Novel Debris Material Identification Method Based on Impedance Microsensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Coil-Based Impedance Detection Method
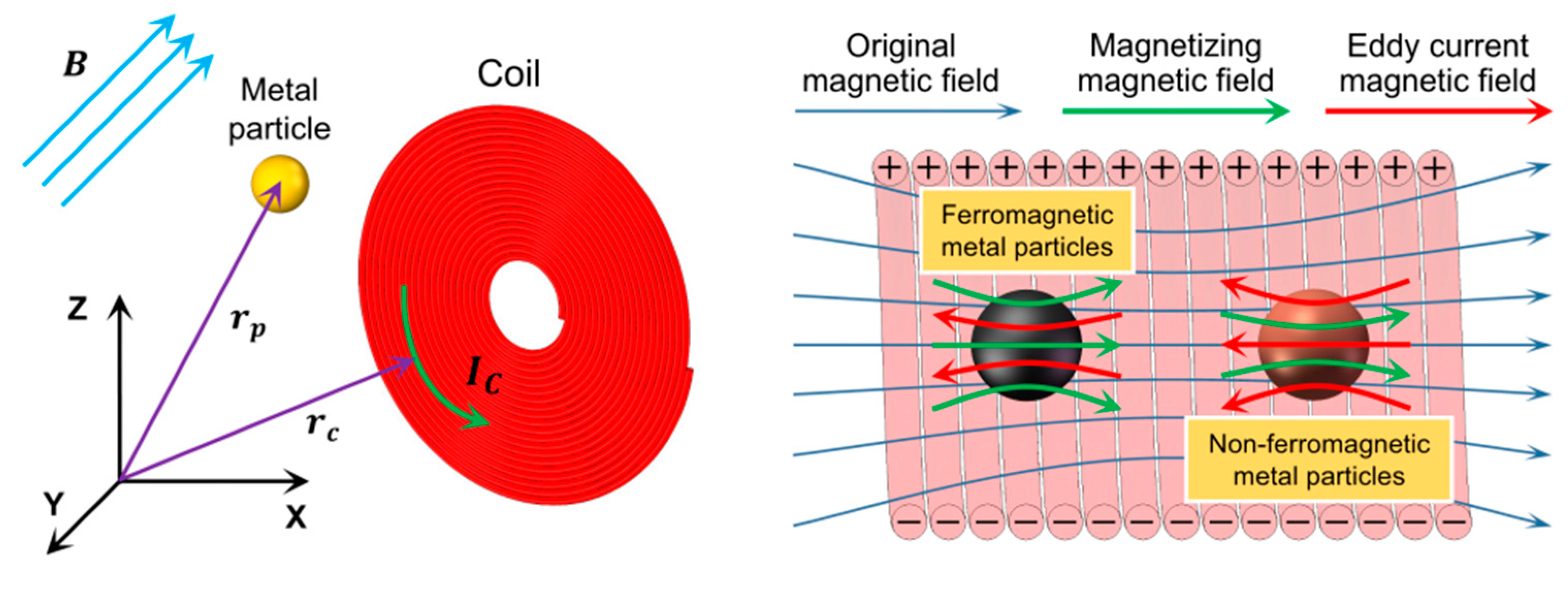
2.1. The Impedance Debris Microsensor
2.2. The Impedance Detection Principle Based on Coil
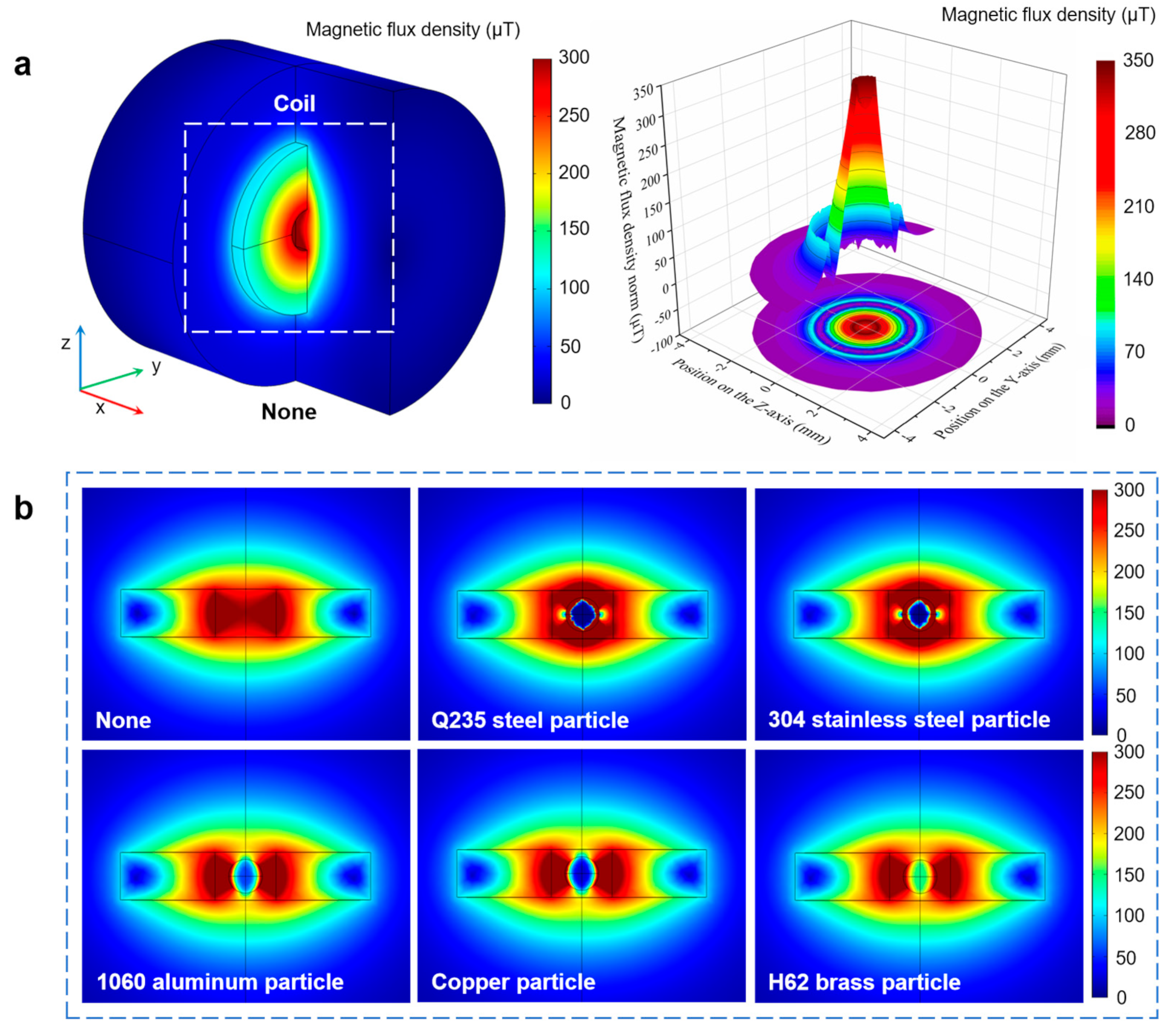
2.3. The Simulation Analysis of Impedance Detection
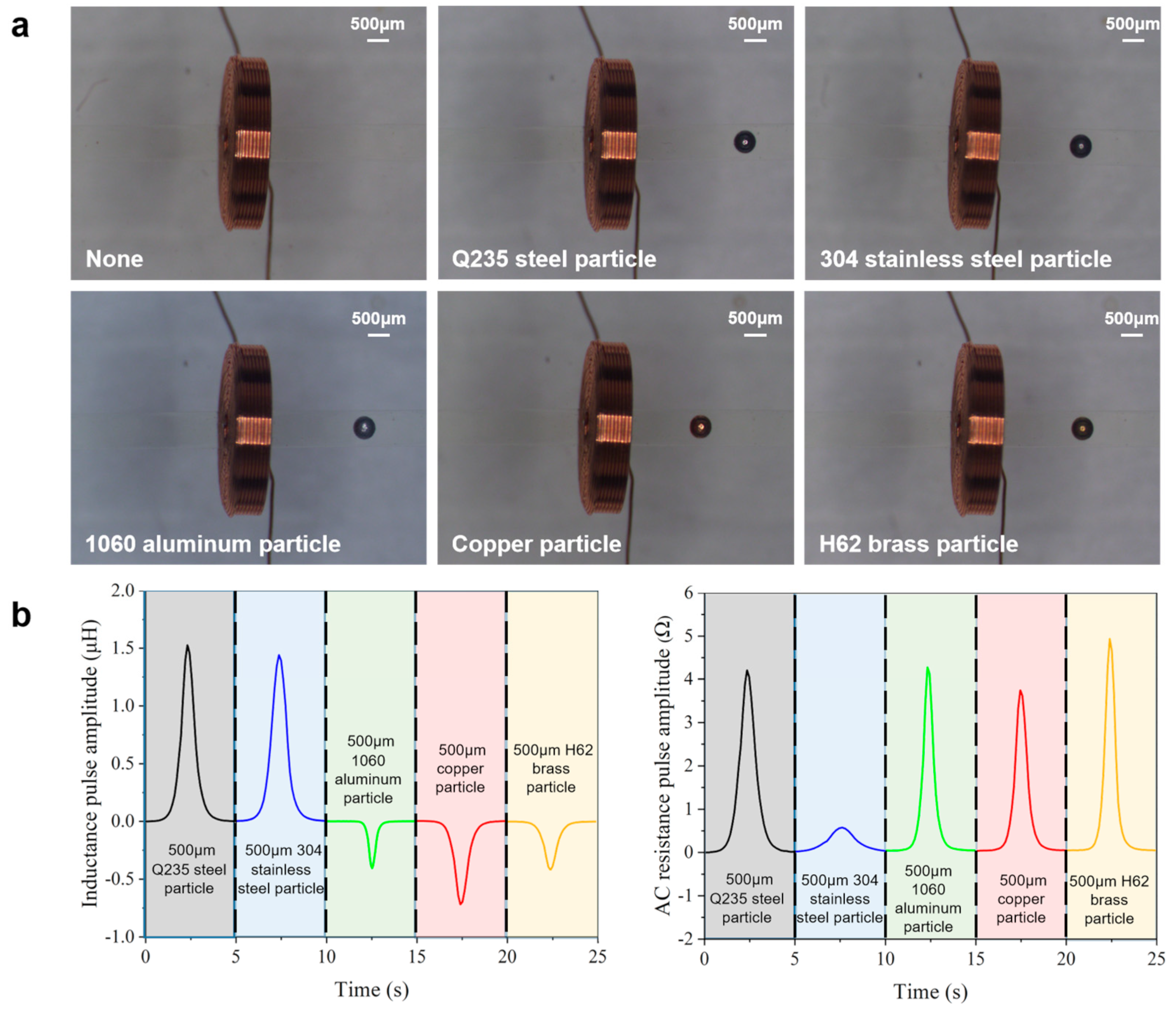
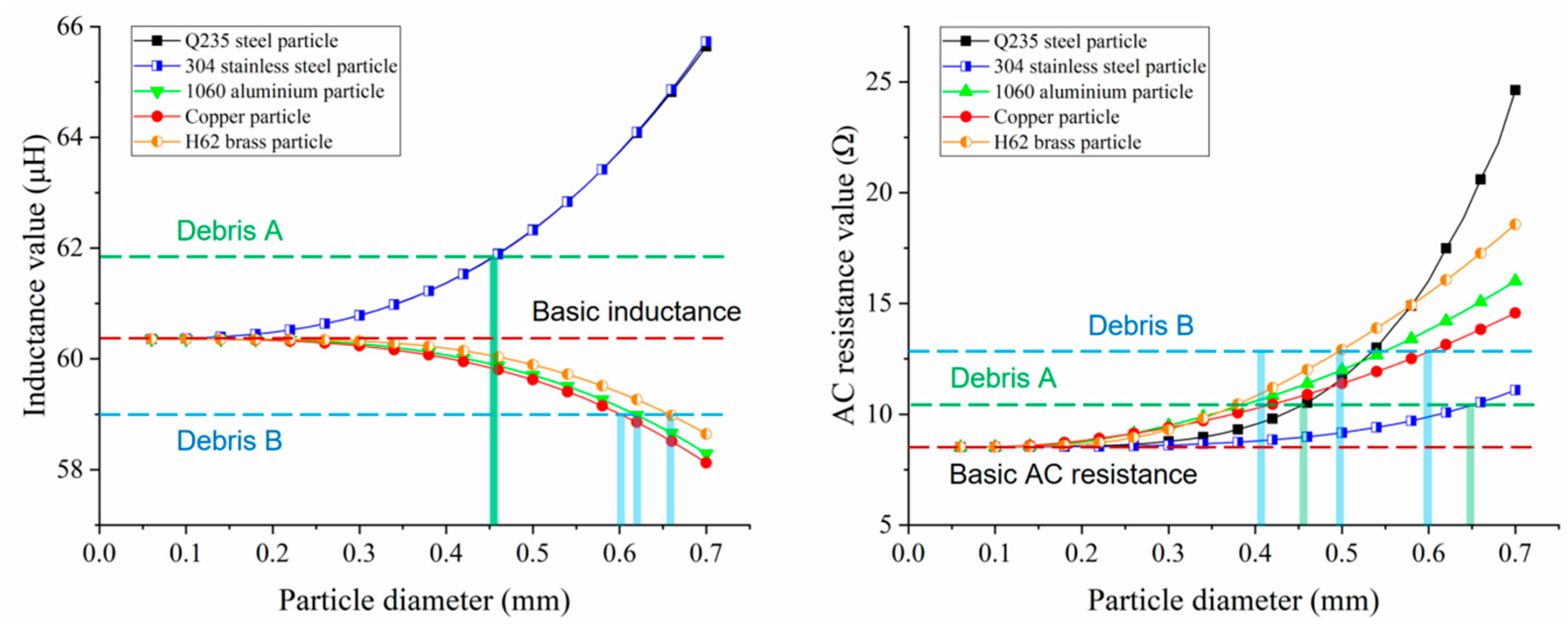
3. Experiments and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, P.; Powrie, H.; Wood, R.; Harvey, T.; Harris, N. Early wear detection and its significance for condition monitoring. Tribol. Int. 2021, 159, 106946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag, V.; Meyer, T.; Caspers, L.; Schlanbusch, R. Failure monitoring and predictive maintenance of hydraulic cylinder-state-of-the-art review. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 26, 3087–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddar, S.; Tandon, N. Detection of particle contamination in journal bearing using acoustic emission and vibration monitoring techniques. Tribol. Int. 2019, 134, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, O.; Loccufier, M.; Hoecke, S. Thermal imaging and vibration based multi-sensor fault detection for rotating machinery. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakiru, J.; Pintelon, L.; Muchiri, P.; Peter, K. A review on lubricant condition monitoring information analysis for maintenance decision support. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 118, 108–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhong, C.; Zhe, J. Lubricating oil conditioning sensors for online machine health monitoring—A review. Tribol. Int. 2017, 109, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Dong, G.; Xie, Y.; Peng, Z. Prediction of wear trend of engines via on-line wear debris monitoring. Tribol. Int. 2018, 120, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogsøe, K.; Henneberg, M.; Eriksen, R. Model of a light extinction sensor for assessing wear particle distribution in a lubricated oil system. Sensors 2018, 18, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Fang, Y. An on-line imaging sensor based on magnetic deposition and flowing dispersion for wear debris feature monitoring. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 212, 111321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, P.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Lv, C. Ultrasonic echo waveshape features extraction based on QPSO-matching pursuit for online wear debris discrimination. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 60–61, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, T.; Fritzen, C. A novel baseline-free approach for acousto-ultrasonic crack monitoring of rotating axles. Struct. Health Monit. 2021, 20, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkin, P.; Linfield, S.; Denuault, G.; Jones, R.; Youngs, J.; Wain, E. An analytical differential resistance pulse system relying on a time shift signal analysis–applications in Coulter Counting. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2190–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murali, S.; Xia, X.; Jagtiani, A.; Carletta, J.; Zhe, J. Capacitive Coulter counting: Detection of metal wear particles in lubricant using a microfluidic device. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 18, 037001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, G.; Feng, Z. Ultrasensitive inductive debris sensor with a two-stage autoasymmetrical compensation circuit. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 8885–8893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wu, W.; Zhou, M.; Xi, Y.; Wei, H.; Mao, J. A full field-of-view online visual ferrograph debris detector based on reflected light microscopic imaging. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 16584–16597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, O.; Walle, R.; Loccufier, M.; Hoecke, S. Deep learning for infrared thermal image based machine health monitoring. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Munaim, A.; Reuter, M.; Abdulmunem, O.; Balzer, J.; Koch, M.; Watson, D. Using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy to discriminate among water contamination levels in diesel engine oil. Trans. Asabe 2016, 59, 795–801. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Li, R.; Kwok, N.; Peng, Y.; Wu, T.; Peng, Z. Restoration of low-informative image for robust debris shape measurement in on-line wear debris monitoring. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 114, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokouchi, T.; Kagawa, F.; Hirschberger, M.; Otani, Y.; Tokura, Y. Emergent electromagnetic induction in a helical-spin magnet. Nature 2020, 586, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Ding, Z. High-precision induction coil sensor with high magnetic field homogeneity for online debris monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 25, 18236–18248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhe, J. A high throughput inductive pulse sensor for online oil debris monitoring. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhang, H.; Ma, L.; Rogers, F.; Zhao, X.; Zeng, L. An impedance debris sensor based on a high-gradient magnetic field for high sensitivity and high throughput. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 5376–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Guo, Q. Electromagnetic sensor for detecting wear debris in lubricating oil. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 2533–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Li, J.; Lu, H. Online oil debris monitoring of rotating machinery: A detailed review of more than three decades. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 149, 107341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Xie, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, S.; He, R.; Sun, Y.; Li, G.; et al. A novel distinction method of metal debris material based on inductive sensor with multi-sensing units. Tribol. Int. 2023, 177, 107948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H. Sensing model of metal particles in nonuniform time-harmonic magnetic field for high-sensitivity debris sensor. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 3514609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, H.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H. Novel Debris Material Identification Method Based on Impedance Microsensor. Micromachines 2025, 16, 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070812
Shi H, Xie Y, Zhang H. Novel Debris Material Identification Method Based on Impedance Microsensor. Micromachines. 2025; 16(7):812. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070812
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Haotian, Yucai Xie, and Hongpeng Zhang. 2025. "Novel Debris Material Identification Method Based on Impedance Microsensor" Micromachines 16, no. 7: 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070812
APA StyleShi, H., Xie, Y., & Zhang, H. (2025). Novel Debris Material Identification Method Based on Impedance Microsensor. Micromachines, 16(7), 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16070812






