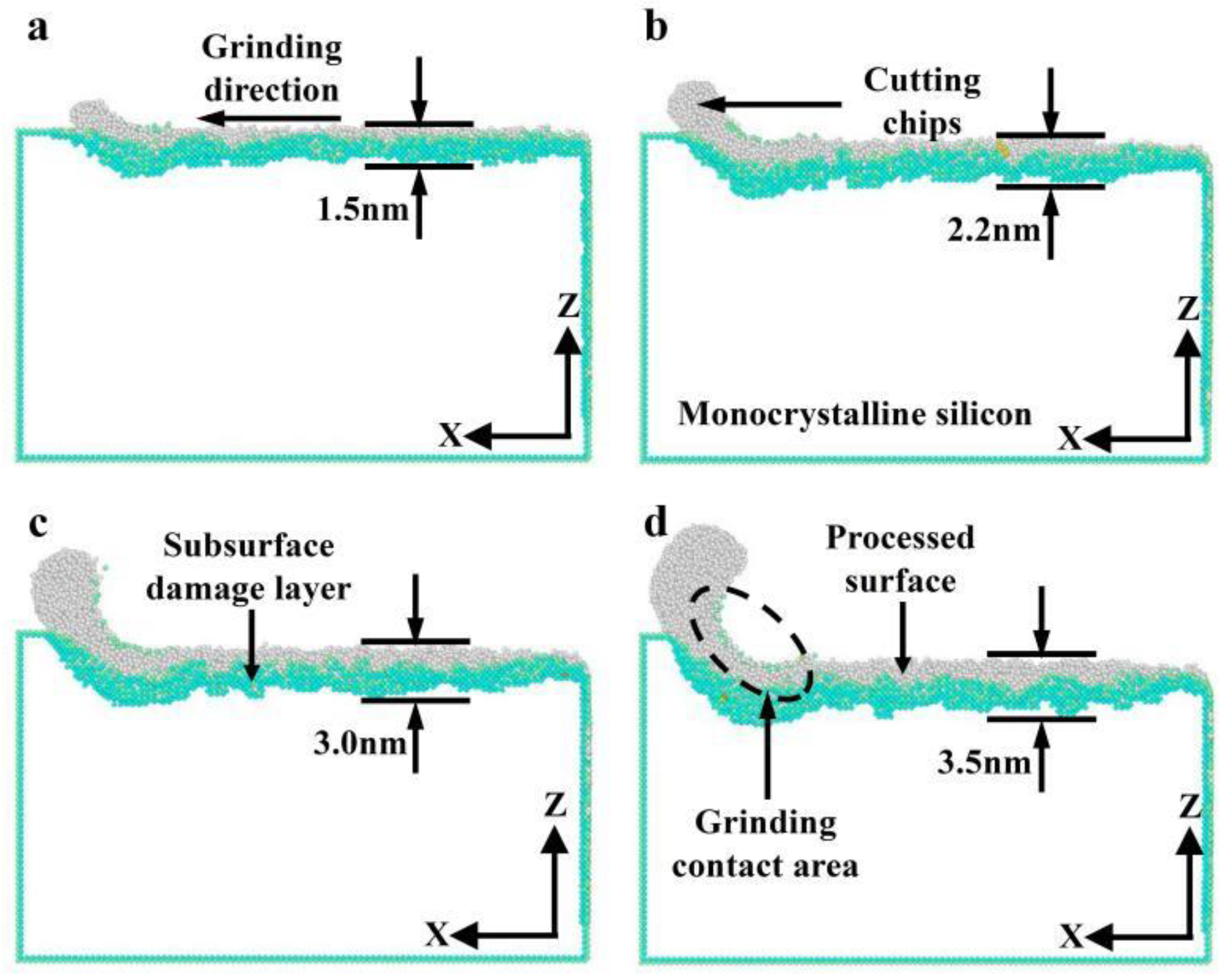
3.2.2. Effect of Grinding Depth on Subsurface Damage
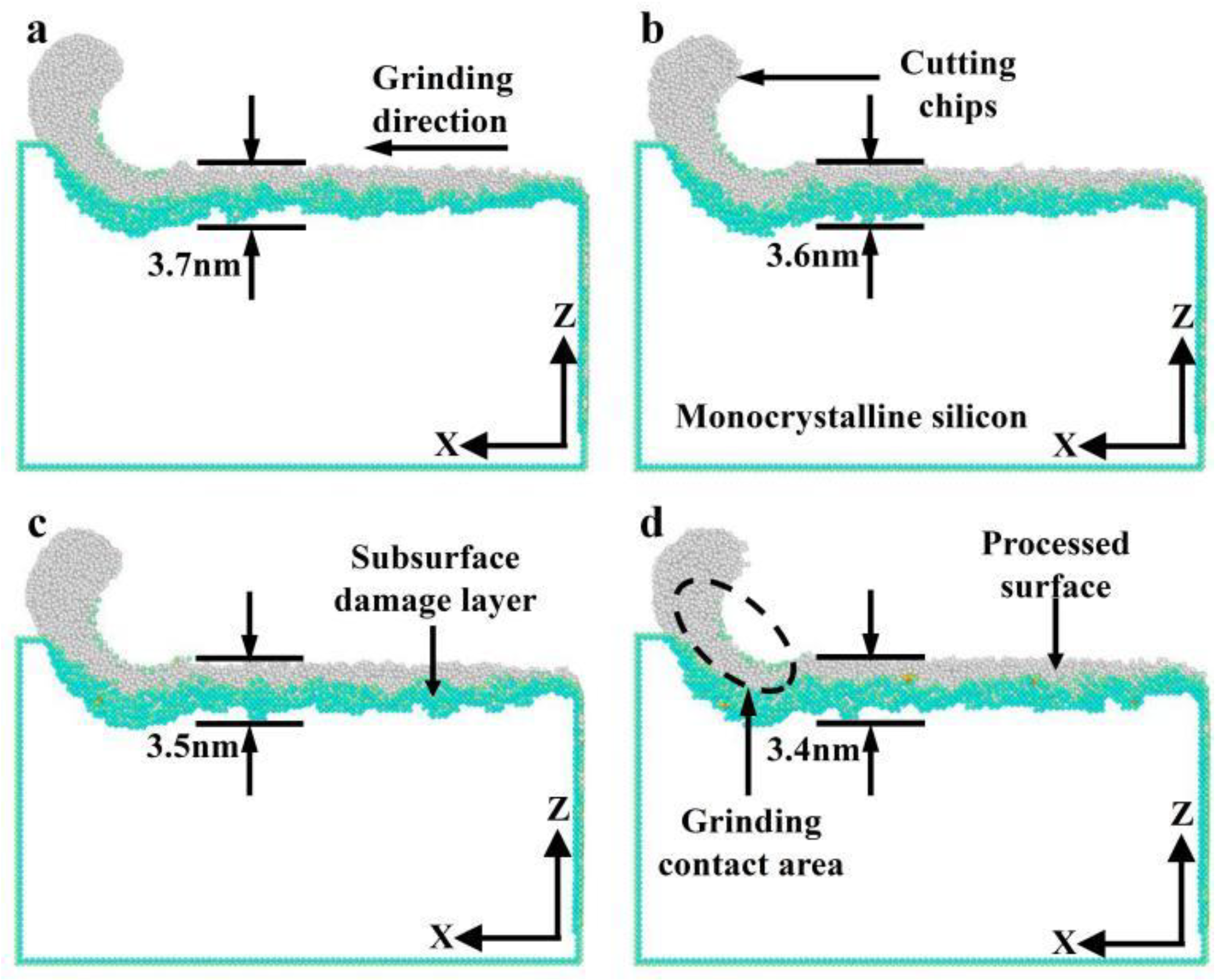
3.2.3. Effect of Grinding Speed on SUBSURFACE Damage
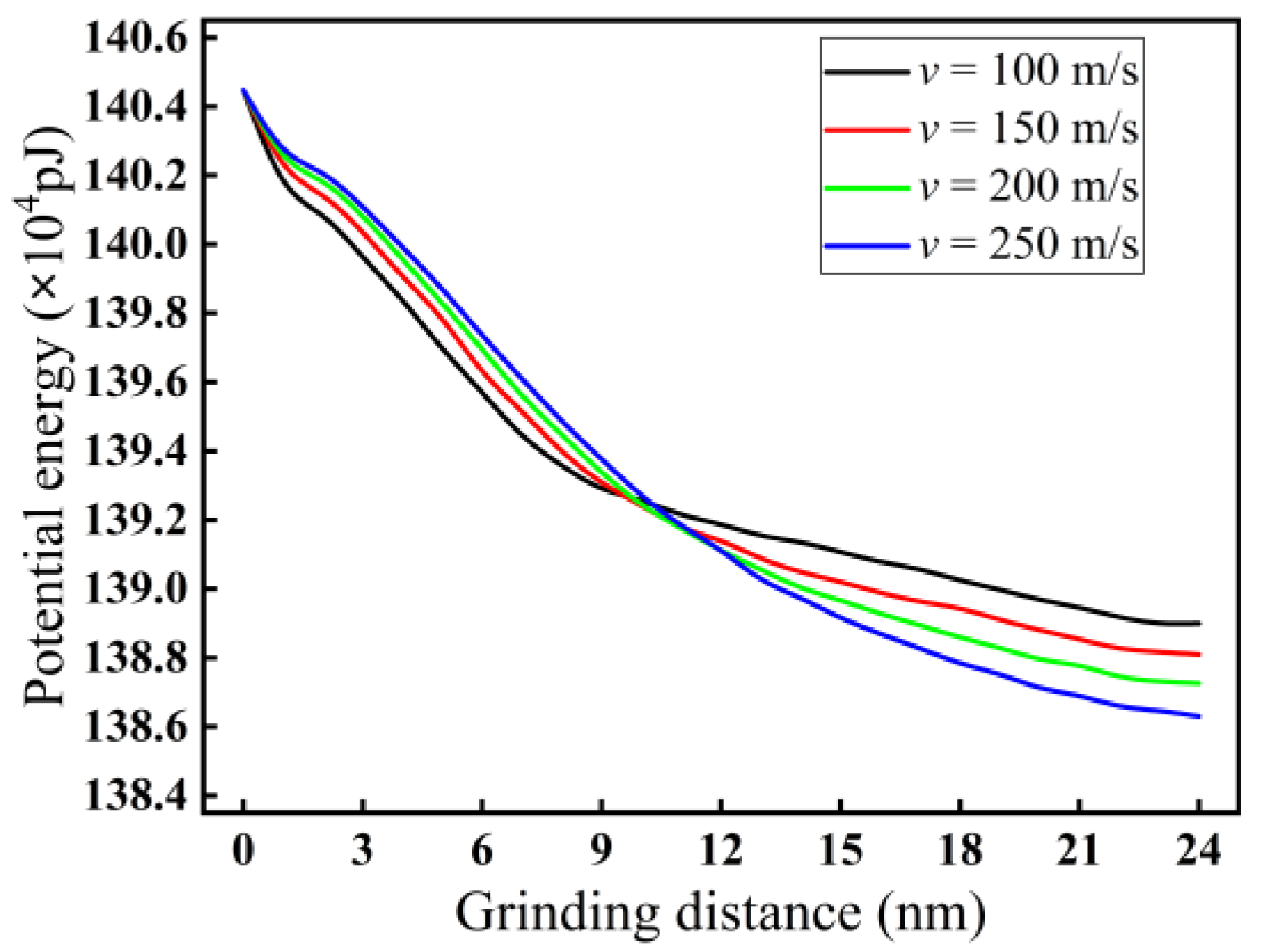
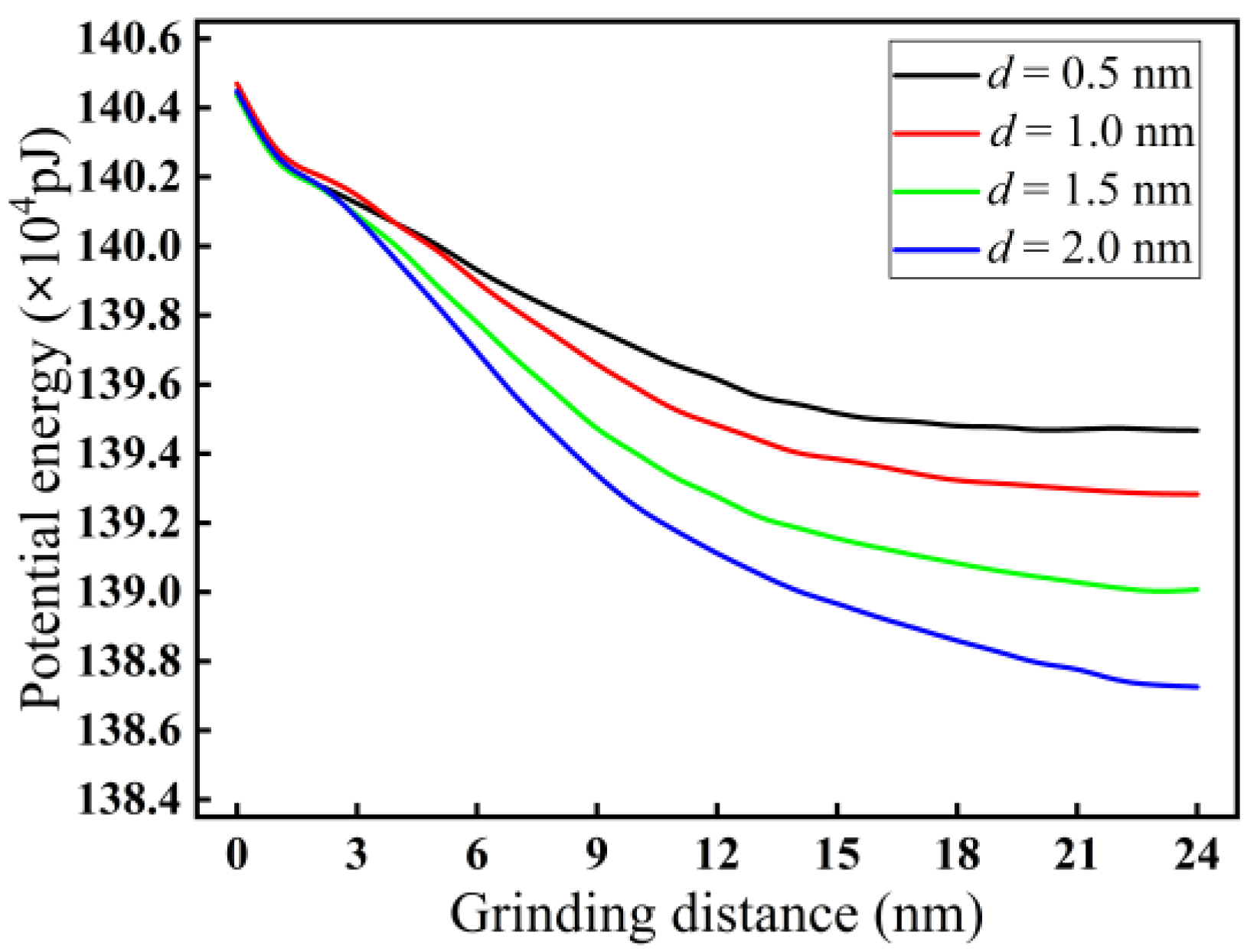
3.3. Analysis of Potential Energy
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Among the three grinding forces—tangential, lateral, and normal—the lateral grinding force fluctuates around zero and can be ignored. The grinding force in the tangential direction is slightly higher than that in the normal direction and plays a crucial role in material removal. Grinding force, shear stress, and friction coefficient all increase with increasing grinding depth and decreasing grinding speed.
- (2)
- The heat in the grinding area mainly accumulates near the cutting chips and abrasive particles, and the heat in the chips is higher than the heat distribution near the abrasive grains. The heat in front of and below the abrasive grains is higher than that behind them. The grinding temperature rises with increasing grinding depth. At the incipient stage of nano-grinding of monocrystalline silicon, the higher the grinding speed, the lower the grinding temperature. However, in the stable grinding stage beyond a distance of 12 nm, the grinding temperature shows an increasing trend with increasing grinding speed. With increasing grinding speed, the potential energy between silicon atoms shows an opposite trend compared to the grinding temperature.
- (3)
- Both phase transformation and amorphization are the main formation mechanisms of subsurface damage in nano-grinding of monocrystalline silicon. The quantity of damaged atoms and the thickness of the subsurface damage layer increase with increasing grinding depth and decreasing grinding speed. Therefore, in nano-grinding processes, reducing the grinding depth (e.g., a small grinding depth of 0.5 nm) and increasing the grinding speed (e.g., a high grinding speed of 250 m/s) should be prioritized to effectively suppress subsurface damage in monocrystalline silicon.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, P.H.; Guo, X.G.; Yuan, S.; Li, M.; Kang, R.K.; Guo, D.M. Effects of grinding speeds on the subsurface damage of single crystal silicon based on molecular dynamics simulations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 554, 149668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Zhou, P.; Goel, S. Microscopic stress analysis of nanoscratch induced sub-surface defects in a single-crystal silicon wafer. Precis. Eng. 2023, 82, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.N.; Yu, T.B.; Zhu, L.D.; Wang, W.S. Analytical modeling of ground surface topography in monocrystalline silicon grinding considering the ductile-regime effect. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2017, 17, 880–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.K.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, S.; Huang, J.X.; Zhu, X.L. High surface integrity fabrication of silicon wafers using a newly developed nonwoven structured grind-polishing wheel. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 77, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Dong, Z.G.; Yuan, S.; Guo, X.G.; Kang, R.K.; Guo, D.M. Study on subsurface damage mechanism of gallium nitride in nano-grinding. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Proc. 2021, 128, 105760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dong, Z.G.; Yuan, S.; Guo, X.G.; Kang, R.K.; Bao, Y. Effects of tool geometry on tungsten removal behavior during nano-cutting. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 225, 107384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kang, R.K.; Bao, Y.; Wang, K.X.; Guo, X.G.; Dong, Z.G. Microstructure evolution mechanism of tungsten induced by ultrasonic elliptical vibration cutting at atomic/nano scale. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 253, 108397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guo, X.; Huang, N.; Yang, Y.; Kang, R.; Guo, D.; Zhou, P. Dislocation slip mechanism and prediction method during the ultra-precision grinding process of monocrystalline silicon. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Proc. 2024, 177, 108388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Zhang, Q.L.; Zhou, J.; Tian, X.Q.; Chen, S.; Dong, F.F.; Han, J. Residual stress distribution of silicon wafers machined by rotational grinding based on molecular dynamics. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 119, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L. On the deformation mechanism and dislocations evolution in monocrystalline silicon under ramp nanoscratching. Tribol. Int. 2024, 193, 109395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.W.; Asami, T.; Harada, H.; Kuriyagawa, T. Fundamental investigation of subsurface damage in single crystalline silicon caused by diamond machining. Precis. Eng. 2009, 33, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Guo, X.G.; Yuan, S.; Dong, Z.G.; Kang, R.K. Effects of initial temperature on the damage of GaN during nanogrinding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 556, 149771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; To, S.; Sheng, X.X.; Xu, J.F. Molecular dynamics simulation on crystal defects of single-crystal silicon during elliptical vibration cutting. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 244, 108072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.T.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhao, T.L.; Yang, P.; Yue, C. Analysis of nano grinding removal mechanism of 3C-SiC material under the coupling action of double abrasive grains. Comp. Mater. Sci. 2023, 227, 112279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.Y.; Pan, J.S.; Zhao, B.; Wu, J.W. Molecular dynamics study of crystal orientation effect on surface generation mechanism of single-crystal silicon during the nano-grinding process. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 74, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Deng, J.Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Peng, N.J. Study of subsurface damage during nano-grinding of B3-GaN using molecular dynamics simulations. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Proc. 2024, 171, 107991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.M.; Gao, G.M.; Yang, C.; Zhao, C.Y. Modeling and simulation research on the semi elliptical grinding area and temperature field of rail abrasive belt grinding. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2025, 39, 100003. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, R.G.; Peng, Z.Y.; Li, P.L.; Ding, H. Investigation on Grinding Temperature Evolutions and Surface Characteristics of CFRTP in Robotic Grinding. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications, Xi’an, China, 31 July–2 August 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Plescia, P.; Tempesta, E. Analysis of friction coefficients in a vibrating cup mill (ring mill) during grinding. Tribol. Int. 2017, 114, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Cai, M.; Gong, Y.D.; Zhu, T.; Gao, X.J.; Zhang, M.L. Grinding subsurface damage mechanism of nickel-based single crystal superalloy based on stress-strain. Precis. Eng. 2024, 86, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Dong, Z.G.; Zhang, S.H.; Guo, X.G.; Yuan, S.; Jin, Z.J.; Kang, R.K.; Guo, D.M. The deformation mechanism of gallium-faces and nitrogen-faces gallium nitride during nanogrinding. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 214, 106888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.Y.; Gao, X.F.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.B.; Zhang, D.; Wu, X.; Huang, S.J.; Li, D.; Wu, J.W. Investigation on nano-grinding process of GaN using molecular dynamics simulation: Nano-grinding parameters effect. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 102, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.W.; Tang, J.Y.; Zhou, W.H.; Shao, W.; Yi, M.H.; Zhao, X.; Wen, J. Revealing nanoscale material deformation mechanism and surface/subsurface characteristics in vibration-assisted nano-grinding of single-crystal iron. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 597, 153692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Guo, Z.T.; Feng, R.C.; Li, H.Y.; Fu, R.; Zhou, Y.C. Numerical simulation of nano-cutting behaviors for polycrystalline γ-TiAl alloy: The effect of grain sizes. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 102, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhao, P.y.; Liu, H.; Pan, J.s.; Wu, J.W. Investigation on surface generation mechanism of single-crystal silicon in grinding: Surface crystal orientation effect. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.C.; Liu, J.; Qiu, H.J.; Wang, X.Z. Removal behavior and performance analysis of defective silicon carbide in nano-grinding. Precis. Eng. 2021, 72, 858–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tersoff, J. Empirical interatomic potential for silicon with improved elastic properties. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 38, 9902–9905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimpton, S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukowski, A. Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO–the Open Visualization Tool. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 18, 2154–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvari, S.M.H. Inverse determination of heat source distribution in conductive-radiative media with irregular geometry. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. 2005, 93, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.Z.; Chen, G.Y.; Shan, Z.Z. Study on ultra-high speed nano-grinding of monocrystalline copper with V-shaped diamond abrasive grains based on molecular dynamics method. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2021, 111, 108224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.H.; He, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.C. On the deformation mechanism of SiC under nano-scratching: An experimental investigation. Wear 2023, 522, 204871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.G.; Wang, H.; Qi, Y.N.; Guo, X.G.; Kang, R.K.; Bao, Y. Effects of minimum uncut chip thickness on tungsten nano-cutting mechanism. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 37, 107790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulse, C.O.; Copley, S.M.; Pask, J.A. Effect of crystal orientation on plastic deformation of magnesium oxide. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1963, 46, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.P.; Deng, F.; Qin, Z.Y.; Zhu, J.D.; Chang, H.J.; Niu, H.L. Effects of grinding parameters on the processing temperature, crack propagation and residual stress in silicon nitride ceramics. Micromachines 2023, 14, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Yang, H.J.; Kong, R.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Liu, J.Q.; Pang, K. Simulation and experimental study on limited cutting and heat effect of silicon carbide. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Simulation Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Workpiece size (nm × nm × nm) | 26 × 14 × 15 |
| Total number of atoms, N | 296,936 |
| Lattice constant of workpiece (nm) | 0.543 |
| Lattice constant of diamond (nm) | 0.357 |
| Diamond abrasive radius, r (nm) | 3 |
| Grinding depth, d (nm) | 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 |
| Grinding speed, v (m/s) | 100, 150, 200, 250 |
| Grinding distance, l (nm) | 0–24 |
| Grinding direction | [−100] (100) |
| Time step, t (fs) | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, H.; Zhang, H.; Cao, S.; Wang, C. Study on Nano-Grinding Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Subsurface Damage in Monocrystalline Silicon. Micromachines 2025, 16, 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090976
Yan H, Zhang H, Cao S, Wang C. Study on Nano-Grinding Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Subsurface Damage in Monocrystalline Silicon. Micromachines. 2025; 16(9):976. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090976
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Haipeng, Haining Zhang, Siyuan Cao, and Chao Wang. 2025. "Study on Nano-Grinding Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Subsurface Damage in Monocrystalline Silicon" Micromachines 16, no. 9: 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090976
APA StyleYan, H., Zhang, H., Cao, S., & Wang, C. (2025). Study on Nano-Grinding Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Subsurface Damage in Monocrystalline Silicon. Micromachines, 16(9), 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090976






