3D-Printed Soft Structure of Polyurethane and Magnetorheological Fluid: A Proof-of-Concept Investigation of its Stiffness Tunability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
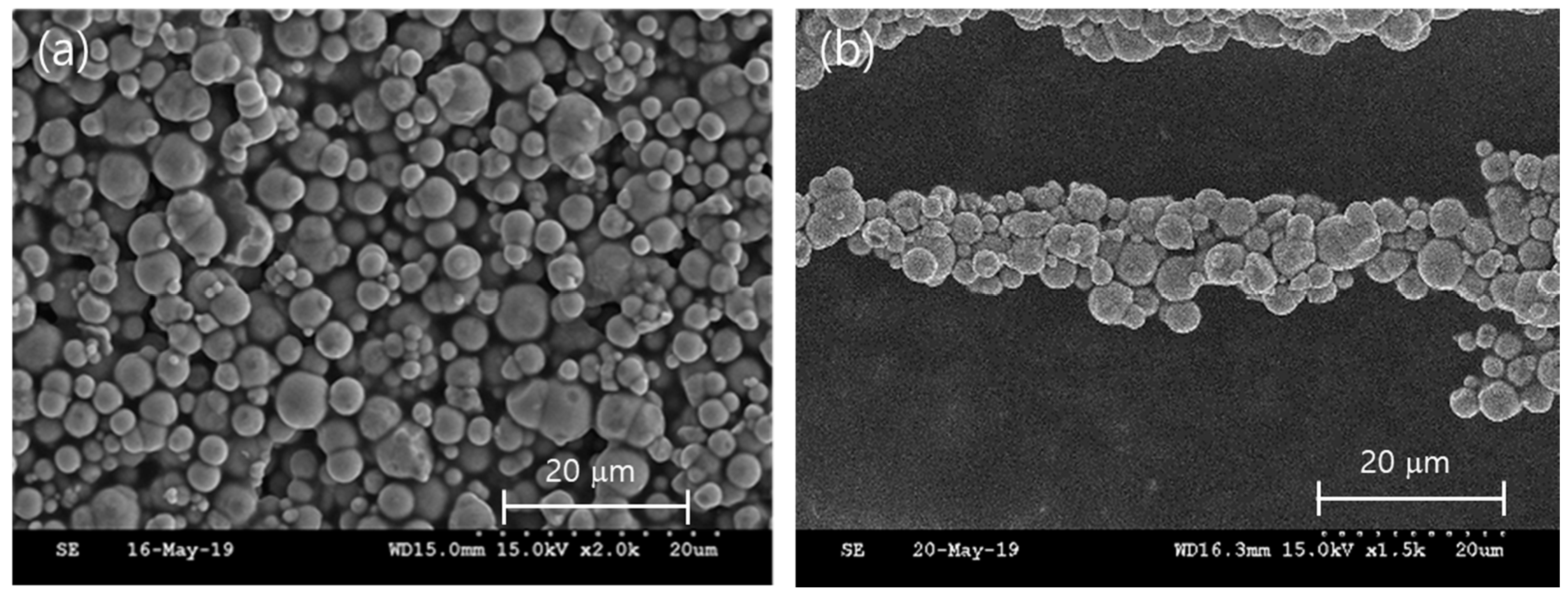
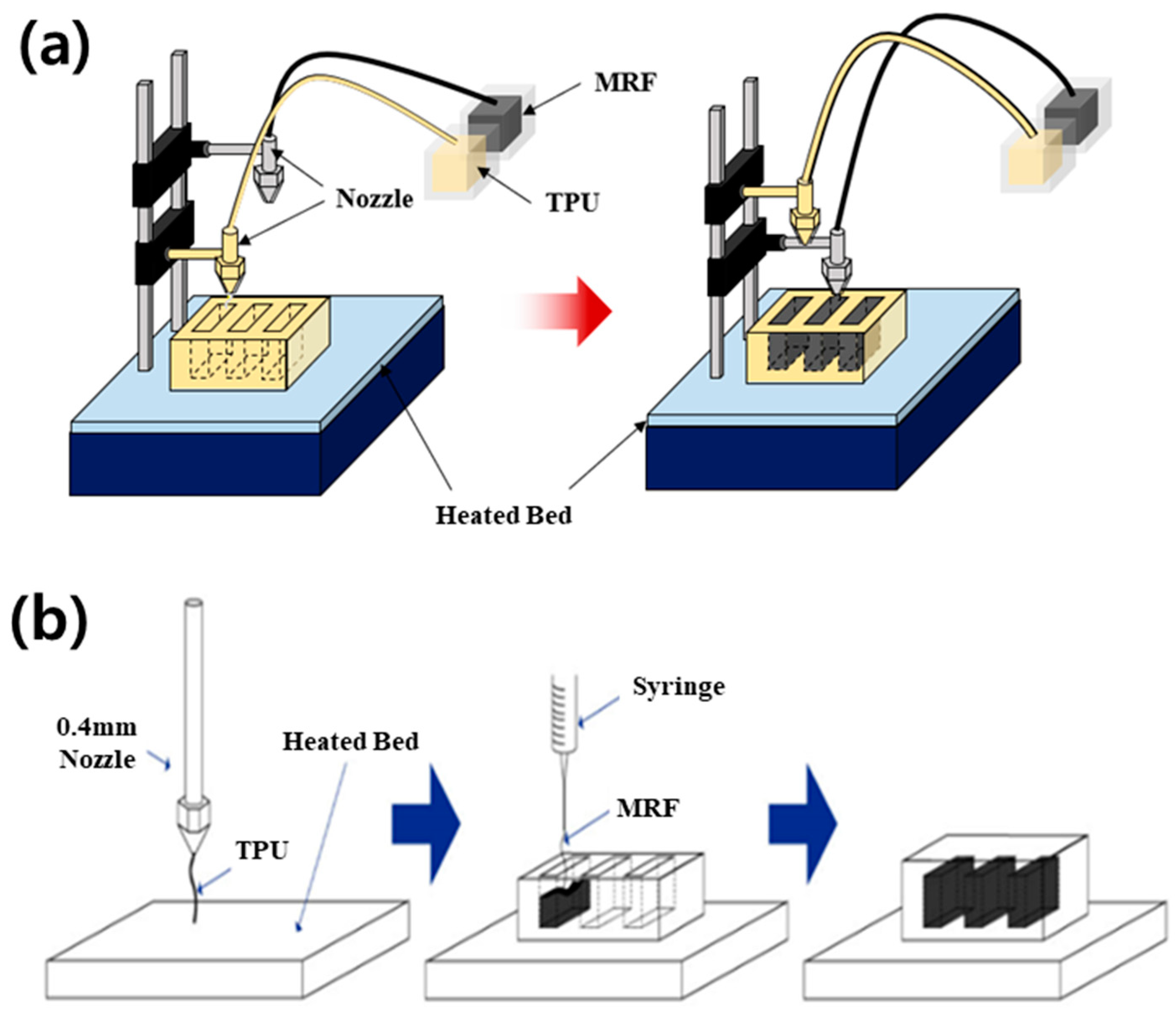
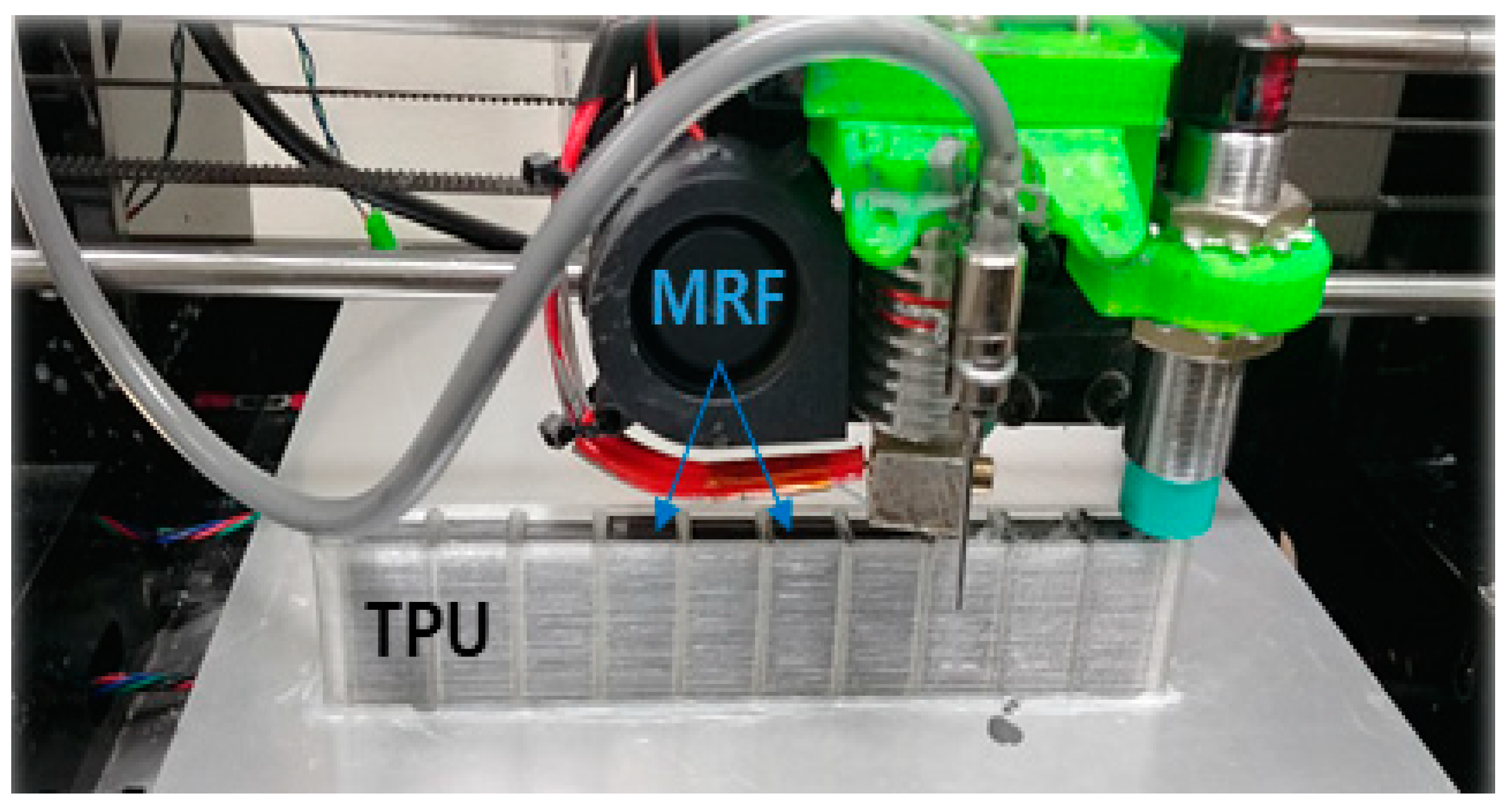
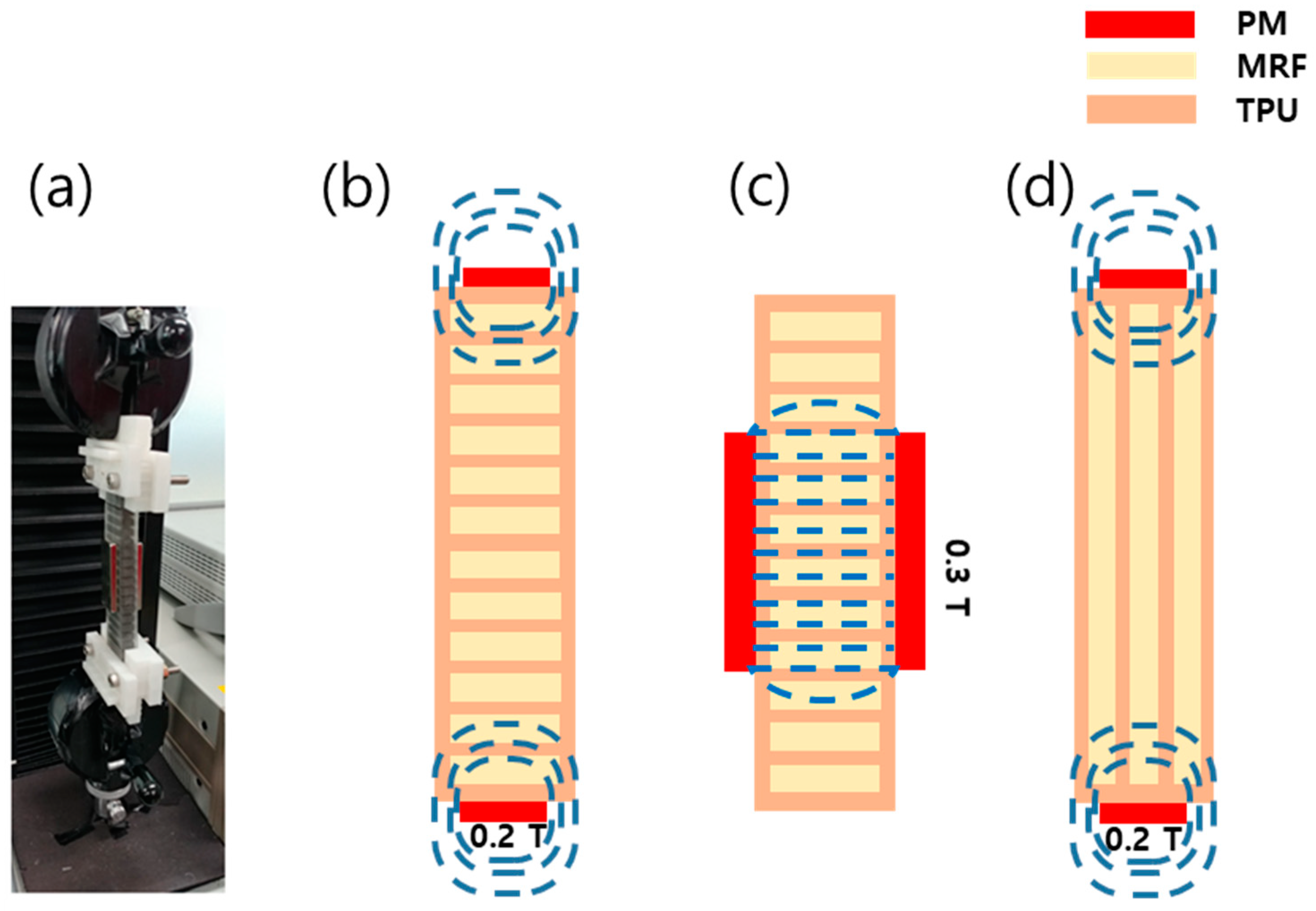
2. Fabrication of the Beam Structure
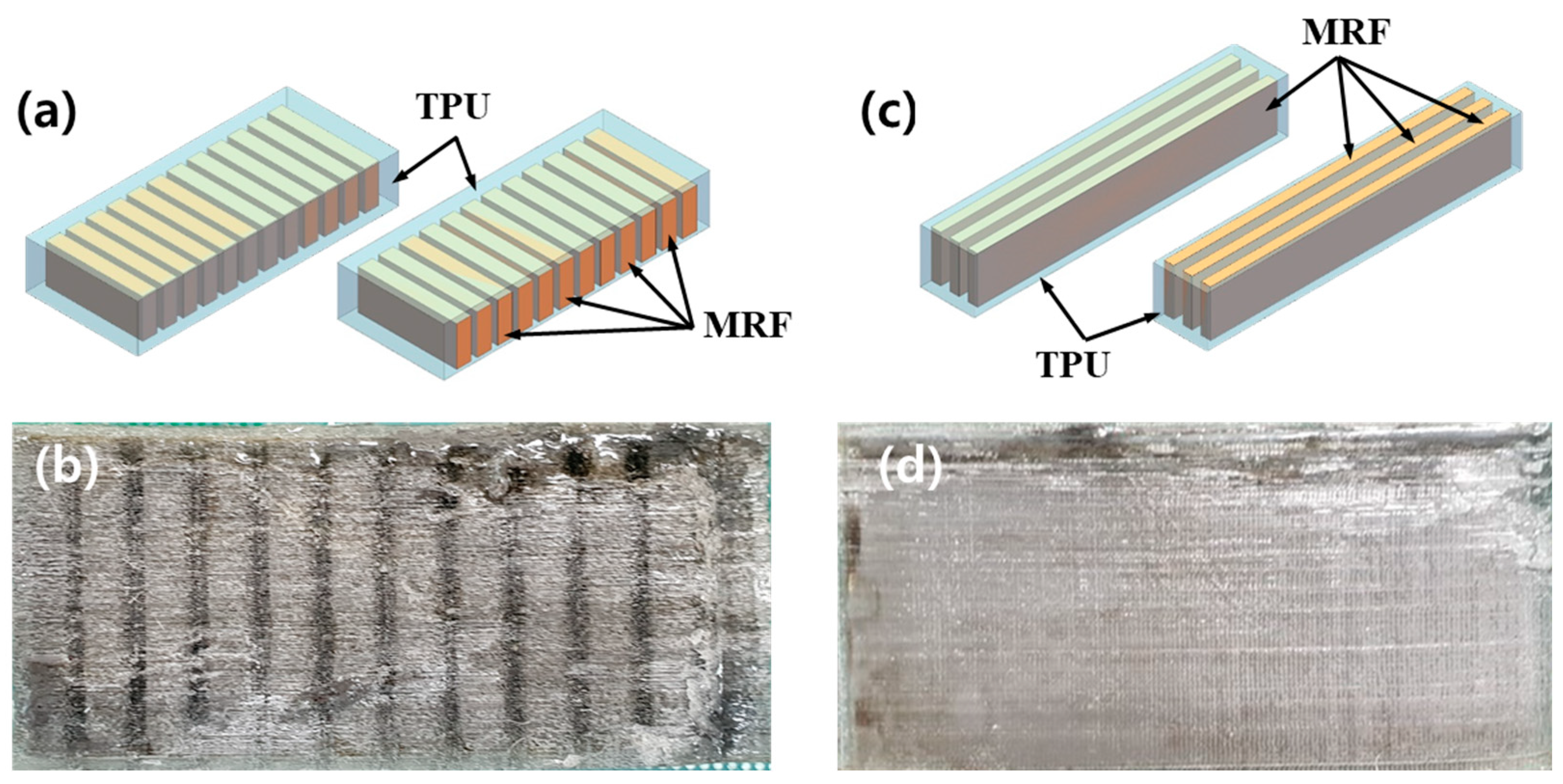
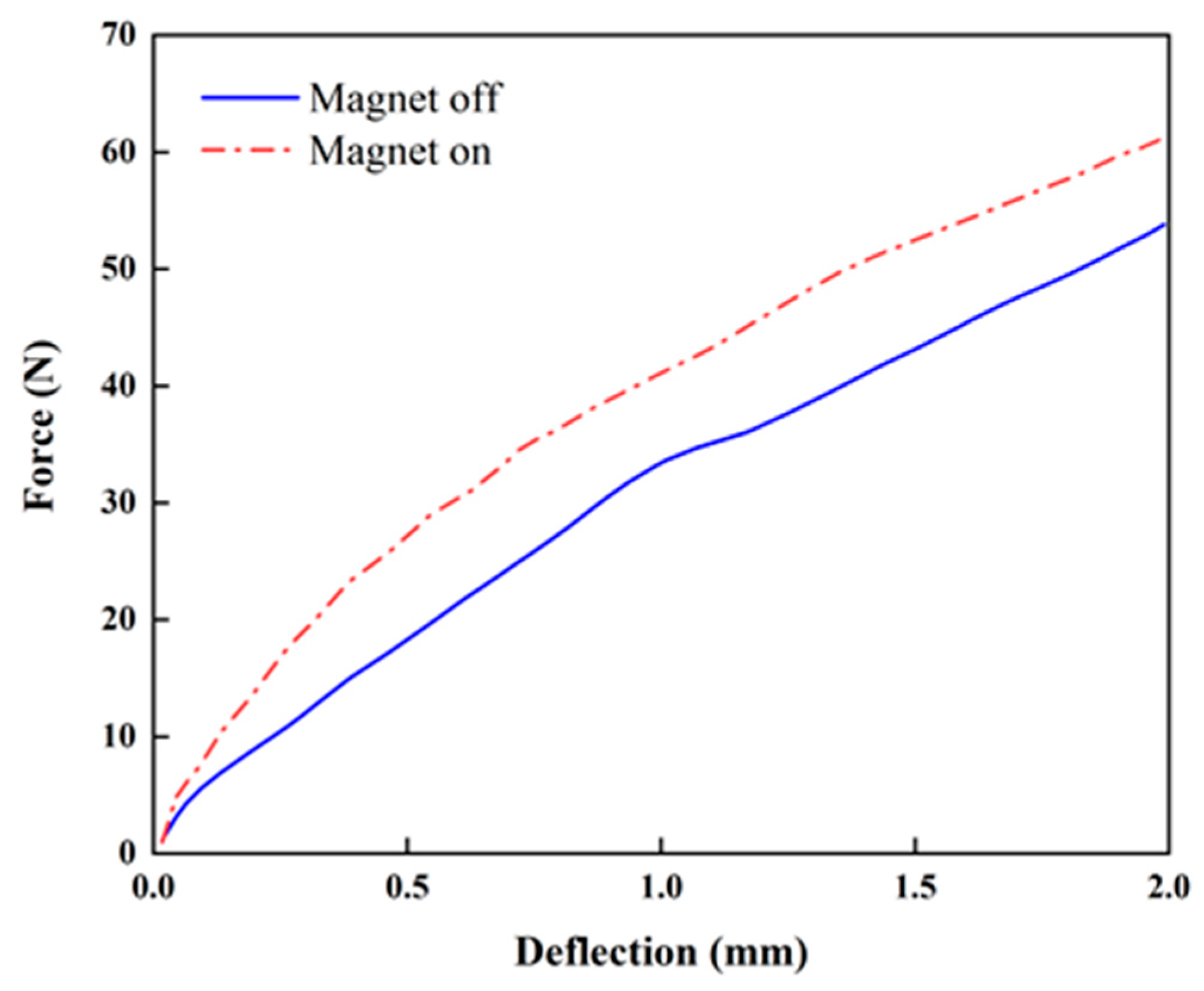
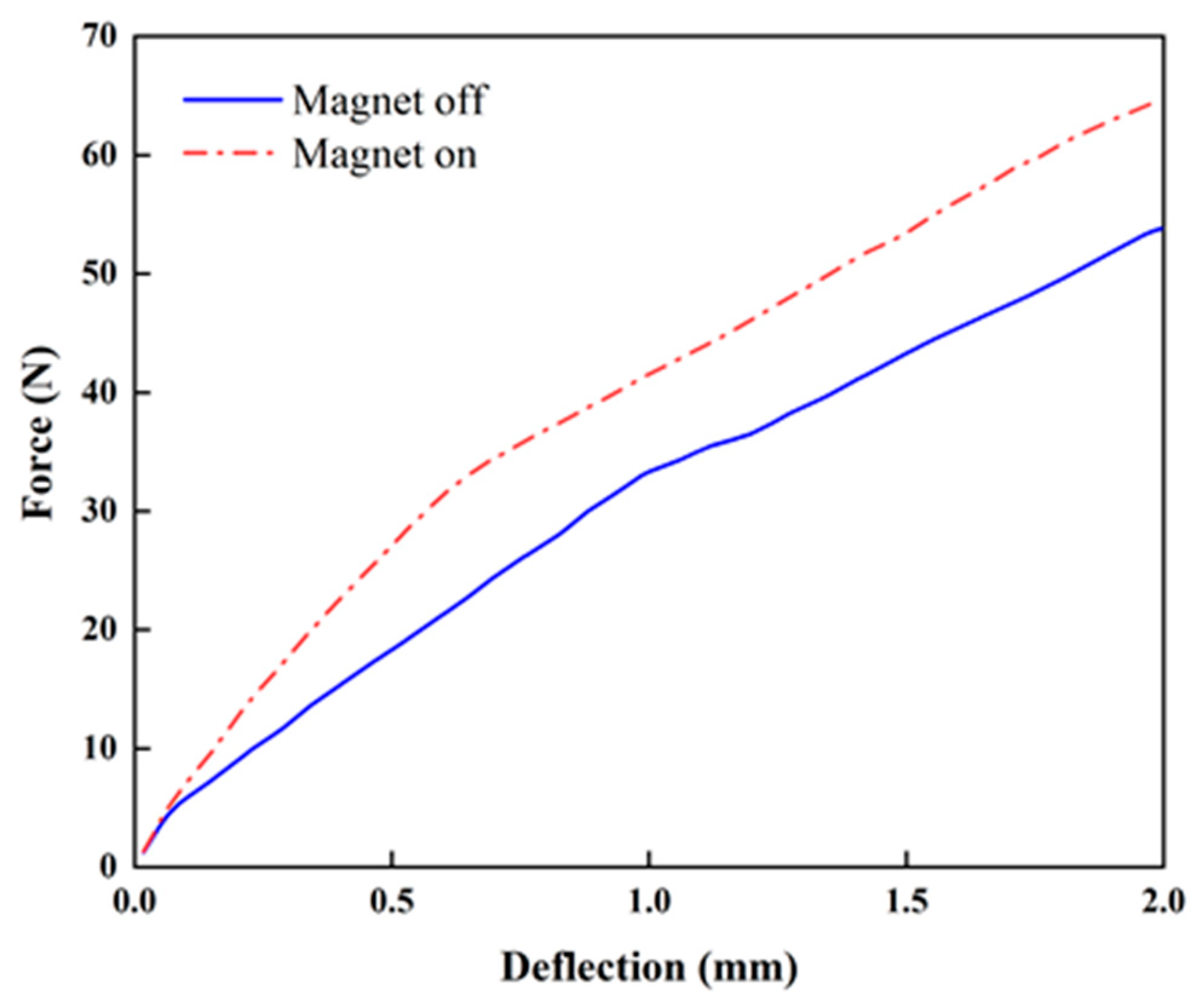
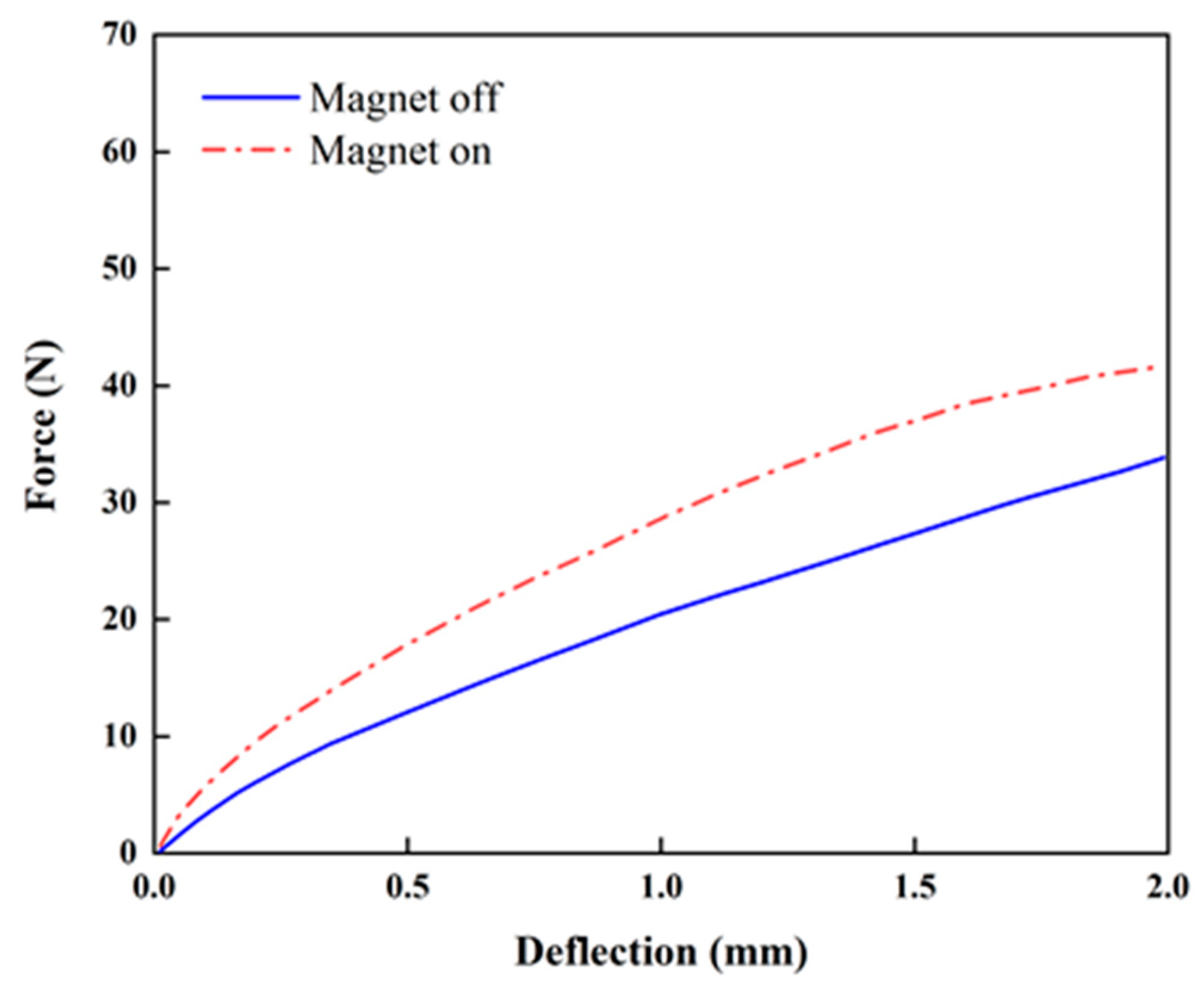
3. Experiment and Results
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, S.B.; Park, Y.K.; Kim, J.D. Vibration characteristics of hollow cantilevered beams containing an electro-rheological fluid. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 1993, 35, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.B.; Park, Y.K.; Suh, M.S. Elastodynamic characteristics of hollow cantilever beams containing an electro-rheological fluid: Experimental results. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 438–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.B.; Thompson, B.S.; Gandhi, M.V. Experimental control of a single-link flexible arm incorporating electro-rheological fluids. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 1995, 18, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.B.; Park, Y.K.; Cheong, C.C. Active vibration control of intelligent composite laminate structures incorporating an electro-rheological fluid. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1996, 7, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MalekzadehFard, K.; Gholam, M.; Reshadi, F. Free vibration and buckling analyses of cylindrical sandwich panel with magneto-rheological fluid layer. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 2017, 19, 397–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Sun, L.; Hu, G. Dynamic properties of an axially moving sandwich beam with magnetorheological fluid core. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedkar, Y.M. Manufacturing and testing of cantilever beam using magnetorheological approach. Int. J. Innov. Eng. Technol. 2016, 7, 463–469. [Google Scholar]
- Rajamohan, V.; Sundararaman, V.; Govindarajan, B. Finite element vibration analysis of a magnetorheological fluid sandwich beam. Procedia Eng. 2013, 64, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.; Dwivedy, S.K.; Murthy, K.S.R.K. Dynamic analysis of magnetorheological elastomers based sandwich beam with conductive skins under various boundary conditions. J. Sound Vib. 2011, 330, 1837–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.Y. Vibration analysis of sandwich rectangular plates with magnetorheological elastomers damping treatment. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 035010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyniewicz, B.; Bajkowski, J.M.; Bajer, C.I. Semi-active control of a sandwich beam partially filled with magnetorheological elastomer. Mech. Syst. Sig. Process. 2015, 60, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Guol, M.; Li, W.; Du, H.; Alici, G. Experimental investigation of the vibration characteristics of a magnetorheological elastomer sandwich beam under non-homogeneous small magnetic fields. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 127001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Bauer, S. Materials for stretchable electronics. Mrs Bull. 2012, 27, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Yu, M.; Fu, J.; Zhu, M.; Xi, Y.; Li, W. An EPDM/MVQ polymer blend based magnetorheological elastomer with good thermostability and mechanical performance. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 8521–8528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, W.; Lu, T.; Majidi, C. Soft-matter composites with electrically tunable elastic rigidity. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 085005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, E.A.; Taylor, L.D.; Swensen, J.P. Smart material composites for discrete stiffness materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 074007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, S.-W.; Yoon, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, S.-K.; Kim, Y.-R.; Park, Y.-J.; Kim, G.-W.; Choi, S.-B. 3D-Printed Soft Structure of Polyurethane and Magnetorheological Fluid: A Proof-of-Concept Investigation of its Stiffness Tunability. Micromachines 2019, 10, 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10100655
Hong S-W, Yoon J-Y, Kim S-H, Lee S-K, Kim Y-R, Park Y-J, Kim G-W, Choi S-B. 3D-Printed Soft Structure of Polyurethane and Magnetorheological Fluid: A Proof-of-Concept Investigation of its Stiffness Tunability. Micromachines. 2019; 10(10):655. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10100655
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Seong-Woo, Ji-Young Yoon, Seong-Hwan Kim, Sun-Kon Lee, Yong-Rae Kim, Yu-Jin Park, Gi-Woo Kim, and Seung-Bok Choi. 2019. "3D-Printed Soft Structure of Polyurethane and Magnetorheological Fluid: A Proof-of-Concept Investigation of its Stiffness Tunability" Micromachines 10, no. 10: 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10100655
APA StyleHong, S.-W., Yoon, J.-Y., Kim, S.-H., Lee, S.-K., Kim, Y.-R., Park, Y.-J., Kim, G.-W., & Choi, S.-B. (2019). 3D-Printed Soft Structure of Polyurethane and Magnetorheological Fluid: A Proof-of-Concept Investigation of its Stiffness Tunability. Micromachines, 10(10), 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10100655





