Optimization of PLGA Nanoparticle Formulation via Microfluidic and Batch Nanoprecipitation Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Batch Preparation of PLGA Nanoparticles with DoE
2.2.1. Hydrodynamic and Statistical Analysis
Hydrodynamic Characterization
Regression Modelling of Formulation Variables
- PLGA/ACN (mg/μL): PLGA concentration in organic phase
- % PVA: w/v % of PVA in aqueous solution
- Aq/Org (v/v): volume ratio of aqueous phase to organic phase
2.3. Preparation of PLGA Nanoparticles Using Microfluidic Mixing
2.4. Colloidal Characterization of PLGA Nanoparticles
2.4.1. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.4.2. Atomic Force Microscopy
2.5. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
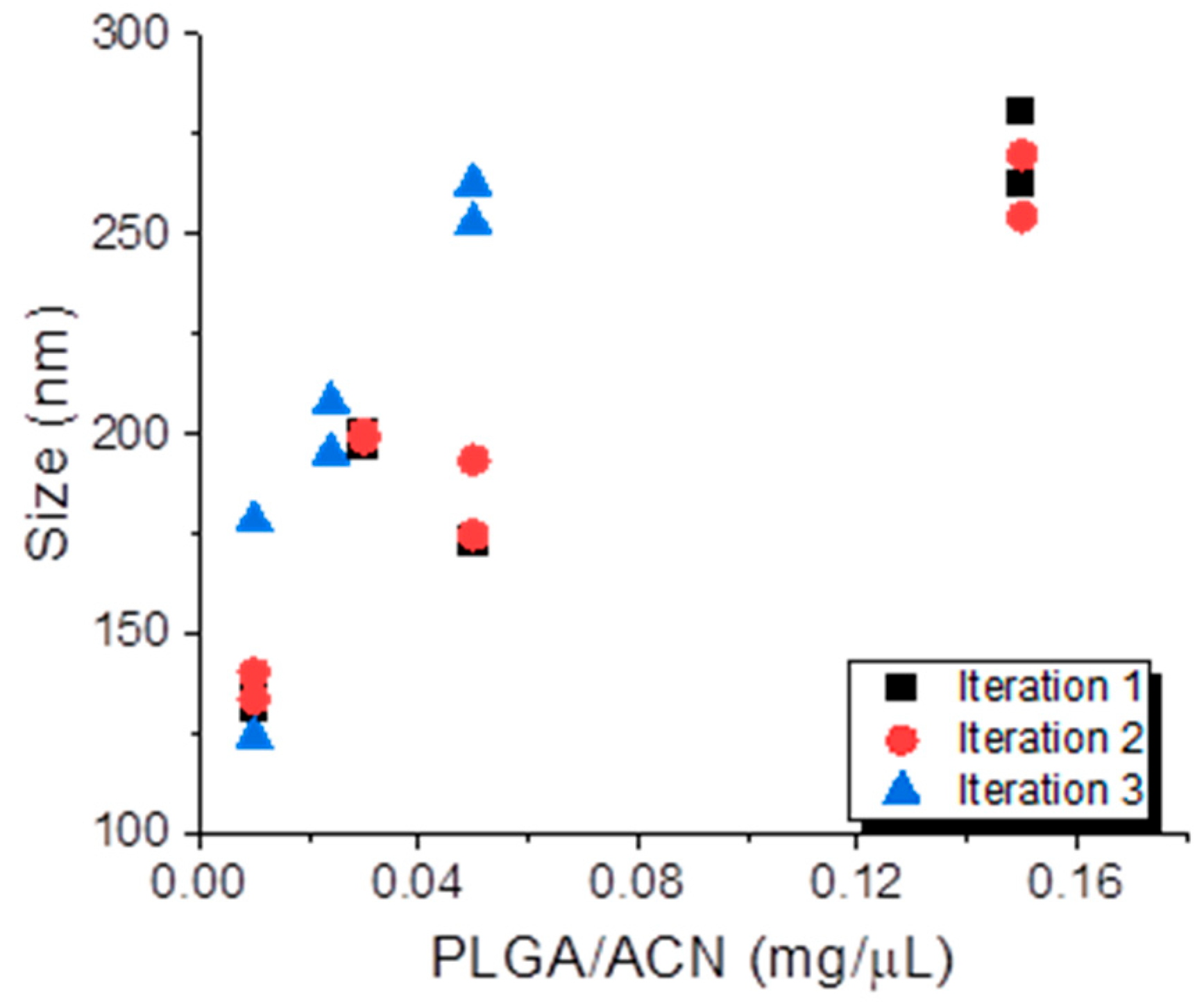
3.1. Batch Preparation of PLGA NPs Using DoE
3.2. Microfluidic Preparation of PLGA NPs
The Impact of Mixer Inlet Geometry on the Colloidal Properties of PLGA NPs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agrahari, V.; Hiremath, P. Challenges Associated and Approaches for Successful Translation of Nanomedicines Into Commercial Products. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimondi, S.; Ferreira, H.; Reis, R.L.; Neves, N.M. Microfluidic Devices: A Tool for Nanoparticle Synthesis and Performance Evaluation. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 14205–14228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Operti, M.C.; Fecher, D.; van Dinther, E.A.W.; Grimm, S.; Jaber, R.; Figdor, C.G.; Tagit, O. A comparative assessment of continuous production techniques to generate sub-micron size PLGA particles. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 550, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Parmar, A.; Kori, S.; Sandhir, R. PLGA-based nanoparticles: A new paradigm in biomedical applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Won, Y.Y. Phenomenology of the Initial Burst Release of Drugs from PLGA Microparticles. ACS Biomater Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 6053–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muddineti, O.S.; Omri, A. Current trends in PLGA based long-acting injectable products: The industry perspective. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiati, S.A.; Damiati, S. Microfluidic Synthesis of Indomethacin-Loaded PLGA Microparticles Optimized by Machine Learning. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 677547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Operti, M.C.; Bernhardt, A.; Pots, J.; Sincari, V.; Jager, E.; Grimm, S.; Engel, A.; Benedikt, A.; Hrubý, M.; De Vries, I.J.M.; et al. Translating the Manufacture of Immunotherapeutic PLGA Nanoparticles from Lab to Industrial Scale: Process Transfer and In Vitro Testing. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Operti, M.C.; Bernhardt, A.; Grimm, S.; Engel, A.; Figdor, C.G.; Tagit, O. PLGA-based nanomedicines manufacturing: Technologies overview and challenges in industrial scale-up. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 605, 120807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fessi, H.; Puisieux, F.; Devissaguet, J.P.; Ammoury, N.; Benita, S. Nanocapsule formation by interfacial polymer deposition following solvent displacement. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 55, R1–R4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Patel, M.; Yang, X.; Mitra, A.K. Recent advances in protein and Peptide drug delivery: A special emphasis on polymeric nanoparticles. Protein Pept. Lett. 2014, 21, 1102–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beg, S.; Swain, S.; Rahman, M.; Hasnain, M.S.; Imam, S.S. Chapter 3–Application of Design of Experiments (DoE) in Pharmaceutical Product and Process Optimization. In Pharmaceutical Quality by Design; Beg, S., Hasnain, M.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.; Seo, K.D.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, B.C.; Kim, D.S. Recent advances in engineering microparticles and their nascent utilization in biomedical delivery and diagnostic applications. Lab A Chip 2017, 17, 591–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Operti, M.C.; Bernhardt, A.; Sincari, V.; Jager, E.; Grimm, S.; Engel, A.; Hruby, M.; Figdor, C.G.; Tagit, O. Industrial Scale Manufacturing and Downstream Processing of PLGA-Based Nanomedicines Suitable for Fully Continuous Operation. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politis, S.N.; Colombo, P.; Colombo, G.; MRekkas, D. Design of experiments (DoE) in pharmaceutical development. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convery, N.; Gadegaard, N. 30 years of microfluidics. Micro Nano Eng. 2019, 2, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Operti, M.C.; Dölen, Y.; Keulen, J.; van Dinther, E.A.W.; Figdor, C.G.; Tagit, O. Microfluidics-Assisted Size Tuning and Biological Evaluation of PLGA Particles. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khizar, S.; Zine, N.; Errachid, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Elaissari, A. Microfluidic-based nanoparticle synthesis and their potential applications. Electrophoresis 2022, 43, 819–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Wang, S. Application of microfluidic chip technology in pharmaceutical analysis: A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2019, 9, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, S.T.; Zhou, W.; Dou, M.; Tavakoli, H.; Ma, L.; Xu, F.; Li, X. Recent advances of controlled drug delivery using microfluidic platforms. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 128, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Shang, L.; Zhao, Y. Microfluidics for Drug Development: From Synthesis to Evaluation. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 7468–7529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, M.B.; Goel, S. Microfluidic devices for synthesizing nanomaterials—A review. Nano Express 2020, 1, 032004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Ma, Y.; Sun, J. Microfluidic Methods for Fabrication and Engineering of Nanoparticle Drug Delivery Systems. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, A.; Kim, K.-Y. Three-objective optimization of a staggered herringbone micromixer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agha, A.; Waheed, W.; Stiharu, I.; Nerguizian, V.; Destgeer, G.; Abu-Nada, E.; Alazzam, A. A review on microfluidic-assisted nanoparticle synthesis, and their applications using multiscale simulation methods. Discov. Nano 2023, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, P.M. Chapter 7–Fluid Flow. In Bioprocess Engineering Principles, 7th ed.; Doran, P.M., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2013; pp. 201–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temam, R. Navier–Stokes Equations: Theory and Numerical Analysis; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 2024; Volume 343. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zou, A.; Wang, S. A method for calculating space charge distribution in ultra-high voltage direct current transmission lines based on the transport of diluted species theory. AIP Adv. 2024, 14, 055119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Bernard, J.; Ganachaud, F. Nanoprecipitation as a simple and straightforward process to create complex polymeric colloidal morphologies. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 294, 102474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miladi, K.; Sfar, S.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Nanoprecipitation Process: From Particle Preparation to In Vivo Applications. In Polymer Nanoparticles for Nanomedicines: A Guide for their Design, Preparation and Development; Vauthier, C., Ponchel, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 17–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bally, F.; Garg, D.K.; Serra, C.A.; Hoarau, Y.; Anton, N.; Brochon, C.; Parida, D.; Vandamme, T.; Hadziioannou, G. Improved size-tunable preparation of polymeric nanoparticles by microfluidic nanoprecipitation. Polymer 2012, 53, 5045–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokoohinia, P.; Hajialyani, M.; Sadrjavadi, K.; Akbari, M.; Rahimi, M.; Khaledian, S.; Fattahi, A. Microfluidic-assisted preparation of PLGA nanoparticles for drug delivery purposes: Experimental study and computational fluid dynamic simulation. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 14, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroock, A.D.; Dertinger, S.K.; Ajdari, A.; Mezic, I.; Stone, H.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Chaotic mixer for microchannels. Science 2002, 295, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.S.; Longmuir, K.J.; Yager, P. A practical guide to the staggered herringbone mixer. Lab A Chip 2008, 8, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, Y.; Tagami, T.; Hoshikawa, A.; Ozeki, T. The Use of an Efficient Microfluidic Mixing System for Generating Stabilized Polymeric Nanoparticles for Controlled Drug Release. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, A.-G.; Mihaiescu, D.E.; Grumezescu, A.M. A Review of Microfluidic Experimental Designs for Nanoparticle Synthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahed, W.; Degobert, G.; Stainmesse, S.; Fessi, H. Freeze-drying of nanoparticles: Formulation, process and storage considerations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1688–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonte, P.; Andrade, F.; Azevedo, C.; Pinto, J.; Seabra, V.; van de Weert, M.; Reis, S.; Sarmento, B. Effect of the Freezing Step in the Stability and Bioactivity of Protein-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Upon Lyophilization. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2777–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia, P.M.; Pridgen, E.M.; Rhee, M.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Karnik, R. Microfluidic Platform for Combinatorial Synthesis and Optimization of Targeted Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 10671–10680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, E.; Bellotti, M.; Caimi, A.; Conti, B.; Dorati, R.; Conti, M.; Genta, I.; Auricchio, F. Development and optimization of microfluidic assisted manufacturing process to produce PLGA nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 629, 122368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnik, R.; Gu, F.; Basto, P.; Cannizzaro, C.; Dean, L.; Kyei-Manu, W.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Microfluidic Platform for Controlled Synthesis of Polymeric Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2906–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lababidi, N.; Sigal, V.; Koenneke, A.; Schwarzkopf, K.; Manz, A.; Schneider, M. Microfluidics as tool to prepare size-tunable PLGA nanoparticles with high curcumin encapsulation for efficient mucus penetration. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2280–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Hui, Y.; Ranaweera, S.; Zhao, C.-X. Microfluidic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Small 2022, 18, 2106580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, J.; Meng, F.; Deng, C.; Zhong, Z. Micellar nanoformulation of lipophilized bortezomib: High drug loading, improved tolerability and targeted treatment of triple negative breast cancer. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 5658–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Mochida, A.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Nanodrug Delivery: Is the Enhanced Permeability and Retention Effect Sufficient for Curing Cancer? Bioconjugate Chem. 2016, 27, 2225–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roces, C.B.; Port, E.C.; Daskalakis, N.N.; Watts, J.A.; Aylott, J.W.; Halbert, G.W.; Perrie, Y. Rapid scale-up and production of active-loaded PEGylated liposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, S.K.; Khusnutdinov, R.; Murmiliuk, A.; Inam, W.; Zakharova, L.Y.; Zhang, H.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Dynamic light scattering and transmission electron microscopy in drug delivery: A roadmap for correct characterization of nanoparticles and interpretation of results. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 5354–5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Gao, X. Nanoparticle counting: Towards accurate determination of the molar concentration. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7267–7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Iteration | VACN [μL] | VPVA [mL] | CPLGA [mg] | CPVA [%] | Size [nm] | Std Dev | PDI | Std Dev | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F1.1 | 500 | 1 | 5 | 2.5 | 136 | ±1.0 | 0.07 | ±0.01 |
| F1.2 | 500 | 1 | 15 | 1.5 | 198 | ±1.0 | 0.10 | ±0.02 | |
| F1.3 | 100 | 3 | 5 | 2.5 | 173 | ±1.0 | 0.07 | ±0.01 | |
| F1.4 | 100 | 3 | 15 | 1.5 | 263 | ±5.0 | 0.32 | ±0.01 | |
| F1.5 | 500 | 3 | 5 | 1.5 | 132 | ±1.0 | 0.05 | ±0.02 | |
| F1.6 | 100 | 1 | 15 | 2.5 | 281 | ±3.0 | 0.29 | ±0.01 | |
| F1.7 | 100 | 1 | 5 | 1.5 | 173 | ±1.0 | 0.08 | ±0.04 | |
| F1.8 | 500 | 3 | 15 | 2.5 | 200 | ±1.0 | 0.10 | ±0.02 | |
| 2 | F2.1 | 100 | 3 | 15 | 1.5 | 270 | ±9.0 | 0.27 | ±0.04 |
| F2.2 | 100 | 1 | 5 | 1.5 | 175 | ±1.0 | 0.08 | ±0.01 | |
| F2.3 | 100 | 3 | 5 | 2.5 | 194 | ±1.0 | 0.07 | ±0.04 | |
| F2.4 | 500 | 1 | 15 | 1.5 | 199 | ±2.0 | 0.09 | ±0.01 | |
| F2.5 | 500 | 3 | 15 | 2.5 | 200 | ±1.0 | 0.07 | ±0.01 | |
| F2.6 | 100 | 1 | 15 | 2.5 | 255 | ±2.0 | 0.18 | ±0.02 | |
| F2.7 | 500 | 3 | 5 | 1.5 | 134 | ±1.0 | 0.05 | ±0.02 | |
| F2.8 | 500 | 1 | 5 | 2.5 | 140 | ±1.0 | 0.06 | ±0.02 | |
| 3 | F3.1 | 100 | 3 | 12 | 1.5 | 1483 | ±820 | 0.84 | ±0.14 |
| F3.2 | 100 | 1 | 12 | 2.5 | 4793 | ±834 | 0.91 | ±0.08 | |
| F3.3 | 500 | 3 | 12 | 2.5 | 208 | ±1.0 | 0.24 | ±0.02 | |
| F3.4 | 500 | 3 | 5 | 1.5 | 124 | ±1.0 | 0.15 | ±0.01 | |
| F3.5 | 500 | 1 | 12 | 1.5 | 195 | ±2.0 | 0.06 | ±0.01 | |
| F3.6 | 500 | 1 | 5 | 2.5 | 156 | ±1.0 | 0.06 | ±0.03 | |
| F3.7 | 100 | 3 | 5 | 2.5 | 253 | ±1.0 | 0.29 | ±0.02 | |
| F3.8 | 100 | 1 | 5 | 1.5 | 273 | ±3.0 | 0.38 | ±0.02 |
| Iteration | Size R2 | pPLGA/ACN | p%PVA | pAq/Org |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.888 | * 0.007 | 0.725 | 0.379 |
| 2 | 0.842 | * 0.020 | 0.237 | 0.756 |
| 3 | 0.908 | * 0.004 | 0.139 | * 0.039 |
| Iteration | PDI R2 | pPLGA/ACN | p%PVA | pAq/Org |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.172 | 0.698 | 0.468 | 0.754 |
| 2 | 0.899 | * 0.009 | 0.108 | 0.847 |
| 3 | 0.967 | * 0.001 | 0.273 | 0.591 |
| Inlet Geometry | Before Lyophilization | After Lyophilization | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Diameter (nm) | PDI | Mean Diameter (nm) | PDI | |
| Y-junction | 158.1 ± 0.6 | 0.101 | 200.6 ± 2.2 | 0.240 |
| Three-inlet junction | 157.5 ± 2.6 | 0.084 | 173.1 ± 1.5 | 0.141 |
| Inlet Geometry | Number of Elements | Minimum Element Quality | Average Element Quality | Element Volume Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three-inlet junction | 3,414,891 | 0.06555 | 0.676 | 6.21 × 10−4 |
| Y-junction | 11,330,936 | 0.06417 | 0.6803 | 5.21 × 10−6 |
| Inlet Geometry | Molar Concentration of PLGA at Inlet (mol/m3) | Molar Concentration of PLGA at Outlet (mol/m3) | Mean Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Three-inlet junction | 0.83 | 0.12 | 171 |
| Y-junction | 0.83 | 0.21 | 206 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozalak, G.; Heyat Davoudian, S.; Natsaridis, E.; Gogniat, N.; Koşar, A.; Tagit, O. Optimization of PLGA Nanoparticle Formulation via Microfluidic and Batch Nanoprecipitation Techniques. Micromachines 2025, 16, 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090972
Kozalak G, Heyat Davoudian S, Natsaridis E, Gogniat N, Koşar A, Tagit O. Optimization of PLGA Nanoparticle Formulation via Microfluidic and Batch Nanoprecipitation Techniques. Micromachines. 2025; 16(9):972. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090972
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozalak, Gül, Salar Heyat Davoudian, Evangelos Natsaridis, Nubia Gogniat, Ali Koşar, and Oya Tagit. 2025. "Optimization of PLGA Nanoparticle Formulation via Microfluidic and Batch Nanoprecipitation Techniques" Micromachines 16, no. 9: 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090972
APA StyleKozalak, G., Heyat Davoudian, S., Natsaridis, E., Gogniat, N., Koşar, A., & Tagit, O. (2025). Optimization of PLGA Nanoparticle Formulation via Microfluidic and Batch Nanoprecipitation Techniques. Micromachines, 16(9), 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16090972









