Investigation on High-Temperature and High-Field Reliability of NMOS Devices Fabricated Using 28 nm Technology After Heavy-Ion Irradiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
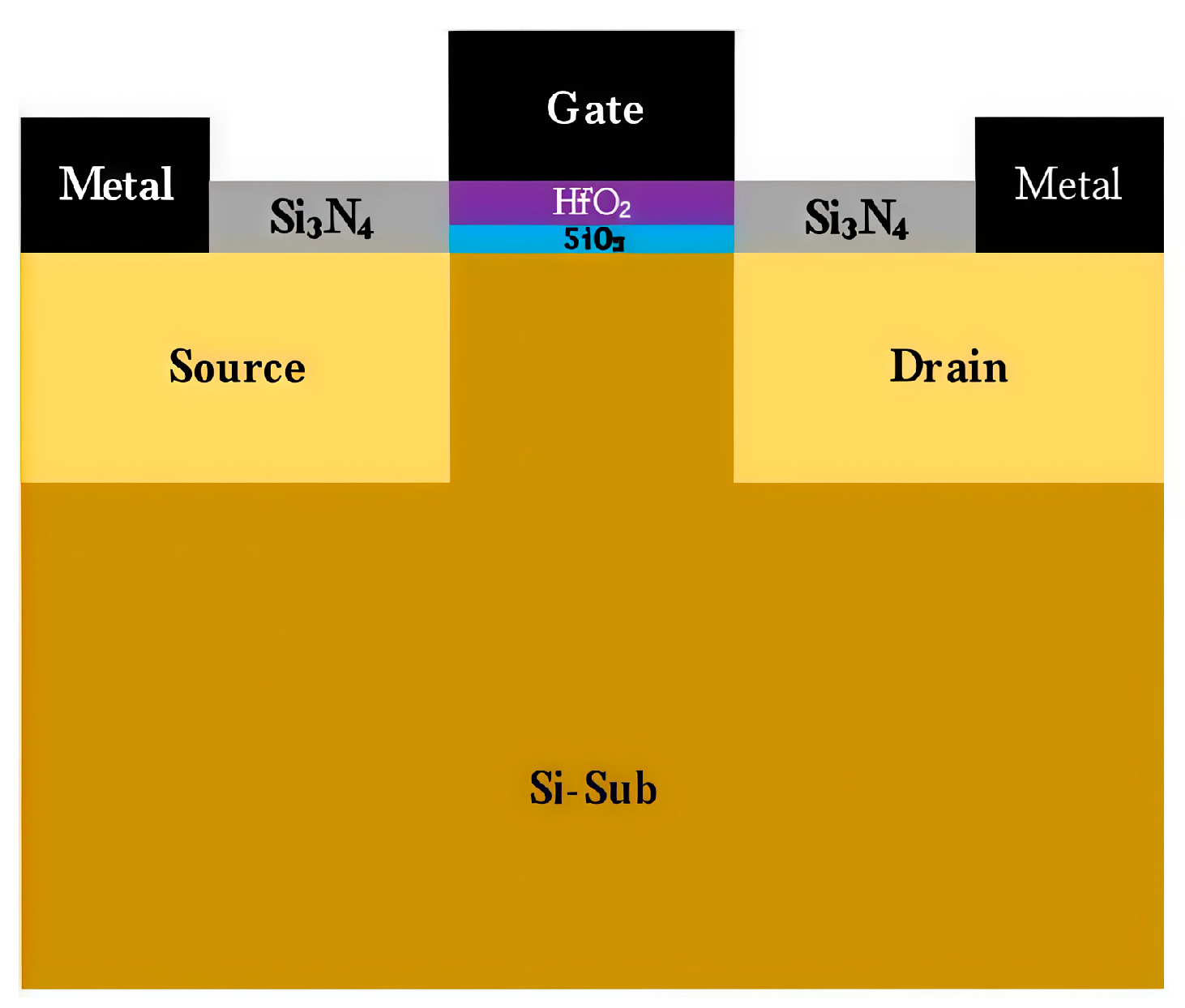
2. Experimental Devices and Conditions
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
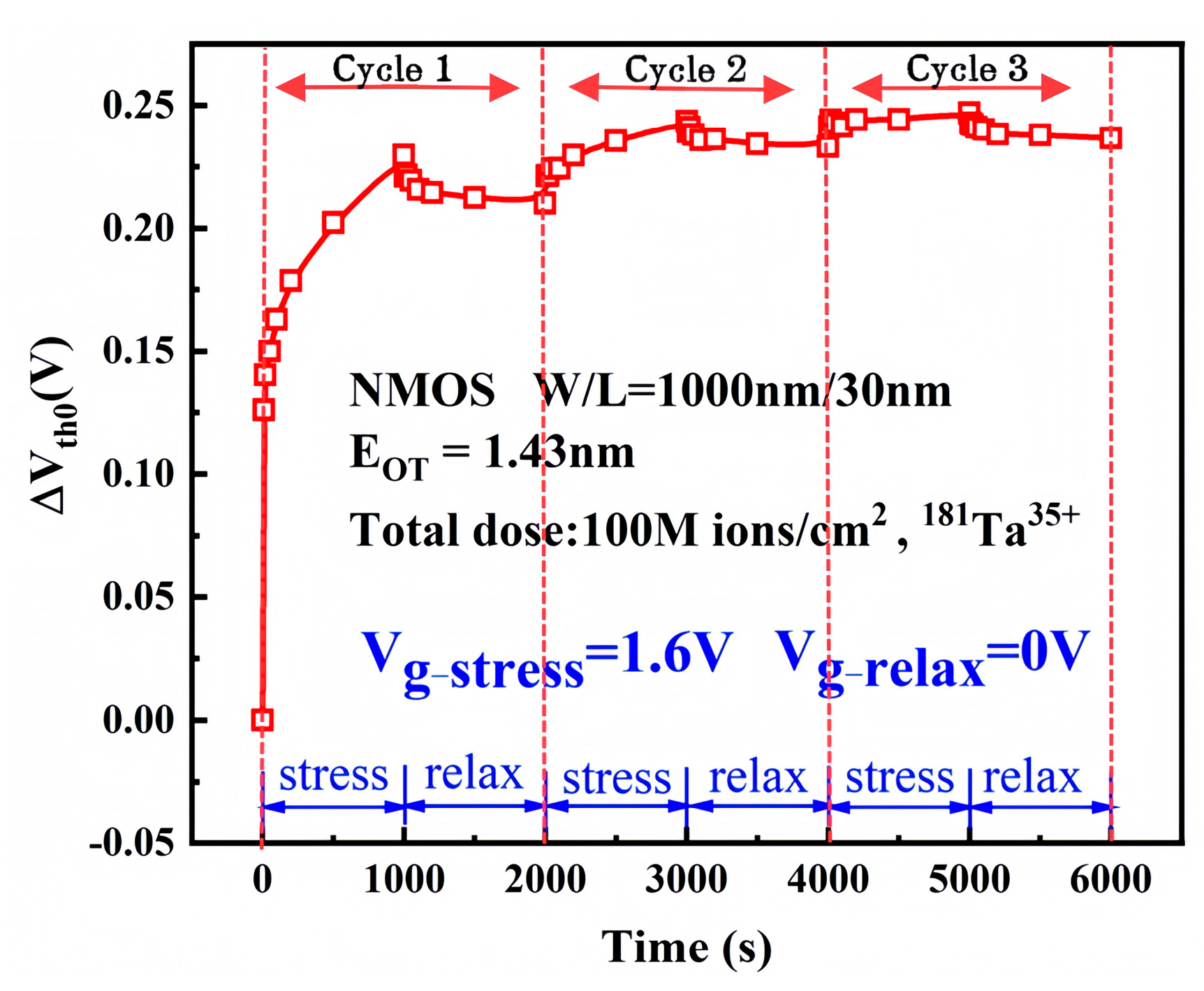
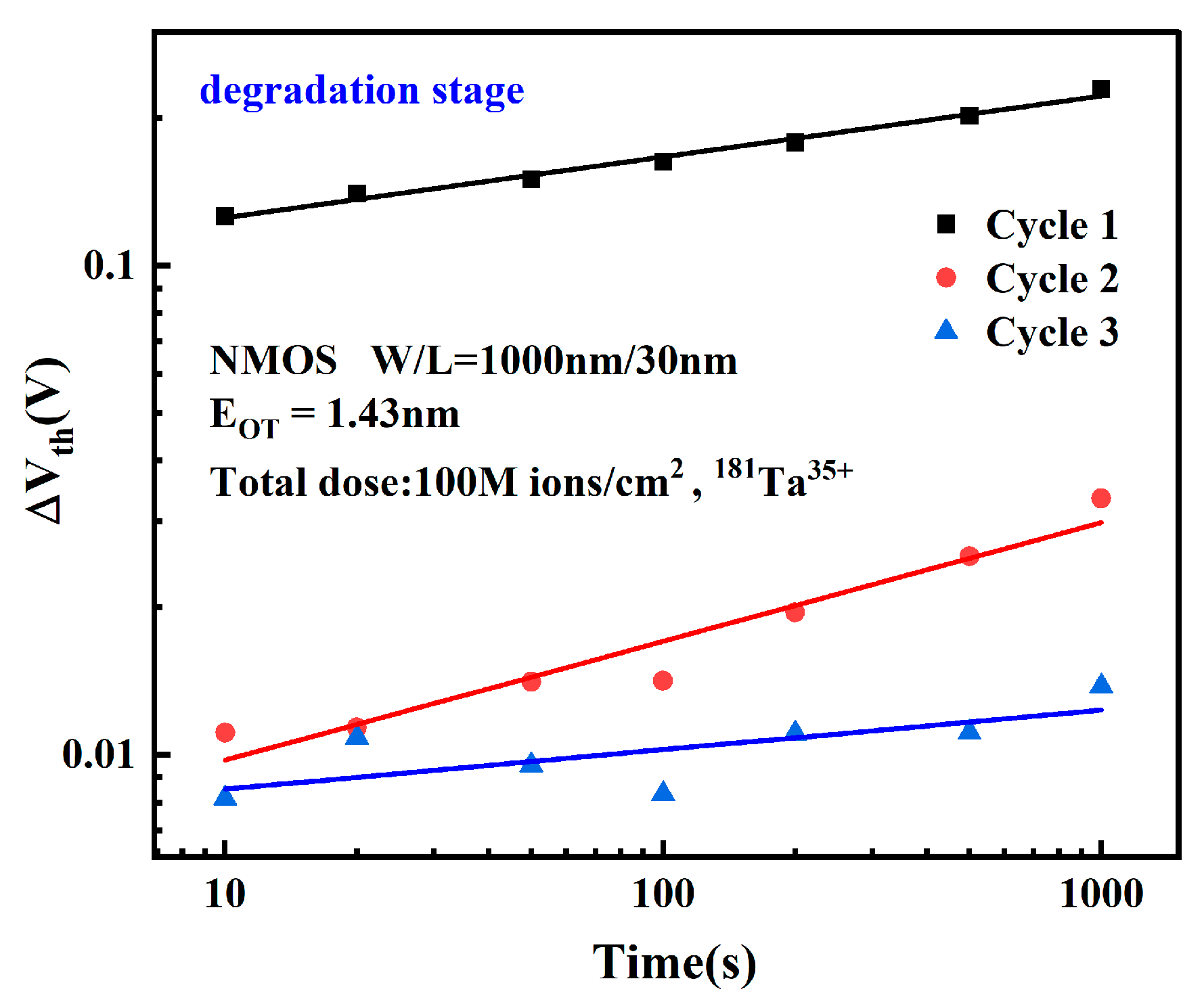
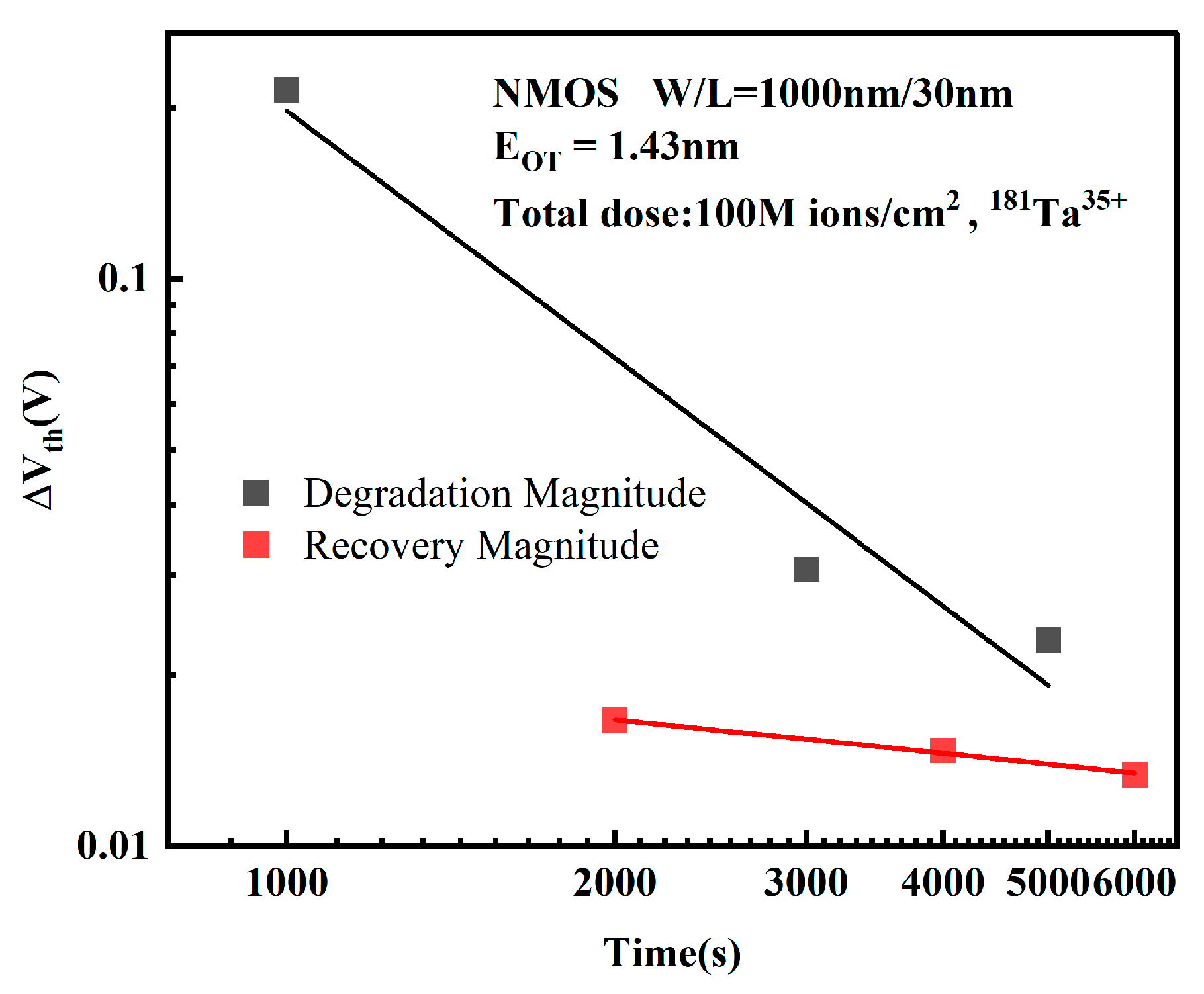
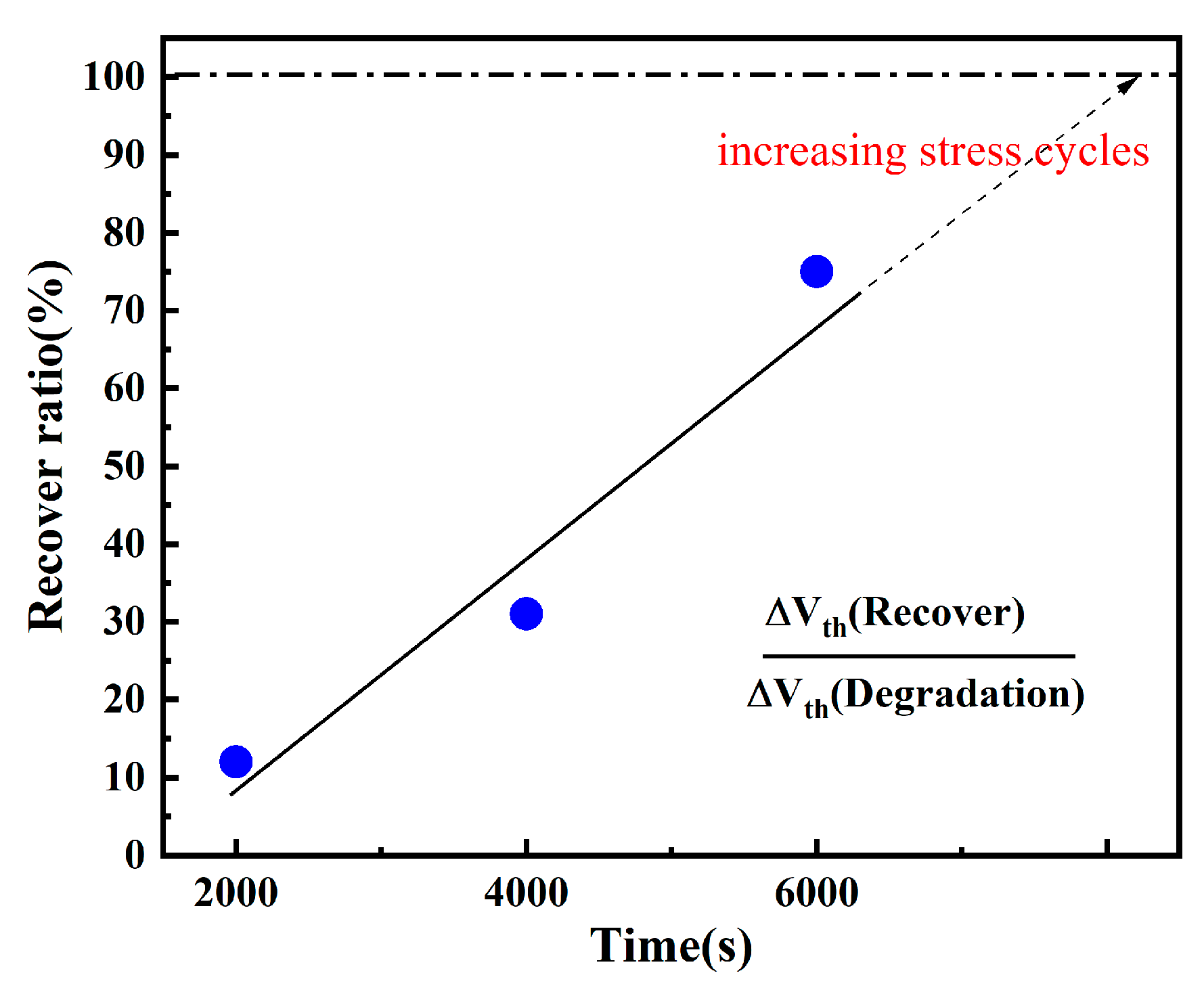
3.1. Effect of Electrical Stress Time on Device Degradation
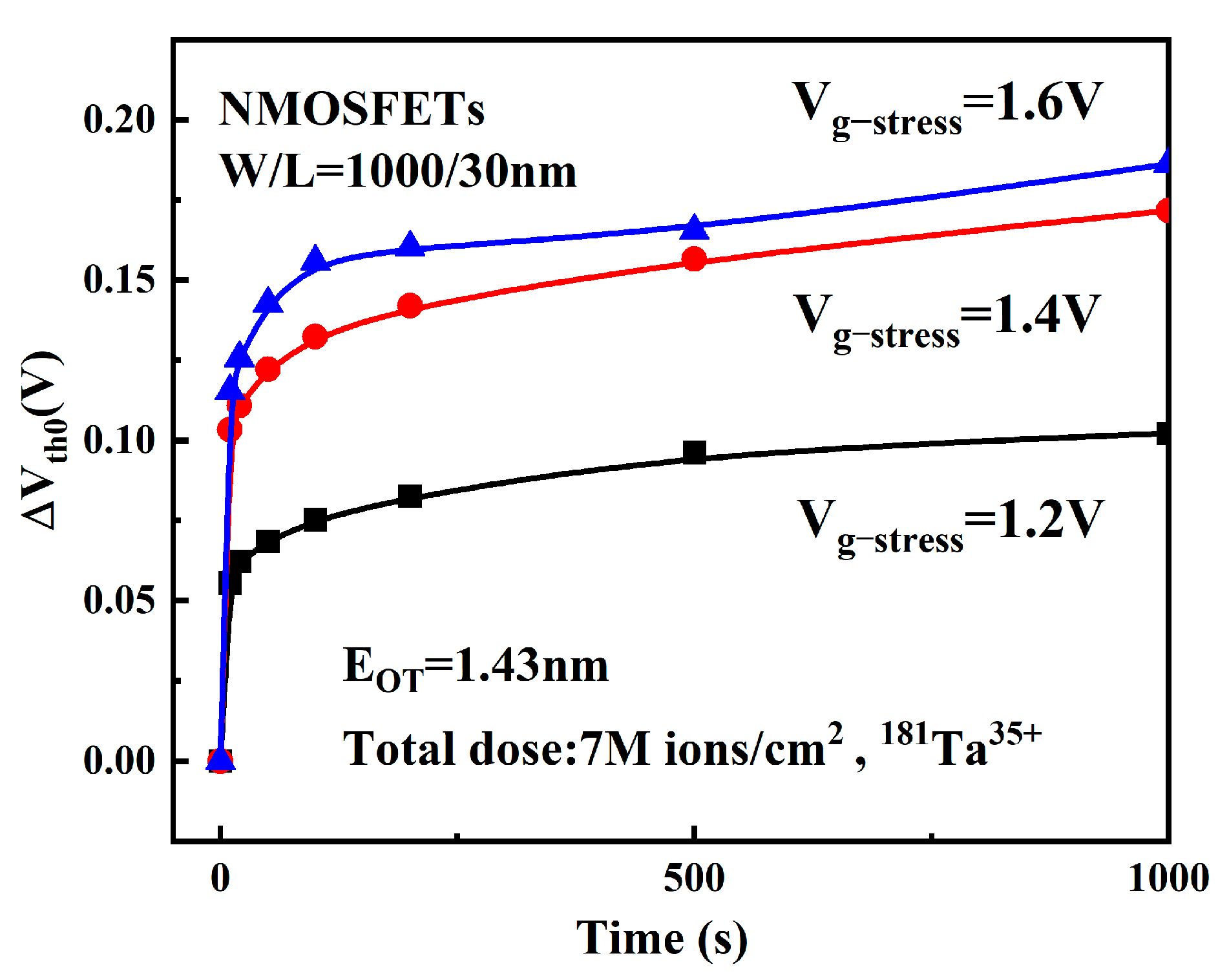
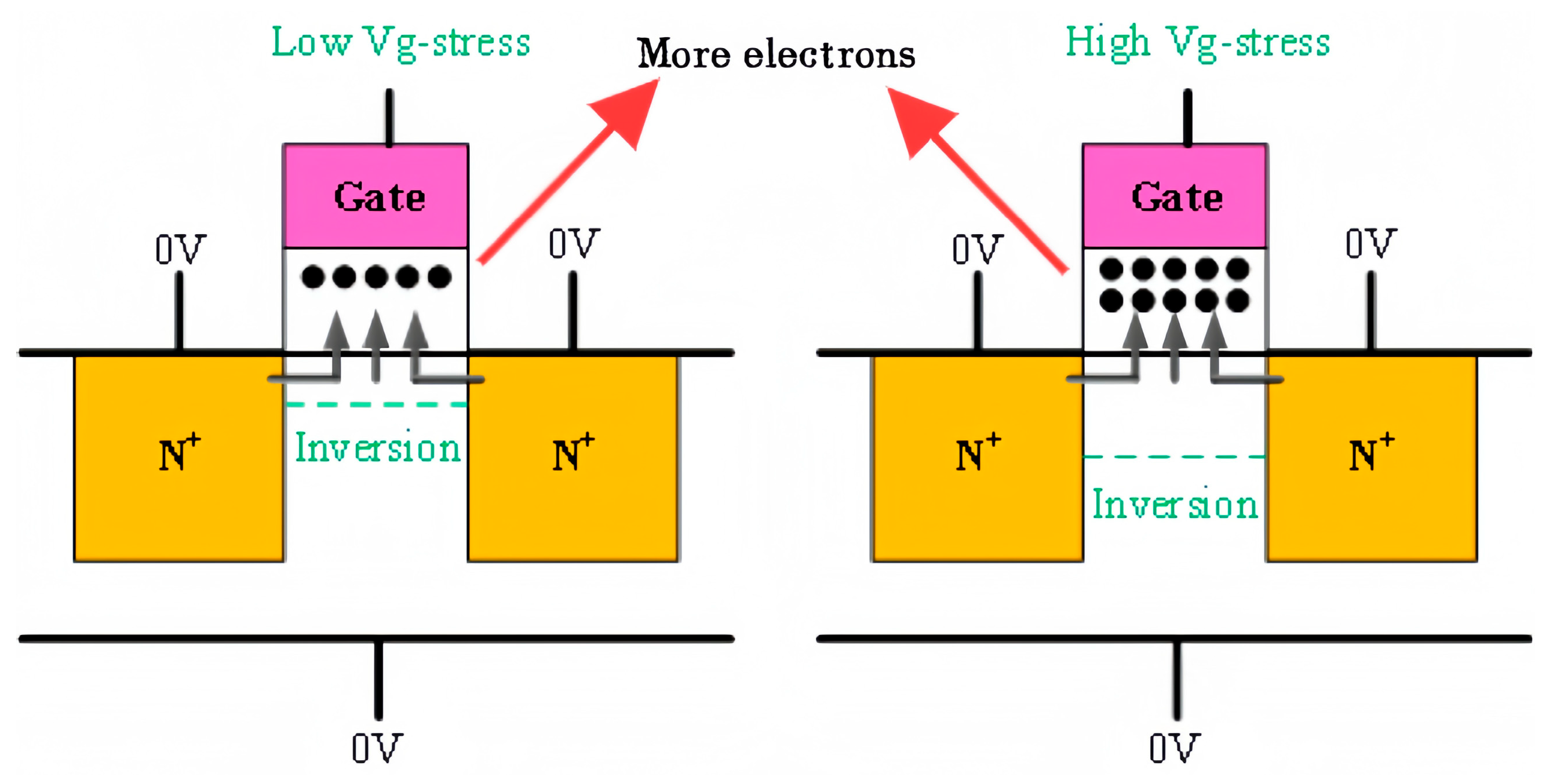
3.2. Effect of Electric Stress on Device Degradation
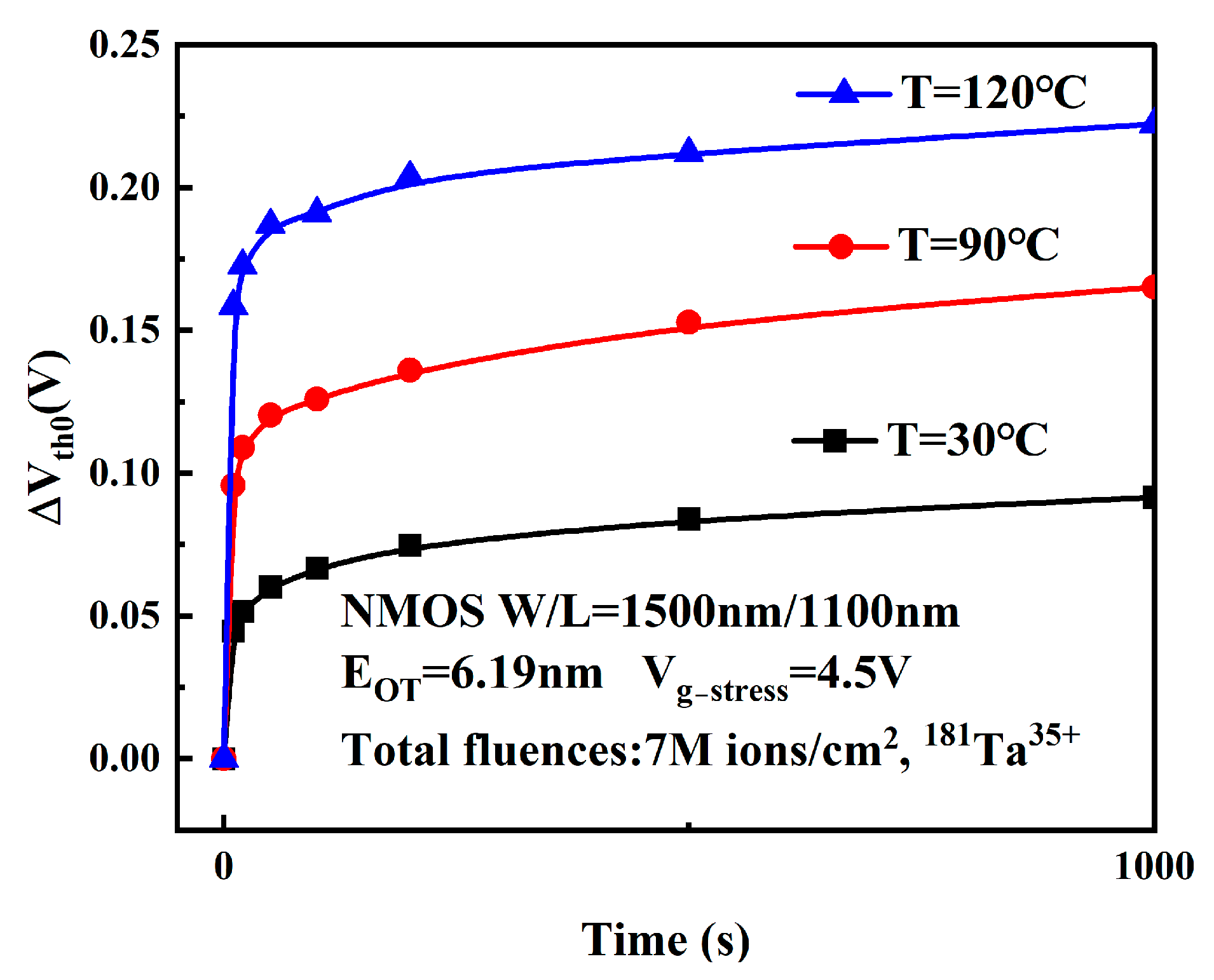
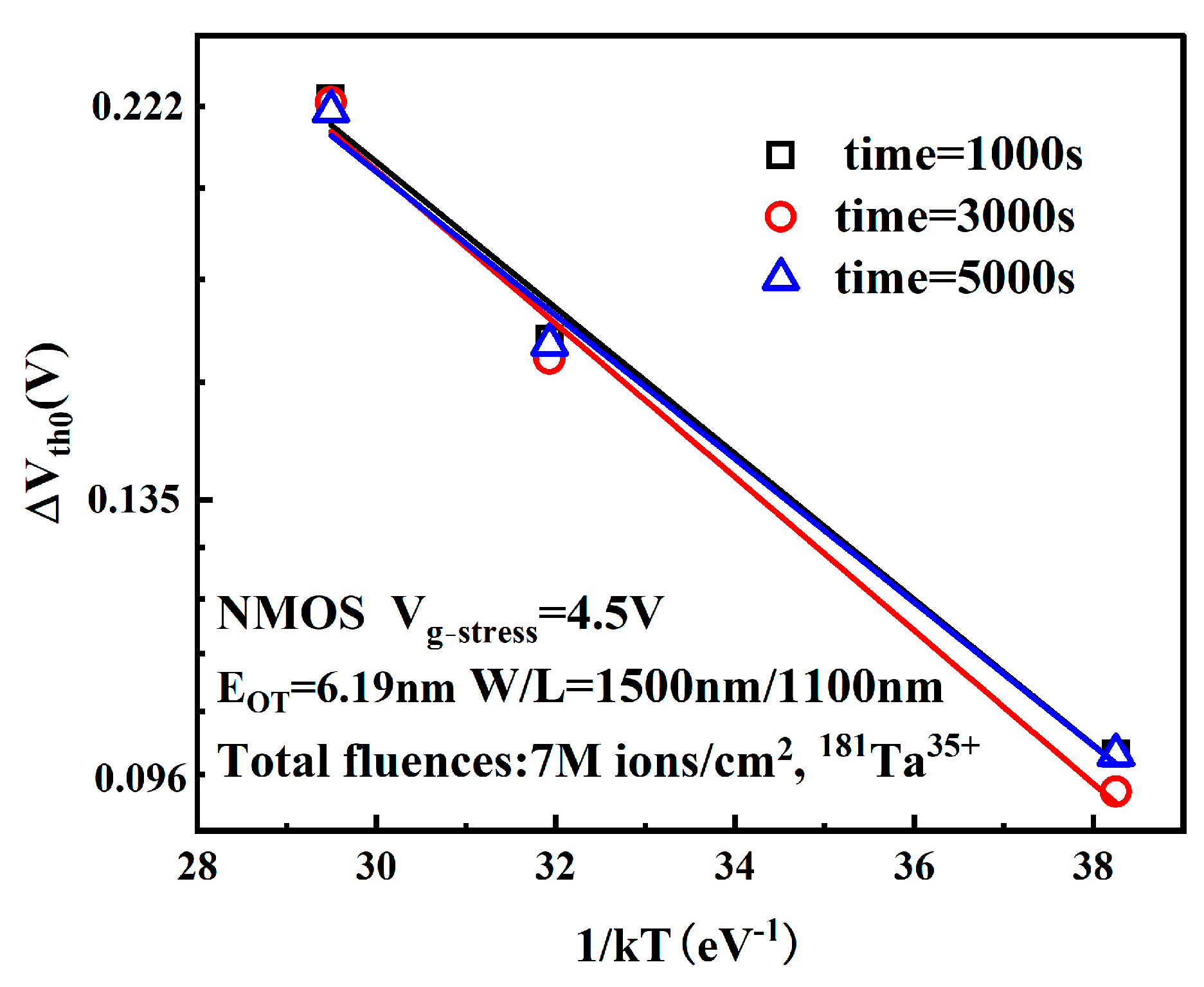
3.3. Effect of Temperature Stress on Device Degradation
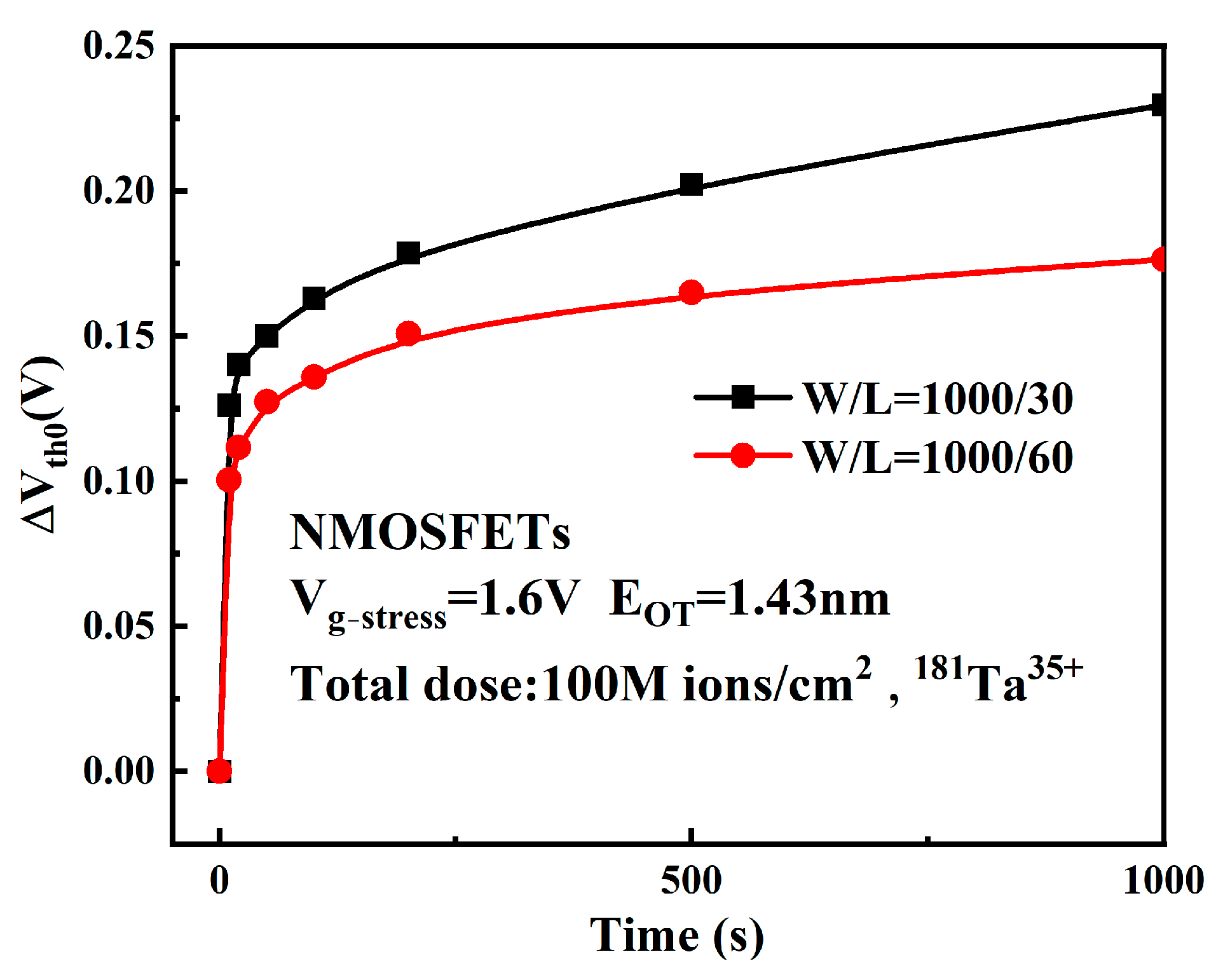
3.4. Effect of Gate Length on Device Degradation
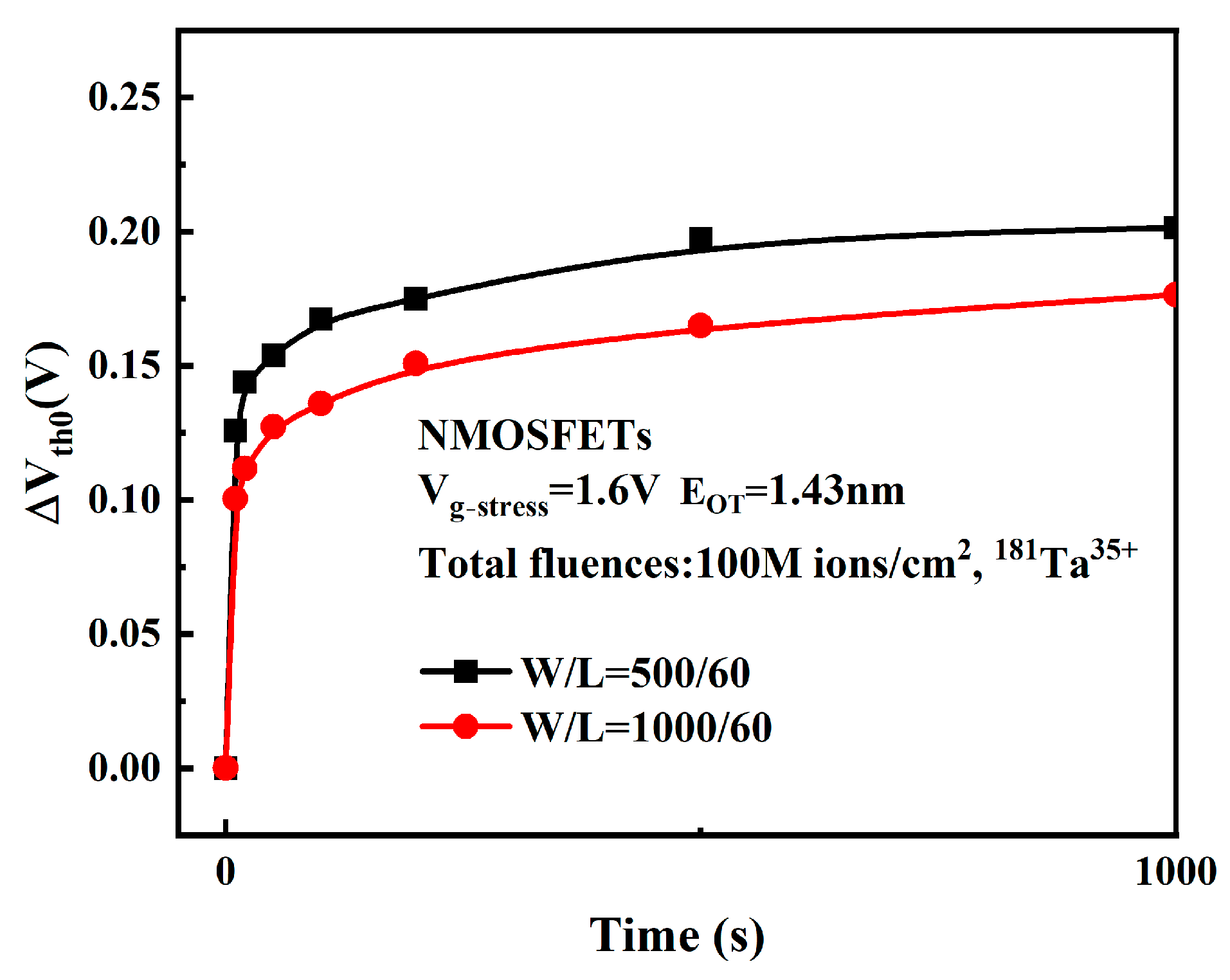
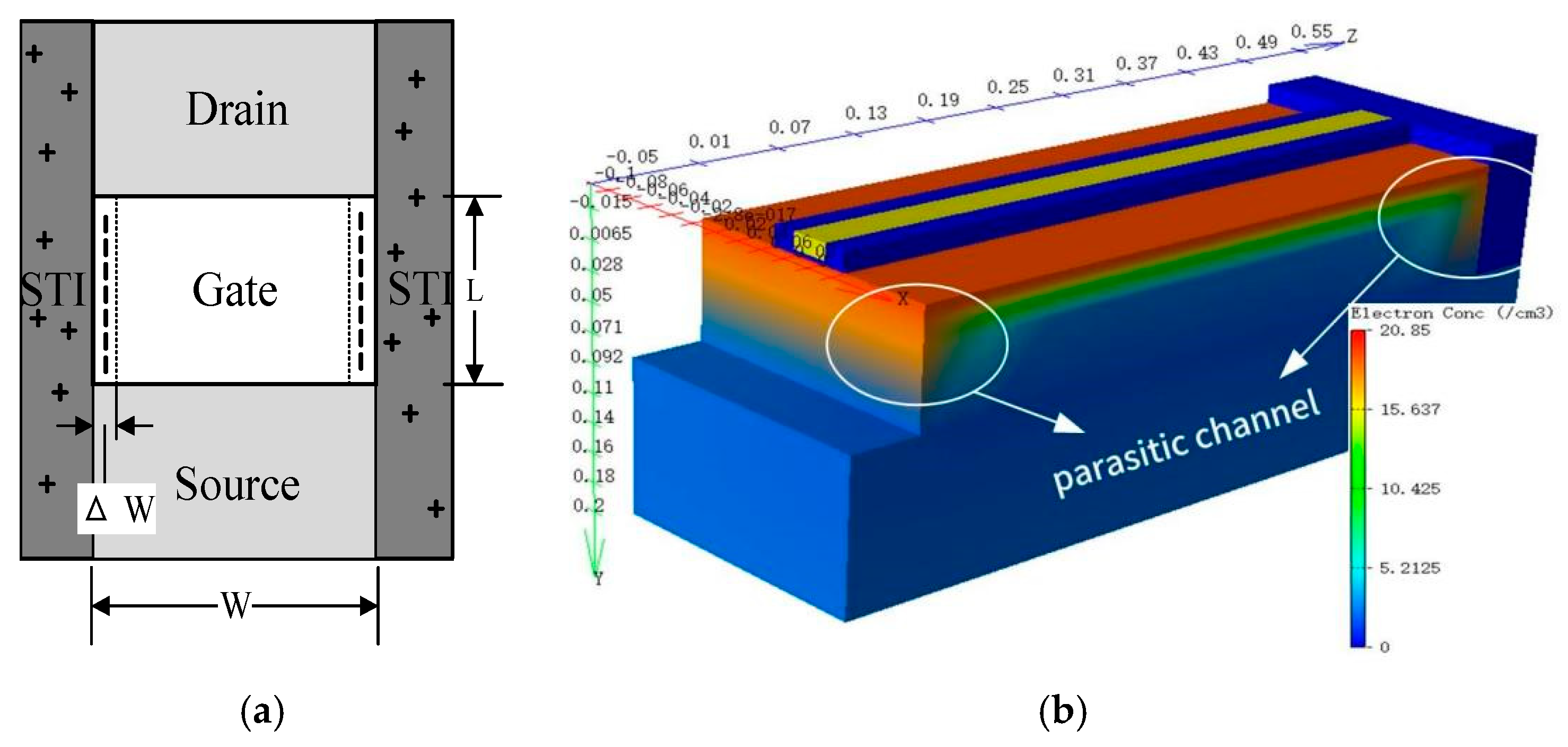
3.5. Effect of Gate Width on Device Degradation
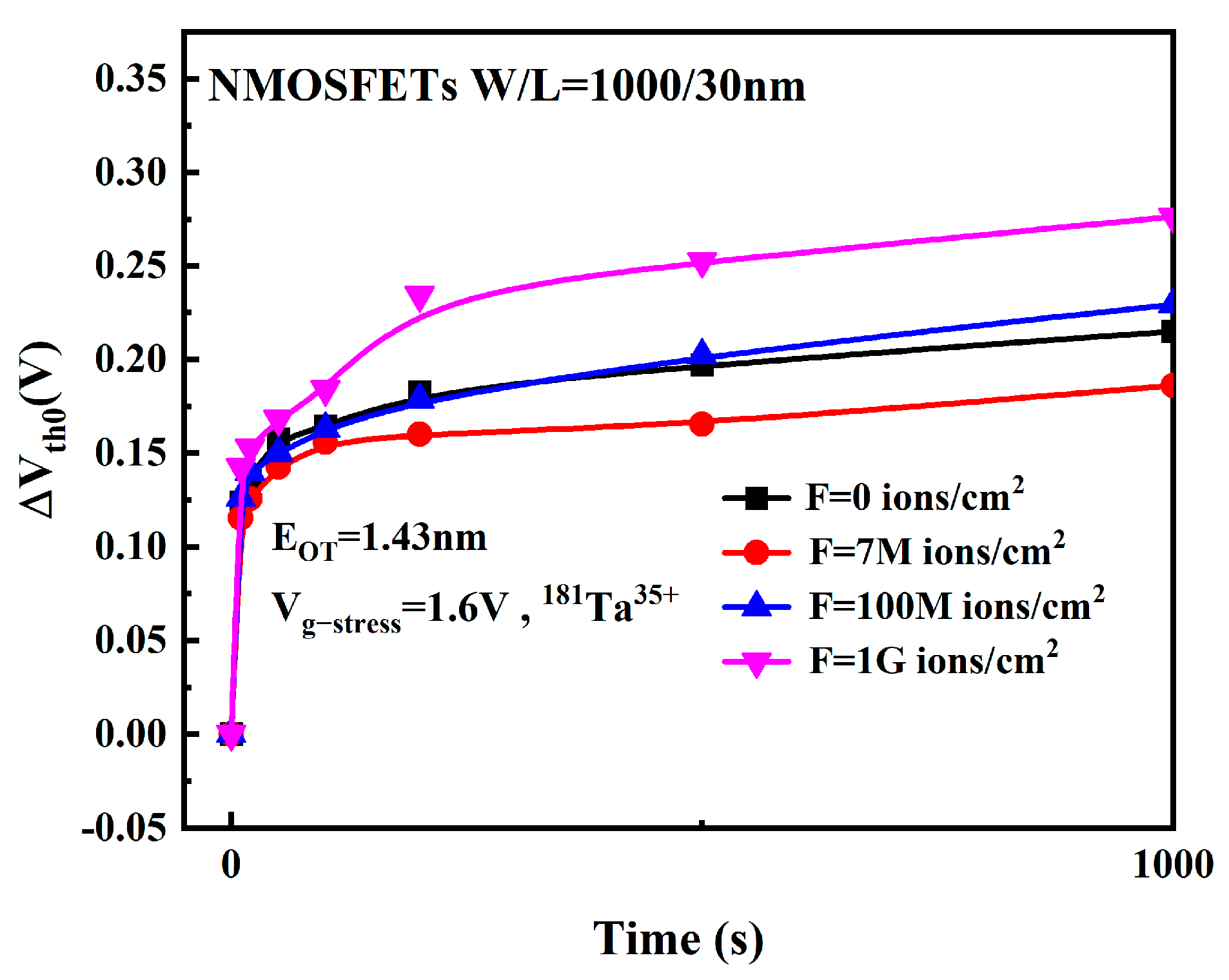
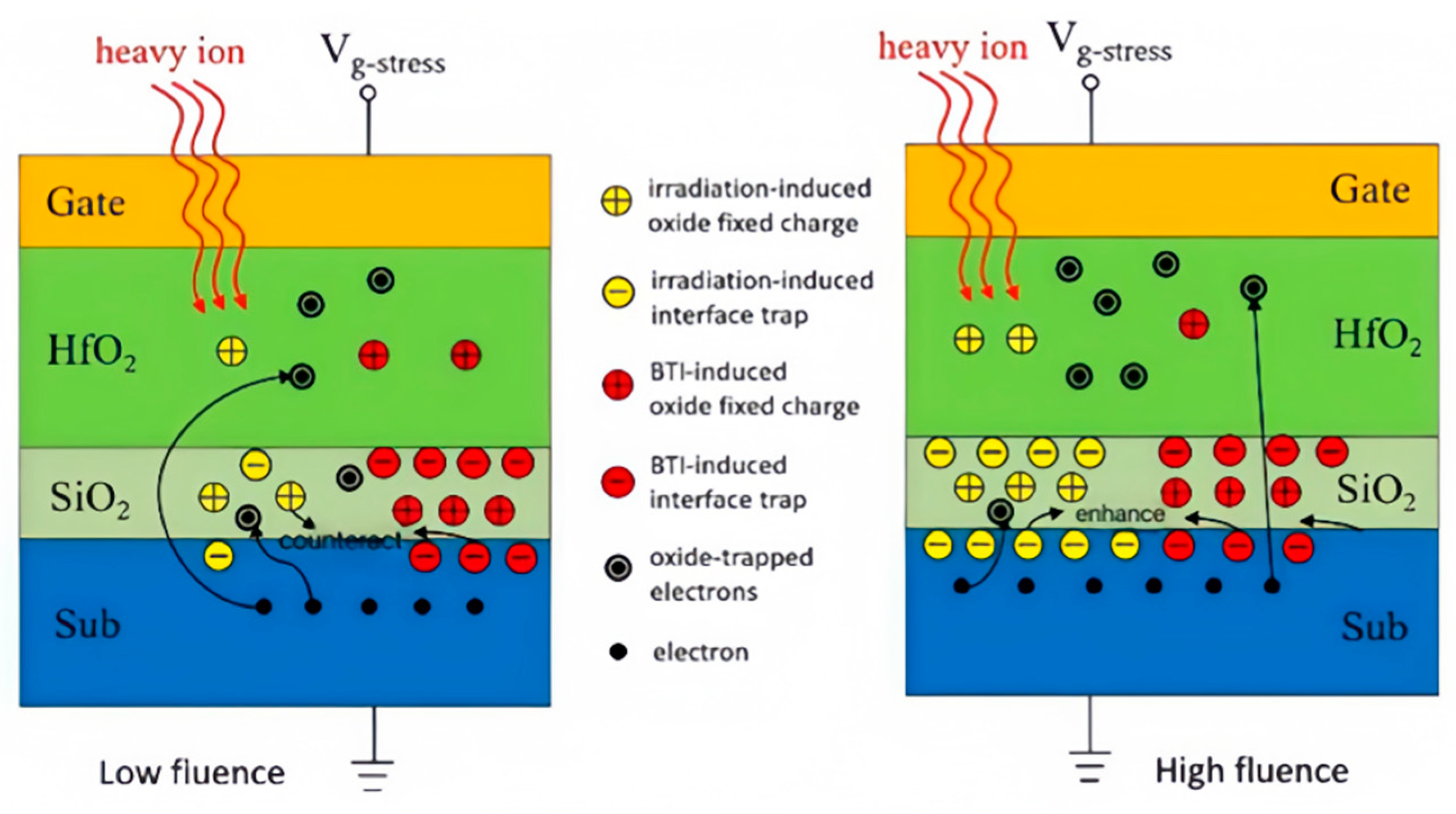
3.6. Effect of Heavy Ion Fluence on Device Degradation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barcellos-Hoff, M.H.; Blakely, E.A.; Burma, S.; Fornace, A.J.; Gerson, S.; Hlatky, L.; Kirsch, D.G.; Luderer, U.; Shay, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Concepts and challenges in cancer risk prediction for the space radiation environment. Life Sci. Space Res. 2015, 6, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yu, X.F.; Liang, X.W.; Guo, Q.; Xiang, Y.T.; Feng, J. Study on gate oxide reliability of SiC power MOSFETs under 300 MeV proton irradiation. Microelectron. Reliab. 2025, 169, 115750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.H.; Yu, Q.Z.; Hu, Z.L.; Zhou, B.; Yi, T.C.; Yuan, L.B.; Lin, L.; Shen, F.; Liang, T.J. Single event burnout of SiC MOSFET induced by atmospheric neutrons. Microelectron. Reliab. 2023, 146, 114997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Liang, X.; Sun, J.; Feng, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, T.; Pu, X.; Zhang, D.; Xiang, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Total ionizing dose effects of 60Co-γ ray radiation on SiC MOSFETs with different gate oxide thickness. Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 2023, 178, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, R.; Li, R.; Chen, G.; Fu, D.; Lu, W. Total dose effects on the matching properties of deep submicron MOS transistors. J. Semicond. 2014, 35, 064007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.X. Radiation Effects of Semiconductor Devices and Integrated Circuits; National Defense Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, C. Moore’s law: What comes next? Commun. ACM 2021, 64, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefflinger, B. ITRS 2028—International roadmap of semiconductors. In CHIPS 2020 VOL. 2; Höfflinger, B., Ed.; The Frontiers Collection; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Zhan, K.-C.; Zhang, J.-M.; Chen, J.-M.; Chang, C.-H.-T.; Wang, S.-J.; Wang, M.-C. Junction integrity for 28 nm high-k nMOSFETs with thermal stress. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd IEEE International Conference on Knowledge Innovation and Invention (ICKII), Kaohsiung, Taiwan, China, 21–23 August 2020; pp. 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J. Interfaces and defects of high-K oxides on silicon. Solid-State Electron. 2005, 49, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.T. Single-Event Effect and Long-Term Reliability of 28 nm MOS Devices. Master’s Thesis, Xidian University, Xi’an, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, B.K.; Fleetwood, D.M.; Schrimpf, R.D.; Massengill, L.W.; Galloway, K.F.; Shaneyfelt, M.R.; Meisenfieimer, T.L.; Dodd, P.E.; Schwank, J.R.; Lee, Y.M.; et al. Long-term reliability degradation of ultrathin dielectric films due to heavy-ion irradiation. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2002, 49, 3045–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cester, A.; Cimino, S.; Paccagnella, A.; Ghibaudo, G.; Ghidini, G.; Wyss, J. Accelerated wear-out of ultra-thin gate oxides after irradiation. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2003, 50, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, J.F., Jr.; Suehle, J.S.; Johnston, A.H.; Wang, B.; Miyahara, T.; Vogel, E.M.; Bernstein, J.B. Heavy-ion-induced soft breakdown of thin gate oxides. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2001, 48, 1913–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Parihar, N.; Goel, N.; Mahapatra, S. A comprehensive DC and AC PBTI modeling framework for HKMG n-MOSFETs. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2017, 64, 1474–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Y.; Bi, J.S.; Xi, K.; Wang, G. PBTI stress-induced 1/f noise in n-channel FinFET. Chin. Phys. B 2020, 29, 128501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagatin, M.; Gerardin, S.; Paccagnella, A.; Faccio, F. Impact of NBTI aging on the single-event upset of SRAM cells. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2010, 57, 3245–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, R.; Mitsuyama, Y.; Hashimoto, M.; Onoye, T. Impact of NBTI-induced pulse-width modulation on SET pulse-width measurement. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2013, 60, 2630–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, J.H.; Chen, N.J.; Lu, G.M.; Zhang, Y. Effects of three factors under BTI on the soft error rate of integrated circuits. J. Comput. Res. Dev. 2018, 55, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.H.; Li, J.J.; Fan, X.; Yang, Z.Z.; Zou, H.; Li, W. Study on total ionizing dose radiation effects of NMOS devices with 0.5 μm process. Res. Prog. Solid State Electron. 2018, 38, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Joshi, K.; Chaudhary, V.; Goel, N.; De, S.; Pandey, R.K.; Murali, K.V.R.M.; Mahapatra, S. Trap generation in IL and HK layers during BTI/TDDB stress in scaled HKMG N and P MOSFETs. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 1–5 June 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizubayashi, W.; Mori, T.; Fukuda, K.; Liu, Y.X.; Matsukawa, T.; Ishikawa, Y.; Endo, K.; O’uchi, S.I.; Tsukada, J.; Yamauchi, H.; et al. PBTI for N-type tunnel FinFETs. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on IC Design & Technology (ICICDT), Leuven, Belgium, 1–3 June 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.R.; Yang, Y.; Cao, C.; He, W.L.; Zheng, X.F.; Ma, X.H.; Hao, Y. Recovery of PMOSFET NBTI under different conditions. Chin. Phys. B 2015, 24, 097304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhan, P.; Rao, V.R.; Mohapatra, N.R. PBTI in HKMG nMOS transistors—Effect of width, layout, and other technological parameters. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2017, 64, 4018–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Mahapatra, S. A comprehensive model of PMOS NBTI degradation. Microelectron. Reliab. 2005, 45, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.Q. Study of NBTI Effect of Ultra-Deep Submicron PMOSFET. Master’s Thesis, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cellere, G.; Valentini, M.G.; Paccagnella, A. Effect of channel width, length, and latent damage on NBTI. In Proceedings of the 2004 International Conference on Integrated Circuit Design and Technology, Austin, TX, USA, 17–20 May 2004; pp. 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.S.; Chen, S.J.; Yang, W.J.; Yang, J.J. A new physical and quantitative width dependent hot carrier model for shallow-trench-isolated CMOS devices. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium Proceedings. 39th Annual, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 April–3 May 2001; pp. 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.S.; Yeh, C.H.; Feng, H.J.; Lai, C.S.; Yang, J.J.; Chen, C.C.; Jin, Y.; Chen, S.C.; Liang, M.S. Impact of STI on the reliability of narrow-width pMOSFETs with advanced ALD N/O gate stack. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2006, 6, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Radiation ions | 181Ta35+ |
| Energy/MeV | 2560 |
| LET/MeV/(mg/cm2) | 70.06 |
| Range/μm | 149.22 |
| No. | Influence Factors | Constant Parameters | Varied Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Electrical stress | T = 30 °C | Vg−stress = 1.2 V, 1.4 V, 1.6 V |
| 2 | Temperature | Vg−stress = 4.5 V | T = 30 °C, 90 °C, 120 °C |
| 3 | Gate length | Vg−stress = 1.6 V, T = 30 °C, W = 1000 nm | L = 30 nm, 60 nm |
| 4 | Gate width | Vg−stress = 1.6 V, T = 30 °C, L = 30 nm | W = 1000 nm, 500 nm |
| 5 | Heavy ion fluence | Vg−stress = 1.6 V, T = 30 °C | Heavy Ion Fluence = 0 ions/cm2, 7 × 106 ions/cm2, 1 × 108 ions/cm2, 1 × 1010 ions/cm2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Su, S.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Huang, D.; Liu, L.; Lv, L.; et al. Investigation on High-Temperature and High-Field Reliability of NMOS Devices Fabricated Using 28 nm Technology After Heavy-Ion Irradiation. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111216
Cao Y, Zhang Z, Zhang L, Li M, Su S, Zhang W, Xu Y, Huang D, Liu L, Lv L, et al. Investigation on High-Temperature and High-Field Reliability of NMOS Devices Fabricated Using 28 nm Technology After Heavy-Ion Irradiation. Micromachines. 2025; 16(11):1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111216
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Yanrong, Zhixian Zhang, Longtao Zhang, Miaofen Li, Shuo Su, Weiwei Zhang, Youli Xu, Dingqi Huang, Le Liu, Ling Lv, and et al. 2025. "Investigation on High-Temperature and High-Field Reliability of NMOS Devices Fabricated Using 28 nm Technology After Heavy-Ion Irradiation" Micromachines 16, no. 11: 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111216
APA StyleCao, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhang, L., Li, M., Su, S., Zhang, W., Xu, Y., Huang, D., Liu, L., Lv, L., & Ma, X. (2025). Investigation on High-Temperature and High-Field Reliability of NMOS Devices Fabricated Using 28 nm Technology After Heavy-Ion Irradiation. Micromachines, 16(11), 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16111216




