Machine Learning-Driven Inspired MTM and Parasitic Ring Optimization for Enhanced Isolation and Gain in 26 GHz MIMO Antenna Arrays
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Related Work
1.2. Contribution
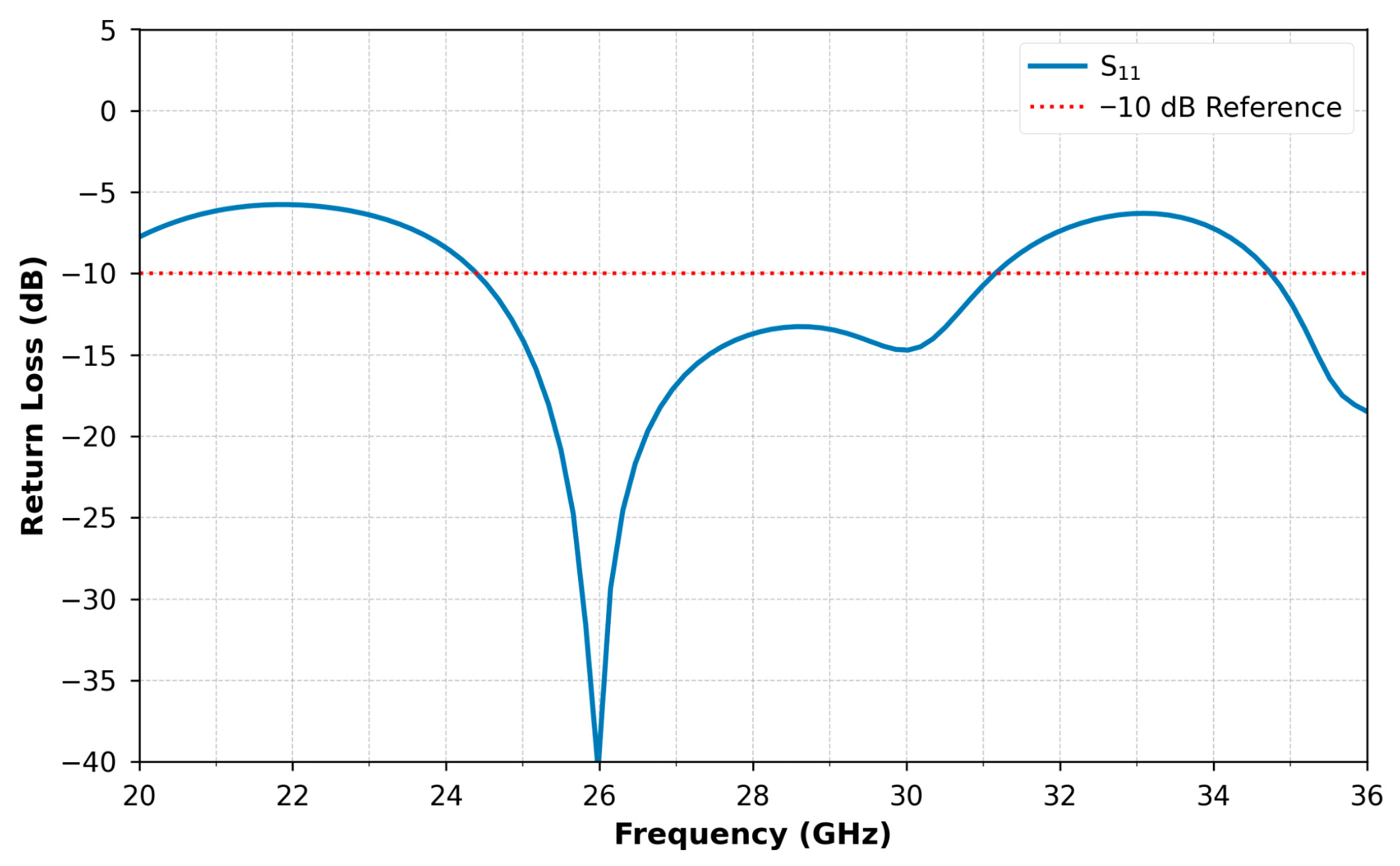
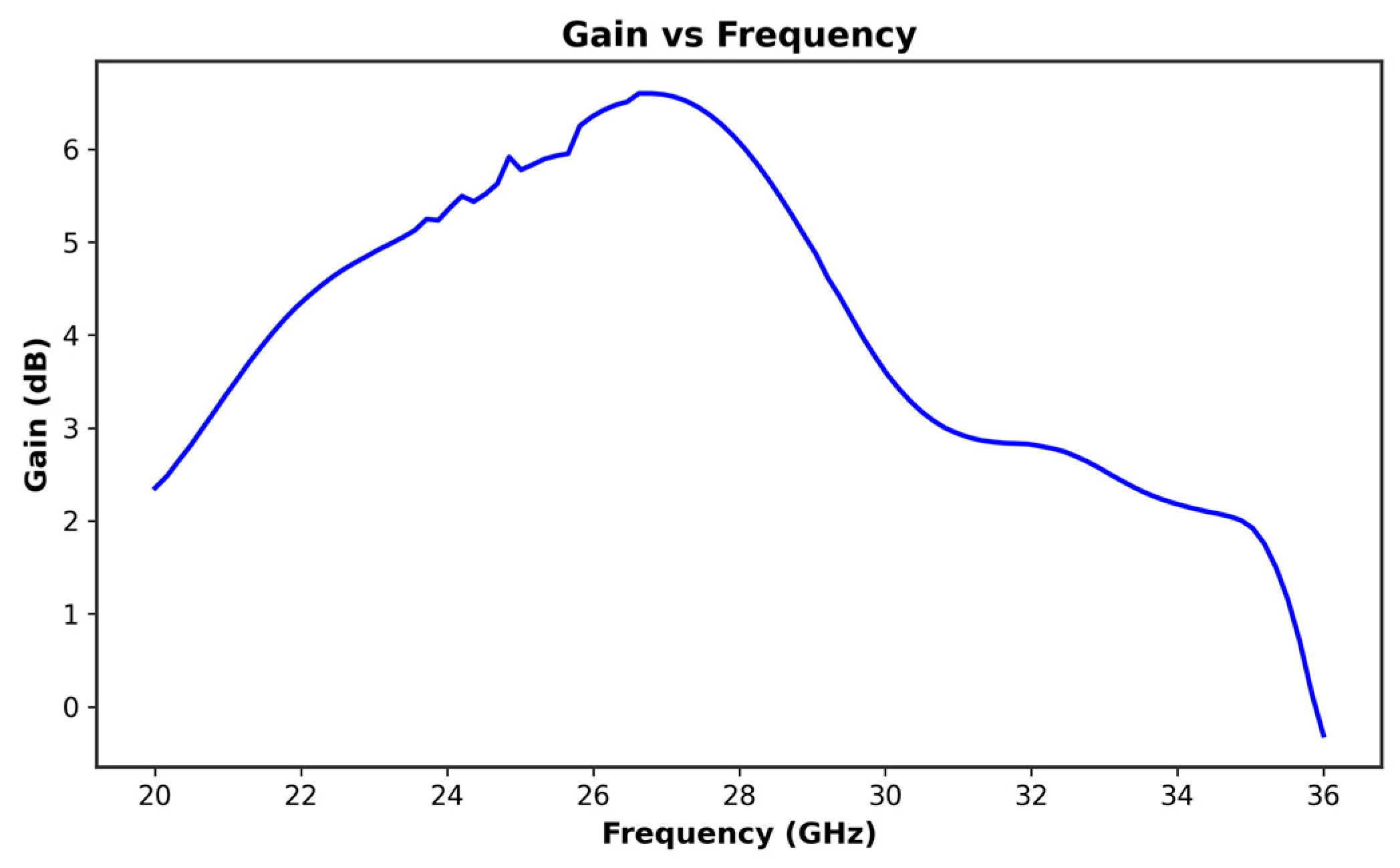
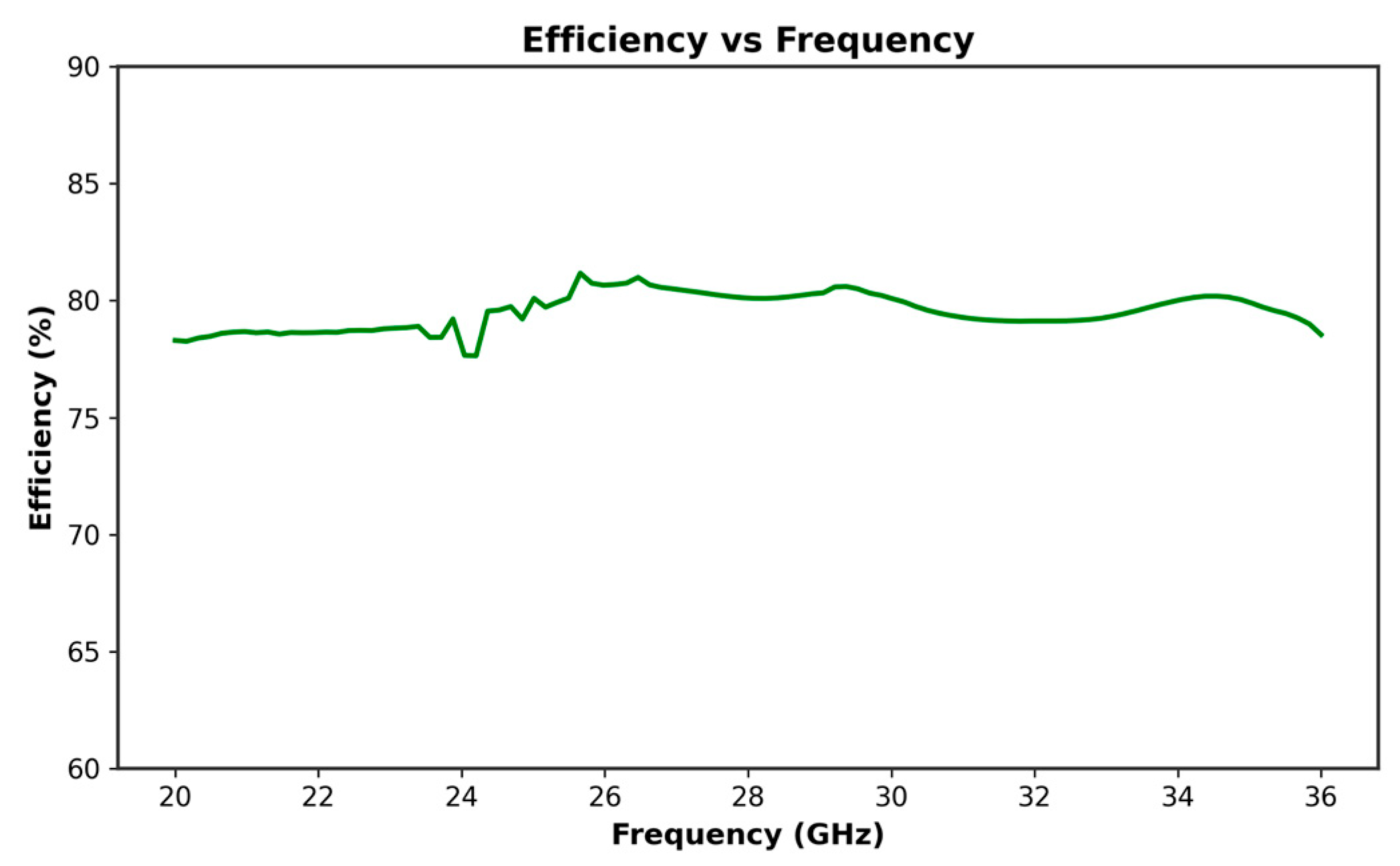
2. Single Antenna Design and Simulation Results
3. Two-Element Array Configuration
3.1. Array Design Strategy
3.2. Introducing Inspired MTM Cells Based on ML for Enhanced Gain
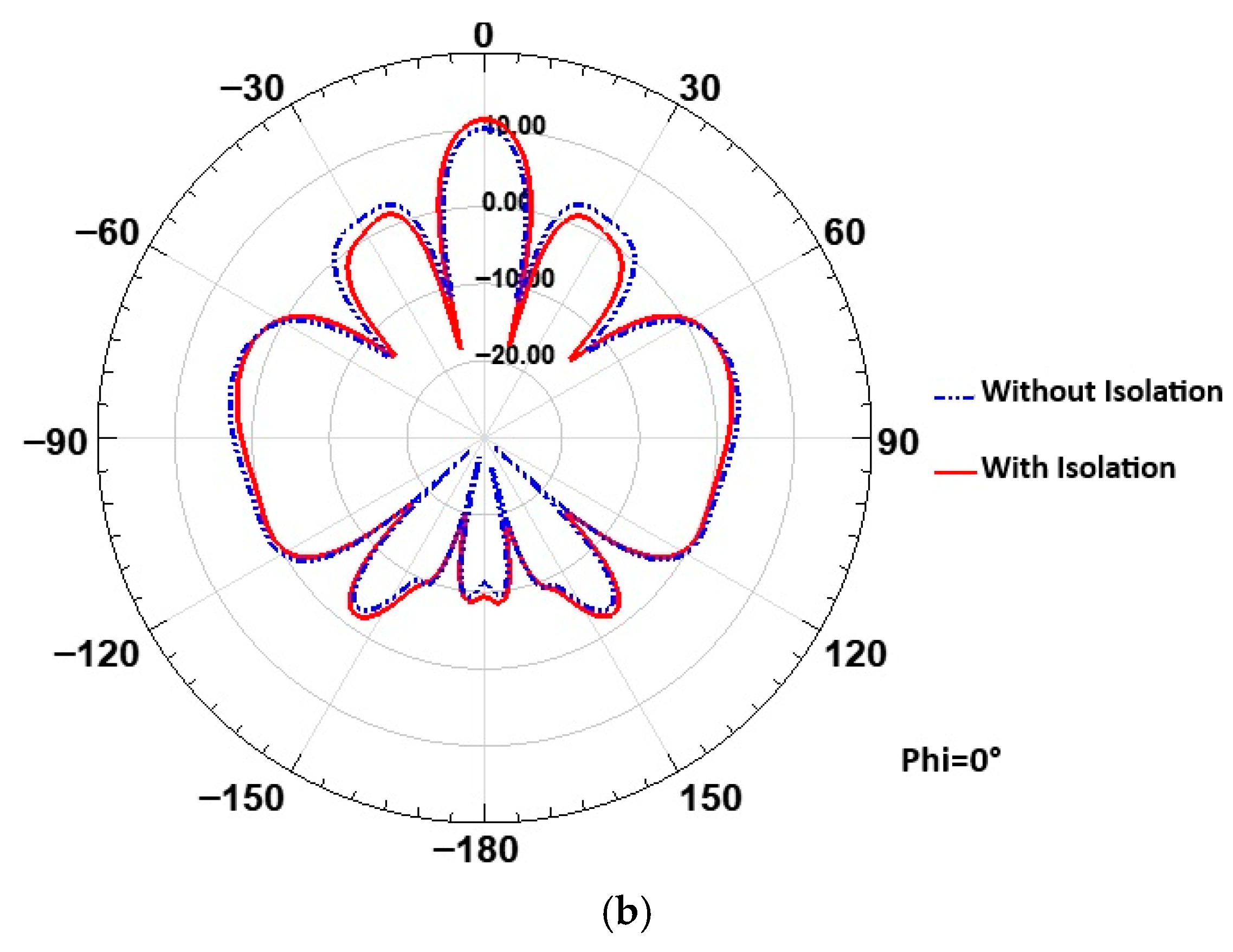
4. Proposed MIMO Antenna with Isolation Technique
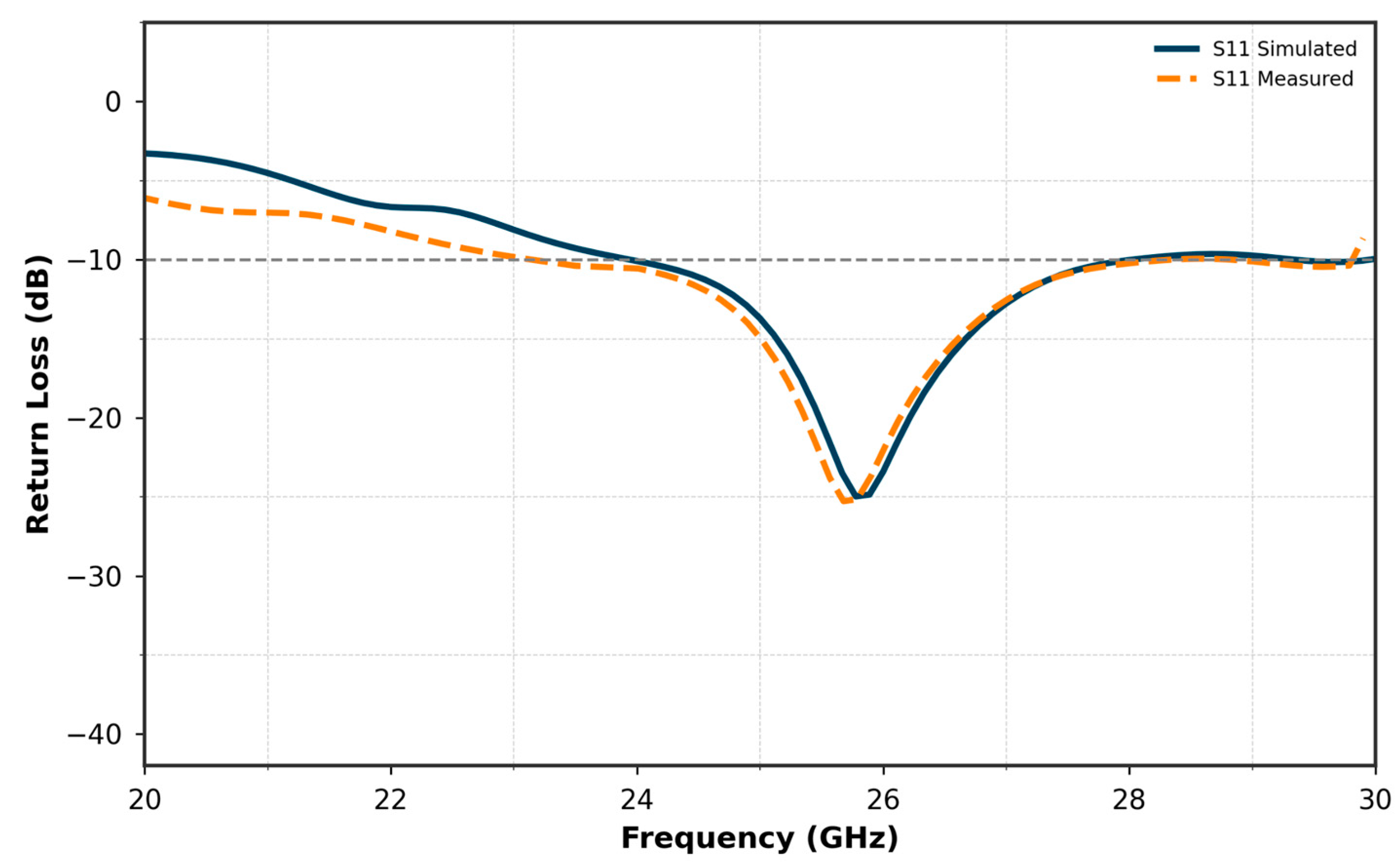
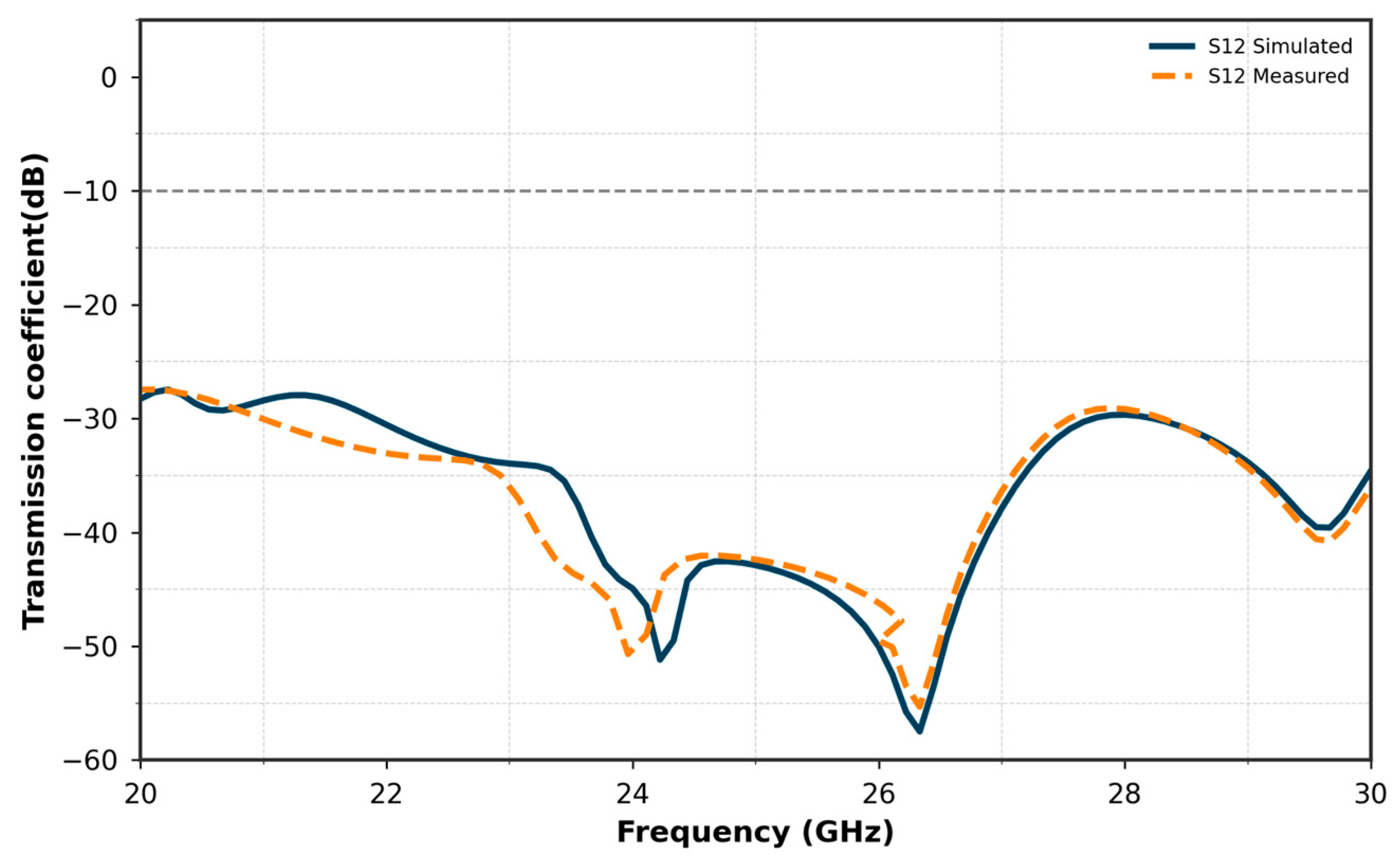
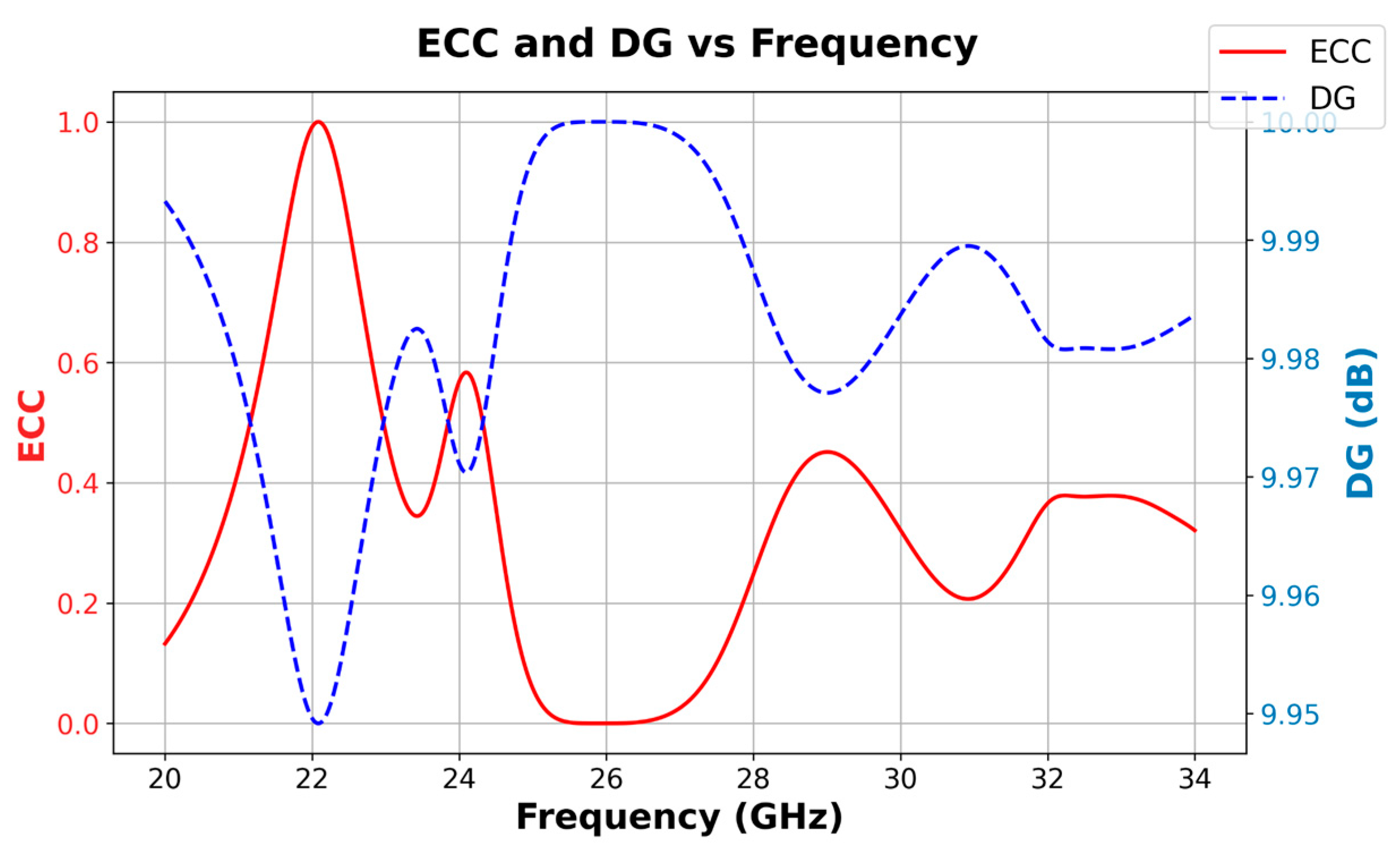
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seker, C.; Güneser, M.T.; Ozturk, T. A Review of Millimeter Wave Communication for 5G. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies (ISMSIT), Ankara, Turkey, 19–21 July 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, D.; Su, L.; Vasilakos, A.V. A Survey of Millimeter Wave Communications (mmWave) for 5G: Opportunities and Challenges. Wirel. Netw. 2015, 21, 2657–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taori, R.; Sridharan, A. Point to Multi-Point, In-Band mmWave Backhaul for 5G Networks. In Towards 5G: Applications, Requirements and Candidate Technologies; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 395–407. [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh, A.; Kaur, M.J. Comprehensive Survey of Massive MIMO for 5G Communications. In Proceedings of the 2019 Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences (ASET), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 26 March–10 April 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, B.P.; Kommuri, U.K. Review on 5G Small Cell Base Station Antennas: Design Challenges and Technologies. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 35560–35584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogale, T.E.; Le, L.B. Massive MIMO and mmWave for 5G Wireless HetNet: Potential Benefits and Challenges. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2016, 11, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mchangama, A.; Elfergani, I.; Rodriguez, J.; Abd-Alhameed, R. MmWave Massive MIMO Small Cells for 5G and Beyond Mobile Networks: An Overview. In Proceedings of the 2020 12th International Symposium on Communication Systems, Networks and Digital Signal Processing (CSNDSP), Porto, Portugal, 20–22 July 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Memon, M.H.; Jamro, D.A.; Kim, S. mmWave Four-Element MIMO Antenna for Future 5G Systems. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nej, S.; Bairappaka, S.K.; Ram, D.B.D.S.R.; Jana, S.; Ghosh, A. Design of a High Order Dual Band MIMO Antenna with Improved Isolation and Gain for Wireless Communications. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 50, 5727–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Yue, H.; Zhang, F.; Fan, Y.; Fu, Q.; Zhu, W.; Yang, R.; Xu, J. Broadband Reduction in Mutual Coupling in Compact MIMO Vehicle Antennas by Using Electric SRRs. Electronics 2025, 14, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, S.; Ramzan, M.; Sen, P. An EBG-Driven 2-Port MIMO Antenna Featuring Enhanced Isolation and Circular Polarization for IEEE 802.11 ad JC&S Terminals. In Proceedings of the IEEE 5th International Symposium on Joint Communications & Sensing (JC&S), Oulu, Finland, 28–30 January 2025; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Munusami, C.; Venkatesan, R. A compact boat shaped dual-band MIMO antenna with enhanced isolation for 5G/WLAN application. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 11631–11641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannepaga, B.; Varadarajan, S. Enhancing RF energy harvesting in smart cities with two port MIMO-UWB antenna design using machine learning algorithms. Frequenz 2024, 78, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadadi, N.; Abotaleb, M.; Dutta, P.K. Design of Antenna Parameters Using Optimization Techniques: A Review. Full Length Art. 2023, 3, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roustaei, N. Application and Interpretation of Linear-Regression Analysis. Med. Hypothesis Discov. Innov. Ophthalmol. 2024, 13, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.; Sharma, R.; Dubey, R. A Modified Regression Model for Analysing the Performance of Metamaterial Antenna Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2024, 136, 1769–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Tsao, H.H.; Hsu, C.C.; Ali, A.; Liao, S.Y. Antenna Structure Prediction and Optimization Based on Machine Learning and Grid Search. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Workshop on Electromagnetics (iWEM), Taipei, Taiwan, 24–26 July 2024; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.H.; Ali, A.; Hsu, C.C.; Tsao, H.H. Enhanced Antenna Design through Hyperparameter Optimization of Diverse Machine Learning Models Using Bayesian Optimization. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Yin, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, S.; Zhao, H.; Su, Z.; Yin, X. Time-Domain Scattering Parameters Based Neural Network Inverse Model for Antenna Designs. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2024, 23, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perić, N.; Pešić, K.; Dončov, N.; Stanković, Z.; Pronić-Rančić, O. MLP-PNN Model of Dual-Band Microstrip Patch Antenna for GNSS Receivers. In Proceedings of the 2024 59th International Scientific Conference on Information, Communication and Energy Systems and Technologies (ICEST), Niš, Serbia, 16–18 June 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Roqui, J.; Pegatoquet, A.; Santamaria, L.; Lizzi, L. Predicting the Maximum Achievable Antenna Bandwidth and Efficiency Using Machine Learning: A Terminal-Integrated Meander IFA Case Study. IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag. 2024, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.T.; Lin, F.H. Approaching Performance Bound of Microstrip Antennas Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 12th Asia-Pacific Conference on Antennas and Propagation (APCAP), Gold Coast, Australia, 2–5 September 2024; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Chhaule, N.; Kumar, A.; Singh, R.; Sharma, S. A Comprehensive Review on Conventional and Machine Learning-Assisted Design of 5G Microstrip Patch Antenna. Electronics 2024, 13, 3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Patel, R.; Yadav, S.; Kumar, D. Machine Learning-Based Reflection Coefficient and Impedance Prediction for a Meandered Slot Patch Antenna. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2025, 188, 109245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, D.; Kundu, A.K. Design and Optimization of a Meander Line Radiator Inspired Miniaturized Microstrip Patch Antenna Using Machine Learning. MAPAN 2025, 40, 371–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanaswamy, N.K.; Reddy, K.S.; Kumar, P.; Mishra, S. Machine Learning Aided Tapered 4-Port MIMO Antenna for V2X Communications with Enhanced Gain and Isolation. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 32411–32423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waly, M.; Ibrahim, A.; El-Hameed, H.S.A.; Abouelatta, M. Optimization of a Compact Wearable LoRa Patch Antenna for Vital Sign Monitoring in WBAN Medical Applications Using Machine Learning. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 103860–103879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.T.; Singh, M.J. Regression Supervised Model Techniques THz MIMO Antenna for 6G Wireless Communication and IoT Application with Isolation Prediction. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.T.; Singh, M.J. Broadband High Gain Performance MIMO Antenna Array for 5G mm-Wave Applications-Based Gain Prediction Using Machine Learning Approach. Alexandria Eng. J. 2024, 104, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.T.; Singh, M.J. Machine Learning Based Compact MIMO Antenna Array for 38 GHz Millimeter Wave Application with Robust Isolation and High Efficiency Performance. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 104006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.T.; Singh, M.J. Machine Learning-Based Technique for Gain Prediction of mm-Wave Miniaturized 5G MIMO Slotted Antenna Array with High Isolation Characteristics. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Alibakhshikenari, M.; Dalarsson, M. A Novel Multiband Low Mutual Coupling Quad-Element MIMO Antenna for Advanced Communication Systems. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 65198–65215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerrouk, A.; Tounsi, M.L.; Vuong, T.P.; Corrao, N.; Yagoub, M.C.E. Miniaturized patch array antenna using CSRR structures for 5G millimeter-wave communication systems. Electronics 2025, 14, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bawri, S.S.; Islam, M.T.; Wong, H.Y.; Jamlos, M.F. Machine Learning Technique Based Highly Efficient Slotted 4-Port MIMO Antenna Using Decoupling Structure for Sub-THz and THz 6G Band Applications. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2024, 56, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, A.M.; Ross, G.F. Measurement of the Intrinsic Properties of Materials by Time-Domain Techniques. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1970, 19, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simovski, C.R. Material Parameters of Metamaterials (A Review). Opt. Spectrosc. 2009, 107, 726–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yon, H.; Rahman, T.A.; Jamaluddin, M.H.; Alomainy, A. Development of C-Shaped Parasitic MIMO Antennas for Mutual Coupling Reduction. Electronics 2021, 10, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.; Upadhyaya, T.; Patel, R.; Kaushal, H. Compact Wideband Four Element Optically Transparent MIMO Antenna for mm-Wave 5G Applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 194206–194217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Ahmad, I.; Raheem, Y.; Ullah, S.; Ahmad, T.; Habib, U. Development of 60-GHz Millimeter Wave, Electromagnetic Bandgap Ground Planes for Multiple-Input Multiple-Output Antenna Applications. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Machine-Learning-Assisted Optimization for Antenna Geometry Design. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2024, 72, 2083–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, J.K.; Kumar, P.; Mishra, S.; Singh, R. Design and Optimization of Dual Port Dielectric Resonator Based Frequency Tunable MIMO Antenna with Machine Learning Approach for 5G New Radio Application. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2024, 37, e5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Thakare, V.V.; Singhal, P.K. Design and Comparative Analysis of THz Antenna through Machine Learning for 6G Connectivity. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2024, 22, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, J.K.; Kumar, P.; Mishra, S.; Singh, R. Machine Learning-Enabled Two-Port Wideband MIMO Hybrid Rectangular Dielectric Resonator Antenna for n261 5G NR Millimeter Wave. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2024, 37, e5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
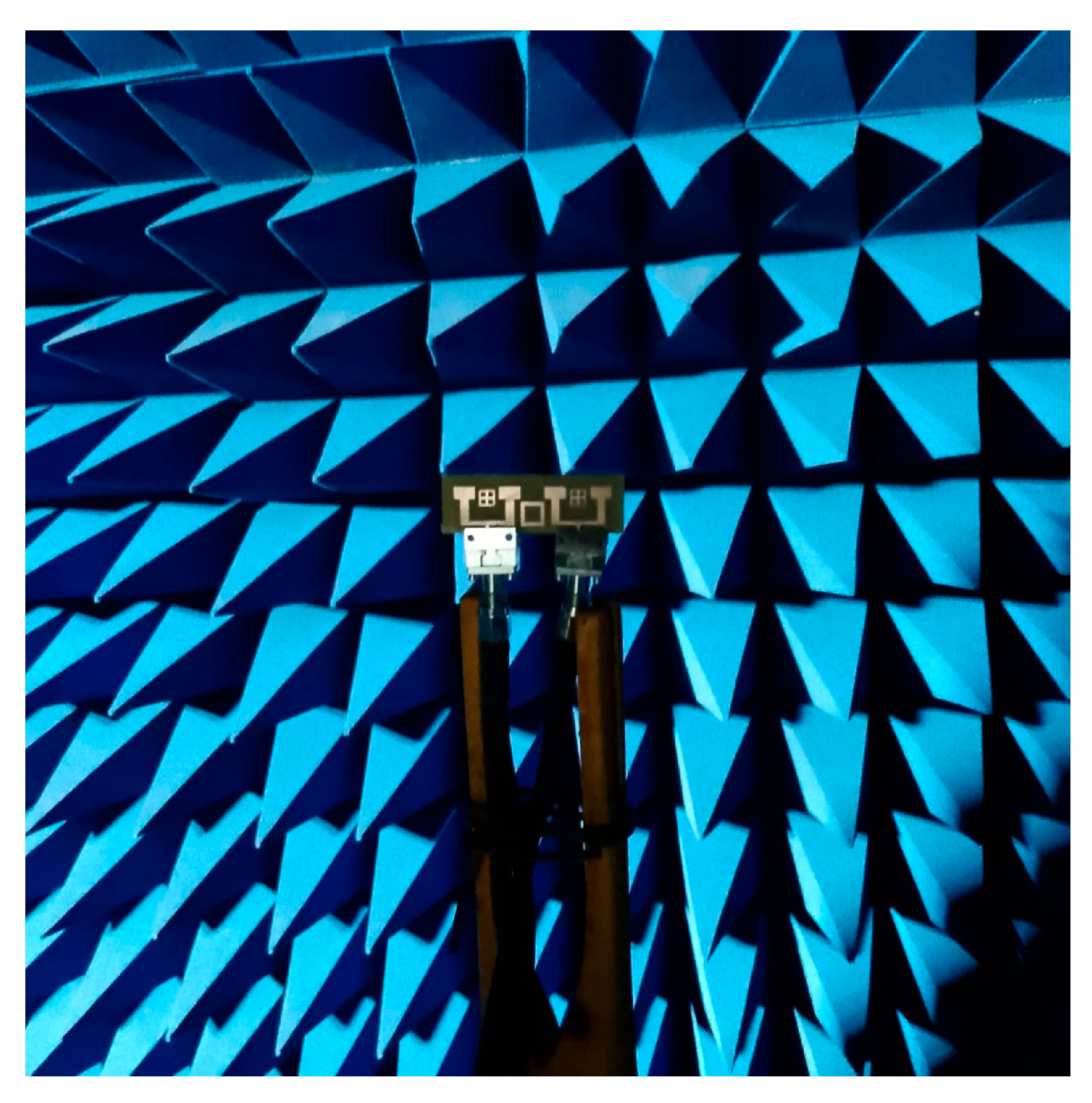
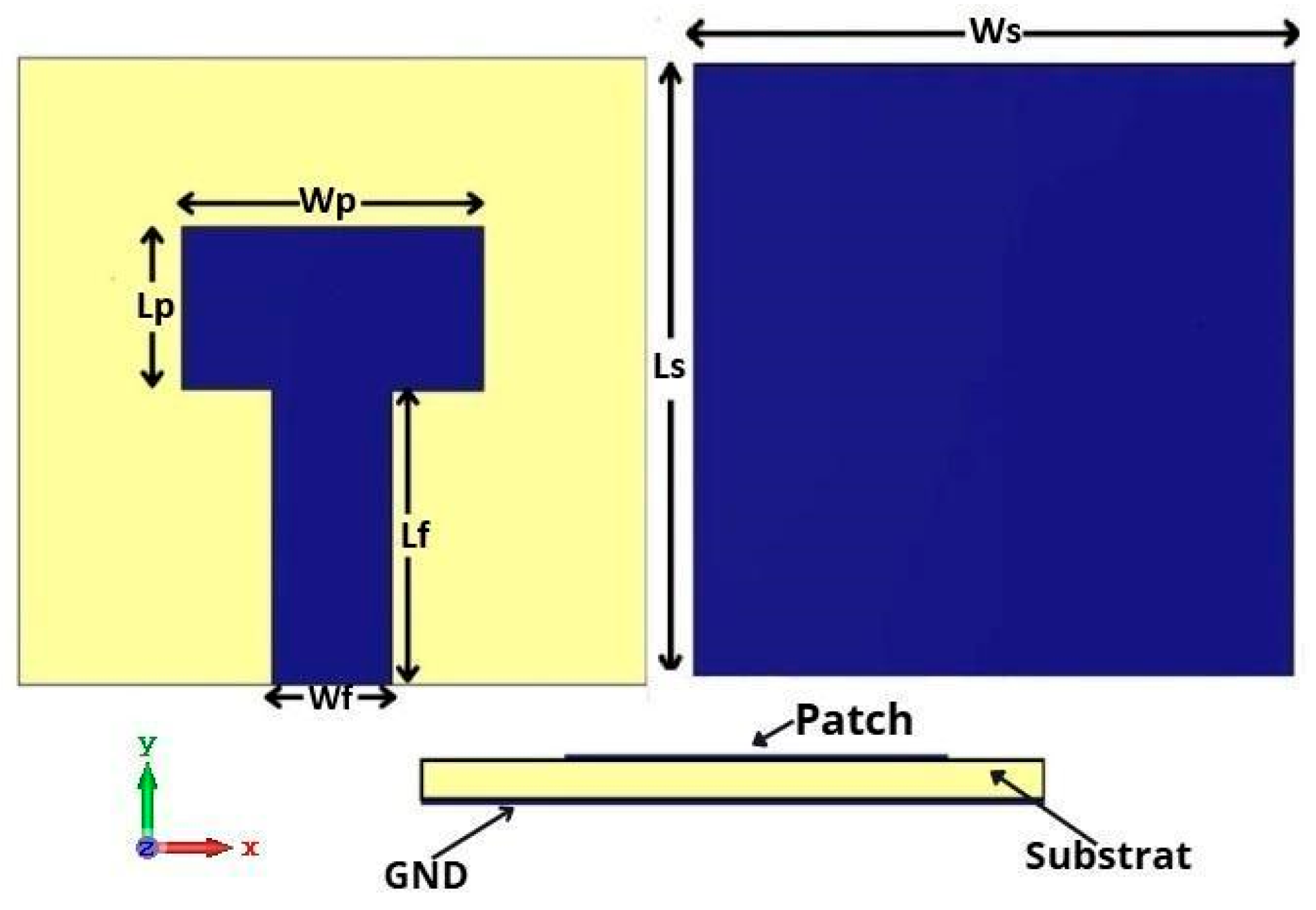

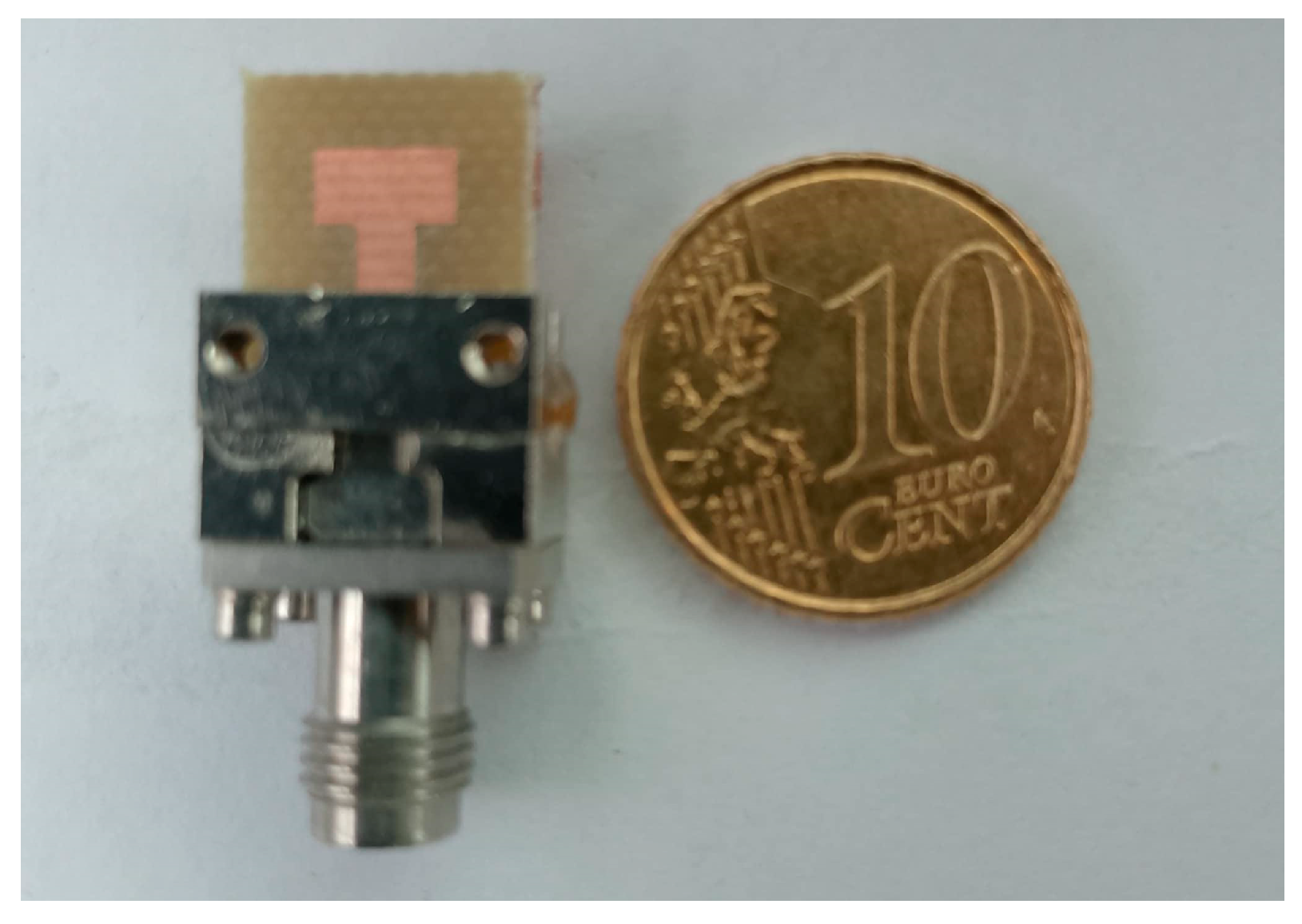
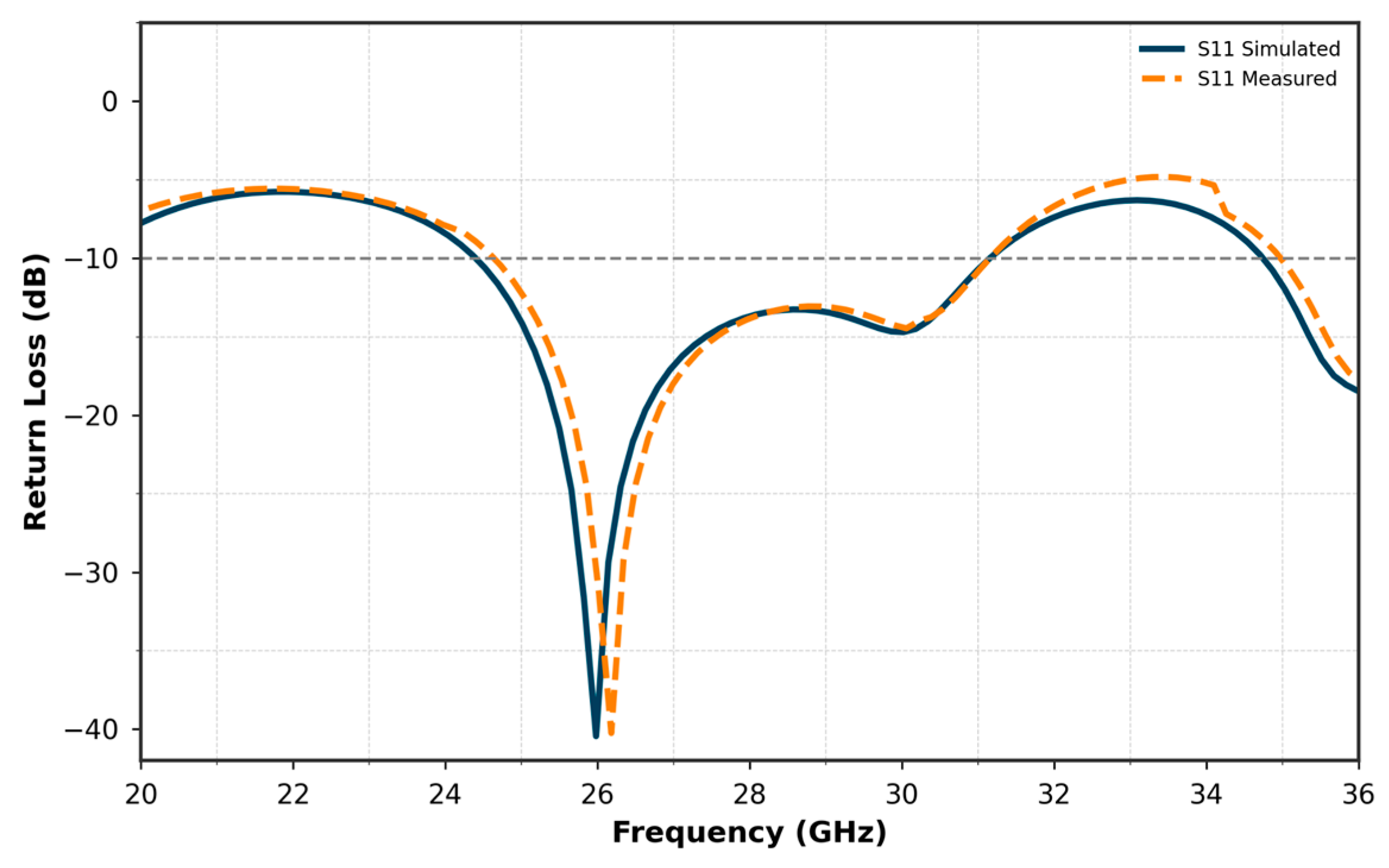


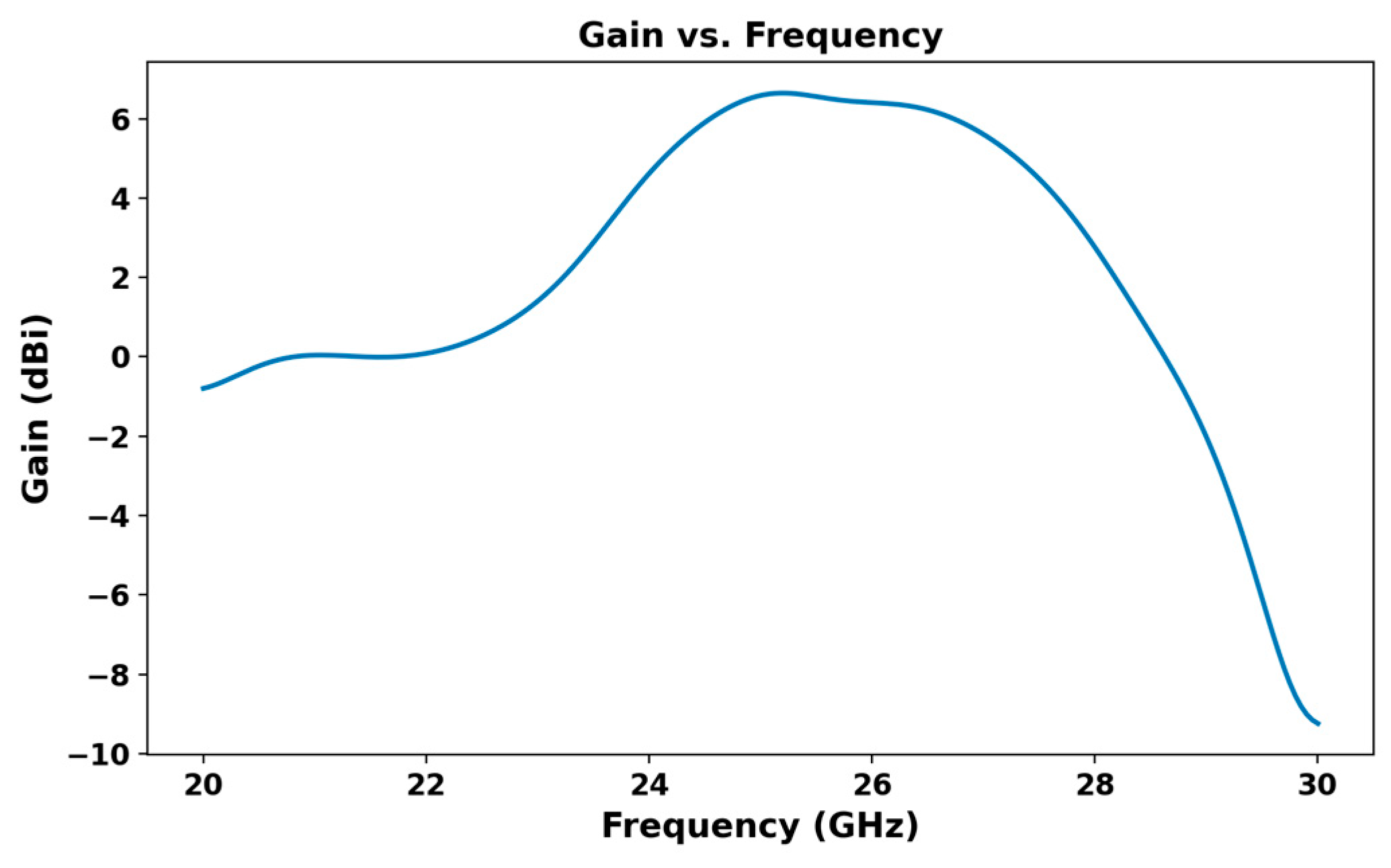
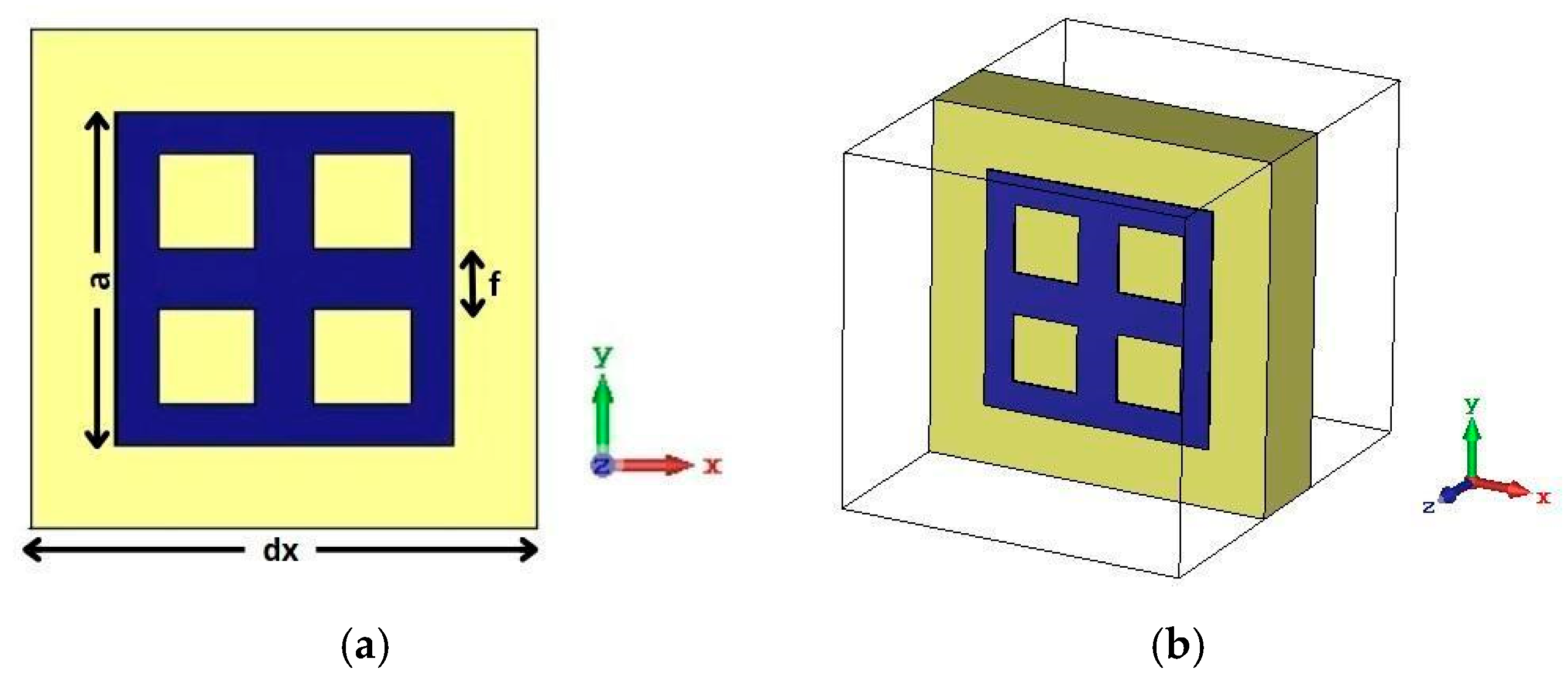
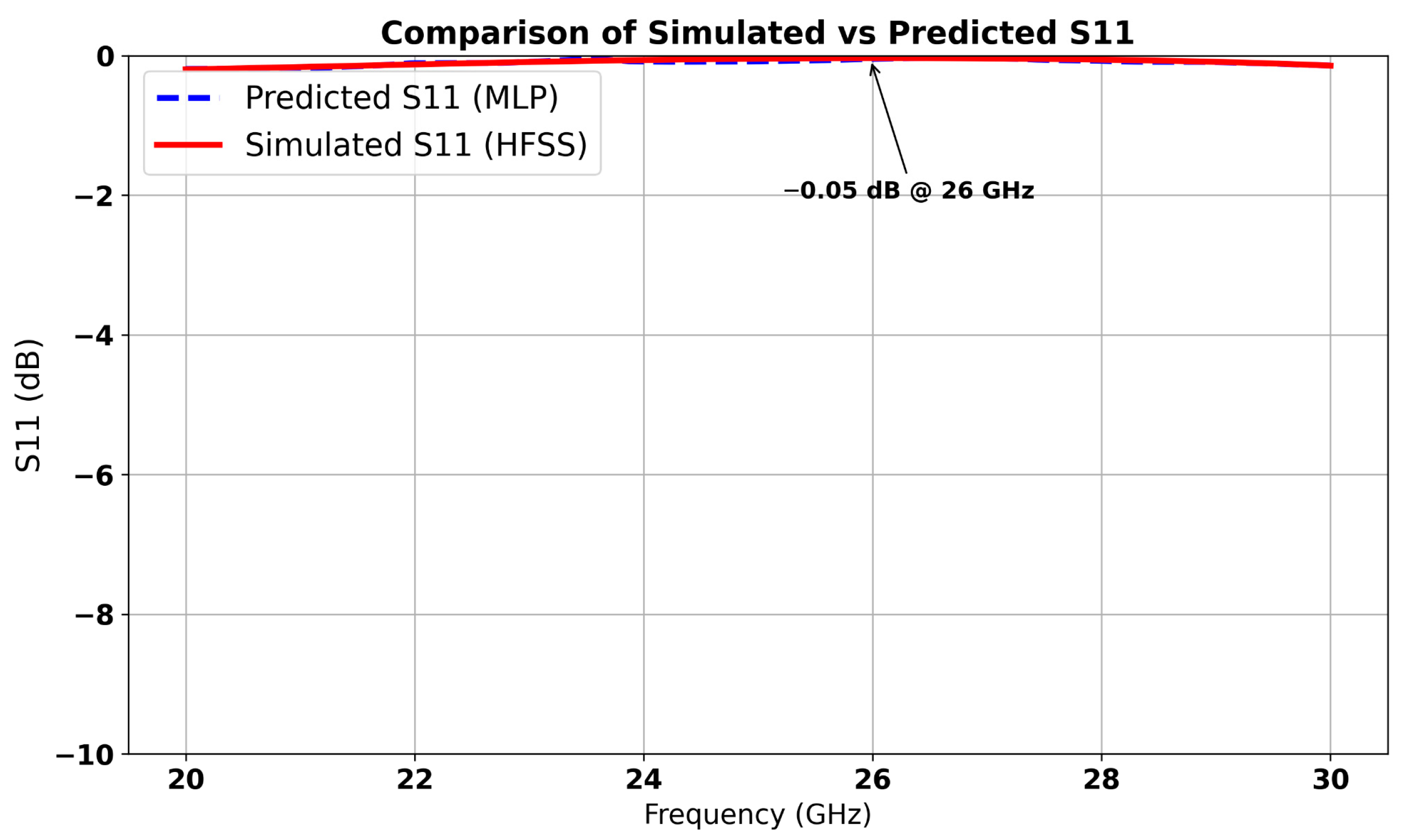
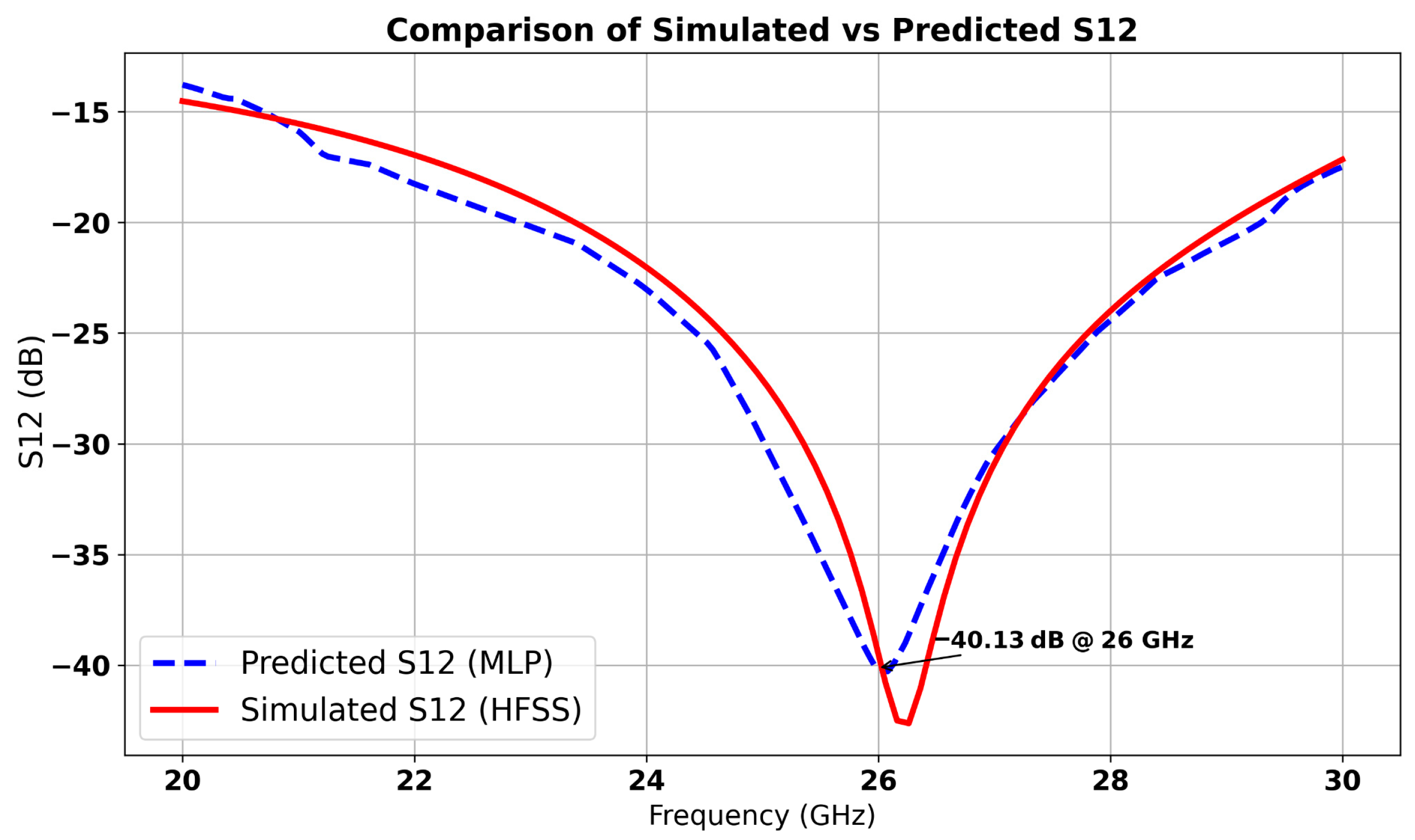


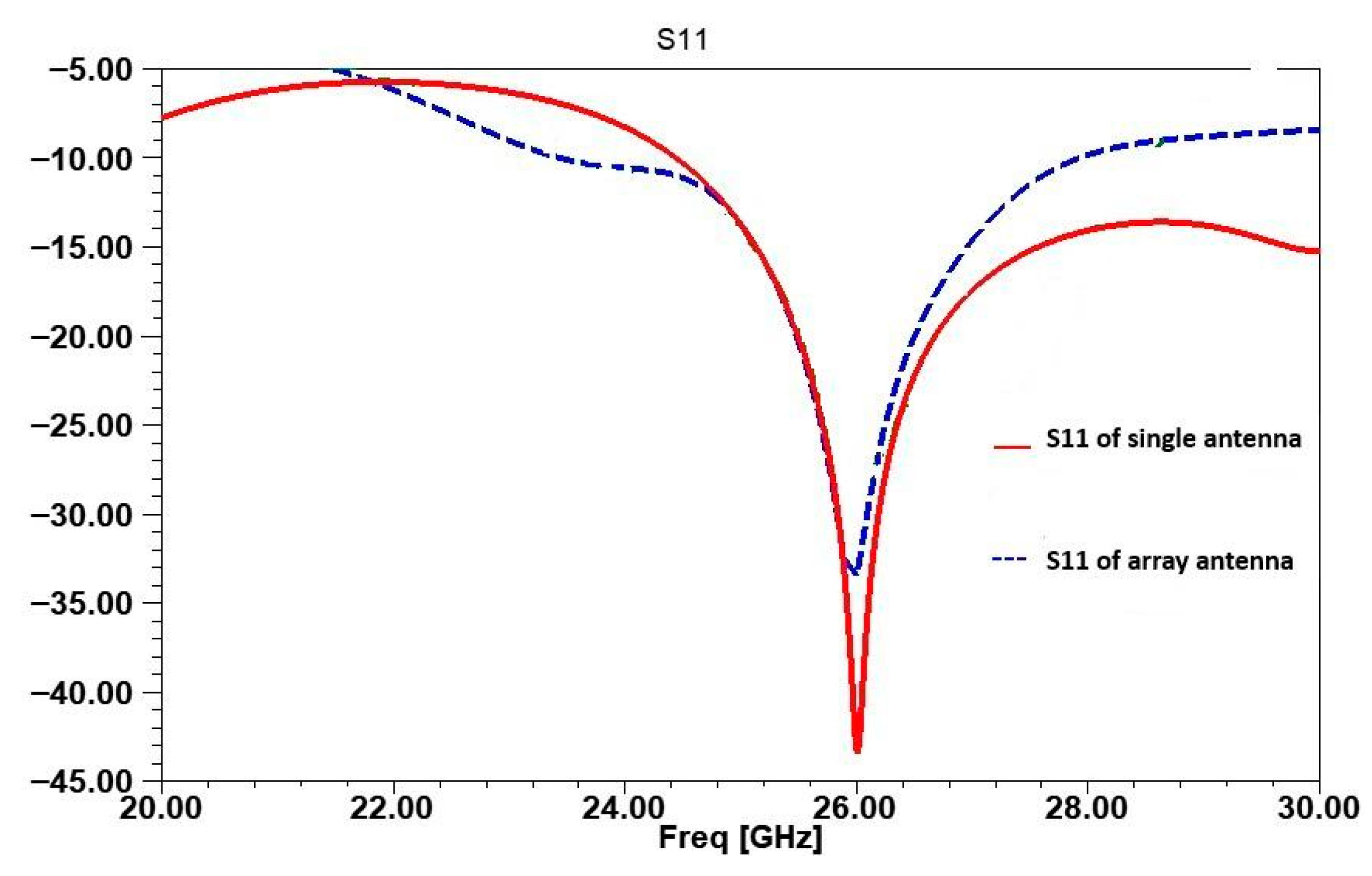

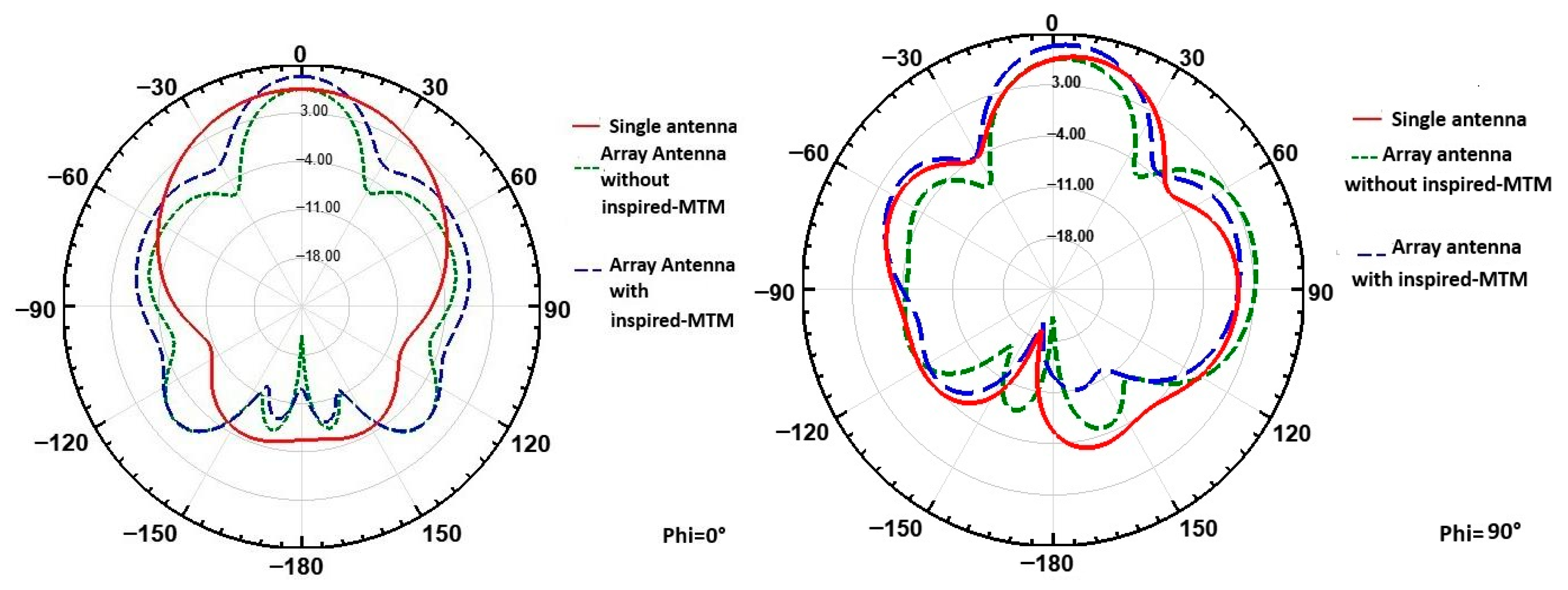
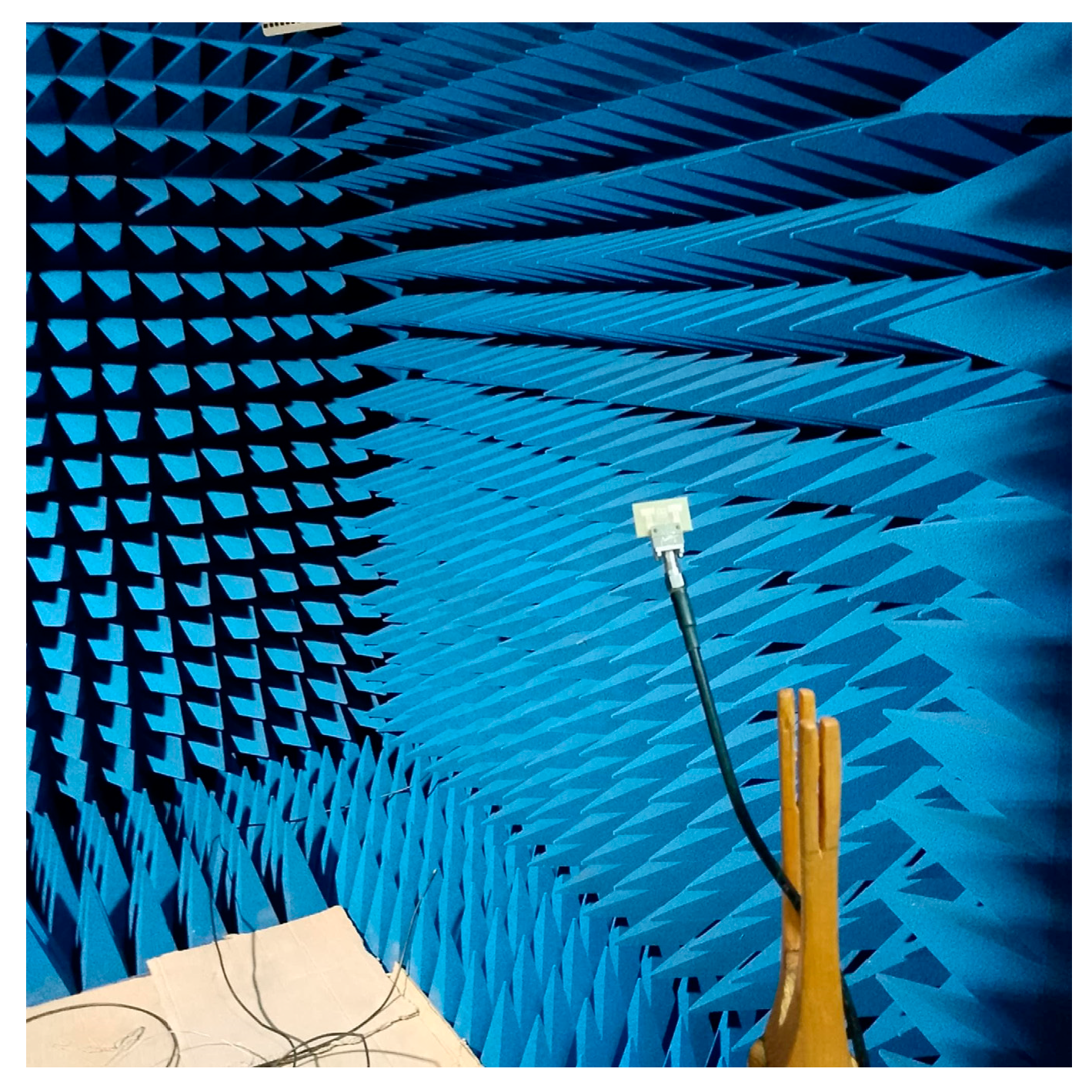
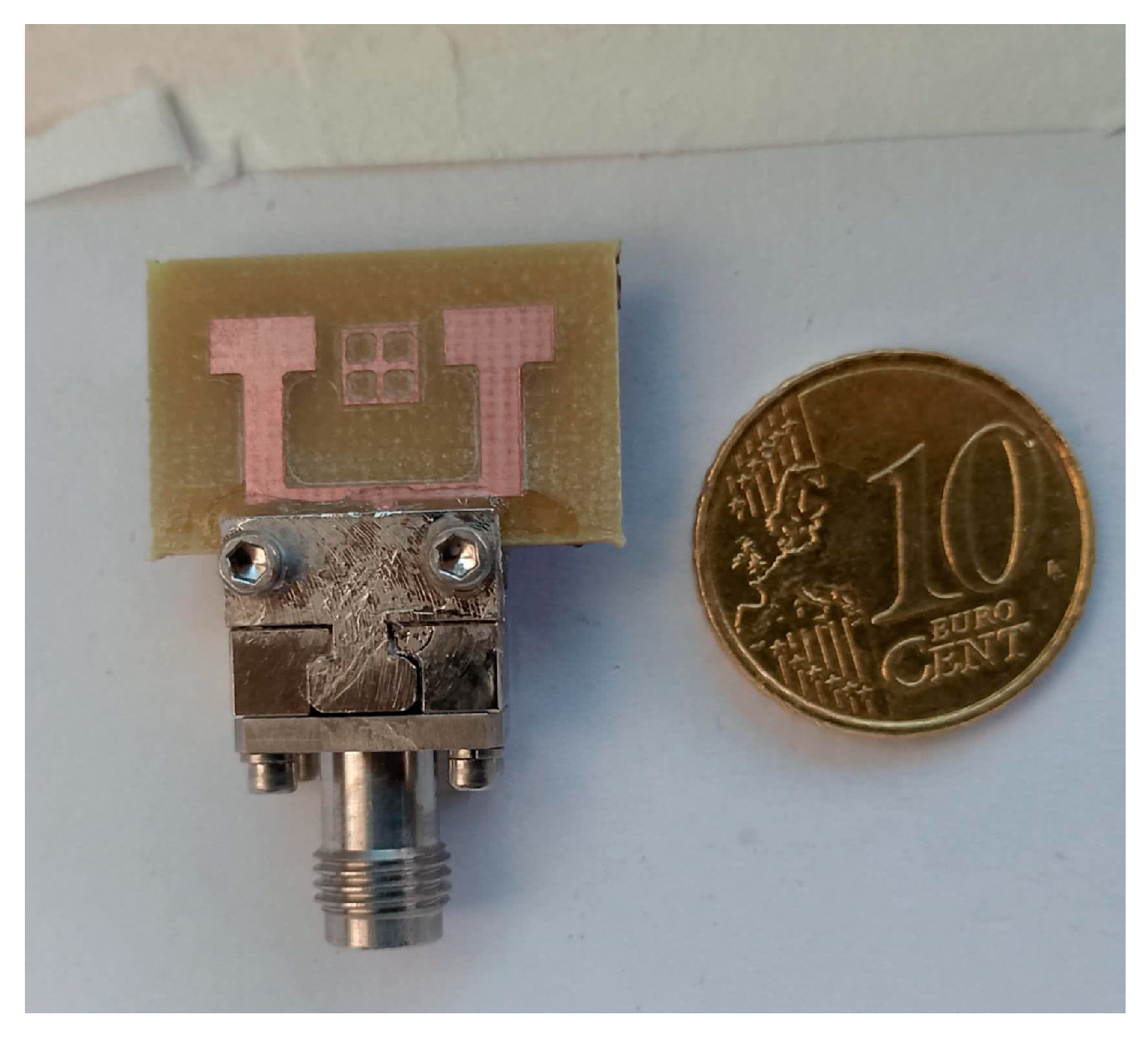
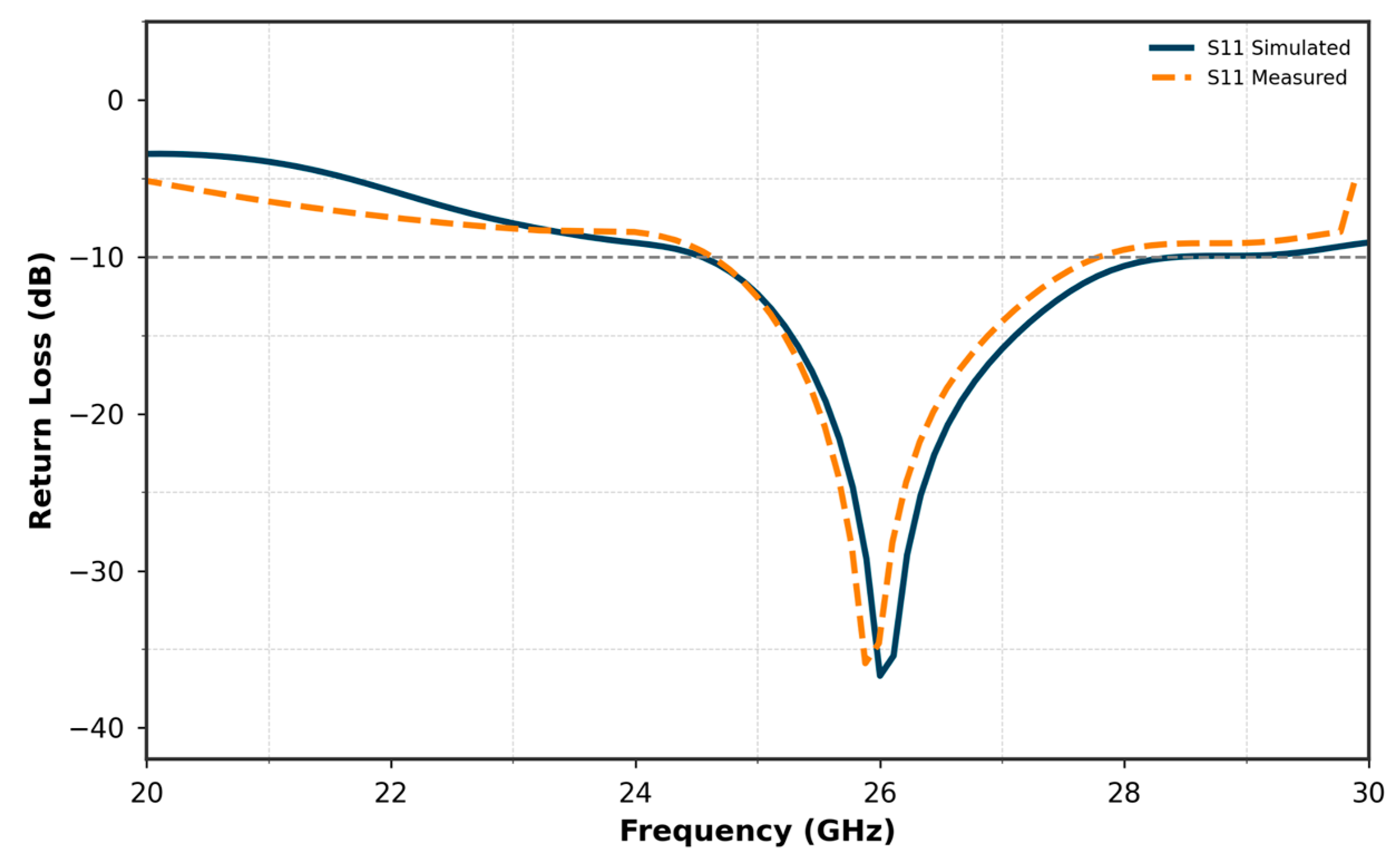
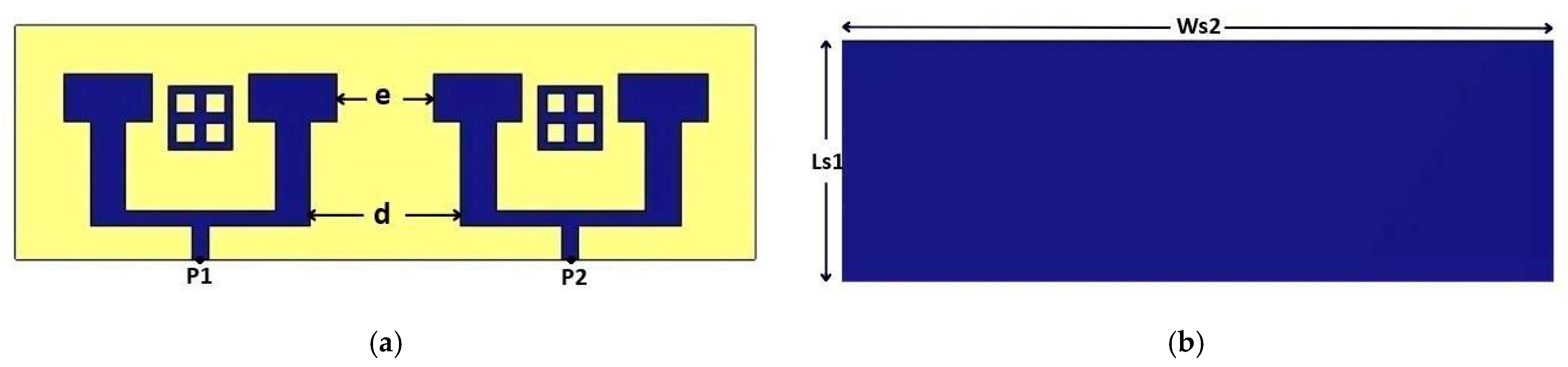
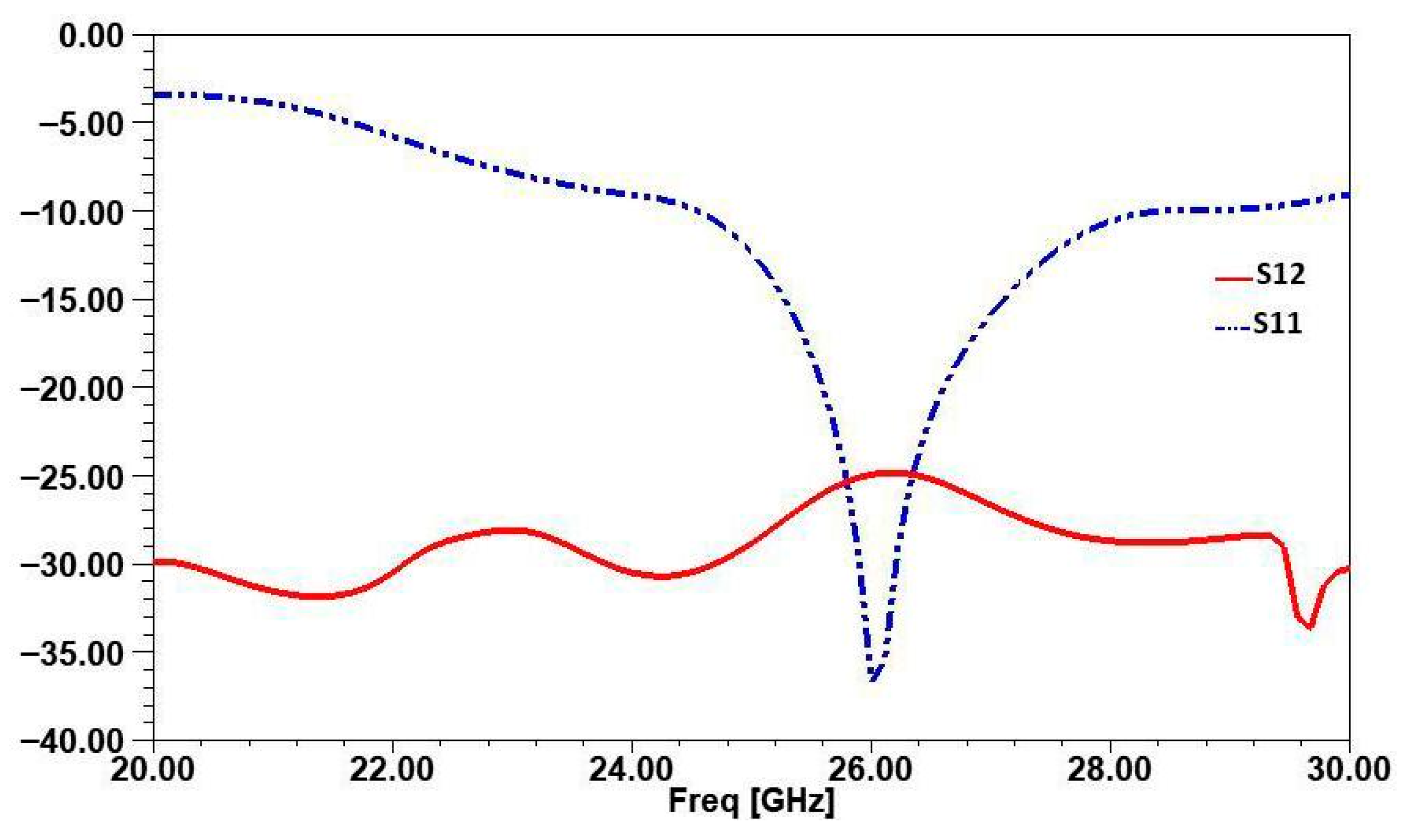


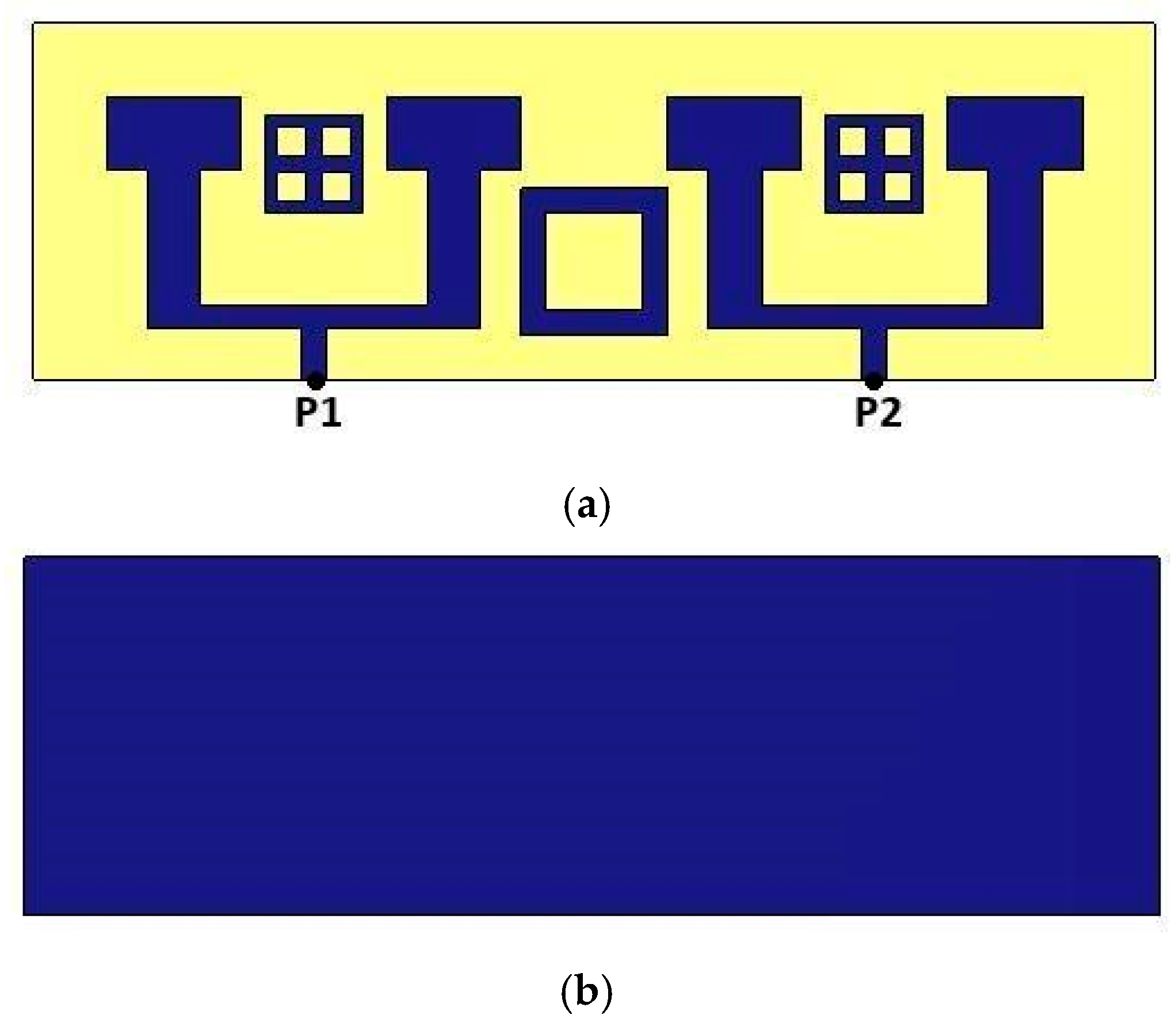
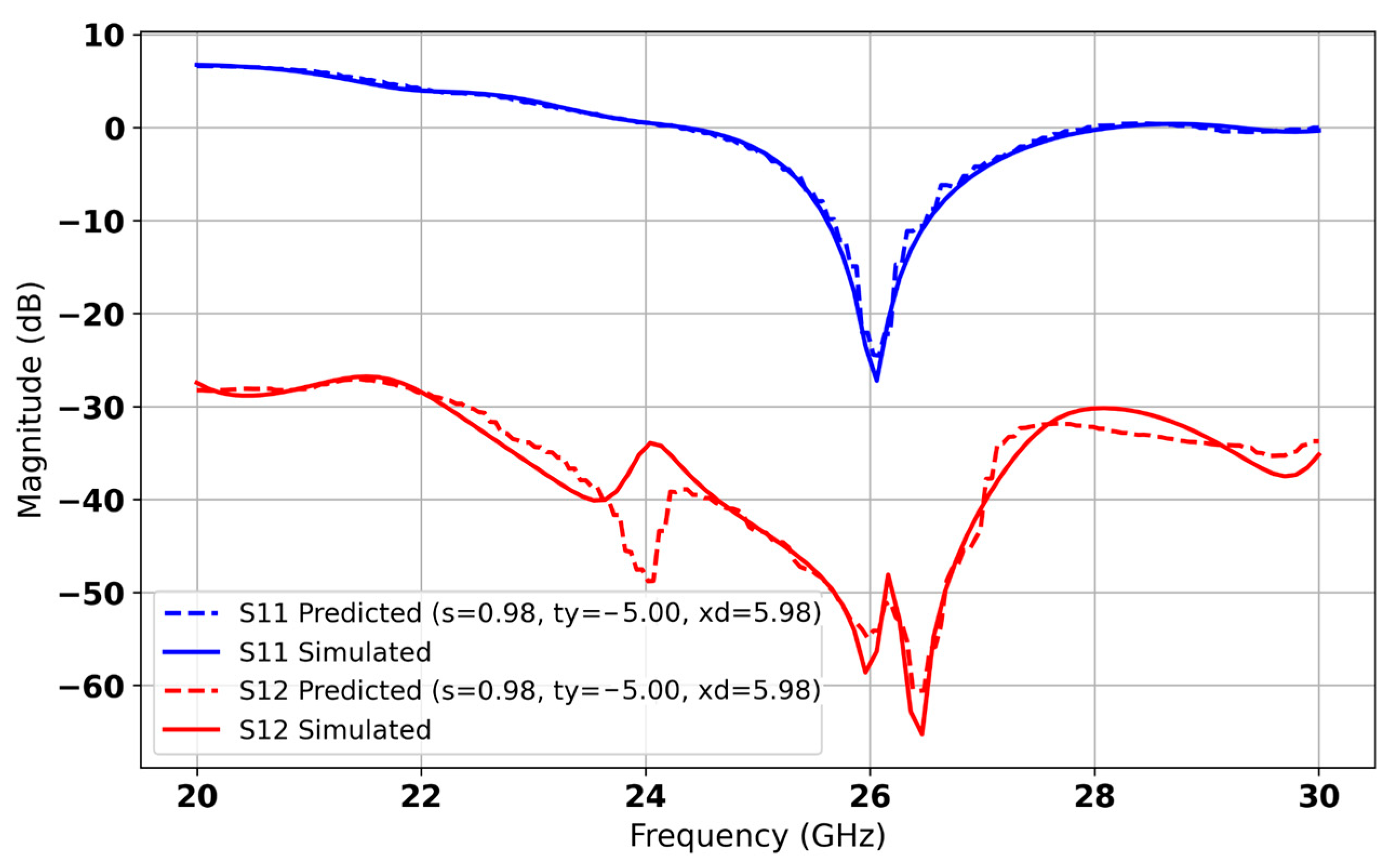
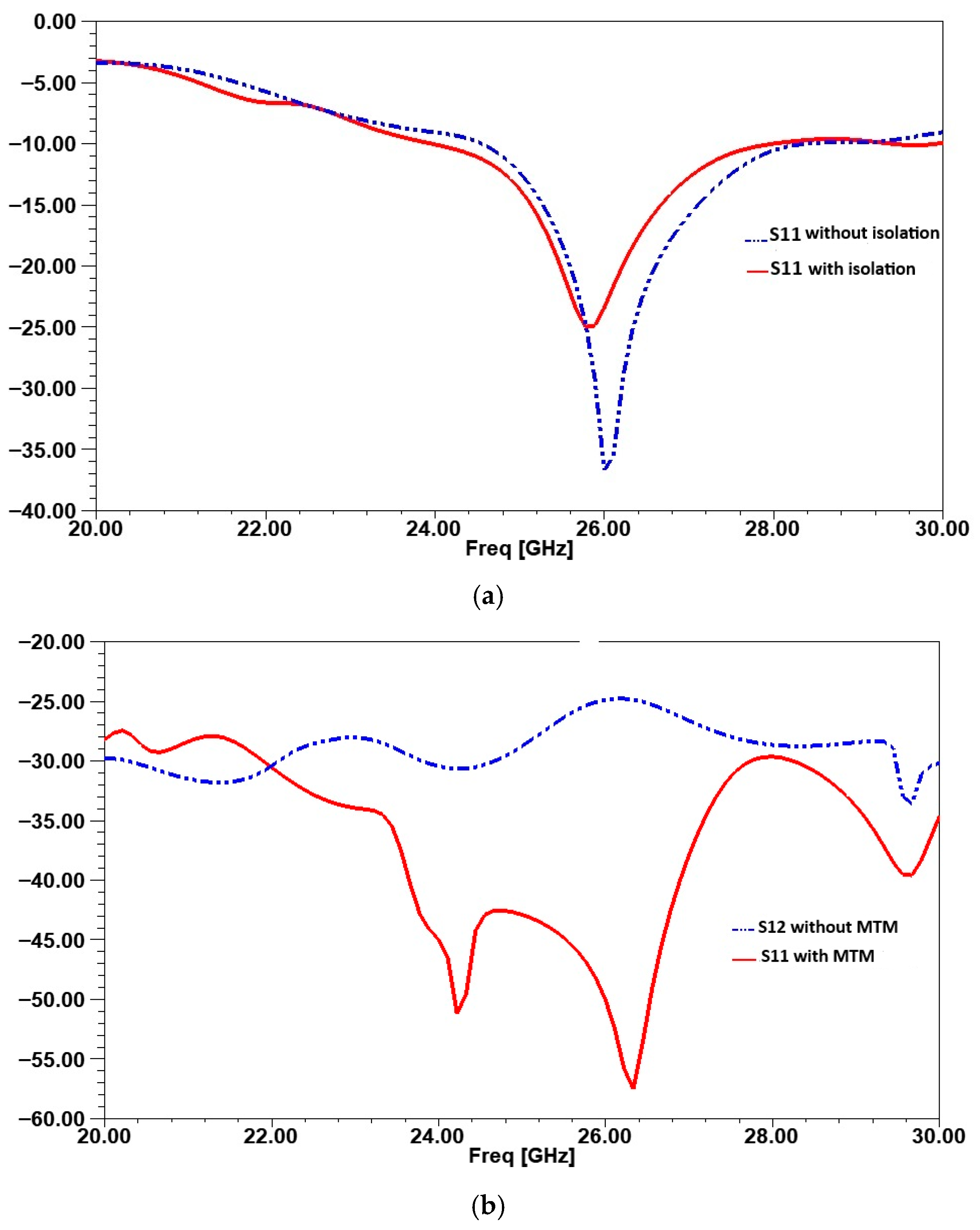




| Parameters | Ls | Ws | Lp | Wp | Lf | Wf |
| Value(mm) | 11.50 | 11.50 | 2.95 | 6.20 | 5.54 | 3.00 |
| Algorithm | R2 | MSE |
|---|---|---|
| XGBoost | 0.98 | 1.03 |
| MLP | 0.99 | 0.62 |
| KNN | 0.99 | 0.78 |
| catBoost | 0.97 | 1.41 |
| Random Forest | 0.99 | 0.69 |
| Algorithm | Metric | S11 | S12 |
| XGBoost | R2 | 0.9924 | 0.9468 |
| MAE | 0.1987 | 0.6766 | |
| MLP | R2 | 0.9574 | 0.6437 |
| MAE | 0.6116 | 2.0497 | |
| KNN | R2 | 0.9911 | 0.9590 |
| MAE | 0.2241 | 0.5834 | |
| CatBoost | R2 | 0.9921 | 0.9407 |
| MAE | 0.2247 | 0.7198 | |
| Random Forest | R2 | 0.9895 | 0.9607 |
| MAE | 0.2415 | 0.4919 |
| N. Ref | Frequency (GHz) | Substrate Material | Gain (dBi) | Isolation Level (dB) | Structure Complexity | Machine Learning Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [35] | 24.44–26.5 | Rogers RT Duroid 5880 | 33 | 10.27 | Complex | No |
| [36] | 16 | Rogers RT Duroid 5880 | - | 32 | Complex | No |
| [37] | 24.1–27.18 | Plexiglass-2.3 | 3 | 16 | Complex | No |
| [38] | 24.1–27.18 | Rogers ULTRALAM | 8 | 32 | Complex | No |
| [39] | 1.59–2.26, 3.1–3.87, 5.25–6.91 | - | 15 | 20 | Complex | No |
| [40] | Tunable (wide range) | FR4-epoxy | 19 | 19 | Complex | Yes |
| [41] | THz (6G band) | RT/Duroid 5880 | 6.2 | - | - | Yes |
| [42] | - | RT/Duroid 5880 | 10 | 19 | Simple | Yes |
| [43] | 3.10–10.42 | 3.10–10.42 | - | 21 | Simple | Yes |
| Our work | 24.4–31.2 | FR4-epoxy | 8.3 | 33 | Simple | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chouikhi, L.; Essid, C.; Ben Salah, B.; Ben Moussa, M.; Sakli, H. Machine Learning-Driven Inspired MTM and Parasitic Ring Optimization for Enhanced Isolation and Gain in 26 GHz MIMO Antenna Arrays. Micromachines 2025, 16, 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101082
Chouikhi L, Essid C, Ben Salah B, Ben Moussa M, Sakli H. Machine Learning-Driven Inspired MTM and Parasitic Ring Optimization for Enhanced Isolation and Gain in 26 GHz MIMO Antenna Arrays. Micromachines. 2025; 16(10):1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101082
Chicago/Turabian StyleChouikhi, Linda, Chaker Essid, Bassem Ben Salah, Mongi Ben Moussa, and Hedi Sakli. 2025. "Machine Learning-Driven Inspired MTM and Parasitic Ring Optimization for Enhanced Isolation and Gain in 26 GHz MIMO Antenna Arrays" Micromachines 16, no. 10: 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101082
APA StyleChouikhi, L., Essid, C., Ben Salah, B., Ben Moussa, M., & Sakli, H. (2025). Machine Learning-Driven Inspired MTM and Parasitic Ring Optimization for Enhanced Isolation and Gain in 26 GHz MIMO Antenna Arrays. Micromachines, 16(10), 1082. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16101082









