The Effect of Scratch-Induced Microscale Surface Roughness on Signal Transmission in Radio Frequency Coaxial Connectors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sample Preparation and Data Collection
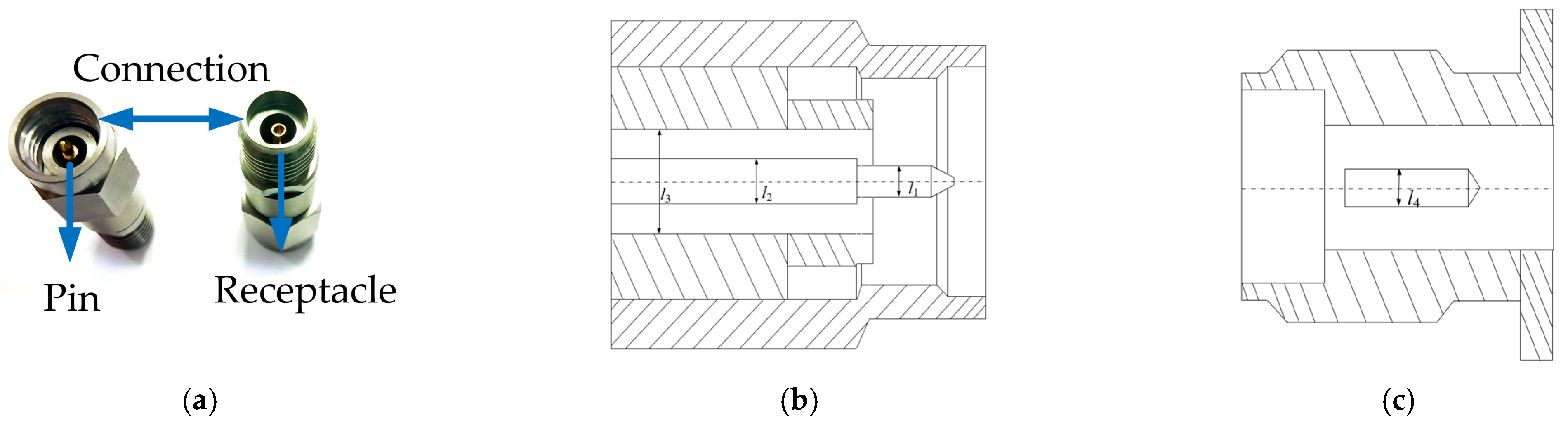
2.1. Connector Sample Fabrication
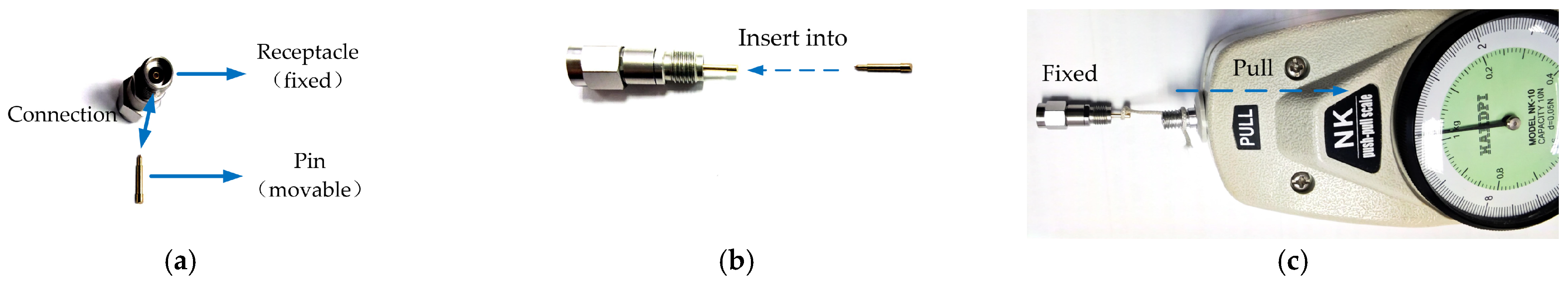
2.2. Evaluation of Pin–Receptacle Contact Force
3. Mathematical Modeling
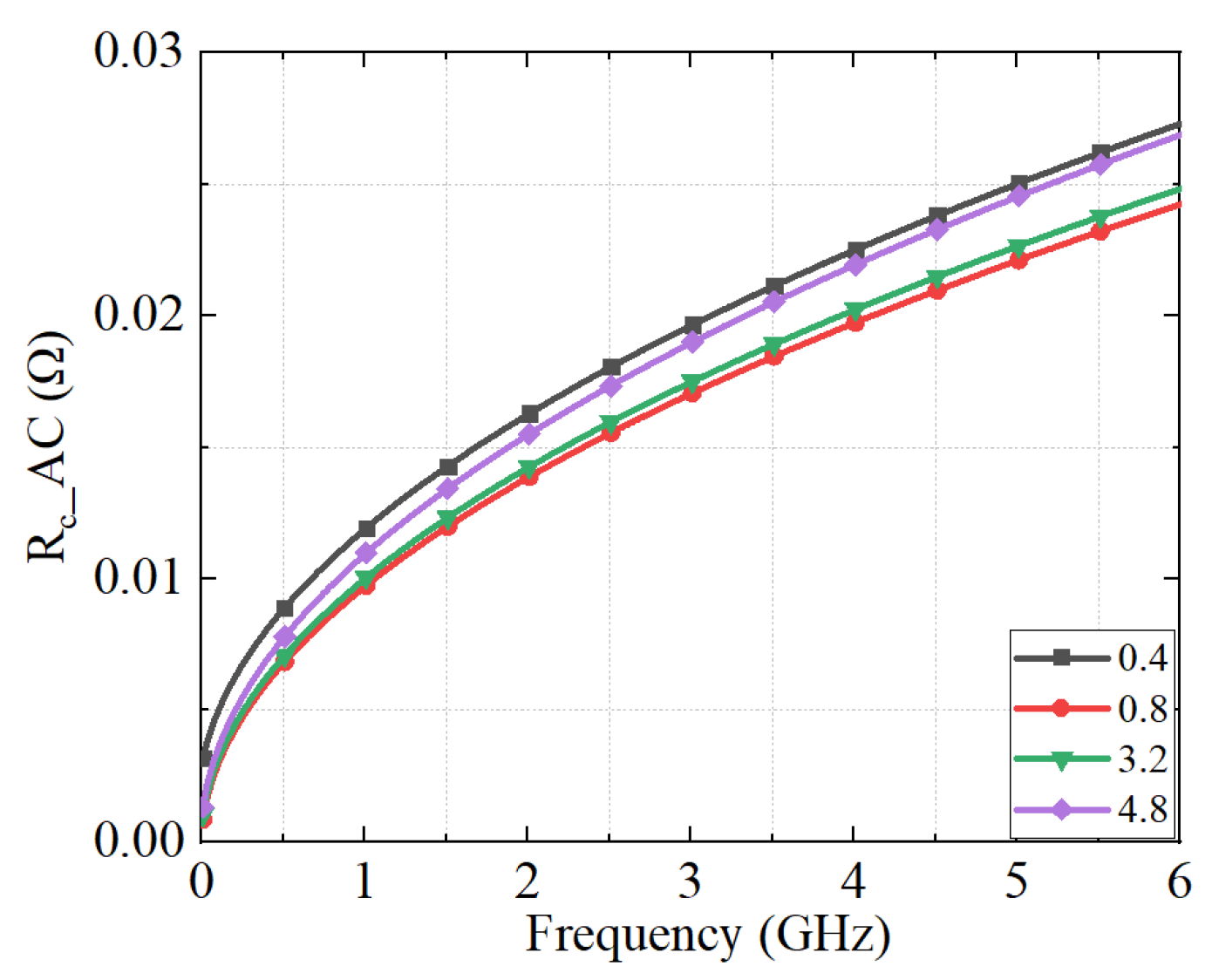
3.1. Modeling of High-Frequency Contact Resistance
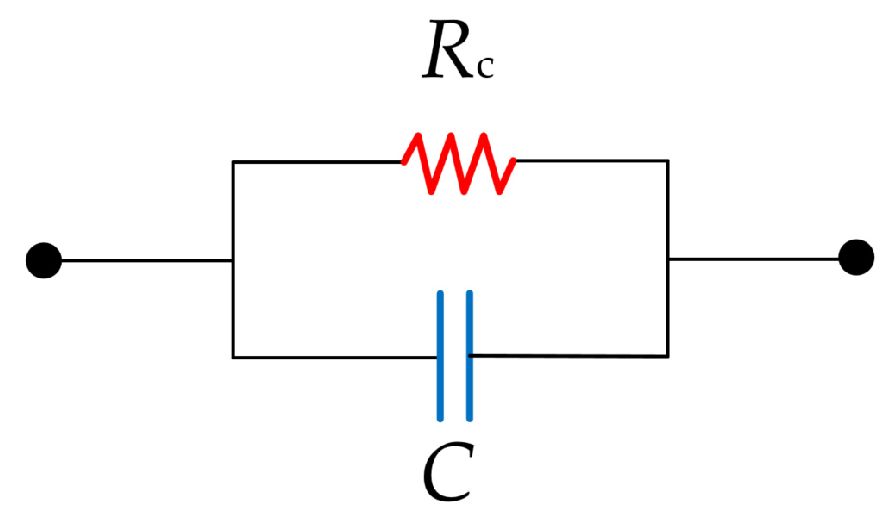
3.2. Modeling of High-Frequency Contact Impedance
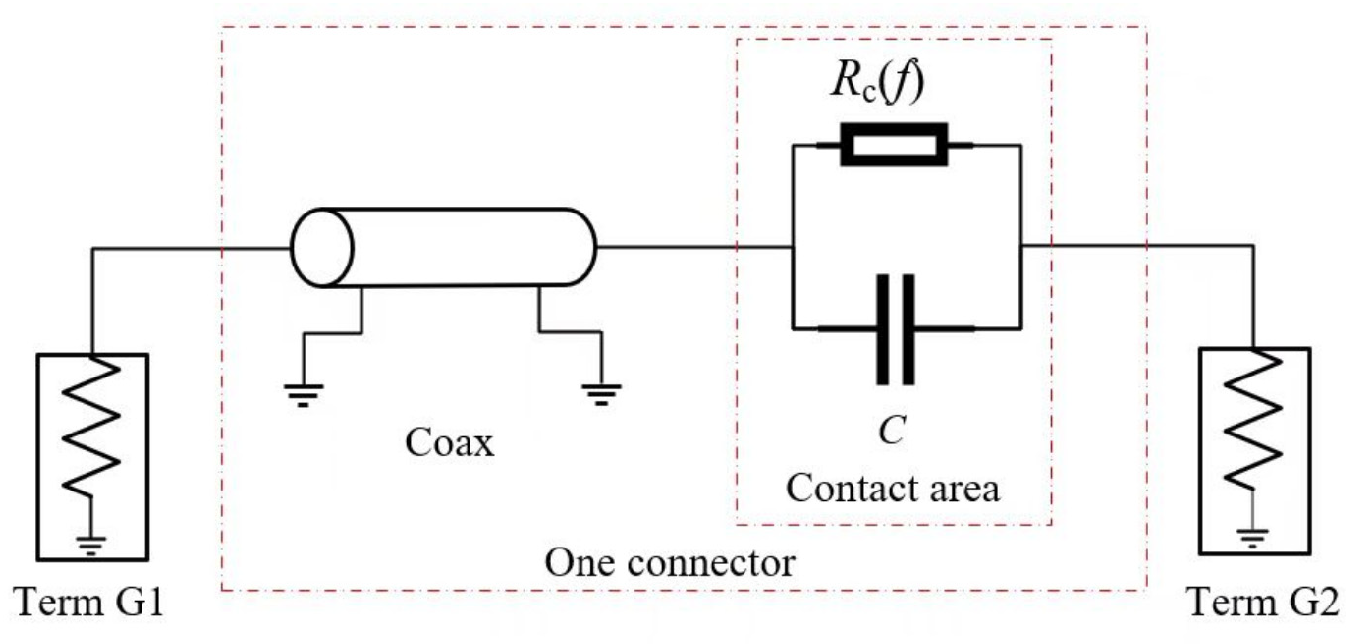
4. Equivalent Circuit Analysis and Simulation
4.1. Equivalent Circuit Model Development
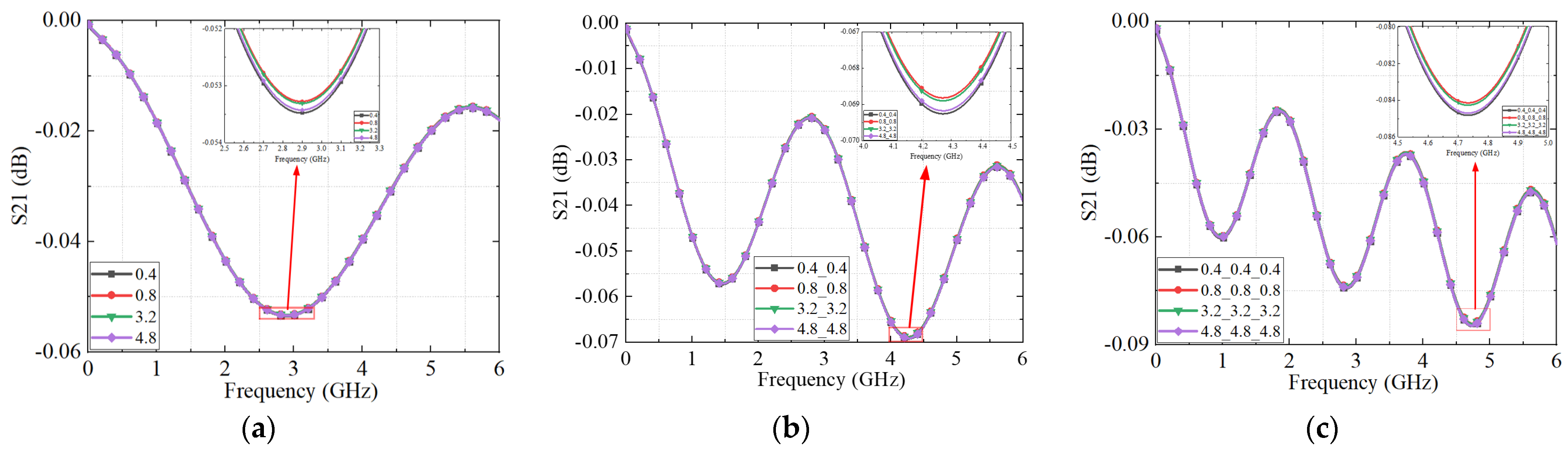
4.2. Results and Discussion of the Simulation
5. Experimental Verification
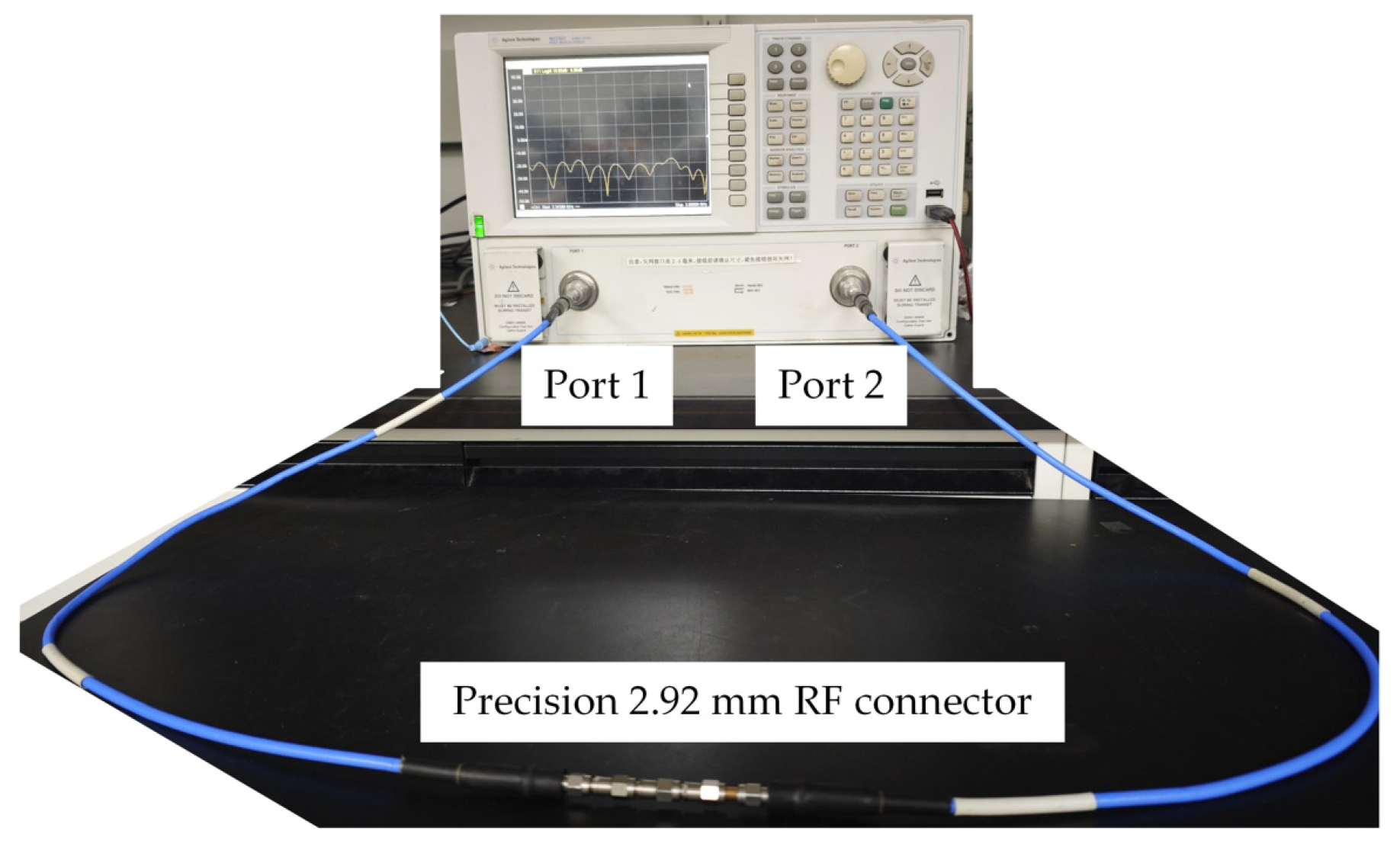
5.1. Experimental Setup
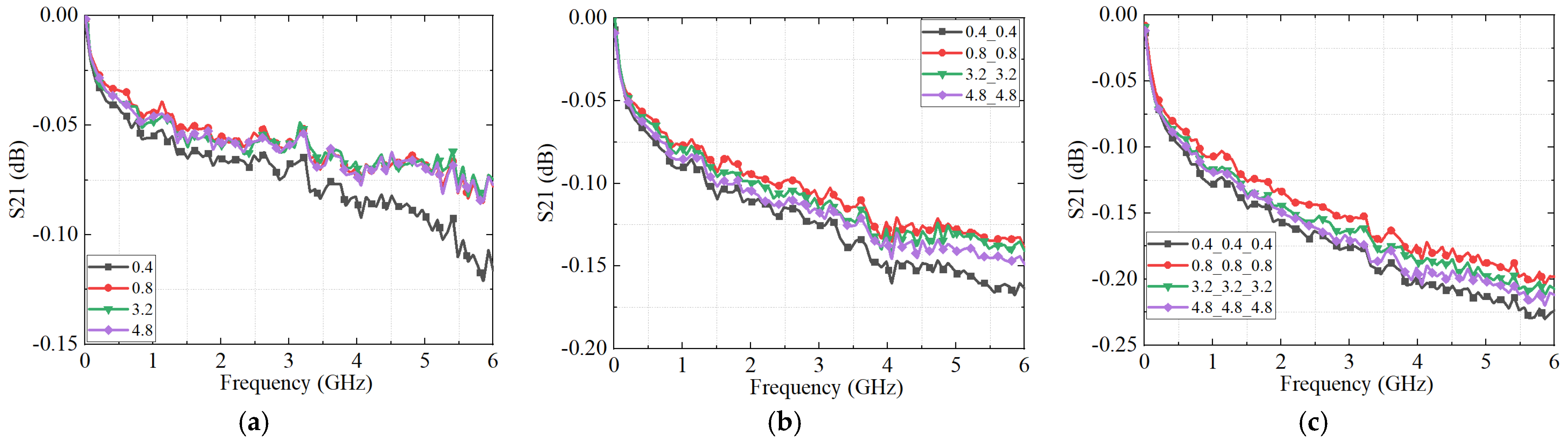
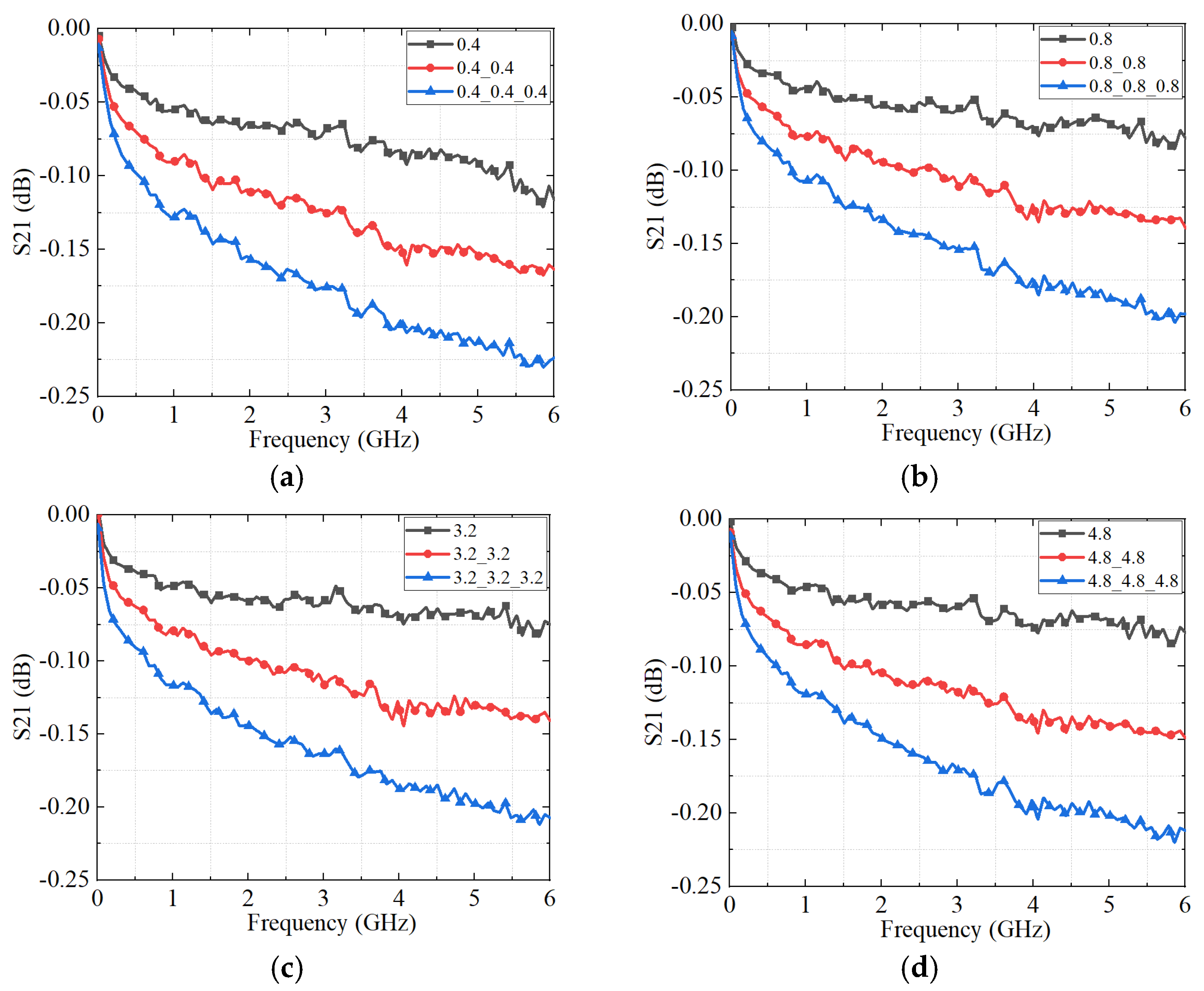
5.2. Results and Discussion of the Measurement
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RF | ratio frequency |
| DC | direct current |
| AC | alternating current |
| RC | resistance-capacitance |
| SEM | scanning electron microscope |
| PIM | passive intermodulation |
References
- Paleček, J.; Vestenický, M.; Vestenický, P.; Spalek, J. Examination of SMA connector parameters. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Engineering Systems (INES), Lisbon, Portugal, 13–15 June 2012; pp. 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandic, T.; Magerl, M.; Baric, A. Sequential Buildup of Broadband Equivalent Circuit Model for Low-Cost SMA Connectors. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2019, 61, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Feng, Q. Frequency and Power Dependence of Passive Intermodulation in Connectors With Contact-Material Nonlinear Modeling. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2021, 31, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wen, H. TDR Prediction Method for PIM Distortion in Loose Contact Coaxial Connectors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 4689–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Huang, Y.; Lin, M.; Kung, T. Measurement analysis and improvement technique of signal integrity for high-speed connectors. In Proceedings of the 2012 Asia-Pacific Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, Singapore, 21–24 May 2012; pp. 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, F.A.; Mascolo, V.; Hussain, F.; Rietveld, G. Calculating S-Parameters and Uncertainties of Coaxial Air-Dielectric Transmission Lines. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 8000511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ji, R.; Ma, H.; Zang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, E. State Influence of Adjacent Conductors Distributed Around Tested Channel in High-Speed Connector on Electromagnetic Measurement. IEEE Electromagn. Compat. Mag. 2024, 13, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; He, X.; Li, L.; Duan, M. An Evaluation Method for Electrical Contact Failure Based on High-Frequency Impedance Model. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 11, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Yu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, K.; Chen, Y. Investigation on Electrical and Thermal Performance of Electrical Connectors Under Rough Surface Contact. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 15, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, F.; Riba, J.R.; Rupérez, E.; Sanllehí, J. A Genetic-Algorithm-Optimized Fractal Model to Predict the Constriction Resistance From Surface Roughness Measurements. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 2437–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachman, N.A.; Risdiyanto, A.; Khayam, U.; Suwarno. Analysis of surface roughness and contact pressure at copper connector using nickel and silver plating for EV battery. In Proceedings of the 2013 Joint International Conference on Rural Information & Communication Technology and Electric-Vehicle Technology (rICT & ICeV-T), Bandung, Indonesia, 26–28 November 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angadi, S.V.; Wilson, W.E.; Jackson, R.L.; Flowers, G.T.; Rickett, B.I. A Multi-Physics Finite Element Model of an Electrical Connector Considering Rough Surface Contact. In Proceedings of the 54th IEEE Holm Conference on Electrical Contacts, Orlando, FL, USA, 27–29 October 2008; pp. 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.E.; Angadi, S.V.; Jackson, R.L. Electrical Contact Resistance Considering Multi-Scale Roughness. In Proceedings of the 54th IEEE Holm Conference on Electrical Contacts, Orlando, FL, USA, 27–29 October 2008; pp. 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malucci, R. The Impact of Plating on Equipotential Surfaces and Contact Resistance. In Proceedings of the 66th IEEE Holm Conference on Electrical Contacts, San Antonio, TX, USA, 24–27 October 2021; pp. 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinaghizadeh, A.; Azarhoushang, B.; Hadad, M. The Influence of Contour Form Geometric Features and the Number of Cutting Passes on the Surface Quality Characteristics and Critical Points of Cutting Tools Fabricated by Wire Electrical Discharge Machining (WEDM). Micromachines 2025, 16, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Ding, S.; Pan, L.; Xu, Y. VSG-FC: A Combined Virtual Sample Generation and Feature Construction Model for Effective Prediction of Surface Roughness in Polishing Processes. Micromachines 2025, 16, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, R. Electric Contacts, Theory and Applications; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Timsit, R.S. Electrical Contact Resistance: Properties of Stationary Interfaces. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 1999, 22, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


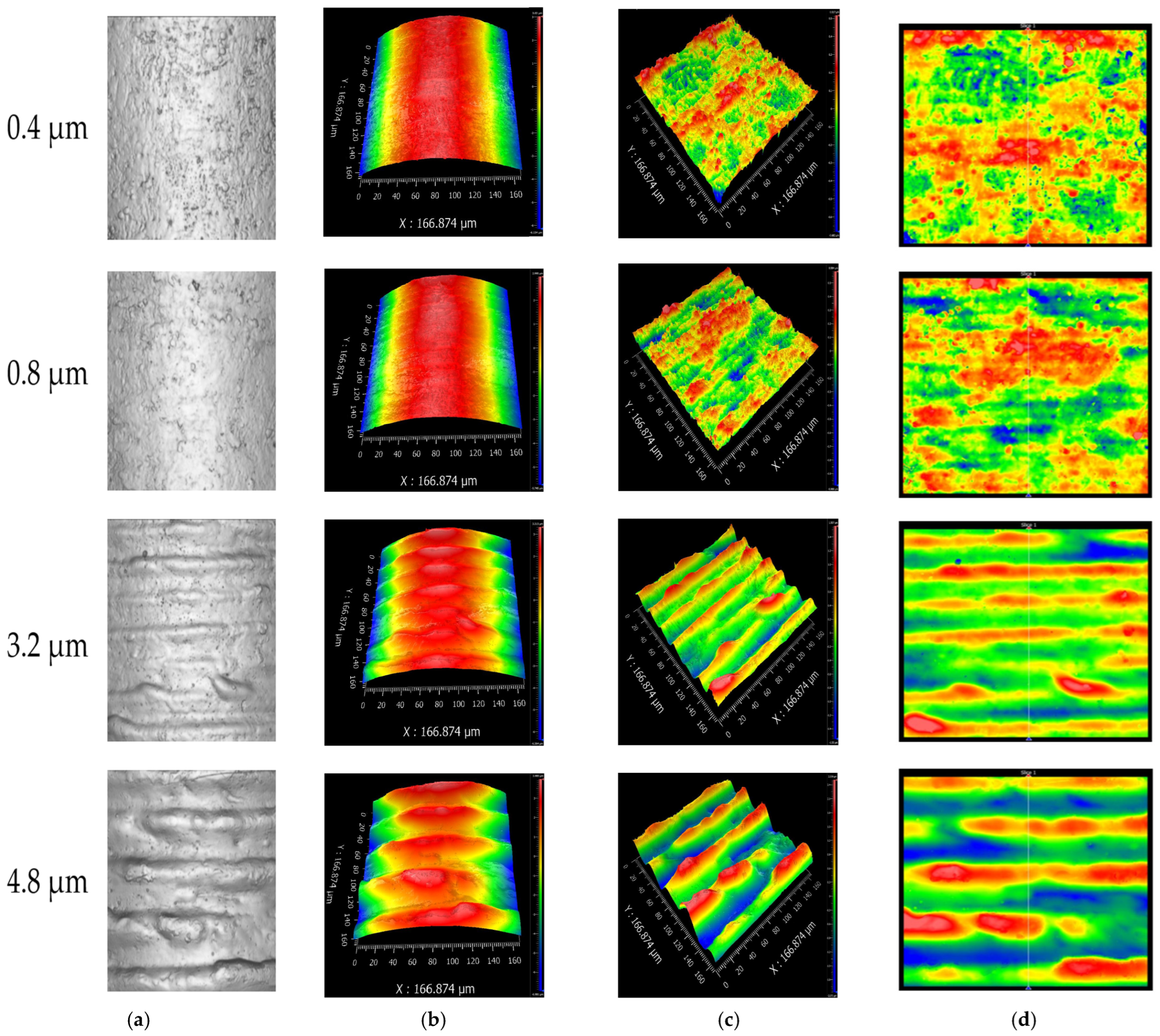
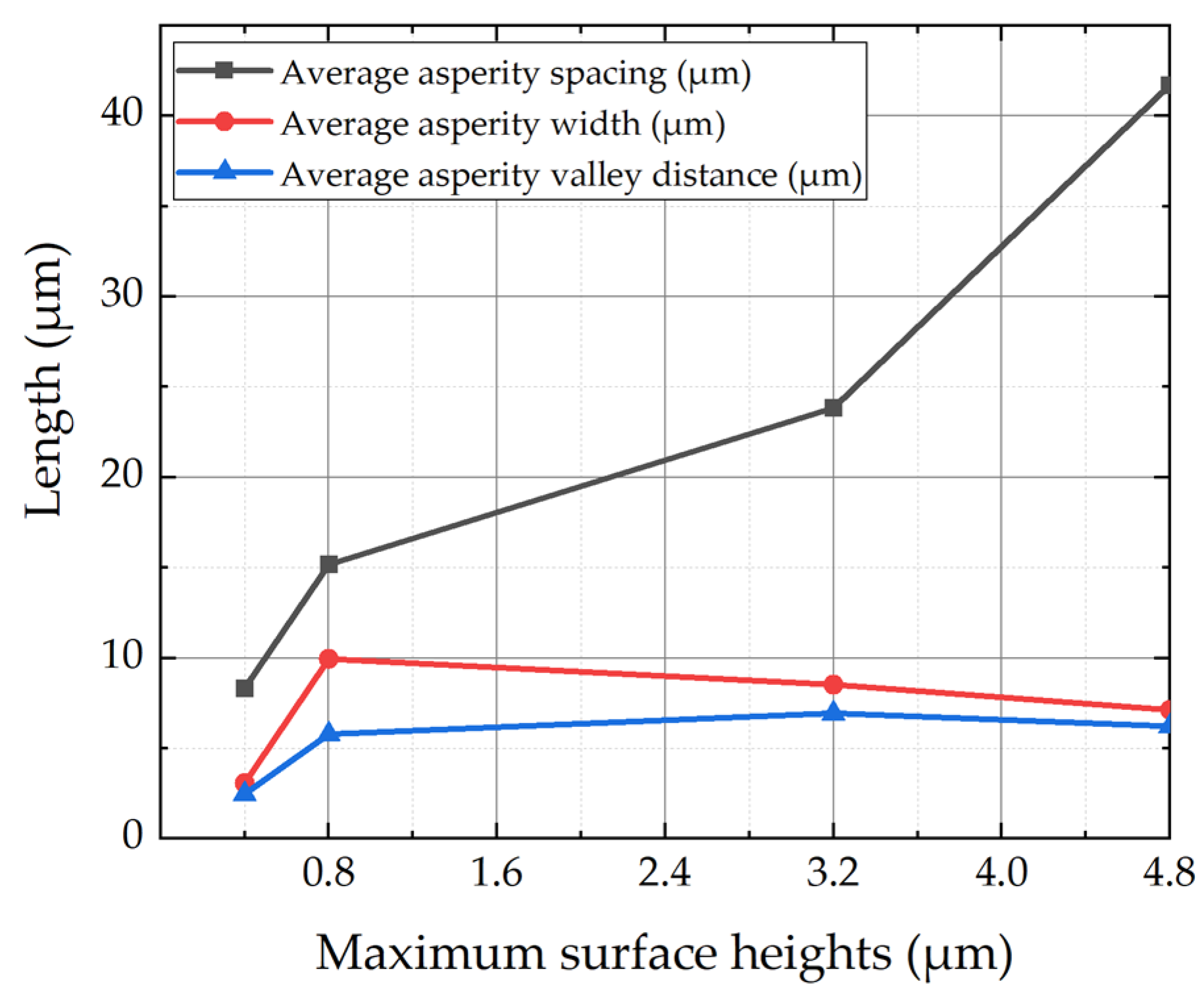



| Maximum Surface Heights SZ (μm) | Average Asperity Spacing b (μm) | Average Asperity Width a (μm) | Average Asperity Valley Distance a1 (μm) | Number of Asperities N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.4 | 8.33 | 3.07 | 2.47 | 7.00 |
| 0.8 | 15.17 | 9.94 | 5.78 | 6.50 |
| 3.2 | 23.84 | 8.52 | 6.94 | 4.67 |
| 4.8 | 41.72 | 7.12 | 6.21 | 5.34 |
| Maximum Surface Heights SZ (μm) | Friction Coefficient μ | Contact Force Fn (N) | Asperity Density η (×108/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.4 | 0.263 | 4.56 | 2.514 |
| 0.8 | 0.289 | 6.92 | 2.334 |
| 3.2 | 0.379 | 4.35 | 1.677 |
| 4.8 | 0.350 | 3.00 | 1.918 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xie, G.; Gao, J. The Effect of Scratch-Induced Microscale Surface Roughness on Signal Transmission in Radio Frequency Coaxial Connectors. Micromachines 2025, 16, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080837
Zhou Y, Zhang T, Xie G, Gao J. The Effect of Scratch-Induced Microscale Surface Roughness on Signal Transmission in Radio Frequency Coaxial Connectors. Micromachines. 2025; 16(8):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080837
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yuqi, Tianmeng Zhang, Gang Xie, and Jinchun Gao. 2025. "The Effect of Scratch-Induced Microscale Surface Roughness on Signal Transmission in Radio Frequency Coaxial Connectors" Micromachines 16, no. 8: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080837
APA StyleZhou, Y., Zhang, T., Xie, G., & Gao, J. (2025). The Effect of Scratch-Induced Microscale Surface Roughness on Signal Transmission in Radio Frequency Coaxial Connectors. Micromachines, 16(8), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16080837








