Cyclic Voltammetric-Paper-Based Genosensor for Detection of the Target DNA of Zika Virus
Abstract
Highlights
- Recent report on paper-based genosensor for the diagnosis of ZIKV target DNA.
- Silver nanoparticles were characterized by XRD/UV-Vis/TEM.
- Cross-reactivity of genosensor was deduced.
- Electrochemical validation was performed through CV.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Reagents, Apparatus
2.2. Synthesis of Silver NPs
2.3. Preparation of Synthetic Serum
2.4. Development of PBGs
2.5. Deposition of the Silver Nanoparticles and Immobilization on the PBG
2.6. Stages for Electrochemical Detection
2.7. Optimization of Physicochemical Parameters
2.8. Binding of the Analyte on AgNPs/Probe/Target/PBGs
2.9. Procedure for Experimental Sample Analysis, Repeatability, and Stability Analysis
2.10. Principle behind Sensing
3. Results
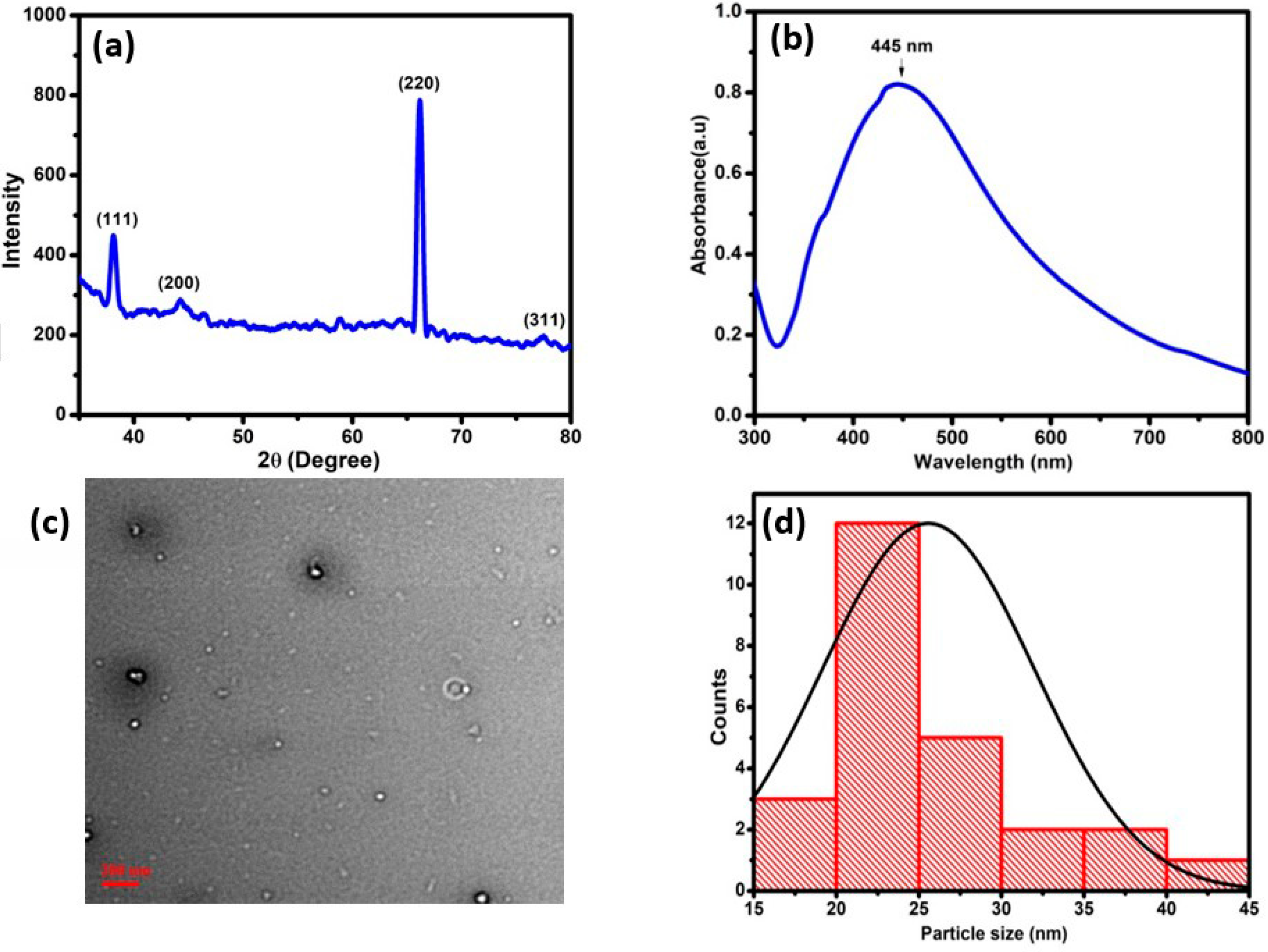
3.1. Morphological Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles
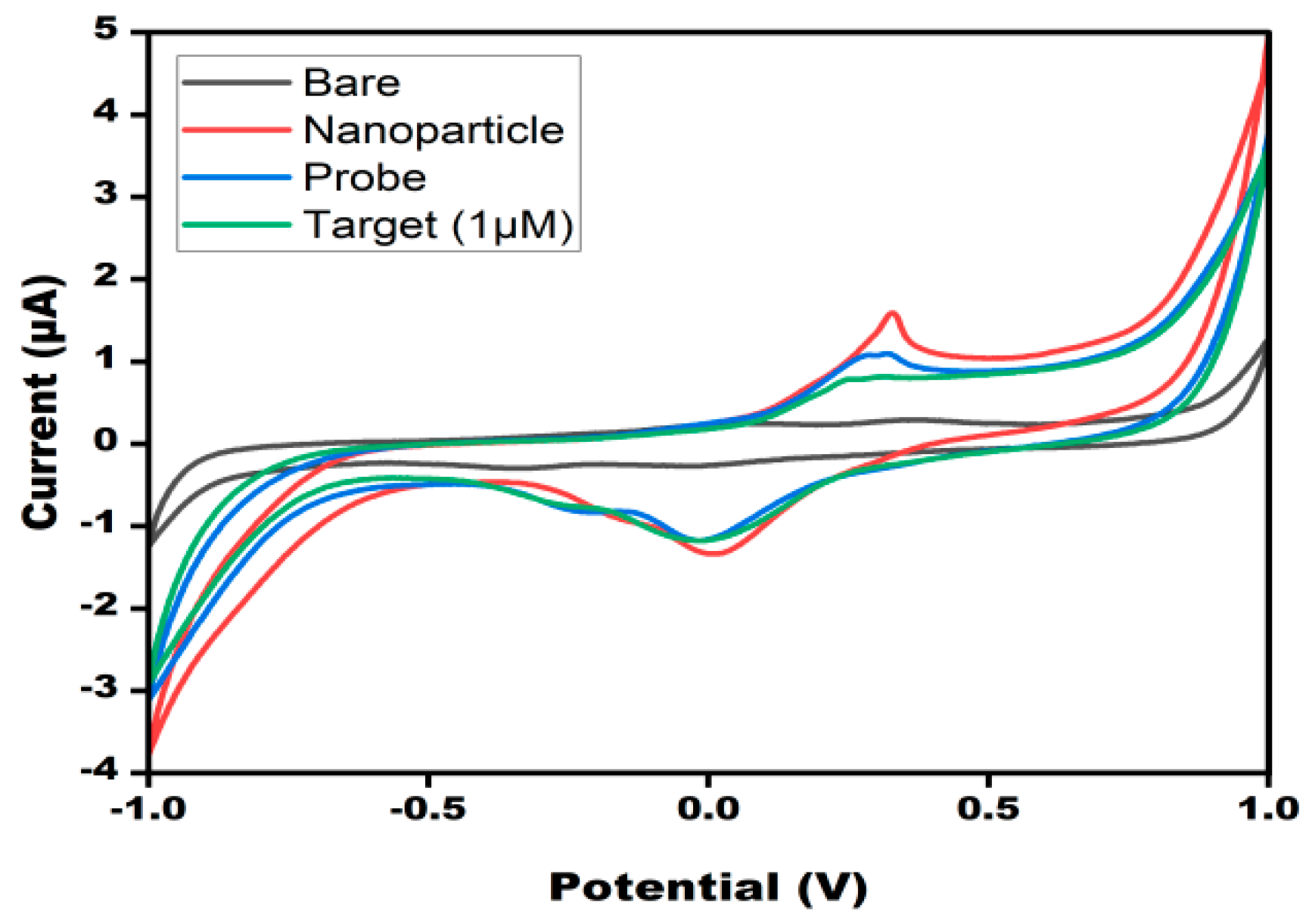
3.2. Electrochemical Properties of DNA Probe/AgNPs/PBGs
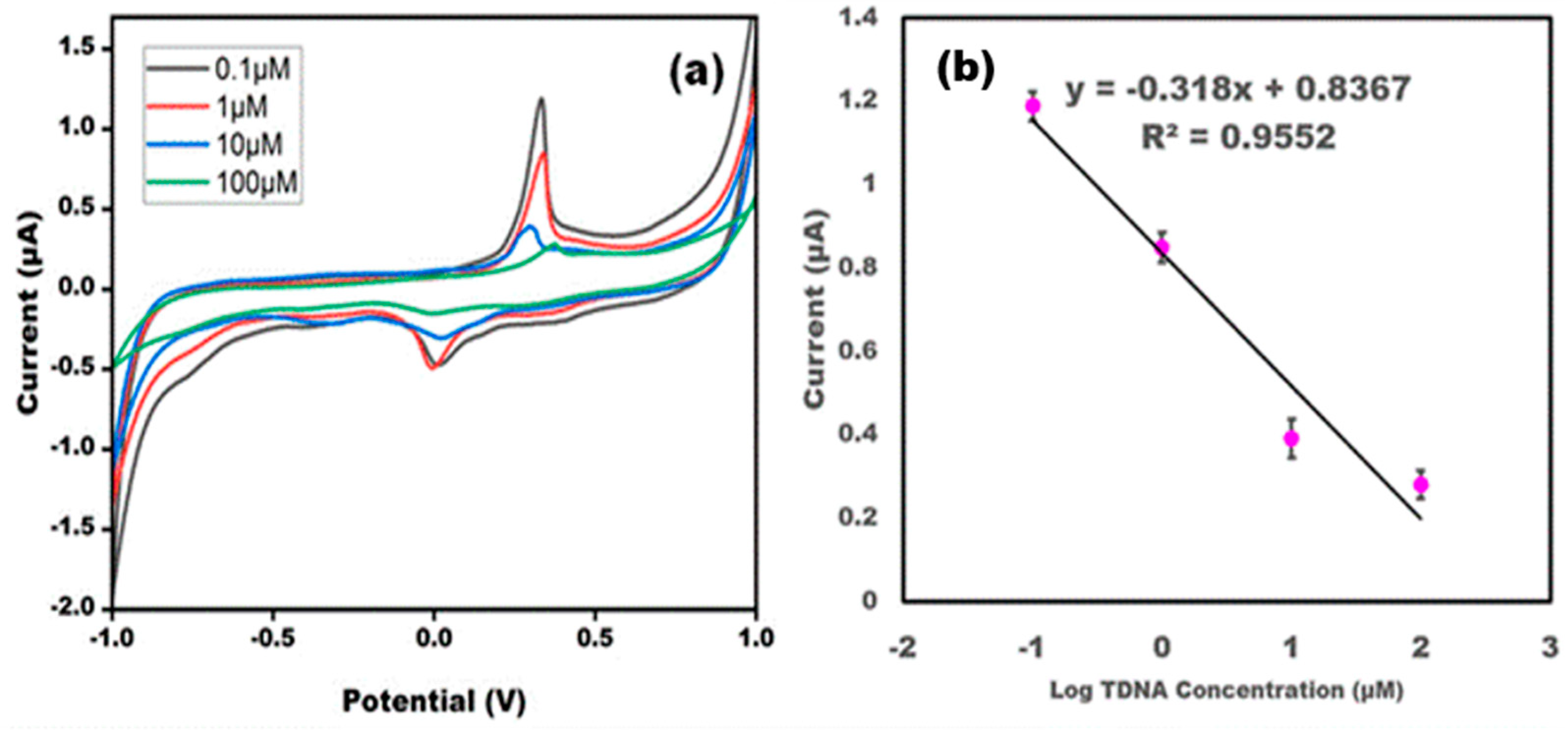
3.3. Effect of Different Target DNA Concentrations on the DNA Probe/AgNPs/PBGs
3.4. Optimization of DNA Probe/AgNP/PBG Platform in Terms of Temperature and Time
3.5. Evaluation Parameters
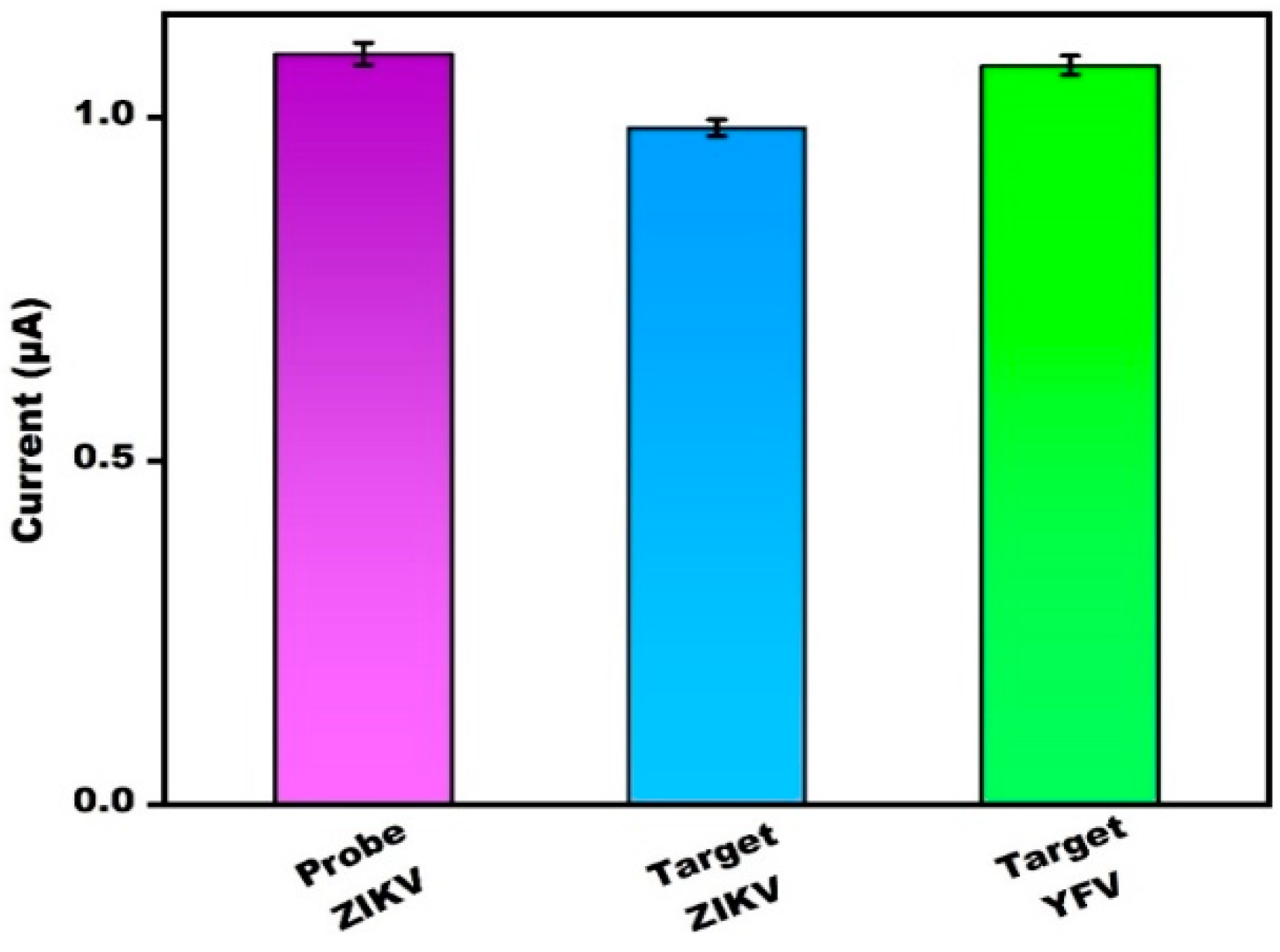
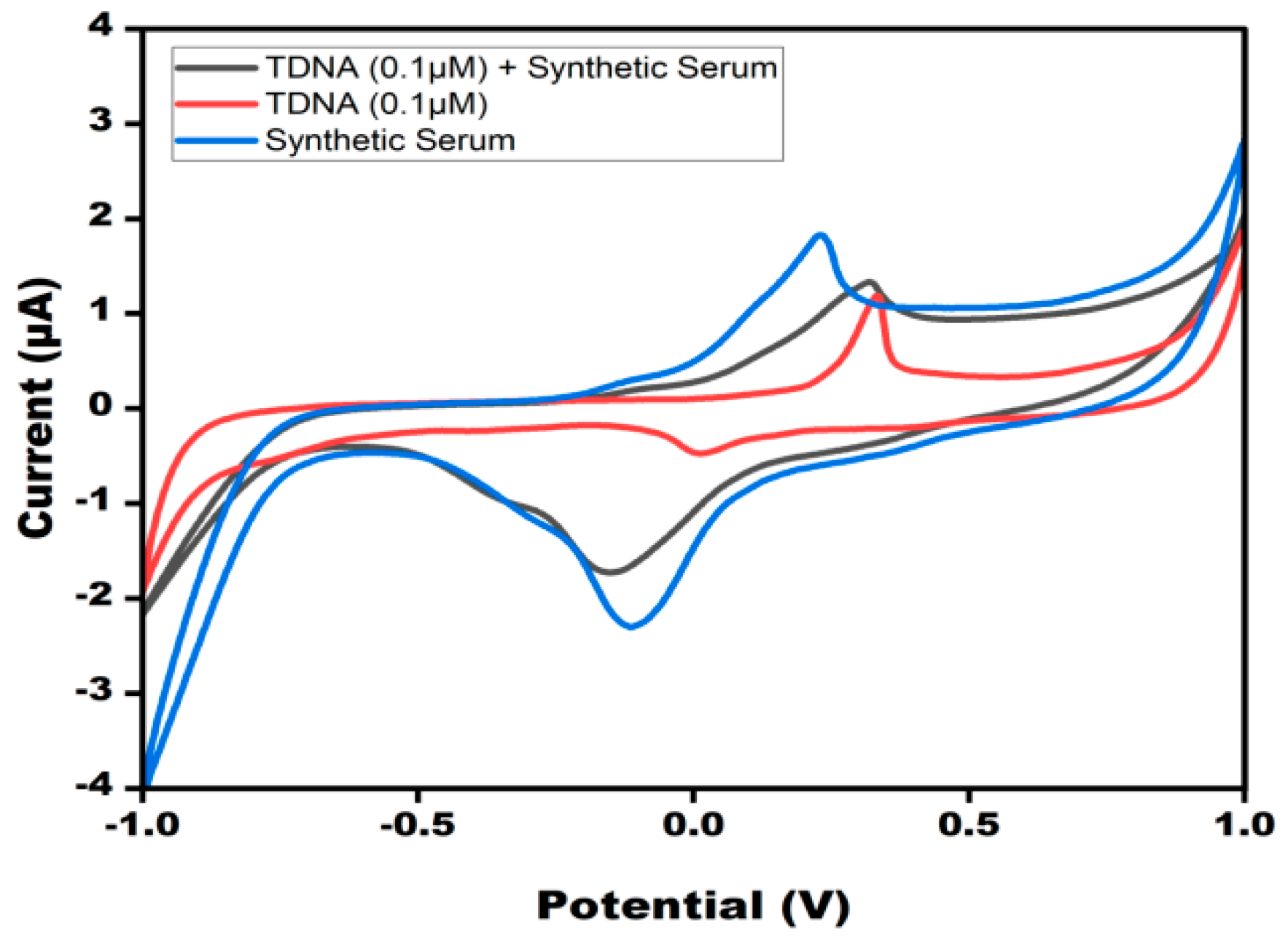
3.6. Specificity and Reliability
3.7. Analysis of Experimental Sample
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plourde, A.R.; Bloch, E.M. A literature review of Zika virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorshkov, K.; Shiryaev, S.A.; Fertel, S.; Lin, Y.W.; Huang, C.T.; Pinto, A.; Farhy, C.; Strongin, A.Y.; Zheng, W.; Terskikh, A.V. Zika virus: Origins, pathological action, and treatment strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Hansen, G.; Nitsche, C.; Klein, C.D.; Zhang, L.; Hilgenfeld, R. Crystal structure of Zika virus NS2B-NS3 protease in complex with a boronate inhibitor. Science 2016, 503, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abushouk, A.I.; Negida, A.; Ahmed, H. An updated review of Zika virus. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 53, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, A.; Yndart, A.; Kumar, S.; Jayant, R.D.; Vashist, A.; Brown, A.N.; Li, C.Z.; Nair, M. A sensitive electrochemical immunosensor for label-free detection of Zika-virus protein. Sci. Rep. 2018, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noorbakhsh, F.; Abdolmohammadi, K.; Fatahi, Y.; Dalili, H.; Rasoolinejad, M.; Rezaei, F.; Salehi-Vaziri, M.; Shafiei-Jandaghi, N.Z.; Gooshki, E.S.; Zaim, M.; et al. Zika virus infection, basic and clinical aspects: A review article. Iran. J. Public Health 2019, 48, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyamvada, L.; Quicke, K.M.; Hudson, W.H.; Onlamoon, N.; Sewatanon, J.; Edupuganti, S.; Pattanapanyasat, K.; Chokephaibulkit, K.; Mulligan, M.J.; Wilson, P.C.; et al. Human antibody responses after dengue virus infection are highly cross-reactive to Zika virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 7852, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.J.; Furuya, A.; Zou, J.; Xie, X.; Dupuis, A.P.; Kramer, L.D.; Shi, P.Y. A multiplex microsphere immunoassay for Zika virus diagnosis. eBioMedicine 2017, 36, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, I.; Puig, d.; Hiley, M.; Carré-Camps, M.; Perdomo-Celis, F.; Narváez, C.F.; Salgado, D.M.; Senthoor, D.; O’Grady, M.; Phillips, E.; et al. Rapid antigen tests for dengue virus serotypes and Zika virus in patient serum. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 27, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetti, N.P.; Bukkitgar, S.D.; Reddy, K.R.; Reddy, C.V.; Aminabhavi, T.M. ZnO-based nanostructured electrodes for electrochemical sensors and biosensors in biomedical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 15, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, M.; Faheem, A.; Asghar, W.; Cinti, S. Nano-engineered screen-printed electrodes: A dynamic tool for detection of viruses. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 1, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajigas, S.; Alzate, D.; Orozco, J. Gold nanoparticle/DNA-based nanobioconjugate for electrochemical detection of Zika virus. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moço, A.C.; Guedes, P.H.; Flauzino, J.M.; da Silva, H.S.; Vieira, J.G.; Castro, A.C.; Gomes, É.V.; Tolentino, F.M.; Soares, M.M.; Madurro, J.M.; et al. Electrochemical detection of zika virus in biological samples: A step for diagnosis point-of-care. Electroanalysis 2019, 580, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Fonseca Alves, R.; Franco, D.L.; Cordeiro, M.T.; de Oliveira Junior, E.M.; Dutra, R.A.; Sotomayor, M.D. Novel electrochemical genosensor for Zika virus based on a poly-(3-amino-4-hydroxybenzoic acid)-modified pencil carbon graphite electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 296, 126681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, H.A.; Zucolotto, V. Label-free electrochemical DNA biosensor for zika virus identification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 131, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xu, D.; Ye, Q.; Hong, S.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, N.; Shi, L.; Qin, C.F.; Xu, Z. Zika Virus Disrupts Neural Progenitor Development and Leads to Microcephaly in Mice. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Zuo, X.; Wan, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, S.; Fan, C. Electrochemical Interrogation of Interactions between Surface-Confined DNA and Methylene Blue. Sensors 2007, 7, 2671–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, M.; Lima, D.; Viana, A.G.; Fujiwara, S.T.; Pessôa, C.A.; Etto, R.M.; Wohnrath, K. A sensitive label-free impedimetric DNA biosensor based on silsesquioxane-functionalized gold nanoparticles for Zika Virus detection. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancharoen, C.; Sukjee, W.; Thepparit, C.; Jaimipuk, T.; Auewarakul, P.; Thitithanyanont, A.; Sangma, C. Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Surface Imprinting for Zika Virus Detection in Serum. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazlan, N.F.; Tan, L.L.; Karim, N.H.A.; Heng, L.Y.; Jamaluddin, N.D.; Yusof, N.Y.M.; Quay, D.H.X.; Khalid, B. Acrylic-based genosensor utilizing metal salphen labeling approach for reflectometric dengue virus detection. Talanta 2019, 198, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Chandar, Y.J.; Cao, S.; Kharasch, E.D.; Singamaneni, S.; Morrissey, J.J. Rapid, Point-of-Care, Paper-Based Plasmonic Biosensor for Zika Virus Diagnosis. Adv. Biosyst. 2017, 1, e1700096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, A.M.; Mazon, T. Early diagnosis of Zika infection using a ZnO nanostructures-based rapid electrochemical biosensor. Talanta 2019, 203, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Initial Concentration (µM) | Concentration Added (µM) | Concentration Found (µM) | Recovery (Percentage) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 | 5.1 | 102 |
| Biosensors | Linear Range | LOD | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical genosensor for Zika virus based on a poly-(3-amino4-hydroxybenzoic acid)-modified pencil carbon graphite electrode | 84.0 pM to 1.41 nM | 25.4 pM | [14] |
| Gold nanoparticle/DNA-based nanobioconjugate for electrochemical detection of Zika virus | 10 to 600 fM and from 500 fM to 10 pM of the target | 0.2 and 33 fM at the SPAuE and SPCE/Au | [12] |
| Label-free electrochemical DNA biosensor for Zika virus identification | - | 25.0 ± 1.7 nM | [15] |
| A sensitive label-free impedimetric DNA biosensor based on silsesquioxane-functionalized gold nanoparticles for Zika virus detection. | 1.0 ×10−12–1.0 ×10−6 M | 0.82 pM | [18] |
| Electrochemical biosensor based on surface imprinting for Zika virus detection in serum | 10 fM–1 μM | 9.4 fM | [19] |
| Acrylic-based genosensor utilizing metal salphen labeling approach for reflectometric dengue virus detection | 1 × 10−15 M to 1 × 10−3 M | 1.21 × 10−16 M | [20] |
| Rapid, point-of-care, paper-based plasmonic biosensor for Zika virus diagnosis | 10–105 nM | 1 nM | [21] |
| Diagnosis of Zika infection using a ZnO nanostructure-based rapid electrochemical biosensor | 0.1 nM to 100 nM | 1.00 pM | [22] |
| Cyclic voltammetric PBG-based detection of the target DNA of Zika virus | 0.1 to 100 µM | 0.1 µM | This present work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bishoyi, A.; Alam, M.A.; Hasan, M.R.; Khanuja, M.; Pilloton, R.; Narang, J. Cyclic Voltammetric-Paper-Based Genosensor for Detection of the Target DNA of Zika Virus. Micromachines 2022, 13, 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13122037
Bishoyi A, Alam MA, Hasan MR, Khanuja M, Pilloton R, Narang J. Cyclic Voltammetric-Paper-Based Genosensor for Detection of the Target DNA of Zika Virus. Micromachines. 2022; 13(12):2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13122037
Chicago/Turabian StyleBishoyi, Anirudh, Md. Anish Alam, Mohd. Rahil Hasan, Manika Khanuja, Roberto Pilloton, and Jagriti Narang. 2022. "Cyclic Voltammetric-Paper-Based Genosensor for Detection of the Target DNA of Zika Virus" Micromachines 13, no. 12: 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13122037
APA StyleBishoyi, A., Alam, M. A., Hasan, M. R., Khanuja, M., Pilloton, R., & Narang, J. (2022). Cyclic Voltammetric-Paper-Based Genosensor for Detection of the Target DNA of Zika Virus. Micromachines, 13(12), 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13122037








