Effect of Red Mud Addition on Electrical and Magnetic Properties of Hemp-Derived-Biochar-Containing Epoxy Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. RM-BC Production
2.2.2. RM-BC Containing Epoxy Composites Production
2.2.3. RM-BC and RM-BC Containing Composites Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of RM-BC Materials
3.1.1. Ultimate, Proximate, and Surface Analysis
3.1.2. Structural Analysis
3.2. Characterization of RM-BC Composites
3.2.1. DC Electrical Characterization
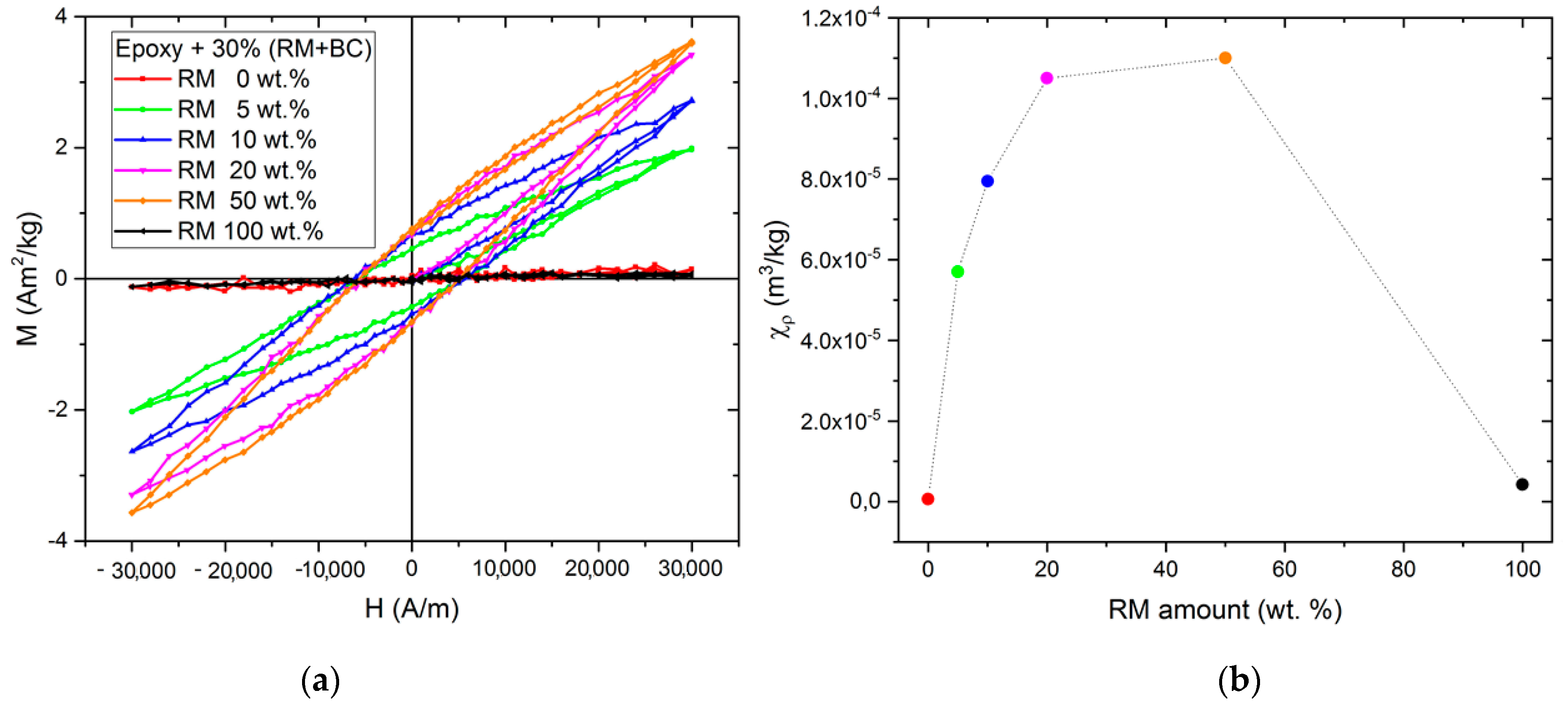
3.2.2. Magnetic Characterization
3.2.3. High-Frequency Electrical Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crossman, R. Conductive composites past, present, and future. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1985, 25, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemour, B.; Yaacob, M.; Lim, H.; Hassan, M.R. Review of Electrical Properties of Graphene Conductive Composites. Int. J. Nanoelectron. Mater. 2018, 11, 371–398. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Peng, H.; Liu, Z. Synthesis challenges for graphene industry. Nat. Mater. 2019, 18, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döscher, H.; Schmaltz, T.; Neef, C.; Thielmann, A.; Reiss, T. Graphene Roadmap Briefs (No. 2): Industrialization status and prospects 2020. 2D Mater. 2021, 8, 022005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemour, B.; Badran, O.; Hassan, M.R. A Review of Using Conductive Composite Materials in Solving Lightening Strike and Ice Accumulation Problems in Aviation. J. Aerosp. Technol. Manag. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, S.; Glaser, B.; Quicker, P. Technical, Economical, and Climate-Related Aspects of Biochar Production Technologies: A Literature Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9473–9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroušek, J.; Trakal, L. Techno-economic analysis reveals the untapped potential of wood biochar. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 133000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoli, M.; Arrigo, R.; Malucelli, G.; Tagliaferro, A.; Duraccio, D. Recent Advances in Biochar Polymer Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoli, M.; Duraccio, D.; Faga, M.G.; Piatti, E.; Torsello, D.; Ghigo, G.; Malucelli, G. Mechanical, electrical, thermal and tribological behavior of epoxy resin composites reinforced with waste hemp-derived carbon fibers. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 14861–14876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorcelli, M.; Bartoli, M. Development of Coffee Biochar Filler for the Production of Electrical Conductive Reinforced Plastic. Polymers 2019, 11, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoli, M.; Torsello, D.; Piatti, E.; Giorcelli, M.; Sparavigna, A.C.; Rovere, M.; Ghigo, G.; Tagliaferro, A. Pressure-Responsive Conductive Poly(vinyl alcohol) Composites Containing Waste Cotton Fibers Biochar. Micromachines 2022, 13, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorcelli, M.; Bartoli, M.; Sanginario, A.; Padovano, E.; Rosso, C.; Rovere, M.; Tagliaferro, A. High-Temperature Annealed Biochar as a Conductive Filler for the Production of Piezoresistive Materials for Energy Conversion Application. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, A.; Bartoli, M.; Frache, A.; Piatti, E.; Giorcelli, M.; Tagliaferro, A. Development of Pressure-Responsive PolyPropylene and Biochar-Based Materials. Micromachines 2020, 11, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepak-Kuc, S.; Kiciński, M.; Michalski, P.P.; Pavlov, K.; Giorcelli, M.; Bartoli, M.; Jakubowska, M. Innovative Biochar-Based Composite Fibres from Recycled Material. Materials 2021, 14, 5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torsello, D.; Ghigo, G.; Giorcelli, M.; Bartoli, M.; Rovere, M.; Tagliaferro, A. Tuning the microwave electromagnetic properties of biochar-based composites by annealing. Carbon Trends 2021, 4, 100062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rumaihi, A.; Shahbaz, M.; Mckay, G.; Mackey, H.; Al-Ansari, T. A review of pyrolysis technologies and feedstock: A blending approach for plastic and biomass towards optimum biochar yield. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Amirahmadi, E.; Neugschwandtner, R.W.; Konvalina, P.; Kopecký, M.; Moudrý, J.; Perná, K.; Murindangabo, Y.T. The Impact of Pyrolysis Temperature on Biochar Properties and Its Effects on Soil Hydrological Properties. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torsello, D.; Bartoli, M.; Giorcelli, M.; Rovere, M.; Arrigo, R.; Malucelli, G.; Tagliaferro, A.; Ghigo, G. High Frequency Electromagnetic Shielding by Biochar-Based Composites. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.K.; Kim, K.Y.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, B.J. Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of monolayer graphene. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 455704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayub, S.; Guan, B.; Ahmad, F.; Oluwatobi, Y.; Nisa, Z.; Javed, M.; Mosavi, A. Graphene and Iron Reinforced Polymer Composite Electromagnetic Shielding Applications: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Zhao, Y.-H.; Bai, S.-L.; Ping, W.C. High shielding effectiveness of multilayer graphene oxide aerogel film/polymer composites. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 92168–92174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.P.; Cheng, D.M.; Ma, W.J.; Hu, J.W.; Yin, Y.H.; Hu, Y.Y.; Li, Y.S.; Yang, J.G.; Xu, Q.F. Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of composite carbon nanotube macro-film at a high frequency range of 40 GHz to 60 GHz. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 067130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, N.; Ma, Y.; Du, F.; Li, F.; He, X.; Lin, X.; Gao, H.; Chen, Y. The influence of single-walled carbon nanotube structure on the electromagnetic interference shielding efficiency of its epoxy composites. Carbon 2007, 45, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdipour, A.; Rosca, I.D.; Trueman, C.W.; Sebak, A.-R.; Van Hoa, S. Multiwall Carbon Nanotube–Epoxy Composites With High Shielding Effectiveness for Aeronautic Applications. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2011, 54, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chung, D. Increasing the electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of carbon fiber polymer–matrix composite by using activated carbon fibers. Carbon 2002, 40, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Chung, D. Electromagnetic interference shielding using continuous carbon-fiber carbon-matrix and polymer-matrix composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 1999, 30, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, R.C.; Peng, L.-M.; Duan, X.F.; Chen, Q.; Liang, X.L. Microwave Absorption Enhancement and Complex Permittivity and Permeability of Fe Encapsulated within Carbon Nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaraki, N.I.; Poursalehi, R. Shielding Effectiveness of Polymeric Nanocomposites Filled with Iron/Wüstite Nanoparticles. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2015, 11, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Choudhary, H.K.; Pawar, S.P.; Bose, S.; Sahoo, B. Carbon encapsulated nanoscale iron/iron-carbide/graphite particles for EMI shielding and microwave absorption. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 23268–23279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yan, S.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, Y.; Rong, H.; Zhao, R.; Qin, G. Wood-Derived Porous Carbon/Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Composites for Enhanced Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 8537–8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velhal, N.; Patil, N.; Kulkarni, G.; Shinde, S.; Valekar, N.; Barshilia, H.; Puri, V. Electromagnetic shielding, magnetic and microwave absorbing properties of Polypyrrole/Ba0.6Sr0.4Fe12O19 composite synthesized via in-situ polymerization technique. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 777, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peymanfar, R.; Ahmadi, A.; Selseleh-Zakerin, E. Evaluation of the size and medium effects on the microwave absorbing, magnetic, electromagnetic shielding, and optical properties using CuCo2S4 nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 848, 156453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peymanfar, R.; Ghorbanian-Gezaforodi, S.; Selseleh-Zakerin, E.; Ahmadi, A.; Ghaffari, A. Tailoring La0.8Sr0.2MnO3/La/Sr nanocomposite using a novel complementary method as well as dissecting its microwave, shielding, optical, and magnetic characteristics. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 20896–20904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamborrino, V.; Costamagna, G.; Bartoli, M.; Rovere, M.; Jagdale, P.; Lavagna, L.; Ginepro, M.; Tagliaferro, A. Catalytic oxidative desulphurization of pyrolytic oils to fuels over different waste derived carbon-based catalysts. Fuel 2021, 296, 120693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, J.J.; Gaston, L.A.; Zhou, B.; Li, M.; Xiao, R.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, H.; Liang, W.; et al. An overview of carbothermal synthesis of metal–biochar composites for the removal of oxyanion contaminants from aqueous solution. Carbon 2018, 129, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, J.; Gen, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Qi, W.; Wang, F. Synthesis of zero-valent iron/biochar by carbothermal reduction from wood waste and iron mud for removing rhodamine B. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 48556–48568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; You, T.; Guo, Y.; Yao, S.; Zang, S.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y. High dispersions of nano zero valent iron supported on biochar by one-step carbothermal synthesis and its application in chromate removal. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 12428–12435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khairul, M.; Zanganeh, J.; Moghtaderi, B. The composition, recycling and utilisation of Bayer red mud. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutar, H.; Mishra, S.C.; Sahoo, S.K.; Chakraverty, A.P.; Maharana, H.S. Progress of Red Mud Utilization: An Overview. Am. Chem. Sci. J. 2014, 4, 255–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukiza, E.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, N. Utilization of red mud in road base and subgrade materials: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H. Metallurgical process for valuable elements recovery from red mud—A review. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 155, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinoveev, D.; Pasechnik, L.; Fedotov, M.; Dyubanov, V.; Grudinsky, P.; Alpatov, A. Extraction of Valuable Elements from Red Mud with a Focus on Using Liquid Media—A Review. Recycling 2021, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Dhawan, N. Evaluation of red mud as a polymetallic source—A review. Miner. Eng. 2021, 171, 107084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Naidu, R. Hidden values in bauxite residue (red mud): Recovery of metals. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2662–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, N. Utilization of red mud in cement production: A review. Waste Manag. Res. 2011, 29, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, H.; Han, C. Recycling of waste red mud for production of ceramic floor tile with high strength and lightweight. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 748, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, G.; Zhang, B.; Liu, C.; Li, S.; Ye, Y.; Jiang, M. Large-Scale Consumption and Zero-Waste Recycling Method of Red Mud in Steel Making Process. Minerals 2018, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, M.; Giorcelli, M.; Rosso, C.; Rovere, M.; Jagdale, P.; Tagliaferro, A. Influence of Commercial Biochar Fillers on Brittleness/Ductility of Epoxy Resin Composites. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliaferro, A.; Rovere, M.; Padovano, E.; Bartoli, M.; Giorcelli, M. Introducing the Novel Mixed Gaussian-Lorentzian Lineshape in the Analysis of the Raman Signal of Biochar. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagdale, P.; Nair, J.R.; Khan, A.; Armandi, M.; Meligrana, G.; Hernandez, F.R.; Rusakova, I.; Piatti, E.; Rovere, M.; Tagliaferro, A.; et al. Waste to life: Low-cost, self-standing, 2D carbon fiber green Li-ion battery anode made from end-of-life cotton textile. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 368, 137644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, D.; Sabouroux, P. EpsiMu, A toolkit for permittivity and permeability measurement in microwave domain at real time of all materials: Applications to solid and semisolid materials. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2010, 52, 2643–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, A.M.; Ross, G.F. Measurement of the Intrinsic Properties of Materials by Time-Domain Techniques. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1970, 19, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker-Jarvis, J.; Vanzura, E.; Kissick, W. Improved technique for determining complex permittivity with the transmission/reflection method. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1990, 38, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, X.; Sanna, A.; Andrésen, J.M. Influence of red mud impregnation on the pyrolysis of oil palm biomass-EFB. Fuel 2014, 119, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Vov, B.V. Mechanism of carbothermal reduction of iron, cobalt, nickel and copper oxides. Thermochim. Acta 2000, 360, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, H.; Takao, S.; Higashi, K.; Kaneko, T.; Samjeské, G.; Uruga, T.; Tada, M.; Iwasawa, Y. Operando Imaging of Ce Radical Scavengers in a Practical Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell by 3D Fluorescence CT–XAFS and Depth-Profiling Nano-XAFS–SEM/EDS Techniques. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 6762–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, A.; Franceschini, F.; Muscas, C.; Pidkova, S.; Bartoli, M.; Rovere, M.; Tagliaferro, A. A Comprehensive Review on Raman Spectroscopy Applications. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Afonso, Y.; Asín, L.; Beola, L.; Moros, M.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Fratila, R.M.; Grazú, V.; Gutiérrez, L. Iron Speciation in Animal Tissues Using AC Magnetic Susceptibility Measurements: Quantification of Magnetic Nanoparticles, Ferritin, and Other Iron-Containing Species. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 1879–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
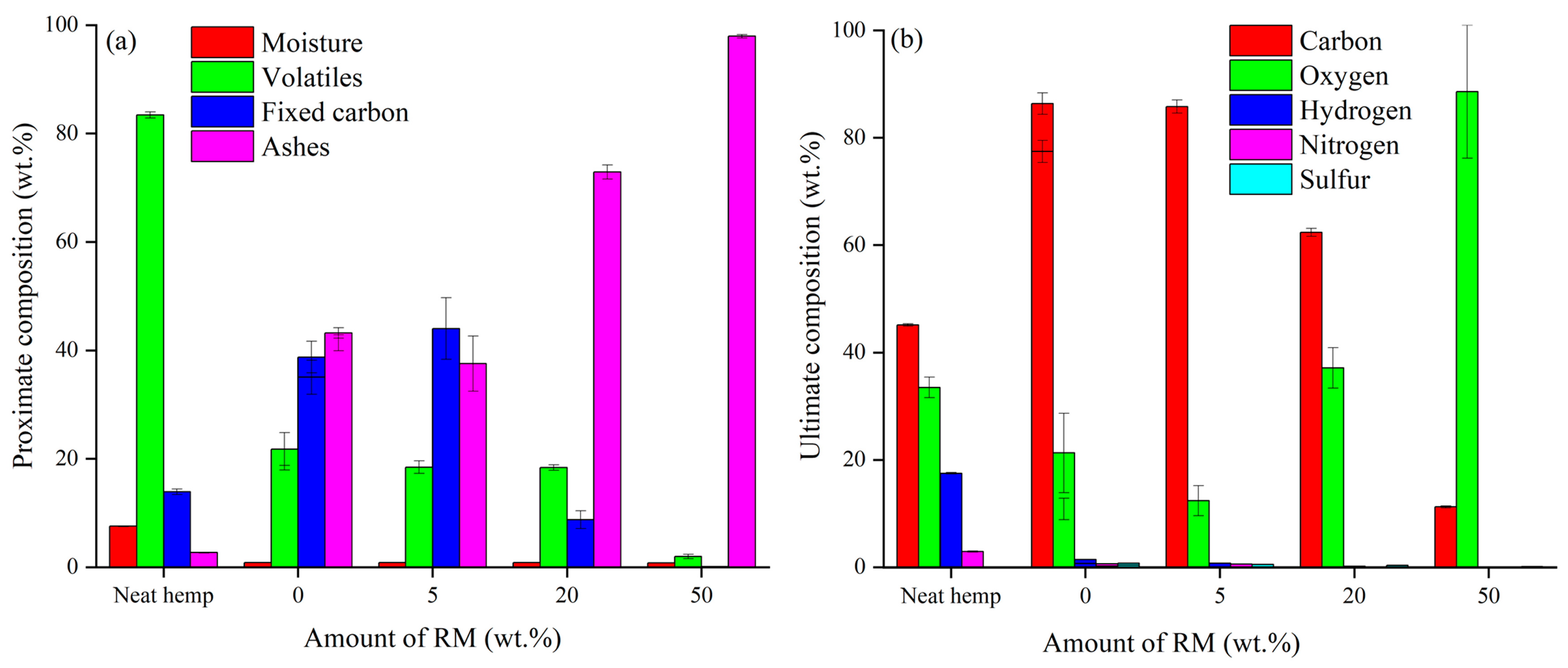

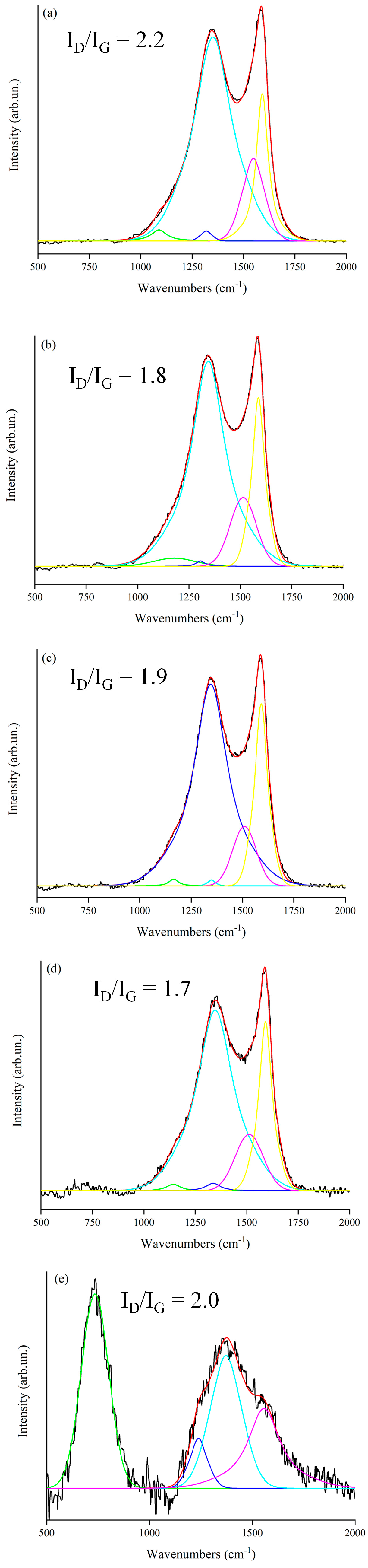
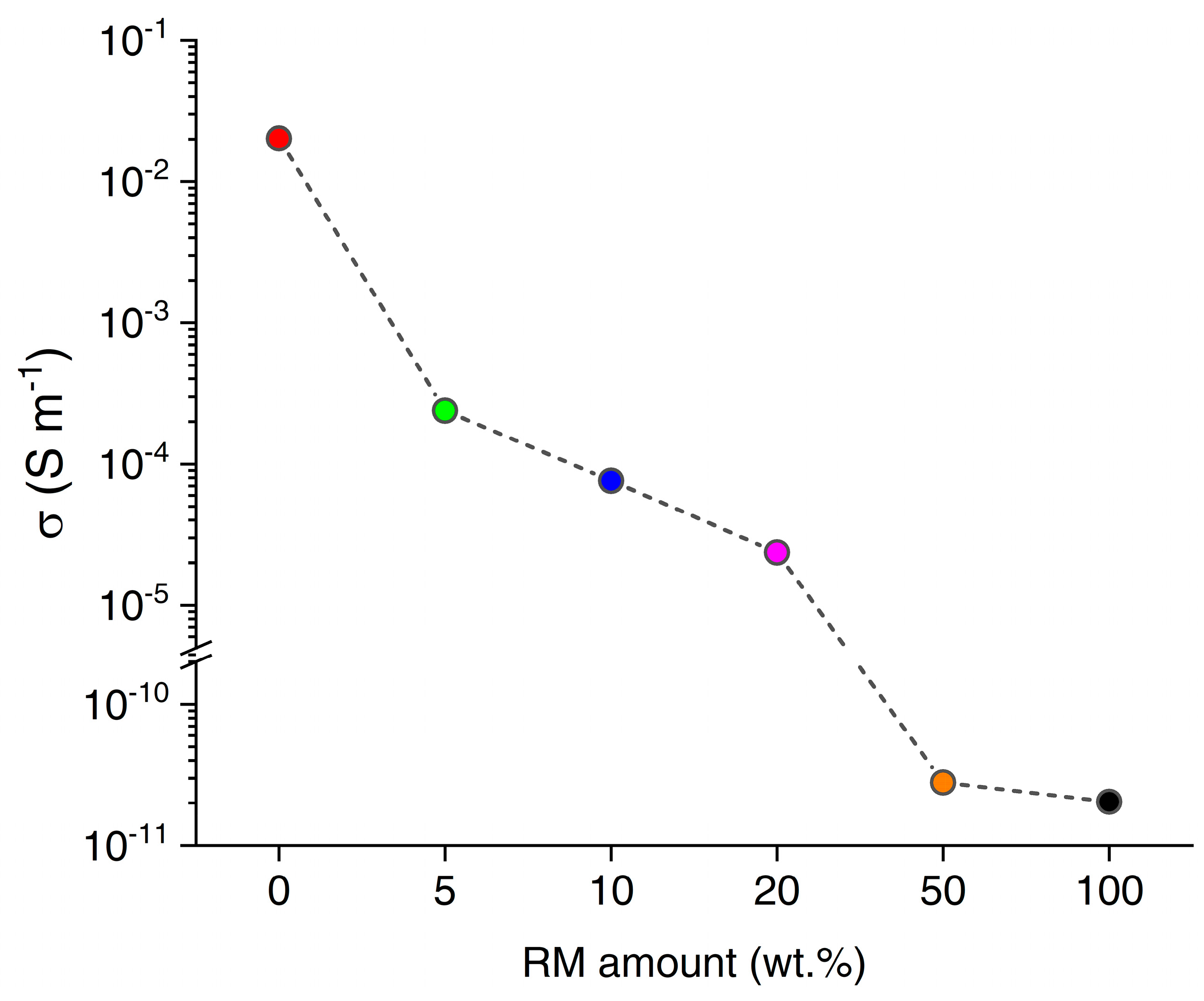
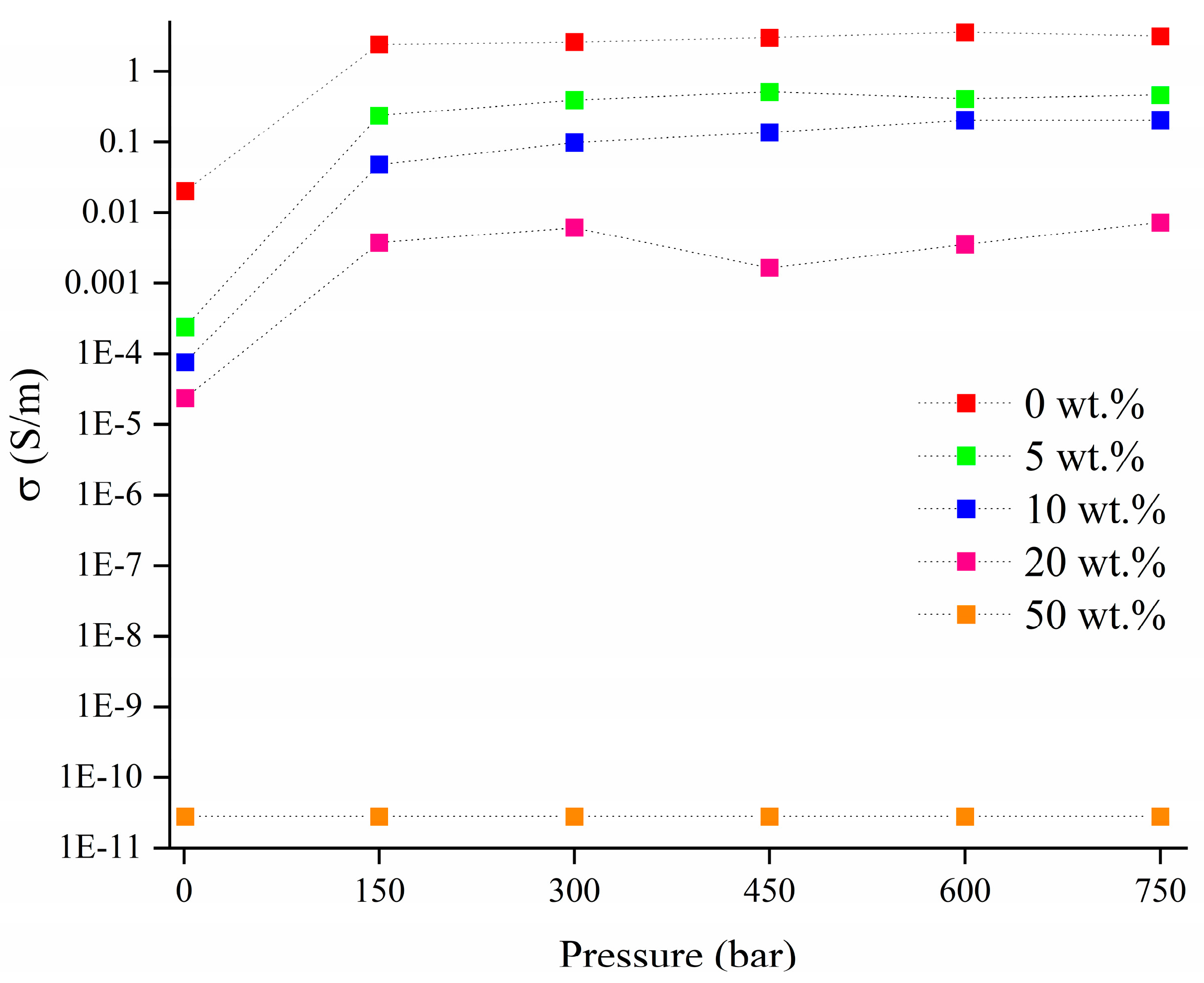

| Amount of RM (wt.%) | Surface Area (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Radius (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 250 | 0.15 | 1.2 |
| 5 | 237 | 0.16 | 1.3 |
| 10 | 167 | 0.12 | 1.4 |
| 20 | 135 | 0.08 | 1.5 |
| 50 | 20 | 0.02 | 1.7 |
| Element (wt.%) | RM Amount (wt.%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RM | 0 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 50 | |
| C | 0.0 | 71.3 | 75.8 | 46.9 | 23.7 | 7.1 |
| O | 42.9 | 7.6 | 7.8 | 22.5 | 32.0 | 35.3 |
| Na | 6.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.5 | 3.6 | 4.2 |
| K | 0.3 | 0.0 | 9.0 | 2.8 | 3.7 | 0.9 |
| Mg | 0.0 | 3.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.0 |
| Ca | 0.6 | 5.2 | 2.5 | 5.2 | 2.5 | 4.8 |
| Al | 12.1 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 6.1 | 10.1 | 15.1 |
| Si | 6.8 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 2.8 | 5.1 | 6.1 |
| P | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| S | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Ti | 3.5 | 0.0 | 3.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 4.2 |
| Fe | 26.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 8.1 | 16.3 | 22.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zecchi, S.; Ruscillo, F.; Cristoforo, G.; Bartoli, M.; Loebsack, G.; Kang, K.; Piatti, E.; Torsello, D.; Ghigo, G.; Gerbaldo, R.; et al. Effect of Red Mud Addition on Electrical and Magnetic Properties of Hemp-Derived-Biochar-Containing Epoxy Composites. Micromachines 2023, 14, 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020429
Zecchi S, Ruscillo F, Cristoforo G, Bartoli M, Loebsack G, Kang K, Piatti E, Torsello D, Ghigo G, Gerbaldo R, et al. Effect of Red Mud Addition on Electrical and Magnetic Properties of Hemp-Derived-Biochar-Containing Epoxy Composites. Micromachines. 2023; 14(2):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020429
Chicago/Turabian StyleZecchi, Silvia, Fabrizio Ruscillo, Giovanni Cristoforo, Mattia Bartoli, Griffin Loebsack, Kang Kang, Erik Piatti, Daniele Torsello, Gianluca Ghigo, Roberto Gerbaldo, and et al. 2023. "Effect of Red Mud Addition on Electrical and Magnetic Properties of Hemp-Derived-Biochar-Containing Epoxy Composites" Micromachines 14, no. 2: 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020429
APA StyleZecchi, S., Ruscillo, F., Cristoforo, G., Bartoli, M., Loebsack, G., Kang, K., Piatti, E., Torsello, D., Ghigo, G., Gerbaldo, R., Giorcelli, M., Berruti, F., & Tagliaferro, A. (2023). Effect of Red Mud Addition on Electrical and Magnetic Properties of Hemp-Derived-Biochar-Containing Epoxy Composites. Micromachines, 14(2), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020429













