Fabrication of Sub-50 nm Three-Dimensional Rhombic Zero-Depth PDMS Nanopores with Enhanced Conductance via Silicon Micro-Blade Molding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
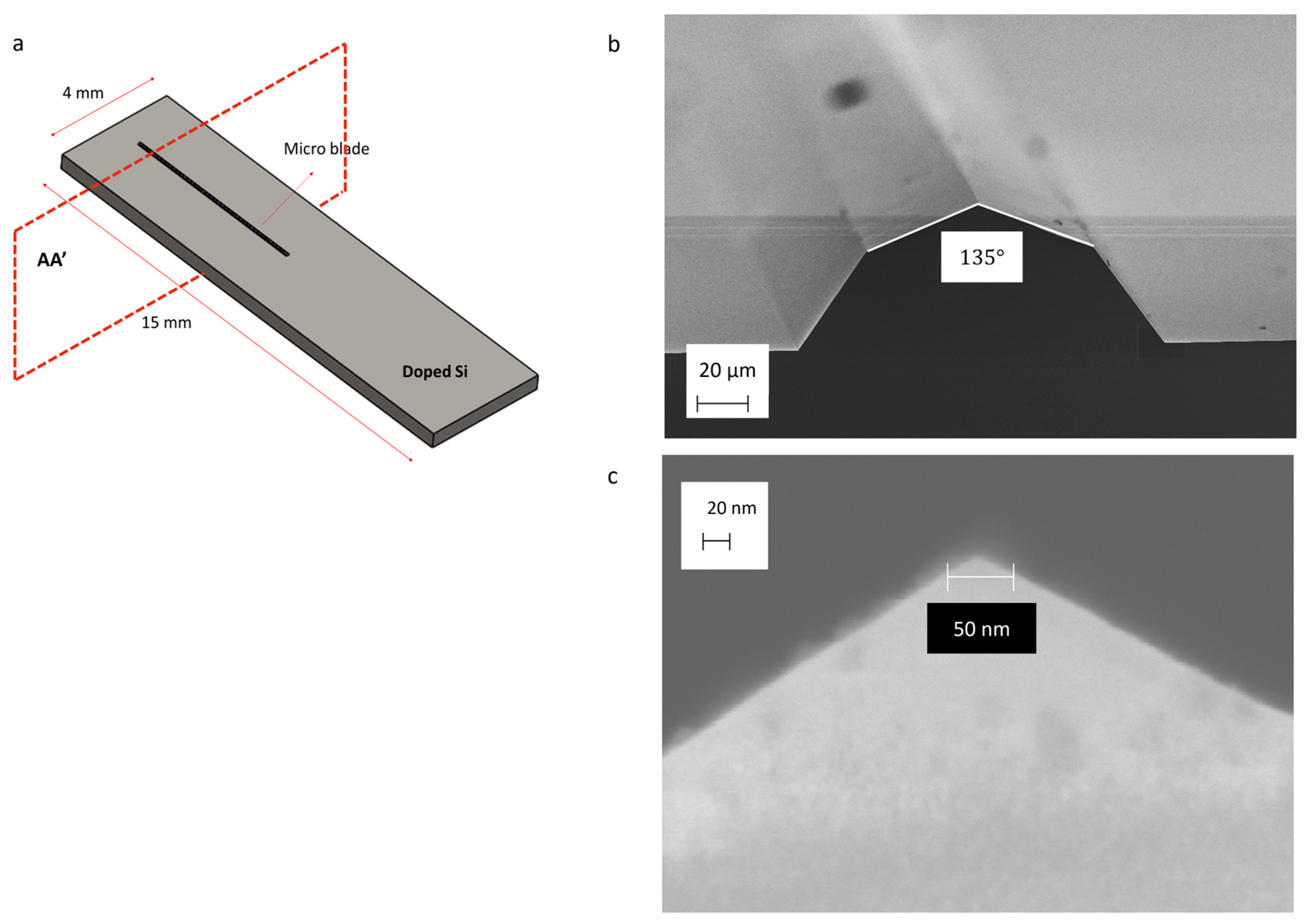
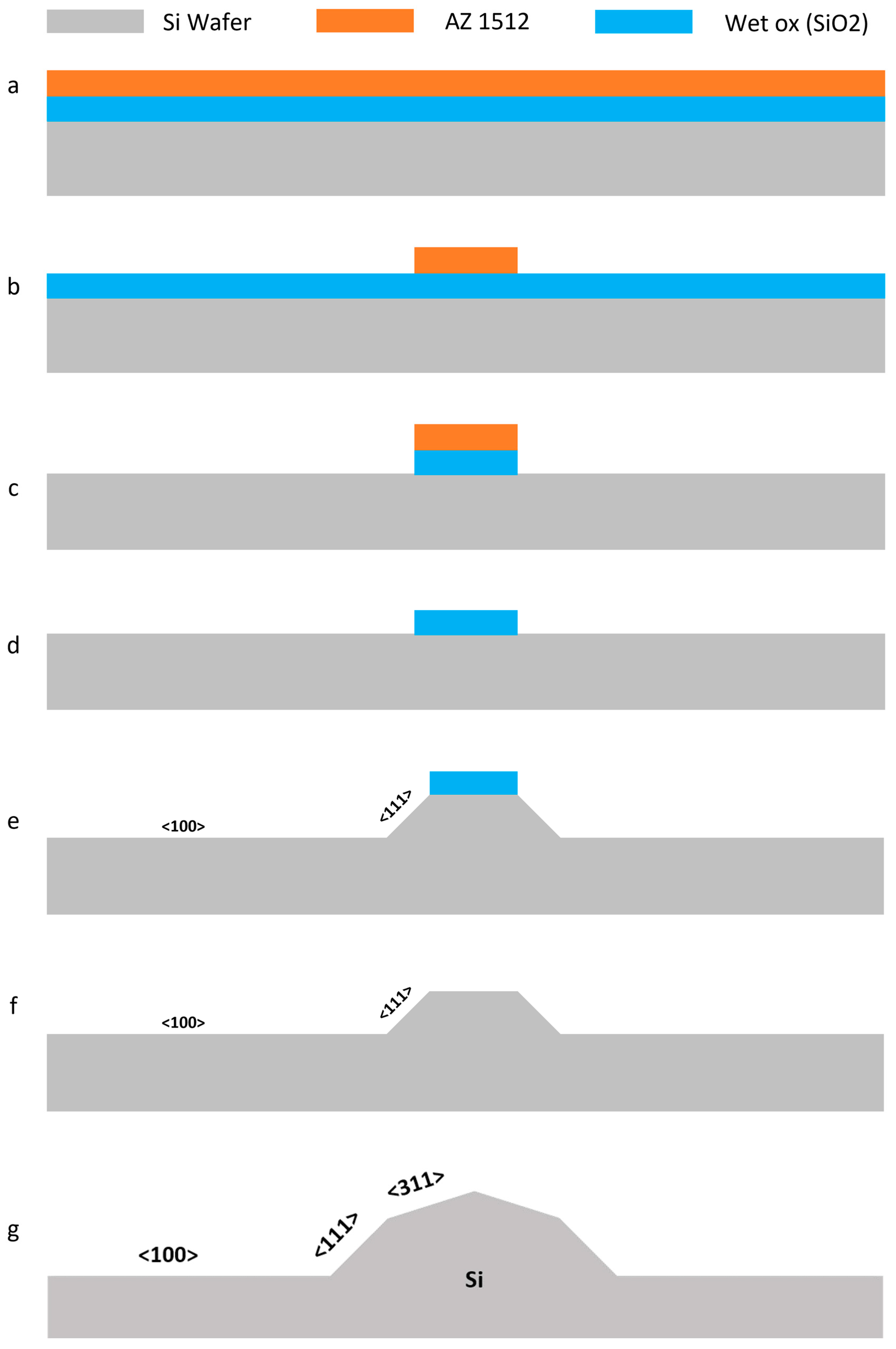
2.1. Micro-Blade Fabrication
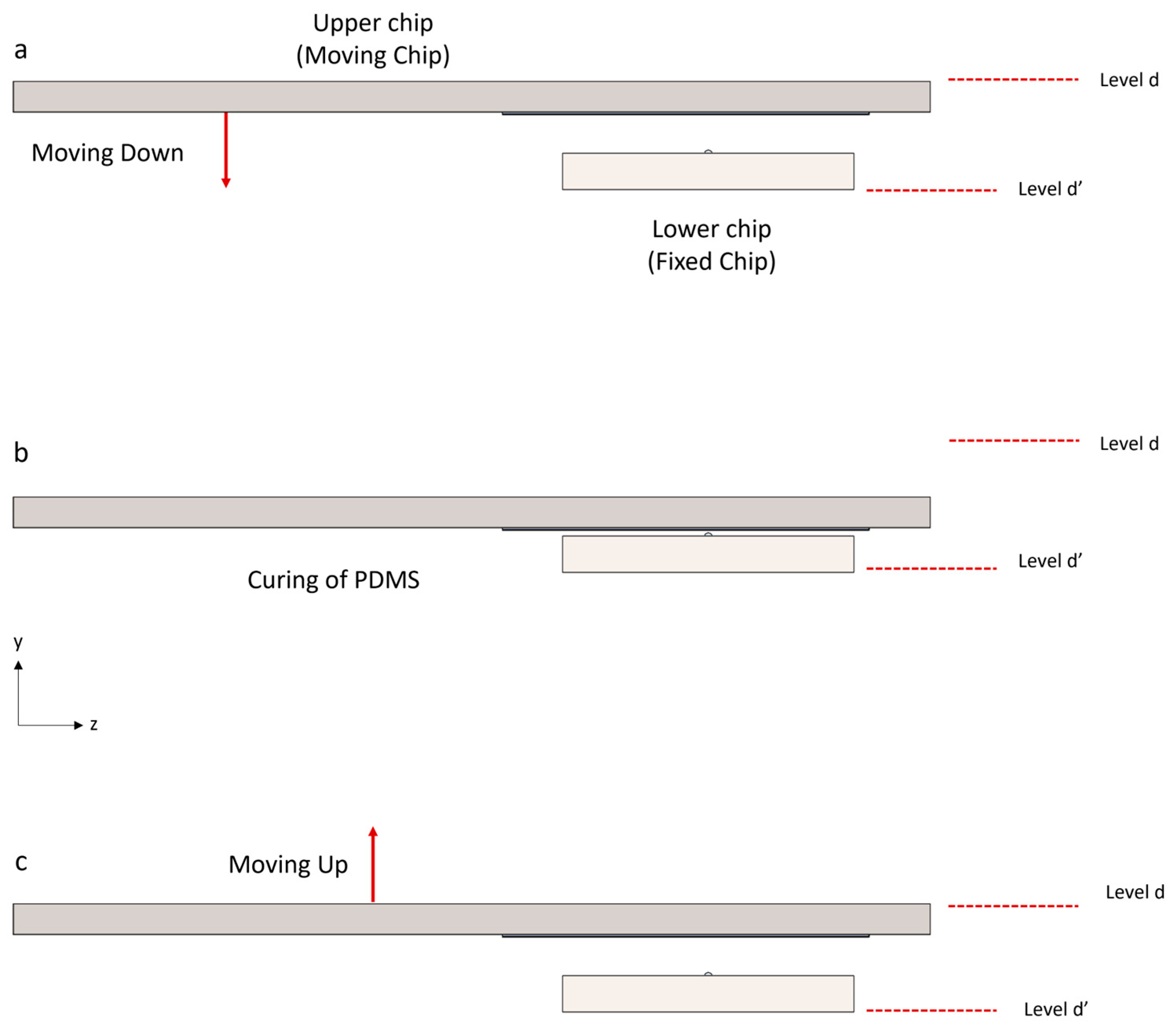
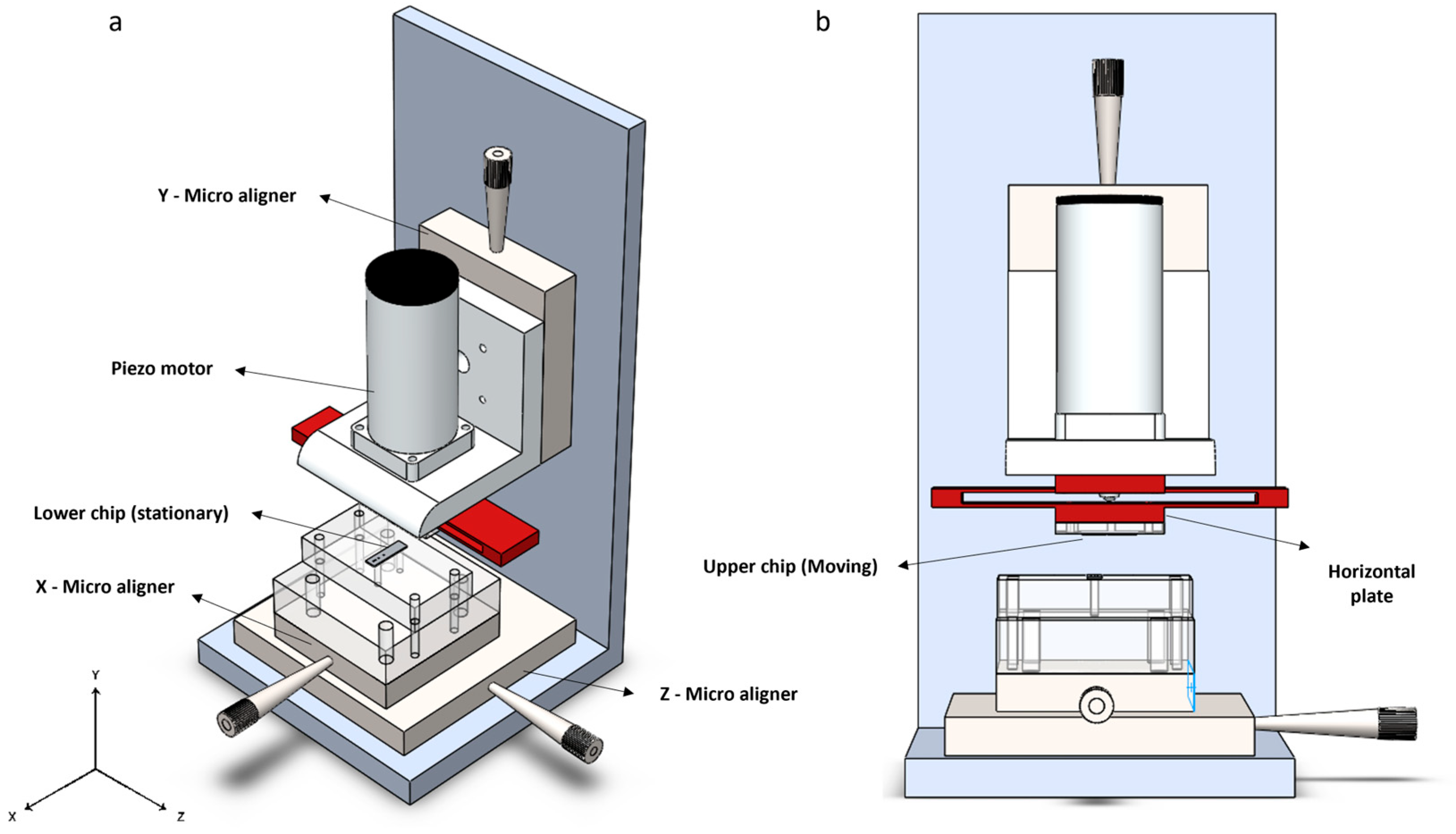
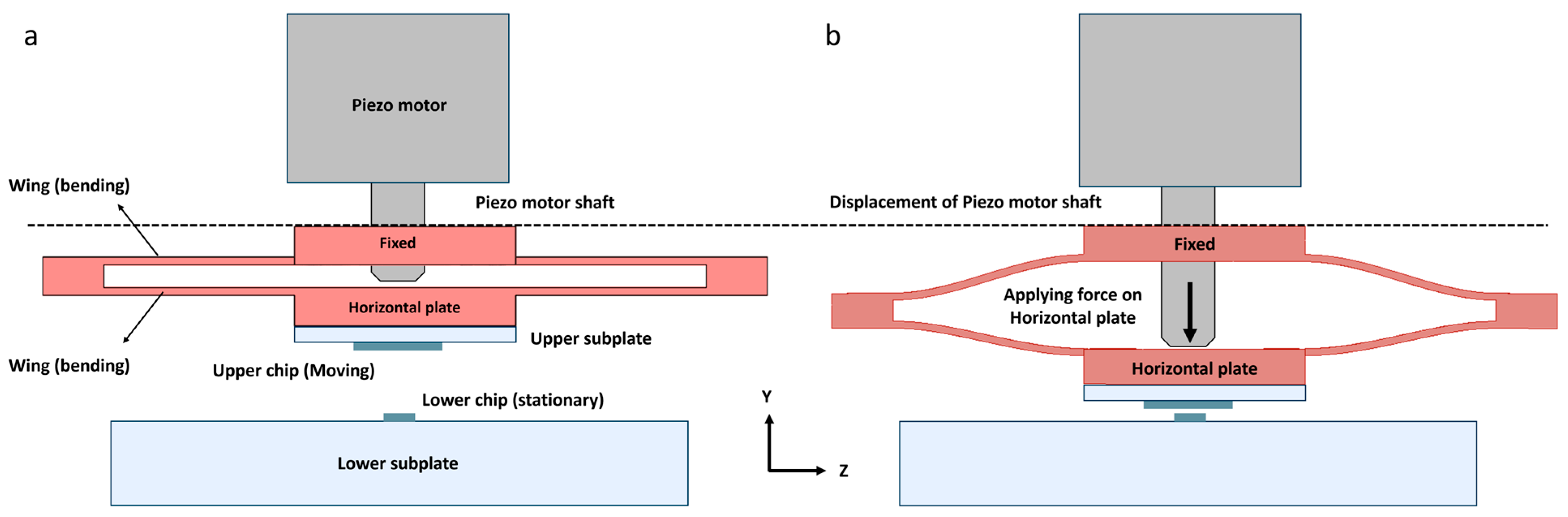
2.2. Nano-Positioning Setup
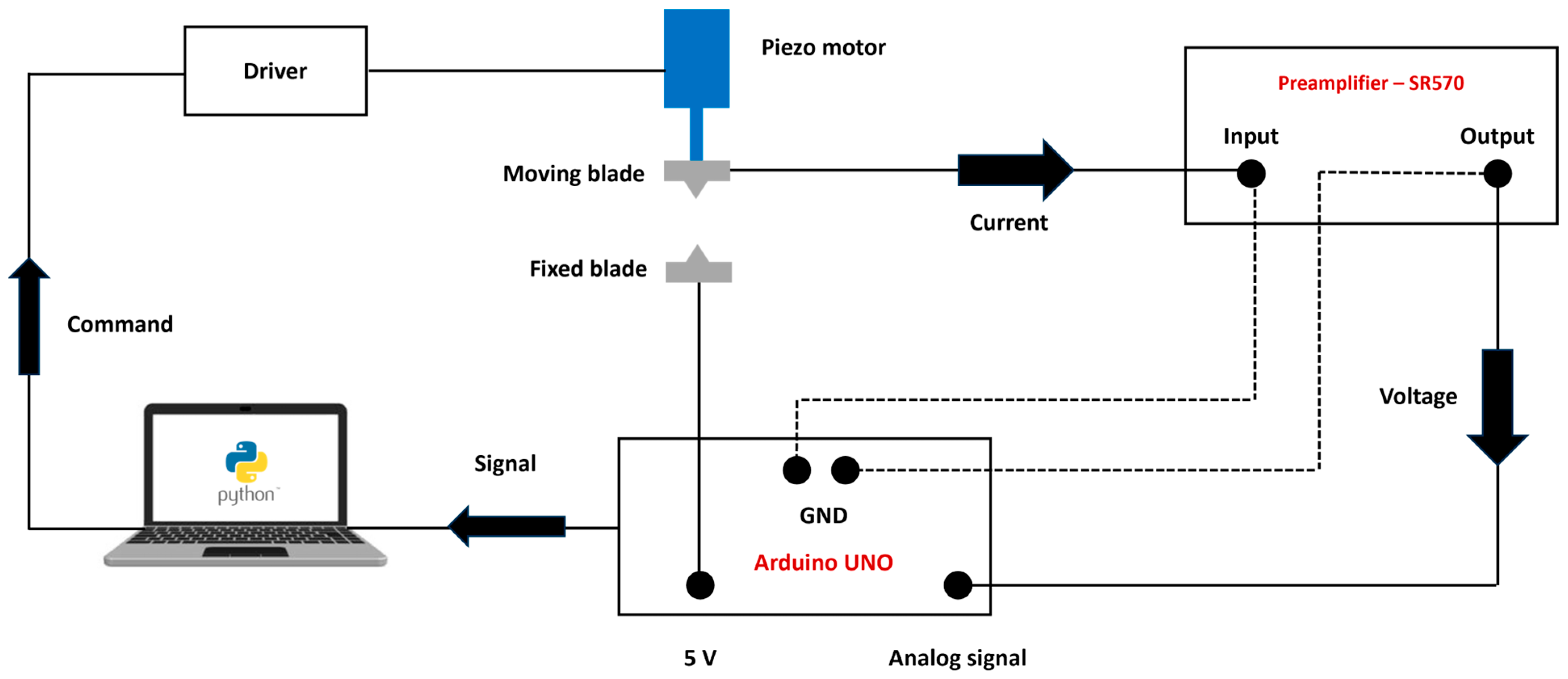
2.3. Electronic Measurement
2.4. PDMS Curing
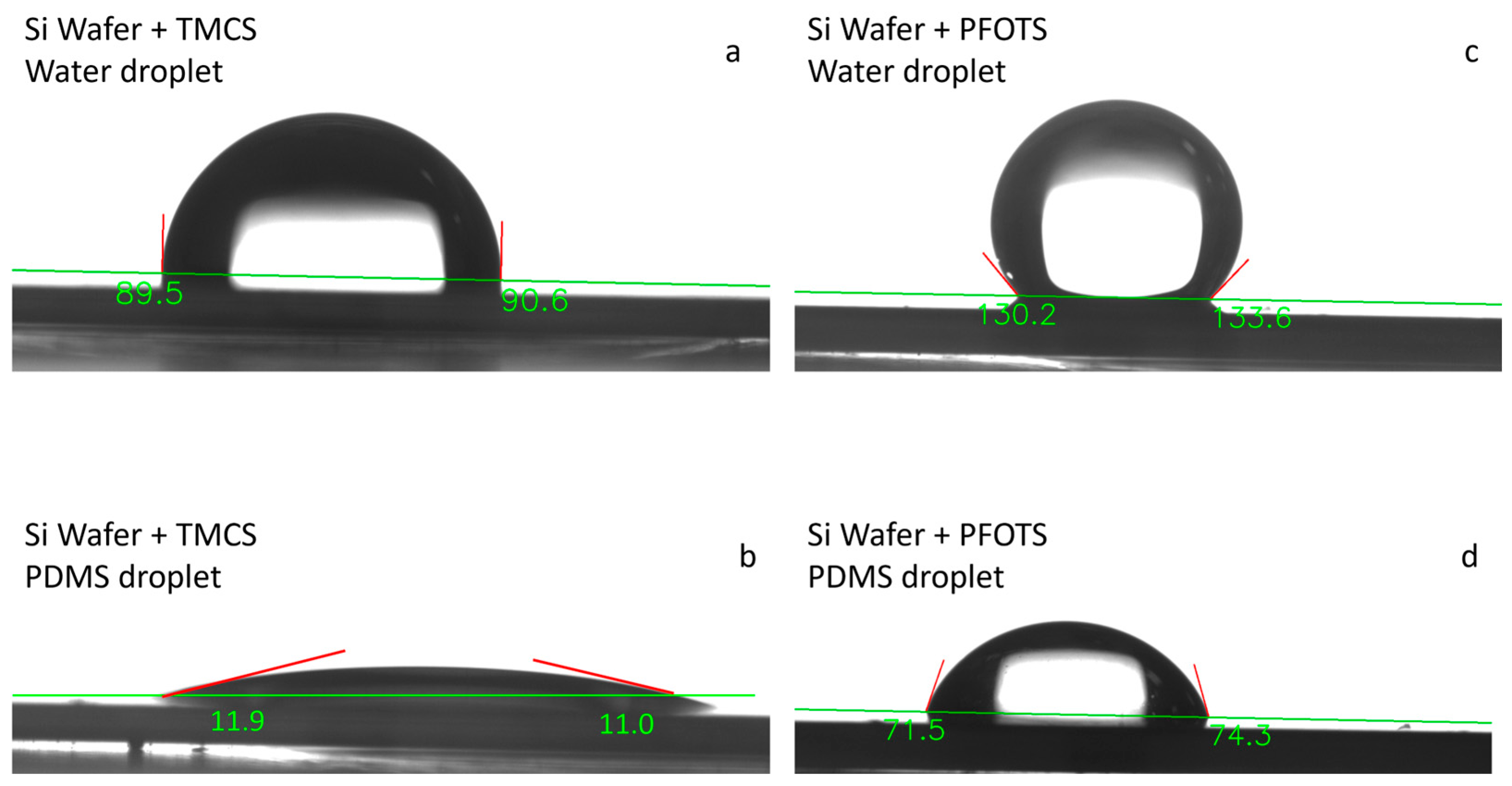
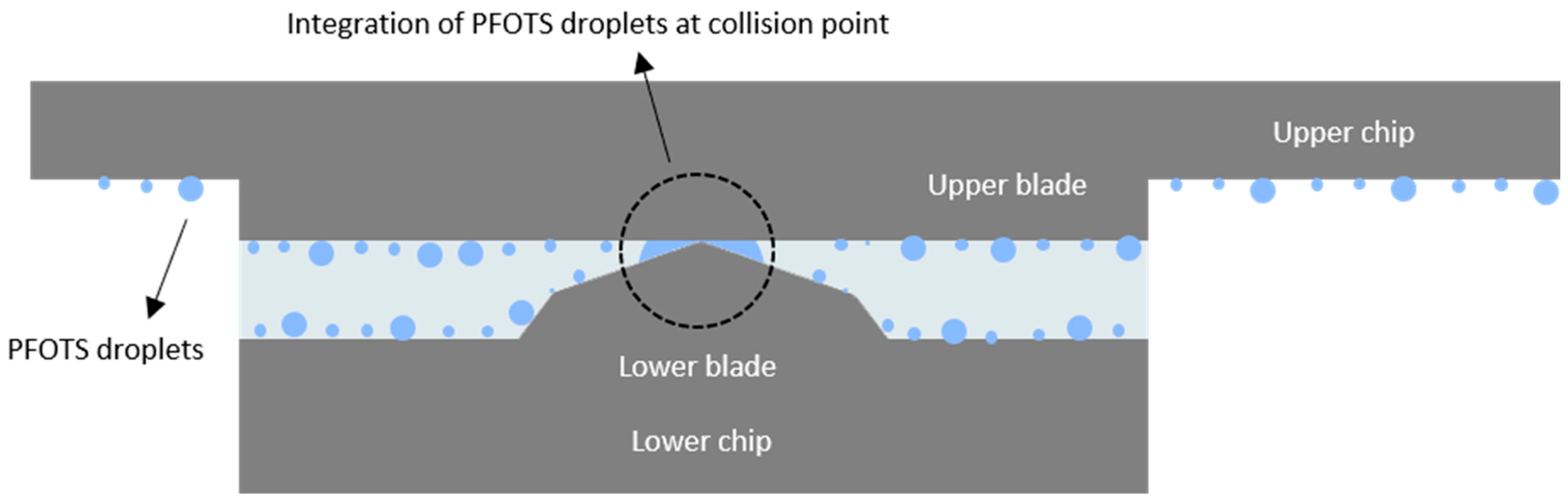
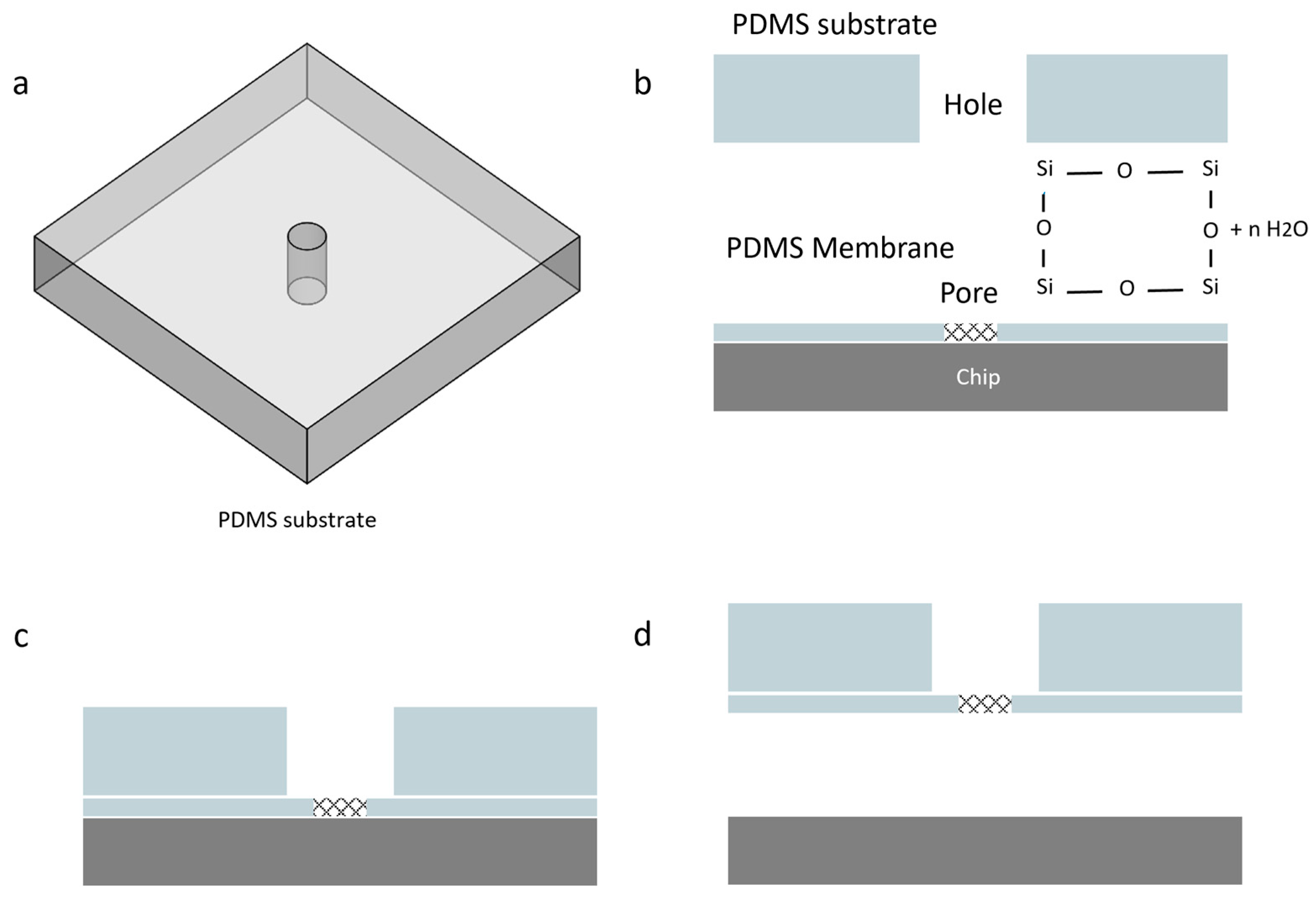
2.5. PDMS Adhesion to Silicon
2.6. Removing the Membrane
3. Results and Discussion
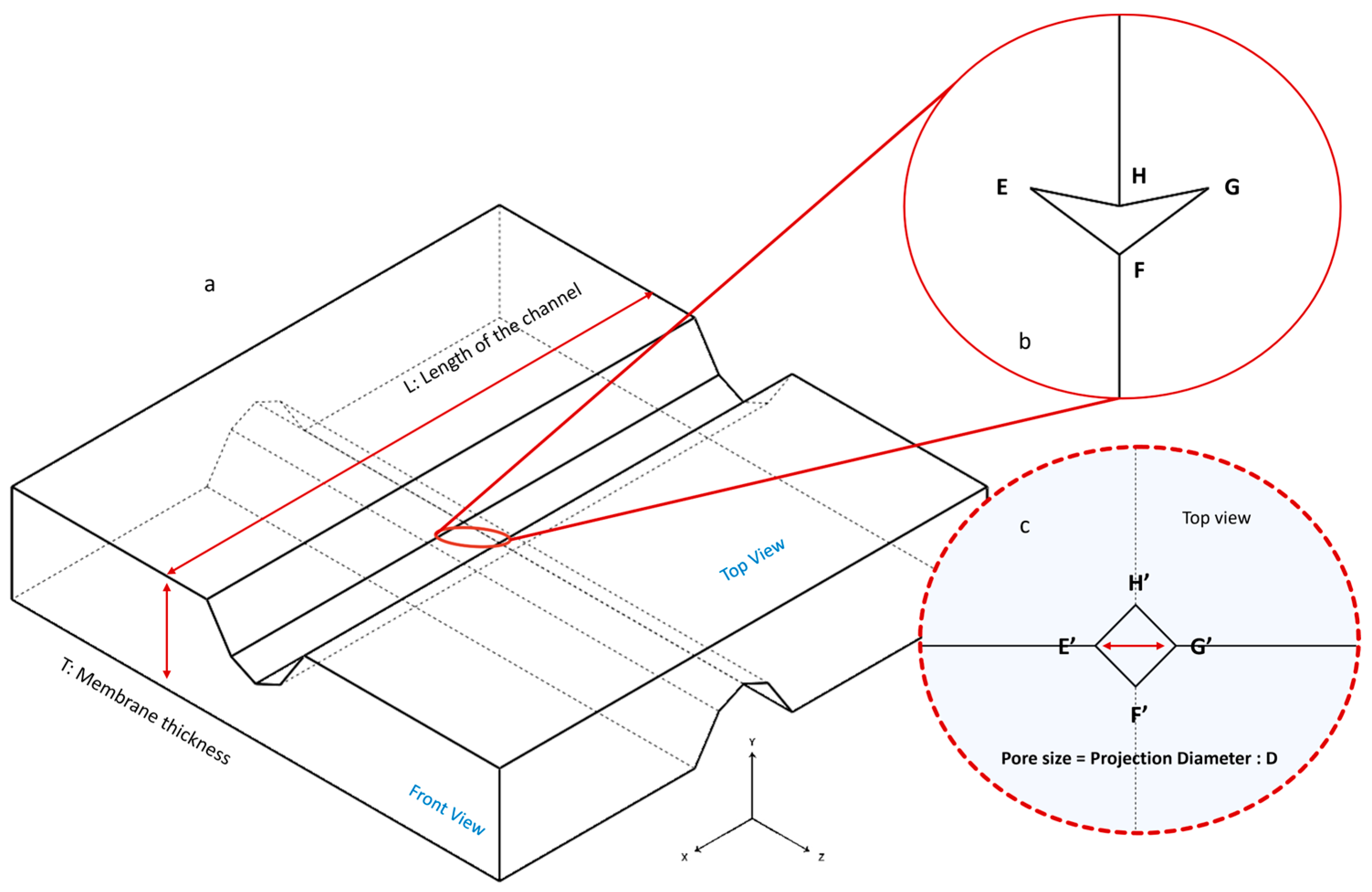
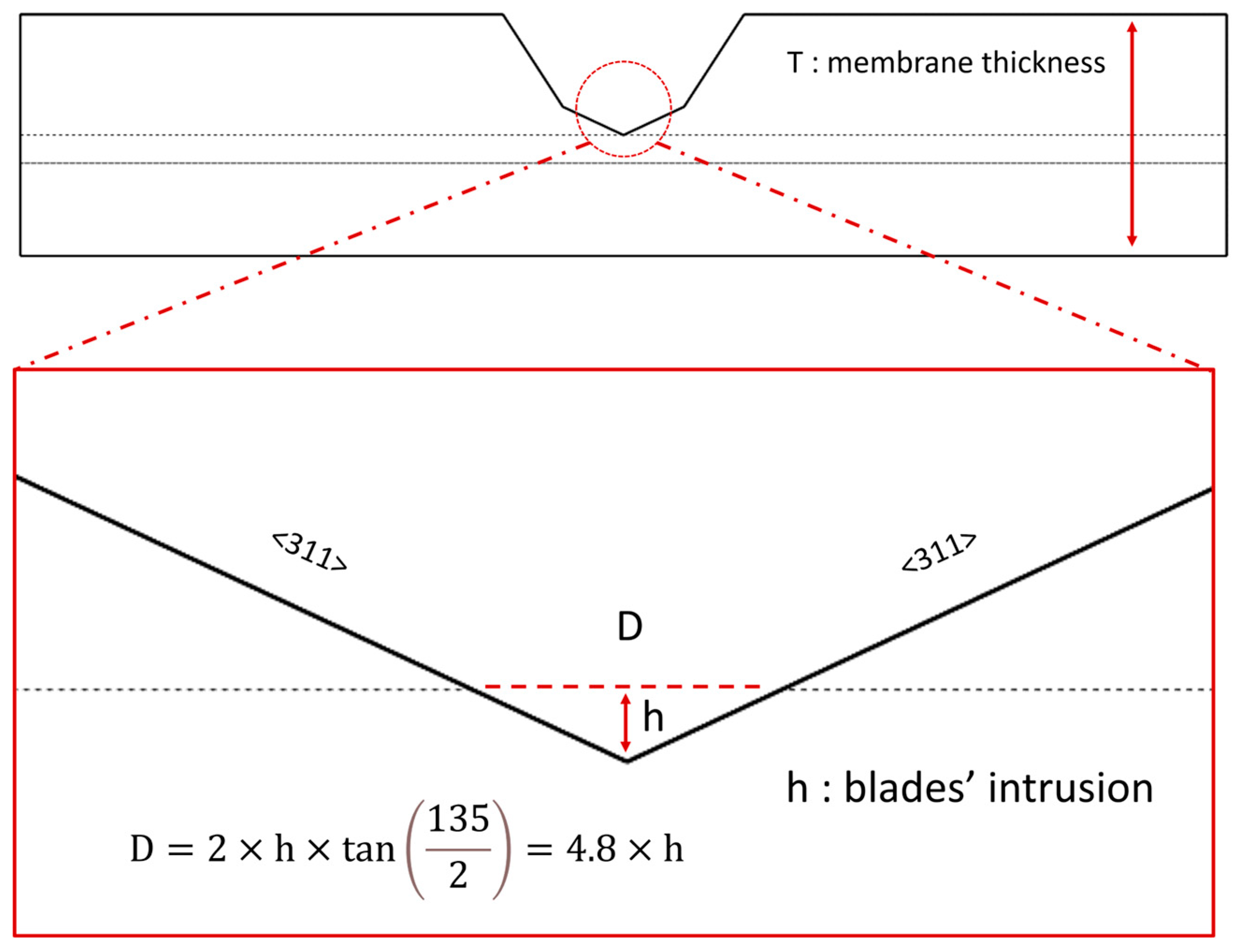
3.1. Zero-Depth Micro-Nanopores
3.2. Simulation Result
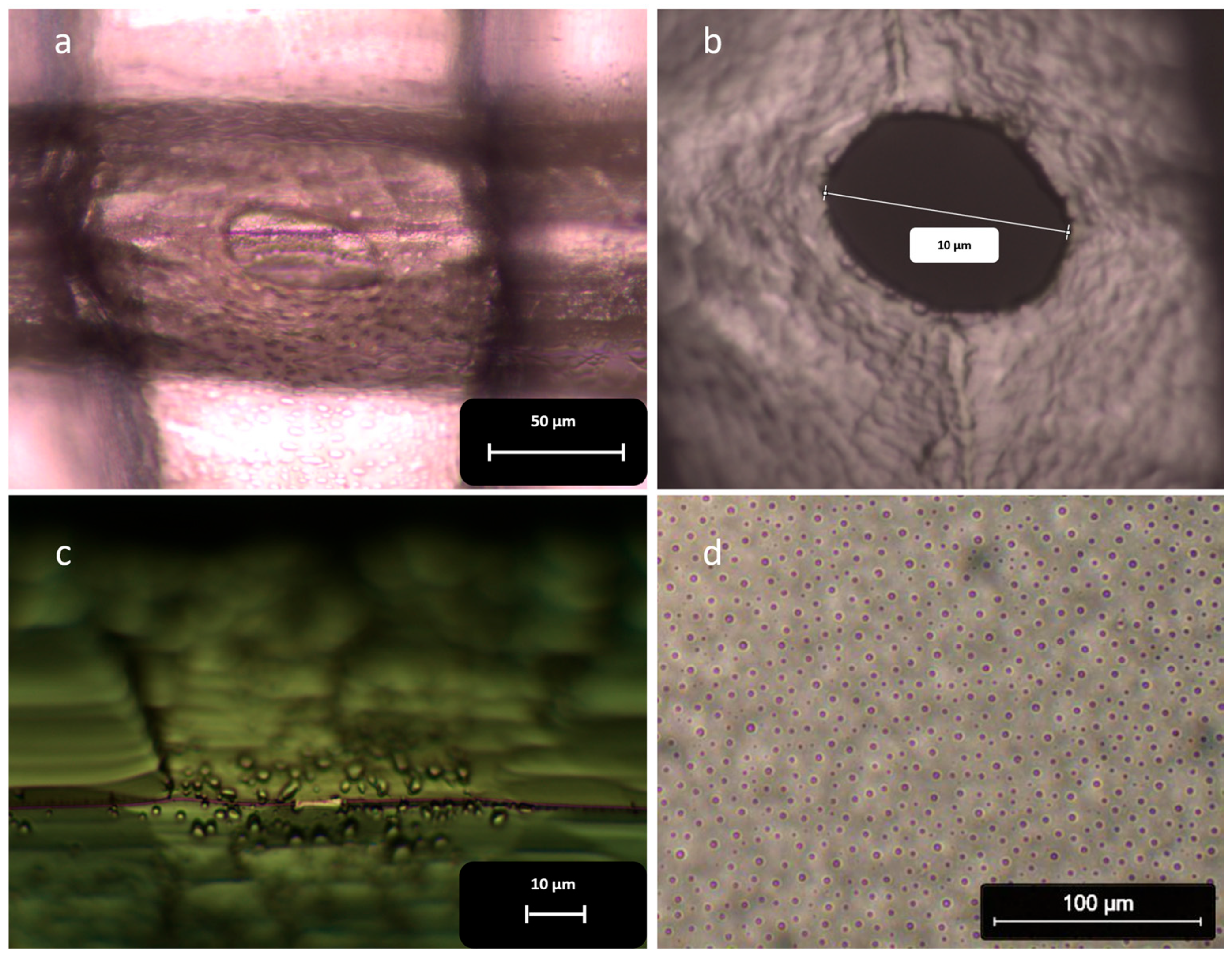
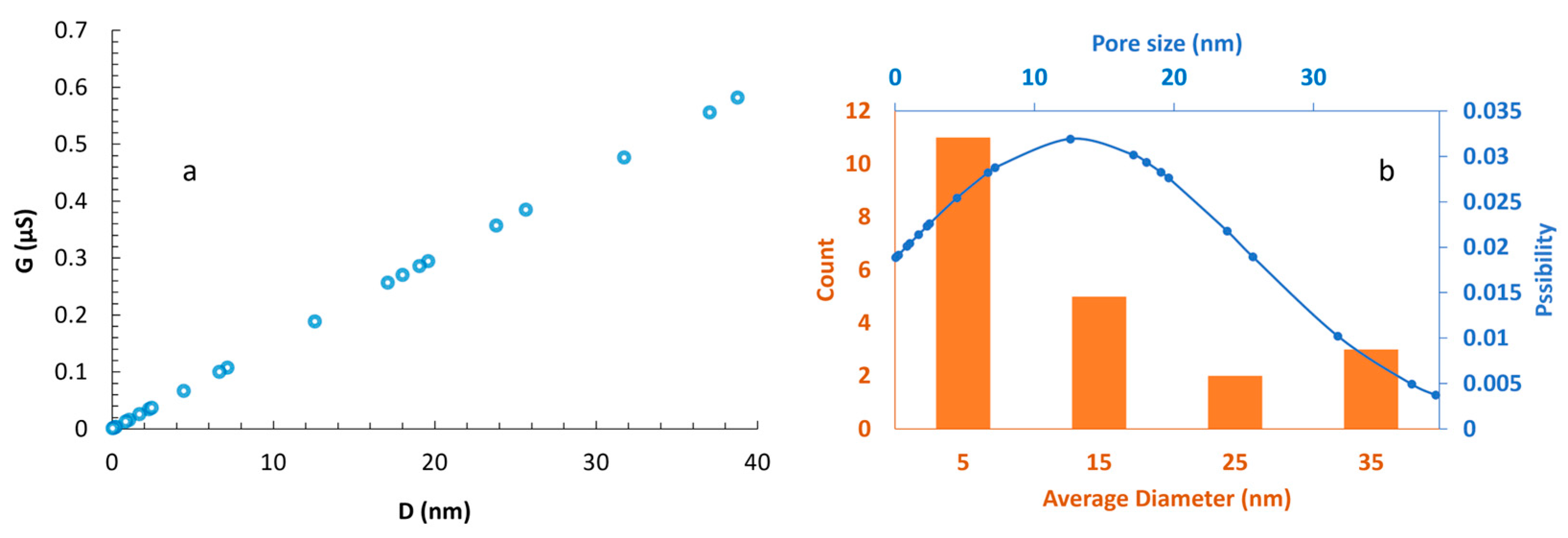
3.3. Nanopore Fabrication
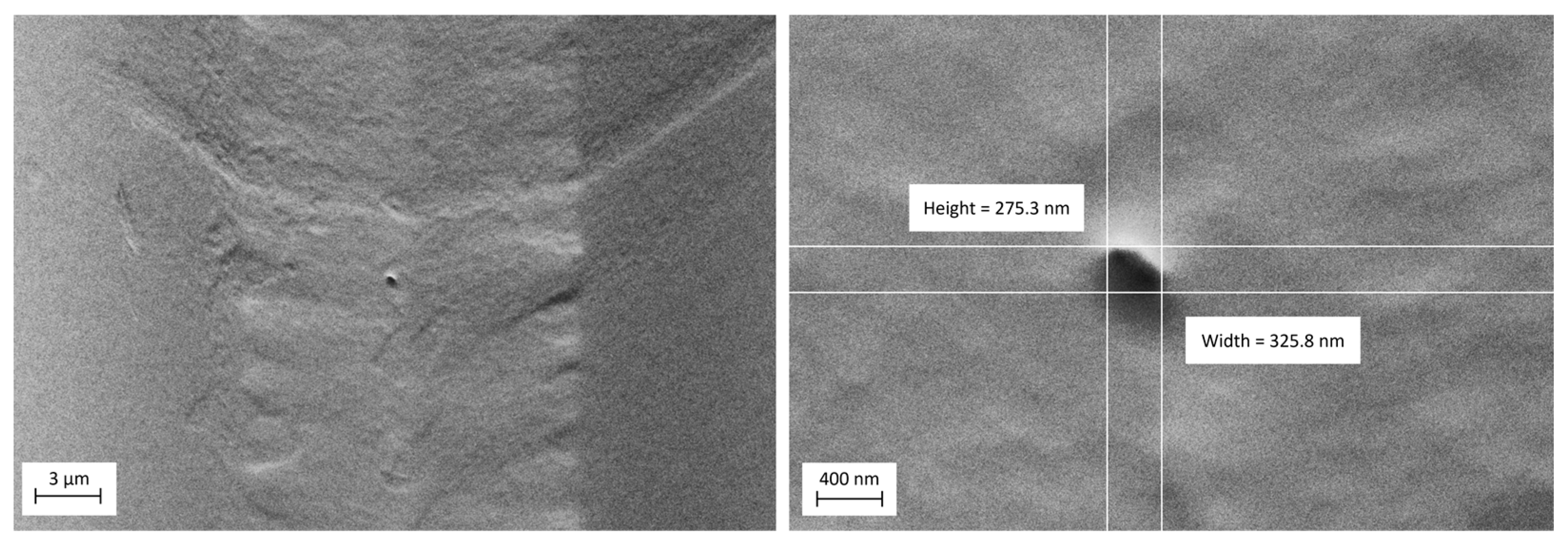
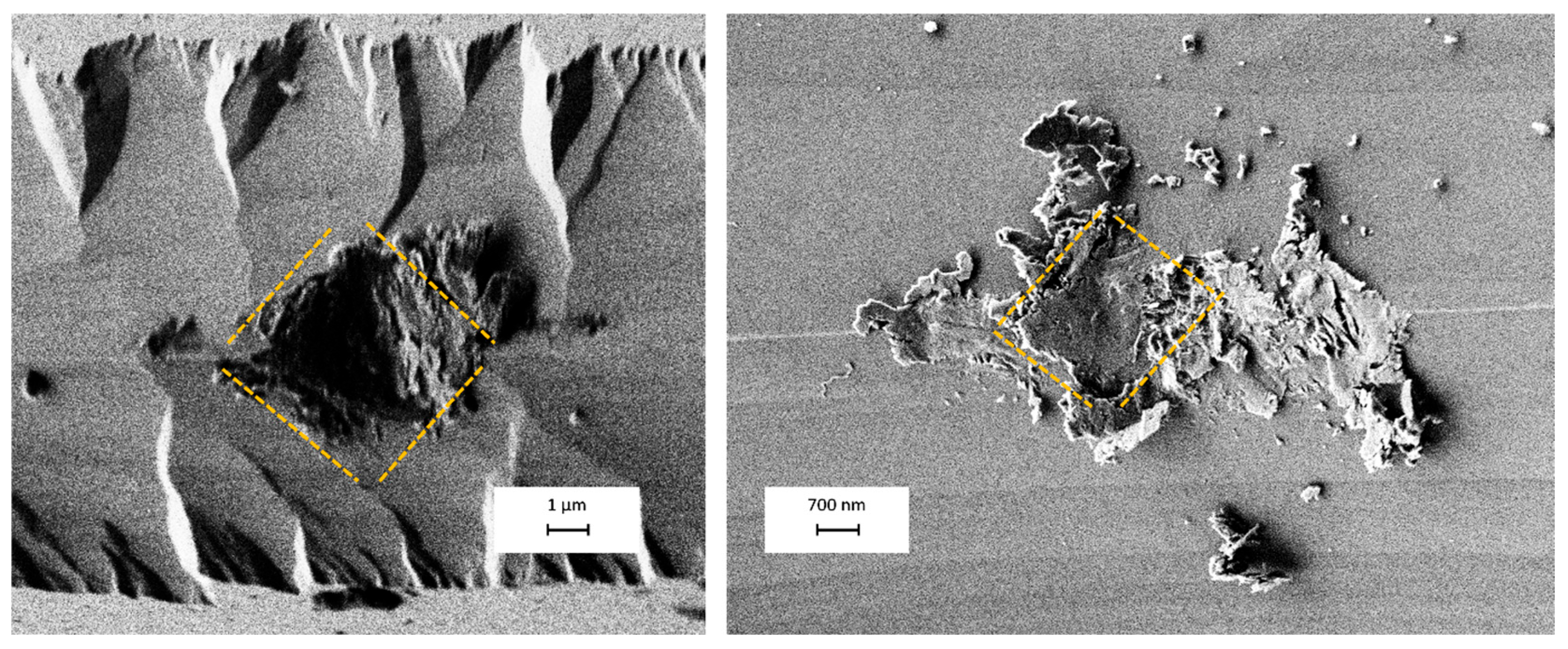
3.4. Indentability of Silicon Micro-Blades
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RPS | Resistive Pulse Sensing |
| RZD | Rhombic Zero-Depth |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| 2D | Two-Dimensional |
| 3D | Three-Dimensional |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| TMCS | Trimethylchlorosilane |
| PFOTS | Trichloro-1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctyl silane |
| MAPE | Mean Absolute Percentage Error |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CV | Coefficient of Variation |
References
- Vaclavek, T.; Prikryl, J.; Foret, F. Resistive Pulse Sensing as Particle Counting and Sizing Method in Microfluidic Systems: Designs and Applications Review. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Q.D.; Wu, L. Recent Advances of Small Molecule Detection in Nanopore Sensing. Talanta 2024, 277, 126323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherall, E.; Willmott, G.R. Applications of Tunable Resistive Pulse Sensing. Analyst 2015, 140, 3318–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, I.; Platt, M. Peptide Nanocarriers for Detection of Heavy Metal Ions Using Resistive Pulse Sensing. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11291–11296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, M.; Hunsicker, E.; Platt, M. A Tunable Three-Dimensional Printed Microfluidic Resistive Pulse Sensor for the Characterization of Algae and Microplastics. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2578–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugi, R.; Gamble, B.; Bunka, D.; Platt, M. A Simple Displacement Aptamer Assay on Resistive Pulse Sensor for Small Molecule Detection. Talanta 2021, 225, 122068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybakova, D.; Radjainia, M.; Turner, A.; Sen, A.; Mitra, A.K.; Hurst, M.R. Role of Antifeeding Prophage (Afp) Protein Afp 16 in Terminating the Length of the Afp Tailocin and Stabilizing Its Sheath. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 89, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.C.; Loo, J.F.; Yu, S.; Kong, S.; Chan, T.-F. Monitoring Bacterial Growth Using Tunable Resistive Pulse Sensing with a Pore-Based Technique. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, Y.; Naono, N.; Sakamoto, O.; Takeuchi, H.; Yamaoka, S.; Miyahara, Y. Methodology to Detect Biological Particles Using a Biosensing Surface Integrated in Resistive Pulse Sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 20168–20178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Call, E.D.; Kappler, M.P.; Biever, M.P.; Young, K.; Zlotnick, A.; Jacobson, S.C. Effective Diameters of Virus-Like Particles Measured by Resistive-Pulse Sensing on in-Plane Nanopore Devices. Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 16168–16174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arima, A.; Tsutsui, M.; Harlisa, I.H.; Yoshida, T.; Tanaka, M.; Yokota, K.; Tonomura, W.; Taniguchi, M.; Okochi, M.; Washio, T. Selective Detections of Single-Viruses Using Solid-State Nanopores. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Xu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Sun, N.; Qiu, L.; Zhao, J. Highly Sensitive Detection of Tumor Cell-Derived Exosomes Using Solid-State Nanopores Assisted with a Slight Salt Gradient. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 49218–49226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidyanathan, S.; Wijerathne, H.; Gamage, S.S.; Shiri, F.; Zhao, Z.; Choi, J.; Park, S.; Witek, M.A.; McKinney, C.; Verber, M. High Sensitivity Extended Nano-Coulter Counter for Detection of Viral Particles and Extracellular Vesicles. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 9892–9900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.W.; Kappler, M.P.; Hockaden, N.M.; Carpenter, R.L.; Jacobson, S.C. Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles by Resistive-Pulse Sensing on In-Plane Multipore Nanofluidic Devices. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 16710–16716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, R.; Kapoor, D.; Polaka, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Prajapati, B. Roadmap for Commercial Nanomedicine Development: Integrating Quality by Design Principles with Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology. Mol. Pharm. 2025, 22, 4337–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeltzer, A.J.; Peterson, E.M.; Harris, J.M.; Lathrop, D.K.; German, S.R.; White, H.S. Simultaneous Multipass Resistive-Pulse Sensing and Fluorescence Imaging of Liposomes. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 7241–7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaguech, M.A.; Sethi, K.; Hall, A.R. Solid-State Nanopore Quantification of Discrete Sequence Motifs from DNA and RNA Targets in Human Plasma. Analyst 2025, 150, 3400–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Hong, H.; Wang, X.; Lei, X.; Ye, M.; Liu, Z. Nanopore-Based Sensors for DNA Sequencing: A Review. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 18732–18766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Wu, L.; Qiao, Y.; Tu, J.; Lu, Z. Microfluidic Systems Applied in Solid-State Nanopore Sensors. Micromachines 2020, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, D. Microfluidic and Nanofluidic Resistive Pulse Sensing: A Review. Micromachines 2017, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasianowicz, J.J.; Brandin, E.; Branton, D.; Deamer, D.W. Characterization of Individual Polynucleotide Molecules Using a Membrane Channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 13770–13773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritmejeris, J.; Chen, X.; Dekker, C. Single-Molecule Protein Sequencing with Nanopores. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2024, 3, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Penkauskas, T.; Reiner, J.E.; Kennard, C.; Uline, M.J.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Aksimentiev, A.; Robertson, J.W.; Liu, C. Engineering Biological Nanopore Approaches Toward Protein Sequencing. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 16369–16395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liang, D.; Yang, E.; Zeb, M.; Huang, H.; Sun, H.; Zhang, W.; Peng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, W. Bio-nanopore Technology for Biomolecules Detection. Adv. Biotechnol. 2024, 2, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, M.; Argyropoulos, C. An Introduction to Nanopore Sequencing: Past, Present, and Future Considerations. Micromachines 2023, 14, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Jiang, X.; Yang, N. Carbon Nanopores for DNA Sequencing: A Review on Nanopore Materials. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 4838–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Tong, X.; Zhao, Q. Four Aspects About Solid-State Nanopores for Protein Sensing: Fabrication, Sensitivity, Selectivity, and Durability. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 2000933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, W.; Fang, F.; Zhang, J. Solid-State Nanopore Array: Manufacturing and Applications. Small 2023, 19, 2205680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Tsutsui, M.; Zhou, Y.; Miao, X.-S. Solid-State Nanopore Systems: From Materials to Applications. NPG Asia Mater. 2021, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Shao, L.; Kan, Y. Sequence-Specific Detection of DNA Strands Using a Solid-State Nanopore Assisted by Microbeads. Micromachines 2020, 11, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Song, Y.; Pan, X.; Li, D. Improving Particle Detection Sensitivity of a Microfluidic Resistive Pulse Sensor by a Novel Electrokinetic Flow Focusing Method. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2017, 21, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Cui, L.-F.; Ruan, L.-Q.; Ying, Y.-L.; Long, Y.-T. A Closed-Type Wireless Nanopore Electrode for Analyzing Single Nanoparticles. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2019, 145, e59003. [Google Scholar]
- Apel, P.Y. Heavy Particle Tracks in Polymers and Polymeric Track Membranes. Radiat. Meas. 1995, 25, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Park, S.R.; Ling, X.S. Lithography-Free Formation of Nanopores in Plastic Membranes Using Laser Heating. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 2571–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vreede, L.J.; van den Berg, A.; Eijkel, J.C. Nanopore Fabrication by Heating Au Particles on Ceramic Substrates. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Lee, C.C.; Park, S. Scalable Fabrication of Sub-10 Nm Polymer Nanopores for DNA Analysis. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2019, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowerby, S.J.; Broom, M.F.; Petersen, G.B. Dynamically Resizable Nanometre-Scale Apertures for Molecular Sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 123, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Long, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, D.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, Y. Advances and Challenges in Solid-State Nanopores for DNA Sequencing. Langmuir 2025, 41, 5736–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, H.; Hu, R.; Zhao, Q.; Wanunu, M. Photothermally Assisted Thinning of Silicon Nitride Membranes for Ultrathin Asymmetric Nanopores. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 12472–12481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macha, M.; Marion, S.; Tripathi, M.; Thakur, M.; Lihter, M.; Kis, A.; Smolyanitsky, A.; Radenovic, A. High-Throughput Nanopore Fabrication and Classification Using Xe-Ion Irradiation and Automated Pore-Edge Analysis. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 16249–16259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürjes, P. Controlled Focused Ion Beam Milling of Composite Solid State Nanopore Arrays for Molecule Sensing. Micromachines 2019, 10, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nukala, P.; Varma, M.M. TEM Based Applications in Solid State Nanopores: From Fabrication to Liquid In-Situ Bio-Imaging. Micron 2022, 162, 103347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waugh, M.; Briggs, K.; Gunn, D.; Gibeault, M.; King, S.; Ingram, Q.; Jimenez, A.M.; Berryman, S.; Lomovtsev, D.; Andrzejewski, L. Solid-State Nanopore Fabrication by Automated Controlled Breakdown. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 122–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, Y.N.D.; Karawdeniya, B.I.; Dutt, S.; Kluth, P.; Tricoli, A. Nanopore Fabrication Made Easy: A Portable, Affordable Microcontroller-Assisted Approach for Tailored Pore Formation via Controlled Breakdown. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 2124–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H. High-Precision Fabrication of Single-Crystal Silicon Nanopores with Extremely Small Feature Sizes. Doctoral’s Thesis, TU Delft—Electronic Components, Technology and Materials, Delft, The Netherland, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Zhang, J.; Hong, H.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, Z. Controllable Shrinking Fabrication of Solid-State Nanopores. Micromachines 2022, 13, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Gilboa, T.; Song, J.; Huttner, D.; Grinstaff, M.W.; Meller, A. Single-Molecule Discrimination of Labeled DNAs and Polypeptides Using Photoluminescent-Free TiO2 Nanopores. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 11648–11656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, J.; Henley, R.Y.; Jadhav, V.; Korlach, J.; Wanunu, M. Length-Independent DNA Packing into Nanopore Zero-Mode Waveguides for Low-Input DNA Sequencing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, V.; Hoogerheide, D.P.; Korlach, J.; Wanunu, M. Porous Zero-Mode Waveguides for Picogram-Level DNA Capture. Nano Lett. 2018, 19, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kececi, K.; Dinler, A. Recent Applications of Resistive-Pulse Sensing Using 2D Nanopores. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2024, 171, 037505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Dai, M.; Hong, J.; Feng, S.; Wang, C.; Yuan, Z. Graphene Nanopore Fabrication and Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Lin, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, C. Controllable Fabrication of Sub-10 Nm Graphene Nanopores Via Helium Ion Microscopy and DNA Detection. Biosensors 2024, 14, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lu, B.; Zhao, Q.; Li, J.; Gao, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Z.; Yang, F. Boron Nitride Nanopores: Highly Sensitive DNA Single-Molecule Detectors. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 4549–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharia, J.; Bandara, Y.N.D.; Lee, J.S.; Wang, Q.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, M.J. Fabrication of Hexagonal Boron Nitride Based 2D Nanopore Sensor for the Assessment of Electro-Chemical Responsiveness of Human Serum Transferrin Protein. Electrophoresis 2020, 41, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Oviedo, J.P.; Bandara, Y.M.N.D.Y.; Peng, X.; Xia, L.; Wang, Q.; Garcia, K.; Wang, J.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, M.J. Detection of Nucleotides in Hydrated SsDNA via 2D h-BN Nanopore with Ionic-Liquid/Salt–Water Interface. Electrophoresis 2021, 42, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, M.; Lihter, M.; Thakur, M.; Georgiou, V.; Topolancik, J.; Ilic, B.R.; Liu, K.; Feng, J.; Astier, Y.; Radenovic, A. Fabrication and Practical Applications of Molybdenum Disulfide Nanopores. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 1130–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibakhshi, M.A.; Kang, X.; Clymer, D.; Zhang, Z.; Vargas, A.; Meunier, V.; Wanunu, M. Scaled-up Synthesis of Freestanding Molybdenum Disulfide Membranes for Nanopore Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2207089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danda, G.; Masih Das, P.; Chou, Y.-C.; Mlack, J.T.; Parkin, W.M.; Naylor, C.H.; Fujisawa, K.; Zhang, T.; Fulton, L.B.; Terrones, M. Monolayer WS2 Nanopores for DNA Translocation with Light-Adjustable Sizes. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 1937–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, N.; Shoji, K.; Maki, T.; Kawano, R. Simple Fabrication of Solid-State Nanopores on a Carbon Film. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, J.G. Lithographic Fabrication of Nanoapertures. U.S. Patent US6503409 B1, 7 January 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, X.S. Addressable Nanopores and Micropores Including Methods for Making and Using Same. U.S. Patent No. 7,678,562, 16 March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, B.; Bai, J.; Stolovitzky, G. Fabricatable Nanopore Sensors with an Atomic Thickness. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 183501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmandi-Tash, H.; Bellunato, A.; Wen, C.; Olsthoorn, R.C.; Scheicher, R.H.; Zhang, S.L.; Schneider, G.F. Zero-Depth Interfacial Nanopore Capillaries. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1703602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, H.; Ardebili, A.H.A.; Taghipoor, M. Fabrication of Low Aspect Ratio Solid-State Pores from Sub-Micron to Microscales Utilizing Crossing Blades. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 377, 115682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakouei, M.; Abdorahimzadeh, S.; Taghipoor, M. Effects of cone angle and length of nanopores on the resistive pulse quality. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 43, 25306–25314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasimha Rao, A.V.; Swarnalatha, V.; Pandey, A.K.; Pal, P. Determination of Precise Crystallographic Directions on Si {111} Wafers Using Self-Aligning Pre-Etched Pattern. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 2018, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnik, D.; Vrtacnik, D.; Aljancic, U.; Amon, S. Wet Etching of Silicon Structures Bounded by (311) Sidewalls. Microelectron. Eng. 2000, 51, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Li, D. Detection and Sizing of Nanoparticles and DNA on PDMS Nanofluidic Chips Based on Differential Resistive Pulse Sensing. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 5964–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, Y.-H.; Karnik, R. Investigating the Translocation of λ-DNA Molecules through PDMS Nanopores. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabard-Cossa, V.; Trivedi, D.; Wiggin, M.; Jetha, N.N.; Marziali, A. Noise Analysis and Reduction in Solid-State Nanopores. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 305505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Zhang, B.; Huang, X.; Zhong, R.; Huang, S. Nonlinear Identification and Decoupling Sliding Mode Control of Macro-Micro Dual-Drive Motion Platform with Mechanical Backlash. Machines 2023, 11, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yu, Y.; Cui, L.; Ji, N.; Deng, X. Research on Micro-/Nano-Positioning System Driven by a Stepper Motor. Actuators 2024, 13, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Seeger, S. Superamphiphobic Surfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 2784–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghipoor, M.; Bertsch, A.; Renaud, P. An Improved Model for Predicting Electrical Conductance in Nanochannels. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 4160–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jodeyri, Z.; Taghipoor, M. Multivariate Analysis of Nanoparticle Translocation through a Nanopore to Improve the Accuracy of Resistive Pulse Sensing. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 5097–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, M.-H.; Yeon, J.-W.; Hwang, J.; Hong, C.S.; Song, K. A Calibration Technique for an Ag/AgCl Reference Electrode Utilizing the Relationship between the Electrical Conductivity and the KCl Concentration of the Internal Electrolyte. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2009, 39, 2587–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Koch, W.; Pratt, K. Proposed New Electrolytic Conductivity Primary Standards for KCl Solutions. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 1991, 96, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei Souderjani, A.; Bakouei, M.; Saidi, M.H.; Taghipoor, M. Electrophoretic Motion of Hydrophobic Spherical Particles in Nanopore: Characteristics, Separation, and Resistive Pulse Sensing. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 022005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Gao, Z.; Man, J.; Li, J.; Du, G.; Qiu, Y. Theoretical Prediction of Diffusive Ionic Current through Nanopores under Salt Gradients. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 092007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, T.D.; Lee, C.; Ryu, J. Numerical Study of Rectified Electroosmotic Flow in Nanofluidics: Influence of Surface Charge and Geometrical Asymmetry. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 092017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.-D. Quantum Tunneling and Field Electron Emission Theories; World Scientific: Singapore, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Koenders, M. Field Emission and Stability. Master’s Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.; Zhang, L.C. The Deformation Mechanism at Pop-In: Monocrystalline Silicon under Nanoindentation with a Berkovich Indenter. Key Eng. Mater. 2009, 389, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abram, R.; Chrobak, D.; Nowak, R. Origin of a Nanoindentation Pop-In Event in Silicon Crystal. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 095502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
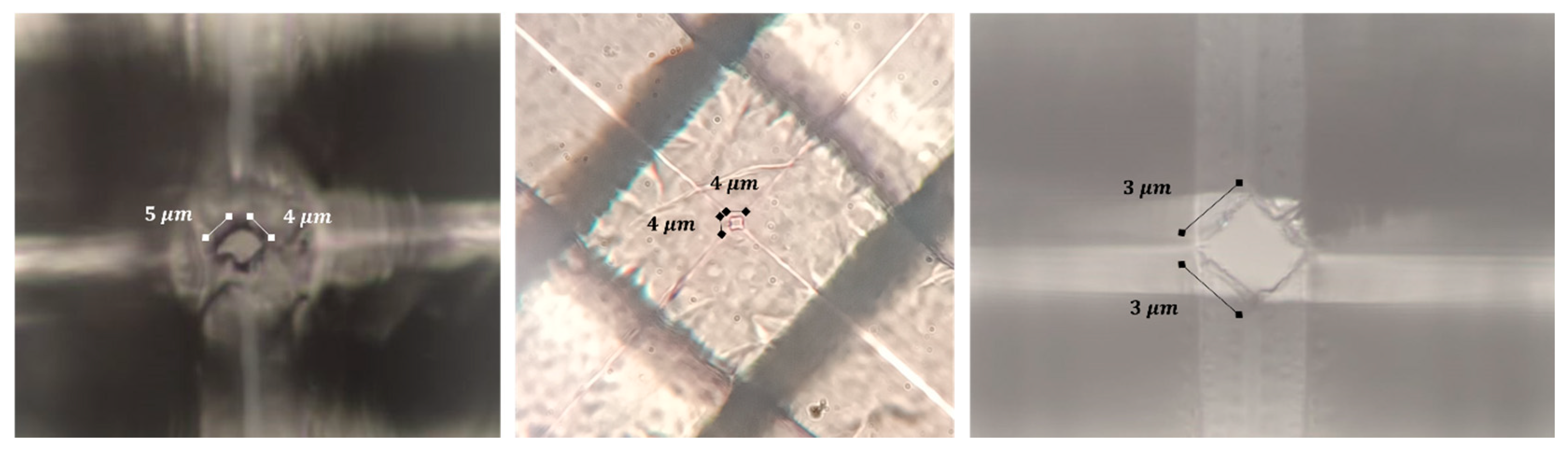

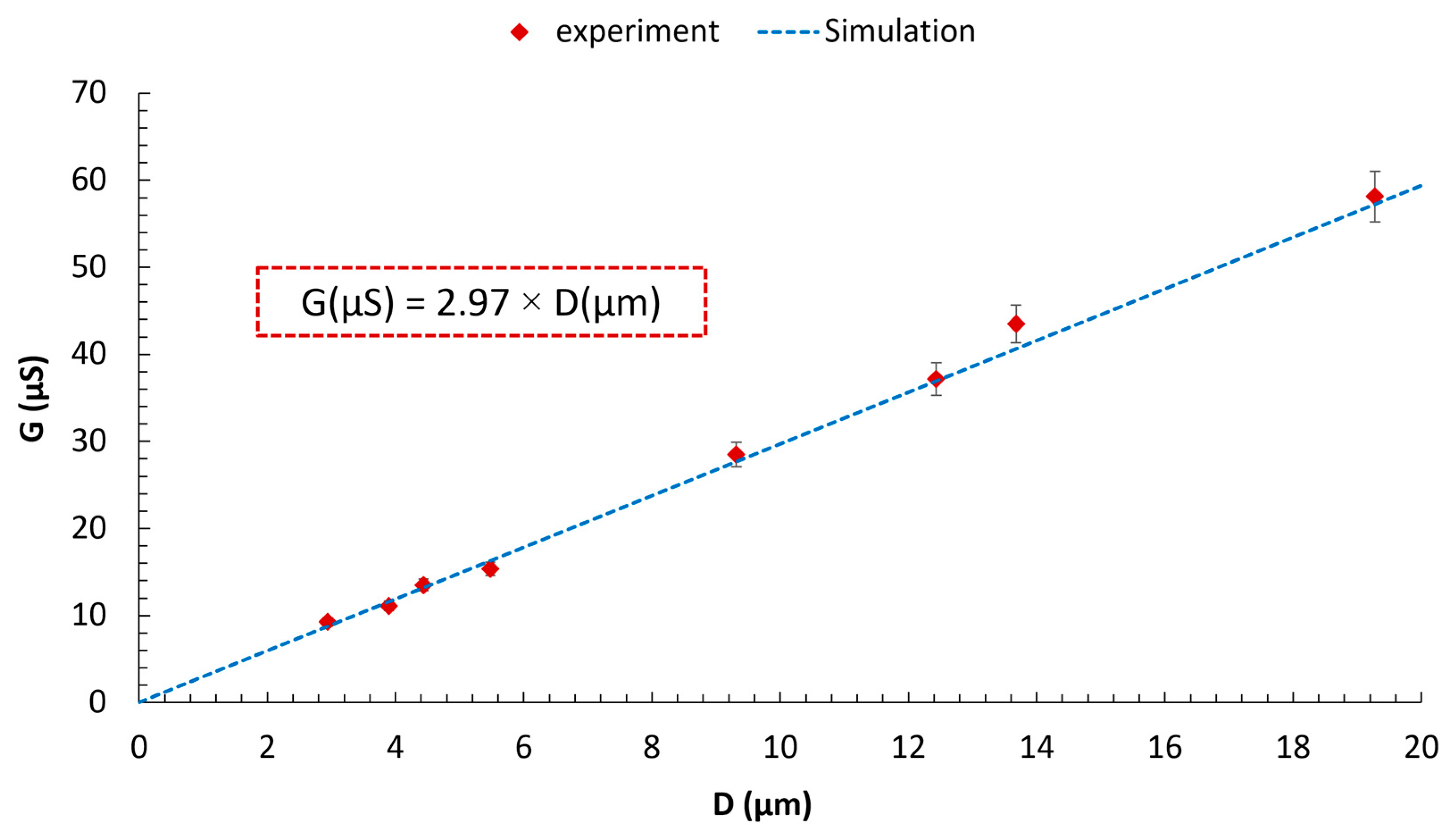
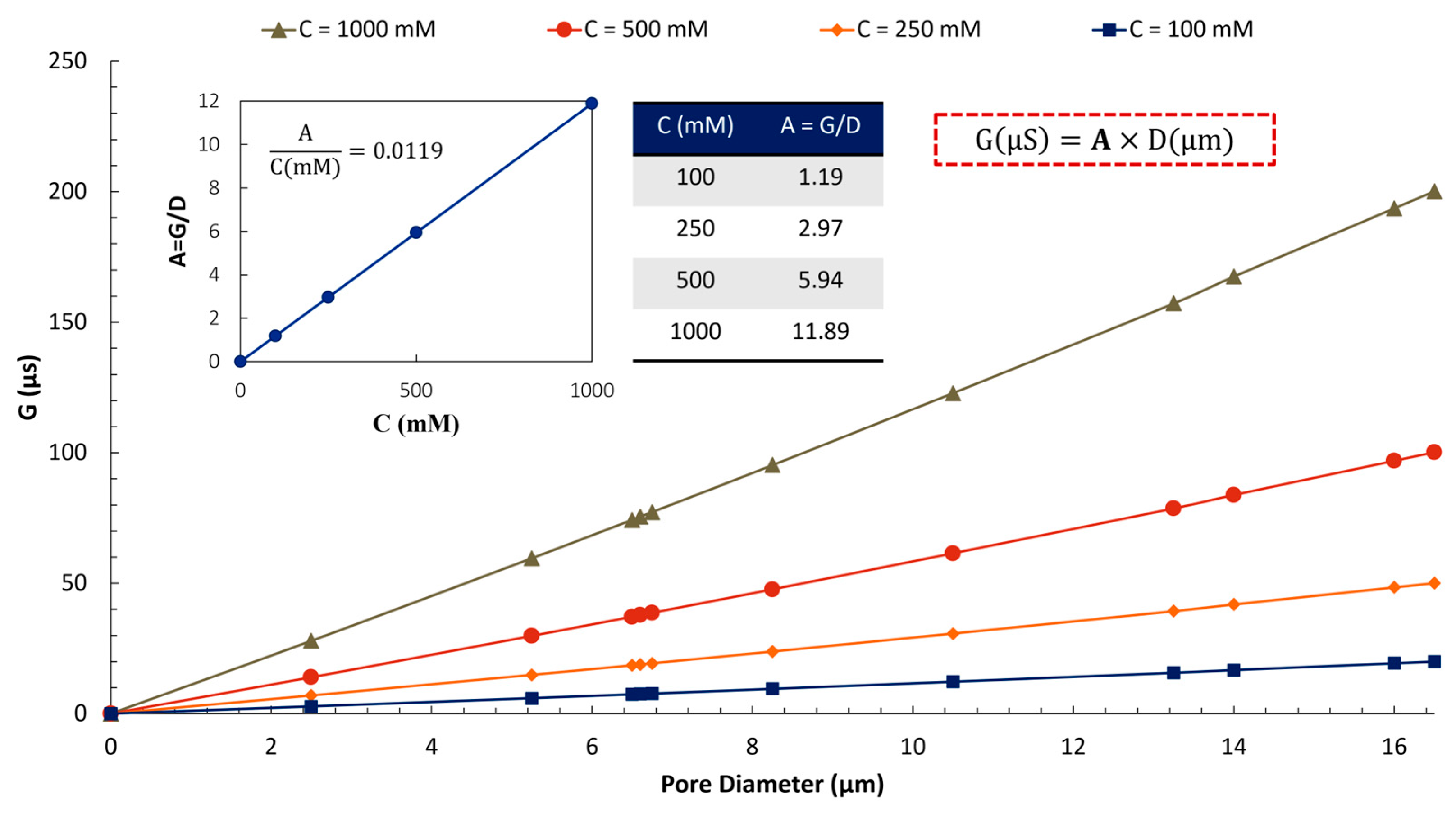
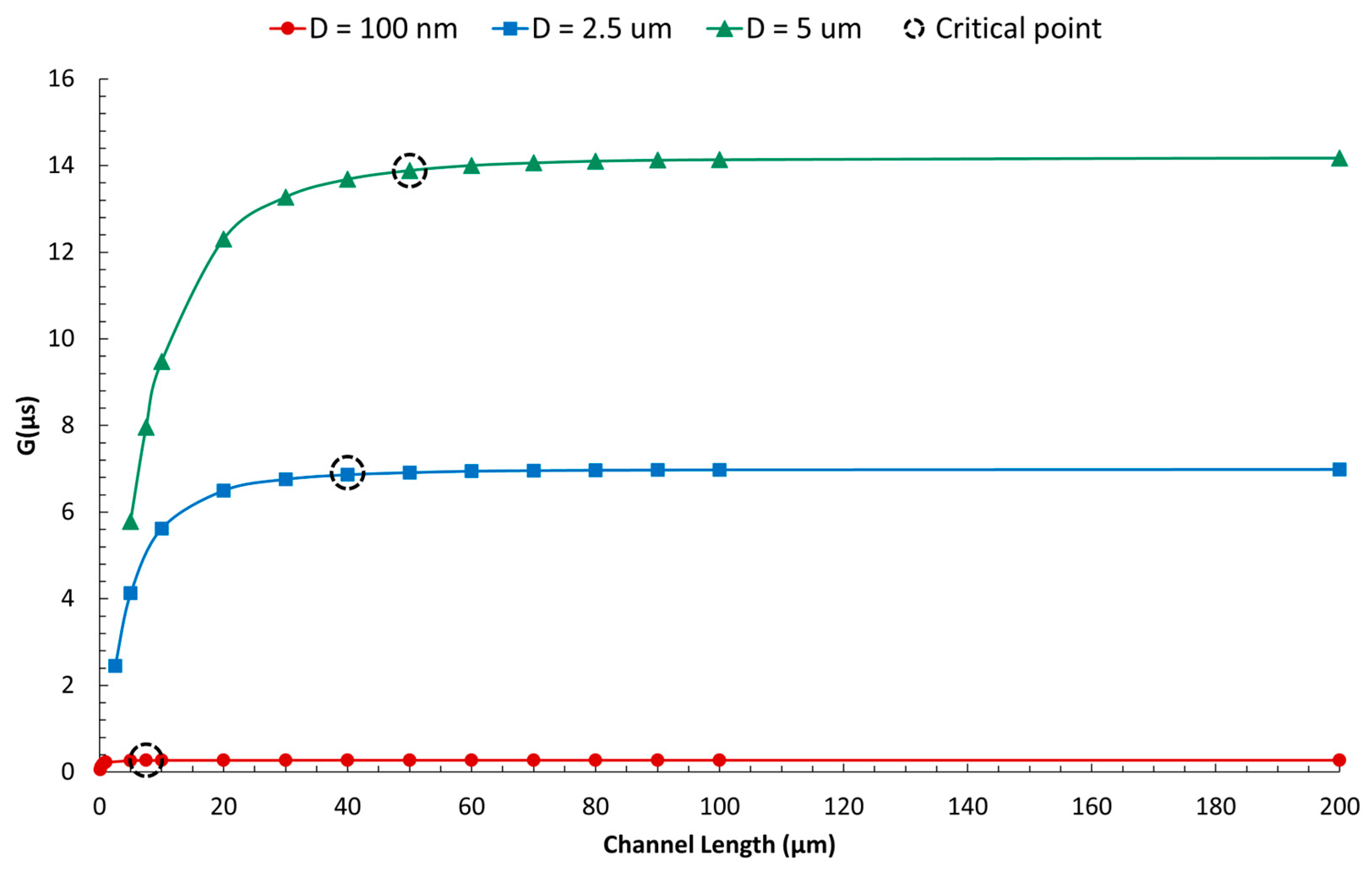

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Behzadi, M.M.; Renaud, P.; Taghipoor, M. Fabrication of Sub-50 nm Three-Dimensional Rhombic Zero-Depth PDMS Nanopores with Enhanced Conductance via Silicon Micro-Blade Molding. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16121375
Behzadi MM, Renaud P, Taghipoor M. Fabrication of Sub-50 nm Three-Dimensional Rhombic Zero-Depth PDMS Nanopores with Enhanced Conductance via Silicon Micro-Blade Molding. Micromachines. 2025; 16(12):1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16121375
Chicago/Turabian StyleBehzadi, Mohammad Matin, Philippe Renaud, and Mojtaba Taghipoor. 2025. "Fabrication of Sub-50 nm Three-Dimensional Rhombic Zero-Depth PDMS Nanopores with Enhanced Conductance via Silicon Micro-Blade Molding" Micromachines 16, no. 12: 1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16121375
APA StyleBehzadi, M. M., Renaud, P., & Taghipoor, M. (2025). Fabrication of Sub-50 nm Three-Dimensional Rhombic Zero-Depth PDMS Nanopores with Enhanced Conductance via Silicon Micro-Blade Molding. Micromachines, 16(12), 1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16121375





