Atomic-Scale Revelation of Voltage-Modulated Electrochemical Corrosion Mechanism in 4H-SiC Substrate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
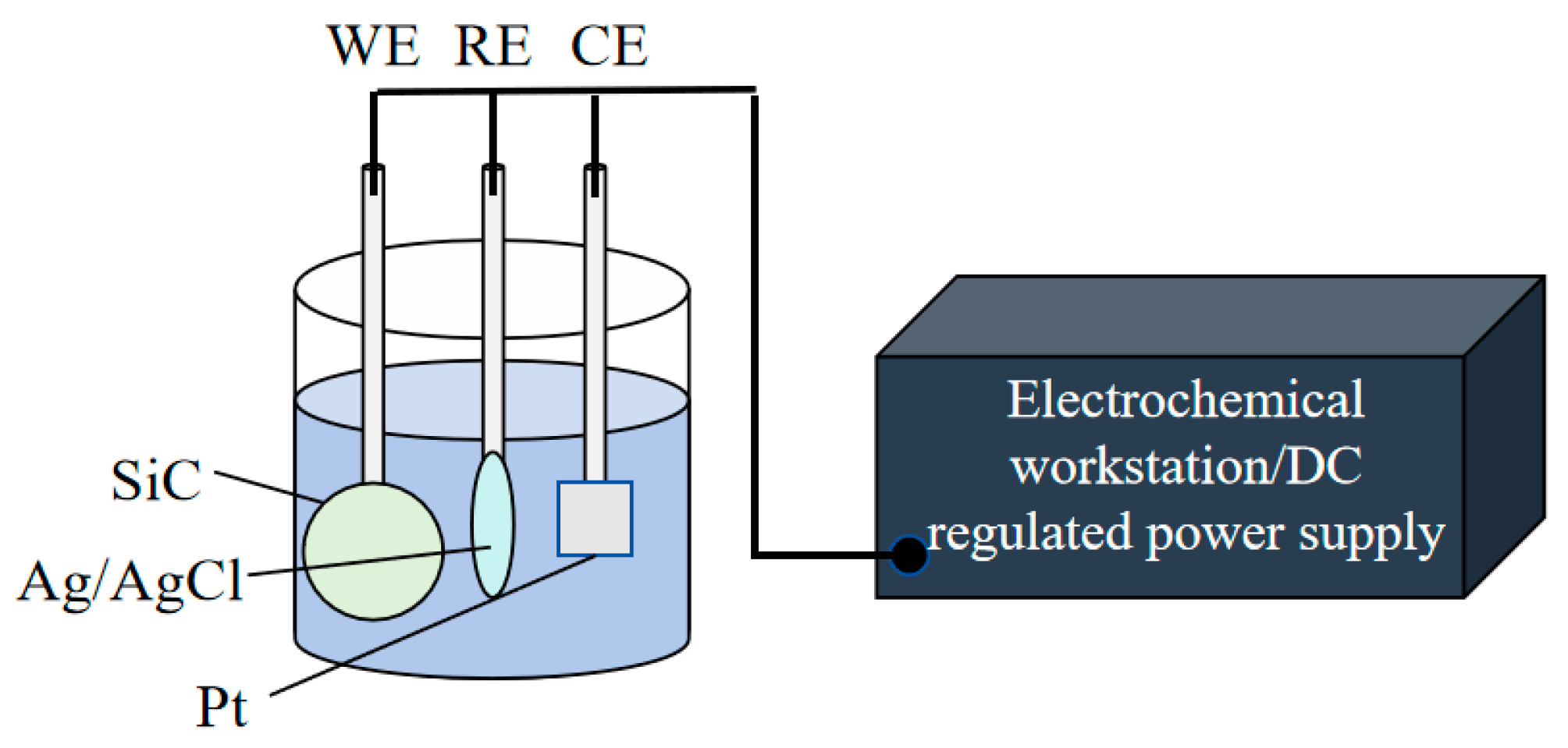
2.1. Experimental Details
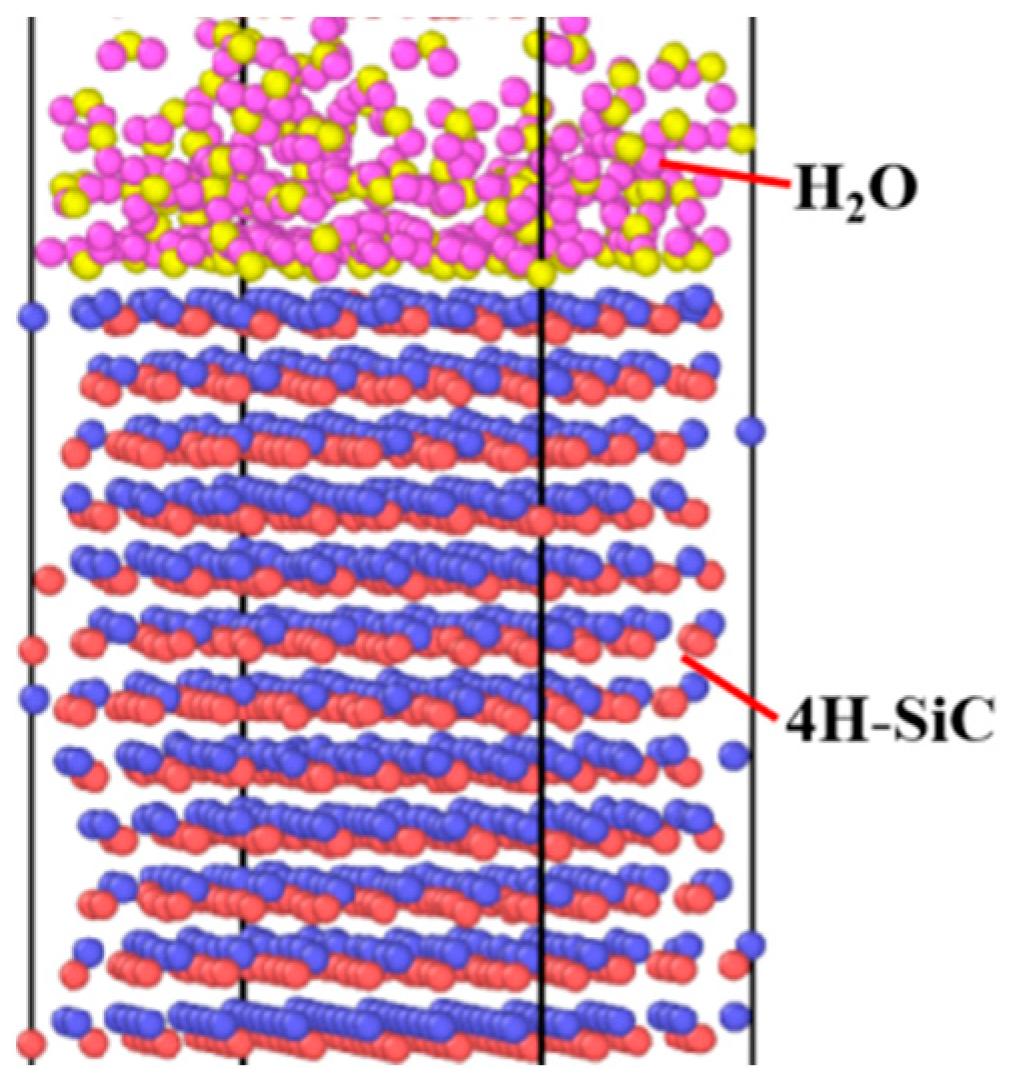
2.2. Reactive Molecular Dynamics Simulation Details
3. Results
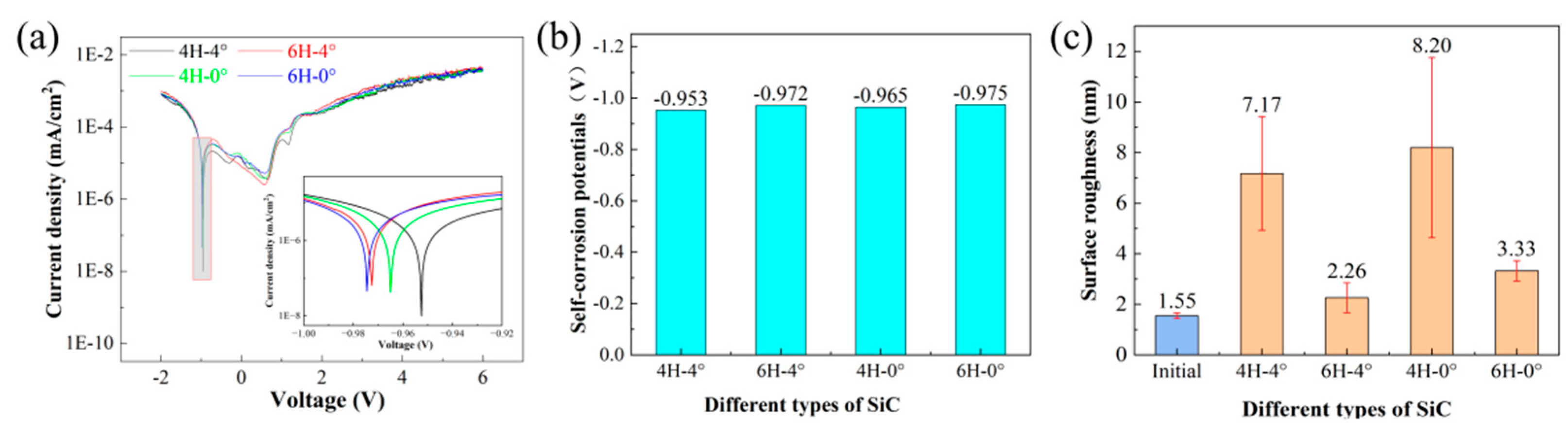
3.1. Corrosion Behavior of SiC Polytypes
3.2. Corrosion Behavior of SiC with Different Electrolyte Concentrations
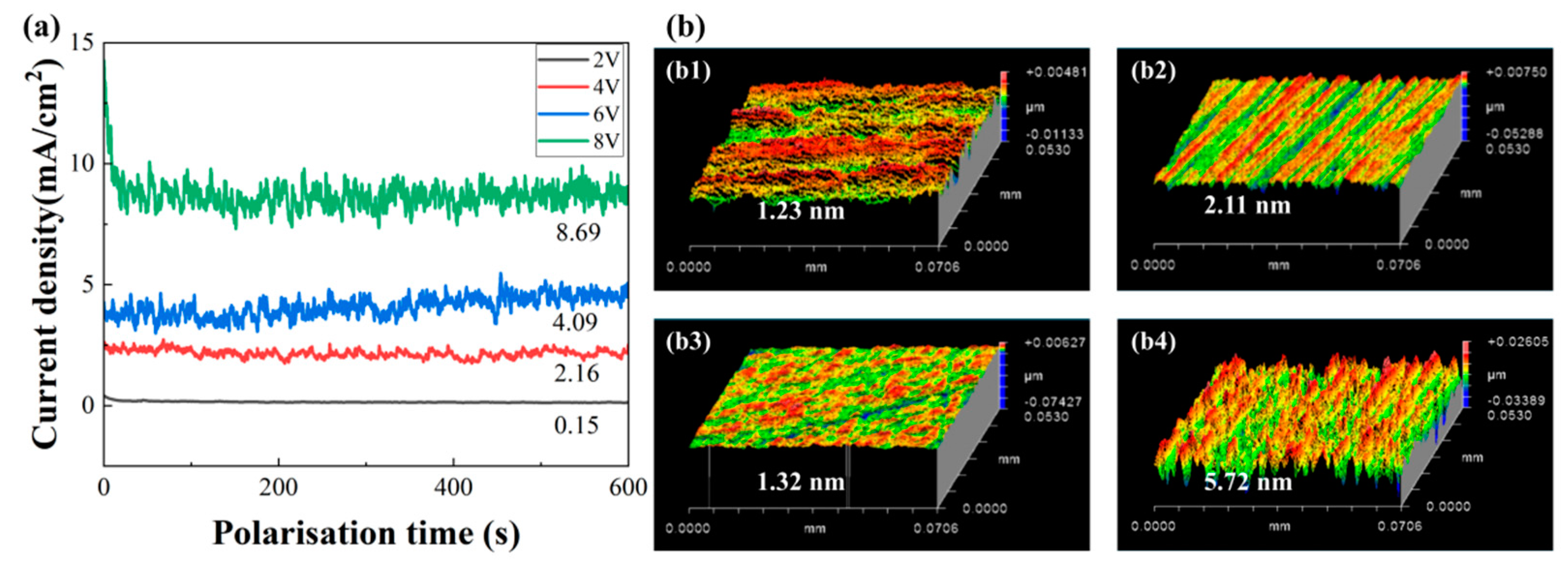
3.3. Corrosion Behavior of SiC at Different Voltages
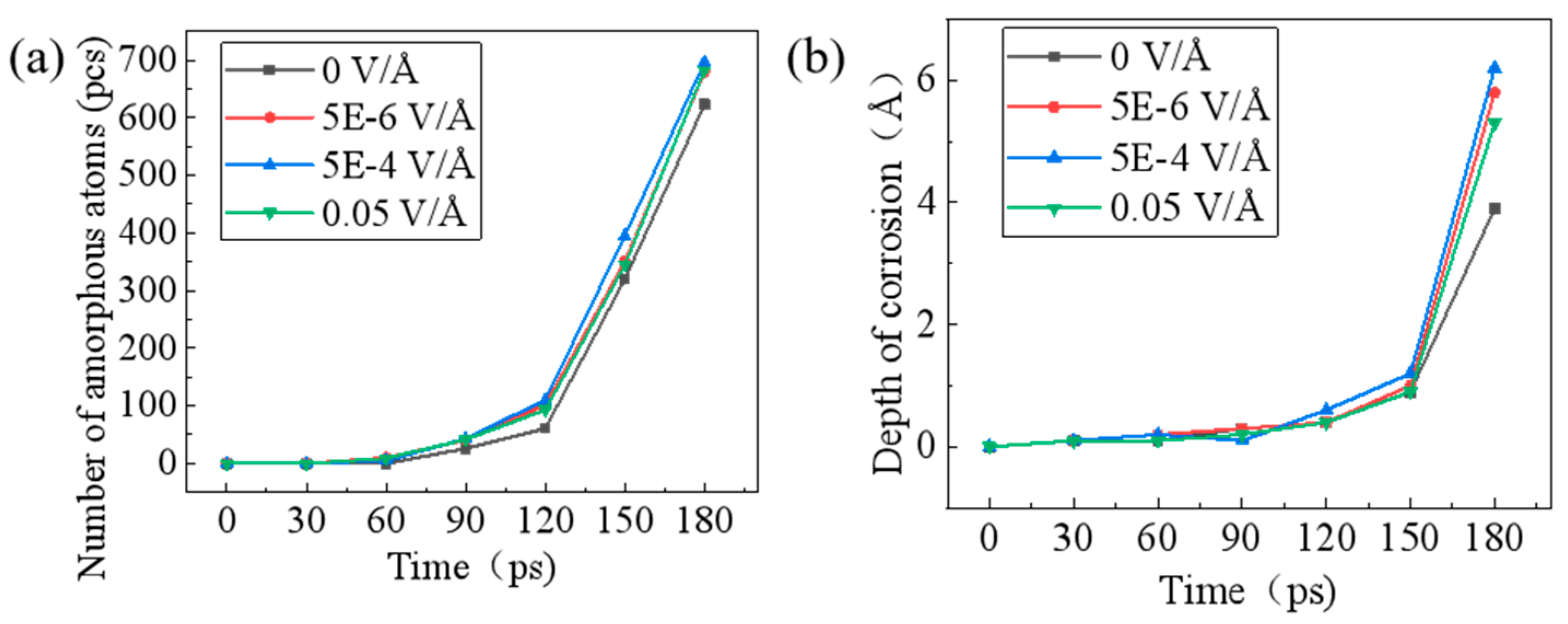
3.4. Reactive Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Corrosion Behavior on SiC Surface
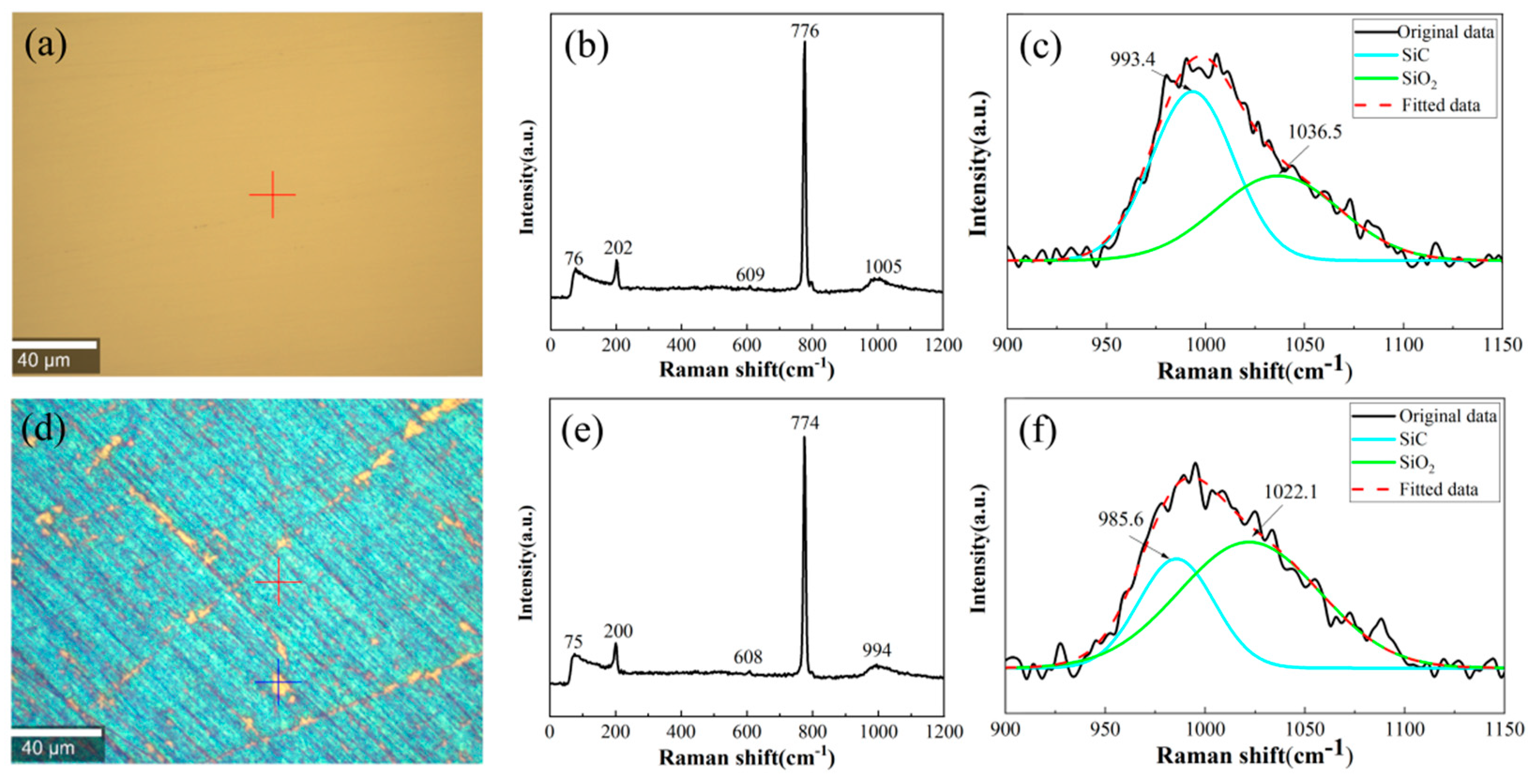
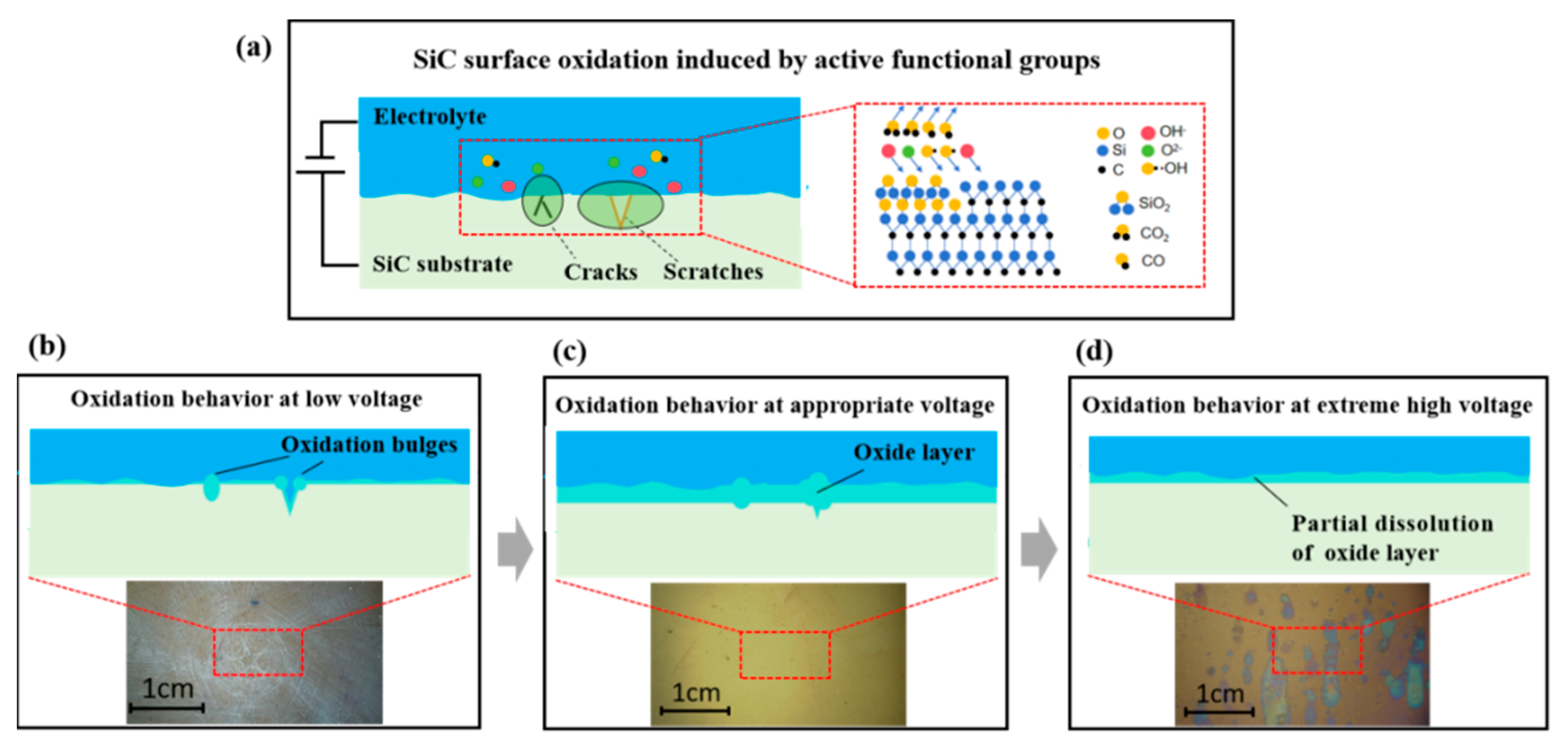
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The crystalline structure exhibited a dominant influence on the corrosion characteristics of the SiC substrate, while the inclination angle played a minimal role. The 4H-0° SiC substrate demonstrated the highest corrosion rate among the tested samples. Moreover, the peak corrosion rate was achieved using a 0.6 mol/L NaCl electrolyte solution.
- (2)
- The electrochemical corrosion behaviors of SiC substrates revealed three voltage-dependent characteristics: active dissolution (2–20 V), stable passivation (20–25 V), and transpassive dissolution (25–30 V). Reactive molecular dynamics simulations further revealed that both amorphization degree and penetration depth of external atoms on the SiC surface showed a decreasing trend at elevated voltages, suggesting a corresponding reduction in the corrosion rate when the voltage exceeded the optimal range.
- (3)
- OH−, O2−, and •OH generated by the electrolysis of water during electrochemical corrosion immediately reacted with the SiC surface to form a SiO2 modified layer. At lower voltages, preferential oxidation occurred at surface defects, accentuating existing scratches and cracks. Moderate voltages promoted uniform surface oxidation across the entire substrate. Elevated voltages induced passivation layer formation, effectively inhibiting further oxidation. Under extreme voltage conditions, the passivation layer underwent breakdown, leading to dissolution of the oxide layer. This comprehensive analysis provided fundamental insights into SiC electrochemical corrosion mechanisms, offering valuable guidance for material processing and applications.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, R.; Zhou, K.; Yue, C.; Wei, J.; Pan, Y. Recent progress in synthesis, properties and potential applications of SiC nanomaterials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 72, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Yang, W. One-dimensional SiC nanostructures, Designed growth, properties, and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 104, 138–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpakaran, B.; Subburaj, A.; Bayne, S.; Mookken, J. Impact of silicon carbide semiconductor technology in photovoltaic energy system. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 971–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaucamp, A.; Simon, P.; Charlton, P.; King, C.; Matsubara, A.; Wegener, K. Brittle-ductile transition in shape adaptive grinding (SAG) of SiC aspheric optics. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2017, 115, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, H.; Hu, W. Organic semiconductor single crystals for electronics and photonics. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1801048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzurak, A. Diamond and silicon converge. Nature 2011, 479, 47–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuci, G.; Liu, Y.; Rossin, A.; Guo, X.; Pham, C.; Giambastiani, G.; Pham-Huu, C. Porous silicon carbide (SiC), a chance for improving catalysts or just another active-phase carrier. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 10559–10665. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, M. Recent progress in wide bandgap semiconductor-based power electronics. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2553. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Huang, H.; Zhu, X.; Kang, R. Surface integrity and removal mechanism of silicon wafers in chemo-mechanical grinding using a newly developed soft abrasive grinding wheel. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2017, 63, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Lu, J.; Jiang, F.; Lin, J.; Tian, Z. Tribochemical mechanisms of abrasives for SiC and sapphire substrates in nanoscale polishing. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 15675–15685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, Z.; Zang, Y.; Feng, S. Atomic-scale characterization of Si (110)/6H-SiC (0001) heterostructure by HRTEM. Mater. Lett. 2016, 163, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Endo, K.; Yamamura, K. Competition between surface modification and abrasive polishing, a method of controlling the surface atomic structure of 4H-SiC (0001). Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8947. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Li, J.; Long, J.; Luo, H.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, X.; Pan, G. Surface modulation to enhance chemical mechanical polishing performance of sliced silicon carbide Si-face. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 536, 147963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Lu, J.; Luo, Q.; Xu, X. Chemical reaction on silicon carbide wafer (0001 and 000−1) with water molecules in nanoscale polishing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 607, 155090. [Google Scholar]
- Roccaforte, F.; Fiorenza, P.; Greco, G.; Vivona, M.; Lo Nigro, R.; Giannazzo, F.; Patti, A.; Saggio, M. Recent advances on dielectrics technology for SiC and GaN power devices. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 301, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wu, X.; Wu, P.; Yuan, J.; Zhu, Y. Effects of polishing media on the surface chemical and micromechanical properties of SiC. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2024, 233, 112753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Pan, G.; Zou, C.; Wang, L. Chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) of SiC wafer using photo-catalyst incorporated pad. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2017, 6, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, R.; Zeng, N. Improved chemical mechanical polishing performance in 4H-SiC substrate by combining novel mixed abrasive slurry and photocatalytic effect. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 575, 151676. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Sun, Z.; Guo, B. Material removal mechanism in ultrasonic vibration assisted polishing of micro cylindrical surface on SiC. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2016, 103, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wei, C.; Cao, Z.; Peng, X.; Jiang, Z.; Wan, S.; Shao, J. Improving polishing efficiency of RB-SiC through femtosecond laser pretreatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 631, 157574. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.; Feng, J.; Yan, W.; Tian, S.; Sun, J.; Liu, X.; Wei, D.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Lam, J.; et al. Piezocatalysis for chemical-mechanical polishing of SiC, dual roles of t-BaTiO3 as a piezocatalyst and an abrasive. Small 2024, 20, 2310117. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wang, R.; Seiler, J.; Bhat, I. Electro-chemical mechanical polishing of silicon carbide. J. Electron. Mater. 2004, 33, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jin, Z.; Wu, D.; Guo, J. Investigation on material removal uniformity in electrochemical mechanical polishing by polishing pad with holes. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 3047–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Zhai, W.; Zhai, Q.; Shi, Y. Electro-chemical mechanical polishing of 4H-SiC for scratch-free surfaces with less oxide layer at high efficiency. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 677–684. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.; Zhai, W.; Zhai, Q.; Shi, Y. Polystyrene/CeO2 core/shell abrasives for high-quality 4H-SiC surface in ECMP, the effects of shell thickness. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 044005. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y. Investigation into electrochemical oxidation behavior of 4H-SiC with varying anodizing conditions. Electrochem. Commun. 2019, 109, 106608. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Deng, L.; Li, S. Study on enhancement mechanisms in ultrasonic-assisted plasma electrochemical oxidation for SiC single crystal. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 49, 599–611. [Google Scholar]
- Inada, N.; Takizawa, M.; Adachi, M.; Murata, J. Sustainable electrochemical mechanical polishing (ECMP) for 4H-SiC wafer using chemical-free polishing slurry with hydrocarbon-based solid polymer electrolyte. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 664, 160241. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Sun, R.; Ohkubo, Y.; Kawai, K.; Arima, K.; Endo, K.; Yamamura, K. Investigation of anodic oxidation mechanism of 4H-SiC (0001) for electrochemical mechanical polishing. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 271, 666–676. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, J.; Hayama, K.; Takizawa, M. Environment-friendly electrochemical mechanical polishing using solid polymer electrolyte/CeO2 composite pad for highly efficient finishing of 4H-SiC (0001) surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 625, 157190. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Hosoya, K.; Imanishi, Y.; Endo, K.; Yamamura, K. Electro-chemical mechanical polishing of single-crystal SiC using CeO2 slurry. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 52, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, J.; Yodogawa, K.; Ban, K. Polishing-pad-free electrochemical mechanical polishing of single-crystalline SiC surfaces using polyurethane-CeO2 core-shell particles. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2017, 114, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Yamamura, K. Selective electrochemical mechanical polishing of 4H–SiC surface employing porous material impregnated with electrolyte. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 34569–34581. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Yamamura, K. Effects of electrolyte type and concentration on the anodic oxidation of 4H-SiC (0001) in slurryless electrochemical mechanical polishing. Electrochim. Acta 2024, 474, 143531. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Sun, R.; Kawai, K.; Arima, K.; Yamamura, K. Surface modification and microstructuring of 4H-SiC (0001) by anodic oxidation with sodium chloride aqueous solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 11, 2535–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ohkubo, Y.; Endo, K.; Yamamura, K. AFM observation of initial oxidation stage of 4H-SiC (0001) in electrochemical mechanical polishing. Procedia CIRP 2018, 68, 735–740. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Gu, H.; Kawai, K.; Arima, K.; Yamamura, K. Charge utilization efficiency and side reactions in the electrochemical mechanical polishing of 4H-SiC (0001). J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 023501. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Chen, X.; Xu, X. Molecular dynamics simulation of the material removal in the scratching of 4H-SiC and 6H-SiC substrates. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2020, 2, 045104. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhou, S.; Zeng, L.; Dai, B.; Xu, Q.; Ge, N. Temperature-dependent oxidation behavior of silicon carbide surface, reactive molecular dynamics simulations. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 56376–56386. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, P.; Xu, H.; Xu, J.; Chen, L.; Qian, L.; Wang, Y. Temperature-dependent water corrosion mechanism of silicon carbide, Atomic insights from reactive molecular dynamics simulation. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 26133–26139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Li, S.; Ma, G.; Jia, Z.; Liu, X. Investigation of oxidation mechanism of SiC single crystal for plasma electrochemical oxidation. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 27338–27345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Q.; Lin, D.; Lu, J.; Ke, C.; Tian, Z.; Jiang, F.; Zhu, J.; Huang, H. Atomic-Scale Revelation of Voltage-Modulated Electrochemical Corrosion Mechanism in 4H-SiC Substrate. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101129
Luo Q, Lin D, Lu J, Ke C, Tian Z, Jiang F, Zhu J, Huang H. Atomic-Scale Revelation of Voltage-Modulated Electrochemical Corrosion Mechanism in 4H-SiC Substrate. Micromachines. 2025; 16(10):1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101129
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Qiufa, Dianlong Lin, Jing Lu, Congming Ke, Zige Tian, Feng Jiang, Jianhui Zhu, and Hui Huang. 2025. "Atomic-Scale Revelation of Voltage-Modulated Electrochemical Corrosion Mechanism in 4H-SiC Substrate" Micromachines 16, no. 10: 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101129
APA StyleLuo, Q., Lin, D., Lu, J., Ke, C., Tian, Z., Jiang, F., Zhu, J., & Huang, H. (2025). Atomic-Scale Revelation of Voltage-Modulated Electrochemical Corrosion Mechanism in 4H-SiC Substrate. Micromachines, 16(10), 1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101129






