The Influence of Pulsed Superimposed DC Electric Field Synergistically Inducing Orientation Arrangement of BNNSs on Thermal Properties of Epoxy Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation Method
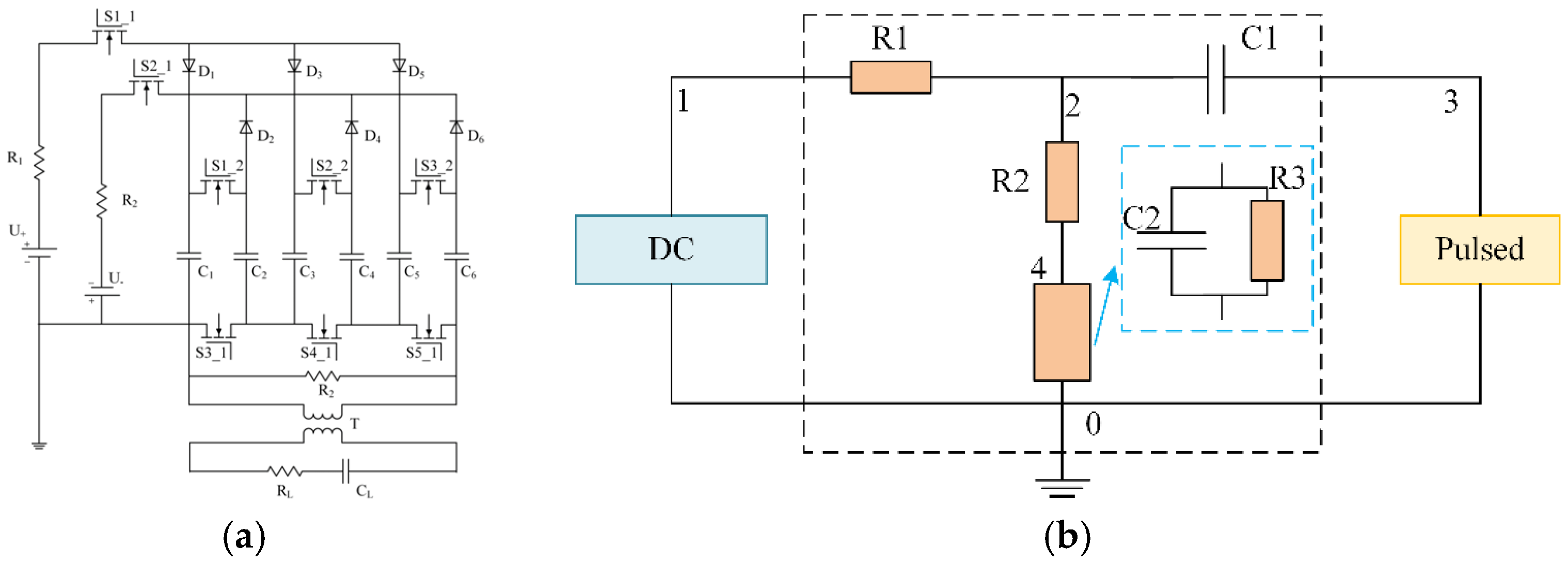
2.3. Induction Power Supply
2.4. Material Performance Testing
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Cross-Sectional SEM Images
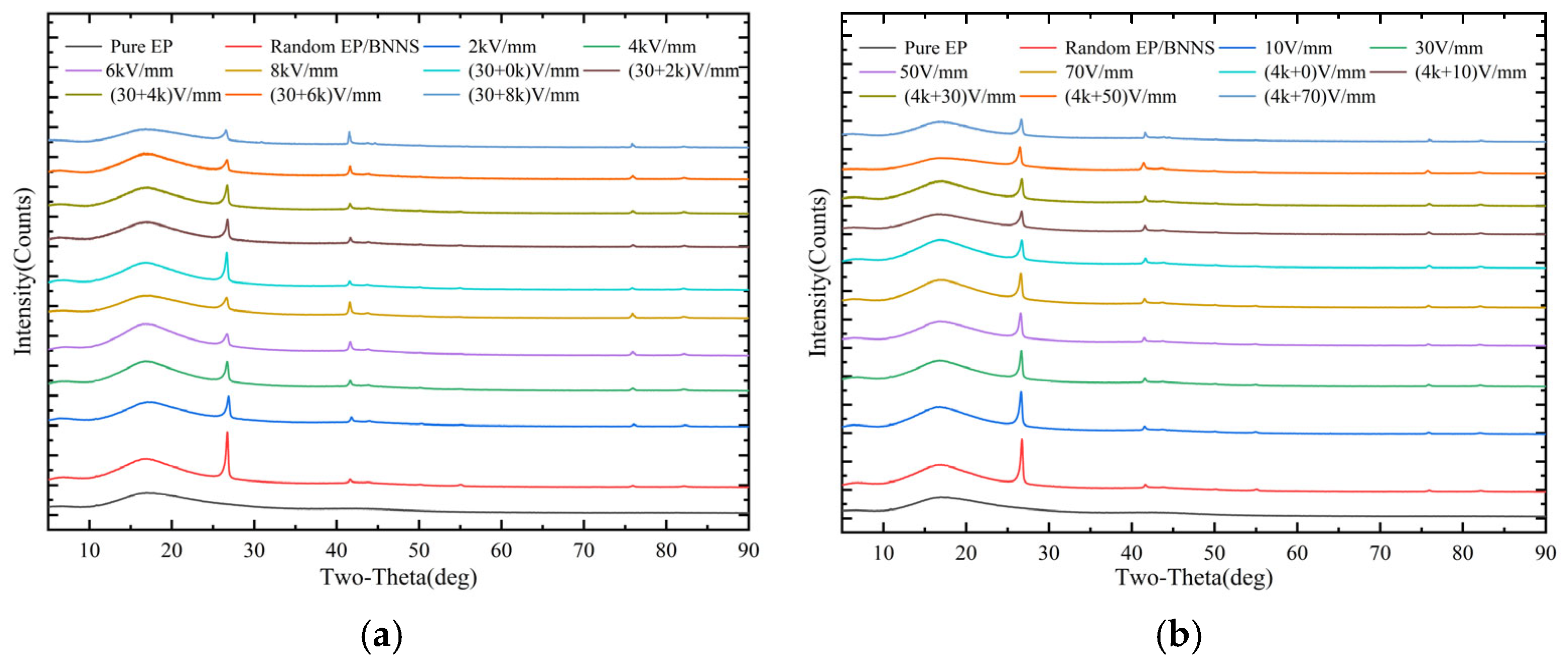
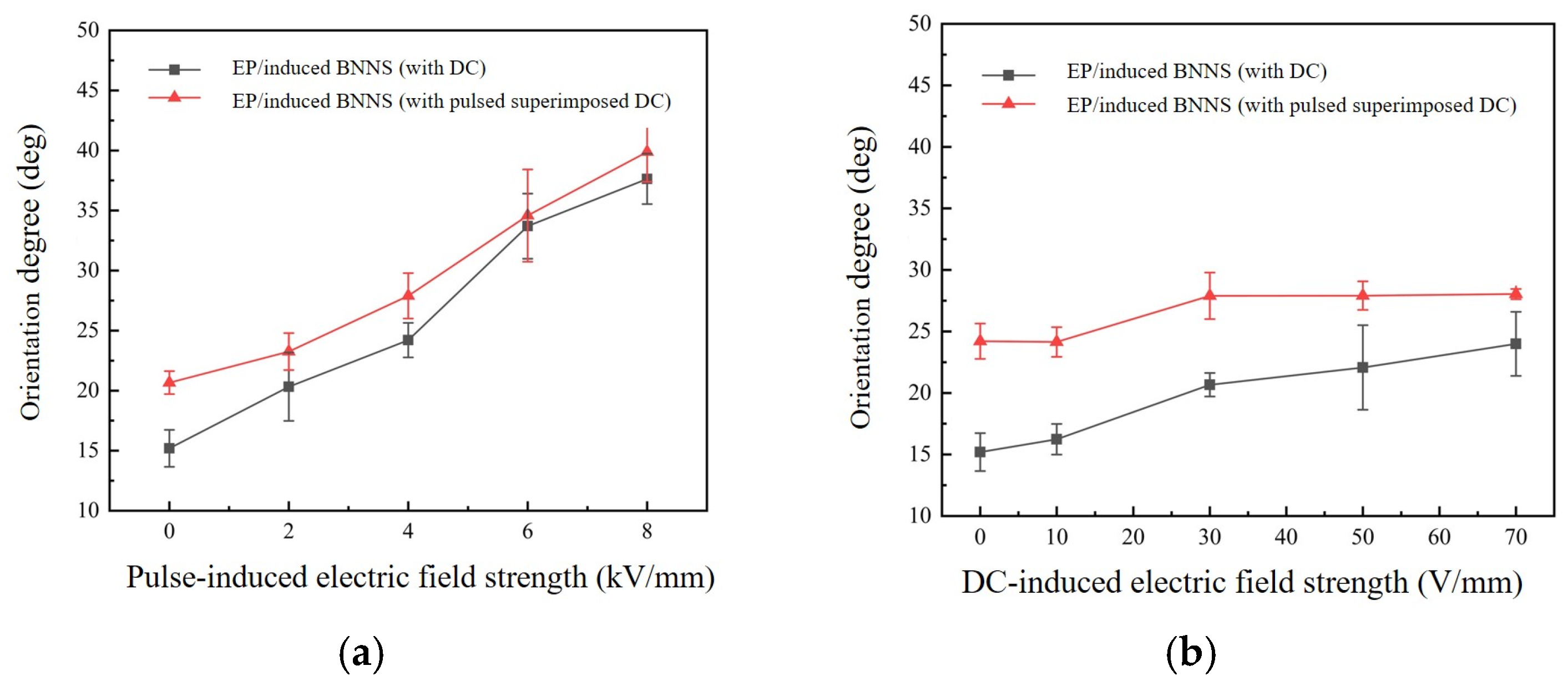
3.2. XRD Patterns of Nanocomposites and Average Orientation Angle of BNNSs
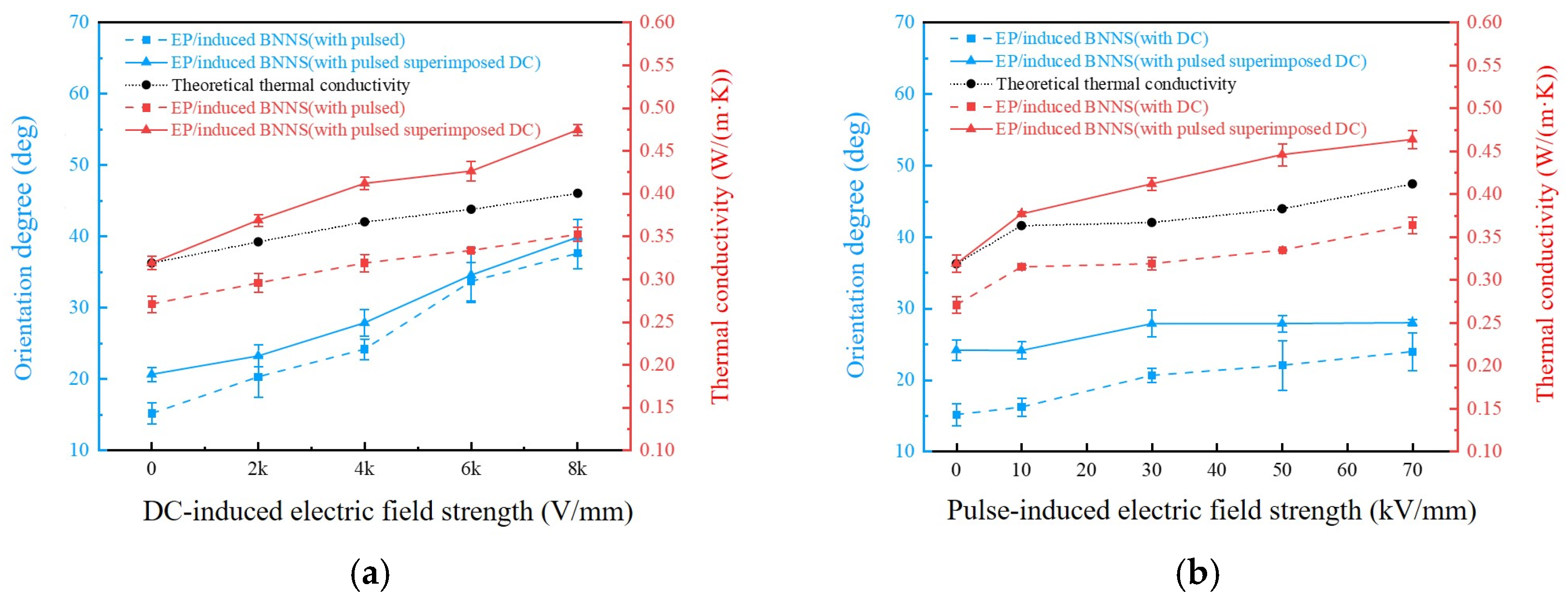
3.3. Thermal Conductivity of the Composite
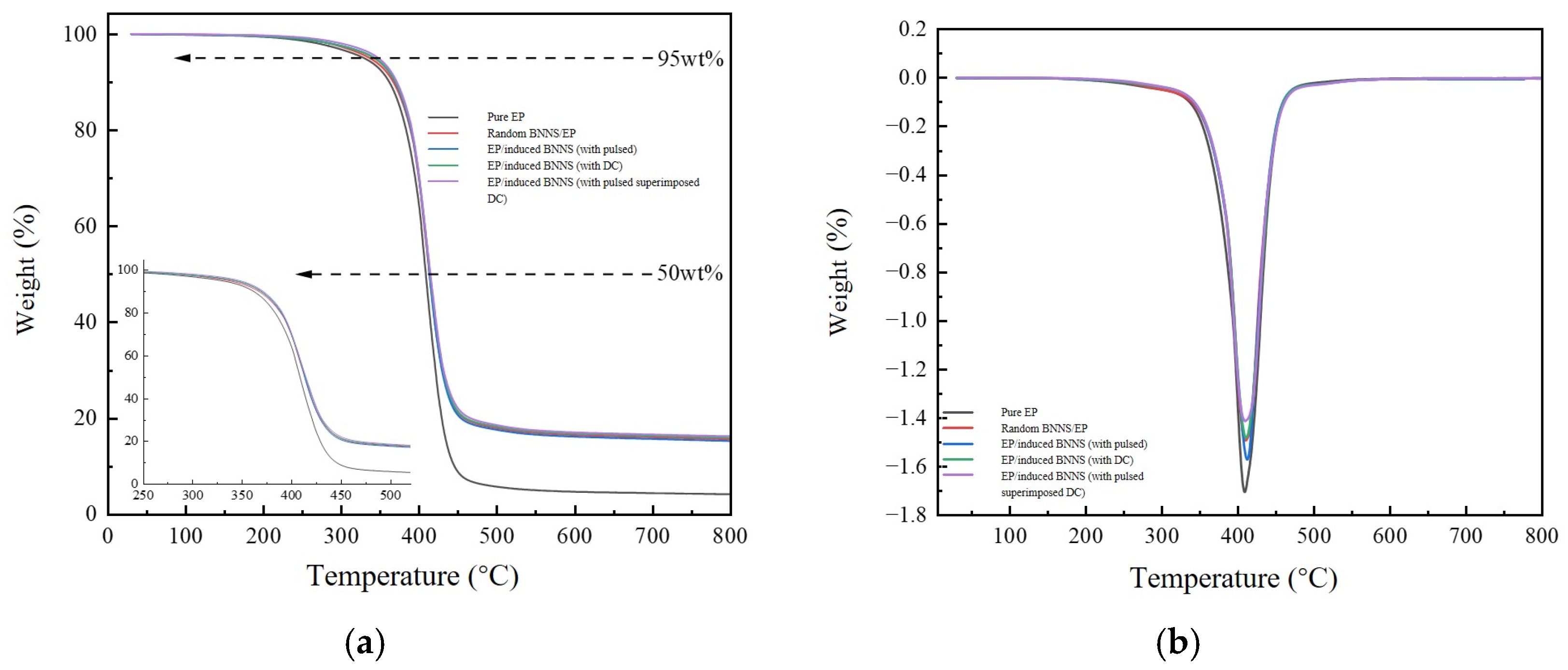
3.4. Thermogravimetric Properties of Composites
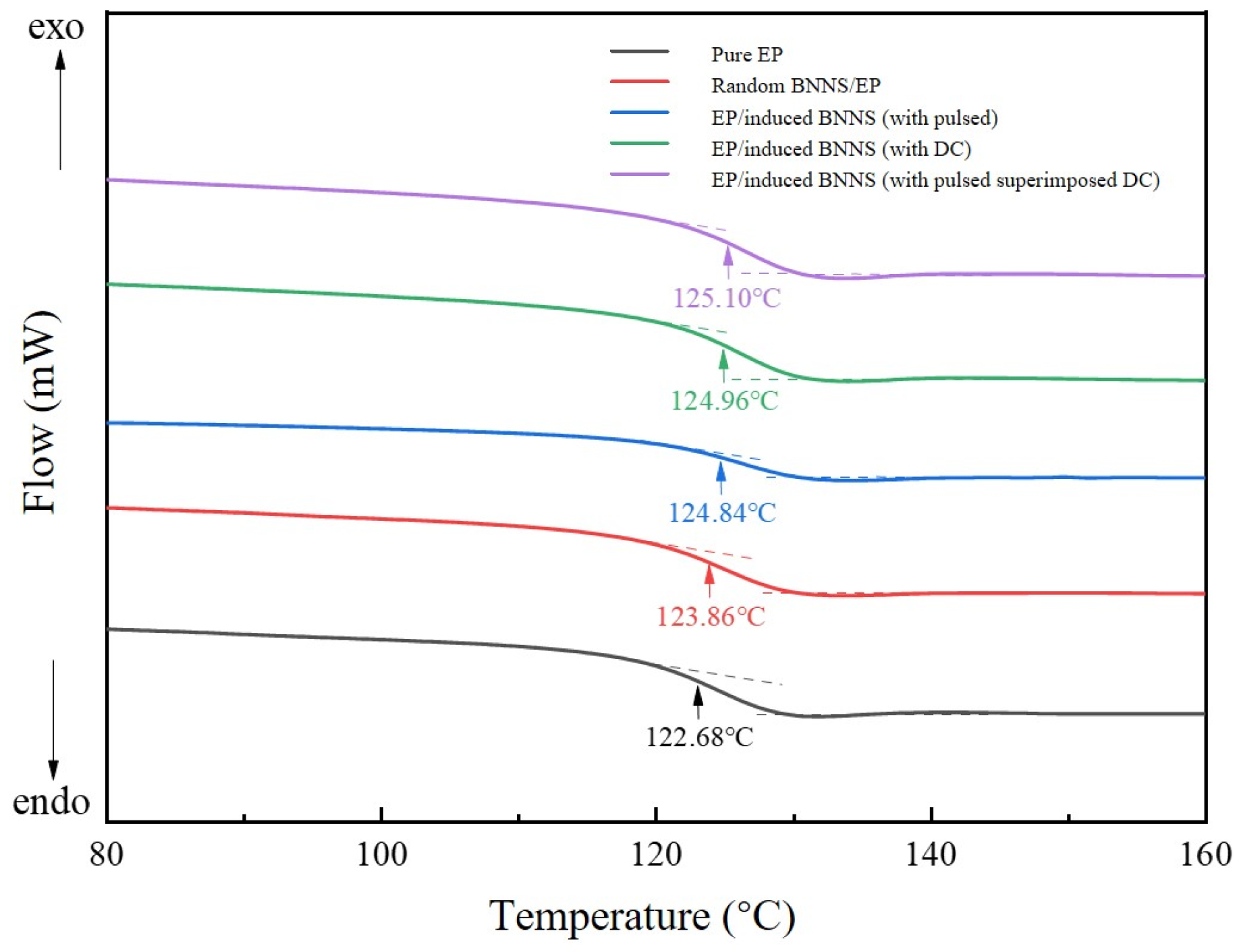
3.5. Glass Transition Temperature of Composites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, B.; Chen, R.; Fu, R.; Agathopoulos, S.; Su, X.; Liu, H. Low thermal expansion coefficient and high thermal conductivity epoxy/Al2O3/T-ZnOw composites with dual-scale interpenetrating network structure. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 137, 105993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Chen, C.; Ye, Y.; Xue, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Xie, X.; Mai, Y. Advances on Thermally Conductive Epoxy-Based Composites as Electronic Packaging Underfill Materials—A Review. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2201023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, C.; Songfeng, E.; Xie, L.; Geng, R.; Lin, C.-T.; Li, L.; Yao, Y. Enhanced thermal conductivity of polyurethane composites via engineering small/large sizes interconnected boron nitride nanosheets. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 170, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Zha, J.-W.; Wang, S.-J.; Zhong, S.-L.; Zhang, C.; Dang, Z.-M. Effect of high-thermal conductivity epoxy resin on heat dissipation performance of saturated reactor. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2017, 24, 3898–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Li, G.; Hou, J.; Yu, X.; Ding, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, N.; Qu, X. Preparation, characterization, and thermal properties of poly (methyl methacrylate)/boron nitride composites by bulk polymerization. Polym. Compos. 2015, 36, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, D.; Qurratulain, R.; Anand, S.; Kim, R. Recent advances in structural designs and fabrication of flexible polymer composite films with high thermal conductivity and electromagnetic interference shielding performance. J. Mater. Chem. C 2025, 13, 8890–8933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katada, A.; Konishi, Y.; Isogai, T.; Tominaga, Y.; Asai, S.; Sumita, M. Dynamic percolation phenomenon of poly (methyl methacrylate)/surface fluorinated carbon black composite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, D.; Vu, M.; Jeong, T.; Kim, J.; Lim, C.; Lim, J. 3D structured graphene fluoride-based epoxy composites with high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 149, 106585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorifuji, D.; Ando, S. Enhanced Thermal Diffusivity by Vertical Double Percolation Structures in Polyimide Blend Films Containing Silver Nanoparticles. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2010, 211, 2118–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorifuji, D.; Ando, S. Enhanced thermal conductivity over percolation threshold in polyimide blend films containing ZnO nano-pyramidal particles: Advantage of vertical double percolation structure. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Sun, J.; Zeng, X.; Chen, P.; Qian, J.; Xia, R.; Sun, R. Hot-pressing induced orientation of boron nitride in polycarbonate composites with enhanced thermal conductivity. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 110, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Hwang, T.; Jang, E.; Kim, J.; Su, P.-C.; Kim, J. Synthesis of highly thermal conductive and electrical insulating composites with SiC@r-GO aerogel and BN using the hot-pressing method. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 30269–30276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshitomi, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Nishino, T. Highly Thermally Conductive Nanocomposites Prepared by the Ice-Templating Alignment of Nanodiamonds in the Thickness Direction. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 8349–8358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Lv, P.; Hu, E.; Zheng, J.; Yu, K.; Wei, W. Formation of thermal conductive network in boron nitride/polyvinyl alcohol by ice-templated self-assembly. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 33926–33929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, D.; Anand, S.; Vu, C.; Islam, A.; Kim, R. Janus polyurethane composite film with highly aligned graphene fluoride and liquid metal: A versatile technique for thermal management and electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 182, 108179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, D.; Vu, C.; Anand, S.; Kim, B.; Jeong, H.; Kim, H.; Seo, K.; Islam, A.; Kim, R. Elongated liquid metal based self-healing polyurethane composites for tunable thermal conductivity and magnetic interference shielding. Compos. Commun. 2023, 44, 101735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, D.; Vu, C.; Lim, S.; Kim, B.; Jeong, H.; Kim, J.; Islam, A.; Lim, H.; Kim, M.; Kim, R. Stretching induced alignment of graphene nanoplatelets in polyurethane films for superior in-plane thermal conductivity and electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 2023, 201, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Song, M.; Guo, J.; Yin, X.; Gao, X.; Zhu, B.; Yuan, X. Preparation processes and thermal conductivities of magnetic field- and torsional vibration-induced superoriented carbon fiber composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2024, 252, 110617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Q.; Ma, T.; Dong, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Lei, Q. Enhanced Thermal Conductivity and Dielectric Properties of Iron Oxide/Polyethylene Nanocomposites Induced by a Magnetic Field. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z. Magnetic field-induced alignment of nickel-coated copper nanowires in epoxy composites for highly thermal conductivity with low filler loading. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 218, 109137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cao, J.; Xiao, M.; Du, B.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.W.; Gong, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Thermal and Electrical Properties of Nanoparticle Oriented Epoxy/BN/SiC Composites for Superconducting Magnet. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2019, 29, 4900805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Feng, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, Q. High thermal conductivity composite h-BN/EP obtained by pulsed square-wave electric field induction. Polymer 2024, 290, 126491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, E.; Cakmak, M. Roll-to-Roll Continuous Manufacturing Multifunctional Nanocomposites by Electric-Field-Assisted “Z” Direction Alignment of Graphite Flakes in Poly(dimethylsiloxane). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, P.; Ismail, A.; Ng, B. Directional alignment of carbon nanotubes in polymer matrices: Contemporary approaches and future advances. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 56, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjua, M.; Nudurupati, S.; Fischer, I. Electric field induced alignment and self-assembly of rods on fluid-fluid interfaces. Mech. Res. Commun. 2009, 36, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Sun, B. Highly thermally conductive yet electrically insulating polymer/boron nitride nanosheets nanocomposite films for improved thermal management capability. ACS Nano 2018, 13, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Liu, L.; Gui, L.; Ge, X. Effect of frequency of microsecond pulsed electric field on orientation of boron nitride nanosheets and thermal conductivity of epoxy resin-based composites. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 126, 205105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, H.; Qiao, J.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, C.; Yu, L.; Ren, L.; Zhao, X. Improved energy storage performances of P(VDF-HFP)/BNNSs composite: Role of nanosecond electric pulse. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 177880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Li, Z.; Sheng, G. Effect of BN Nanosheet Orientation on Thermal Conductivity and Insulation Properties of BN/Epoxy Resin Composite. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (CEIDP), Denver, CO, USA, 30 October–2 November 2022; pp. 301–304. [Google Scholar]
- Sima, W.; Pang, W.; Sun, P.; Yuan, T.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, H. Cactus-like double-oriented magnetic SiC and BN networks leading to simultaneously enhanced dielectric strength and thermal conductivity of epoxy composites. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 19950–19959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qu, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhou, G. Improving thermal conductivity of poly(aryl ether nitrile ketone) composites by incorporating functionalized boron nitride and silicon carbide via electrospinning-hot press method. J. Polym. Res. 2023, 30, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Peng, Y.; Liu, W.; Deng, L.; Shu, B. The Influence of Microsecond Pulsed Electric Field and Direct Current Electric Field on the Orientation Angle of Boron Nitride Nanosheets and the Thermal Conductivity of Epoxy Resin Composites. Micromachines 2025, 16, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahashi, M.; Ishihara, M.; Sassa, K.; Asai, S. Control of Crystal Orientation in Deposited Films of Bismuth Vaporized in Laser and Resistance Heating Methods under a High Magnetic Field. Mater. Trans. 2003, 44, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.; Nakayama, T.; Suematsu, H.; Suzuki, T.; Jiang, W.; Niihara, K.; Song, E.; Eom, A.; Kim, S.; Choa, H. Insulating Polymer Nanocomposites with High-Thermal-Conduction Routes via Linear Densely Packed Boron Nitride Nanosheets. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 129, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Qin, Z.; Yue, Y.; Yan, B.; Hu, M. External Electric Field Driving the Ultra-Low Thermal Conductivity of Silicene. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 7227–7234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Feng, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, Q. High Thermal Conductivity Electrical Insulation Composite EP/h-BN Obtained by DC Electric Field Induction. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liang, C.; Ma, T.; Guo, Y.; Kong, J.; Gu, J.; Chen, M.; Zhu, J. A Review on Thermally Conductive Polymeric Composites: Classification, Measurement, Model and Equations, Mechanism and Fabrication Methods. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2018, 1, 207–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozniakovskii, A.; Vozniakovskii, P.; Kidalov, V.; Otvalko, J.; Neverovskaja, Y. Characteristics and Mechanical Properties of Composites Based on Nitrile Butadiene Rubber Using Graphene Nanoplatelets. J. Compos. Mater. 2020, 54, 3351–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Shkel, Y.M. Polymeric Composites Tailored by Electric Field. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gast, A.P.; Zukoski, C.F. Electrorheological fluids as colloidal suspensions. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 1989, 30, 153–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Mu, H.; Li, H.; Qian, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, G. The mechanism of tuning filler orientation degree in composites based on AC electric field assist: From microscopic dynamical model to macroscopic electrical properties. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2024, 57, 445501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Mu, H.; Shen, M.; Cavallini, A.; Li, H.; Zhao, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, G. Bamboo-inspired metamaterials design: Microstructure dielectrophoretic orientation for enhancing insulation performance of advanced power modules. Appl. Mater. Today 2025, 42, 102560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ding, S.; Yuan, S.; Gou, X.; Cai, F.; Wang, D.; Zhao, H. Study on the thermal properties and insulation resistance of epoxy resin modified by hexagonal boron nitride. E-Polymers 2021, 21, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, N.R.; Fornaciari, B.; Mali, S.; Carvalho, G.M. Acetylated Starch-Based Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Studies of Interaction with Antioxidants. Starch-Stärke 2018, 70, 1700170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

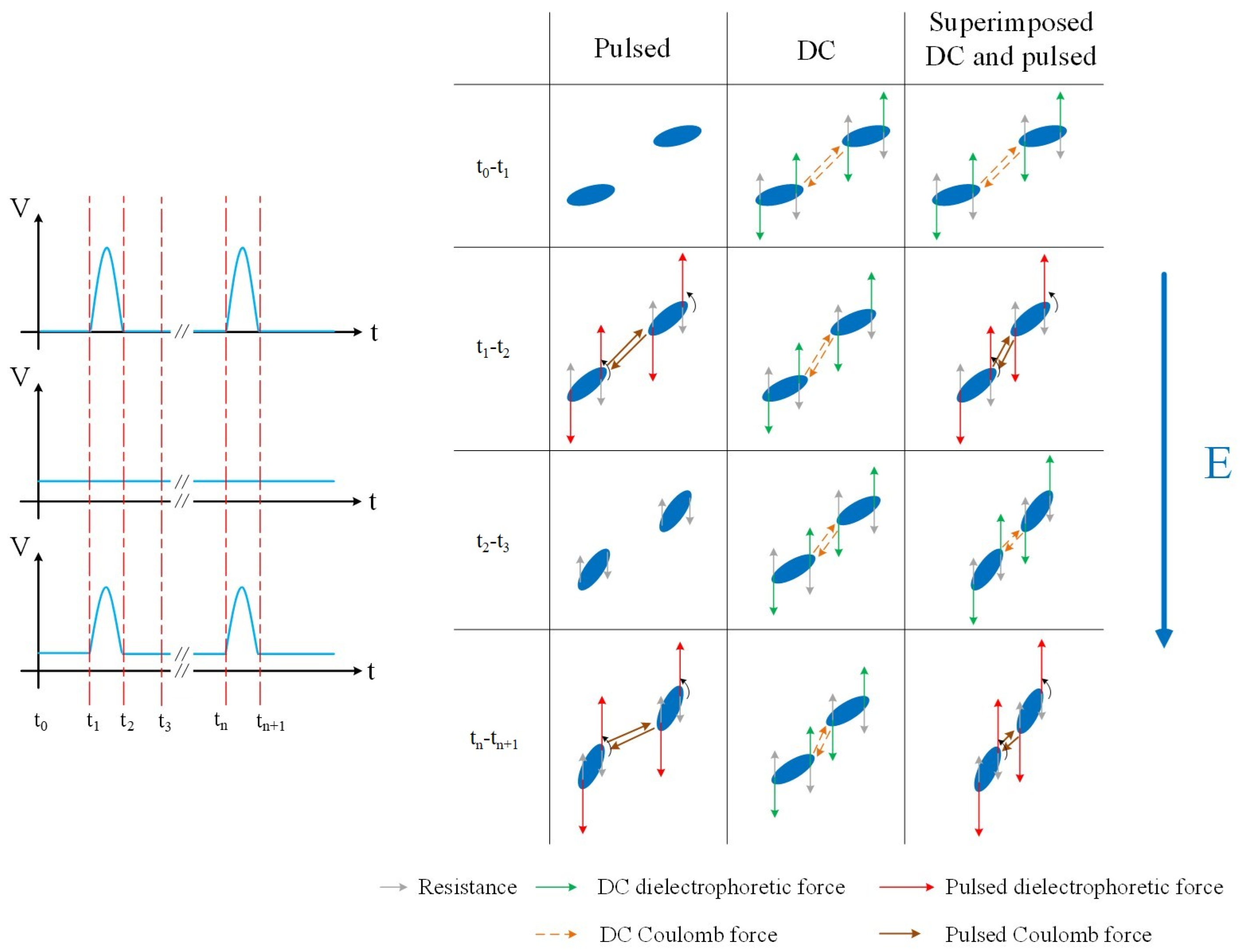
| Filler Type and Content | Filler Type and Content | Thermal Conductivity λ (W/m·K) | Alignment Type | Cite |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| External DC electric field | No filler | 0.091 | Lattice vibration modulation (non-filler alignment) | [34] |
| Pulsed square-wave electric field | h-BN, 10 wt% | 0.453 | In-plane alignment | [22] |
| AC/DC electric field | h-BN, 15 vol% | 1.56 | Linear densely packed bundles (LDPBNs) | [21] |
| DC electric field | h-BN, 10 wt% | 0.544 | Out-of-plane vertical alignment | [35] |
| AC/DC electric field | BN: 25 wt%; SiC: 5 wt% | 0.3425 | Hybrid filler co-alignment | [36] |
| Pulsed Superimposed DC Electric Field | BN:10% | 0.474 | Local and global alignment | This paper |
| Samples | T5%/°C | T50%/°C | Tmax/°C | Weight Loss Rate (800 °C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure EP | 329.2 | 408.5 | 408.8 | 94.86% |
| Random BNNS/EP | 336.5 | 413.2 | 410.2 | 84.40% |
| EP/induced BNNS (with pulsed) | 342.7 | 413.3 | 411.5 | 84.77% |
| EP/induced BNNS (with DC) | 342.8 | 414.0 | 410.8 | 84.10% |
| EP/induced BNNS (with pulsed superimposed DC) | 347.7 | 414.3 | 410.0 | 83.79% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Li, S.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, L.; Peng, Y.; Mi, Y. The Influence of Pulsed Superimposed DC Electric Field Synergistically Inducing Orientation Arrangement of BNNSs on Thermal Properties of Epoxy Composites. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1126. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101126
Wang X, Li S, Yin Z, Zhang Q, Deng L, Peng Y, Mi Y. The Influence of Pulsed Superimposed DC Electric Field Synergistically Inducing Orientation Arrangement of BNNSs on Thermal Properties of Epoxy Composites. Micromachines. 2025; 16(10):1126. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101126
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaopeng, Songyuan Li, Zhen Yin, Qi Zhang, Lei Deng, Yiqin Peng, and Yan Mi. 2025. "The Influence of Pulsed Superimposed DC Electric Field Synergistically Inducing Orientation Arrangement of BNNSs on Thermal Properties of Epoxy Composites" Micromachines 16, no. 10: 1126. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101126
APA StyleWang, X., Li, S., Yin, Z., Zhang, Q., Deng, L., Peng, Y., & Mi, Y. (2025). The Influence of Pulsed Superimposed DC Electric Field Synergistically Inducing Orientation Arrangement of BNNSs on Thermal Properties of Epoxy Composites. Micromachines, 16(10), 1126. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101126






