Numerical Study on the Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer Characteristics of Al2O3-Water Nanofluids in Microchannels of Different Aspect Ratio
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Numerical Method and Model Description
2.1. Mathematical Model
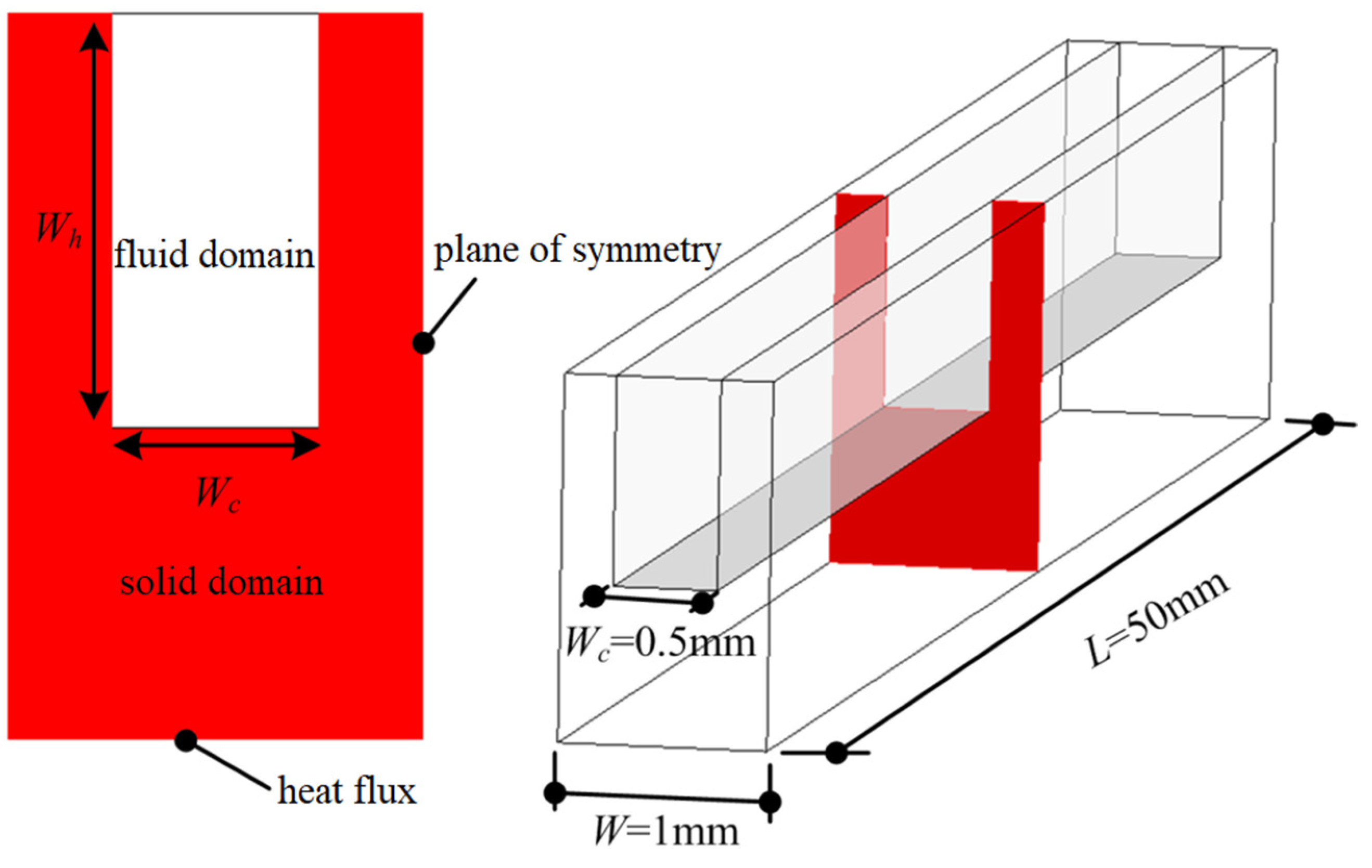
2.2. D Model and Boundary Conditions
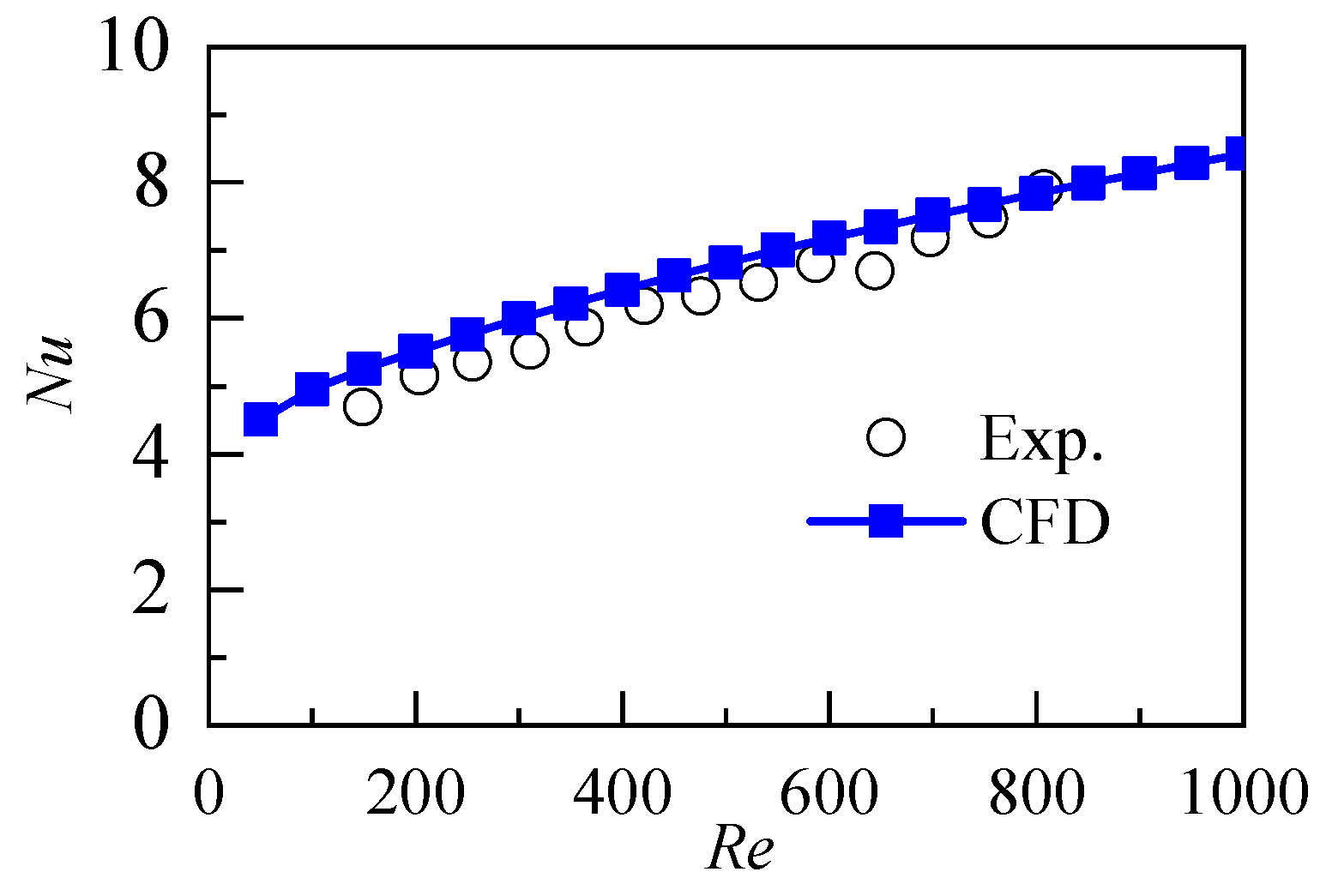
2.3. Model Validation
3. Result Analysis and Discussion
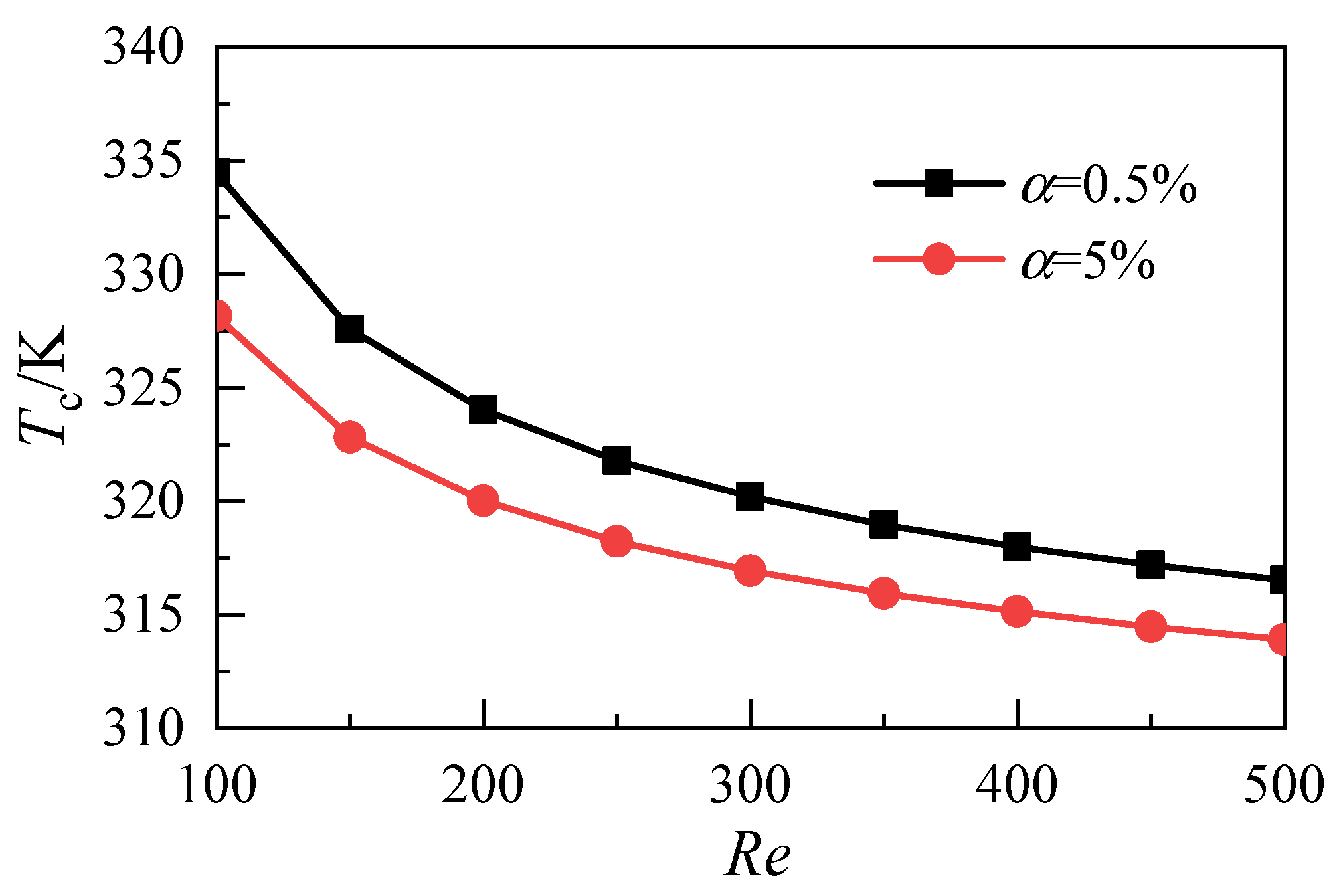
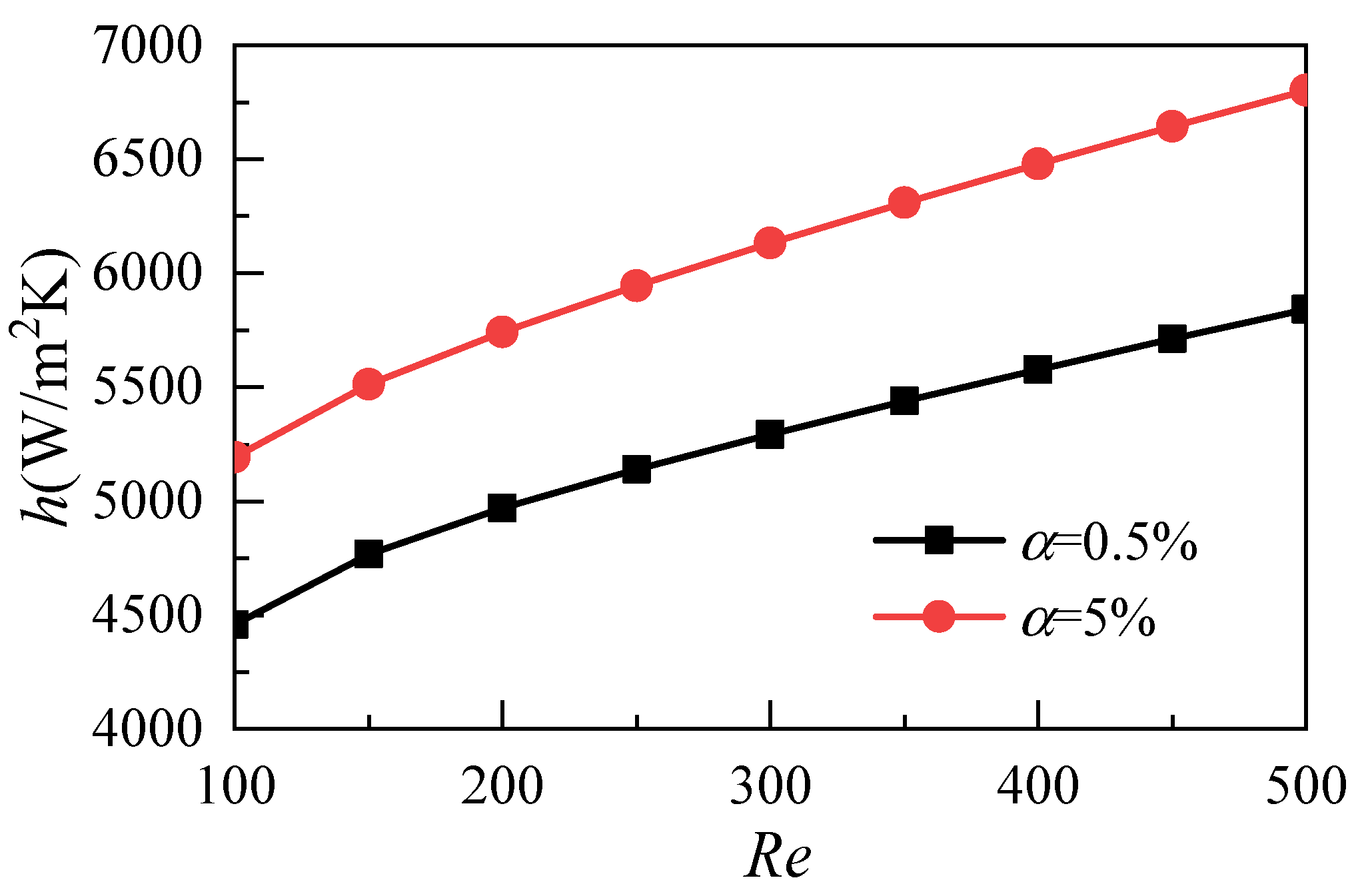
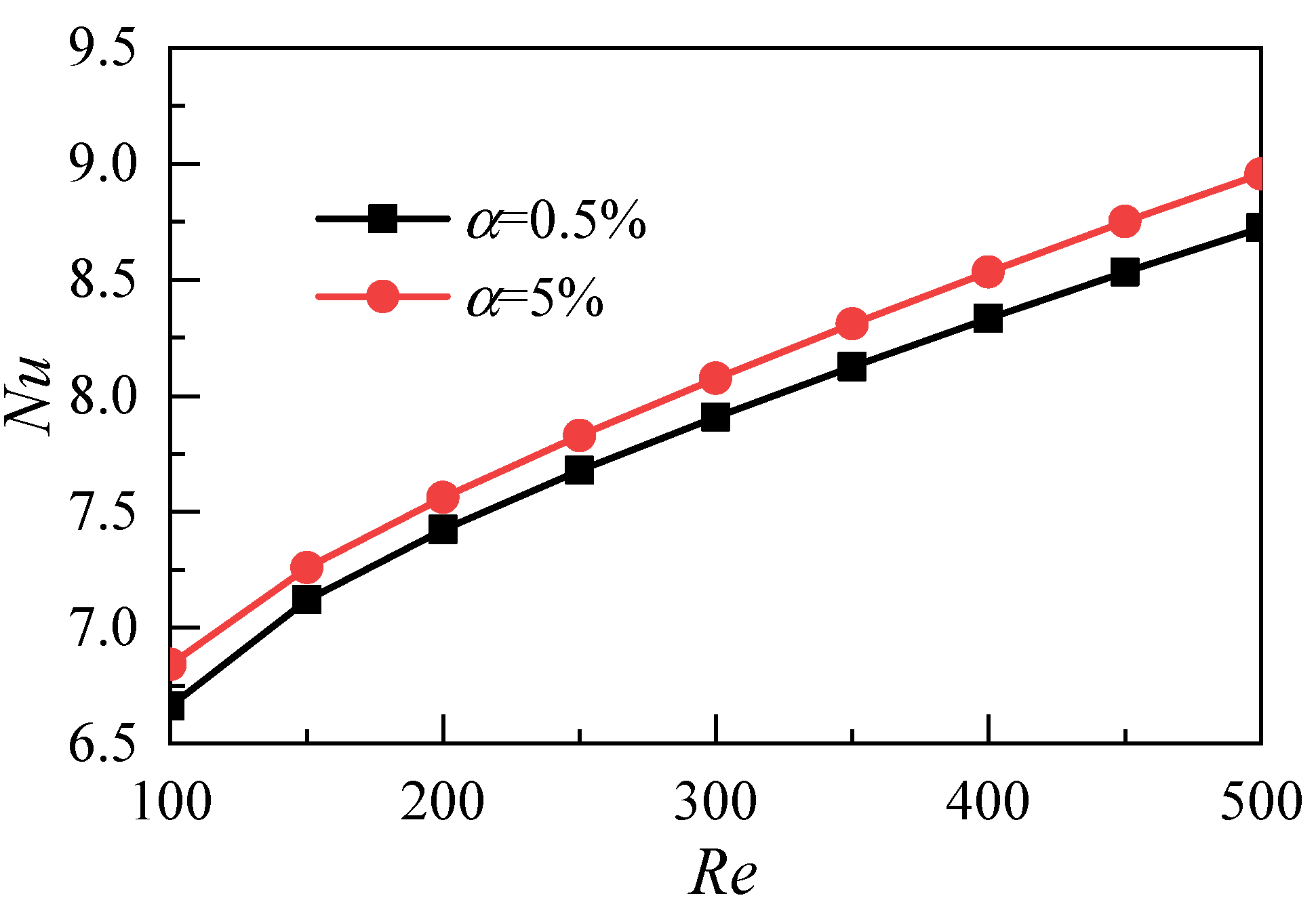
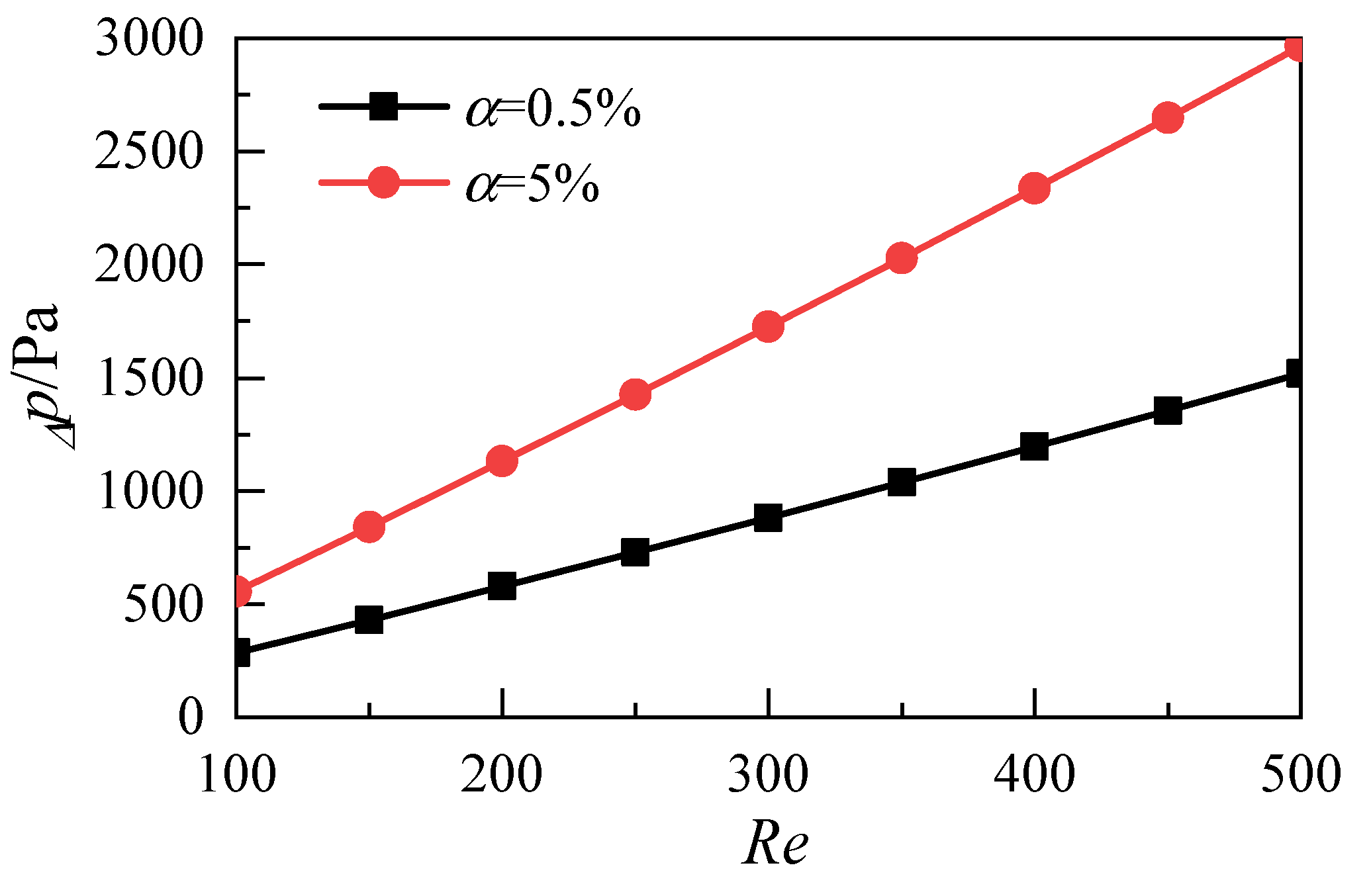
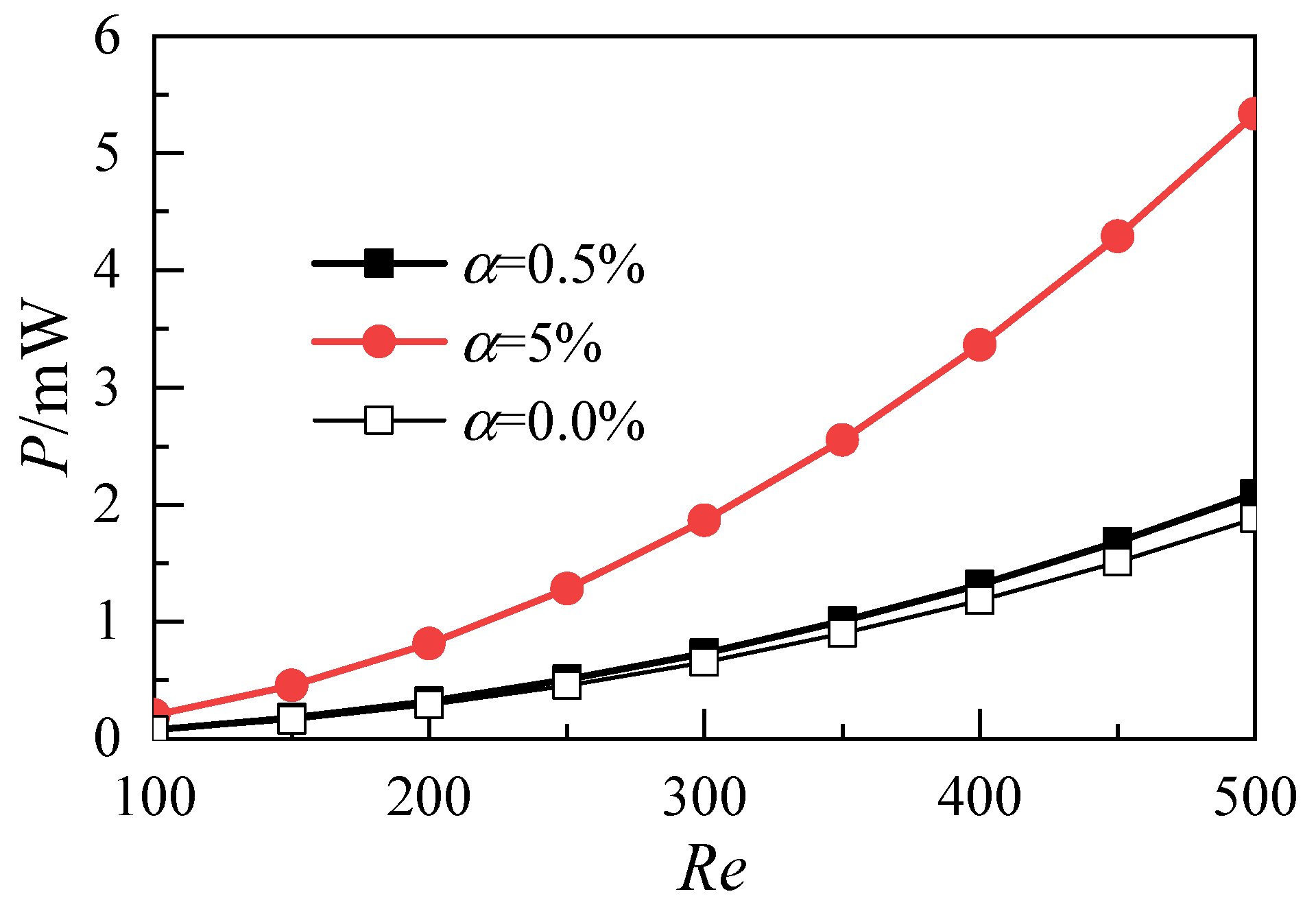
3.1. Influence of Nanoparticle Volume Fraction
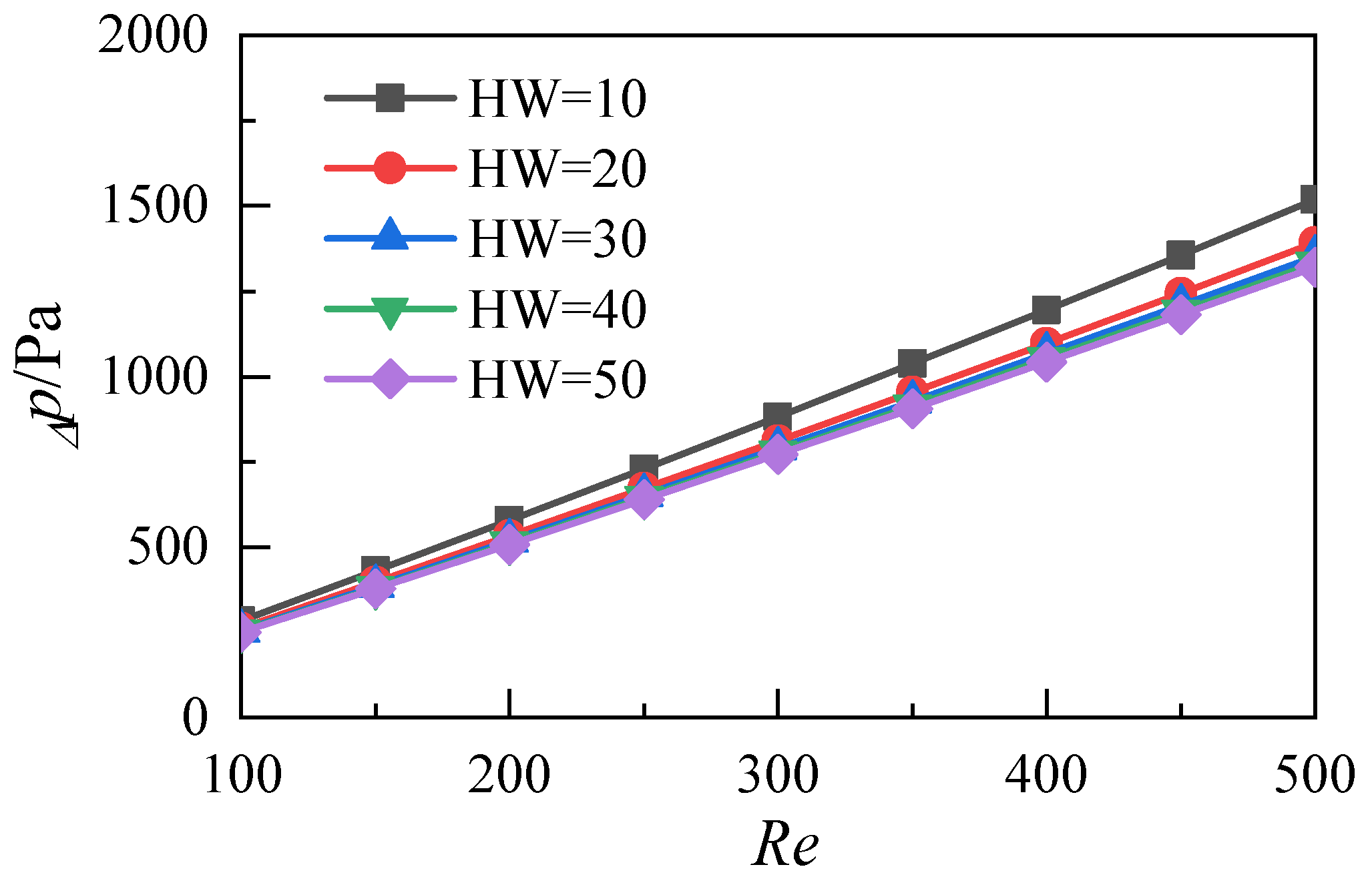
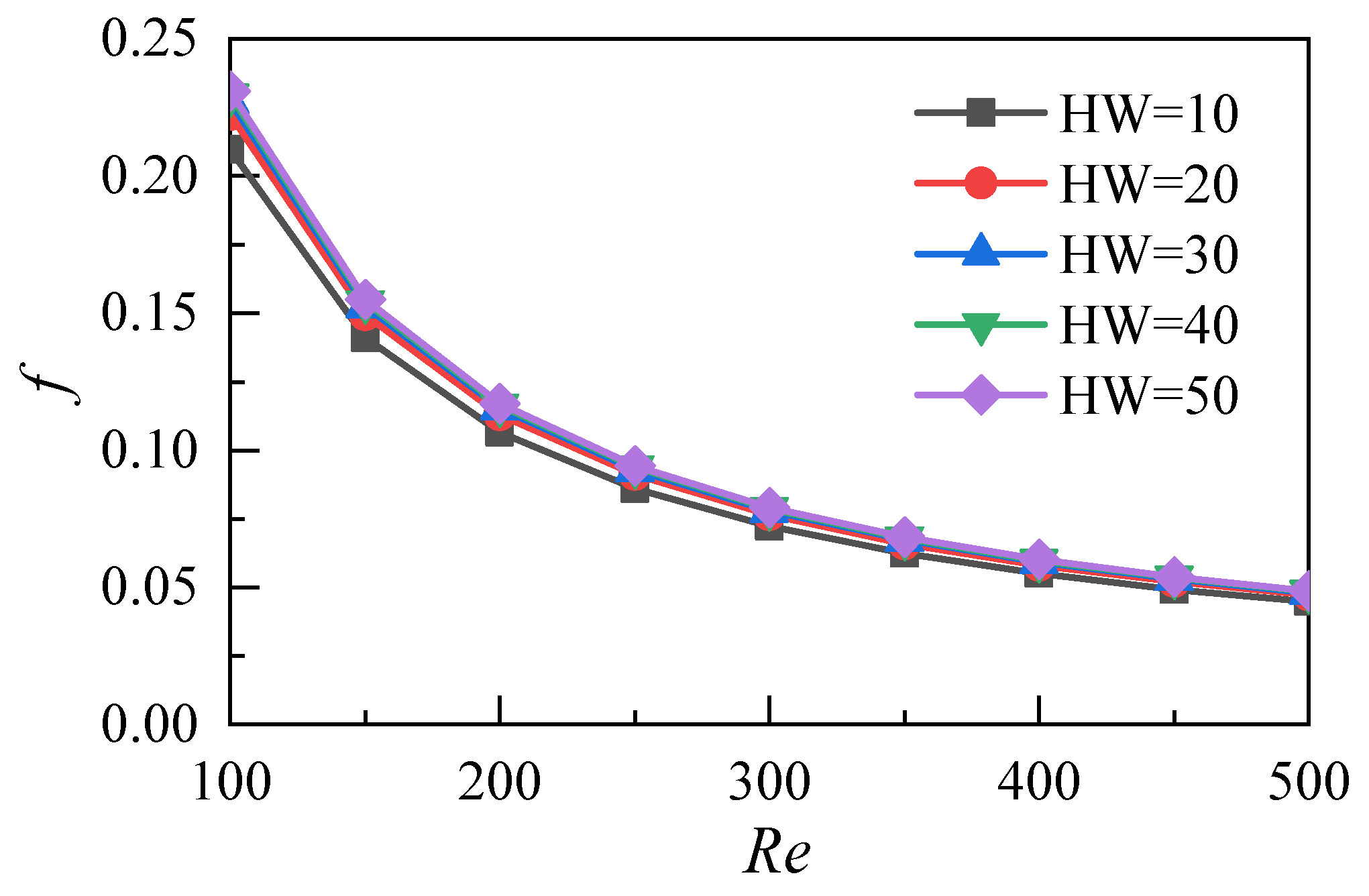
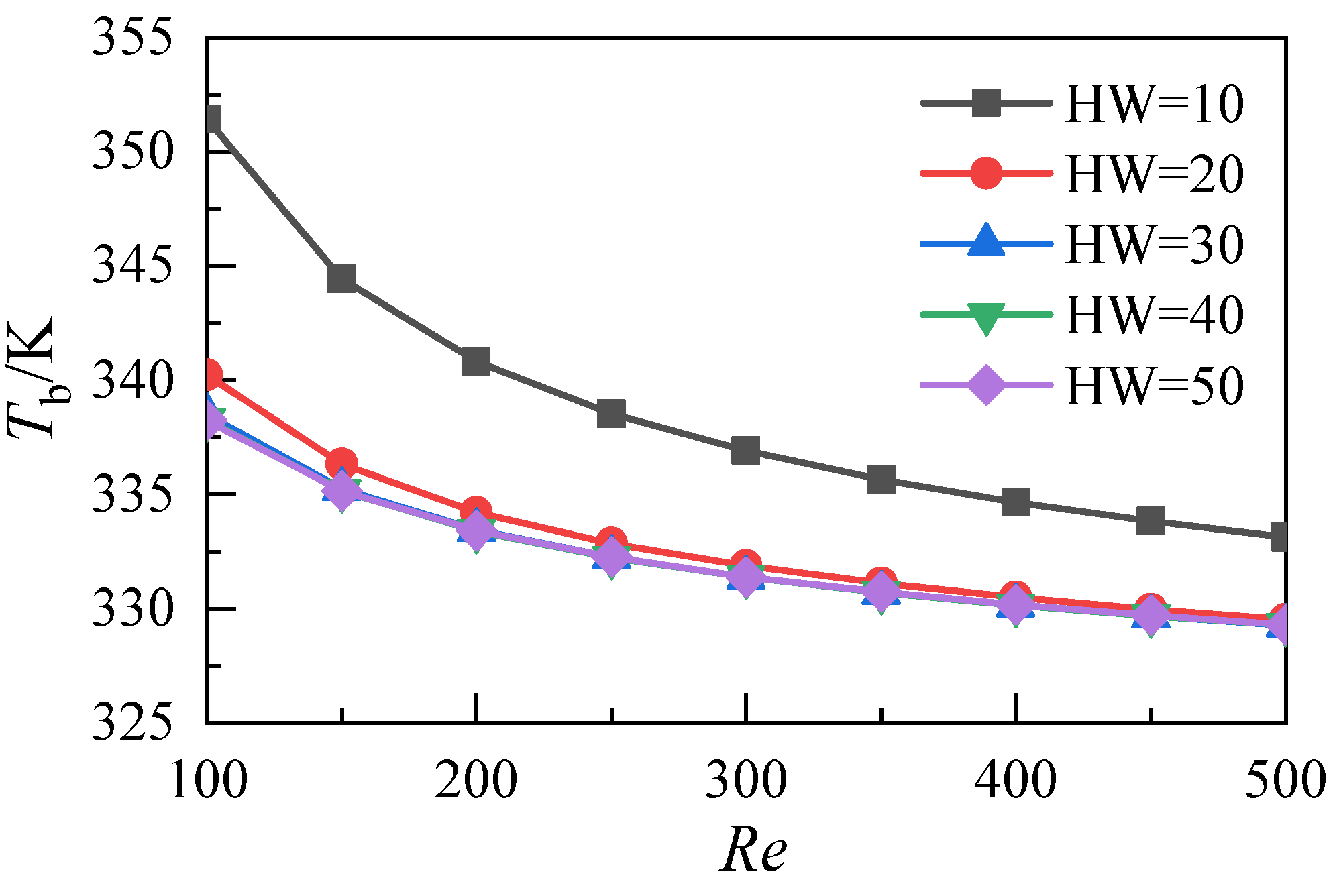
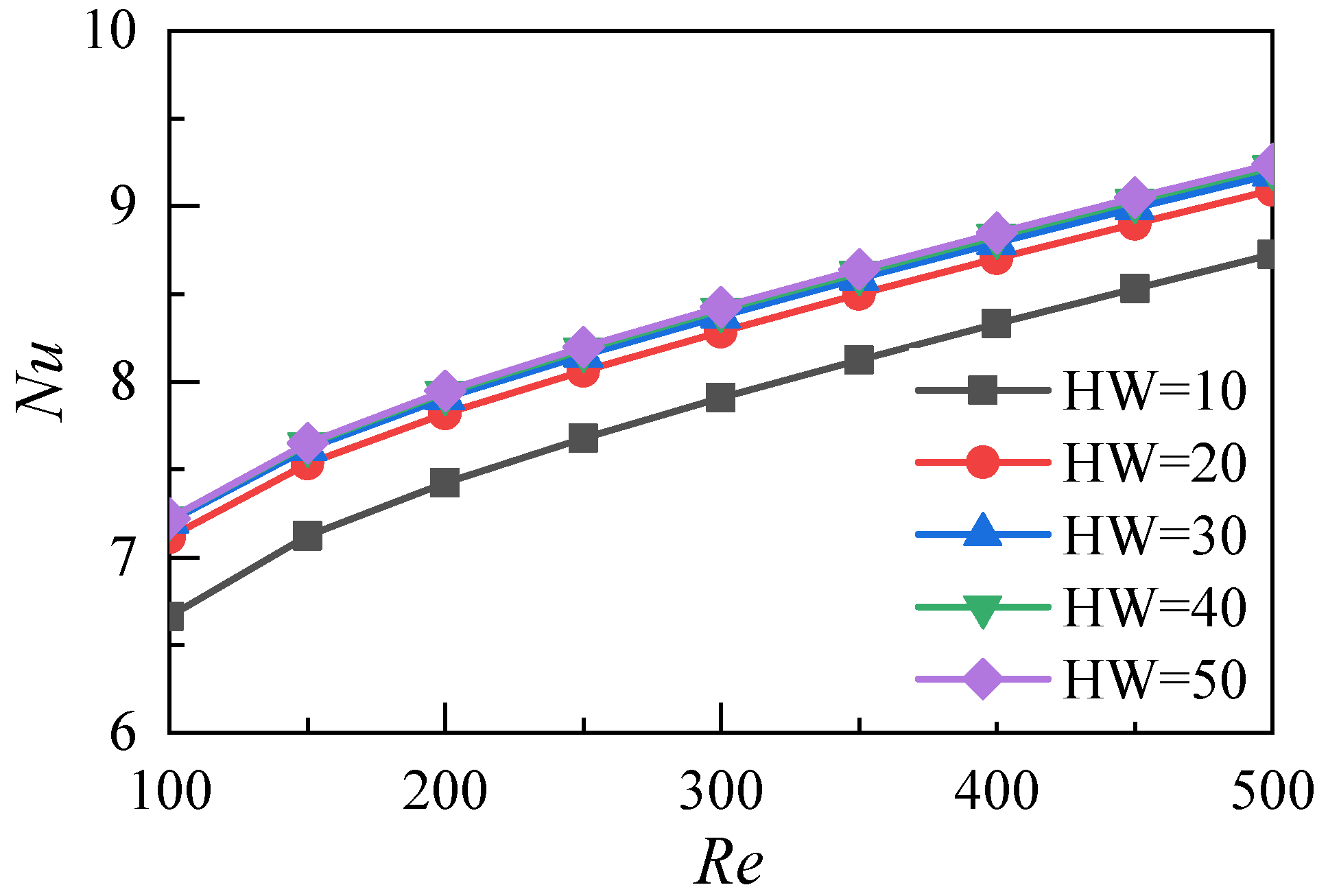
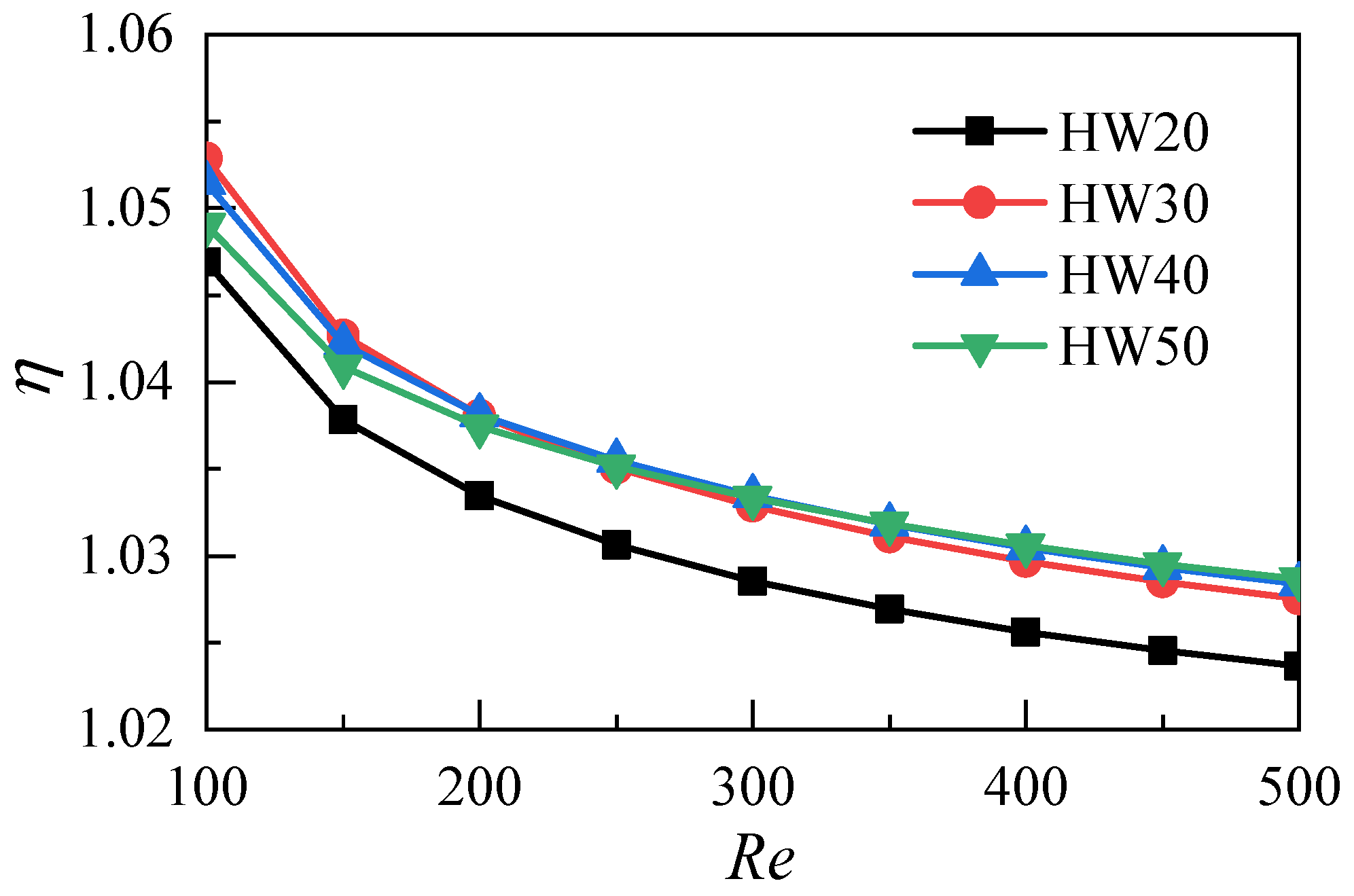
3.2. Influence of the Aspect Ratio of Microchannels
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Increasing the volume fraction of nanoparticles can effectively reduce the average temperature of the heat transfer surface and improve the heat transfer capability of nanofluids. However, because of the dual increase of the inlet velocity and flow resistance, the power consumption of the whole system increases greatly;
- (2)
- Increasing the aspect ratio of the microchannel does not cause significant flow resistance loss, and the resistance coefficient of the microchannel tends to be consistent with the increase of the Reynolds number at different aspect ratios;
- (3)
- Increasing the aspect ratio of the microchannel can reduce the temperature of the heat sink. When the aspect ratio exceeds 30, the average temperature at the bottom of the microchannel does not decrease, and the heat transfer coefficient does not increase;
- (4)
- In the range of the parameters studied in this paper, the aspect ratio of the microchannel heat sink with a thickness of 6 mm has an optimal value. Based on the comprehensive heat transfer performance parameters, the optimal value of the aspect ratio of the microchannel heat sink is 30.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| ui | velocity components in direction i |
| uj | velocity components in direction j |
| xi | cartesian coordinate components |
| xj | cartesian coordinate components |
| p | pressure in the flow field |
| T | temperature |
| ρnf | density of nanofluids |
| μnf | dynamic viscosity |
| Cpf | specific heat capacity |
| λnf | thermal conductivity |
| w | corresponding thermophysical properties of the base fluid |
| p | corresponding thermophysical properties of the nanoparticles |
| α | volume fraction of nanoparticles |
| n | shape factor of nanoparticles |
| Uin | fluid inlet velocity |
| q | heat flux |
| Nu | Nusselt number |
| N | the number of microchannels |
| Ts | the temperature of solid region |
| λs | the thermal conductivity of the solid region. |
References
- Wu, R.; Hong, T.; Cheng, Q.; Zou, H.; Fan, Y.; Luo, X. Thermal modeling and comparative analysis of jet impingement liquid cooling for high power electronics. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 137, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.J.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, S.P.; Yang, D.J.; Byeon, Y.M. Heat transfer enhancement of a radiator with mass-producing nanofluids (EG/water-based Al2O3 nanofluids) for cooling a 100 kW high power system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 180, 115780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuckerman, D.B.; Pease, R. High-performance heat sinking for VLSI. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 1981, 2, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Eastman, J.A. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the 1995 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exhibition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–17 November 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, J.; Kleinstreuer, C. Laminar nanofluid flow in microheat-sinks. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2005, 48, 2652–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apmann, K.; Fulmer, R.; Soto, A.; Vafaei, S. Thermal conductivity and viscosity: Review and optimization of effects of nanoparticles. Materials 2021, 14, 1291–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvandi, A.; Safaei, M.R.; Kaffash, M.H.; Ganji, D.D. MHD mixed convection in a vertical annulus filled with Al2O3-water nanofluid considering nanoparticle migration. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 3, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, M.; Amiri, A.; Goodarzi, M.S.; Safaei, M.R.; Karimipour, A.; Languri, E.M.; Dahari, M. Investigation of heat transfer and pressure drop of a contour flow corrugated plate heat exchanger using MWCNT based nanofluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 66, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoth, R.; Kumar, D.S. Experimental investigation on heat transfer characteristics of an oblique finned microchannel heat sink with different channel cross sections. Heat Mass Transfer 2018, 54, 3809–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaryjat, A.A.; Mohammed, H.A.; Adam, N.M.; Ariffin, M.K.A.; Najafabadi, M.I. Influence of geometrical parameters of hexagonal, circular, and rhombus microchannel heat sinks on the thermohydraulic characteristics. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 52, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.E.; Ahmed, M.I. Optimum thermal design of triangular, trapezoidal and rectangular grooved microchannel heat sinks. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 66, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KumaR, P. Numerical investigation of fluid flow and heat transfer in trapezoidal microchannel with groove structure. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 136, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsad, E.; Abbasi, S.P.; Zabihi, M.S.; Sabbaghzadeh, J. Numerical simulation of heat transfer in a micro channel heat sinks using nanofluids. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 47, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Li, S.; Wei, Y.; Gao, Y. Multi objective optimization of structural parameters of nanofluid rectangular microchannel heat sink. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 2018, 52, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ghale, Z.Y.; Haghshenasfard, M.; Esfahany, M.N. Investigation of nanofluids heat transfer in a ribbed microchannel heat sink using singlephase and multiphase CFD models. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 68, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, O.; Nardini, S.; Ricci, D. A numerical study of nanofluid forced convection in ribbed channels. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2012, 37, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Fujii, M.; Zhang, X. Effect of interfacial nanolayer on the effective thermal conductivity of nanoparticle-fluid mixture. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2004, 48, 2926–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkountas, A.A.; Benos, L.T.; Nikas, K.S.; Sarris, I.E. Heat transfer improvement by an Al2O3-water nanofluid coolant in printed-circuit heat exchangers of supercritical CO2 Brayton cycle. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2020, 20, 1025–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohel, M.R.; Khaleduzzaman, S.S.; Saidur, R.; Hepbasli, A.; Sabri, M.F.M.; Mahbubul, I.M. An experimental investigation of heat transfer enhancement of a minichannel heat sink using Al2O3–H2O nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 74, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, J.; Salehi, F.; Sheikholeslami, M.; Masoudi, M.; Lee, A. Optimization of nanofluid heat transfer in a microchannel heat sink with multiple synthetic jets based on CFD-DPM and MLA. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 167, 107008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafer, K.; Vafai, K. A critical syn study of thermophysical characteristics of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 54, 4410–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Xia, G.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Cui, Z. Heat transfer enhancement in microchannel heat sinks with periodic expansion-constriction cross-sections. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 62, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Mudawar, I. Assessment of the effectiveness of nanofluids for single-phase and two-phase heat transfer in micro-channels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 50, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, H.; Zhang, S. Numerical Study on the Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer Characteristics of Al2O3-Water Nanofluids in Microchannels of Different Aspect Ratio. Micromachines 2021, 12, 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080868
Wu H, Zhang S. Numerical Study on the Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer Characteristics of Al2O3-Water Nanofluids in Microchannels of Different Aspect Ratio. Micromachines. 2021; 12(8):868. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080868
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Huajie, and Shanwen Zhang. 2021. "Numerical Study on the Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer Characteristics of Al2O3-Water Nanofluids in Microchannels of Different Aspect Ratio" Micromachines 12, no. 8: 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080868
APA StyleWu, H., & Zhang, S. (2021). Numerical Study on the Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer Characteristics of Al2O3-Water Nanofluids in Microchannels of Different Aspect Ratio. Micromachines, 12(8), 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080868





