Formation and Elimination of Satellite Droplets during Monodisperse Droplet Generation by Using Piezoelectric Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
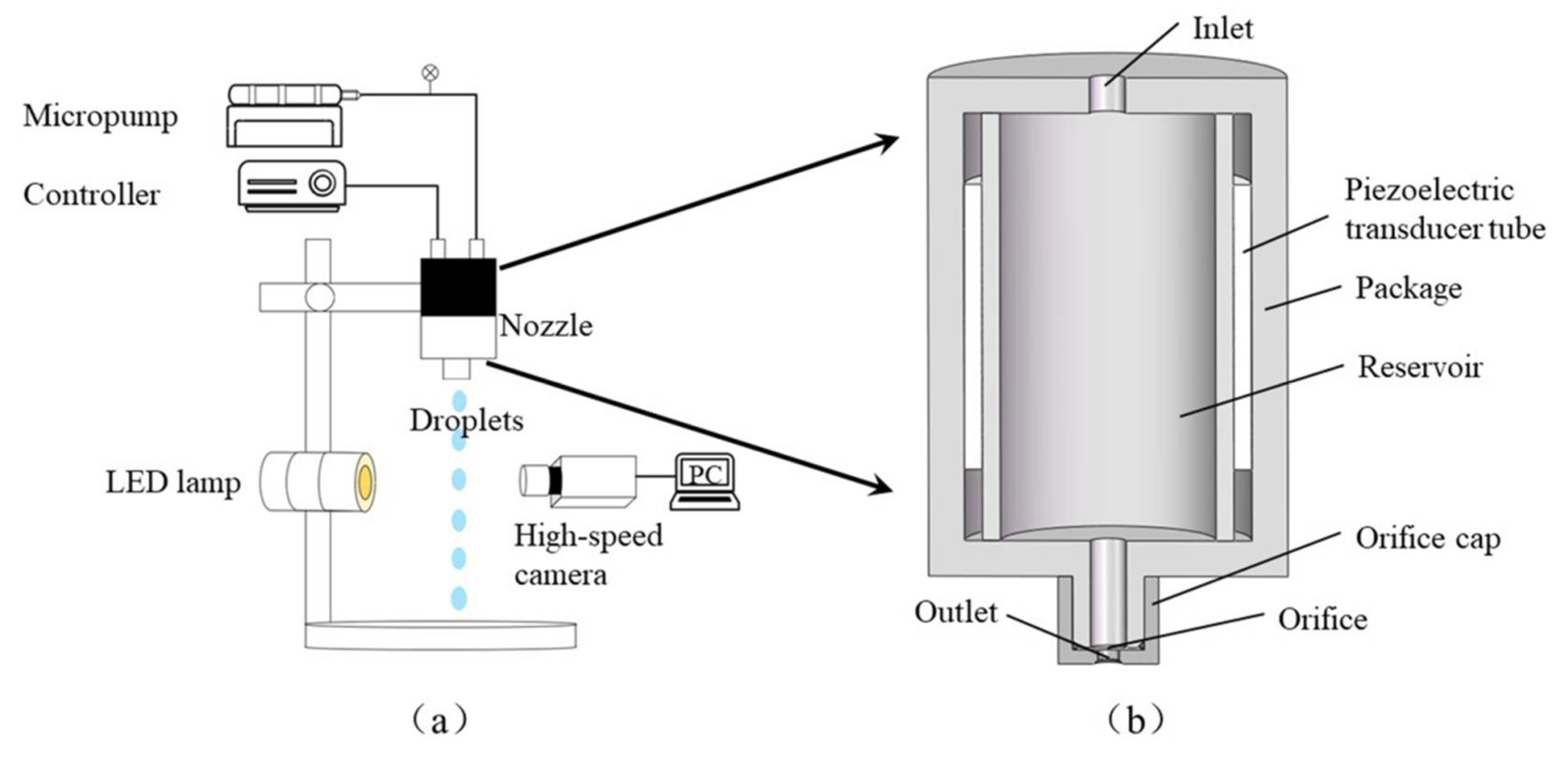
2. Experimental Methods
3. Results and Discussion
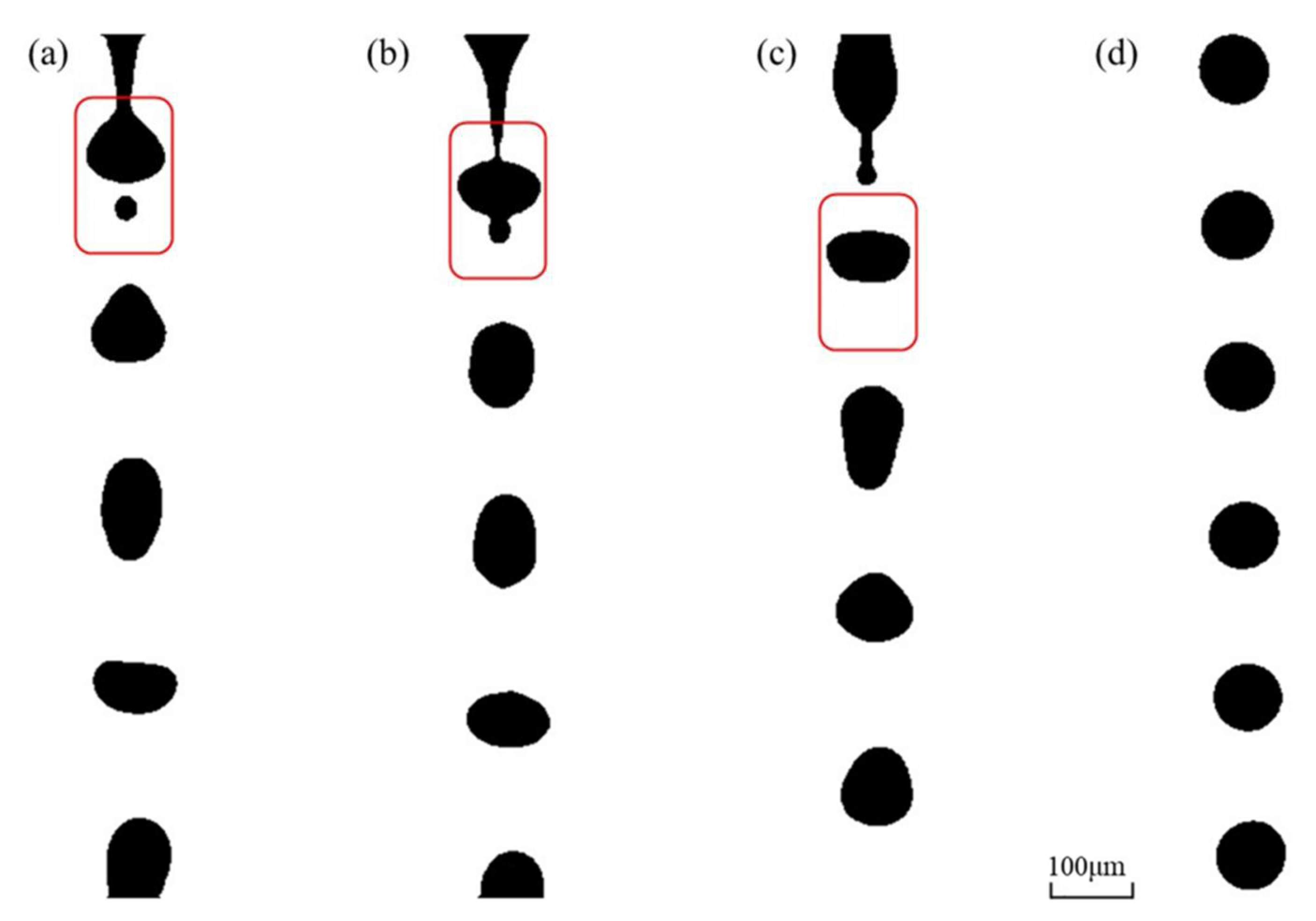
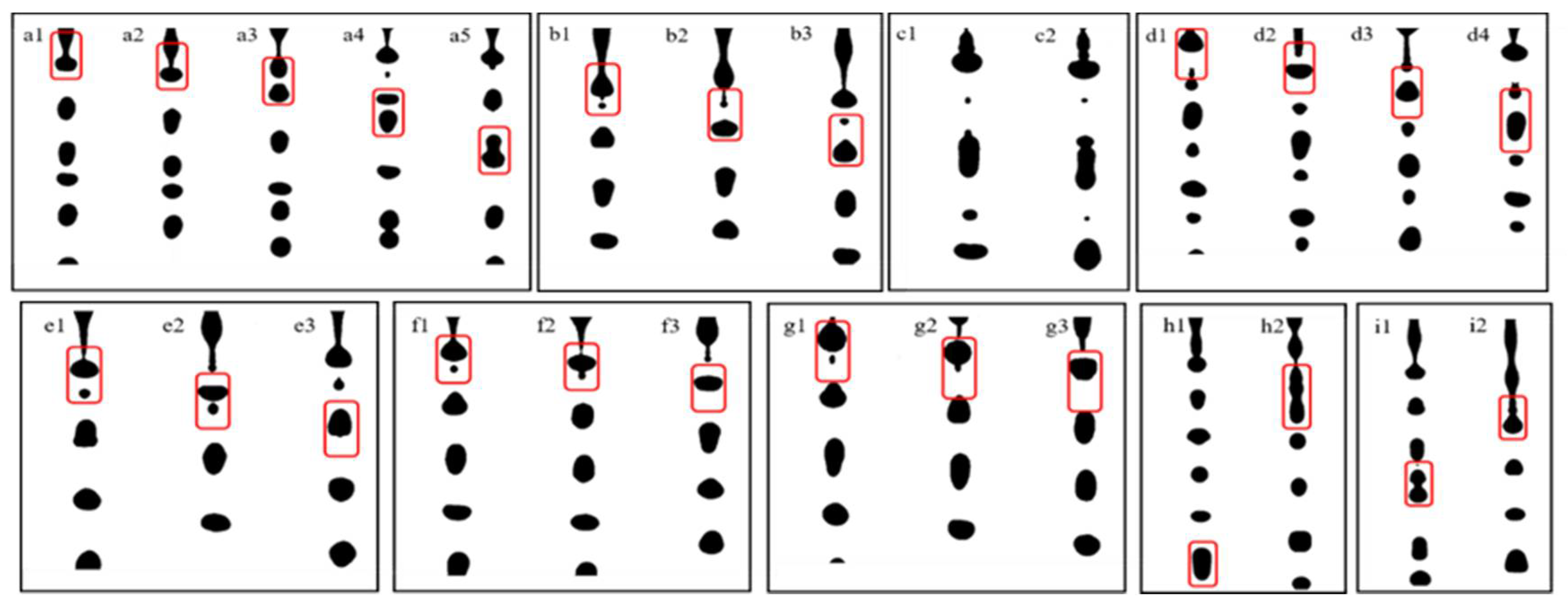
3.1. Pinch-Off of Liquid Filament and Generation of Satellite Droplets
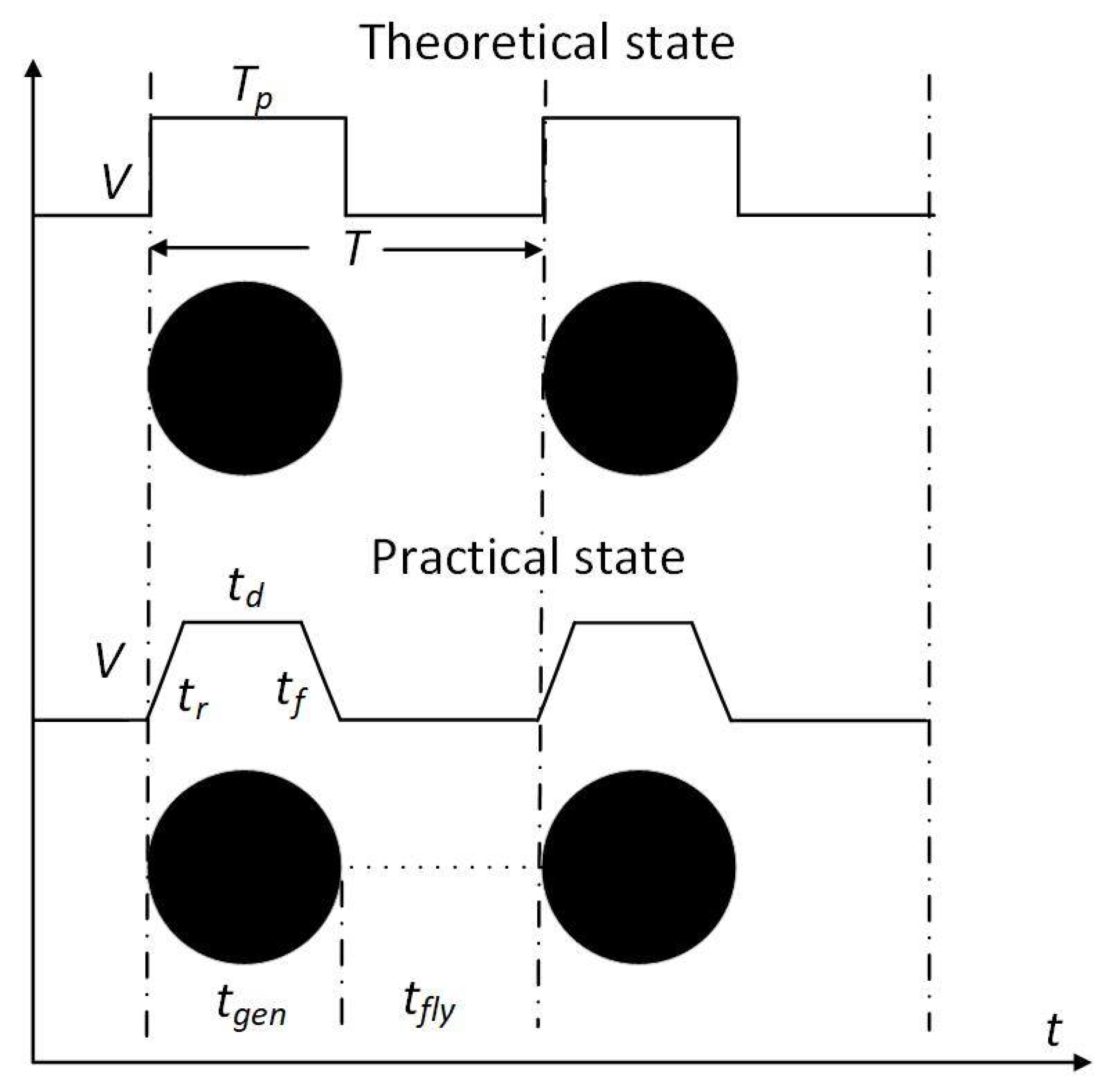
3.2. Elimination of Satellite Droplets
3.3. Effect of Pulse Frequency on the Elimination of Satellite Droplets
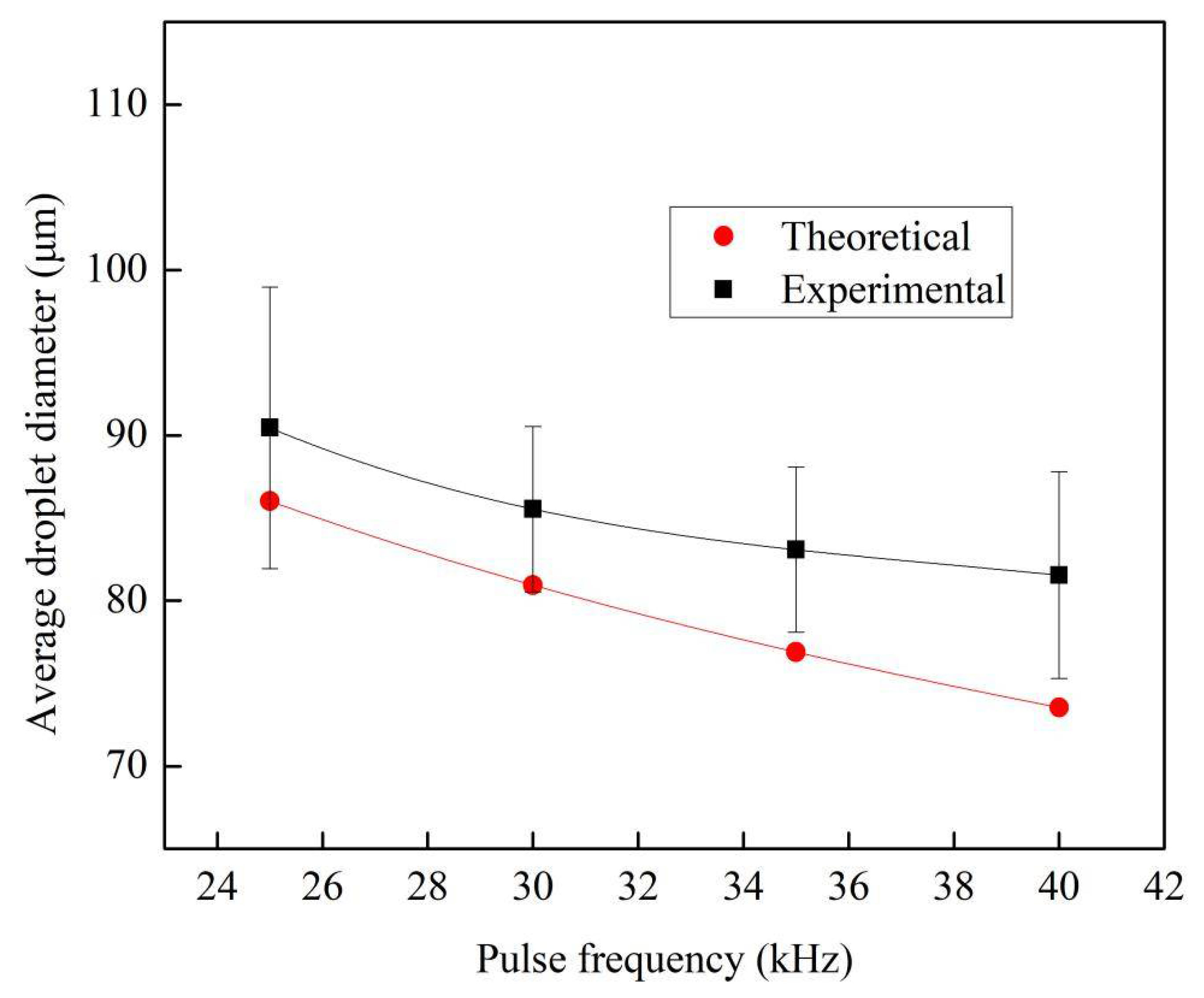
3.4. Effect of Pulse Frequency on the Average Diameter of Droplets
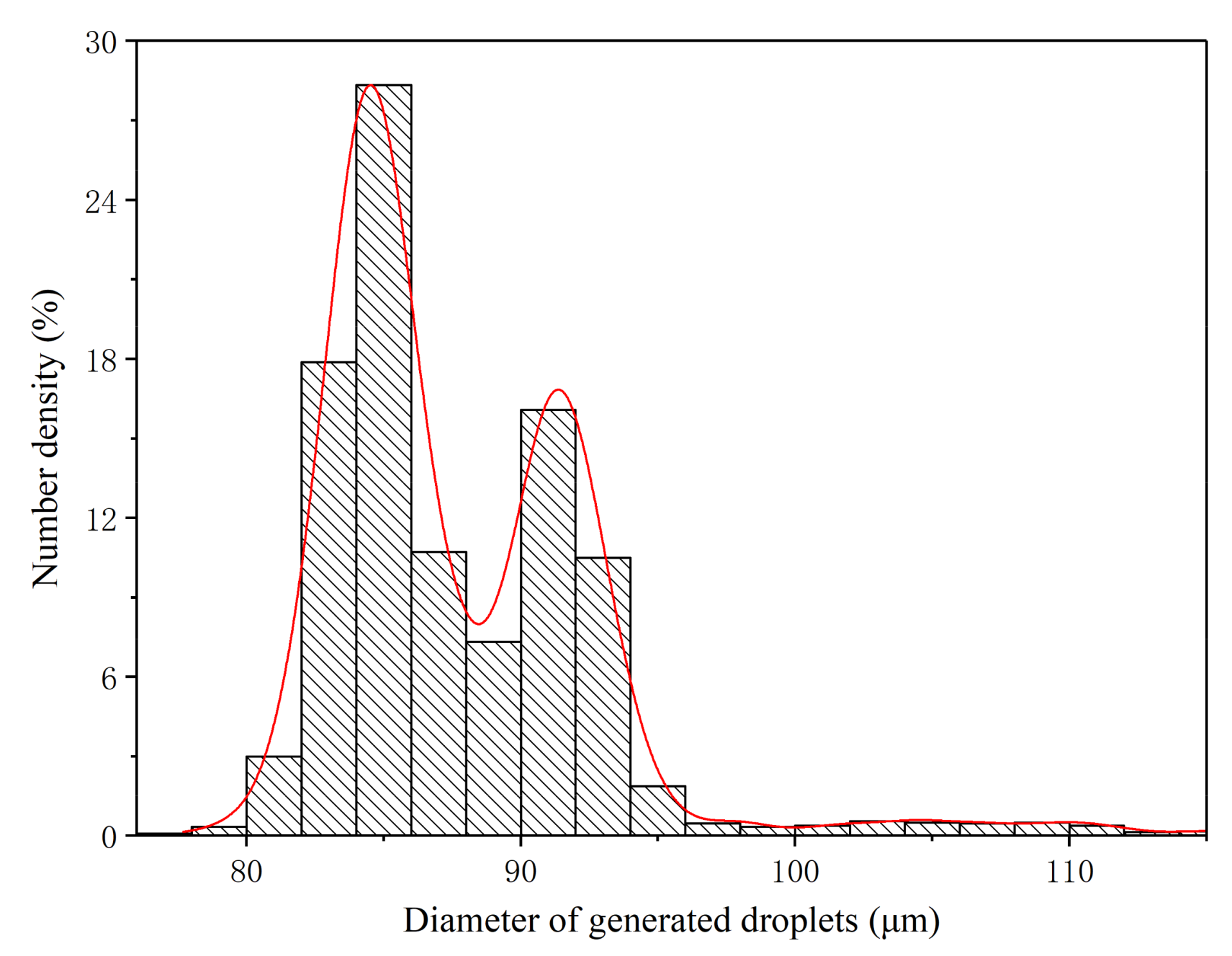
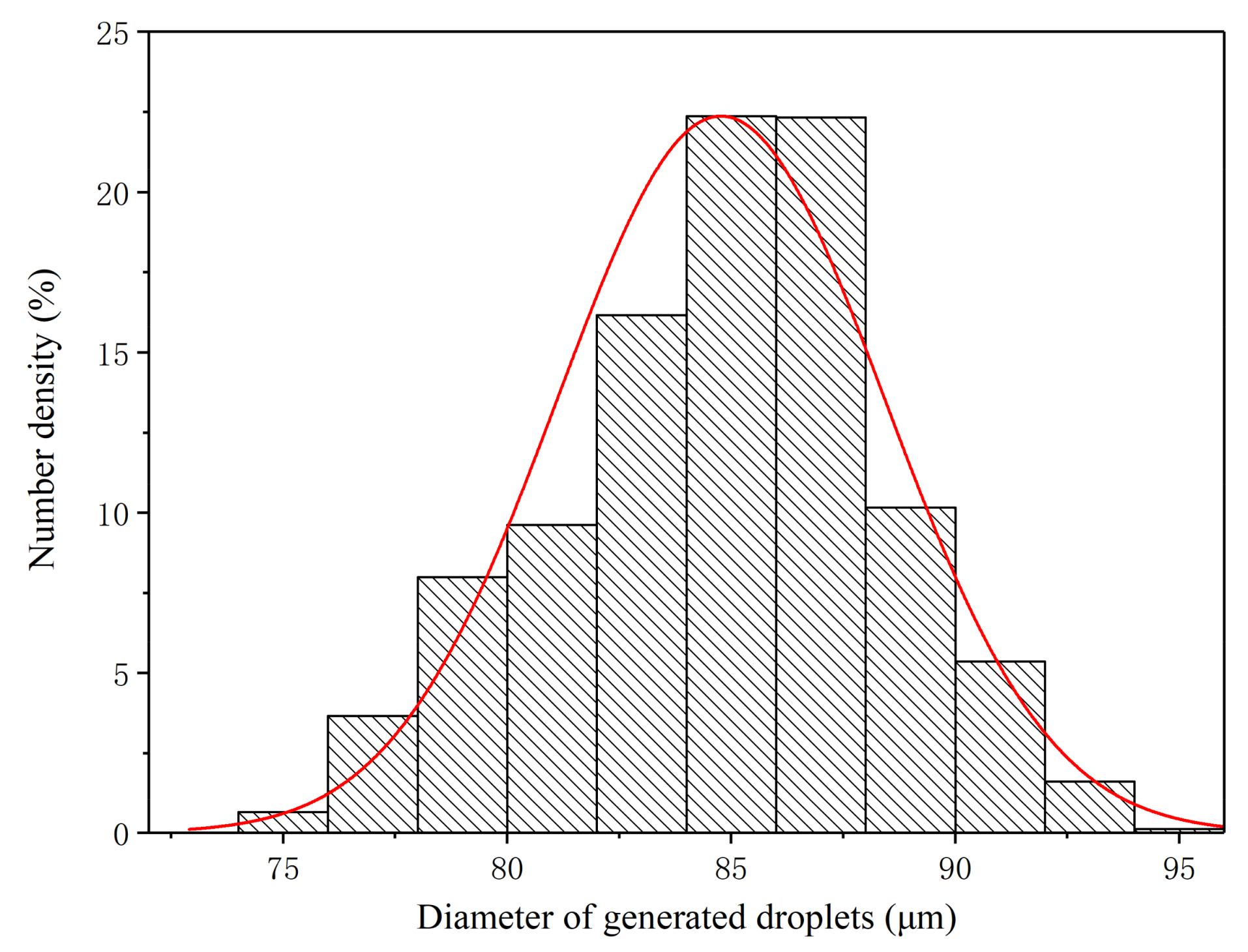
3.5. Size Distribution of Monodisperse Droplets under Optimum Operating Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamaguchi, K.; Sakai, K.; Yamanaka, T. Generation of Three-Dimensional Micro Structure Using Metal Jet. Precis. Eng. 2000, 24, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, D.; Cullinan, M. Current Challenges and Potential Directions Towards Precision Microscale Additive Manufacturing—Part I: Direct Ink Writing/Jetting Processes. Precis. Eng. 2021, 68, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Yang, J.; Katagiri, D.; Ying, R.; Xue, S.; Nakajim, H.; Uchiyama, K. Investigation of Monodisperse Droplet Generation in Liquids by Inkjet. Sensor. Actuat. B Chem. 2015, 220, 958–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Park, S.J.; Sim, W. Modeling and Characterization of an Industrial Inkjet Head for Micro-Patterning on Printed Circuit Boards. Comput. Fluids 2009, 38, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.C.; Alvis, R.M.; Brown, S.B. Fabricating optical Fiber Imaging Sensors Using Inkjet Printing Technology: A pH Sensor Proof-Of-Concept. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Orme, M. High Precision Solder Droplet Printing Technology and the State-Of-The-Art. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 115, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Luckham, R.E.; Smith, A.M. Development of a Bioactive Paper Sensor for Detection of Neurotoxins Using Piezoelectric Inkjet Printing of Sol? Gel-Derived Bioinks. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5474–5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sackmann, E.K.; Fulton, A.L.; Beebe, D.J. The Present and Future Role of Microfluidics in Biomedical Research. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 507, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochstetter, A. Lab-on-a-Chip Technologies for the Single Cell Level: Separation, Analysis and Diagnostics. Micromachines 2020, 11, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delene, D.J.; Deshler, T. Calibration of a Photometric Cloud Condensation Nucleus Counter Designed for Deployment on a Balloon Package. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantarifard, A.; Alizadeh-Haghighi, E.; Saateh, A.; Elbuken, C. Theoretical and Experimental Limits of Monodisperse Droplet Generation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 229, 116093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wise, K.D. A High-Resolution Silicon Monolithic Nozzle Array for Inkjet Printing. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1997, 44, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadamson, S.; Manager, S.P.; Wang, A.D. A Change in Dispensing Technology-Jetting Takes Off. Semicond. Tech. 2004, 3, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Chandra, S. A Pneumatic Droplet-On-Demand Generator. Exp. Fluids 2003, 34, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.X.; Li, T.; Chandra, S. Producing Molten Metal Droplets with a Pneumatic Droplet-On-Demand Generator. J. Mater. Process. Technol 2005, 159, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.M.; Wei, X.F.; Huang, B.Q. Influence of the Viscosity of Edible Ink to Piezoelectric Ink-Jet Printing Drop State. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 200, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, A.A.; Lee, M.H.; Zhao, B. Design and Operation of a Droplet Deposition System for Freeform Fabrication of Metal Parts. J. Eng. Mater. Tech. 2001, 123, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, A.J.T.; Li, K.-H.H.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Guo, W.; Heere, N.; Xi, H.-D.; Tsao, C.-W.; Li, W.; Tan, S.H. Negative Pressure Induced Droplet Generation in a Microfluidic Flow-Focusing Device. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4387–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filatov, N.A.; Evstrapov, A.A.; Bukatin, A.S. Negative Pressure Provides Simple and Stable Droplet Generation in a Flow-Focusing Microfluidic Device. Micromachines 2021, 12, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.H.Y.; Cui, B.; Song, R.; Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Yao, S. Scalable Production of Monodisperse Functional Microspheres by Multilayer Parallelization of High Aspect Ratio Microfluidic Channels. Micromachines 2019, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Liu, F.; Li, Y. The Characteristics of 20 μm-Diameter Single Droplets. Acta Phys. Sin. 2007, 56, 5926–5930. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, K.C.; Chen, J.Y.; Wang, C.H. Development of Drop-On-Demand Droplet Generator for One-Drop-Filling Technology. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2008, 147, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, P.; Sung, J. The Effect of Driving Waveforms on Droplet Formation in a Piezoelectric Inkjet Nozzle. In Proceedings of the 2009 11th Electronics Packaging Technology Conference, Singapore, 9–11 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Wu, H.; Shan, T. The Effects of Operating Parameters on Micro-Droplet Formation in a Piezoelectric Inkjet Printhead Using a Double Pulse Voltage Pattern. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Zhuo, Z.; He, L.; Huang, X. Atomization Characteristics of Nano-Al/Ethanol Nanofluid Fuel in Electrostatic Field. Fuel 2019, 236, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjahjadi, M.; Stone, H.A.; Ottino, J.M. Satellite and Subsatellite Formation in Capillary Breakup. J. Fluid Mech. 1992, 243, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogy, D.B.; Talke, F.E. Experimental and Theoretical Study of Wave Propagation Phenomena in Drop-On-Demand Ink Jet Devices. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1984, 28, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

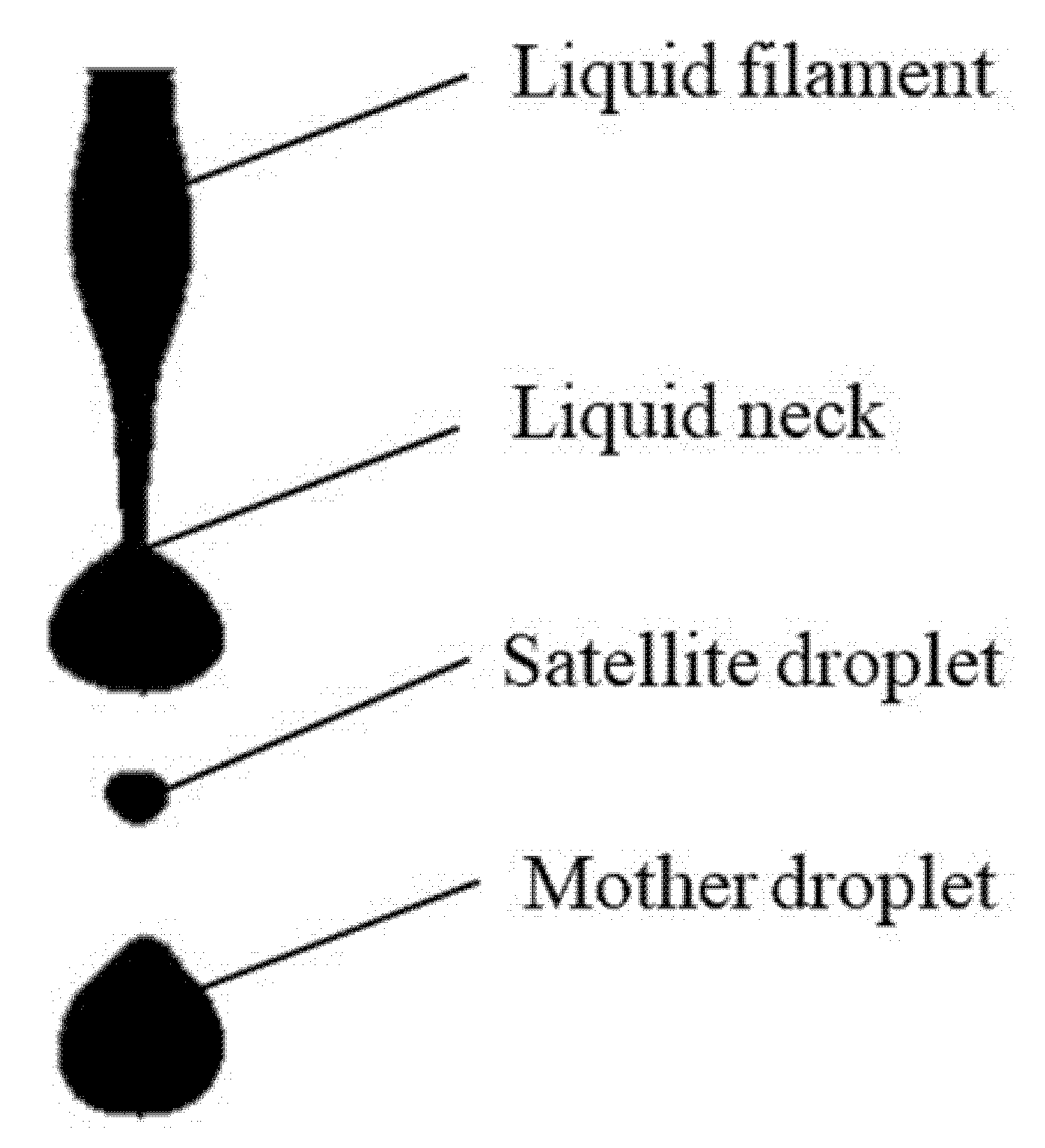



| Items | Density (kg/m3) | Surface Tension (N/m) @25 °C | Viscosity (Pa·s) @15 °C | Acoustic Velocity (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 1.0 × 103 | 0.072 | 1.14 × 10−3 | 1435 [24] |
| Items | Amplitude | Frequency | Duty Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 4.2 V | 5~40 kHz | 0.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Z.; Li, S.; Yang, F.; Lin, X.; Pan, S.; Huang, X.; Xu, J. Formation and Elimination of Satellite Droplets during Monodisperse Droplet Generation by Using Piezoelectric Method. Micromachines 2021, 12, 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080921
Hu Z, Li S, Yang F, Lin X, Pan S, Huang X, Xu J. Formation and Elimination of Satellite Droplets during Monodisperse Droplet Generation by Using Piezoelectric Method. Micromachines. 2021; 12(8):921. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080921
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Zejian, Shengji Li, Fan Yang, Xunjie Lin, Sunqiang Pan, Xuefeng Huang, and Jiangrong Xu. 2021. "Formation and Elimination of Satellite Droplets during Monodisperse Droplet Generation by Using Piezoelectric Method" Micromachines 12, no. 8: 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080921
APA StyleHu, Z., Li, S., Yang, F., Lin, X., Pan, S., Huang, X., & Xu, J. (2021). Formation and Elimination of Satellite Droplets during Monodisperse Droplet Generation by Using Piezoelectric Method. Micromachines, 12(8), 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080921






