Engineering of Optical and Electrical Properties of Electrodeposited Highly Doped Al:ZnO and In:ZnO for Cost-Effective Photovoltaic Device Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Reflectance Spectra of Al:ZnO and In:ZnO
3.1.1. Determination of Band-Gap Energies by Application of the KUBELKA-MUNK Approximation and the TAUC Formalism
3.1.2. Calculation of Carrier Concentrations Based on the Burstein–Moss Effect
3.1.3. Calibration of the Dependence of the Al:ZnO and In:ZnO Carrier Concentration on the AlCl3 and InCl3 Solute Dopant Concentration
3.2. Resistivity of Al:ZnO and In:ZnO Characterized by Optical and Electrical Techniques
3.3. I(V) Characteristics of Au/In:ZnO/ZnO/ZnSe/CIGS/Mo/Glass and c-Si Junctions
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papadimitriou, D.; Roupakas, G.; Sáez-Araoz, R.; Lux-Steiner, M.-C.; Nickel, N.H.; Alamé, S.; Vogt, P.; Kneissl, M. Quality CuInSe2 and Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin films processed by single-step electrochemical deposition techniques. Mater. Res. Express 2015, 2, 056402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, D.N. Structural, optical, electrical properties, and strain/stress of electrochemically deposited highly doped ZnO layers and nanostructured ZnO antireflective coatings for cost-effective photovoltaic device technology. Thin Solid Films 2016, 605, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, D.N.; Roupakas, G.; Roumeliotis, G.G.; Vogt, P.; Köhler, T. Optimization of Electrochemically Deposited Highly Doped ZnO Bilayers on Ga-Rich Chalcopyrite Selenide for Cost-Effective Photovoltaic Device Technology. Energies 2016, 9, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, D.N. Vacuum and Liquid-Phase Processing of ZnSe Buffer-Layer for Chalcopyrite Absorber Based Photovoltaic Technology. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2018, 7, P541–P561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Papadimitriou, D.; Raptis, Y.S.; Esser, N.; Richter, W.; Siebentritt, S.; Lux-Steiner, M.C. Compositional dependence of Raman scattering and photoluminescence emission in CuxGaySe2 thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 4341–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Papadimitriou, D.; Esser, N. Mapping of gradient composition CuxGaySe2 film properties using Raman and PL-spectroscopy. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2004, 37, 2267–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Papadimitriou, D.; Esser, N. Optical characterization of epitaxial CuxGaySe2-layers by photoreflectance spectroscopy. Thin Solid Films 2004, 451–452, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, D.; Esser, N.; Xue, C. Structural properties of chalcopyrite thin films studied by Raman spectroscopy. Phys. Status Sol. 2005, 242, 2633–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoropoulou, S.; Papadimitriou, D.; Rega, N.; Siebentritt, S.; Lux-Steiner, M.-C. Raman and photoreflectance study of CuIn1−xGaxSe2 epitaxial layers. Thin Solid Films 2006, 511–512, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-Y.; Papadimitriou, D.; Zoumpoulakis, L.; Simitzis, J.; Lux-Steiner, M.-C. Compositional and temperature dependence of the energy band gap of CuxInySe2 epitaxial layers. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 165102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoropoulou, S.; Papadimitriou, D.; Anestou, K.; Cobet, C.; Esser, N. Optical properties of CuIn1−xGaxSe2 quaternary alloys for solar-energy conversion. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2009, 24, 015014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anestou, K.; Papadimitriou, D. Optical modulation techniques applied in the analysis of chalcopyrite semiconductor heterostructures. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 215305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, D. Application of optical spectroscopic techniques in the characterization of elastic strain effects in semiconductor heterostructures and nanostructures and in semiconductor-based thin-film solar cells. Phys. Status Solidi B 2015, 252, 30–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, R.; Kaufmann, C.A.; Efimova, V.; Rissom, T.; Hoffmann, V.; Schock, H.-W. Investigation of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin-film formation during the multi-stage co-evaporation process. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2013, 21, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainz, R.; Weber, A.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, H.; Levcenko, S.; Klaus, M.; Pistor, P.; Klenk, R.; Schock, H.-W. Time-resolved investigation of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 growth and Ga gradient formation during fast selenization of metallic precursors. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2015, 23, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, U.; Schmidt, M. Electronic properties of ZnO/CdS/Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells-aspects of heterojunction formation. Thin Solid Films 2001, 387, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulmeyer, T.; Kniese, R.; Hunger, R.; Jaegermann, W.; Powalla, M.; Klein, A. Influence of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 band gap on the valence band offset with CdS. Thin Solid Films 2004, 451–452, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, K.L.; Paulson, P.D.; Dutta, V. Thin-Film Solar Cells: An Overview. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2004, 12, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariskos, D.; Spiering, S.; Powalla, M. Buffer layers in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells and modules. Thin Solid Films 2005, 480–481, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, A.; Pettenkofer, C. Surface orientation dependent band alignment for CuInSe2–ZnSe–ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 113503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellmer, K.; Klein, A. ZnO and Its Applications. In Transparent Conductive Zinc Oxide: Basics and Applications in Thin Film Solar Cells; Ellmer, K., Klein, A., Rech, B., Eds.; Springer Series in Materials Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Aé, L.; Aichele, C.; Lux-Steiner, M.-C. High internal quantum efficiency ZnO nanorods prepared at low temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 161906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janotti, A.; Van de Walle, C.G. Fundamentals of zinc oxide as a semiconductor. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2009, 72, 126501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingshirn, C.; Hauschild, R.; Priller, H.; Decker, M.; Zeller, J. ZnO rediscovered—Once again!? Superlattices Microstruct. 2005, 38, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingshirn, C.; Fallert, J.; Zhou, H.; Sartor, J.; Thiele, C.; Maier-Flaig, F.; Schneider, D.; Kalt, H. 65 years of ZnO research—Old and very recent results. Phys. Status Solidi B 2010, 247, 1424–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, F.; Xu, J.; Joshi, P.C.; Bridges, C.A.; Paranthaman, M.P. ZnO Doping and Defect Engineering—A Review. In Semiconductor Materials for Solar Photovoltaic Cells; Paranthaman, M.P., Wong-Ng, W., Bhattacharya, R.N., Eds.; Springer Series in Materials Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 105–140. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Isshiki, M. Wide-Bandgap II-VI Semiconductors: Growth and Properties. In Springer Handbook of Electronic and Photonic Materials; Kasap, S., Capper, P., Eds.; Springer Science+Business Media, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 325–342. [Google Scholar]
- Özgür, Ü.; Alivov, Y.I.; Liu, C.; Teke, A.; Reshchikov, M.A.; Doğan, S.; Avrutin, V.; Cho, S.-J.; Morkoç, H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morkoç, H.; Özgür, Ü. Zinc Oxide: Fundamentals, Materials and Device Technology; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–467. [Google Scholar]
- Adachi, S. Properties of Group-IV, III-V and II-VI Semiconductors; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Adachi, S. III-V Ternary and Quaternary Compounds. In Springer Handbook of Electronic and Photonic Materials; Kasap, S., Capper, P., Eds.; Springer Science+Business Media, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 735–752. [Google Scholar]
- Hanada, T. Basic Properties of ZnO, GaN, and Related Materials. In Oxide and Nitride Semiconductors: Processing, Properties, and Applications; Yao, T., Hong, S.-K., Eds.; Springer Advances in Materials Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Papadimitriou, D.N. Calibration of Polarization Fields and Electro-Optical Response of Group-III Nitride Based c-Plane Quantum-Well Heterostructures by Application of Electro-Modulation Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietl, T.; Ohno, H.; Matsukura, F.; Cibert, J.; Ferrand, D. Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science 2000, 287, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, D.P.; Heo, Y.W.; Ivill, M.P.; Ip, K.; Pearton, S.J.; Chisholm, M.F.; Steiner, T. ZnO: Growth, doping & processing. Mater. Today 2004, 7, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, J.G.; Reynolds, C.L. Progress in ZnO Acceptor Doping: What Is the Best Strategy? Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2014, 2014, 457058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Gu, S.-L.; Ye, J.-D.; Zhu, S.-M.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, Y.-D. Recent progress of the native defects and p-type doping of zinc oxide. Chin. Phys. B 2017, 26, 047702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, T.; Nandur, A.S.; Christian, R.; Vasekar, P.; Desu, S.; Westgate, C.; Koukis, D.I.; Arenas, D.J.; Tanner, D.B. Transmittance from visible to mid infra-red in AZO films grown by atomic layer deposition system. Sol. Energy 2012, 86, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, R.; Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Wu, J.; Wu, X.; Qin, W. Enhanced Performance in Al-Doped ZnO Based Transparent Flexible Transparent Thin-Film Transistors Due to Oxygen Vacancy in ZnO Film with Zn–Al–O Interfaces Fabricated by Atomic Layer Deposition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 11711–11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, F.; Stashans, A. Al-doped ZnO: Electronic, electrical and structural properties. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2010, 71, 784–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avadhut, Y.S.; Weber, J.; Hammarberg, E.; Feldmann, C.; Schmedt-auf-der-Günne, J. Structural investigation of aluminium doped ZnO nanoparticles by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 11610–11625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Yang, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cao, J. Electronic Structure and Optical Properties of Al-doped ZnO from Hybrid Functional Calculations. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2015, 46, 985–990. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Alonso, D.; Potts, S.E.; van Helvoirt, C.A.A.; Verheijen, M.A.; Kessels, W.M.M. Atomic layer deposition of B-doped ZnO using triisopropyl borate as the boron precursor and comparison with Al-doped ZnO. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 3095–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Du, J.; Tang, L.; Tian, Y.; Xue, F.; Jiang, Q.; Pan, S. Influence of boron doping amount on properties of ZnO:B films grown by LPCVD technique and its correlation to a-Si:H/μc-Si:H tandem solar cells. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 6654–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranovich, J.; Ortiz, A.; Bube, R.H. Optical and electrical properties of ZnO films prepared by spray pyrolysis for solar cell applications. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1979, 16, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraguay, F.D.; Estrada, W.L.; Acosta, D.R.N.; Andrade, E.; Miki-Yoshidac, M. Growth, structure and optical characterization of high quality ZnO thin films obtained by spray pyrolysis. Thin Solid Films 1999, 350, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayouchi, R.; Leinen, D.; Martın, F.; Gabas, M.; Dalchiele, E.; Ramos-Barrado, J.R. Preparation and characterization of transparent ZnO thin films obtained by spray pyrolysis. Thin Solid Films 2003, 426, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, A.; Kaid, M.A.; El-Sayed, N.Z.; Ibrahim, A.A. Physical properties of ZnO thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis technique. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 7844–7848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayan, E.M.; Petrov, V.V.; Volkova, M.G.; Yu Storozhenko, V.; Chernyshev, A.V. SnO2–ZnO nanocomposite thin films: The influence of structure, composition and crystallinity on optical and electrophysical properties. J. Adv. Dielectr. 2021, 11, 2160008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, K.; Oyama, S.; Kato, M.; Oshima, M.; Yoneta, M.; Ikari, T. Annealing effects of In-doped ZnO films grown by spray pyrolysis method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2008, 100, 082019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licurgo, J.S.C.; de Almeida Neto, G.R.; Paes Junior, H.R. Structural, electrical and optical properties of copper-doped zinc oxide films deposited by spray pyrolysis. Cerâmica 2020, 66, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, R.; Maldonado, A.; Vega-Pérez, J.; Acosta, D.R.; De La Luz Olvera, M. Indium Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films Deposited by Ultrasonic Chemical Spray Technique, Starting from Zinc Acetylacetonate and Indium Chloride. Materials 2014, 7, 5038–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roguai, S.; Djelloul, A. Structural and optical properties of Cu-doped ZnO films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumahoro, I.; Schmerber, G.; Douayar, A.; Colis, S.; Abd-Lefdil, M.; Hassanain, N.; Berrada, A.; Muller, D.; Slaoui, A.; Rinnert, H.; et al. Structural, optical, and electrical properties of Yb-doped ZnO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis method. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 033708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El hat, A.; Chaki, I.; Essajai, R.; Mzerd, A.; Schmerber, G.; Regragui, M.; Belayachi, A.; Sekkat, Z.; Dinia, A.; Slaoui, A.; et al. Growth and Characterization of (Tb,Yb) Co-Doping Sprayed ZnO Thin Films. Crystals 2020, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, S.; Li, L. Fabrication, structure, and photocatalytic activities of boron-doped ZnO nanorods hydrothermally grown on CVD diamond film. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2012, 539–540, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.H.; Sharma, N.; Varkia, A.; Kumar, J. Structural and optical properties of copper doped ZnO nanoparticles and thin films. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2014, 5, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, A.; Ahmad, M.; Rahmanuddin; Khan, S.H.; Aziz, U.; Ali, Z.; Khan, A.; Mahmood, A. The role of Al doping on ZnO nanowire evolution and optical band gap tuning. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojorge, C.D.; Cánepa, H.R.; Gilabert, U.E.; Silva, D.; Dalchiele, E.A.; Marotti, R.E. Synthesis and optical characterization of ZnO and ZnO:Al nanocrystalline films obtained by the sol-gel dip-coating process. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2007, 18, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsayn, C.-Y.; Hsu, W.-T. Sol–gel derived undoped and boron-doped ZnO semiconductor thin films: Preparation and characterization. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 7425–7432. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, B.C.; Chaudhri, A.K. Sol−Gel-Derived Cu-Doped ZnO Thin Films for Optoelectronic Applications. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 21877–21881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, G.; Guerra, D.N.; Leinen, D.; Ramos-Barrado, J.R.; Marotti, R.E.; Dalchiele, E.A. Indium doped zinc oxide thin films obtained by electrodeposition. Thin Solid Films 2005, 490, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovchinov, K.; Ganchev, M.; Rachkova, A.; Nichev, H.; Angelov, O.; Mikli, V.; Dimova-Malinovska, D. Structural and optical properties of electrochemically deposited ZnO films in electrolyte containing Al2(SO4)3. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 398, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.; Li, S. Growth and Electrical Properties of Doped ZnO by Electrochemical Deposition. New J. Glass Ceram. 2012, 2, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, D.; Roupakas, G.; Chatzitheodoridis, E.; Halambalakis, G.; Tselepis, S.; Sáez-Araoz, R.; Lux-Steiner, M.C.; Nickel, N.H.; Alamé, S.; Vogt, P.; et al. Chemical and Electrochemical Processing of High Quality CIS/CIGS Absorber, Buffer, Window, and Anti-Reflective Coating for Low Cost Photovoltaic Technology. In Proceedings of the 29th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition, PVSEC, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 22–26 September 2014; pp. 1812–1815. [Google Scholar]
- Cullity, B.D. Elements of X-ray Diffraction; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, A.D.V.; Arruda, C.C.; Fernandes, L.; Antunes, M.L.P.; Kiyohara, P.K.; Salomão, R. Characterization of aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3) for use as a porogenic agent in castable ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrent, J.; Barrón, V. Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy of Iron Oxides. In Encyclopedia of Surface and Colloid Science; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 1438–1446. [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo Morales, A.; Sánchez Mora, E.; Pal, U. Use of diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for optical characterization of un-supported nanostructures. Rev. Mex. Fís. 2007, 53, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval, C.; Kim, A.D. Deriving Kubelka–Munk theory from radiative transport. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2014, 31, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc, J.; Grigorovici, R.; Vancu, A. Optical Properties and Electronic Structure of Amorphous Germanium. Phys. Stat. Sol. 1966, 15, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooten, F. Optical Properties of Solids; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, T.S.; Burrell, G.J.; Ellis, B. Semiconductor Opto-Electronics; Halsted Press Division, Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Amirtharaj, P.M.; Seiler, D.G. Optical Properties of Semiconductors. In Handbook of Optics Volume II Devices Measurements and Properties, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 36.1–36.96. [Google Scholar]
- Grolik, B.; Kopp, J. Optical Properties of Thin Semiconductor Films. 2003. Available online: Academia.edu (accessed on 3 November 2022).
- Mistrik, J.; Kasap, S.; Ruda, H.E.; Koughia, C.; Singh, J. Optical Properties of Electronic Materials: Fundamentals and Characterization. In Springer Handbook of Electronic and Photonic Materials; Kasap, S., Capper, P., Eds.; Springer Science+Business Media, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 47–78. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, J.C.S.; Taveira, R.J.S.; Lima, C.F.R.A.C.; Mendes, A.; Santos, L.M.N.B.F. Optical band gaps of organic semiconductor materials. Opt. Mater. 2016, 58, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souri, D.; Tahan, Z.E. A new method for the determination of optical band gap and the nature of optical transitions in semiconductors. Appl. Phys. B 2015, 119, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgonos, A.; Mason, T.O.; Poeppelmeier, K.R. Direct optical band gap measurement in polycrystalline semiconductors: A critical look at the Tauc method. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 240, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zeghbroeck, B. Principles of Semiconductor Devices, Chapter 2: Semiconductor Fundamentals, 2.6. Carrier Densities. 2011. Available online: http://ecee.colorado.edu/~bart/book/book/chapter2/ch2_6.htm (accessed on 3 November 2022).
- Burstein, E. Anoma1ous Optical Absorption Limit in InSb. Phys. Rev. 1954, 93, 632–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, T.S. The Interpretation of the Properties of Indium Antimonide. Proc. Phys. Soc. B 1954, 67, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingshirn, C.F.; Meyer, B.K.; Waag, A.; Hoffmann, A.; Geurts, J. Zinc Oxide: From Fundamental Properties towards Novel Applications; Springer Series in Materials Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield, J.J. Fine structure in the optical absorption edge of anisotropic crystals. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1960, 15, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.K.; Alves, H.; Hofmann, D.M.; Kriegseis, W.; Forster, D.; Bertram, F.; Christen, J.; Hoffmann, A.; Straßburg, M.; Dworzak, M.; et al. Bound exciton and donor-acceptor pair recombinations in ZnO. Phys. Stat. Sol. (B) 2004, 241, 231–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankove, J.I. Optical Processes in Semiconductors; Prentice-Hall Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Pankove, J.I.; Aigrain, P. Optical Absorption of Arsenic-Doped Degenerate Germanium. Phys. Rev. 1962, 126, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fistul’, V.I. Optical Properties of Heavily Doped Semiconductors. In Heavily Doped Semiconductors. Monographs in Semiconductor Physics; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1969; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, P.K. Theory of Optical Processes in Semiconductors: Bulk and Microstructures; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.C.; McGregor, J.M.; Roulston, D.J. Band-gap narrowing in novel III-V semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 68, 3747–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.C.; Roulston, D.J. A simple expression for band gap narrowing (BGN) in heavily doped Si, Ge, GaAs and GexSi1−x strained layers. Solid-State Electron. 1991, 34, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.E.; Moon, P.; Kim, S.; Myoung, J.-M.; Jang, H.W.; Bang, J.; Yun, I. Effect of carrier concentration on optical bandgap shift in ZnO:Ga thin films. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 6304–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziabari, A.A.; Rozati, S.M. Carrier transport and bandgap shift in n-type degenerate ZnO thin films: The effect of band edge nonparabolicity. Phys. B 2012, 407, 4512–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, K.G.; Aznan, N.M.; Yam, F.K.; Ng, S.S.; Pung, S.Y. New Insights on the Burstein-Moss Shift and Band Gap Narrowing in Indium-Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Ghosh, S.; Chaudhuri, S.; Pal, A.K. Studies on Electron Transport Properties and the Burstein-Moss Shift in Indium-doped ZnO Films. Thin Solid Films 1991, 204, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröger, F.A. The Chemistry of Imperfect Crystals; North-Holland Pub. Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Serier, H.; Gaudon, M.; Ménétrier, M. Al-doped ZnO powdered materials: Al solubility limit and IR absorption properties. Solid State Sci. 2009, 11, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanzaro, S.; la Magna, A.; Smecca, E.; Mannino, G.; Pellegrino, G.; Fazio, E.; Neri, F.; Alberti, A. Controlled Al3+ Incorporation in the ZnO Lattice at 188 °C by Soft Reactive Co-Sputtering for Transparent Conductive Oxides. Energies 2016, 9, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevva, H.; Palla, S.; Sankaranarayanan, S. Characterization and Properties Evaluation of Conducting Al-doped ZnO at low temperature by ECD Method. Orient. J. Chem. 2015, 31, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanyuk, V.; Dmitruk, N.; Karpyna, V.; Lashkarev, G.; Popovych, V.; Dranchuk, M.; Pietruszka, R.; Godlewski, M.; Dovbeshko, G.; Timofeeva, I.; et al. Optical and Electrical Properties of Highly Doped ZnO:Al Films Deposited by Atomic Layer Deposition on Si Substrates in Visible and Near Infrared Region. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2016, 129, A-36–A-40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, R.; Ko, Y.; Dutta, P.S. Burstein-Moss shift in impurity-compensated bulk Ga1−xInxSb substrates. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 96, 5349–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.; Yang, C.S.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, K.H. The Burstein-Moss effect in Cu2GeSe3:Co2+ single crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 2914–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Chowdhury, A.H.; Bahrami, B.; Khan, M.R.; Qiao, Q.; Kumar, M. Origin of enhanced carrier mobility and electrical conductivity in seed-layer assisted sputtered grown Al doped ZnO thin films. Thin Solid Films 2020, 700, 137916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, S.; Banerji, P.; Majumder, S.B. Properties of indium doped nanocrystalline ZnO thin films and their enhanced gas sensing performance. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 61230–61238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhuo, Y.; Tu, W.; Li, Z.; Ma, X.; Pei, Y.; Wang, G. High mobility indium tin oxide thin film and its application at infrared wavelengths: Model and experiment. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 22123–22134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Lim, K.; Song, J. Highly textured ZnO thin films doped with indium prepared by the pyrosol method. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 1996, 43, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Mende, L.; MacManus-Driscoll, J.L. ZnO—Nanostructures, defects, and devices. Mater. Today 2007, 10, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellmer, K.; Bikowski, A. Intrinsic and extrinsic doping of ZnO and ZnO alloys. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 413002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desal, P.D.; Chu, T.K.; James, H.M.; Ho, C.Y. Electrical Resistivity of Selected Elements. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1984, 13, 1069–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Scofield, J.H.; Duda, A.; Albin, D.; Ballard, B.L.; Predecki, P.K. Sputtered Molybdenum Bilayer Back Contact for Copper Indium Diselenide-Based Polycrystalline Thin-Film Solar Cells. Thin Solid Films 1995, 260, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-F.; Wang, S.-J.; Lee, W.-D.; Chen, M.-H.; Wei, C.-N.; Bor, H.-Y.Y. Preparation and Characterization of Molybdenum Thin Films by Direct-Current Magnetron Sputtering. Atlas J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 2, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klenk, R.; Lux-Steiner, M.-C. Chalcopyrite Based Solar Cells. In Thin Film Solar Cells: Fabrication, Characterization and Applications; Poortmans, J., Arkhipov, V., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2006; pp. 237–275. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, P.; Hariskos, D.; Lotter, E.; Paetel, S.; Wuerz, R.; Menner, R.; Wischmann, W.; Powalla, M. New world record efficiency for Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin-film solar cells beyond 20%. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2011, 19, 894–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.; Wuerz, R.; Hariskos, D.; Lotter, E.; Witte, W.; Powalla, M. Effects of heavy alkali elements in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells with efficiencies up to 22.6%. Phys. Status Solidi RRL 2016, 10, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, R.; Yagioka, T.; Adachi, S.; Handa, A.; Tai, K.F.; Kato, T.; Sugimoto, H. New World Record Cu(In,Ga)(Se,S)2 Thin Film Solar Cell Efficiency Beyond 22%. In Proceedings of the IEEE 43rd Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC), Portland, OR, USA, 5–10 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, T.; Wu, J.-L.; Hirai, Y.; Sugimoto, Y.H.; Bermudez, V. Record Efficiency for Thin-Film Polycrystalline Solar Cells Up to 22.9% Achieved by Cs Treated Cu(In,Ga)(Se,S)2. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2019, 9, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kimoto, Y.; Yasaki, Y.; Kato, T.; Sugimoto, H. Cd-Free Cu(In,Ga)(Se,S)2 Thin-Film Solar Cell With Record Efficiency of 23.35%. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2019, 9, 1863–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Koch, A.; Wan, C.; Rensberg, J.; Zhang, Z.; Salman, J.; Hafermann, M.; Schaal, M.; Xiao, Y.; Wambold, R.; et al. Tuning carrier density and phase transitions in oxide semiconductors using focused ion beams. Nanophotonics 2022, 11, 3923–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
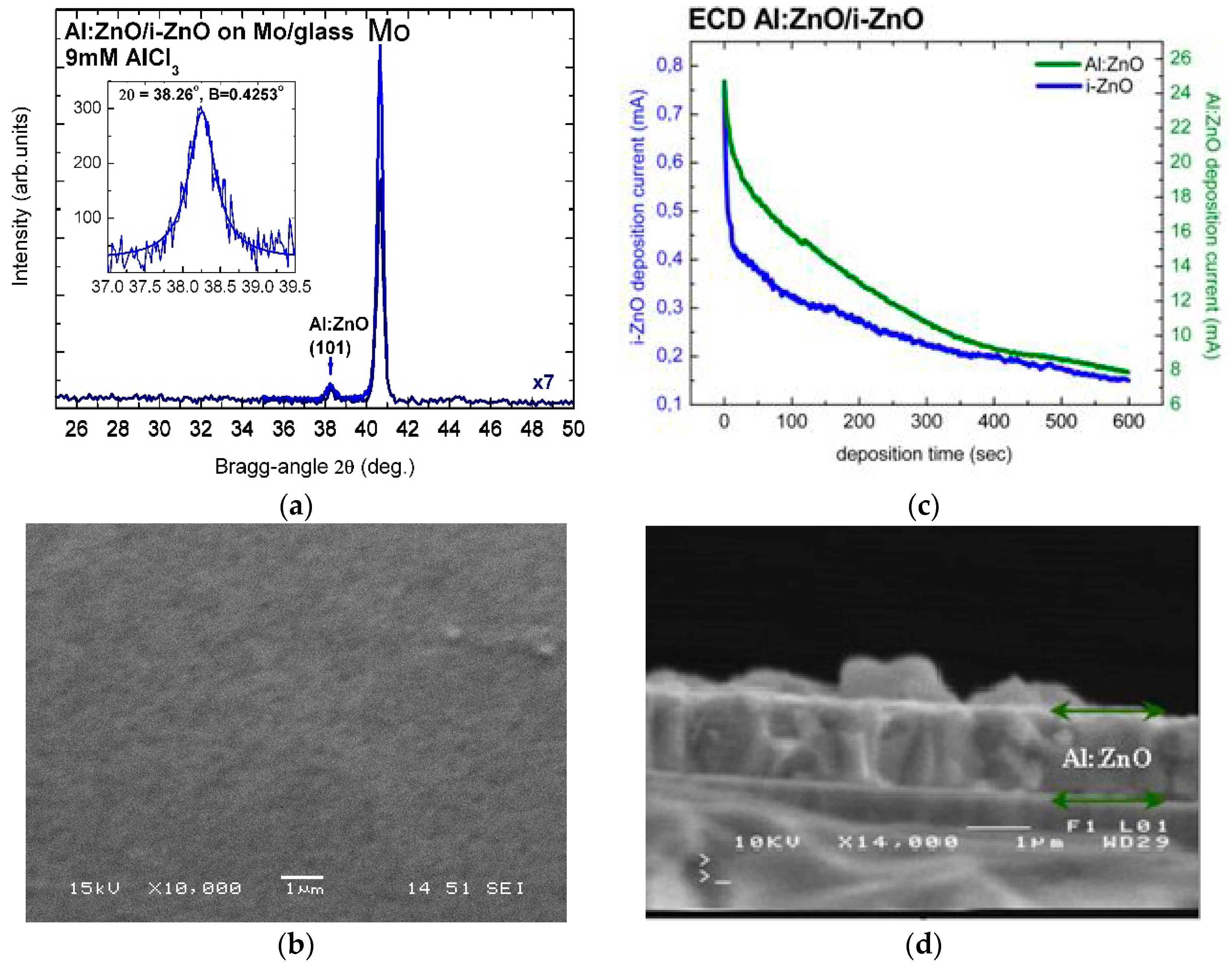
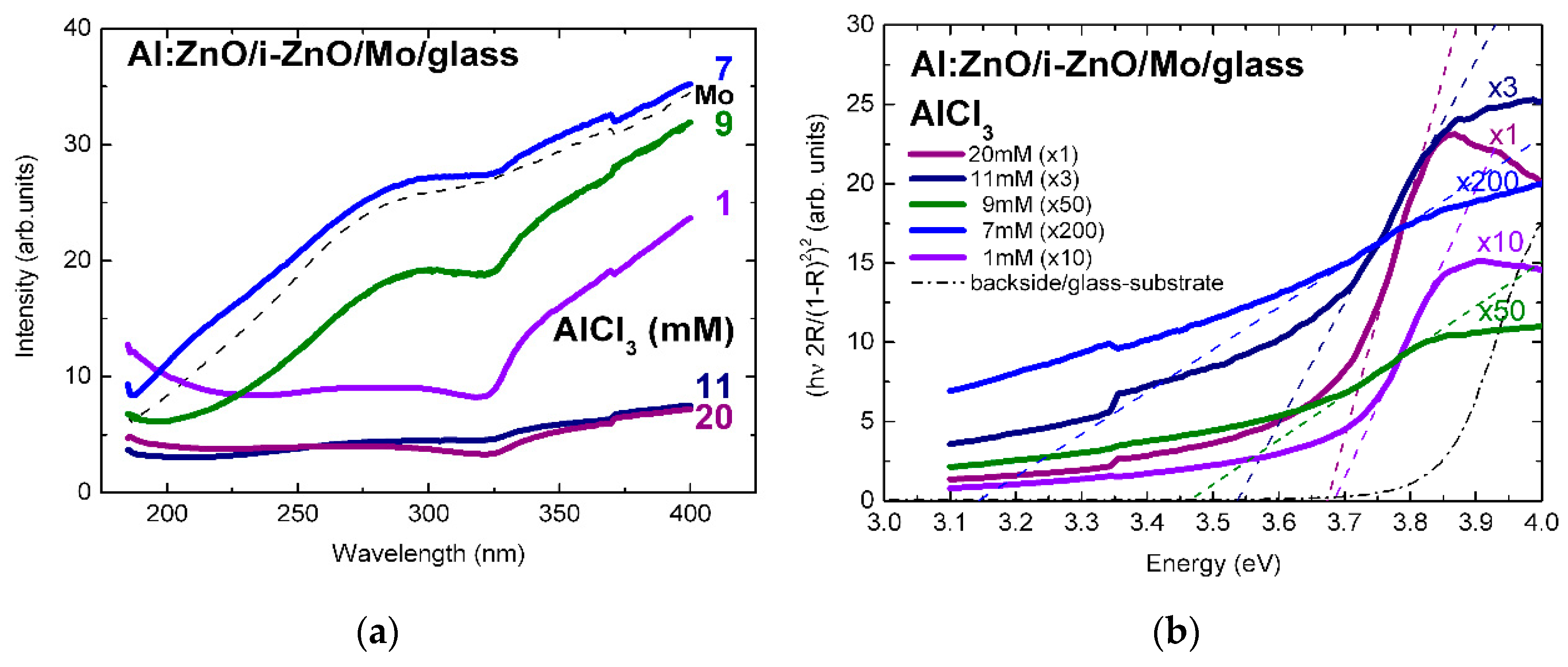
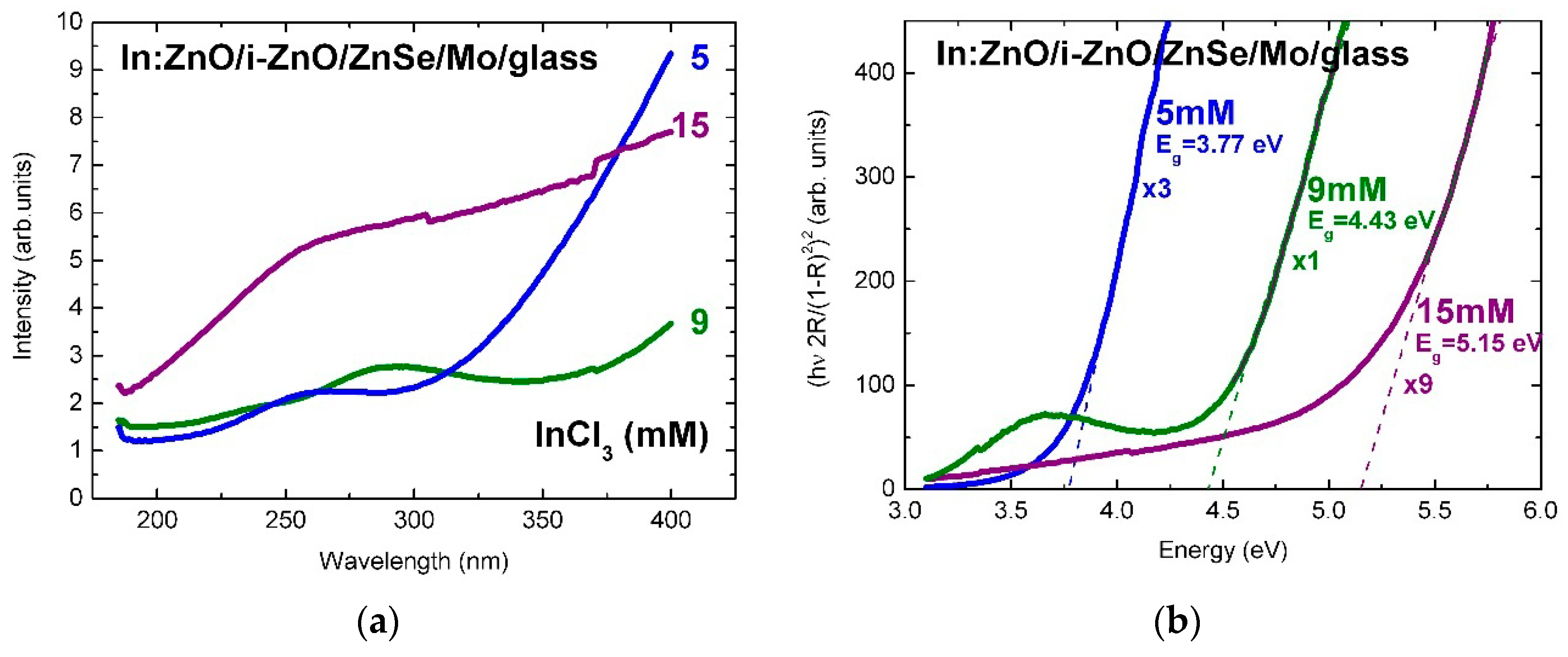
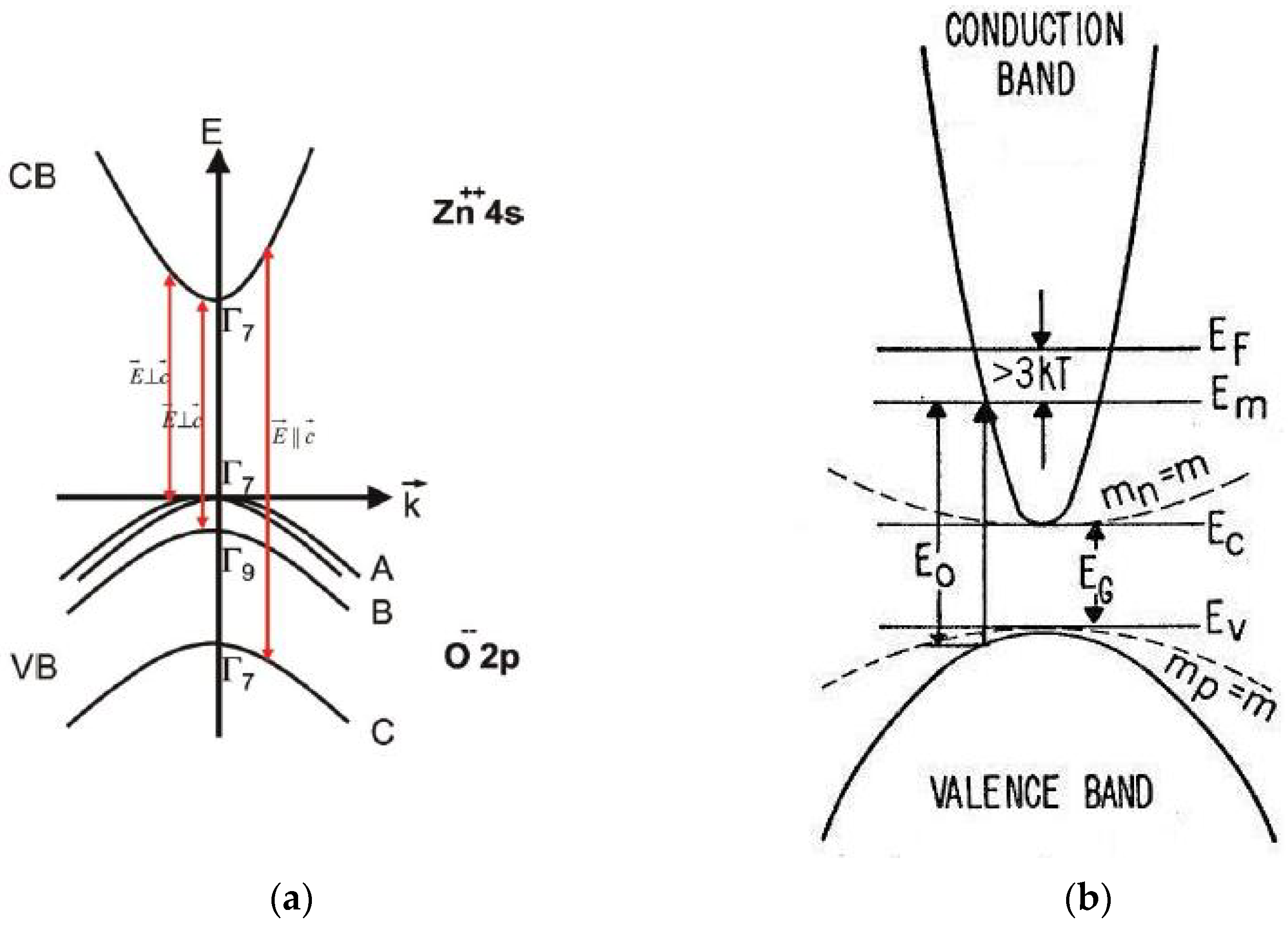
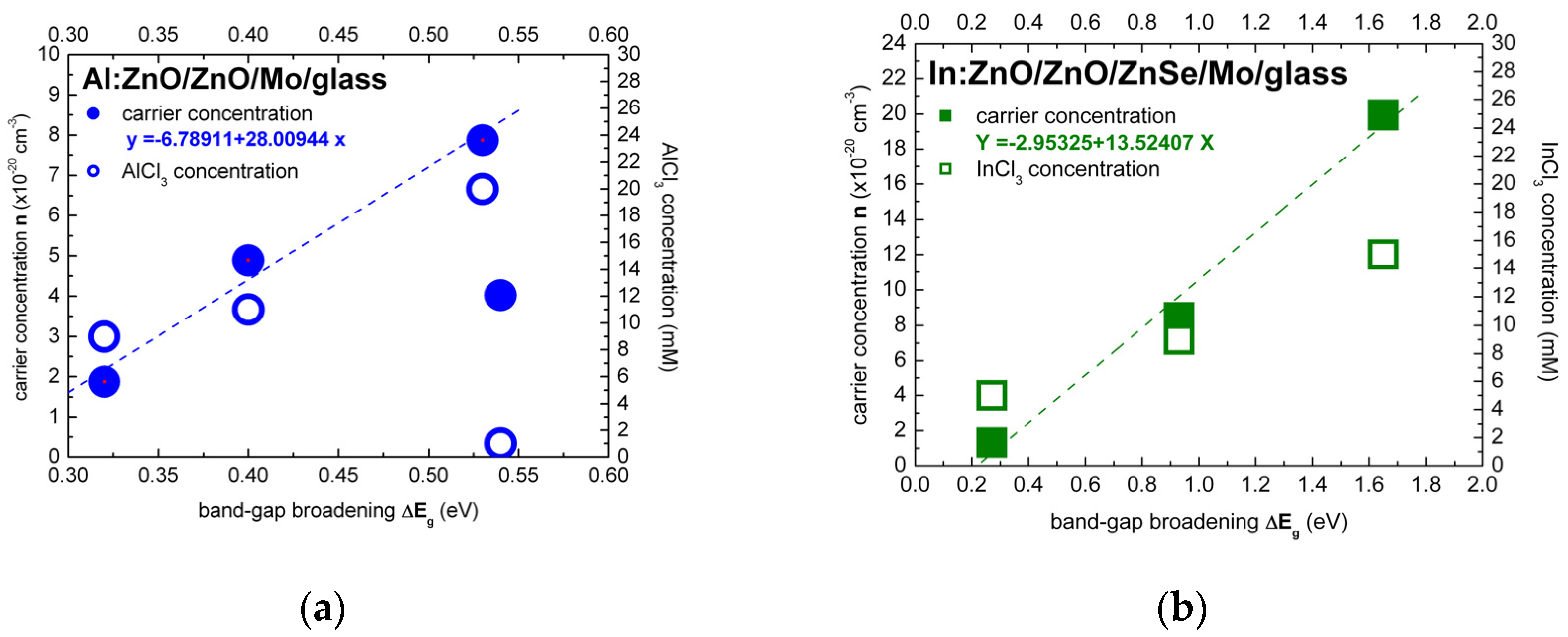
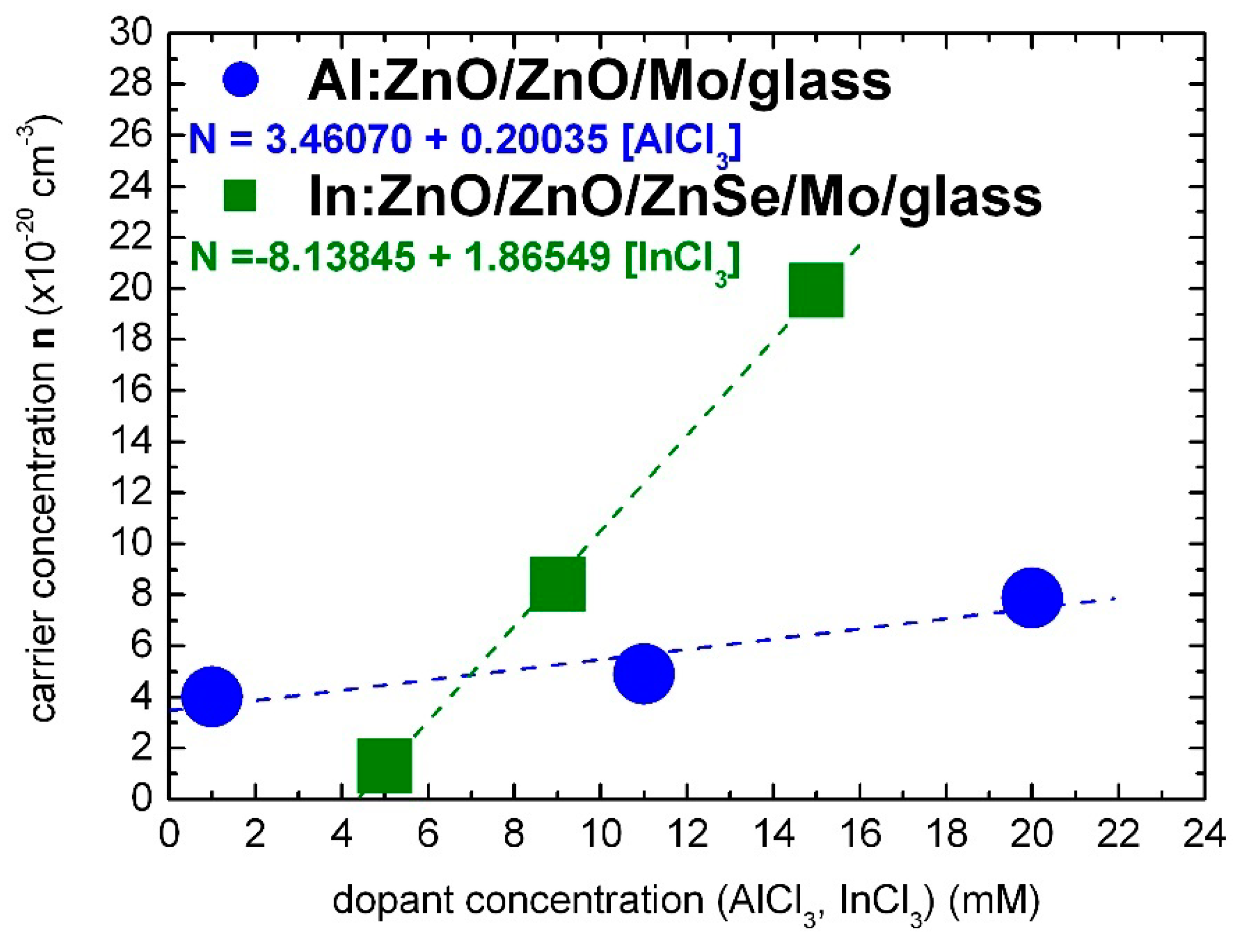
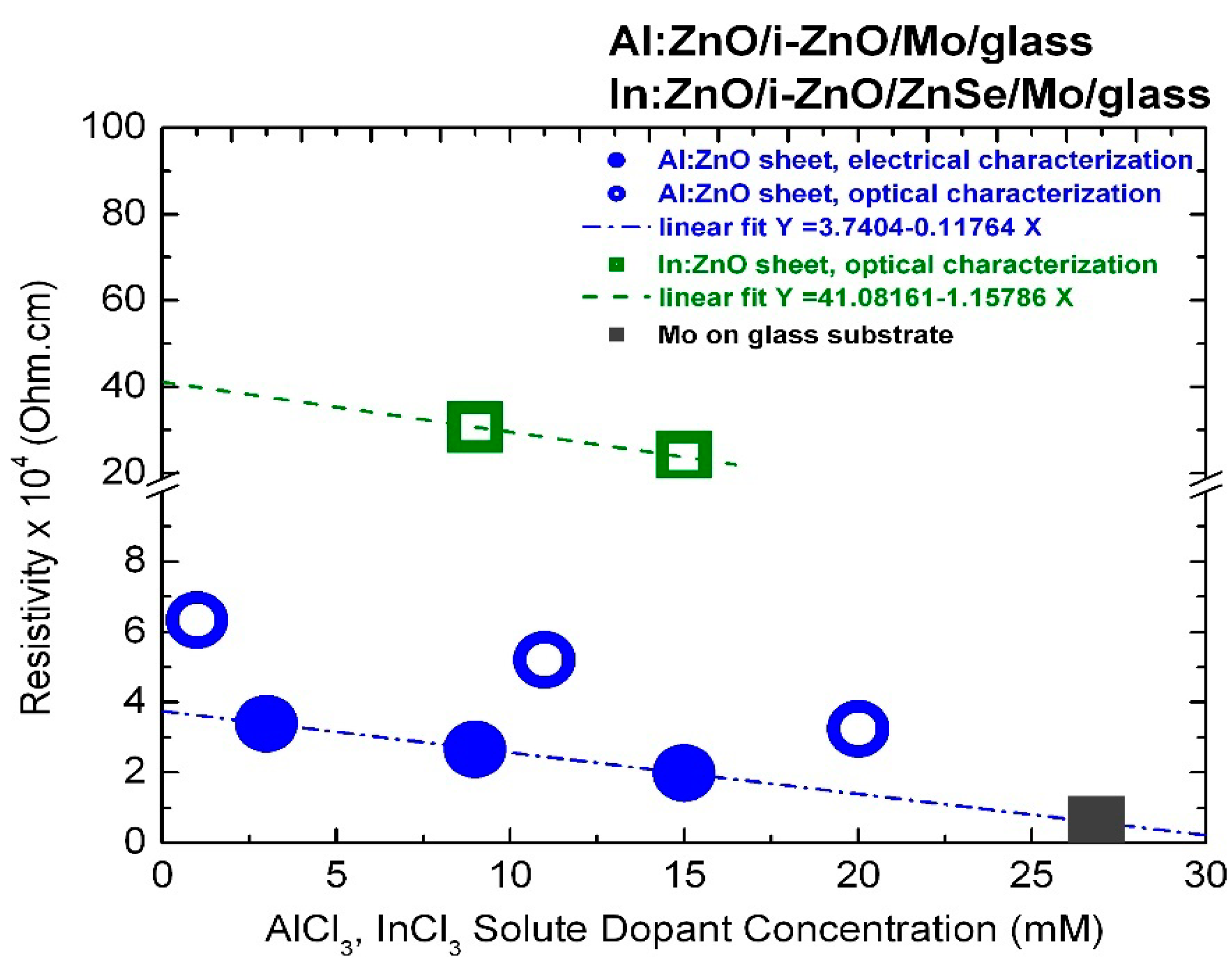
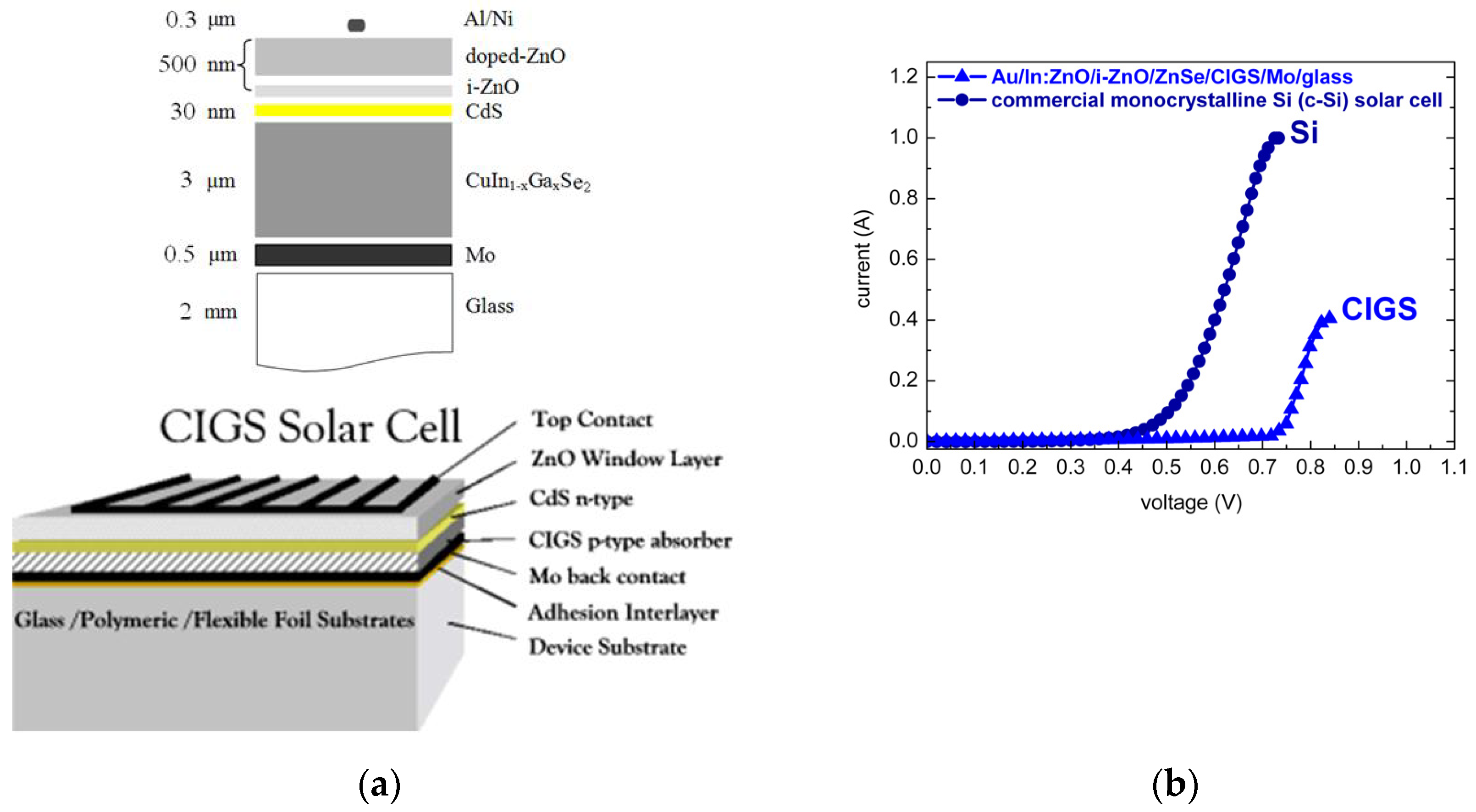
| Sample | [AlCl3] mM | Al at.% | Eg eV | NAl:ZnO × 1020 cm−3 | ρ Optical × 10−4 Ohm·cm | ρ Electrical × 10−4 Ohm·cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al:ZnO on ZnO/Mo/glass | 1 | 0.36 | 3.68 | 4.03 | 6.34 | |
| 3 | 3.39 | |||||
| 7 | 0.52 | 3.14 | ||||
| 9 | 0.66 | 3.46 | 1.88 | 2.66 | ||
| 11 | 11.39 | 3.54 | 4.89 | 5.21 | ||
| 15 | 1.98 | |||||
| 20 | 12.53 | 3.57 | 7.87 | 3.24 |
| Sample | [InCl3] mM | In at.% | Eg eV | NIn:ZnO × 1020 cm−3 | ρ Optical × 10−4 Ohm·cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO on ZnSe/Cu * | 0 | 3.5 | |||
| In:ZnO on ZnO/ZnSe/Mo/glass | 5 | 3.77 | 1.32 | ||
| 9 | 10.58 | 4.43 | 8.43 | 30.66 | |
| 15 | 23.69 | 5.15 | 19.93 | 23.71 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papadimitriou, D.N. Engineering of Optical and Electrical Properties of Electrodeposited Highly Doped Al:ZnO and In:ZnO for Cost-Effective Photovoltaic Device Technology. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1966. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111966
Papadimitriou DN. Engineering of Optical and Electrical Properties of Electrodeposited Highly Doped Al:ZnO and In:ZnO for Cost-Effective Photovoltaic Device Technology. Micromachines. 2022; 13(11):1966. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111966
Chicago/Turabian StylePapadimitriou, Dimitra N. 2022. "Engineering of Optical and Electrical Properties of Electrodeposited Highly Doped Al:ZnO and In:ZnO for Cost-Effective Photovoltaic Device Technology" Micromachines 13, no. 11: 1966. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111966
APA StylePapadimitriou, D. N. (2022). Engineering of Optical and Electrical Properties of Electrodeposited Highly Doped Al:ZnO and In:ZnO for Cost-Effective Photovoltaic Device Technology. Micromachines, 13(11), 1966. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111966





